Tarantulas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tarantulas comprise a group of large and often hairy
 '' Theraphosa apophysis'' (the pinkfoot goliath) was described 187 years after the goliath birdeater, so its characteristics are not as well attested. '' T. blondi'' is generally thought to be the heaviest tarantula, and '' T. apophysis'' has the greatest leg span. Two other species, '' Lasiodora parahybana'' (the Brazilian salmon birdeater) and '' Lasiodora klugi'', rival the size of the two goliath spiders.
'' Theraphosa apophysis'' (the pinkfoot goliath) was described 187 years after the goliath birdeater, so its characteristics are not as well attested. '' T. blondi'' is generally thought to be the heaviest tarantula, and '' T. apophysis'' has the greatest leg span. Two other species, '' Lasiodora parahybana'' (the Brazilian salmon birdeater) and '' Lasiodora klugi'', rival the size of the two goliath spiders.
 Most species of North American tarantulas are brown. Elsewhere, species have been found that variously display cobalt blue (''
Most species of North American tarantulas are brown. Elsewhere, species have been found that variously display cobalt blue (''
spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
s of the family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Theraphosidae. , 1,040 species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of ...
have been identified, with 156 genera. The term "tarantula" is usually used to describe members of the family Theraphosidae, although many other members of the same infraorder ( Mygalomorphae) are commonly referred to as "tarantulas" or "false tarantulas". Some of the more common species have become popular in the exotic pet
An exotic pet is a pet which is relatively rare or unusual to keep, or is generally thought of as a wild species rather than as a domesticated pet. The definition varies by culture, location, and over time—as animals become firmly enough est ...
trade. Many New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
species kept as pets have setae known as urticating hairs that can cause irritation to the skin, and in extreme cases, cause damage to the eyes.
Overview
Like allarthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s, the tarantula is an invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
that relies on an exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
for muscular support.Pomeroy, R. (2014, February 4). Pub. Real Clear Science, "Spiders, and Their Amazing Hydraulic Legs and Genitalia". Retrieved October 13, 2019, from https://www.realclearscience.com/blog/2013/02/spiders-their-amazing-hydraulic-legs-and-genitals.html. Like other Arachnid
Arachnida () is a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals ( arthropods), in the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, camel spiders, whip spiders and ...
a, a tarantula's body comprises two main parts, the prosoma (or cephalothorax) and the opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma ( cephalothorax). It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata (arachnids, horseshoe crabs and others). Although it is similar in most respects ...
(or abdomen). The prosoma and opisthosoma are connected by the pedicel, or pregenital somite. This waist-like connecting piece is actually part of the prosoma and gives the opisthosoma a wide range of motion relative to the prosoma.
Tarantula sizes can range from as small as the size of a BB pelletSchneider, J. (2017, October 19). Farewell to the World's Smallest Tarantula? Retrieved October 13, 2019, from https://www.nwf.org/Magazines/National-Wildlife/2017/Oct-Nov/Conservation/Spruce-Fir-Moss-Spider. to as large as a dinner plate when the legs are fully extended.Dolasia, M. (2019, September 26). World's Biggest Spider Weighs As Much As A Newborn Puppy. Retrieved October 13, 2019, from https://www.dogonews.com/2014/10/26/worlds-biggest-spider-weighs-as-much-as-a-newborn-puppy. Depending on the species, the body length of tarantulas ranges from about ,Jovan, Dennis, Kj, & Kenneth. (2019, May 1). Theraphosa blondi. Retrieved October 13, 2019, from https://www.theraphosidae.be/en/theraphosa-blondi/ . with leg spans of . Leg span is determined by measuring from the tip of the back leg to the tip of the front leg on the opposite side. Some of the largest species of tarantula may weigh over ; the largest of all, the goliath birdeater (''Theraphosa blondi'') from Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
and Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, has been reported to attain a weight of and a leg-span up to , males being longer and females greater in girth. The fang size of this tarantula reaches a maximum of .
 '' Theraphosa apophysis'' (the pinkfoot goliath) was described 187 years after the goliath birdeater, so its characteristics are not as well attested. '' T. blondi'' is generally thought to be the heaviest tarantula, and '' T. apophysis'' has the greatest leg span. Two other species, '' Lasiodora parahybana'' (the Brazilian salmon birdeater) and '' Lasiodora klugi'', rival the size of the two goliath spiders.
'' Theraphosa apophysis'' (the pinkfoot goliath) was described 187 years after the goliath birdeater, so its characteristics are not as well attested. '' T. blondi'' is generally thought to be the heaviest tarantula, and '' T. apophysis'' has the greatest leg span. Two other species, '' Lasiodora parahybana'' (the Brazilian salmon birdeater) and '' Lasiodora klugi'', rival the size of the two goliath spiders.
 Most species of North American tarantulas are brown. Elsewhere, species have been found that variously display cobalt blue (''
Most species of North American tarantulas are brown. Elsewhere, species have been found that variously display cobalt blue (''Cyriopagopus lividus
The cobalt blue tarantula or ''Cyriopagopus lividus'' is a species of tarantula which is in the family Theraphosidae which is native to Myanmar and over the border into Thailand. It was originally described as ''Haplopelma lividum''.
Descriptio ...
''), black with white stripes ('' Aphonopelma seemanni''), yellow leg markings (''Eupalaestrus campestratus
''Eupalaestrus campestratus'', known as the pink zebra beauty,
pictured at (private) Scott's Tarantulas website is a terrestrial ''), metallic blue legs with vibrant orange abdomen and green prosoma ('' Chromatopelma cyaneopubescens''). Their natural habitats include savanna,
File:Kaldari Phidippus johnsoni male defense.jpg, alt=, A '' 
The Life of the spider
Dodd, Mead, New York. The name is derived from the southern Italian town of Taranto. The term ''tarantula'' was subsequently applied to almost any large, unfamiliar species of ground-dwelling spider, in particular to the Mygalomorphae and especially the The name ''tarantula'' is also incorrectly applied to other large-bodied spiders, including the purseweb spiders or atypical tarantulas, the funnel-webs (
The name ''tarantula'' is also incorrectly applied to other large-bodied spiders, including the purseweb spiders or atypical tarantulas, the funnel-webs (
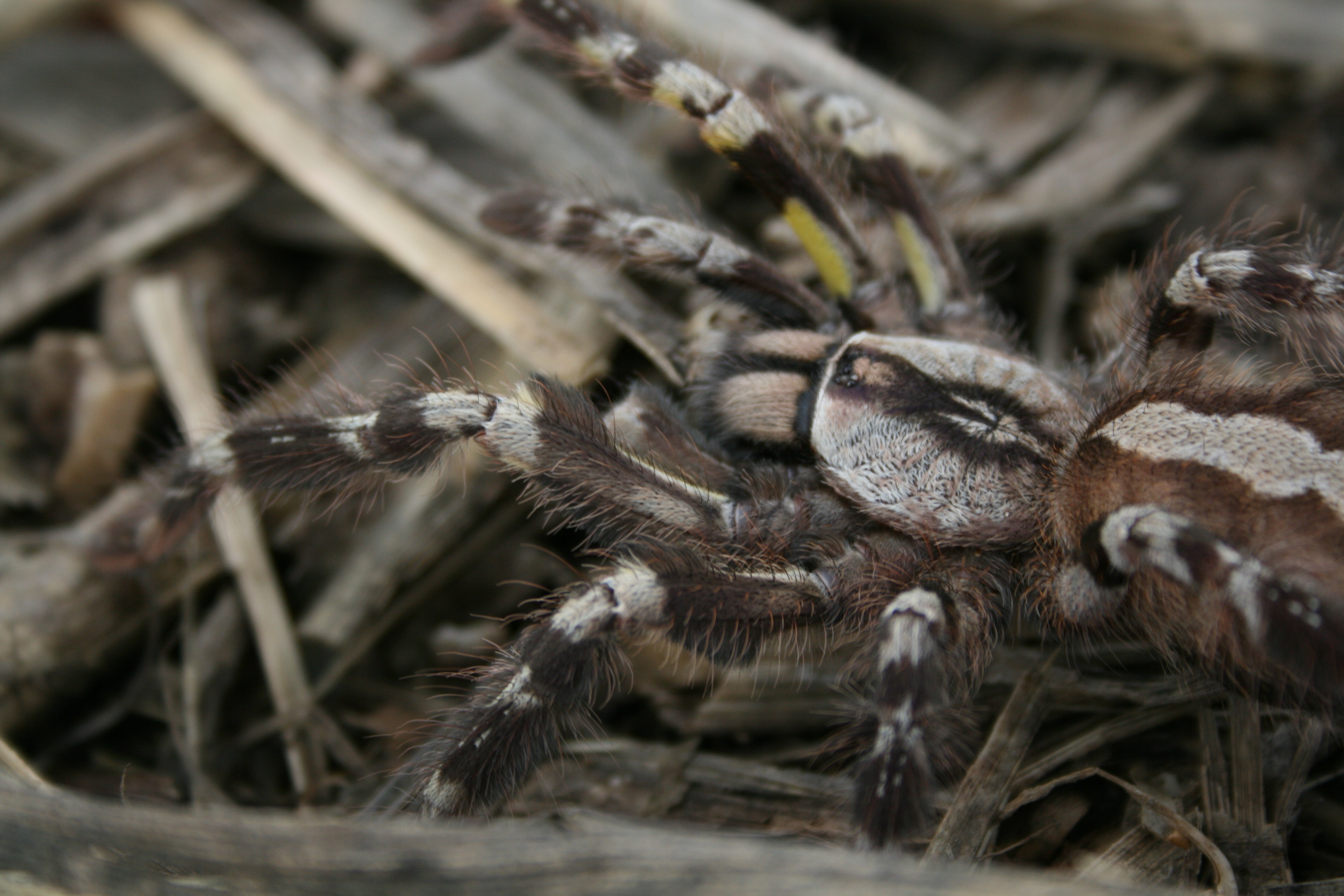 The eight legs, the two chelicerae with their fangs, and the pedipalps are attached to the prosoma. The chelicerae are two double-segmented appendages located just below the eyes and directly forward of the mouth. The chelicerae contain the venom glands that vent through the fangs. The fangs are hollow extensions of the chelicerae that inject venom into prey or animals that the tarantula bites in defense, and they are also used to masticate. These fangs are articulated so that they can extend downward and outward in preparation to bite or can fold back toward the chelicerae as a pocket knife blade folds back into its handle. The chelicerae of a tarantula completely contain the venom glands and the muscles that surround them, and can cause the venom to be forcefully injected into prey.
The pedipalpi are two six-segmented appendages connected to the prosoma near the mouth and protruding on either side of both chelicerae. In most species of tarantulas, the pedipalpi contain sharp, jagged plates used to cut and crush food often called the coxae or
The eight legs, the two chelicerae with their fangs, and the pedipalps are attached to the prosoma. The chelicerae are two double-segmented appendages located just below the eyes and directly forward of the mouth. The chelicerae contain the venom glands that vent through the fangs. The fangs are hollow extensions of the chelicerae that inject venom into prey or animals that the tarantula bites in defense, and they are also used to masticate. These fangs are articulated so that they can extend downward and outward in preparation to bite or can fold back toward the chelicerae as a pocket knife blade folds back into its handle. The chelicerae of a tarantula completely contain the venom glands and the muscles that surround them, and can cause the venom to be forcefully injected into prey.
The pedipalpi are two six-segmented appendages connected to the prosoma near the mouth and protruding on either side of both chelicerae. In most species of tarantulas, the pedipalpi contain sharp, jagged plates used to cut and crush food often called the coxae or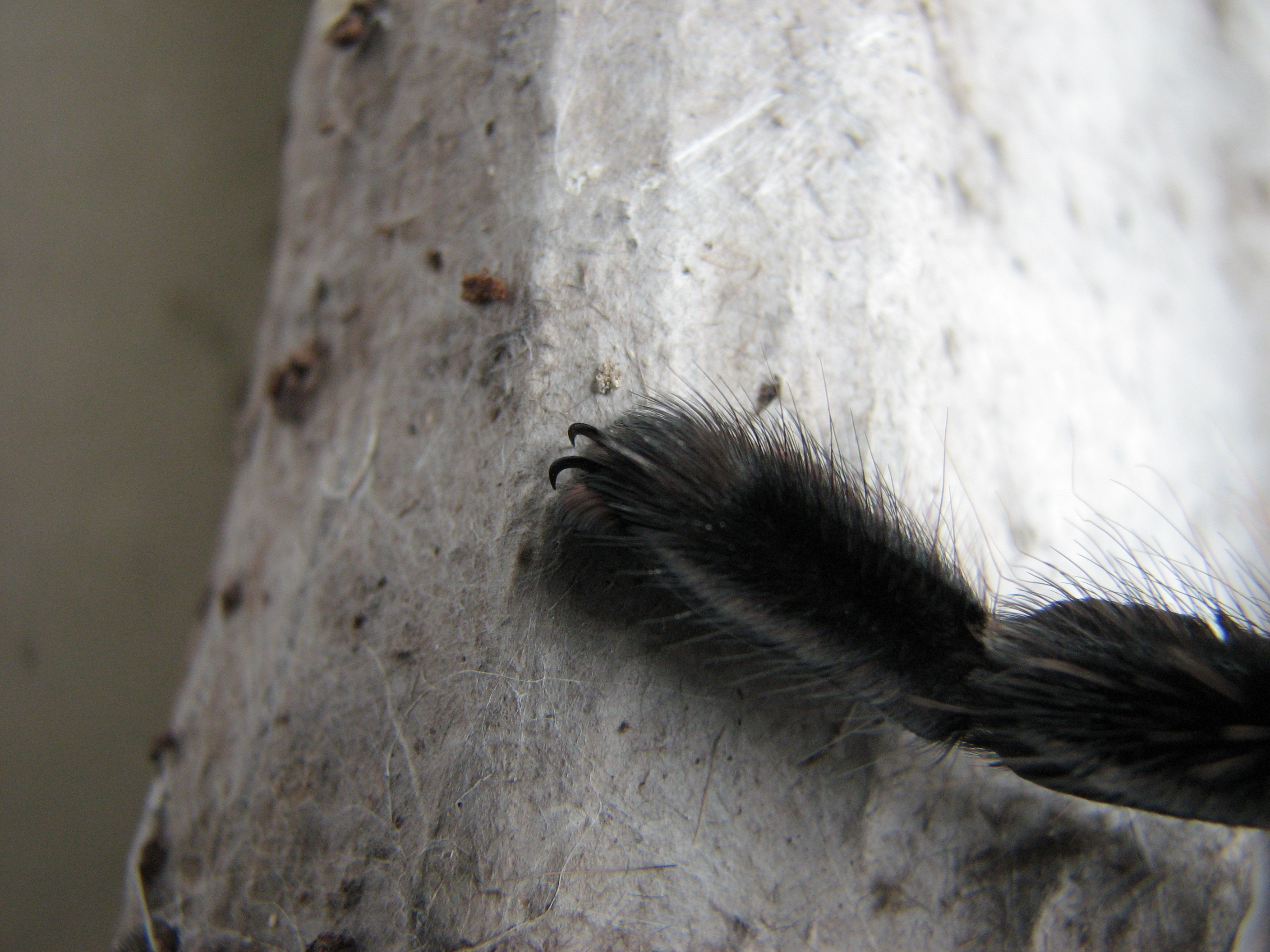 
 A tarantula has four pairs of legs and two additional pairs of appendages. Each leg has seven segments, which from the prosoma out are: coxa, trochanter, femur, patella, tibia, tarsus and pretarsus, and claw. Two or three retractable claws at the end of each leg are used to grip surfaces for climbing. Also on the end of each leg, surrounding the claws, is a group of bristles, called the scopula, which help the tarantula to grip better when climbing surfaces such as glass. The fifth pair is the pedipalps, which aid in feeling, gripping prey, and mating in the case of a mature male. The sixth pair of appendages is the chelicerae and their attached fangs. When walking, a tarantula's first and third legs on one side move at the same time as the second and fourth legs on the other side of its body. The muscles in a tarantula's legs cause the legs to bend at the joints, but to extend a leg, the tarantula increases the pressure of haemolymph entering the leg.
Tarantulas, like almost all other spiders, have their primary spinnerets at the end of the opisthosoma. Unlike most spider species in the infraorder Araneomorphae, which includes the majority of extant spider species, and most of which have six, tarantula species have two or four spinnerets. Spinnerets are flexible, tube-like structures from which the
A tarantula has four pairs of legs and two additional pairs of appendages. Each leg has seven segments, which from the prosoma out are: coxa, trochanter, femur, patella, tibia, tarsus and pretarsus, and claw. Two or three retractable claws at the end of each leg are used to grip surfaces for climbing. Also on the end of each leg, surrounding the claws, is a group of bristles, called the scopula, which help the tarantula to grip better when climbing surfaces such as glass. The fifth pair is the pedipalps, which aid in feeling, gripping prey, and mating in the case of a mature male. The sixth pair of appendages is the chelicerae and their attached fangs. When walking, a tarantula's first and third legs on one side move at the same time as the second and fourth legs on the other side of its body. The muscles in a tarantula's legs cause the legs to bend at the joints, but to extend a leg, the tarantula increases the pressure of haemolymph entering the leg.
Tarantulas, like almost all other spiders, have their primary spinnerets at the end of the opisthosoma. Unlike most spider species in the infraorder Araneomorphae, which includes the majority of extant spider species, and most of which have six, tarantula species have two or four spinnerets. Spinnerets are flexible, tube-like structures from which the

 The tarantula's mouth is located under its chelicerae on the lower front part of its prosoma. The mouth is a short, straw-shaped opening that can only suck, meaning that anything taken into it must be in liquid form. Prey with large amounts of solid parts, such as mice, must be crushed and ground up or predigested, which is accomplished by coating the prey with digestive juices secreted from openings in the chelicerae.
The tarantula's digestive organ (stomach) is a tube that runs the length of its body. In the prosoma, this tube is wider and forms the sucking stomach. When the sucking stomach's powerful muscles contract, the stomach is increased in cross-section, creating a strong sucking action that permits the tarantula to suck its liquefied prey up through the mouth and into the intestines. Once the liquefied food enters the intestines, it is broken down into particles small enough to pass through the intestine walls into the hemolymph (blood stream), where it is distributed throughout the body. After feeding, the leftovers are formed into a small ball by the tarantula and thrown away. In a terrarium, they often put them into the same corner.
The tarantula's mouth is located under its chelicerae on the lower front part of its prosoma. The mouth is a short, straw-shaped opening that can only suck, meaning that anything taken into it must be in liquid form. Prey with large amounts of solid parts, such as mice, must be crushed and ground up or predigested, which is accomplished by coating the prey with digestive juices secreted from openings in the chelicerae.
The tarantula's digestive organ (stomach) is a tube that runs the length of its body. In the prosoma, this tube is wider and forms the sucking stomach. When the sucking stomach's powerful muscles contract, the stomach is increased in cross-section, creating a strong sucking action that permits the tarantula to suck its liquefied prey up through the mouth and into the intestines. Once the liquefied food enters the intestines, it is broken down into particles small enough to pass through the intestine walls into the hemolymph (blood stream), where it is distributed throughout the body. After feeding, the leftovers are formed into a small ball by the tarantula and thrown away. In a terrarium, they often put them into the same corner.
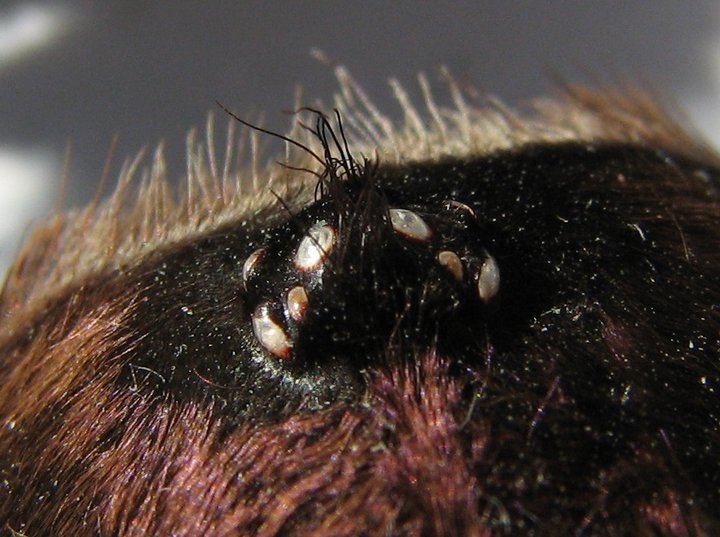 The eyes are located above the chelicerae on the forward part of the prosoma. They are small and usually set in two rows of four. Most tarantulas are not able to see much more than light, darkness, and motion. Arboreal tarantulas generally have better vision compared with terrestrial tarantulas.
The eyes are located above the chelicerae on the forward part of the prosoma. They are small and usually set in two rows of four. Most tarantulas are not able to see much more than light, darkness, and motion. Arboreal tarantulas generally have better vision compared with terrestrial tarantulas.
 A tarantula's blood is unique (not only in appearance); an oxygen-transporting protein is present (the copper-based hemocyanin), but not enclosed in blood cells such as the erythrocytes of mammals. A tarantula's blood is not true blood, but rather a liquid called hemolymph (or haemolymph). At least four types of hemocytes, or hemolymph cells, are known.
The tarantula's heart is a long, slender tube located along the top of the
A tarantula's blood is unique (not only in appearance); an oxygen-transporting protein is present (the copper-based hemocyanin), but not enclosed in blood cells such as the erythrocytes of mammals. A tarantula's blood is not true blood, but rather a liquid called hemolymph (or haemolymph). At least four types of hemocytes, or hemolymph cells, are known.
The tarantula's heart is a long, slender tube located along the top of the
 Tarantulas have evolved specialized bristles, or setae, to defend themselves against predators. Besides the normal bristles covering the body, some tarantulas also have a dense covering of irritating bristles called urticating hairs, on the
Tarantulas have evolved specialized bristles, or setae, to defend themselves against predators. Besides the normal bristles covering the body, some tarantulas also have a dense covering of irritating bristles called urticating hairs, on the
 All tarantulas are venomous. Although their venom is not deadly to humans, some bites cause serious discomfort that might persist for several days. In general, the effects of the bites of all kinds of tarantula are not well known. While the bites of many species are known to be no worse than a wasp sting, accounts of bites by some species are reported to be very painful and to produce intense spasms that may recur over a period of several days; the venom of the African tarantula ''
All tarantulas are venomous. Although their venom is not deadly to humans, some bites cause serious discomfort that might persist for several days. In general, the effects of the bites of all kinds of tarantula are not well known. While the bites of many species are known to be no worse than a wasp sting, accounts of bites by some species are reported to be very painful and to produce intense spasms that may recur over a period of several days; the venom of the African tarantula ''
 A juvenile male's sex can be determined by looking at a cast exuvia for epiandrous fusillae or spermathecae. Females possess
A juvenile male's sex can be determined by looking at a cast exuvia for epiandrous fusillae or spermathecae. Females possess
 Like other spiders, tarantulas have to shed their
Like other spiders, tarantulas have to shed their
 After reaching sexual maturity, a female tarantula normally mates and lays eggs once per year, although they do not always do so.
As with other spiders, the mechanics of intercourse are quite different from those of mammals. Once a male spider reaches maturity and becomes motivated to mate, he weaves a web mat on a flat surface. The spider then rubs his abdomen on the surface of this mat, and in so doing, releases a quantity of semen. He may then insert his pedipalps (short, leg-like appendages between the chelicerae and front legs) into the pool of semen. The pedipalps absorb the semen and keep it viable until a mate can be found. When a male spider detects the presence of a female, the two exchange signals to establish that they are of the same species. These signals may also lull the female into a receptive state. If the female is receptive, then the male approaches her and inserts his pedipalps into an opening in the lower surface of her abdomen, the
After reaching sexual maturity, a female tarantula normally mates and lays eggs once per year, although they do not always do so.
