Tantalum Mines In China on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tantalum is a chemical element with the
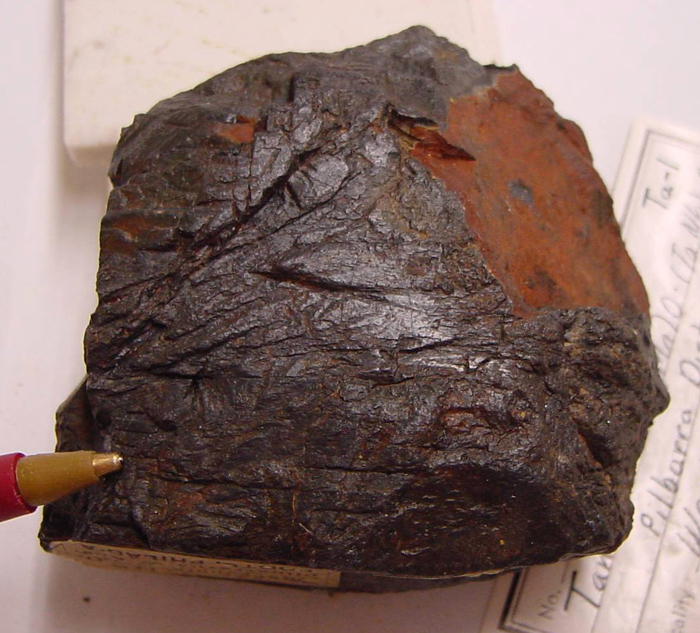
 Tantalum is estimated to make up about 1 ppm or 2 ppm of the Earth's crust by weight. There are many species of tantalum minerals, only some of which are so far being used by industry as raw materials: tantalite (a series consisting of tantalite-(Fe), tantalite-(Mn) and tantalite-(Mg)) microlite (now a group name), wodginite, euxenite (actually euxenite-(Y)), and polycrase (actually polycrase-(Y)). Tantalite ( Fe, Mn)Ta2 O6 is the most important mineral for tantalum extraction. Tantalite has the same mineral structure as columbite ( Fe, Mn) (Ta, Nb)2 O6; when there is more tantalum than niobium it is called tantalite and when there is more niobium than tantalum is it called columbite (or niobite). The high density of tantalite and other tantalum containing minerals makes the use of gravitational separation the best method. Other minerals include samarskite and fergusonite.
Tantalum is estimated to make up about 1 ppm or 2 ppm of the Earth's crust by weight. There are many species of tantalum minerals, only some of which are so far being used by industry as raw materials: tantalite (a series consisting of tantalite-(Fe), tantalite-(Mn) and tantalite-(Mg)) microlite (now a group name), wodginite, euxenite (actually euxenite-(Y)), and polycrase (actually polycrase-(Y)). Tantalite ( Fe, Mn)Ta2 O6 is the most important mineral for tantalum extraction. Tantalite has the same mineral structure as columbite ( Fe, Mn) (Ta, Nb)2 O6; when there is more tantalum than niobium it is called tantalite and when there is more niobium than tantalum is it called columbite (or niobite). The high density of tantalite and other tantalum containing minerals makes the use of gravitational separation the best method. Other minerals include samarskite and fergusonite.

 World tantalum mine production has undergone an important geographic shift since the start of the 21st century when production was predominantly from Australia and Brazil. Beginning in 2007 and through 2014, the major sources of tantalum production from mines dramatically shifted to the Democratic Republic of the Congo,
World tantalum mine production has undergone an important geographic shift since the start of the 21st century when production was predominantly from Australia and Brazil. Beginning in 2007 and through 2014, the major sources of tantalum production from mines dramatically shifted to the Democratic Republic of the Congo,
 Several steps are involved in the extraction of tantalum from tantalite. First, the mineral is crushed and concentrated by gravity separation. This is generally carried out near the mine site.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of tantalum from tantalite. First, the mineral is crushed and concentrated by gravity separation. This is generally carried out near the mine site.
