|
BEACOPP
BEACOPP is a chemotherapy regimen for treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma developed by the German Hodgkin Study Group used for patients in Stages > II or early (IA or IB) with unfavorable risk factors. Patients typically receive treatment in cycles of 21 days with no drugs given on days 15–21. There also exists a more intensive regimen with cycles of 14 days. Usually a course of BEACOPP therapy consists of four, sometimes six to eight cycles, or in combination with ABVD. In some countries BEACOPP still is experimental, in others (e.g. Germany and Austria) it is a standard therapy. In the United States, ABVD (or Stanford V) is generally given instead, because BEACOPP is perceived by practicing oncologists to have the potential to induce more secondary neoplasias (such as leukemias). However, the final results from the GHSG HD14 trial indicate that "there were no overall differences in treatment-related mortality or secondary malignancies" of BEACOPP relative to ABVD. Oncologists in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition was named after the English physician Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. Symptoms may include fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Often, nonpainful enlarged lymph nodes occur in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin. Those affected may feel tired or be itchy. The two major types of Hodgkin lymphoma are classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. About half of cases of Hodgkin lymphoma are due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and these are generally the classic form. Other risk factors include a family history of the condition and having HIV/AIDS. Diagnosis is conducted by confirming the presence of cancer and identifying RS cells in lymph node biopsies. The virus-positive cases are cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABVD
ABVD is a chemotherapy regimen used in the first-line treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma, replacing the older MOPP protocol. It consists of concurrent treatment with the chemotherapy drugs: * Adriamycin (also known as doxorubicin/hydroxydaunorubicin, designated as H in CHOP) * Bleomycin * Vinblastine * Dacarbazine (similar to procarbazine, designated as P in MOPP and in COPP) Medical uses As of 2007, ABVD is widely used as the initial chemotherapy treatment for newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma. It has been the most effective and least toxic chemotherapy regimen available for treating early-stage Hodgkin Lymphoma. The other chemotherapy regimens that are widely used in this setting is the Stanford V and BEACOPP regimens. Administration One cycle of ABVD chemotherapy is typically given over 4 weeks in two doses, with the first on day 1 and the second dose on day 15. All four of the chemotherapy drugs are given intravenously. ABVD chemotherapy is usually given in the outpatient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy Regimen
A chemotherapy regimen is a regimen for chemotherapy, defining the drugs to be used, their dosage, the frequency and duration of treatments, and other considerations. In modern oncology, many regimens combine several chemotherapy drugs in combination chemotherapy. The majority of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy are cytostatic, many via cytotoxicity. A fundamental philosophy of medical oncology, including combination chemotherapy, is that different drugs work through different mechanisms, and that the results of using multiple drugs will be synergistic Synergy is an interaction or cooperation giving rise to a whole that is greater than the simple sum of its parts. The term ''synergy'' comes from the Attic Greek word συνεργία ' from ', , meaning "working together". History In Christi ... to some extent. Because they have different dose-limiting adverse effects, they can be given together at full doses in chemotherapy regimens. The first successful combination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procarbazine