As with other spiders, the mechanics of intercourse are quite different from those of mammals. Once a male spider reaches maturity and becomes motivated to mate, he weaves a web mat on a flat surface. The spider then rubs his abdomen on the surface of this mat, and in so doing, releases a quantity of semen. He may then insert his pedipalps (short, leg-like appendages between the chelicerae and front legs) into the pool of semen. The pedipalps absorb the semen and keep it viable until a mate can be found. When a male spider detects the presence of a female, the two exchange signals to establish that they are of the same species. These signals may also lull the female into a receptive state. If the female is receptive, then the male approaches her and inserts his pedipalps into an opening in the lower surface of her abdomen, the
TarantulaForum.com
*
Tarantulas US Forum
Word of the Day: Tarantula and Tarantella
etymology and folklore
* ttp://research.amnh.org/entomology/spiders/catalog/THERAPHOSIDAE.html Listing of all currently named Theraphosidae
American Tarantula Society Headquarters
Amazing Tarantulas
*
Watch Tarantula (Theraphosidae) video clips from the BBC archive on Wildlife Finder
Theraphosidae Belgium, everything about bird eaters
{{Authority control Theraphosidae, Extant Miocene first appearances
pictured at (private) Scott's Tarantulas website is a terrestrial ''), metallic blue legs with vibrant orange abdomen and green prosoma ('' Chromatopelma cyaneopubescens''). Their natural habitats include savanna,
grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
such as in the pampas, rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfo ...
, desert, scrubland, mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
s, and cloud forest. They are generally classed among the terrestrial types. They are burrowers that live in the ground.
Tarantulas are becoming increasingly popular as pets and some species are readily available in captivity.
Identification
Tarantulas can be confused with other members of the order Mygalomorphae, such as trapdoor spiders, funnel-web spiders and purseweb spiders. They can also be confused with some members of the order Araneomorphae such as the Lycosidae family. There are multiple ways to identify a tarantula. First the hairs: in the Americas most tarantulas have urticating hairs, though some, such as the '' Hemirrhagus'' genus, lack these. The hairs are usually more noticeable than with most otherspider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
s. Another is the size, as tarantulas tend to be bigger, but this is again not a failproof way. They also don't use their webs for hunting, instead using them as building material or tripwire.
One of the most decisive ways to tell is by looking at their fangs. Tarantula fangs face downwards, as opposed to those of true spiders, which face each other, allowing them to make pincerlike motions. They also own two book lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange that is present in many arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is located inside an open ventral abdominal, air-filled cavity (atrium) and conn ...
s, as opposed to true spiders which only have one. Their lifespan is also longer than most spiders.Phidippus johnsoni
''Phidippus johnsoni'', the red-backed jumping spider, is one of the largest and most commonly encountered jumping spiders of western North America. It is not to be confused with the unrelated and highly venomous redback spider (''Latrodectus h ...
'' jumping spider's fangs
File:Lasiodora parahybana, chelicerae.JPG, alt=, A '' Lasiodora parahybana'' tarantula's fangs

Etymology
The spider originally bearing the name ''tarantula'' was '' Lycosa tarantula'', a species of wolf spider native to Mediterranean Europe.Fabre, Jean-Henri; Translated by Alexander Teixeira de Mattos (1916The Life of the spider
Dodd, Mead, New York. The name is derived from the southern Italian town of Taranto. The term ''tarantula'' was subsequently applied to almost any large, unfamiliar species of ground-dwelling spider, in particular to the Mygalomorphae and especially the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
Theraphosidae. Compared to tarantulas, wolf spiders are not particularly large or hairy, and so among English speakers in particular, usage eventually shifted in favour of the Theraphosidae, even though they are not closely related to wolf spiders at all, being in a different infraorder. The name ''tarantula'' is also incorrectly applied to other large-bodied spiders, including the purseweb spiders or atypical tarantulas, the funnel-webs (
The name ''tarantula'' is also incorrectly applied to other large-bodied spiders, including the purseweb spiders or atypical tarantulas, the funnel-webs (Dipluridae
The family Dipluridae, known as curtain-web spiders (or confusingly with other distantly related ones as funnel-web tarantulas) are a group of spiders in the infraorder Mygalomorphae, that have two pairs of booklungs, and chelicerae (fangs) that ...
and Hexathelidae), and the dwarf tarantulas. These spiders are related to tarantulas (all being mygalomorphs
The Mygalomorphae, or mygalomorphs, are an infraorder of spiders, and comprise one of three major groups of living spiders with over 3000 species, found on all continents except Antarctica. Many members are known as trapdoor spiders due to th ...
) but fall into different families from them. Huntsman spider
Huntsman spiders, members of the family Sparassidae (formerly Heteropodidae), are known by this name because of their speed and mode of hunting. They are also called giant crab spiders because of their size and appearance. Larger species sometim ...
s of the family Sparassidae have also been termed ''tarantulas'' because of their large size, when, in fact, they are not related. Instead, huntsman spiders belong to the infraorder Araneomorphae.
The element ''pelma'' in genus names
Many theraphosid genera have names, either accepted or synonymous, containing the element ''pelma''. This can be traced back to Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850, who in describing his new genus ''Eurypelma'' wrote, "" (). German arachnologists use the word to refer to the tarsus (the last article of a spider's leg). Translations of into Latin use the word . Hence in English arachnological terminology, Koch meant 'the scopula of the base of the tarsus very wide'. ''Eury-'' is derived from theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(), meaning 'wide', while () means 'the sole of the foot', paralleling Koch's use of (in modern spelling). Thus ''Eurypelma'' literally means 'wide footsole'; however, arachnologists have conventionally taken ''pelma'' in such names to refer to the scopula, so producing the meaning 'with a wide scopula'.
Other genus names or synonyms that Estrada-Alvarez and Cameron regard as having 'footsole' or 'scopula' meanings include:
*''Acanthopelma'' – Greek () 'thorn, spine'; overall meaning 'spiny footsole'
*''Brachypelma'' – Greek () 'short'; overall meaning 'short scopula'
*''Metriopelma'' – Greek () 'of moderate size'; overall meaning 'medium length scopula'
*''Schizopelma'' – from the Greek origin combining form ''schizo-'' () 'split'; overall meaning 'split footsole'
*''Sericopelma'' – Greek () 'silky'; overall meaning 'silken scopula'
Later, particularly following genus names published by R.I. Pocock in 1901, the element ''pelma'' appears to have become synonymous with 'theraphosid'. For example, the author of ''Cardiopelma'' writes, "" ('Cardiopelma refers to the female genitalia that evoke the shape of a heart'), with no reference to either 'footsole' or 'scopula'. Names interpreted in this way include:
*''Aphonopelma'' – Greek () 'soundless'; overall meaning 'theraphosid without sound'
*''Cardiopelma'' – Greek () 'heart'; overall meaning 'heart theraphosid' (referring to the heart-shaped female genitalia)
*''Clavopelma'' – Latin 'club'; overall meaning 'theraphosid with club-shaped hairs'
*''Delopelma'' – Greek () 'clear, obvious, visible, conspicuous, plain'; overall meaning 'theraphosid without plumose hair'
*''Gosipelma'' – the element ''gosi-'' means 'desert', relating to the Gosiute people; overall meaning 'desert theraphosid'
*''Spelopelma'' – Greek () 'cave'; overall meaning 'cave theraphosid'
Distribution
Tarantulas of various species occur throughout theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
, in Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, and throughout South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
. Other species occur variously throughout Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, much of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an ...
(including the Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Taiwan: the Ōsumi, Tokara, Amami, Okinawa, and Sakishima Islands (further divided into the Miyako and Yaeyama Islands), with Yona ...
in southern Japan), and all of Australia. In Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
, some species occur in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, southern Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
.
Habits
Some genera of tarantulas hunt prey primarily in trees; others hunt on or near the ground. All tarantulas can producesilk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
; while arboreal species typically reside in a silken "tube tent", terrestrial species line their burrow
An Eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow
A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of locomotion. Burrows provide a form of s ...
s with silk to stabilize the burrow
An Eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow
A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of locomotion. Burrows provide a form of s ...
wall and facilitate climbing up and down. Tarantulas mainly eat large insects and other arthropods such as centipedes, millipedes, and other spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
s, using ambush as their primary method of prey capture. Armed with their massive, powerful chelicerae tipped with long, chitinous fangs, tarantulas are well-adapted to killing other large arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s. The biggest tarantulas sometimes kill and consume small vertebrates such as lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia al ...
s, mice, bats, bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s, and small snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s.
Appendages
 The eight legs, the two chelicerae with their fangs, and the pedipalps are attached to the prosoma. The chelicerae are two double-segmented appendages located just below the eyes and directly forward of the mouth. The chelicerae contain the venom glands that vent through the fangs. The fangs are hollow extensions of the chelicerae that inject venom into prey or animals that the tarantula bites in defense, and they are also used to masticate. These fangs are articulated so that they can extend downward and outward in preparation to bite or can fold back toward the chelicerae as a pocket knife blade folds back into its handle. The chelicerae of a tarantula completely contain the venom glands and the muscles that surround them, and can cause the venom to be forcefully injected into prey.
The pedipalpi are two six-segmented appendages connected to the prosoma near the mouth and protruding on either side of both chelicerae. In most species of tarantulas, the pedipalpi contain sharp, jagged plates used to cut and crush food often called the coxae or
The eight legs, the two chelicerae with their fangs, and the pedipalps are attached to the prosoma. The chelicerae are two double-segmented appendages located just below the eyes and directly forward of the mouth. The chelicerae contain the venom glands that vent through the fangs. The fangs are hollow extensions of the chelicerae that inject venom into prey or animals that the tarantula bites in defense, and they are also used to masticate. These fangs are articulated so that they can extend downward and outward in preparation to bite or can fold back toward the chelicerae as a pocket knife blade folds back into its handle. The chelicerae of a tarantula completely contain the venom glands and the muscles that surround them, and can cause the venom to be forcefully injected into prey.
The pedipalpi are two six-segmented appendages connected to the prosoma near the mouth and protruding on either side of both chelicerae. In most species of tarantulas, the pedipalpi contain sharp, jagged plates used to cut and crush food often called the coxae or maxillae
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The tw ...
. As with other spiders, the terminal portions of the pedipalpi of males function as part of their reproductive system. Male spiders spin a silken platform (sperm web) on the ground onto which they release semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic bodily fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. Semen ...
from glands in their opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma ( cephalothorax). It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata (arachnids, horseshoe crabs and others). Although it is similar in most respects ...
. Then they insert their pedipalps into the semen, absorb the semen into the pedipalps, and later insert the pedipalps (one at a time) into the reproductive organ of the female, which is located in her abdomen. The terminal segments of the pedipalps of male tarantulas are moderately larger in circumference than those of a female tarantula. Male tarantulas have special spinnerets surrounding the genital opening. Silk for the sperm web of the tarantula is exuded from these special spinnerets.
 A tarantula has four pairs of legs and two additional pairs of appendages. Each leg has seven segments, which from the prosoma out are: coxa, trochanter, femur, patella, tibia, tarsus and pretarsus, and claw. Two or three retractable claws at the end of each leg are used to grip surfaces for climbing. Also on the end of each leg, surrounding the claws, is a group of bristles, called the scopula, which help the tarantula to grip better when climbing surfaces such as glass. The fifth pair is the pedipalps, which aid in feeling, gripping prey, and mating in the case of a mature male. The sixth pair of appendages is the chelicerae and their attached fangs. When walking, a tarantula's first and third legs on one side move at the same time as the second and fourth legs on the other side of its body. The muscles in a tarantula's legs cause the legs to bend at the joints, but to extend a leg, the tarantula increases the pressure of haemolymph entering the leg.
Tarantulas, like almost all other spiders, have their primary spinnerets at the end of the opisthosoma. Unlike most spider species in the infraorder Araneomorphae, which includes the majority of extant spider species, and most of which have six, tarantula species have two or four spinnerets. Spinnerets are flexible, tube-like structures from which the
A tarantula has four pairs of legs and two additional pairs of appendages. Each leg has seven segments, which from the prosoma out are: coxa, trochanter, femur, patella, tibia, tarsus and pretarsus, and claw. Two or three retractable claws at the end of each leg are used to grip surfaces for climbing. Also on the end of each leg, surrounding the claws, is a group of bristles, called the scopula, which help the tarantula to grip better when climbing surfaces such as glass. The fifth pair is the pedipalps, which aid in feeling, gripping prey, and mating in the case of a mature male. The sixth pair of appendages is the chelicerae and their attached fangs. When walking, a tarantula's first and third legs on one side move at the same time as the second and fourth legs on the other side of its body. The muscles in a tarantula's legs cause the legs to bend at the joints, but to extend a leg, the tarantula increases the pressure of haemolymph entering the leg.
Tarantulas, like almost all other spiders, have their primary spinnerets at the end of the opisthosoma. Unlike most spider species in the infraorder Araneomorphae, which includes the majority of extant spider species, and most of which have six, tarantula species have two or four spinnerets. Spinnerets are flexible, tube-like structures from which the spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
exudes its silk. The tip of each spinneret is called the spinning field. Each spinning field is covered by as many as 100 spinning tubes through which silk is exuded. As the silk is pulled out of the spinnerets, the shear forces cause proteins in the silk to crystallize, transforming it from a liquid to a solid thread.
Digestive system
Nervous system
A tarantula's central nervous system (brain) is located in the bottom of the inner prosoma. A tarantula perceives its surroundings primarily via sensory organs called setae (bristles or spines, sometimes referred to as hairs). Although a tarantula has eight eyes like mostspider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
s, touch is its keenest sense, and in hunting, it primarily depends on vibrations given off by the movements of its prey. A tarantula's setae are very sensitive organs and are used to sense chemical signatures, vibrations, wind direction, and possibly even sound. Tarantulas are also very responsive to the presence of certain chemicals such as pheromones.
 The eyes are located above the chelicerae on the forward part of the prosoma. They are small and usually set in two rows of four. Most tarantulas are not able to see much more than light, darkness, and motion. Arboreal tarantulas generally have better vision compared with terrestrial tarantulas.
The eyes are located above the chelicerae on the forward part of the prosoma. They are small and usually set in two rows of four. Most tarantulas are not able to see much more than light, darkness, and motion. Arboreal tarantulas generally have better vision compared with terrestrial tarantulas.
Respiratory system
All types of tarantulas have two sets ofbook lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange that is present in many arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is located inside an open ventral abdominal, air-filled cavity (atrium) and conn ...
s (breathing organs); the first pair is located in a cavity inside the lower front part of the abdomen near where the abdomen connects to the cephalothorax
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. (The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' are equivalent to ''ceph ...
, and the second pair is slightly farther back on the abdomen. Air enters the cavity through a tiny slit on each side of and near the front of the abdomen. Each lung consists of 15 or more thin sheets of folded tissue arranged like the pages of a book. These sheets of tissue are supplied by blood vessels. As air enters each lung, oxygen is taken into the blood stream through the blood vessels in the lungs. Needed moisture may also be absorbed from humid air by these organs.
Circulatory system
 A tarantula's blood is unique (not only in appearance); an oxygen-transporting protein is present (the copper-based hemocyanin), but not enclosed in blood cells such as the erythrocytes of mammals. A tarantula's blood is not true blood, but rather a liquid called hemolymph (or haemolymph). At least four types of hemocytes, or hemolymph cells, are known.
The tarantula's heart is a long, slender tube located along the top of the
A tarantula's blood is unique (not only in appearance); an oxygen-transporting protein is present (the copper-based hemocyanin), but not enclosed in blood cells such as the erythrocytes of mammals. A tarantula's blood is not true blood, but rather a liquid called hemolymph (or haemolymph). At least four types of hemocytes, or hemolymph cells, are known.
The tarantula's heart is a long, slender tube located along the top of the opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma ( cephalothorax). It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata (arachnids, horseshoe crabs and others). Although it is similar in most respects ...
. The heart is neurogenic as opposed to myogenic, so nerve cells instead of muscle cells initiate and coordinate the heart. It pumps hemolymph to all parts of the body through open passages often referred to as sinuses, and not through a circular system of blood vessels. If the exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
is breached, loss of hemolymph will kill the spider unless the wound is small enough that the hemolymph can dry and close it.
Predators
Despite their large size and fearsome appearance and reputation, tarantulas themselves are prey for many other animals. The most specialized of these predators are large members of the wasp family Pompilidae such as the wasp ''Hemipepsis ustulata
''Hemipepsis ustulata'' is a species of tarantula hawk wasp native to the Southwestern United States. Tarantula hawks are a large, conspicuous family of long-legged wasps that prey on tarantulas. They use their long legs to grapple with their pre ...
''. These wasps are called " tarantula hawks". The largest tarantula hawks, such as those in the genus '' Pepsis'', track, attack, and kill large tarantulas. They use olfaction to find the lair of a tarantula. The wasp must deliver a sting to the underside of the spider's cephalothorax, exploiting the thin membrane between the basal leg segments. This paralyzes the spider, and the wasp then drags it back into its burrow before depositing an egg on the prey's abdomen. The wasp then seals the spider in its burrow and flies off to search for more hosts. The wasp egg hatches into a larva and feeds on the spider's inessential parts, and as it approaches pupation, it consumes the remainder. Other arthropods, such as large scorpions and giant centipedes, are also known to prey on tarantulas.
Tarantulas are also preyed upon by a wide variety of vertebrates. Many of these, including lizards, frogs, birds, snakes and mammals, are generalist predators of all kinds of large arthropods. Mammals that have been known to prey on tarantulas, such as the coati, kinkajou, and opossum
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 93 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered Nort ...
in the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
, and mongoose
A mongoose is a small terrestrial carnivorous mammal belonging to the family Herpestidae. This family is currently split into two subfamilies, the Herpestinae and the Mungotinae. The Herpestinae comprises 23 living species that are native to ...
s and the honey badger in the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by th ...
, are often immune to the venom of their arthropod prey.
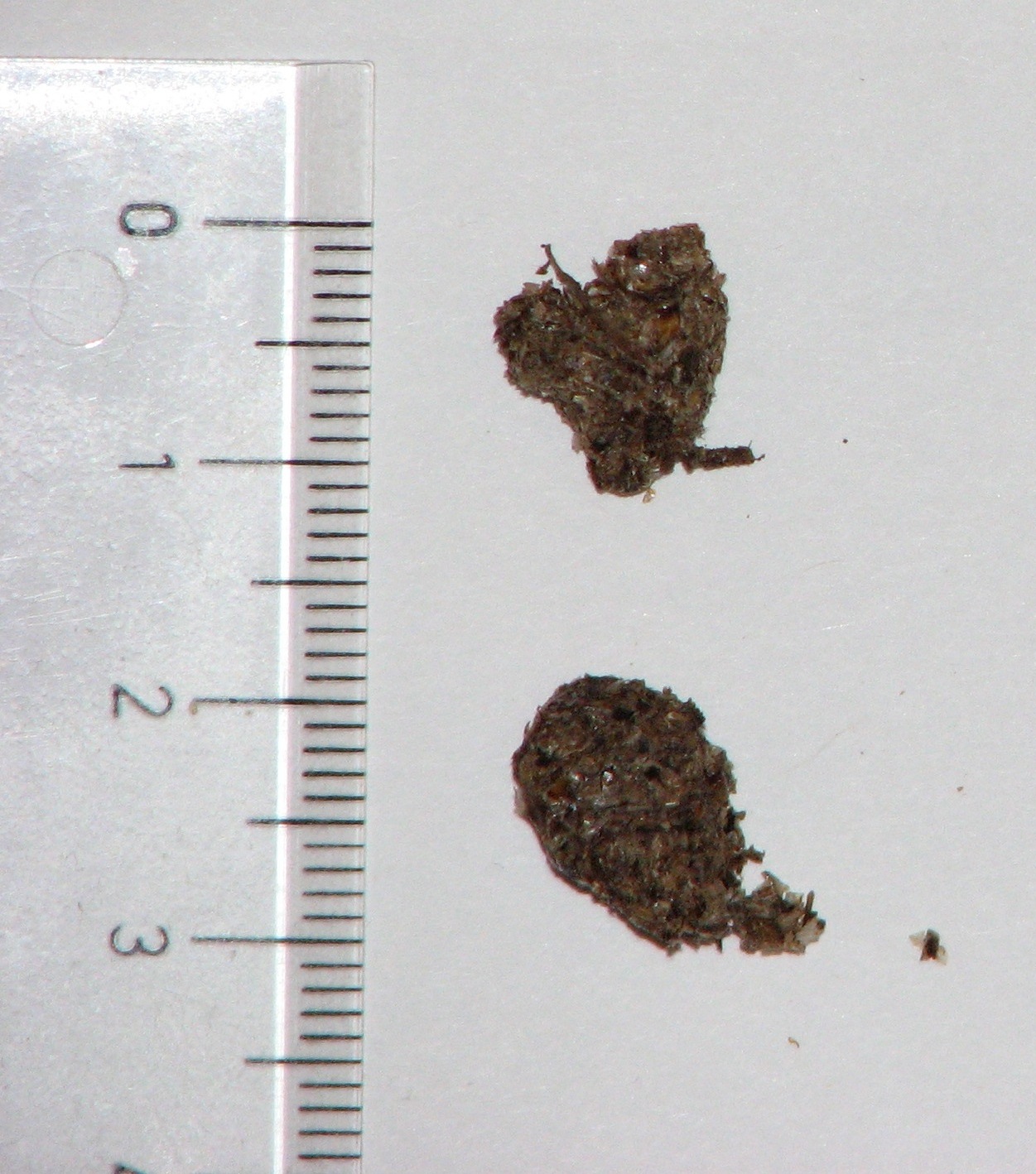
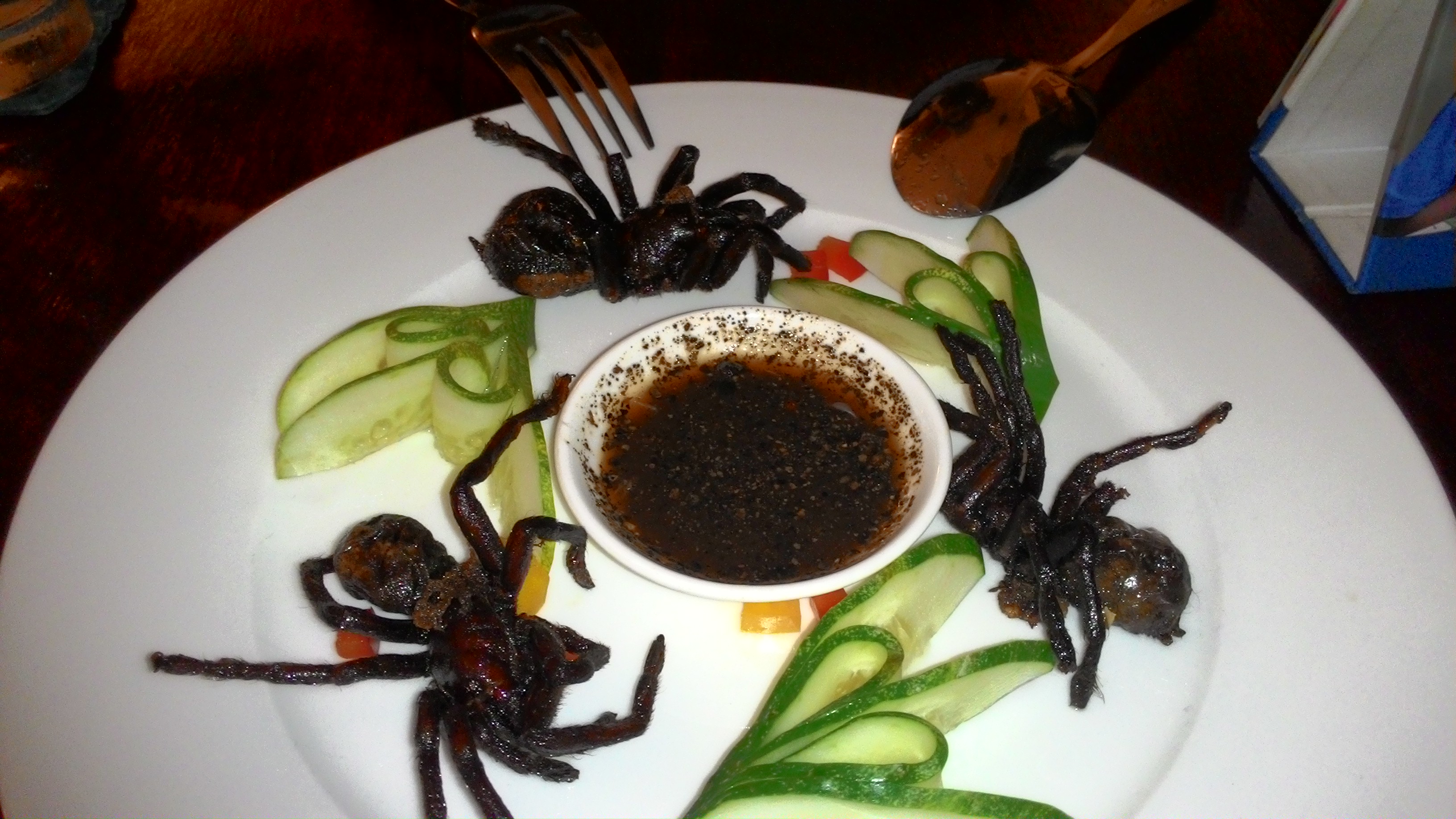
Humans also consume tarantulas for food in their native ranges. They are considered a delicacy in certain cultures (e.g. Venezuela and Cambodia). They can be roasted over an open fire to remove the bristles (described further below) and then eaten.