 The major use for tantalum, as the metal powder, is in the production of electronic components, mainly capacitors and some high-power
The major use for tantalum, as the metal powder, is in the production of electronic components, mainly capacitors and some high-power
 Tantalum was used by NASA to shield components of spacecraft, such as '' Voyager 1'' and '' Voyager 2'', from radiation. The high melting point and oxidation resistance led to the use of the metal in the production of vacuum furnace parts. Tantalum is extremely inert and is therefore formed into a variety of corrosion resistant parts, such as thermowells, valve bodies, and tantalum fasteners. Due to its high density, shaped charge and explosively formed penetrator liners have been constructed from tantalum. Tantalum greatly increases the armor penetration capabilities of a shaped charge due to its high density and high melting point.
It is also occasionally used in precious watches e.g. from Audemars Piguet, F.P. Journe, Hublot, Montblanc, Omega, and
Tantalum was used by NASA to shield components of spacecraft, such as '' Voyager 1'' and '' Voyager 2'', from radiation. The high melting point and oxidation resistance led to the use of the metal in the production of vacuum furnace parts. Tantalum is extremely inert and is therefore formed into a variety of corrosion resistant parts, such as thermowells, valve bodies, and tantalum fasteners. Due to its high density, shaped charge and explosively formed penetrator liners have been constructed from tantalum. Tantalum greatly increases the armor penetration capabilities of a shaped charge due to its high density and high melting point.
It is also occasionally used in precious watches e.g. from Audemars Piguet, F.P. Journe, Hublot, Montblanc, Omega, and
Tantalum-Niobium International Study Center
{{Authority control Biomaterials Chemical elements with body-centered cubic structure Chemical elements Native element minerals Noble metals Refractory metals Transition metals
symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as ''tantalium'', it is named after Tantalus, a villain in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is highly corrosion-resistant. It is part of the refractory metals group, which are widely used as components of strong high-melting-point alloys. It is a group 5 element, along with vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer ( pas ...
and niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
, and it always occurs in geologic sources together with the chemically similar niobium, mainly in the mineral groups tantalite, columbite and coltan.
The chemical inertness and very high melting point of tantalum make it valuable for laboratory and industrial equipment such as reaction vessels and vacuum furnaces. It is used in tantalum capacitors for electronic equipment such as computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
s. Tantalum is considered a technology-critical element by the European Commission.
History
Tantalum was discovered in Sweden in 1802 byAnders Ekeberg
Anders Gustaf Ekeberg ( Stockholm, Sweden, 16 January 1767 – Uppsala, Sweden, 11 February 1813) was a Swedish analytical chemist who discovered tantalum in 1802. - subscription required
He was notably deaf.
Education
Anders Gustav Ekeberg ...
, in two mineral samples – one from Sweden and the other from Finland. One year earlier, Charles Hatchett had discovered columbium (now niobium), and in 1809 the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston compared its oxide, columbite with a density of 5.918 g/cm3, to that of tantalum, tantalite with a density of 7.935 g/cm3. He concluded that the two oxides, despite their difference in measured density, were identical and kept the name tantalum. After Friedrich Wöhler
Friedrich Wöhler () FRS(For) HonFRSE (31 July 180023 September 1882) was a German chemist known for his work in inorganic chemistry, being the first to isolate the chemical elements beryllium and yttrium in pure metallic form. He was the firs ...
confirmed these results, it was thought that columbium and tantalum were the same element. This conclusion was disputed in 1846 by the German chemist Heinrich Rose, who argued that there were two additional elements in the tantalite sample, and he named them after the children of Tantalus: niobium (from Niobe, the goddess of tears), and pelopium (from Pelops). The supposed element "pelopium" was later identified as a mixture of tantalum and niobium, and it was found that the niobium was identical to the columbium already discovered in 1801 by Hatchett.
The differences between tantalum and niobium were demonstrated unequivocally in 1864 by Christian Wilhelm Blomstrand
Christian Wilhelm Blomstrand (20 October 1826 – 5 November 1897) was a Swedish mineralogist and chemist. He was a professor at the University of Lund from 1862-1895, where he isolated the element niobium in 1864. He developed an early version of ...
, and Henri Etienne Sainte-Claire Deville
Henri is an Estonian, Finnish, French, German and Luxembourgish form of the masculine given name Henry.
People with this given name
; French noblemen
:'' See the 'List of rulers named Henry' for Kings of France named Henri.''
* Henri I de Montm ...
, as well as by Louis J. Troost
Louis Joseph Troost (17 October 1825, Paris – 30 September 1911) was a French chemist.
Biography
In 1848 he began his studies at the École Normale Supérieure in Paris, where from 1851 he worked as an assistant chemist. In 1856 he receiv ...
