|
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Spider Terms
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids. Links within the glossary are shown . Terms A Abdomen or opisthosoma: One of the two main body parts ( tagmata), located towards the posterior end; see also Abdomen § Other animals Accessory claw: Modified at the tip of the in web-building spiders; used with to grip strands of the web Anal tubercle: A small protuberance (tubercule) above the through which the anus opens Apodeme → Apophysis (plural apophyses): An outgrowth or process changing the general shape of a body part, particularly the appendages; often used in describing the male → Atrium (plural atria): An internal chamber at the entrance to the in female haplogyne spiders B Bidentate: Having two Book lungs: Respiratory organs on the ventral side (underside) of the , in front of the , opening through narrow slits; see also Book lungs Branchial operculum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerata
The subphylum Chelicerata (from New Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. It contains the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, solifuges, ticks, and mites, among many others), as well as a number of extinct lineages, such as the eurypterids (sea scorpions) and chasmataspidids. The Chelicerata originated as marine animals in the Middle Cambrian period; the first confirmed chelicerate fossils, belonging to ''Sanctacaris'', date from 508 million years ago. The surviving marine species include the four species of xiphosurans (horseshoe crabs), and possibly the 1,300 species of pycnogonids (sea spiders), if the latter are indeed chelicerates. On the other hand, there are over 77,000 well-identified species of air-breathing chelicerates, and there may be about 500,000 unidentified species. Like all arthropods, chelicerates have segmented bodies with jointed limbs, all covered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
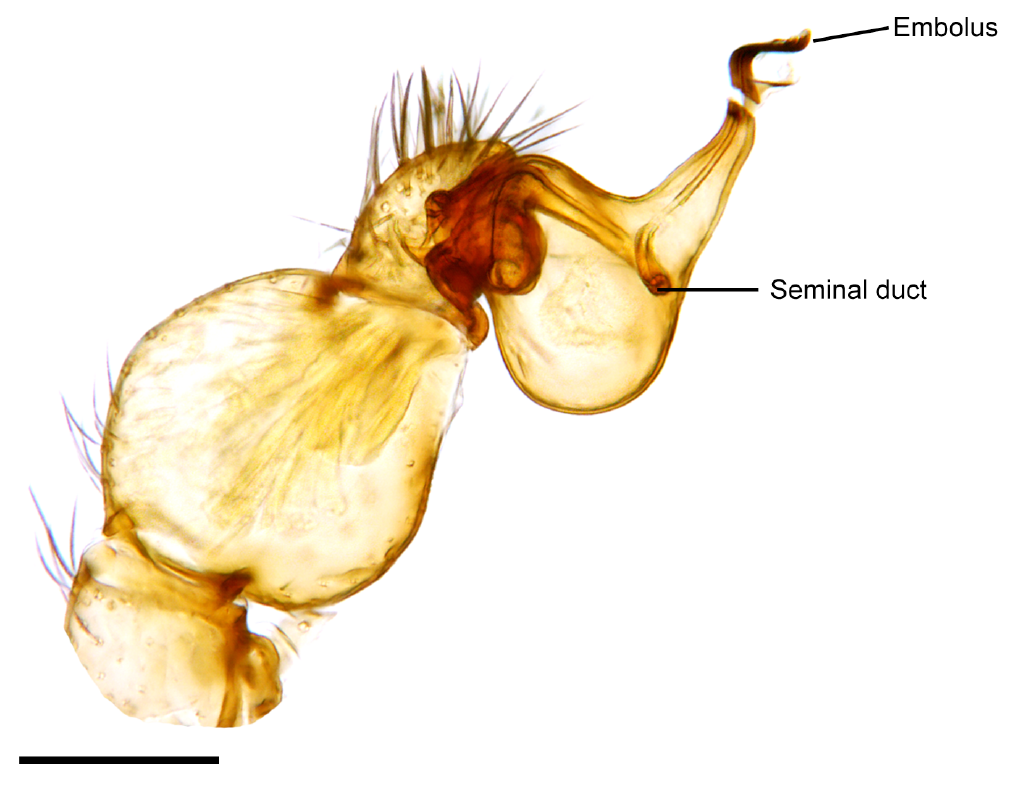
Spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solifugae
Solifugae is an order of animals in the class Arachnida known variously as camel spiders, wind scorpions, sun spiders, or solifuges. The order includes more than 1,000 described species in about 147 genera. Despite the common names, they are neither true scorpions (order Scorpiones), nor true spiders (order Araneae). Most species of Solifugae live in dry climates and feed opportunistically on ground-dwelling arthropods and other small animals. The largest species grow to a length of , including legs. A number of urban legends exaggerate the size and speed of the Solifugae, and their potential danger to humans, which is negligible. Anatomy Solifuges are moderately small to large arachnids (a few millimeters to several centimeters in body length), with the larger species reaching in length, including legs. In practice, the respective lengths of the legs of various species differ drastically, so the resulting figures are often misleading. More practical measurements refer prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
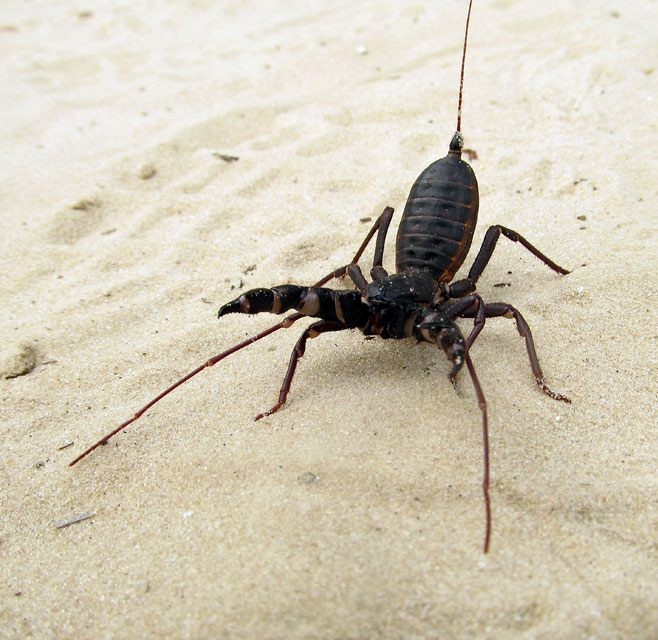
Amblypygi
Amblypygi is an ancient order of arachnid chelicerate arthropods also known as African cave-dwelling spiders, whip spiders and tailless whip scorpions (not to be confused with whip scorpions or vinegaroons that belong to the related order Thelyphonida). The name "amblypygid" means "blunt tail", a reference to a lack of the flagellum that is otherwise seen in whip scorpions. Amblypygids possess no silk glands or venomous fangs. They rarely bite if threatened, but can grab fingers with their pedipalps, resulting in thorn-like puncture injuries. As of 2016, 5 families, 17 genera and around 155 species had been discovered and described. They are found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide; they are mainly found in warm and humid environments and like to stay protected and hidden within leaf litter, caves, or underneath bark. Some species are subterranean; all are nocturnal. Fossilized amblypygids have been found dating back to the Carboniferous period, such as '' Weygoldtina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ricinulei
Ricinulei is a small order of arachnids. Like most arachnids, they are predatory, eating small arthropods. They occur today in west-central Africa ('' Ricinoides'') and the Neotropics ('' Cryptocellus'' and '' Pseudocellus'') as far north as Texas. As of 2021, 91 extant species of ricinuleids have been described worldwide, all in the single family Ricinoididae. In older works they are sometimes referred to as Podogona. Due to their obscurity they do not have a proper common name, though in academic literature they are occasionally referred to as hooded tickspiders. In addition to the three living genera, there are fossil species from the upper Carboniferous of Euramerica and the Cretaceous Burmese amber. Description The most important general account of ricinuleid anatomy remains the 1904 monograph by Hans Jacob Hansen and William Sørensen. Useful further studies can be found in, e.g., the work of Pittard and Mitchell, Gerald Legg and L. van der Hammen. Body Ricinulei are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs, and are easily recognized by a pair of grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always ending with a stinger. The evolutionary history of scorpions goes back 435 million years. They mainly live in deserts but have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. There are over 2,500 described species, with 22 extant (living) families recognized to date. Their taxonomy is being revised to account for 21st-century genomic studies. Scorpions primarily prey on insects and other invertebrates, but some species hunt vertebrates. They use their pincers to restrain and kill prey, or to prevent their own predation. The venomous sting is used for offense and defense. During courtship, the male and female grasp each other's pincers and dance while he tries to move her onto his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Leg
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plural ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (plural ''femora''), ''tibia'' (plural ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (plural ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (plural ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (plural ''patellae''). Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a ''Hox''-gene, could result in parallel gains of leg segments. In arthropods, each of the leg segments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
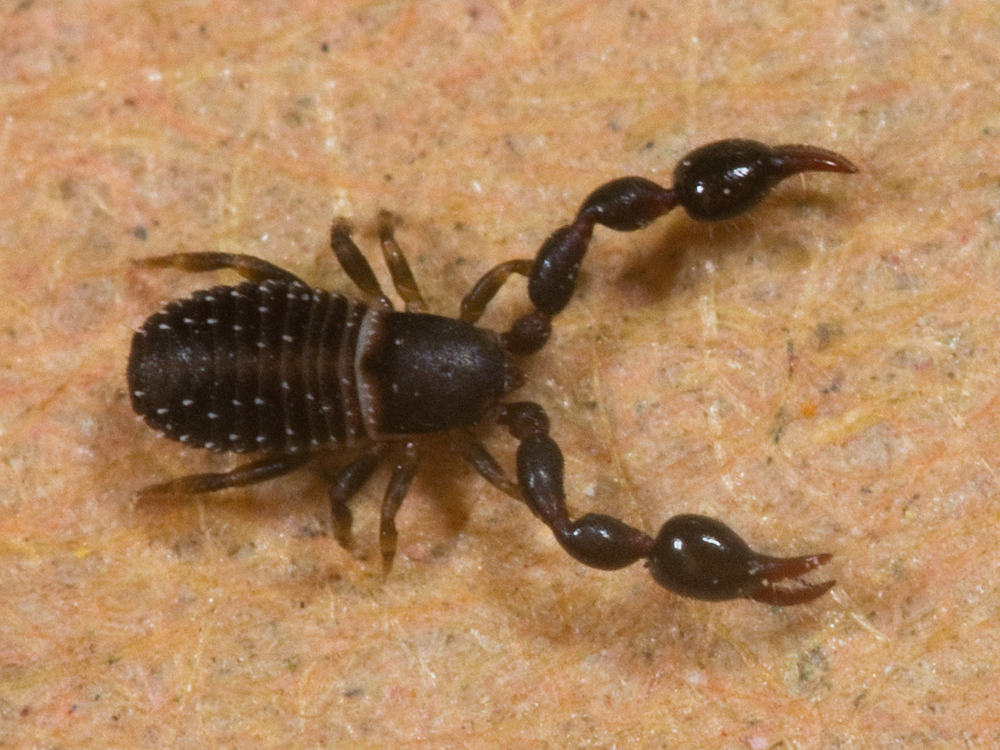
Pseudoscorpion
Pseudoscorpions, also known as false scorpions or book scorpions, are small, scorpion-like arachnids belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida. Pseudoscorpions are generally beneficial to humans since they prey on clothes moth larvae, carpet beetle larvae, booklice, ants, mites, and small flies. They are tiny, and are rarely noticed due to their small size, despite being common in many environments. When people do see pseudoscorpions, especially indoors, they are often mistaken for ticks or small spiders. Pseudoscorpions often carry out phoresis, a form of commensalism in which one organism uses another for the purpose of transport. Characteristics Pseudoscorpions belong to the class Arachnida. They are small arachnids with a flat, pear-shaped body, and pincer-like pedipalps that resemble those of scorpions. They usually range from in length. Pennsylvania State University, DepartmentEntomological Notes: Pseudoscorpion Fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thelyphonida
Thelyphonida is an arachnid order comprising invertebrates commonly known as whip scorpions or vinegaroons (also spelled vinegarroons and vinegarones). They are often called uropygids in the scientific community based on an alternative name for the order, Uropygi (which may then also include the order Schizomida). The name "whip scorpion" refers to their resemblance to true scorpions and possession of a whiplike tail, and "vinegaroon" refers to their ability when attacked to discharge an offensive, vinegar-smelling liquid, which contains acetic acid. Taxonomy Carl Linnaeus first described a whip scorpion in 1758, although he did not distinguish it from what are now regarded as different kinds of arachnid, calling it ''Phalangium caudatum''. '' Phalangium'' is now used as a name for a genus of harvestmen (Opiliones). In 1802, Pierre André Latreille was the first to use a genus name solely for whip scorpions, namely '' Thelyphonus''. Latreille later explained the name as meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(cropped).jpg)