 Tarantulas have evolved specialized bristles, or setae, to defend themselves against predators. Besides the normal bristles covering the body, some tarantulas also have a dense covering of irritating bristles called urticating hairs, on the
Tarantulas have evolved specialized bristles, or setae, to defend themselves against predators. Besides the normal bristles covering the body, some tarantulas also have a dense covering of irritating bristles called urticating hairs, on the opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma ( cephalothorax). It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata (arachnids, horseshoe crabs and others). Although it is similar in most respects ...
, that they sometimes use as protection against enemies. These bristles are present on most New World species, but not on any specimens from the Old World. Urticating hairs are usually kicked off the abdomen by the tarantula, but some may simply rub the abdomen against the target, like the genus '' Avicularia''. These fine bristles are barbed and serve to irritate. They can be lethal to small animals such as rodents. Some people are sensitive to these bristles, and develop serious itching and rashes at the site. Exposure of the eyes and respiratory system to urticating hairs should be strictly avoided. Species with urticating hairs can kick these bristles off; they are flicked into the air at a target using their back pairs of legs. Tarantulas also use these bristles for other purposes, such as to mark territory or to line their shelters (the latter such practice may discourage flies
Flies are insects of the Order (biology), order Diptera, the name being derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwing ...
from feeding on the spiderlings). Urticating hairs do not grow back, but are replaced with each molt. The intensity, number, and flotation of the bristles depends on the species of tarantula.
To predators and other enemies, these bristles can range from being lethal to simply being a deterrent. With humans, they can cause irritation to eyes, nose, and skin, and more dangerously, the lungs and airways, if inhaled. The symptoms range from species to species, from person to person, from a burning itch to a minor rash. In some cases, tarantula bristles have caused permanent damage to human eyes.
Some setae are used to stridulate
Stridulation is the act of producing sound by rubbing together certain body parts. This behavior is mostly associated with insects, but other animals are known to do this as well, such as a number of species of fish, snakes and spiders. The mech ...
, which makes a hissing sound. These bristles are usually found on the chelicerae. Stridulation seems to be more common in Old World species.
Bites and urticating bristles
Pelinobius muticus
''Pelinobius'' or the king baboon is a monotypic genus of east African tarantulas containing the single species, ''Pelinobius muticus''. It was first described by Ferdinand Anton Franz Karsch in 1885, and is found in Tanzania and Kenya.
Descript ...
'' also causes strong hallucinations. For '' Poecilotheria'' species, researchers have described more than 20 bites with the delayed onset of severe and diffuse muscle cramps, lasting for several days, that in most cases resolved completely with the use of benzodiazepines and magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
. In all cases, seeking medical aid is advised. Because other proteins are included when a toxin is injected, some individuals may suffer severe symptoms due to an allergic reaction
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic derm ...
rather than to the venom. Such allergic effects can be life-threatening. Additionally, the large fangs of a tarantula can inflict painful puncture wounds, which can lead to secondary bacterial infections if not properly treated.
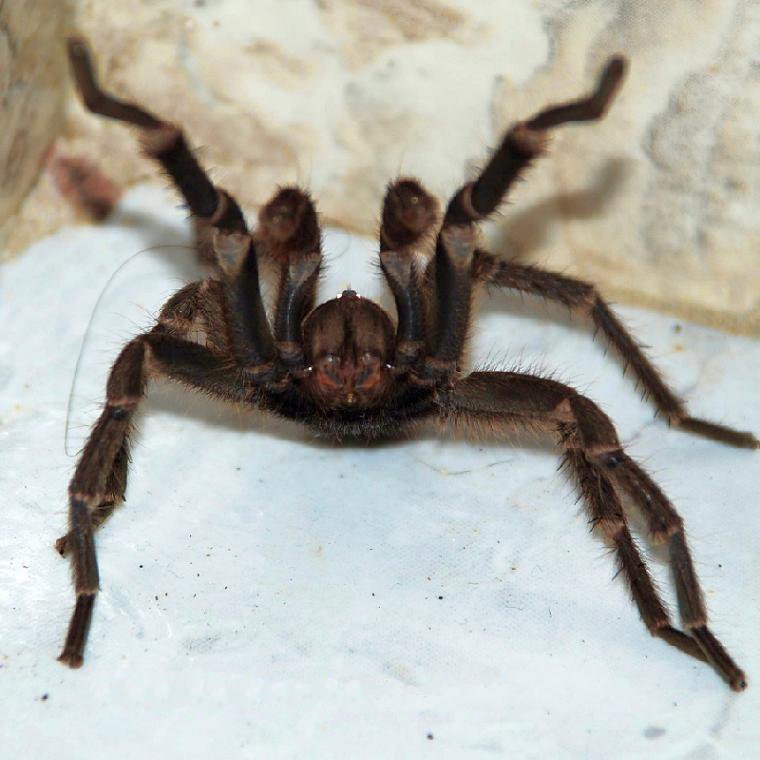
Before biting, a tarantula may signal its intention to attack by rearing up into a "threat posture", which may involve raising its prosoma and lifting its front legs into the air, spreading and extending its fangs, and (in certain species) making a loud hissing by stridulating. Tarantulas often hold this position for longer than the duration of the original threat. Their next step, without biting, may be to slap down on the intruder with their raised front legs. If that response fails to deter the attacker, the tarantulas of the Americas may next turn away and flick urticating hairs toward the pursuing predator. The next response may be to leave the scene entirely, but especially if no line of retreat is available, their final response may also be to whirl suddenly and bite. Some tarantulas are well known to give "dry bites", i.e., they may defensively bite some animal that intrudes on their space and threatens them, but they do not pump venom into the wound.
New-world tarantulas—those indigenous to the Americas—have bites that generally pose little threat to humans (other than causing localized pain). Most of them are equipped with urticating hairs on their abdomens, and almost always throw these barbed bristles as the first line of defense. These bristles irritate sensitive areas of the body and especially seem to target curious animals that may sniff these bristles into the mucous membranes of the nose. Some species have more effective urticating bristles than others. The goliath birdeater is known for its particularly irritating urticating bristles. They can penetrate the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
, so eye protection should be worn when handling such tarantulas.
Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by th ...
tarantulas have no urticating bristles and are more likely to attack when disturbed. They often have more potent, medically significant venom, and are faster and much more nervous and defensive than New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
species.
Some dangerous spider species are related to tarantulas and are frequently confused with them. A popular urban legend maintains that deadly varieties of tarantula exist somewhere in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
. This claim is often made without identifying a particular spider, although the "banana tarantula" is sometimes named. A likely candidate for the true identity of this spider is the dangerous Brazilian wandering spider ('' Phoneutria fera'') of the family Ctenidae, as it is sometimes found hiding in clusters of bananas and is one of several spiders called "banana spiders". It is not technically a tarantula, but it is fairly large (4- to 5-inch legspan), somewhat ″hairy″, and is highly venomous to humans. Another dangerous type of spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
s that have been confused with tarantulas are the Australian funnel-web spiders. The best known species of these is the Sydney funnel-web spider ('' Atrax robustus'') a spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
that is aggressive, highly venomous, and (prior to the development of antivenom in the 1980s) was responsible for numerous deaths in Australia. These spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
s are members of the same infraorder as tarantulas, Mygalomorphae. Some Australians use the slang term "triantelope" (a corruption of the incorrect term tarantula, which is also used) for large, ″hairy″, and harmless members of the huntsman spider
Huntsman spiders, members of the family Sparassidae (formerly Heteropodidae), are known by this name because of their speed and mode of hunting. They are also called giant crab spiders because of their size and appearance. Larger species sometim ...
family, which are often found on interior household walls and in automobiles.
Sexual dimorphism
Some tarantula species exhibit pronouncedsexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
. Males tend to be smaller (especially their abdomens, which can appear quite narrow) and may be dull in color when compared to their female counterparts, as in the species '' Haplopelma lividum''. Mature male tarantulas also may have tibial hooks on their front legs, which are used to restrain the female's fangs during copulation. Males typically have longer legs than the females.
 A juvenile male's sex can be determined by looking at a cast exuvia for epiandrous fusillae or spermathecae. Females possess
A juvenile male's sex can be determined by looking at a cast exuvia for epiandrous fusillae or spermathecae. Females possess spermatheca
The spermatheca (pronounced plural: spermathecae ), also called receptaculum seminis (plural: receptacula seminis), is an organ of the female reproductive tract in insects, e.g. ants, bees, some molluscs, oligochaeta worms and certain othe ...
e, except for the species ''Sickius longibulbi
''Sickius'' is a genus of tarantulas. It has a single species, ''Sickius longibulbi''. It is endemic to Brazil.
Taxonomy
The species ''S. longibulbi'' was described in 1948 by Benedict A. M. Soares and H.F. de A. Camargo, however Robert ...
'' and ''Encyocratella olivacea
''Encyocratella'' is a monotypic genus of Tanzanian tarantulas (family Theraphosidae) containing the single species, ''Encyocratella olivacea'', also known as the Tanzanian black and olive baboon spider. It was first described by Embrik Strand i ...
''. Males have much shorter lifespans than females because they die relatively soon after maturing. Few live long enough for a postultimate molt, which is unlikely in natural habitats because they are vulnerable to predation, but has happened in captivity, though rarely. Most males do not live through this molt, as they tend to get their emboli, mature male sexual organs on pedipalps, stuck in the molt. Most tarantula fanciers regard females as more desirable as pets due to their much longer lifespans. Wild-caught tarantulas are often mature males because they wander out in the open and are more likely to be caught.
Life cycle
 Like other spiders, tarantulas have to shed their
Like other spiders, tarantulas have to shed their exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
periodically as they grow, a process called molting. A young tarantula may do this several times a year as a part of the maturation process, while full-grown specimens only molt once a year or less, or sooner, to replace lost limbs or lost urticating hairs. It is visibly apparent that molting is imminent when the exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
takes on a darker shade. If a tarantula previously used its urticating hairs, the bald patch turns from a peach color to deep blue. The tarantula also stops feeding and becomes more lethargic during this time.
While most Tarantulas species take between two to five years to reach sexual maturity, some species can take up to 10 years. Upon reaching adulthood, males typically have an 18-month period left to live so immediately go in search of a female mate. Although females continue to molt after reaching maturity, male rarely do again once they reach adulthood. Those that do often can become stuck during the molting process due to their sexual organs and die.
Female can live for 30 to 40 years. ''Grammostola rosea
The Chilean rose tarantula (''Grammostola rosea''), also known as the rose hair tarantula, the Chilean fire tarantula, or the Chilean red-haired tarantula (depending on the color morph), is probably the most common species of tarantula available i ...
'' spiders, which eat once or twice a week, have lived up to 20 years in captivity. Some have survived on water alone for up to two years.
Reproduction
opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma ( cephalothorax). It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata (arachnids, horseshoe crabs and others). Although it is similar in most respects ...
. After the semen has been transferred to the receptive female's body, the male swiftly leaves the scene before the female recovers her appetite. Although females may show some aggression after mating, the male rarely becomes a meal.
Females deposit 50 to 2,000 eggs, depending on the species, in a silken egg sac and guard it for six to eight weeks. During this time, the females stay very close to the egg sacs and become more aggressive. Within most species, the females turn the egg sac often, which is called brooding. This keeps the eggs from deforming due to sitting in one position too long. The young spiderlings remain in the nest for some time after hatching, where they live off the remains of their yolk sacs before dispersing.
Taxonomy
Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, t ...
placed all spiders in a single genus, ''Aranea''. In 1802, Charles Athanase Walckenaer separated mygalomorph spiders into a separate genus, ''Mygale'', leaving all other spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
s in '' Aranea''. However, ''Mygale'' had already been used in 1800 by Georges Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, Baron Cuvier (; 23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier, was a French naturalist and zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuvier was a major figure in na ...
for a genus of mammals (in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, ''mygale'' means " shrew"). Accordingly, in 1869, Tamerlan Thorell
Tord Tamerlan Teodor Thorell (3 May 1830 – 22 December 1901) was a Swedish arachnologist.
Thorell studied spiders with Giacomo Doria at the Museo Civico di Storia Naturale de Genoa. He corresponded with other arachnologists, such as Octavius P ...
used the family name "Theraphosoidae" (modern Theraphosidae) for the mygalomorph spiders known to him, rather than "Mygalidae" (as used, for example, by John Blackwall). Thorell later split the family into a number of genera, including ''Theraphosa''.
Subfamilies
A 2019 phylogenomic study recognized 12 subfamilies, one (Ischnocolinae) known not to bemonophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic ...
.
* Aviculariinae
*Eumenophorinae
The Eumenophorinae are a subfamily of tarantula spiders (family Theraphosidae). They are known from genera distributed across Sub-Saharan Africa, the south of the Arabian peninsula, Madagascar and its associated islands, and parts of India.
D ...
*Harpactirinae
The Harpactirinae (commonly called baboon spiders) are a subfamily of tarantulas which are native to the continent of Africa. Like many Old World tarantulas, they have a relatively strong venom, and can inflict a painful bite.
Description
Harp ...
*Ischnocolinae
The Ischnocolinae are a problematic subfamily of tarantulas (family Theraphosidae). In 1892, Eugène Simon based the group, which he noted was only weakly homogeneous, on the presence of divided tarsal scopulae. This feature was later considere ...
* Ornithoctoninae
* Poecilotheriinae
* Psalmopoeinae
* Schismatothelinae
*Selenocosmiinae
The ''Selenocosmiinae'' are a subfamily of tarantulas (Mygalomorphae: Theraphosidae) found throughout South-East Asia and Australia. This subfamily is defined by the presence of a lyra on the maxillae and strikers on the chelicerae, allowing thes ...
*Stromatopelminae
The Stromatopelminae are a subfamily of tarantulas native to West Africa and part of Central Africa. The subfamily was first proposed by Günter Schmidt in 1993.
Taxonomy
The subfamily Stromatopelminae was first proposed by Günter Schmidt in ...
* Theraphosinae
* Thrigmopoeinae
The relationship between the subfamilies found in the study is shown in the following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
. The dual placing of Ischnocolinae is highlighted.
All the species that possess urticating hairs and have been seen to use them in bombardment behavior are placed in the "bombardier clade", although not all species in the included subfamilies possess such hairs (all '' Schismatothelinae'' lack them as do most '' Psalmopoeinae'' genera). It is not clear whether the possession of urticating hairs was an ancestral trait of the clade, and has been lost in some species, or whether it represents multiple gains. Foley ''et al.'' suggested that the second hypothesis appeared to be better supported.
Other subfamilies that have been recognized include:
*Acanthopelminae
''Acanthopelma'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Frederick Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1897. it contains two species, found in Central America and South America: '' A. beccarii'' and '' A. rufescens''.
See also
* List of T ...
– may be treated as synonymous with Ischnocolinae
*Selenogyrinae
The Selenogyrinae are a subfamily of tarantulas found in Africa and Asia."Family: Therap ...
* Spelopelminae – typically not accepted, ''Hemirrhagus'' being treated as Theraphosinae
Genera
, theWorld Spider Catalog
The World Spider Catalog (WSC) is an online searchable database concerned with spider taxonomy. It aims to list all accepted families, genera and species, as well as provide access to the related taxonomic literature. The WSC began as a series of ...
accepted the following genera:
*''Acanthopelma
''Acanthopelma'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Frederick Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1897. it contains two species, found in Central America and South America: '' A. beccarii'' and '' A. rufescens''.
See also
* List of T ...
'' F. O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1897 – Guyana
*''Acanthoscurria
''Acanthoscurria'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Anton Ausserer in 1871.They are found throughout South America including the countries of Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname ...
'' Ausserer, 1871 – South America, Guatemala
*''Acentropelma
''Acentropelma'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae. It was first described in 1901 by Pocock. , it contains 4 species.
Description
Genus ''Acentropelma'' resembles genus ''Metriopelma'', with the distinction of ''Scopula'' on ...
'' Pocock, 1901 – Belize, Mexico, Guatemala
*''Aenigmarachne
''Aenigmarachne'' is a monotypic genus of tarantulas containing the single species, ''Aenigmarachne sinapophysis''. It was first described by Günter E. W. Schmidt in 2005, and has only been found in Costa Rica.
See also
* List of Theraphosidae ...
'' Schmidt, 2005 – Costa Rica
*''Agnostopelma
''Agnostopelma'' is a genus of Colombian tarantulas that was first described by F. Pérez-Miles & D. Weinmann in 2010. it contains two species, found in Colombia: ''Agnostopelma gardel'' and ''Agnostopelma tota''.
See also
* List of Theraphosida ...
'' Pérez-Miles & Weinmann, 2010 – Colombia
*'' Aguapanela'' Perafán & Cifuentes, 2015
*'' Amazonius'' Cifuentes & Bertani, 2022 - South America
*''Annandaliella
''Annandaliella'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by A. S. Hirst in 1909. it contains three species endemic to India: '' A. ernakulamensis'', '' A. pectinifera'', and '' A. travancorica''. They are selenogyrid tarantulas, meanin ...
'' Hirst, 1909 – India
*'' Anoploscelus'' Pocock, 1897 – Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda
*''Anqasha
''Anqasha'' is a monotypic genus of Peruvian tarantulas, containing one species, ''Anqasha picta'', first described by Danniella Sherwood and Ray Gabriel in 2022. The type species was initially described under the name ''Hapalopus pictus'' in 1 ...
'' Sherwood & Gabriel, 2022 - Peru
*'' Antikuna'' Kaderka, Ferretti, West, Lüddecke & Hüsser, 2021 - Peru
*''Antillena
''Antillena'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae (tarantulas). , the genus contained a single species, ''Antillena rickwesti'', found in the Dominican Republic.
Taxonomy
The species was first described in 2013 by Rogério Bertan ...
'' Bertani, Huff & Fukushima, 2017 – Dominican Republic
*'' Aphonopelma'' Pocock, 1901 – North America, Central America
*''Augacephalus
''Augacephalus'' is a genus of harpacterine theraphosid spiders. It has three species, all of which are found in Africa.
Taxonomy and etymology
The type species of ''Augacephalus'' is ''A. breyeri'' which was described as '' Pterinochilus brey ...
'' Gallon, 2002 – South Africa, Mozambique, Eswatini
*'' Avicularia'' Lamarck, 1818 – South America, Trinidad and Tobago, Panama
*''Bacillochilus
''Bacillochilus'' is a monotypic genus of African tarantulas containing the single species, ''Bacillochilus xenostridulans''. The genus and sole species were both described by R. C. Gallon in 2010, and is found in Angola. The name is a combinatio ...
'' Gallon, 2010 – Angola
*''Batesiella
''Batesiella'' is a monotypic genus of African tarantulas containing the single species, ''Batesiella crinita''. It was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1903, and is found in Cameroon. It is named in honor of the collector, G. L. Bates ...
'' Pocock, 1903 – Cameroon
*'' Birupes'' Gabriel & Sherwood, 2019 – Malaysia
*'' Bistriopelma'' Kaderka, 2015 – Peru
*'' Bonnetina'' Vol, 2000 – Mexico
*''Brachionopus
''Brachionopus'' is a genus of South African tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1897. It was transferred to the Theraphosidae from the Barychelidae in 1985.
Species
it contains five species, found in South Africa: ...
'' Pocock, 1897 – South Africa
*'' Brachypelma'' Simon, 1891 – Mexico, Costa Rica, Guatemala
*'' Bumba'' Pérez-Miles, Bonaldo & Miglio, 2014 – Brazil, Venezuela, Ecuador
*''Cardiopelma
''Cardiopelma'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae. It was first described in 1999 by Vol. , it contains only one species, ''Cardiopelma mascatum'', known only from Mexico, in the state of Oaxaca.
Description
''Cardiopelma masca ...
'' Vol, 1999 – Unknown
*'' Caribena'' Fukushima & Bertani, 2017 – Cuba
*'' Catanduba'' Yamamoto, Lucas & Brescovit, 2012 – Brazil
*''Catumiri
''Catumiri'' is a genus of South American tarantulas that was first described by J. P. L. Guadanucci in 2004. The name is derived from the Tupi "''Catumiri''", meaning "very small".
Description
Members of ''Catumiri'' have a labium that is much ...
'' Guadanucci, 2004 – South America
*''Ceratogyrus
''Ceratogyrus'' is a genus of tarantulas found in southern Africa. They are commonly called horned baboons for the foveal horn found on the peltidium in some species.
Diagnosis
They are readily distinguished from other African theraphosid ...
'' Pocock, 1897 – Africa
*''Chaetopelma
''Chaetopelma'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Anton Ausserer in 1871. They are found in Africa including the countries of Turkey, Syria, Egypt, Cyprus, Greece, Sudan and Cameroon.
Diagnosis
They can be distinguished f ...
'' Ausserer, 1871 – Asia, Greece, Africa
*'' Chilobrachys'' Karsch, 1892 – Asia
*'' Chromatopelma'' Schmidt, 1995 – Venezuela
*''Citharacanthus
''Citharacanthus'' is a genus of New World tarantulas. They are found in Central America and the Antilles.
Species
, the World Spider Catalog accepted the following 7 species:
*'' Citharacanthus alayoni'' Rudloff, 1995 – Cuba
*'' Citharacant ...
'' Pocock, 1901 – Cuba, Central America, Mexico
*''Citharognathus
''Citharognathus'' is a genus of Asian tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1895. it contains two species: '' C. hosei'' and '' C. tongmianensis''.
Diagnosis
They can be distinguished by their clypeus, which is less ...
'' Pocock, 1895 – Indonesia
*'' Clavopelma'' Chamberlin, 1940 – Mexico
*'' Coremiocnemis'' Simon, 1892 – Malaysia, Indonesia, Australia
*''Cotztetlana
''Cotztetlana'' is a genus of Mexican tarantulas that was first described by J. I. Mendoza M. in 2012. it contains two species, found in Mexico: '' C. omiltemi'' and '' C. villadai''.
See also
* List of Theraphosidae species
This page lists ...
'' Mendoza, 2012 – Mexico
*''Crassicrus
''Crassicrus'' is a genus of Central and South American tarantulas that was first described by S. B. Reichling & R. C. West in 1996.
Species
it contains six species, found in Belize, Guatemala, and Mexico:
*'' Crassicrus bidxigui'' Candia-Ram� ...
'' Reichling & West, 1996 – Mexico, Belize
*''Cubanana
''Cubanana'' is a monotypic genus of tarantulas containing the single species, ''Cubanana cristinae''. It was first described by D. Ortiz in 2008, and is endemic to Cuba, occurring in the east of the island.
See also
* List of Theraphosidae spe ...
'' Ortiz, 2008 – Cuba
*'' Cyclosternum'' Ausserer, 1871 – South America, Mexico, Costa Rica
*'' Cymbiapophysa'' Gabriel & Sherwood, 2020
*'' Cyriocosmus'' Simon, 1903 – South America, Trinidad and Tobago
*'' Cyriopagopus'' Simon, 1887 – Asia
*'' Cyrtogrammomma"Pocock, 1895 - Guyana and Brazil
*''Cyrtopholis
''Cyrtopholis'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1892.
Diagnosis
This genus can be distinguished by being found in the Caribbean, and by the presence of claviform stridulatory hairs on the trochanter ...
'' Simon, 1892 – Caribbean
*''Davus
''Davus'', also known as the tiger rump tarantulas, is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae (tarantulas). It was formerly included in ''Cyclosternum''. They are medium to large tarantulas, found in Central America and Mexico.
Diagnos ...
'' O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1892 – Central America, Mexico
*''Dolichothele
''Dolichothele'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae found in Brazil and Bolivia. It was first described in 1923 by Mello-Leitão.
Diagnosis
It owns a labium, which has less than 10 cuspules, also owning undivided tarsal sco ...
'' Mello-Leitão, 1923 – Brazil, Bolivia
*''Encyocratella
''Encyocratella'' is a monotypic genus of Tanzanian tarantulas (family Theraphosidae) containing the single species, ''Encyocratella olivacea'', also known as the Tanzanian black and olive baboon spider. It was first described by Embrik Strand i ...
'' Strand, 1907 – Tanzania
*'' Encyocrates'' Simon, 1892 – Madagascar
*'' Ephebopus'' Simon, 1892 – Suriname, Brazil
*'' Euathlus'' Ausserer, 1875 – Chile, Argentina
*''Eucratoscelus
''Eucratoscelus'' is a genus of East African tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1898. it contains two species, found in Tanzania and Kenya: '' E. constrictus'' and '' E. pachypus''.
See also
* List of Theraphosidae ...
'' Pocock, 1898 – Kenya, Tanzania
*''Eumenophorus
}
''Eumenophorus'' is a genus of Sierra Leonean Theraphosidae, tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1897. it contains two species, found in Sierra Leone: '' Eumenophorus clementsi, E. clementsi'' and '' E. murphyorum''. ...
'' Pocock, 1897 – Sierra Leone
*''Eupalaestrus
''Eupalaestrus'' is a genus of South American tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1901.
Species
it contains six species, found in Uruguay, Argentina, Paraguay, and Brazil:
*'' Eupalaestrus campestratus'' (Simon, 1891 ...
'' Pocock, 1901 – South America
*''Euphrictus
''Euphrictus'' is a genus of tarantula (family Theraphosidae) which is found in Africa. It is part of the subfamily Selenogyrinae.
Taxonomy
The genus ''Euphrictus'' was erected by A.S. Hirst in 1908 for the species '' Euphrictus spinosus'', des ...
'' Hirst, 1908 – Cameroon, Congo
*''Euthycaelus
''Euthycaelus'' is a genus of tarantula. It was first described in 1889 by Simon, and is found through Central and South America.
Species
, it contained 7 species:
* '' Euthycaelus amandae'' Guadanucci & Weinmann, 2014 - Colombia
* '' Euthy ...
'' Simon, 1889 – Colombia, Venezuela
*'' Grammostola'' Simon, 1892 – South America
*'' Guyruita'' Guadanucci, Lucas, Indicatti & Yamamoto, 2007 – Brazil, Venezuela
*'' Hapalopus'' Ausserer, 1875 – South America, Panama
*'' Hapalotremus'' Simon, 1903 – Bolivia, Peru, Argentina
*''Haploclastus
''Haploclastus'' is a genus of Indian tarantulas that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1892. It is considered a senior synonym of ''Phlogiodes''.
Diagnosis
They can be distinguished by the deep and procured fovea, with horizonta ...
'' Simon, 1892 – India
*'' Haplocosmia'' Schmidt & von Wirth, 1996 – Nepal
*''Harpactira
''Harpactira'' is a genus of African tarantulas that was first described by Anton Ausserer in 1871.
Species
it contains fifteen species, found in Namibia and South Africa:
*'' Harpactira atra'' (Latreille, 1832) ( type) – South Africa
*'' Harp ...
'' Ausserer, 1871 – South Africa, Namibia
*''Harpactirella
''Harpactirella'' is a genus of African tarantulas that was first described by William Frederick Purcell in 1902. Originally placed with the brushed trapdoor spiders, it was transferred to the tarantulas in 1985.
It is considered a senior synony ...
'' Purcell, 1902 – South Africa, Morocco
*'' Hemirrhagus'' Simon, 1903 – Mexico
*'' Heterophrictus'' Pocock, 1900 – India
*''Heteroscodra
''Heteroscodra'' is a genus of Central African tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1900. Like many Old World tarantulas, they have a strong venom, and can inflict a painful bite. it contains two species, found in Afri ...
'' Pocock, 1900 – Cameroon, Gabon, Congo
*'' Heterothele'' Karsch, 1879 – Africa, Argentina
*'' Holothele'' Karsch, 1879 – Caribbean, South America
*'' Homoeomma'' Ausserer, 1871 – South America
*''Hysterocrates
''Hysterocrates'' is a genus of African tarantulas that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1892.
Species
it contains 18 species and one subspecies, found in Africa:
*'' Hysterocrates apostolicus'' Pocock, 1900 – São Tomé and Pr ...
'' Simon, 1892 – Africa
*''Idiothele
''Idiothele'' is a genus of African tarantulas that was first described by J. Hewitt in 1919. it contains two species, both found in southern Africa: '' I. mira'' and '' I. nigrofulva''.
See also
* List of Theraphosidae species
This page list ...
'' Hewitt, 1919 – South Africa
*''Iridopelma
''Iridopelma'' is a genus of Brazilian tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1901.
Diagnosis
Males of this genus can be distinguished by the tibial spurs on leg 1 and 2, while females differ from most other genera by the ...
'' Pocock, 1901 – Brazil
*''Ischnocolus
''Ischnocolus'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Anton Ausserer in 1871. This tarantula genus includes some of the smallest in the family.
Diagnosis
Males of this genus can be distinguished by the palpal bulb morphology, wh ...
'' Ausserer, 1871 – Africa, Asia, Brazil, Europe
*'' Kankuamo'' Perafán, Galvis & Pérez-Miles, 2016
*'' Kochiana'' Fukushima, Nagahama & Bertani, 2008 – Brazil
*'' Lampropelma'' Simon, 1892 – Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore
*''Lasiodora
''Lasiodora'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Ludwig Carl Christian Koch in 1850. They are often very large; body lengths of up to , including the legs, are not unusual. They are found in South America, including the countries ...
'' C. L. Koch, 1850 – South America, Costa Rica
*''Lasiodorides
''Lasiodorides'' is a genus of South American tarantulas that was first described by Günter E. W. Schmidt & B. Bischoff in 1997.
Species
it contains two species, found in Peru and Ecuador:
*'' Lasiodorides polycuspulatus'' Schmidt & Bischoff, ...
'' Schmidt & Bischoff, 1997 – Ecuador, Peru
*''Longilyra
''Longilyra'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae. It was first described in 2014 by Gabriel. , it contains only one species, ''Longilyra johnlonghorni'', found in El Salvador. This genus differs from the others as it has stridulat ...
'' Gabriel, 2014 – El Salvador
*''Loxomphalia
''Loxomphalia'' is a monotypic genus of tarantulas containing the single species, ''Loxomphalia rubida''. It was first described from a female found by Eugène Louis Simon in 1889, and it has only been found on the Zanzibar Archipelago.
See als ...
'' Simon, 1889 – Tanzania
*''Loxoptygus
''Loxoptygus'' is a genus of African tarantulas that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1903. it contains two species, found in Ethiopia: '' L. coturnatus'' and '' L. ectypus''. It was removed from the synonymy of ''Phoneyusa'', and is ...
'' Simon, 1903 – Ethiopia
*'' Lyrognathus'' Pocock, 1895 – Indonesia, India, Malaysia
*''Magnacarina
''Magnacarina'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae
Tarantulas comprise a group of large and often hairy spiders of the family Theraphosidae. , 1,040 species have been identified, with 156 genera. The term "tarantula" is us ...
'' Mendoza, Locht, Kaderka, Medina & Pérez-Miles, 2016 – Mexico
*''Mascaraneus
''Mascaraneus'' is a monotypic genus of African tarantulas containing the single species, ''Mascaraneus remotus''. It was first described by R. C. Gallon in 2005, and is endemic to Mauritius.
Taxonomy
The genus and species were first described by ...
'' Gallon, 2005 – Mauritius
*''Megaphobema
''Megaphobema'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1901. They look similar to members of '' Pamphobeteus'' except for its legs; the third and fourth pairs of legs are much larger and stronger than the fir ...
'' Pocock, 1901 – Costa Rica, Colombia, Ecuador
*'' Melognathus'' Chamberlin, 1917
*'' Metriopelma'' Becker, 1878 – Mexico
*''Miaschistopus
''Miaschistopus'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae. It was first described in 1897 by Pocock. , it contains only one species, ''Miaschistopus tetricus'', from Venezuela.
References
Theraphosidae
Monotypic Theraphosidae ...
'' Pocock, 1897 – Venezuela
*''Monocentropus
''Monocentropus'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1897. it contains three species, found on Madagascar and in Yemen: '' M. balfouri'', '' M. lambertoni'', and '' M. longimanus''.
''M. balfouri'' has ...
'' Pocock, 1897 – Yemen, Madagascar
*'' Munduruku'' Miglio, Bonaldo & Pérez-Miles, 2013
*''Murphyarachne
''Murphyarachne'' is a monotypic genus of Peruvian tarantulas, with one species, ''Murphyarachne ymasumacae''. It was first described by Sherwood and Gabriel in 2022. The genus is named after Frances Mary Murphy (1926 to 1995) and John Alan Murp ...
'' Sherwood & Gabriel, 2022 - Peru
*'' Mygalarachne'' Ausserer, 1871 – Honduras
*'' Myostola'' Simon, 1903 – Gabon, Cameroon
*''Neischnocolus
''Neischnocolus'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae. It was first described in 1925 by Petrunkevitch. The genus ''Ami'' was separately described in 2008, but was later discovered to be a junior synonym of ''Neischnocolus''. Speci ...
'' Petrunkevitch, 1925 – Panama
*'' Neoheterophrictus'' Siliwal & Raven, 2012 – India
*''Neoholothele
''Neoholothele'' is a genus of tarantula, first described in 2015 by Guadanucci & Weinmann. , it contains 2 species '' Neoholothele fasciaaurinigra'' and '' Neoholothele incei,'' the latter being the type species. They are named after the prefix ...
'' Guadanucci & Weinmann, 2015 – Colombia, Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela
*''Neostenotarsus
''Neostenotarsus'' is a genus of theraphosid spider, in the Theraphosinae subfamily. It is native to French Guiana. It is monotypic, the only species being ''Neostenotarsus scissistylus''.Nesiergus
''Nesiergus'' is a genus of Seychelloise tarantulas that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1903. it contains three species, found on the Seychelles: '' N. gardineri'', '' N. halophilus'', and '' N. insulanus''.
See also
* List of T ...
'' Simon, 1903 – Seychelles
*''Nesipelma
''Nesipelma'' is a genus of tarantulas containing the two species, ''Nesipelma insulare'' and ''Nesipelma medium'' . It was first described by Günter E. W. Schmidt & F. Kovařík in 1996, and is found in Nevis and on the Lesser Antilles.
See ...
'' Schmidt & Kovařík, 1996 – St. Kitts and Nevis
*'' Nhandu'' Lucas, 1983 – Brazil, Paraguay
*'' Omothymus'' Thorell, 1891 – Malaysia
*'' Ornithoctonus'' Pocock, 1892 – Myanmar, Thailand
*'' Orphnaecus'' Simon, 1892 – Papua New Guinea, Philippines
*'' Ozopactus'' Simon, 1889 – Venezuela
*'' Pachistopelma'' Pocock, 1901 – Brazil
*''Pamphobeteus
''Pamphobeteus'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1901. It includes some of the largest spiders in the world. They are found in South America, including the countries of Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, Brazil ...
'' Pocock, 1901 – South America, Panama
*'' Pelinobius'' Karsch, 1885 – Kenya, Tanzania
*'' Phlogiellus'' Pocock, 1897 – Asia, Papua New Guinea
*'' Phoneyusa'' Karsch, 1884 – Africa
*''Phormictopus
''Phormictopus'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae (tarantulas) that occurs in the West Indies, mainly Cuba and Hispaniola, with three species probably misplaced in this genus found in Brazil and Argentina.
Description
''Phormic ...
'' Pocock, 1901 – Cuba, Argentina, Brazil
*'' Phormingochilus'' Pocock, 1895 – Indonesia
*''Phrixotrichus
''Phrixotrichus'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae
Tarantulas comprise a group of large and often hairy spiders of the family Theraphosidae. , 1,040 species have been identified, with 156 genera. The term "tarantula" is u ...
'' Simon, 1889 – Chile, Argentina
*'' Plesiopelma'' Pocock, 1901 – South America
*'' Plesiophrictus'' Pocock, 1899 – India, Micronesia, Sri Lanka
*'' Poecilotheria'' Simon, 1885 – Sri Lanka, India
*'' Proshapalopus'' Mello-Leitão, 1923 – Brazil, Colombia
*'' Psalistops''Simon, 1889 - Colombia and Venezuela
*''Psalmopoeus
Psalmopoeus is a genus of the family ''Theraphosidae'' containing various species of tarantulas. The genus is native to Trinidad and Tobago, Colombia, Ecuador, Venezuela, Guyana, Brazil, Belize, Panama, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Mexico, Guat ...
'' Pocock, 1895 – Trinidad, South America, Central America, Mexico
*''Psednocnemis
''Psednocnemis'' is a genus of Southeast Asian tarantulas that was first described by R. C. West, S. C. Nunn & Henry Roughton Hogg in 2012.
Species
it contains five species, found in Indonesia and Malaysia:
*''Psednocnemis brachyramosa'' ( ...
'' West, Nunn & Hogg, 2012 – Malaysia, Indonesia
*''Pseudhapalopus
''Pseudhapalopus'' is a monotypic genus of Bolivian tarantulas containing the single species, ''Pseudhapalopus aculeatus''. It was first described by Embrik Strand in 1907, and is found in Bolivia.
See also
* List of Theraphosidae species
This ...
'' Strand, 1907 – South America, Trinidad
*'' Pseudoclamoris'' Hüsser, 2018 – Colombia, Peru, Ecuador
*''Pseudoschizopelma
''Cyclosternum'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Anton Ausserer in 1871.
Species
it contains twelve species, found in South America, Costa Rica, and Mexico:
*''Cyclosternum darienense'' Gabriel & Sherwood, 2022 = Panama
*'' ...
''Smith, 1995 - Mexico
*''Pterinochilus
''Pterinochilus'' is a genus of baboon spiders that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1897. They are found all throughout Africa
Species
it contains ten species, all found in Africa:
*'' Pterinochilus alluaudi'' Berland, 1914 � ...
'' Pocock, 1897 – Africa
*''Pterinopelma
''Pterinopelma'' is a genus of Brazilian tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1901. it contains two species, found in Brazil: '' P. felipeleitei'' and '' P. vitiosum''. It was removed from the synonymy of '' Eupalaestru ...
'' Pocock, 1901 – Brazil
*''Reichlingia
''Reichlingia'' is a monotypic genus of Central American tarantulas containing the single species, ''Reichlingia annae''. The genus was first described in 2001, and has only been found in Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and C ...
'' Rudloff, 2001 – Belize
*''Reversopelma
''Reversopelma'' is a monotypic genus of spider in the family Theraphosidae. It is Theraphosine and is native to Peru and Ecuador. The single species is ''Reversopelma petersi''.
Description
''Reversopelma'' shows strong sexual dimorphism, the ...
'' Schmidt, 2001 – Ecuador or Peru
*'' Sahydroaraneus'' Mirza & Sanap, 2014 – India
*'' Sandinista'' Longhorn & Gabriel, 2019
*''Schismatothele
''Schismatothele'' is a genus of South American tarantulas that was first described by Ferdinand Anton Franz Karsch in 1879.
Species
it contains eight species, found in Venezuela, Colombia, and Brazil:
*'' Schismatothele benedettii'' Panzera, ...
'' Karsch, 1879 – Venezuela, Colombia
*''Schizopelma
''Schizopelma'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Frederick Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1897. it contains two species, found in Central America and Mexico: '' S. bicarinatum'' and '' S. juxtantricola''.
See also
* List of Th ...
'' F. O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1897 – Mexico
*''Scopelobates
''Scopelobates'' is a genus of tarantulas containing the single species, ''Scopelobates sericeus''. It was first described by Eugène Simon in 1903, and is only found in Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Domi ...
'' Simon, 1903 – Dominican Republic
*''Selenocosmia
''Selenocosmia'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Anton Ausserer in 1871. The genus is found in China, New Guinea, Indonesia, Australia, Indonesia, Myanmar, Malaysia, Laos, Vietnam, Philippines, India and Pakistan. Th ...
'' Ausserer, 1871 – Oceania, Asia
*''Selenogyrus
''Selenogyrus'' is a genus of spider, or more specifically, selenogyrine theraphosid. The type species is '' Selenogyrus caeruleus''.Selenotholus
''Selenotholus'' is a monotypic genus of tarantulas containing the single species, ''Selenotholus foelschei''. It was first described by Henry Roughton Hogg in 1902, and is found in the Northern Territory. It is distinguished from ''Selenocosmia' ...
'' Hogg, 1902 – Australia
*''Selenotypus
The genus ''Selenotypus'' includes one of the largest of Australia's theraphosids. At present, the only recognised species within this genus is ''Selenotypus plumipes'', but this is expected to change, as it is becoming apparent that the genus h ...
'' Pocock, 1895 – Australia
*'' Sericopelma'' Ausserer, 1875 – Central America, Brazil, Mexico
*''Sickius
''Sickius'' is a genus of tarantulas. It has a single species, ''Sickius longibulbi''. It is endemic to Brazil.
Taxonomy
The species ''S. longibulbi'' was described in 1948 by Benedict A. M. Soares and H.F. de A. Camargo, however Rob ...
'' Soares & Camargo, 1948 – Brazil
*'' Sphaerobothria'' Karsch, 1879 – Costa Rica, Panama
*''Spinosatibiapalpus
''Spinosatibiapalpus'' is a genus of tarantulas erected by Gabriel and Sherwood in 2020 for a newly discovered species and two other previously described species bearing a unique palpal bulb morphology. The name is a reference to the spines found ...
'' Gabriel & Sherwood, 2020
*''Stichoplastoris
''Stichoplastoris'' is a genus of Central American tarantulas that was first described by J.-P. Rudloff in 1997.
Species
it contains eight species, found in Panama, Belize, Costa Rica, and El Salvador:
*''Stichoplastoris angustatus'' (Kraus, 195 ...
'' Rudloff, 1997 – El Salvador, Costa Rica, Panama
*''Stromatopelma
''Stromatopelma'' is a genus of African tarantulas that was first described by Ferdinand Anton Franz Karsch in 1881. They are renowned for their potent venom that uses stromatoxin peptides to induce medically significant effects.
Species
it ...
'' Karsch, 1881 – Africa
*'' Taksinus'' Songsangchote, Sippawat, Khaikaew & Chomphuphuang, 2022 - Thailand
*''Tapinauchenius
''Tapinauchenius'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Anton Ausserer in 1871. The name is a combination of the Greek , meaning "low", and , meaning "neck". In 2022, the genus ''Pseudoclamoris'' was transferred to ''Tapinauchenius ...
'' Ausserer, 1871 – South America, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
*'' Theraphosa'' Thorell, 1870 – South America
*''Thrigmopoeus
''Thrigmopoeus'' is a genus of Indian tarantulas that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1899. it contains two species, found in India: '' T. insignis'' and '' T. truculentus''.
See also
* List of Theraphosidae species
This page ...
'' Pocock, 1899 – India
*''Thrixopelma
''Thrixopelma'' is a genus of South American tarantulas that was first described by Günter E. W. Schmidt in 1994. They are medium to large tarantulas, usually being 35mm to 60mm in body length.
Diagnosis
Males can be distinguished by the pres ...
'' Schmidt, 1994 – Peru, Chile
*''Tliltocatl
''Tliltocatl'' is a genus of North American tarantulas that was split off from ''Brachypelma'' in 2020. They are also large burrowing tarantulas, but don't have the striking red leg markings of ''Brachypelma'' species. A female '' T. vagans'' can ...
'' - Mexico, Costa Rica, Guatemala
*''Tmesiphantes
''Tmesiphantes'' is a genus of Brazilian tarantulas in the subfamily Theraphosinae that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1892. The genera ''Magulla'' and ''Melloleitaoina'' were brought into synonymy in 2019.
Species
it contains ...
'' Simon, 1892 – Brazil
*''Trichognathella
''Trichognathella'' is a monotypic genus of South African tarantulas containing the single species, ''Trichognathella schoenlandi''. It was first described by R. C. Gallon in 2004, and is found in South Africa.
See also
* List of Theraphosidae s ...
'' Gallon, 2004 – South Africa
*''Trichopelma
''Trichopelma'' is a genus of South American and Caribbean tarantulas first described by Eugène Simon in 1888.
Taxonomy
This genus was erected by Eugène Simon in 1888 with '' Trichopelma illetabile'' and the type species '' Trichopelma niti ...
'' Simon, 1888 – Caribbean, South America, Central America
*'' Typhochlaena'' C. L. Koch, 1850 – Brazil
*''Umbyquyra
''Umbyquyra'' is a genus of South American tarantulas
Tarantulas comprise a group of large and often hairy spiders of the family Theraphosidae. , 1,040 species have been identified, with 156 genera. The term "tarantula" is usually used t ...
'' Gargiulo, Brescovit & Lucas, 2018 – Bolivia, Brazil
*'' Vitalius'' Lucas, Silva & Bertani, 1993 – Brazil, Argentina
*''Xenesthis
''Xenesthis'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1891. it contains four species, found in Colombia and Venezuela, though it was previously considered to be found in Panama.
Diagnosis
There distinguish ...
'' Simon, 1891 – Panama, Venezuela, Colombia
*''Yanomamius
''Yanomamius'' is a genus of South American tarantulas first erected by Rogério Bertani and M. Q. Almeida in 2021 for two newly discovered species and one previously described species from Brazil. In one of Bertani's prior studies, he investigat ...
'' Bertani & Almeida, 2021 – Brazil, Venezuela
*''Ybyrapora
''Ybyrapora'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae (tarantulas), found in Brazil. Its species were formerly placed in the genus '' Avicularia''.
Description
''Ybrapora'' consists of species that are smaller than most aviculariines ...
'' Fukushima & Bertani, 2017 – Brazil
Former genera:
*''Ami'' Pérez-Miles, 2008 → ''Neischnocolus
''Neischnocolus'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae. It was first described in 1925 by Petrunkevitch. The genus ''Ami'' was separately described in 2008, but was later discovered to be a junior synonym of ''Neischnocolus''. Speci ...
''
*''Barropelma'' Chamberlin, 1940 → ''Neischnocolus
''Neischnocolus'' is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae. It was first described in 1925 by Petrunkevitch. The genus ''Ami'' was separately described in 2008, but was later discovered to be a junior synonym of ''Neischnocolus''. Speci ...
''
*''Eurypelmella
''Eurypelmella'' is a ''nomen dubium'' (doubtful name) for a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae. It has been regarded as a synonym for ''Schizopelma
''Schizopelma'' is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Frederick Octavi ...
'' Strand, 1907, '' nomen dubium''
*''Magulla'' Simon, 1892 → ''Tmesiphantes
''Tmesiphantes'' is a genus of Brazilian tarantulas in the subfamily Theraphosinae that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1892. The genera ''Magulla'' and ''Melloleitaoina'' were brought into synonymy in 2019.
Species
it contains ...
''
*''Melloleitaoina'' Gerschman & Schiapelli, 1960 → ''Tmesiphantes
''Tmesiphantes'' is a genus of Brazilian tarantulas in the subfamily Theraphosinae that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1892. The genera ''Magulla'' and ''Melloleitaoina'' were brought into synonymy in 2019.
Species
it contains ...
''
Fossil record
Although fossils of mygalomorph spiders date back to theTriassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period ...
, only two specimens have been found so far which can be convincingly assigned to the Theraphosidae. One is from Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In M ...
; the other is from Chiapas
Chiapas (; Tzotzil and Tzeltal: ''Chyapas'' ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas), is one of the states that make up the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 124 municipalities ...
(Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
) amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In M ...
. Both these ambers are quite young, being Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" ...
in age or about 16 million years old.
See also
* Cultural depictions of spiders * Guangxitoxin * Spider bite * Spider taxonomyReferences
Further reading
* *External links
TarantulaForum.com
*
Tarantulas US Forum
Word of the Day: Tarantula and Tarantella
etymology and folklore
* ttp://research.amnh.org/entomology/spiders/catalog/THERAPHOSIDAE.html Listing of all currently named Theraphosidae
American Tarantula Society Headquarters
Amazing Tarantulas
*
Watch Tarantula (Theraphosidae) video clips from the BBC archive on Wildlife Finder
Theraphosidae Belgium, everything about bird eaters
{{Authority control Theraphosidae, Extant Miocene first appearances