, who determined the empirical formulas of some of their compounds in 1865. Further confirmation came from the Swiss chemist Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac, in 1866, who proved that there were only two elements. These discoveries did not stop scientists from publishing articles about the so-called ''ilmenium Ilmenium was the proposed name for a new element found by the chemist R. Hermann in 1847. During the analysis of the mineral samarskite, he concluded that it does contain an element similar to niobium and tantalum. The similar reactivity of niobium ...
'' until 1871. De Marignac was the first to produce the metallic form of tantalum in 1864, when he reduced tantalum chloride by heating it in an atmosphere of hydrogen. Early investigators had only been able to produce impure tantalum, and the first relatively pure ductile metal was produced by Werner von Bolton
Werner von Bolton (8 April 1868 – 28 October 1912) was a German chemist and materials scientist. He devised a technique for producing filaments for incandescent light bulb made out of tantalum in 1902.
Life
Werner von Bolton was born in Tiflis ...
in Charlottenburg in 1903. Wires made with metallic tantalum were used for light bulb
An electric light, lamp, or light bulb is an electrical component that produces light. It is the most common form of artificial lighting. Lamps usually have a base made of ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic, which secures the lamp in the soc ...
filaments until tungsten replaced it in widespread use.
The name tantalum was derived from the name of the mythological Tantalus, the father of Niobe in Greek mythology. In the story, he had been punished after death by being condemned to stand knee-deep in water with perfect fruit growing above his head, both of which eternally ''tantalized'' him. (If he bent to drink the water, it drained below the level he could reach, and if he reached for the fruit, the branches moved out of his grasp.) Anders Ekeberg wrote "This metal I call ''tantalum'' ... partly in allusion to its incapacity, when immersed in acid, to absorb any and be saturated."
For decades, the commercial technology for separating tantalum from niobium involved the fractional crystallization Fractional crystallization may refer to:
* Fractional crystallization (chemistry), a process to separate different solutes from a solution
* Fractional crystallization (geology)
Fractional crystallization, or crystal fractionation, is one of the ...
of potassium heptafluorotantalate away from potassium oxypentafluoroniobate monohydrate, a process that was discovered by Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac in 1866. This method has been supplanted by solvent extraction from fluoride-containing solutions of tantalum.
Characteristics
Physical properties
Tantalum is dark (blue-gray), dense, ductile, very hard, easily fabricated, and highly conductive of heat and electricity. The metal is renowned for its resistance to corrosion byacid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
s; in fact, at temperatures below 150 ° C tantalum is almost completely immune to attack by the normally aggressive aqua regia. It can be dissolved with hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a Solution (chemistry), solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly Corrosive substance, corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include th ...
or acidic solutions containing the fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typ ...
ion and sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide (alternative spelling sulphur trioxide, also known as ''nisso sulfan'') is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. It has been described as "unquestionably the most important economically" sulfur oxide. It is prepared on an ind ...
, as well as with a solution of potassium hydroxide. Tantalum's high melting point of 3017 °C (boiling point 5458 °C) is exceeded among the elements only by tungsten, rhenium and osmium
Osmium (from Greek grc, ὀσμή, osme, smell, label=none) is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white transition metal in the platinum group that is found as a trace element in alloys, mos ...
for metals, and carbon.
Tantalum exists in two crystalline phases, alpha and beta. The alpha phase is relatively ductile and soft; it has body-centered cubic structure ( space group ''Im3m'', lattice constant ''a'' = 0.33058 nm), Knoop hardness
The Knoop hardness test is a microhardness test – a test for mechanical hardness used particularly for very brittle materials or thin sheets, where only a small indentation may be made for testing purposes. A pyramidal diamond point is pressed i ...
200–400 HN and electrical resistivity 15–60 µΩ⋅cm. The beta phase is hard and brittle; its crystal symmetry is tetragonal (space group ''P42/mnm'', ''a'' = 1.0194 nm, ''c'' = 0.5313 nm), Knoop hardness is 1000–1300 HN and electrical resistivity is relatively high at 170–210 µΩ⋅cm. The beta phase is metastable and converts to the alpha phase upon heating to 750–775 °C. Bulk tantalum is almost entirely alpha phase, and the beta phase usually exists as thin films obtained by magnetron
sputtering, chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (substra ...
or electrochemical deposition
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be ...
from a eutectic molten salt solution.
Isotopes
Natural tantalum consists of two isotopes: 180mTa (0.012%) and 181Ta (99.988%). 181Ta is a stable isotope. 180mTa (''m'' denotes a metastable state) is predicted to decay in three ways:isomeric transition
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have ha ...
to the ground state
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. ...
of 180Ta, beta decay to 180 W, or electron capture to 180 Hf. However, radioactivity of this nuclear isomer has never been observed, and only a lower limit on its half-life of 2.0 × 1016 years has been set. The ground state of 180Ta has a half-life of only 8 hours. 180mTa is the only naturally occurring nuclear isomer (excluding radiogenic and cosmogenic short-lived nuclides). It is also the rarest primordial isotope in the Universe, taking into account the elemental abundance of tantalum and isotopic abundance of 180mTa in the natural mixture of isotopes (and again excluding radiogenic and cosmogenic short-lived nuclides).
Tantalum has been examined theoretically as a " salting" material for nuclear weapons ( cobalt is the better-known hypothetical salting material). An external shell of 181Ta would be irradiated by the intensive high-energy neutron flux from a hypothetical exploding nuclear weapon. This would transmute the tantalum into the radioactive isotope 182Ta, which has a half-life of 114.4 days and produces gamma rays with approximately 1.12 million electron-volts (MeV) of energy apiece, which would significantly increase the radioactivity of the nuclear fallout from the explosion for several months. Such "salted" weapons have never been built or tested, as far as is publicly known, and certainly never used as weapons.
Tantalum can be used as a target material for accelerated proton beams for the production of various short-lived isotopes including 8Li, 80Rb, and 160Yb.
Chemical compounds
Tantalum forms compounds in oxidation states −III to +V. Most commonly encountered are oxides of Ta(V), which includes all minerals. The chemical properties of Ta and Nb are very similar. In aqueous media, Ta only exhibit the +V oxidation state. Like niobium, tantalum is barely soluble in dilute solutions of hydrochloric,sulfuric
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
, nitric The chemical element nitrogen is one of the most abundant elements in the universe and can form many compounds. It can take several oxidation states; but the most oxidation states are -3 and +3. Nitrogen can form nitride and nitrate ions. It also fo ...
and phosphoric acids due to the precipitation of hydrous Ta(V) oxide. In basic media, Ta can be solubilized due to the formation of polyoxotantalate species.
Oxides, nitrides, carbides, sulfides
Tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5) is the most important compound from the perspective of applications. Oxides of tantalum in lower oxidation states are numerous, including manydefect structure
A crystallographic defect is an interruption of the regular patterns of arrangement of atoms or molecules in crystalline solids. The positions and orientations of particles, which are repeating at fixed distances determined by the unit cell param ...
s, and are lightly studied or poorly characterized.
Tantalates, compounds containing aO4sup>3− or aO3sup>− are numerous. Lithium tantalate (LiTaO3) adopts a perovskite structure. Lanthanum tantalate (LaTaO4) contains isolated tetrahedra.
As in the cases of other refractory metals, the hardest known compounds of tantalum are nitrides and carbides. Tantalum carbide, TaC, like the more commonly used tungsten carbide, is a hard ceramic that is used in cutting tools. Tantalum(III) nitride is used as a thin film insulator in some microelectronic fabrication processes.
The best studied chalcogenide is TaS2, a layered semiconductor, as seen for other transition metal dichalcogenides. A tantalum-tellurium alloy forms quasicrystals.
Halides
Tantalum halides span the oxidation states of +5, +4, and +3.Tantalum pentafluoride
Tantalum(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula TaF5. It is one of the principal molecular compounds of tantalum. Characteristic of some other pentafluorides, the compound is volatile but exists as an oligomer in the solid state ...
(TaF5) is a white solid with a melting point of 97.0 °C. The anion aF7sup>2- is used for its separation from niobium. The chloride , which exists as a dimer, is the main reagent in synthesis of new Ta compounds. It hydrolyzes readily to an oxychloride
In chemistry, molecular oxohalides (oxyhalides) are a group of chemical compounds in which both oxygen and halogen atoms are attached to another chemical element A in a single molecule. They have the general formula , where X = fluorine (F), ...
. The lower halides and , feature Ta-Ta bonds.
Organotantalum compounds
Organotantalum compounds includepentamethyltantalum
Pentamethyltantalum is a homoleptic organotantalum compound.
It has a propensity to explode when it is melted. Its discovery was part of a sequence that lead to Richard R. Schrock's Nobel Prize discovery in olefin metathesis.
Production
Pentamet ...
, mixed alkyltantalum chlorides, alkyltantalum hydrides, alkylidene complexes as well as cyclopentadienyl derivatives of the same. Diverse salts and substituted derivatives are known for the hexacarbonyl a(CO)6sup>− and related isocyanides.

Occurrence
 Tantalum is estimated to make up about 1 ppm or 2 ppm of the Earth's crust by weight. There are many species of tantalum minerals, only some of which are so far being used by industry as raw materials: tantalite (a series consisting of tantalite-(Fe), tantalite-(Mn) and tantalite-(Mg)) microlite (now a group name), wodginite, euxenite (actually euxenite-(Y)), and polycrase (actually polycrase-(Y)). Tantalite ( Fe, Mn)Ta2 O6 is the most important mineral for tantalum extraction. Tantalite has the same mineral structure as columbite ( Fe, Mn) (Ta, Nb)2 O6; when there is more tantalum than niobium it is called tantalite and when there is more niobium than tantalum is it called columbite (or niobite). The high density of tantalite and other tantalum containing minerals makes the use of gravitational separation the best method. Other minerals include samarskite and fergusonite.
Tantalum is estimated to make up about 1 ppm or 2 ppm of the Earth's crust by weight. There are many species of tantalum minerals, only some of which are so far being used by industry as raw materials: tantalite (a series consisting of tantalite-(Fe), tantalite-(Mn) and tantalite-(Mg)) microlite (now a group name), wodginite, euxenite (actually euxenite-(Y)), and polycrase (actually polycrase-(Y)). Tantalite ( Fe, Mn)Ta2 O6 is the most important mineral for tantalum extraction. Tantalite has the same mineral structure as columbite ( Fe, Mn) (Ta, Nb)2 O6; when there is more tantalum than niobium it is called tantalite and when there is more niobium than tantalum is it called columbite (or niobite). The high density of tantalite and other tantalum containing minerals makes the use of gravitational separation the best method. Other minerals include samarskite and fergusonite.
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
was the main producer of tantalum prior to the 2010s, with Global Advanced Metals (formerly known as Talison Minerals) being the largest tantalum mining company in that country. They operate two mines in Western Australia, Greenbushes
Greenbushes is a timber and mining town located in the South West region of Western Australia. The 2021 population was 365.
History
Greenbushes was founded as a mining town in 1888 following a surveyor's discovery of tin in 1886. Greenbushes wa ...
in the southwest and Wodgina in the Pilbara region. The Wodgina mine was reopened in January 2011 after mining at the site was suspended in late 2008 due to the global financial crisis. Less than a year after it reopened, Global Advanced Metals announced that due to again "... softening tantalum demand ...", and other factors, tantalum mining operations were to cease at the end of February 2012.
Wodgina produces a primary tantalum concentrate which is further upgraded at the Greenbushes operation before being sold to customers. Whereas the large-scale producers of niobium are in Brazil and Canada, the ore there also yields a small percentage of tantalum. Some other countries such as China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, Ethiopia, and Mozambique mine ores with a higher percentage of tantalum, and they produce a significant percentage of the world's output of it. Tantalum is also produced in Thailand and Malaysia as a by-product of the tin mining there. During gravitational separation of the ores from placer deposits, not only is cassiterite
Cassiterite is a tin oxide mineral, SnO2. It is generally opaque, but it is translucent in thin crystals. Its luster and multiple crystal faces produce a desirable gem. Cassiterite was the chief tin ore throughout ancient history and remains t ...
(SnO2) found, but a small percentage of tantalite also included. The slag from the tin smelters then contains economically useful amounts of tantalum, which is leached from the slag.
Rwanda
Rwanda (; rw, u Rwanda ), officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of Central Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator ...
, and some other African countries. Future sources of supply of tantalum, in order of estimated size, are being explored in Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Greenland, China, Mozambique, Canada, Australia, the United States, Finland, and Brazil.
It is estimated that tantalum resources will run out around 2060, based on extraction at current rates, demonstrating the need for increased recycling.
Status as a conflict resource
Tantalum is considered a conflict resource. Coltan, the industrial name for a columbite– tantalite mineral from which niobium and tantalum are extracted, can also be found in Central Africa, which is why tantalum is being linked to warfare in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly Zaire). According to an October 23, 2003 United Nations report, the smuggling and exportation of coltan has helped fuel the war in the Congo, a crisis that has resulted in approximately 5.4 million deaths since 1998 – making it the world's deadliest documented conflict since World War II. Ethical questions have been raised about responsible corporate behavior, human rights, and endangering wildlife, due to the exploitation of resources such as coltan in the armed conflict regions of theCongo Basin
The Congo Basin (french: Bassin du Congo) is the sedimentary basin of the Congo River. The Congo Basin is located in Central Africa, in a region known as west equatorial Africa. The Congo Basin region is sometimes known simply as the Congo. It con ...
. The United States Geological Survey reports in its yearbook that this region produced a little less than 1% of the world's tantalum output in 2002–2006, peaking at 10% in 2000 and 2008. USGS data published in January 2021 indicated that close to 40% of the world's tantalum mine production came from the Democratic Republic of the Congo, with another 18% coming from neighboring Rwanda
Rwanda (; rw, u Rwanda ), officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of Central Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator ...
and Burundi
Burundi (, ), officially the Republic of Burundi ( rn, Repuburika y’Uburundi ; Swahili language, Swahili: ''Jamuhuri ya Burundi''; French language, French: ''République du Burundi'' ), is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley at the ...
.
The stated aim of the ''Solutions for Hope Tantalum Project'' is to "source conflict-free tantalum from the Democratic Republic of Congo"
Production and fabrication
Refining
The refining of tantalum from its ores is one of the more demanding separation processes in industrial metallurgy. The chief problem is that tantalum ores contain significant amounts ofniobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
, which has chemical properties almost identical to those of Ta. A large number of procedures have been developed to address this challenge.
In modern times, the separation is achieved by hydrometallurgy. Extraction begins with leaching the ore with hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a Solution (chemistry), solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly Corrosive substance, corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include th ...
together with sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
or hydrochloric acid. This step allows the tantalum and niobium to be separated from the various non-metallic impurities in the rock. Although Ta occurs as various minerals, it is conveniently represented as the pentoxide, since most oxides of tantalum(V) behave similarly under these conditions. A simplified equation for its extraction is thus:
: Ta2O5 + 14 HF → 2 H2 aF7+ 5 H2O
Completely analogous reactions occur for the niobium component, but the hexafluoride is typically predominant under the conditions of the extraction.
: Nb2O5 + 12 HF → 2 H bF6+ 5 H2O
These equations are simplified: it is suspected that bisulfate (HSO4−) and chloride compete as ligands for the Nb(V) and Ta(V) ions, when sulfuric and hydrochloric acids are used, respectively. The tantalum and niobium fluoride complexes are then removed from the aqueous solution by liquid-liquid extraction into organic solvents, such as cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has an odor reminiscent of acetone. Over time, samples of cyclohexan ...
, octanol, and methyl isobutyl ketone. This simple procedure allows the removal of most metal-containing impurities (e.g. iron, manganese, titanium, zirconium), which remain in the aqueous phase in the form of their fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typ ...
s and other complexes.
Separation of the tantalum ''from'' niobium is then achieved by lowering the ionic strength
The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such as ...
of the acid mixture, which causes the niobium to dissolve in the aqueous phase. It is proposed that oxyfluoride
In chemistry, molecular oxohalides (oxyhalides) are a group of chemical compounds in which both oxygen and halogen atoms are attached to another chemical element A in a single molecule. They have the general formula , where X = fluorine (F), chlor ...
H2 bOF5is formed under these conditions. Subsequent to removal of the niobium, the solution of purified H2 aF7is neutralised with aqueous ammonia to precipitate hydrated tantalum oxide as a solid, which can be calcined to tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5).
Instead of hydrolysis, the H2 aF7can be treated with potassium fluoride to produce potassium heptafluorotantalate:
: H2 aF7+ 2 KF → K2 aF7+ 2 HF
Unlike H2 aF7 the potassium salt is readily crystallized and handled as a solid.
K2 aF7can be converted to metallic tantalum by reduction with sodium, at approximately 800 °C in molten salt.
: K2 aF7+ 5 Na → Ta + 5 NaF + 2 KF
In an older method, called the Marignac process, the mixture of H2 aF7and H2 bOF5was converted to a ''mixture'' of K2 aF7and K2 bOF5 which was then be separated by fractional crystallization Fractional crystallization may refer to:
* Fractional crystallization (chemistry), a process to separate different solutes from a solution
* Fractional crystallization (geology)
Fractional crystallization, or crystal fractionation, is one of the ...
, exploiting their different water solubilities.
Electrolysis
Tantalum can also be refined by electrolysis, using a modified version of the Hall–Héroult process. Instead of requiring the input oxide and output metal to be in liquid form, tantalum electrolysis operates on non-liquid powdered oxides. The initial discovery came in 1997 when Cambridge University researchers immersed small samples of certain oxides in baths of molten salt and reduced the oxide with electric current. The cathode uses powdered metal oxide. The anode is made of carbon. The molten salt at is the electrolyte. The first refinery has enough capacity to supply 3–4% of annual global demand.Fabrication and metalworking
All welding of tantalum must be done in an inert atmosphere of argon or helium in order to shield it from contamination with atmospheric gases. Tantalum is not solderable. Grinding tantalum is difficult, especially so for annealed tantalum. In the annealed condition, tantalum is extremely ductile and can be readily formed as metal sheets.Applications
Electronics
 The major use for tantalum, as the metal powder, is in the production of electronic components, mainly capacitors and some high-power
The major use for tantalum, as the metal powder, is in the production of electronic components, mainly capacitors and some high-power resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active el ...
s. Tantalum electrolytic capacitors exploit the tendency of tantalum to form a protective oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
surface layer, using tantalum powder, pressed into a pellet shape, as one "plate" of the capacitor, the oxide as the dielectric, and an electrolytic solution or conductive solid as the other "plate". Because the dielectric layer can be very thin (thinner than the similar layer in, for instance, an aluminium electrolytic capacitor), a high capacitance can be achieved in a small volume. Because of the size and weight advantages, tantalum capacitors are attractive for portable telephones, personal computers, automotive electronics
Automotive electronics are electronic systems used in vehicles, including engine management, ignition, radio, carputers, telematics, in-car entertainment systems, and others. Ignition, engine and transmission electronics are also found in trucks, ...
and cameras.
Alloys
Tantalum is also used to produce a variety of alloys that have high melting points, strength, and ductility. Alloyed with other metals, it is also used in making carbide tools for metalworking equipment and in the production ofsuperalloy
A superalloy, or high-performance alloy, is an alloy with the ability to operate at a high fraction of its melting point. Several key characteristics of a superalloy are excellent mechanical strength, resistance to thermal creep deformation, g ...
s for jet engine components, chemical process equipment, nuclear reactors, missile parts, heat exchangers, tanks, and vessels. Because of its ductility, tantalum can be drawn into fine wires or filaments, which are used for evaporating metals such as aluminium. Since it resists attack by body fluids and is nonirritating, tantalum is widely used in making surgical instruments and implants. For example, porous tantalum coatings are used in the construction of orthopedic implants due to tantalum's ability to form a direct bond to hard tissue.
Tantalum is inert against most acids except hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a Solution (chemistry), solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly Corrosive substance, corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include th ...
and hot sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
, and hot alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a base (chemistry), basic, ionic compound, ionic salt (chemistry), salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as ...
solutions also cause tantalum to corrode. This property makes it a useful metal for chemical reaction vessels and pipes for corrosive liquids. Heat exchanging coils for the steam heating of hydrochloric acid are made from tantalum. Tantalum was extensively used in the production of ultra high frequency electron tubes for radio transmitters. Tantalum is capable of capturing oxygen and nitrogen by forming nitrides and oxides and therefore helped to sustain the high vacuum needed for the tubes when used for internal parts such as grids and plates.
Other uses
 Tantalum was used by NASA to shield components of spacecraft, such as '' Voyager 1'' and '' Voyager 2'', from radiation. The high melting point and oxidation resistance led to the use of the metal in the production of vacuum furnace parts. Tantalum is extremely inert and is therefore formed into a variety of corrosion resistant parts, such as thermowells, valve bodies, and tantalum fasteners. Due to its high density, shaped charge and explosively formed penetrator liners have been constructed from tantalum. Tantalum greatly increases the armor penetration capabilities of a shaped charge due to its high density and high melting point.
It is also occasionally used in precious watches e.g. from Audemars Piguet, F.P. Journe, Hublot, Montblanc, Omega, and
Tantalum was used by NASA to shield components of spacecraft, such as '' Voyager 1'' and '' Voyager 2'', from radiation. The high melting point and oxidation resistance led to the use of the metal in the production of vacuum furnace parts. Tantalum is extremely inert and is therefore formed into a variety of corrosion resistant parts, such as thermowells, valve bodies, and tantalum fasteners. Due to its high density, shaped charge and explosively formed penetrator liners have been constructed from tantalum. Tantalum greatly increases the armor penetration capabilities of a shaped charge due to its high density and high melting point.
It is also occasionally used in precious watches e.g. from Audemars Piguet, F.P. Journe, Hublot, Montblanc, Omega, and Panerai
Officine Panerai (also known simply as Panerai) is an Italian luxury watch manufacturer, and a wholly owned subsidiary of Compagnie Financière Richemont S.A.
Officine Panerai designs, manufactures and markets watches through authorized dealer ...
. Tantalum is also highly bioinert and is used as an orthopedic implant material. The high stiffness of tantalum makes it necessary to use it as highly porous foam or scaffold with lower stiffness for hip replacement implants to avoid stress shielding
Stress shielding is the reduction in bone density (osteopenia) as a result of removal of typical stress from the bone by an implant (for instance, the femoral component of a hip prosthesis). This is because by Wolff's law
Wolff's law, developed ...
. Because tantalum is a non-ferrous, non-magnetic metal, these implants are considered to be acceptable for patients undergoing MRI procedures. The oxide is used to make special high refractive index glass for camera lenses.
Environmental issues
Tantalum receives far less attention in the environmental field than it does in other geosciences. Upper Crust Concentration (UCC) and the Nb/Ta ratio in the upper crust and in minerals are available because these measurements are useful as a geochemical tool. The latest value for upper crust concentration is 0.92 ppm, and the Nb/Ta(w/w) ratio stands at 12.7. Little data is available on tantalum concentrations in the different environmental compartments, especially in natural waters where reliable estimates of ‘dissolved’ tantalum concentrations in seawater and freshwaters have not even been produced. Some values on dissolved concentrations in oceans have been published, but they are contradictory. Values in freshwaters fare little better, but, in all cases, they are probably below 1 ng L−1, since ‘dissolved’ concentrations in natural waters are well below most current analytical capabilities. Analysis requires pre-concentration procedures that, for the moment, do not give consistent results. And in any case, tantalum appears to be present in natural waters mostly as particulate matter rather than dissolved. Values for concentrations in soils, bed sediments and atmospheric aerosols are easier to come by. Values in soils are close to 1 ppm and thus to UCC values. This indicates detrital origin. For atmospheric aerosols the values available are scattered and limited. When tantalum enrichment is observed, it is probably due to loss of more water-soluble elements in aerosols in the clouds. Pollution linked to human use of the element has not been detected. Tantalum appears to be a very conservative element in biogeochemical terms, but its cycling and reactivity are still not fully understood.Precautions
Compounds containing tantalum are rarely encountered in the laboratory. The metal is highly biocompatible and is used for bodyimplants
Implant can refer to:
Medicine
*Implant (medicine), or specifically:
**Brain implant
**Breast implant
**Buttock implant
**Cochlear implant
**Contraceptive implant
**Dental implant
**Fetal tissue implant
**Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
** ...
and coatings, therefore attention may be focused on other elements or the physical nature of the chemical compound.
People can be exposed to tantalum in the workplace by breathing it in, skin contact, or eye contact. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the legal limit ( permissible exposure limit) for tantalum exposure in the workplace as 5 mg/m3 over an 8-hour workday. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 5 mg/m3 over an 8-hour workday and a short-term limit of 10 mg/m3. At levels of 2500 mg/m3, tantalum is immediately dangerous to life and health
The term immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) is defined by the US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) as exposure to airborne contaminants that is "likely to cause death or immediate or delayed permanent advers ...
.
References
External links
Tantalum-Niobium International Study Center
{{Authority control Biomaterials Chemical elements with body-centered cubic structure Chemical elements Native element minerals Noble metals Refractory metals Transition metals