Procarbazine is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma and brain cancers. For Hodgkin's it is often used together with chlormethine, vincristine, and prednisone while for brain cancers such as glioblastoma multiforme it is used with lomustine and vincristine. It is typically taken by mouth. Common side effect include low blood cell counts and vomiting. Other side effects include tiredness and depression. It is not recommended in people with severe liver or kidney problems. Use in pregnancy is known to harm the baby. Procarbazine is in the alkylating agents family of medication. How it works is not clearly known. Procarbazine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1969. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In the United Kingdom a month of treatment cost the National Health Service 450 to 750 pounds. Medical uses When used to treat Hodgkin's lymphoma, it is often delivered as part of the BEACOPP reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adriamycin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used together with other chemotherapy agents. Doxorubicin is given by injection into a vein. Common side effects include hair loss, bone marrow suppression, vomiting, rash, and inflammation of the mouth. Other serious side effects may include allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis, heart damage, tissue damage at the site of injection, radiation recall, and treatment-related leukemia. People often experience red discoloration of the urine for a few days. Doxorubicin is in the anthracycline and antitumor antibiotic family of medications. It works in part by interfering with the function of DNA. Doxorubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1974. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Versions th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vincristine
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and marketed under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin's disease, neuroblastoma, and small cell lung cancer among others. It is given intravenously. Most people experience some side effects from vincristine treatment. Commonly it causes a change in sensation, hair loss, constipation, difficulty walking, and headaches. Serious side effects may include neuropathic pain, lung damage, or low white blood cells which increases the risk of infection. Use during pregnancy may result in birth defects. It works by stopping cells from dividing properly. It is vital that it not be given intrathecally, as this causes paralysis and in most cases, death. Vincristine was first isolated in 1961. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is a vinca alkaloid that can be obta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncovin
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and marketed under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin's disease, neuroblastoma, and small cell lung cancer among others. It is given intravenously. Most people experience some side effects from vincristine treatment. Commonly it causes a change in sensation, hair loss, constipation, difficulty walking, and headaches. Serious side effects may include neuropathic pain, lung damage, or low white blood cells which increases the risk of infection. Use during pregnancy may result in birth defects. It works by stopping cells from dividing properly. It is vital that it not be given intrathecally, as this causes paralysis and in most cases, death. Vincristine was first isolated in 1961. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is a vinca alkaloid that can be obtained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOPP (chemotherapy)
MOPP is a combination chemotherapy regimen used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma. The acronym is derived from the component drugs of the regimen: * (M)ustargen (also known as mechlorethamine, chlormethine, mustine, nitrogen mustard, or MSD) * (O)ncovin (also known as Vincristine or VCR) * (P)rocarbazine (also known as Matulane or Natulan) * (P)rednisone (also known as Deltasone or Orasone) The treatment is usually administered in four week cycles, often for six cycles. MSD and VCR are administered intravenously, while procarbazine and prednisone are pills taken orally. A newer Hodgkin lymphoma treatment is ABVD. C-MOPP involves switching the nitrogen mustard from mechlorethamine to cyclophosphamide. C-MOPP is thus very similar to COPP, using the same 4 agents and differing at most in dosages and timing. Dosage History MOPP was the first combination chemotherapy brought in that achieved a high success rate. It was developed at the National Cancer Institute in the 1960s by a te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium due to cancer and adrenal insufficiency along with other steroids. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects with long-term use include cataracts, bone loss, easy bruising, muscle weakness, and thrush. Other side effects include weight gain, swelling, high blood sugar, increased risk of infection, and psychosis. It is generally considered safe in pregnancy and low doses appear to be safe when breastfeeding. After prolonged use, prednisone needs to be stopped gradually. Prednisone is a prodrug and must be converted to prednisolone by the liver before it becomes active. Prednisolone then binds to glucocorticoid receptors, activating them and triggering changes in gene expression. Prednisone was patented in 1954 and approved for medical use in the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
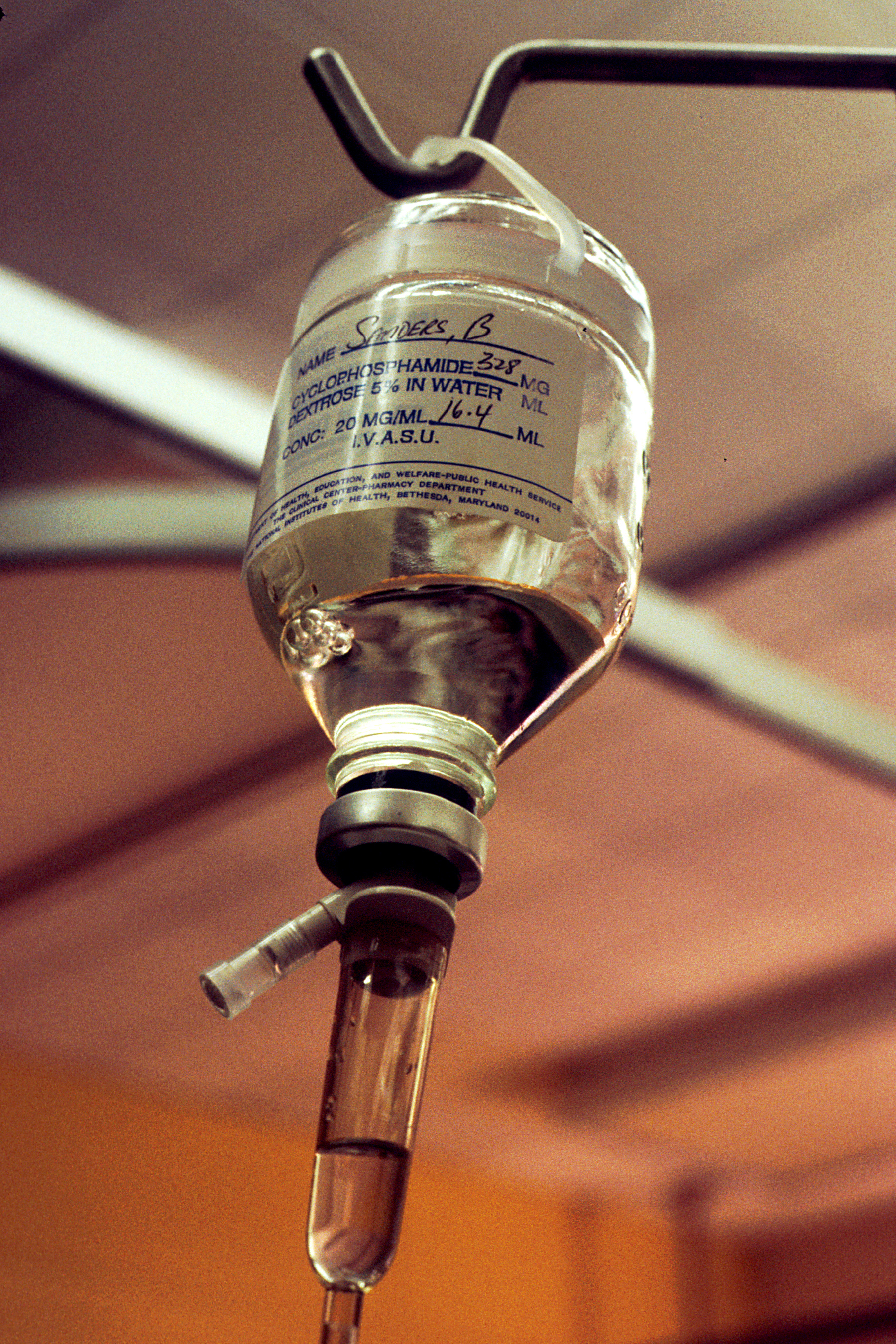
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to immunosuppressant, suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or intravenous, injection into a vein. Most people develop side effects. Common side effects include leukopenia, low white blood cell counts, loss of appetite, vomiting, hair loss, and hemorrhagic cystitis, bleeding from the bladder. Other severe side effects include an increased future risk of cancer, infertility, allergic reactions, and pulmonary fibrosis. Cyclophosphamide is in the alkylating antineoplastic agent, alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It is believed to work by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleomycin
-13- (1''H''-imidazol-5-yl)methyl9-hydroxy-5- 1''R'')-1-hydroxyethyl8,10-dimethyl-4,7,12,15-tetraoxo-3,6,11,14-tetraazapentadec-1-yl}-2,4'-bi-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)carbonyl]amino}propyl)(dimethyl)sulfonium , chemical_formula = , C=55 , H=84 , N=17 , O=21 , S=3 , molecular_weight = 1415.551 , SMILES = CC1=C(N=C(N=C1N) @HCC(=O)N)NC @@HC(=O)N)N)C(=O)N @@HC(C2=CN=CN2)O @H @H @H @@H @@HO3)CO)O)O)O @@H @H @H @@H @HO4)CO)O)OC(=O)N)O)C(=O)N @HC) @H @HC)C(=O)N @@H @@HC)O)C(=O)NCCC5=NC(=CS5)C6=NC(=CS6)C(=O)NCCC +C)C)O , Jmol = , StdInChI_Ref = , StdInChI = 1S/C55H83N17O21S3/c1-20-33(69-46(72-44(20)58)25(12-31(57)76)64-13-24(56)45(59)82)50(86)71-35(41(26-14-61-19-65-26)91-54-43(39(80)37(78)29(15-73)90-54)92-53-40(81)42(93-55(60)88)38(79)30(16-74)89-53)51(87)66-22(3)36(77)21(2)47(83)70-34(23(4)75)49(85)63-10-8-32-67-28(18-94-32)52-68-27(17-95-52)48(84)62-9-7-11-96(5)6/h14,17-19,21-25,29-30,34-43,53-54,64,73-75,77-81H,7-13,15-16,56H2,1-6H3,(H13-,57,58, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etoposide
Etoposide, sold under the brand name Vepesid among others, is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer including testicular cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. It is also used for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. It is used by mouth or injection into a vein. Side effects are very common. They can include low blood cell counts, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, hair loss, and fever. Other severe side effects include allergic reactions and low blood pressure. Use during pregnancy will likely harm the fetus. Etoposide is in the topoisomerase inhibitor family of medication. It is believed to work by damaging DNA. Etoposide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1983. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Etoposide is used as a form of chemotherapy for cancers such as Kaposi’s sarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, lung cancer, testicular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_mixed_cellulary_type.jpg)