lymphoma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the

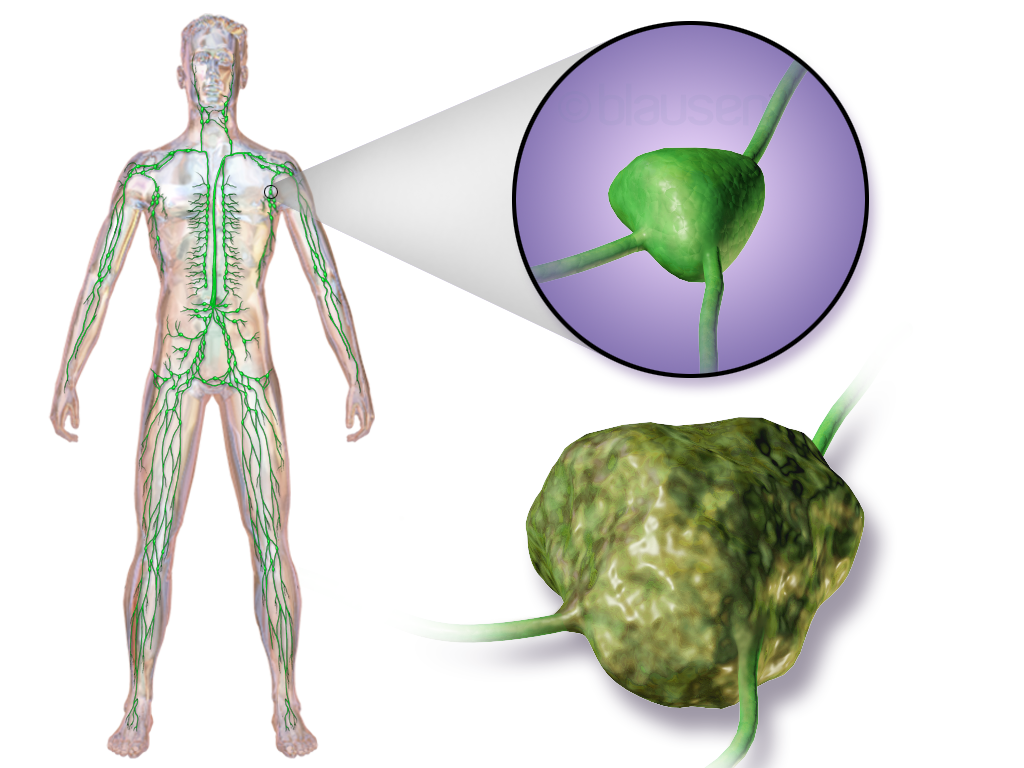 Lymphoma may present with certain nonspecific symptoms; if the symptoms are persistent, an evaluation to determine their cause, including possible lymphoma, should be undertaken.
* Lymphadenopathy or swelling of lymph nodes, is the primary presentation in lymphoma. It is generally painless.
* B symptoms (systemic symptoms) – can be associated with both Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. They consist of:
** Fever
** Night sweats
**
Lymphoma may present with certain nonspecific symptoms; if the symptoms are persistent, an evaluation to determine their cause, including possible lymphoma, should be undertaken.
* Lymphadenopathy or swelling of lymph nodes, is the primary presentation in lymphoma. It is generally painless.
* B symptoms (systemic symptoms) – can be associated with both Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. They consist of:
** Fever
** Night sweats
**
 Lymphoma is definitively diagnosed by a lymph-node biopsy, meaning a partial or total excision of a lymph node examined under the microscope. This examination reveals histopathological features that may indicate lymphoma. After lymphoma is diagnosed, a variety of tests may be carried out to look for specific features characteristic of different types of lymphoma. These include:
*
Lymphoma is definitively diagnosed by a lymph-node biopsy, meaning a partial or total excision of a lymph node examined under the microscope. This examination reveals histopathological features that may indicate lymphoma. After lymphoma is diagnosed, a variety of tests may be carried out to look for specific features characteristic of different types of lymphoma. These include:
*
 * B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small cell lymphoma
:: 3 to 4% of lymphomas in adults
:: Small resting lymphocytes mixed with variable numbers of large activated cells, lymph nodes diffusely effaced
:: CD5, surface
* B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small cell lymphoma
:: 3 to 4% of lymphomas in adults
:: Small resting lymphocytes mixed with variable numbers of large activated cells, lymph nodes diffusely effaced
:: CD5, surface
survival 75% :: Localized or more generalized skin symptoms, generally indolent, in a more aggressive variant, Sézary's disease, skin erythema and peripheral blood involvement * Primary cutaneous CD30-positive T cell lymphoproliferative disorders ** Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma ** Lymphomatoid papulosis * Peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified :: Most common T cell lymphoma :: Variable, usually a mix small to large lymphoid cells with irregular nuclear contours :: CD3 :: Probably consists of several rare tumor types, often disseminated and generally aggressive * Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma * Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: ALK-positive and ALK-negative types * Breast plant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma * B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma not otherwise specified * B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with recurrent genetic abnormalities *
 After a diagnosis and before treatment, cancer is staged. This refers to determining if the cancer has spread, and if so, whether locally or to distant sites. Staging is reported as a grade between I (confined) and IV (spread). The stage of a lymphoma helps predict a patient's prognosis and is used to help select the appropriate therapy.
The Ann Arbor staging system is routinely used for staging of both HL and NHL. In this staging system, stage I represents localized disease contained within a lymph node group, II represents the presence of lymphoma in two or more lymph nodes groups, III represents spread of the lymphoma to lymph nodes groups on both sides of the
After a diagnosis and before treatment, cancer is staged. This refers to determining if the cancer has spread, and if so, whether locally or to distant sites. Staging is reported as a grade between I (confined) and IV (spread). The stage of a lymphoma helps predict a patient's prognosis and is used to help select the appropriate therapy.
The Ann Arbor staging system is routinely used for staging of both HL and NHL. In this staging system, stage I represents localized disease contained within a lymph node group, II represents the presence of lymphoma in two or more lymph nodes groups, III represents spread of the lymphoma to lymph nodes groups on both sides of the
File:Nodular Mantle Cell Lymphoma - high power view - by Gabriel Caponetti.jpg, Mantle cell lymphoma: Notice the irregular nuclear contours of the medium-sized lymphoma cells and the presence of a pink histiocyte. By immunohistochemistry, the lymphoma cells expressed CD20, CD5, and Cyclin D1 (high-power view, H&E)
File:Hodgkin lymphoma, nodular lymphocyte predominant - low power view - H&E - by Gabriel Caponetti.jpg, Hodgkin lymphoma, nodular lymphocyte predominant (low-power view): Notice the nodular architecture and the areas of "mottling".(H&E)
File:Hodgkin lymphoma, nodular lymphocyte predominant - high power view - H&E - by Gabriel Caponetti.jpg, Hodgkin lymphoma, nodular lymphocyte predominant (high-power view): Notice the presence of L&H cells, also known as "popcorn cells". (H&E)
 Thomas Hodgkin published the first description of lymphoma in 1832, specifically of the form named after him. Since then, many other forms of lymphoma have been described.
The term "lymphoma" is from Latin lympha ("water") and from Greek -oma ("morbid growth, tumor").
Thomas Hodgkin published the first description of lymphoma in 1832, specifically of the form named after him. Since then, many other forms of lymphoma have been described.
The term "lymphoma" is from Latin lympha ("water") and from Greek -oma ("morbid growth, tumor").
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
ous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night.
Many subtypes of lymphomas are known. The two main categories of lymphomas are the non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (90% of cases) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (10%). The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
(WHO) includes two other categories as types of lymphoma – multiple myeloma and immunoproliferative diseases. Lymphomas and leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
s are a part of the broader group of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues.
Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include infection with Epstein–Barr virus and a history of the disease in the family. Risk factors for common types of non-Hodgkin lymphomas include autoimmune diseases, HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
, infection with human T-lymphotropic virus, immunosuppressant medications, and some pesticides. Eating large amounts of red meat and tobacco smoking may also increase the risk. Diagnosis, if enlarged lymph nodes are present, is usually by lymph node biopsy. Blood, urine, and bone marrow testing may also be useful in the diagnosis. Medical imaging may then be done to determine if and where the cancer has spread. Lymphoma most often spreads to the lungs, liver, and brain.
Treatment may involve one or more of the following: chemotherapy, radiation therapy, proton therapy, targeted therapy, and surgery. In some non-Hodgkin lymphomas, an increased amount of protein produced by the lymphoma cells causes the blood to become so thick that plasmapheresis is performed to remove the protein. Watchful waiting may be appropriate for certain types. The outcome depends on the subtype with some being curable and treatment prolonging survival in most. The five-year survival rate in the United States for all Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes is 85%, while that for non-Hodgkin lymphomas is 69%. Worldwide, lymphomas developed in 566,000 people in 2012 and caused 305,000 deaths. They make up 3–4% of all cancers, making them as a group the seventh-most common form. In children, they are the third-most common cancer. They occur more often in the developed world than the developing world.
Signs and symptoms
 Lymphoma may present with certain nonspecific symptoms; if the symptoms are persistent, an evaluation to determine their cause, including possible lymphoma, should be undertaken.
* Lymphadenopathy or swelling of lymph nodes, is the primary presentation in lymphoma. It is generally painless.
* B symptoms (systemic symptoms) – can be associated with both Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. They consist of:
** Fever
** Night sweats
**
Lymphoma may present with certain nonspecific symptoms; if the symptoms are persistent, an evaluation to determine their cause, including possible lymphoma, should be undertaken.
* Lymphadenopathy or swelling of lymph nodes, is the primary presentation in lymphoma. It is generally painless.
* B symptoms (systemic symptoms) – can be associated with both Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. They consist of:
** Fever
** Night sweats
** Weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other con ...
* Other symptoms:
** Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, ...
, bleeding, increased susceptibility to infections
** Loss of appetite or anorexia
** Fatigue
** Respiratory distress or dyspnea
** Itching
Mouth
Asymptomatic soft swelling, which may or may not be ulcerated, is primarily seen on the tonsils, buccal mucosa, palate, gums, salivary glands, tongue, the floor of the mouth, and retromolar region.Diagnosis
 Lymphoma is definitively diagnosed by a lymph-node biopsy, meaning a partial or total excision of a lymph node examined under the microscope. This examination reveals histopathological features that may indicate lymphoma. After lymphoma is diagnosed, a variety of tests may be carried out to look for specific features characteristic of different types of lymphoma. These include:
*
Lymphoma is definitively diagnosed by a lymph-node biopsy, meaning a partial or total excision of a lymph node examined under the microscope. This examination reveals histopathological features that may indicate lymphoma. After lymphoma is diagnosed, a variety of tests may be carried out to look for specific features characteristic of different types of lymphoma. These include:
* Immunophenotyping Immunophenotyping is a technique used to study the protein expressed by cells. This technique is commonly used in basic science research and laboratory diagnostic purpose. This can be done on tissue section (fresh or fixed tissue), cell suspension, ...
* Flow cytometry
* Fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization testing
Classification
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), lymphoma classification should reflect in which lymphocyte population the neoplasm arises.Manli Jiang, N. Nora Bennani, and Andrew L. Feldman. Lymphoma classification update: T-cell lymphomas, Hodgkin lymphoma, and histiocytic/dendritic cell neoplasms. Expert Rev Hematol. 2017 Mar; 10(3): 239–249. Author Manuscript. Thus, neoplasms that arise from precursor lymphoid cells are distinguished from those that arise from mature lymphoid cells. Most mature lymphoid neoplasms comprise the non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Historically, mature histiocytic and dendritic cell (HDC) neoplasms have been considered mature lymphoid neoplasms, since these often involve lymphoid tissue. Lymphoma can also spread to thecentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
, often around the brain in the meninges, known as lymphomatous meningitis (LM).
Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma accounts for about 15% of lymphomas. It differs from other forms of lymphomas in itsprognosis
Prognosis (Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing") is a medical term for predicting the likely or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) or remain stabl ...
and several pathological characteristics. A division into Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas is used in several of the older classification systems. A Hodgkin lymphoma is marked by the presence of a type of cell called the Reed–Sternberg cell.
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas, which are defined as being all lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphoma, are more common than Hodgkin lymphoma. A wide variety of lymphomas are in this class, and the causes, the types of cells involved, and the prognoses vary by type. The number of cases per year of non-Hodgkin lymphoma increases with age. It is further divided into several subtypes.Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative diseases
Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative diseases are a group of benign, premalignant, and malignant diseases of lymphoid cells, i.e. B cells, T cells, NK cells, and histiocytic-dendritic cells in which one or more of these cell types is infected with the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). The virus may be responsible for the development and/or progression of these diseases. In addition to EBV-positive Hodgkin lymphomas, the World Health Organization (2016) includes the following lymphomas, when associated with EBV infection, in this group of diseases: Burkitt lymphoma; large B cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified; diffuse large B cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation; fibrin-associated diffuse large B cell lymphoma; primary effusion lymphoma;plasmablastic lymphoma
Plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) is a type of large B-cell lymphoma recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2017 as belonging to a subgroup of lymphomas termed lymphoid neoplasms with plasmablastic differentiation. The other lymphoid neop ...
; extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type; peripheral T cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified; angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma; follicular T cell lymphoma; and systemic T cell lymphoma of childhood.
WHO classification
The WHO classification, published in 2001 and updated in 2008, is based upon the foundations laid within the "revised European–American lymphoma classification" (REAL). This system groups lymphomas by cell type (i.e. the normal cell type that most resembles the tumor) and defining phenotypic, molecular, or cytogenetic characteristics. The five groups are shown in the table. Hodgkin lymphoma is considered separately within the WHO and preceding classifications, although it is recognized as being a tumor, albeit markedly abnormal, of lymphocytes of mature B cell lineage. Of the many forms of lymphoma, some are categorized as indolent (e.g. small lymphocytic lymphoma), compatible with a long life even without treatment, whereas other forms are aggressive (e.g. Burkitt's lymphoma), causing rapid deterioration and death. However, most of the aggressive lymphomas respond well to treatment and are curable. Theprognosis
Prognosis (Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing") is a medical term for predicting the likely or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) or remain stabl ...
, therefore, depends on the correct diagnosis and classification of the disease, which is established after examination of a biopsy by a pathologist (usually a hematopathologist).
Lymphoma subtypes (WHO 2008)
 * B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small cell lymphoma
:: 3 to 4% of lymphomas in adults
:: Small resting lymphocytes mixed with variable numbers of large activated cells, lymph nodes diffusely effaced
:: CD5, surface
* B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small cell lymphoma
:: 3 to 4% of lymphomas in adults
:: Small resting lymphocytes mixed with variable numbers of large activated cells, lymph nodes diffusely effaced
:: CD5, surface immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
:: 5-year survival rate 50%.
:: Occurs in older adults, usually involves lymph nodes, bone marrow and spleen, most patients have peripheral blood involvement, indolent
* B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
* Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (such as Waldenström macroglobulinemia)
* Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
* Hairy cell leukemia
* Plasma cell neoplasms:
** Plasma cell myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, anemi ...
(also known as multiple myeloma)
** Plasmacytoma
** Monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition diseases
** Heavy chain diseases
Heavy chain disease is a form of paraproteinemia and plasma cell dyscrasia that involves the proliferation of cells producing immunoglobulin heavy chains.
This disease is characterized by an excessive production of heavy chains that are short and ...
* Extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma
MALT lymphoma (MALToma) is a form of lymphoma involving the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), frequently of the stomach, but virtually any mucosal site can be affected. It is a cancer originating from B cells in the marginal zone of the ...
, also called MALT lymphoma
:: About 5% of lymphomas in adults
:: Variable cell size and differentiation, 40% show plasma cell differentiation, homing of B cells to epithelium creates lymphoepithelial lesions.
:: CD5, CD10, surface Ig
:: Frequently occurs outside lymph nodes, very indolent, may be cured by local excision
* Nodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma
* Follicular lymphoma
:: About 40% of lymphomas in adults
:: Small "cleaved" leftcells ( centrocytes) mixed with large activated cells ( centroblasts), usually nodular ("follicular") growth pattern
:: CD10, surface Ig
:: About 72–77%
:: Occurs in older adults, usually involves lymph nodes, bone marrow and spleen, associated with t(14;18) translocation
Translocation may refer to:
* Chromosomal translocation, a chromosome abnormality caused by rearrangement of parts
** Robertsonian translocation, a chromosomal rearrangement in pairs 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22
** Nonreciprocal translocation, transfer ...
overexpressing Bcl-2, indolent
* Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma
* Mantle cell lymphoma
:: About 3 to 4% of lymphomas in adults
:: Lymphocytes of small to intermediate size growing in diffuse pattern
:: CD5
:: About 50 to 70%
:::: 50% for limited stage:
:::: 70% for advanced stage:
:: Occurs mainly in adult males, usually involves lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen and GI tract, associated with t(11;14) translocation overexpressing cyclin D1, moderately aggressive
* Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified
:: About 40 to 50% of lymphomas in adults
:: Variable, most resemble B cells of large germinal centers, diffuse growth pattern
:: Variable expression of CD10 and surface Ig
:: Five-year survival rate 60%
:: Occurs in all ages, but most commonly in older adults, may occur outside lymph nodes, aggressive
* Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation
* Epstein–Barr virus positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified
* Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
Lymphomatoid granulomatosis (LYG or LG) is a very rare lymphoproliferative disorder first characterized in 1972. Lymphomatoid means lymphoma-like and granulomatosis denotes the microscopic characteristic of the presence of granulomas with polymor ...
* Primary mediastinal (thymic) large B-cell lymphoma
Primary mediastinal (thymic) large B-cell lymphoma is a distinct type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma involving the mediastinum, recognized in the WHO 2008 classification.
Signs and symptoms
Superior vena cava syndrome occurs in 30–50%, and pl ...
* Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma
* ALK+ large B-cell lymphoma
* Plasmablastic lymphoma
Plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) is a type of large B-cell lymphoma recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2017 as belonging to a subgroup of lymphomas termed lymphoid neoplasms with plasmablastic differentiation. The other lymphoid neop ...
* Primary effusion lymphoma
* Large B-cell lymphoma arising in HHV8-associated multicentric Castleman's disease Large B-cell lymphoma arising in HHV8-associated multicentric Castleman's disease is a type of large B-cell lymphoma, recognized in the WHO 2008 classification. It is sometimes called the plasmablastic form of multicentric Castleman disease. It has ...
* Burkitt lymphoma/leukemia
:: < 1% of lymphomas in the United States
:: Round lymphoid cells of intermediate size with several nucleoli, starry-sky appearance
Burkitt lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, particularly B lymphocytes found in the germinal center. It is named after Denis Parsons Burkitt, the Irish surgeon who first described the disease in 1958 while working in equatorial Africa. ...
by diffuse spread with interspersed apoptosis
:: CD10, surface Ig
:: Five-year survival rate 50%
:: Endemic in Africa, sporadic elsewhere, more common in immunocompromised and children, often visceral involvement, highly aggressive
* T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
* T-cell large granular lymphocyte leukemia
Large granular lymphocytic (LGL) leukemia is a chronic lymphoproliferative disorder that exhibits an unexplained, chronic (> 6 months) elevation in large granular lymphocytes (LGLs) in the peripheral blood.
It is divided in two main categories: T- ...
* Aggressive NK cell leukemia
* Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
* Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type
* Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma
* Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma
Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma is a rare form of lymphoma that is generally incurable, except in the case of an allogeneic stem cell transplant.
It is a systemic neoplasm comprising medium-sized cytotoxic T-cells that show significant sinusoidal in ...
* Blastic NK cell lymphoma
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is a rare hematologic malignancy. It was initially regarded as a form of lymphocyte-derived cutaneous lymphoma and alternatively named CD4+CD56+ hematodermic tumor, blastic NK cell lymphoma, and ...
* Mycosis fungoides/ Sézary syndrome
:: Most common cutaneous lymphoid malignancy
:: Usually small lymphoid cells with convoluted nuclei that often infiltrate the epidermis, creating Pautrier microabscesseses
:: CD4
In molecular biology, CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as T helper cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic ...
:: 5-yearsurvival 75% :: Localized or more generalized skin symptoms, generally indolent, in a more aggressive variant, Sézary's disease, skin erythema and peripheral blood involvement * Primary cutaneous CD30-positive T cell lymphoproliferative disorders ** Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma ** Lymphomatoid papulosis * Peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified :: Most common T cell lymphoma :: Variable, usually a mix small to large lymphoid cells with irregular nuclear contours :: CD3 :: Probably consists of several rare tumor types, often disseminated and generally aggressive * Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma * Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: ALK-positive and ALK-negative types * Breast plant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma * B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma not otherwise specified * B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with recurrent genetic abnormalities *
T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (WHO 2008), previously labeled precursor T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (WHO 2001) is a form of lymphoid leukemia and lymphoma in which too many T-cell lymphoblasts (immature white blood cells) are found in ...
:: 15% of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and 90% of lymphoblastic lymphoma
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, easy bleeding or bruisin ...
.
:: Lymphoblasts with irregular nuclear contours, condensed chromatin, small nucleoli and scant cytoplasm without granules
:: TdT, CD2, CD7
:: It often presents as a mediastinal mass because of involvement of the thymus. It is highly associated with '' NOTCH1'' mutations, and is most common in adolescent males.
* Classical Hodgkin lymphomas:
** Nodular sclerosis form of Hodgkin lymphoma
:: Most common type of Hodgkin lymphoma
:: Reed-Sternberg cell variants and inflammation, usually broad sclerotic bands that consist of collagen
:: CD15, CD30
:: Most common in young adults, often arises in the mediastinum or cervical lymph nodes
** Mixed cellularity Hodgkin lymphoma
:: Second-most common form of Hodgkin lymphoma
:: Many classic Reed-Sternberg cells and inflammation
:: CD15, CD30
:: Most common in men, more likely to be diagnosed at advanced stages than the nodular sclerosis form Epstein–Barr virus involved in 70% of cases
** Lymphocyte-rich
** Lymphocyte depleted or not depleted
* Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
* Associated with a primary immune disorder
* Associated with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immu ...
)
* Post-transplant
* Associated with methotrexate therapy
* Primary central nervous system lymphoma occurs most often in immunocompromised patients, in particular those with AIDS, but it can occur in the immunocompetent, as well. It has a poor prognosis, particularly in those with AIDS. Treatment can consist of corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are in ...
, radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Ra ...
, and chemotherapy, often with methotrexate.
Previous classifications
Several previous classifications have been used, including Rappaport 1956, Lennert/Kiel 1974, BNLI, Working formulation (1982), and REAL (1994). The Working Formulation of 1982 was a classification of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It excluded the Hodgkin lymphomas and divided the remaining lymphomas into four grades (low, intermediate, high, and miscellaneous) related to prognosis, with some further subdivisions based on the size and shape of affected cells. This purely histological classification included no information about cell surface markers, or genetics, and it made no distinction between T-cell lymphomas and B-cell lymphomas. It was widely accepted at the time of its publication but is now obsolete. In 1994, the Revised European-American Lymphoma (REAL) classification applied immunophenotypic and genetic features in identifying distinct clinicopathologic entities among all the lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphoma. For coding purposes, the ICD-O (codes 9590–9999) and ICD-10 (codes C81-C96) are available.Staging
diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
, and IV indicates spread to tissue outside the lymphatic system. Different suffixes imply the involvement of different organs, for example, S for the spleen and H for the liver. Extra-lymphatic involvement is expressed with the letter E. In addition, the presence of B symptoms (one or more of the following: unintentional loss of 10% body weight in the last 6 months, night sweats, or persistent fever of 38 °C or more) or their absence is expressed with B or A, respectively.
CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
or PET scan
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, r ...
imaging modalities are used to stage cancer. PET scanning is advised for fluorodeoxyglucose-avid lymphomas, such as Hodgkin lymphoma, as a staging tool that can even replace bone marrow biopsy. For other lymphomas, CT scanning is recommended for staging.
Age and poor performance status are other established poor prognostic factors. This means that people who are elderly or too sick to take care of themselves are more likely to die from lymphoma than others.
Differential diagnosis
Certain lymphomas ( extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type and type II enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma) can be mimicked by two benign diseases which involve the excessive proliferation of non-malignant NK cells in the GI tract, natural killer cell enteropathy, a disease wherein NK cell infiltrative lesions occur in the intestine, colon, stomach, or esophagus, and lymphomatoid gastropathy, a disease wherein these cells' infiltrative lesions are limited to the stomach. These diseases do not progress to cancer, may regress spontaneously and do not respond to, and do not require, chemotherapy or other lymphoma treatments.Treatment
Prognoses and treatments are different for HL and between all the different forms of NHL, and also depend on the grade of tumour, referring to how quickly a cancer replicates. Paradoxically, high-grade lymphomas are more readily treated and have better prognoses: Burkitt lymphoma, for example, is a high-grade tumour known to double within days, and is highly responsive to treatment.Low-grade
Many low-grade lymphomas remainindolent
Indolent may refer to:
*Laziness
*A music label owned by Bertelsmann Music Group
*indolent condition, a slowly progressive medical condition associated with little or no pain
*The lowest of three grades of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL)
*Indolent ul ...
(growing slowly or not at all) for many years – sometimes, for the rest of the person's life. With an indolent lymphoma, such as follicular lymphoma, watchful waiting is often the initial course of action, because monitoring is less risky and less harmful than early treatment.
If a low-grade lymphoma becomes symptomatic, radiotherapy or chemotherapy are the treatments of choice. Although these treatments do not permanently cure the lymphoma, they can alleviate the symptoms, particularly painful lymphadenopathy. People with these types of lymphoma can live near-normal lifespans, even though the disease is technically incurable.
Some centers advocate the use of single agent rituximab in the treatment of follicular lymphoma rather than the wait-and-watch approach. Watchful waiting is not a desirable strategy for everyone, as it leads to significant distress and anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil
Turmoil may refer to:
* ''Turmoil'' (1984 video game), a 1984 video game released by Bug-Byte
* ''Turmoil'' (2016 video game), a 2016 indie oil tycoon video ...
in some people. It has been called "watch and worry".
High-grade
Treatment of some other, more aggressive, forms of lymphoma can result in a cure in the majority of cases, but the prognosis for people with a poor response to therapy is worse. Treatment for these types of lymphoma typically consists of aggressive chemotherapy, including the CHOP or R-CHOP regimen. A number of people are cured with first-line chemotherapy. Most relapses occur within the first two years, and the relapse risk drops significantly thereafter. For people who relapse, high-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation is a proven approach. The treatment of side effects is also important as they can occur due to the chemotherapy or the stem cell transplantation. It was evaluated whether mesenchymal stromal cells can be used for the treatment and prophylaxis of graft-versus-host diseases. The evidence is very uncertain about the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stromal cells to treat graft-versus-host diseases on the all-cause mortality and complete disappear of chronic acute graft-versus-host diseases. Mesenchymal stromal cells may result in little to no difference in the all-cause mortality, relapse of malignant disease and incidence of acute and chronic graft-versus-host diseases if they are used for prophylactic reason. Moreover, it was seen that platelet transfusions for people undergoing a chemotherapy or a stem cell transplantation for the prevention of bleeding events had different effects on the number of participants with a bleeding event, the number of days on which a bleeding occurred, the mortality secondary to bleeding and the number of platelet transfusions depending on the way they were used (therapeutic, depending on a threshold, different dose schedules or prophylactic). Four chimeric antigen receptor CAR-T cell therapies are FDA-approved for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, includinglisocabtagene maraleucel
Lisocabtagene maraleucel, sold under the brand name Breyanzi, is a cell-based gene therapy used to treat large B-cell lymphoma.
Side effects include hypersensitivity reactions, serious infections, low blood cell counts, and a weakened immune sy ...
(for relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma with two failed systemic treatments), axicabtagene ciloleucel, tisagenlecleucel
Tisagenlecleucel, sold under the brand name Kymriah, is a CAR T cells medication for the treatment of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) which uses the body's own T cells to fight cancer ( adoptive cell transfer).
Serious side effects o ...
(for large B-cell lymphoma), and brexucabtagene autoleucel(for mantle cell lymphoma). These therapies come with certification and other restrictions.
Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma typically is treated with radiotherapy alone, as long as it is localized. Advanced Hodgkin disease requires systemic chemotherapy, sometimes combined with radiotherapy. Chemotherapy used includes the ABVD regimen, which is commonly used in the United States. Other regimens used in the management of Hodgkin lymphoma include BEACOPP and Stanford V. Considerable controversy exists regarding the use of ABVD or BEACOPP. Briefly, both regimens are effective, but BEACOPP is associated with more toxicity. Encouragingly, a significant number of people who relapse after ABVD can still be salvaged by stem cell transplant. Scientists evaluated whether positron-emission-tomography scans between the chemotherapy cycles can be used to make assumptions about the survival. The evidence is very uncertain about the effect of negative (= good prognosis) or positive (= bad prognosis) interim PET scan results on the progression-free survival. Negative interim PET scan results may result in an increase in progression-free survival compared if the adjusted result was measured. Negative interim PET scan results probably result in a large increase in the overall survival compared to those with a positive interim PET scan result. Current research evaluated whether Nivolumab can be used for the treatment of a Hodgkin's lymphoma. The evidence is very uncertain about the effect of Nivolumab for patients with a Hodgkin's lymphoma on the overall survival, the quality of life, the survival without a progression, the response rate (=complete disappear) and grade 3 or 4 serious adverse events.Palliative care
Palliative care
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Wi ...
, a specialized medical care focused on the symptoms, pain, and stress of a serious illness, is recommended by multiple national cancer treatment guidelines as an accompaniment to curative treatments for people with lymphoma. It is used to address both the direct symptoms of lymphoma and many unwanted side effects that arise from treatments. Palliative care can be especially helpful for children who develop lymphoma, helping both children and their families deal with the physical and emotional symptoms of the disease. For these reasons, palliative care is especially important for people requiring bone marrow transplants.
Supportive treatment
Adding physical exercises to the standard treatment for adult patients with haematological malignancies like lymphomas may result in little to no difference in the mortality, the quality of life and the physical functioning. These exercises may result in a slight reduction in depression. Furthermore, aerobic physical exercises probably reduce fatigue. The evidence is very uncertain about the effect on anxiety and serious adverse events.Prognosis
Epidemiology
Lymphoma is the most common form of hematological malignancy, or "blood cancer", in the developed world. Taken together, lymphomas represent 5.3% of all cancers (excluding simple basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers) in the United States and 55.6% of all blood cancers. According to the U.S. National Institutes of Health, lymphomas account for about 5%, and Hodgkin lymphoma in particular accounts for less than 1% of all cases of cancer in the United States. Because the whole lymphatic system is part of the body's immune system, people with a weakened immune system such as from HIV infection or from certain drugs or medication also have a higher number of cases of lymphoma.History
 Thomas Hodgkin published the first description of lymphoma in 1832, specifically of the form named after him. Since then, many other forms of lymphoma have been described.
The term "lymphoma" is from Latin lympha ("water") and from Greek -oma ("morbid growth, tumor").
Thomas Hodgkin published the first description of lymphoma in 1832, specifically of the form named after him. Since then, many other forms of lymphoma have been described.
The term "lymphoma" is from Latin lympha ("water") and from Greek -oma ("morbid growth, tumor").
Research
The two types of lymphoma research are clinical or translational research and basic research. Clinical/translational research focuses on studying the disease in a defined and generally immediately applicable way, such as testing a new drug in people. Studies may focus on effective means of treatment, better ways of treating the disease, improving the quality of life for people, or appropriate care in remission or after cures. Hundreds of clinical trials are being planned or conducted at any given time. Basic science research studies the disease process at a distance, such as seeing whether a suspected carcinogen can cause healthy cells to turn into lymphoma cells in the laboratory or how the DNA changes inside lymphoma cells as the disease progresses. The results from basic research studies are generally less immediately useful to people with the disease, but can improve scientists' understanding of lymphoma and form the foundation for future, more effective treatments.Other animals
References
External links
* {{Authority control Anatomical pathology Hematology Pediatric cancers Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate