|
Thomas Summers West
Thomas Summers West (18 November 1927 – 9 January 2010) was a British chemist. Life Early years He was born in 1927 in Peterhead, Scotland and educated at Old Tarbat Public School in Portmahomack and then Tain Royal Academy. He then studied chemistry and obtained a BSc degree at Aberdeen University. He married Margaret Officer Lawson in 1952 and had three children, Ann (Cochennec, Yvon), Ruth (Byrd) and Tom. Scientific career He moved to Birmingham University in 1949 to carry out research in analytical chemistry under Professor Ron Belcher and obtained his PhD in 1952 and his D.Sc in 1962. In 1956 he was awarded the Meldola Medal and Prize of the Royal Society of Chemistry for advances in chemistry. In 1963 he moved to Imperial College in London as Reader in Analytical Chemistry and became Professor of Analytical Chemistry at Imperial College in 1965. He established a world-famous research team that included Roy Dagnall, Gordon Kirkbright and Bernard Fleet who were pione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peterhead
Peterhead (; gd, Ceann Phàdraig, sco, Peterheid ) is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It is Aberdeenshire's biggest settlement (the city of Aberdeen itself not being a part of the district), with a population of 18,537 at the 2011 Census. It is the biggest fishing port in the United Kingdom for total landings by UK vessels, according to a 2019 survey."Brexit trade deal: What does it mean for fishing?" - BBC News, December 2020 Peterhead sits at the easternmost point in mainland Scotland. It is often referred to as ''The Blue Toun'' (locally spelled "The Bloo Toon") and its natives are known as ''Bloo Touners''. They are also referred to as ''blue mogganers'' (locally spelled "bloomogganners"), supposedly from the blue |
Portmahomack
Portmahomack ( gd, Port Mo Chalmaig; 'Haven of My .e. 'Saint'Colmóc') is a small fishing village in Easter Ross, Scotland. It is situated in the Tarbat Peninsula in the parish of Tarbat. Tarbat Ness Lighthouse is about from the village at the end of the Tarbat Peninsula. Ballone Castle lies about from the village. There is evidence of early settlement, and the area seems to have been the site of significant activity during the time of the Picts, early Christianity and the Vikings. The village is situated on a sandy bay and has a small harbour designed by Thomas Telford: it shares with Hunstanton the unusual distinction of being on the east coast but facing west. Portmahomack lies inside the Moray Firth Special Area of Conservation with the associated dolphin and whale watching activity. The village has a primary school, golf course, hotel, a number of places to eat and a shop with a sub-post office. The nearest rail access is at Fearn railway station and the nearest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biographical Memoirs Of Fellows Of The Royal Society
The ''Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society'' is an academic journal on the history of science published annually by the Royal Society. It publishes obituaries of Fellows of the Royal Society. It was established in 1932 as ''Obituary Notices of Fellows of the Royal Society'' and obtained its current title in 1955, with volume numbering restarting at 1. Prior to 1932, obituaries were published in the ''Proceedings of the Royal Society''. The memoirs are a significant historical record and most include a full bibliography of works by the subjects. The memoirs are often written by a scientist of the next generation, often one of the subject's own former students, or a close colleague. In many cases the author is also a Fellow. Notable biographies published in this journal include Albert Einstein, Alan Turing, Bertrand Russell, Claude Shannon, Clement Attlee, Ernst Mayr, and Erwin Schrödinger. Each year around 40 to 50 memoirs of deceased Fellows of the Royal Soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T S WEST 1987 CBE
T, or t, is the twentieth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''tee'' (pronounced ), plural ''tees''. It is derived from the Semitic Taw 𐤕 of the Phoenician and Paleo-Hebrew script (Aramaic and Hebrew Taw ת/𐡕/, Syriac Taw ܬ, and Arabic ت Tāʼ) via the Greek letter τ (tau). In English, it is most commonly used to represent the voiceless alveolar plosive, a sound it also denotes in the International Phonetic Alphabet. It is the most commonly used consonant and the second most commonly used letter in English-language texts. History ''Taw'' was the last letter of the Western Semitic and Hebrew alphabets. The sound value of Semitic ''Taw'', Greek alphabet Tαυ (''Tau''), Old Italic and Latin T has remained fairly constant, representing in each of these; and it has also kept its original basic shape in most of these alphabets. Use in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Republican Army
The Irish Republican Army (IRA) is a name used by various paramilitary organisations in Ireland throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Organisations by this name have been dedicated to irredentism through Irish republicanism, the belief that all of Ireland should be an independent republic free from British rule. The original Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), often now referred to as the "old IRA", was raised in 1917 from members of the Irish Volunteers and the Irish Citizen Army later reinforced by Irishmen formerly in the British Army in World War I, who returned to Ireland to fight against Britain in the Irish War of Independence. In Irish law, this IRA was the army of the revolutionary Irish Republic as declared by its parliament, Dáil Éireann, in 1919. In the century that followed, the original IRA was reorganised, changed and split on multiple occasions, to such a degree that many subsequent paramilitary organisations have been known by that title – most not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John May (judge)
Sir John Douglas May, PC (28 June 1923 – 15 January 1997) was a British Court of Appeal judge appointed by the British Government to investigate the miscarriages of justice related to the Maguire Seven and other miscarriages linked to IRA bombing offences. Life and career May was educated at Clifton College and Balliol College, Oxford, where he was a Scholar. During World War II, he served with the Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve. He was called to the bar by the Inner Temple in 1947 and took silk in 1965. He was appointed to the High Court and assigned to the Queen's Bench Division in 1972, receiving the customary knighthood. In 1982, he was made a Lord Justice of Appeal and made a Privy Counsellor, serving until 1989. Maguire Seven inquiry On 20 October 1989 following the quashing of the Guildford Four convictions, May was appointed to chair an inquiry into both that case and the related case of the Maguire Seven. On 12 July 1990, the Home Secretary David Waddington p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Edinburgh
The Royal Society of Edinburgh is Scotland's national academy of science and letters. It is a registered charity that operates on a wholly independent and non-partisan basis and provides public benefit throughout Scotland. It was established in 1783. , there are around 1,800 Fellows. The Society covers a broader selection of fields than the Royal Society of London, including literature and history. Fellowship includes people from a wide range of disciplines – science & technology, arts, humanities, medicine, social science, business, and public service. History At the start of the 18th century, Edinburgh's intellectual climate fostered many clubs and societies (see Scottish Enlightenment). Though there were several that treated the arts, sciences and medicine, the most prestigious was the Society for the Improvement of Medical Knowledge, commonly referred to as the Medical Society of Edinburgh, co-founded by the mathematician Colin Maclaurin in 1731. Maclaurin was unhappy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
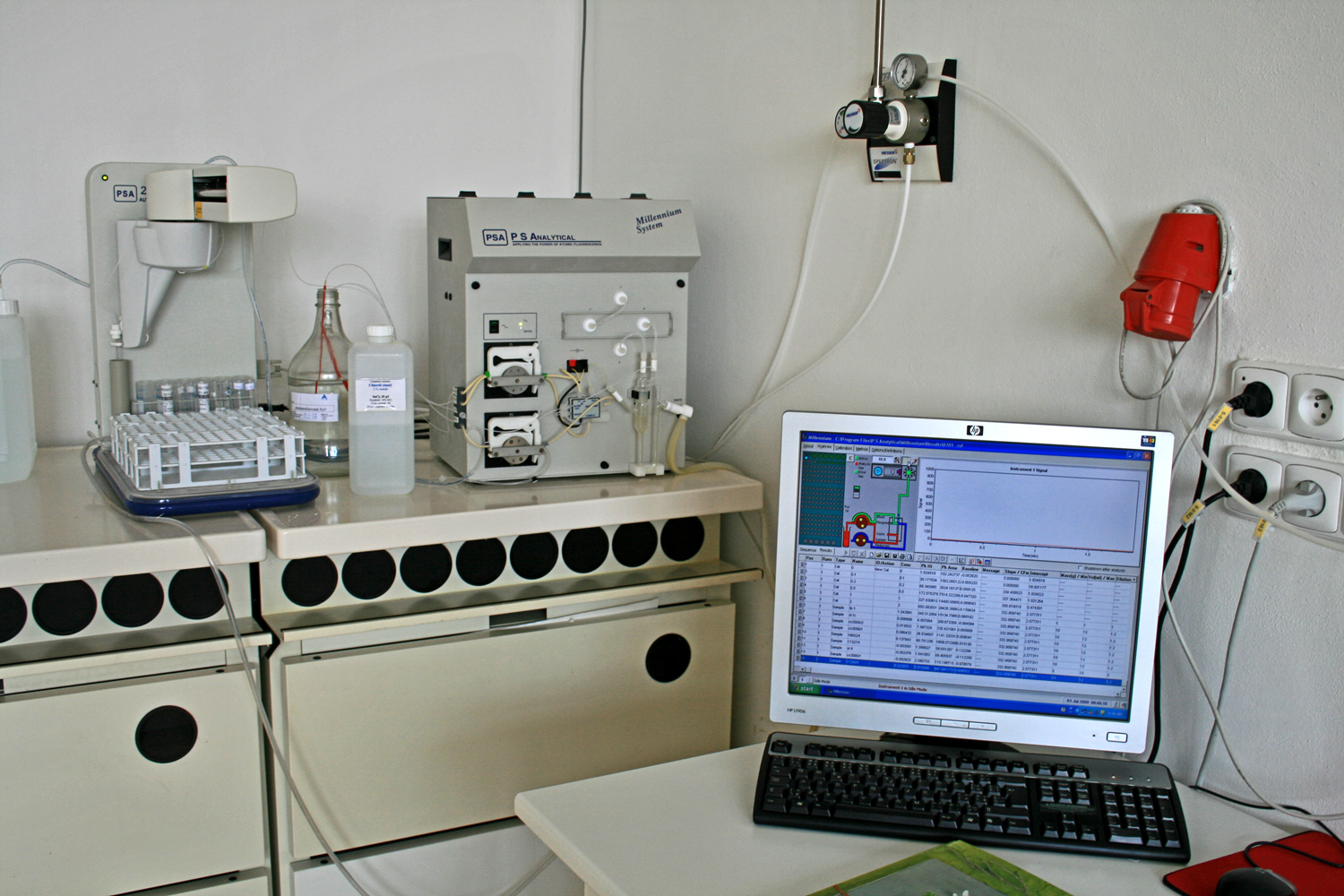
Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample. It involves using a beam of light, usually ultraviolet light, that excites the electrons in molecules of certain compounds and causes them to emit light; typically, but not necessarily, visible light. A complementary technique is absorption spectroscopy. In the special case of single molecule fluorescence spectroscopy, intensity fluctuations from the emitted light are measured from either single fluorophores, or pairs of fluorophores. Devices that measure fluorescence are called fluorometers. Theory Molecules have various states referred to as energy levels. Fluorescence spectroscopy is primarily concerned with electronic and vibrational states. Generally, the species being examined has a ground electronic state (a low energy state) of interest, and an excited electronic state of higher energy. Within each of these elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) is a spectroanalytical procedure for the quantitative determination of chemical elemlight) by free atoms in the gaseous state. Atomic absorption spectroscopy is based on absorption of light by free metallic ions. In analytical chemistry the technique is used for determining the concentration of a particular element (the analyte) in a sample to be analyzed. AAS can be used to determine over 70 different elements in solution, or directly in solid samples via electrothermal vaporization, and is used in pharmacology, biophysics, archaeology and toxicology research. Atomic emission spectroscopy was first used as an analytical technique, and the underlying principles were established in the second half of the 19th century by Robert Wilhelm Bunsen and Gustav Robert Kirchhoff, both professors at the University of Heidelberg, Germany. The modern form of AAS was largely developed during the 1950s by a team of Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial College
Imperial College London (legally Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine) is a public research university in London, United Kingdom. Its history began with Prince Albert, consort of Queen Victoria, who developed his vision for a cultural area that included the Royal Albert Hall, Victoria & Albert Museum, Natural History Museum and royal colleges. In 1907, Imperial College was established by a royal charter, which unified the Royal College of Science, Royal School of Mines, and City and Guilds of London Institute. In 1988, the Imperial College School of Medicine was formed by merging with St Mary's Hospital Medical School. In 2004, Queen Elizabeth II opened the Imperial College Business School. Imperial focuses exclusively on science, technology, medicine, and business. The main campus is located in South Kensington, and there is an innovation campus in White City. Facilities also include teaching hospitals throughout London, and with Imperial College Healthcare NH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |