Swedish (language) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Swedish ( ) is a
 Old Swedish (Swedish: ''fornsvenska'') is the term used for the
Old Swedish (Swedish: ''fornsvenska'') is the term used for the
 Modern Swedish (Swedish: ''nysvenska'') begins with the advent of the
Modern Swedish (Swedish: ''nysvenska'') begins with the advent of the 
 The period that includes Swedish as it is spoken today is termed ''nusvenska'' (lit., "Now-Swedish") in linguistics, and started in the last decades of the 19th century. It saw a democratization of the language with a less formal written form that approached the spoken one. The growth of a public school system also led to the evolution of so-called ''boksvenska'' (literally, "book Swedish"), especially among the working classes, where spelling to some extent influenced pronunciation, particularly in official contexts. With the industrialization and urbanization of Sweden well under way by the last decades of the 19th century, a new breed of authors made their mark on
The period that includes Swedish as it is spoken today is termed ''nusvenska'' (lit., "Now-Swedish") in linguistics, and started in the last decades of the 19th century. It saw a democratization of the language with a less formal written form that approached the spoken one. The growth of a public school system also led to the evolution of so-called ''boksvenska'' (literally, "book Swedish"), especially among the working classes, where spelling to some extent influenced pronunciation, particularly in official contexts. With the industrialization and urbanization of Sweden well under way by the last decades of the 19th century, a new breed of authors made their mark on
Statistics Finland (29 March 2007). Retrieved on 27 November 2007. partially due to a decline following the Russian annexation of Finland after the
 Swedish is the official main language of Sweden. Swedish is also one of two official languages of Finland. In Sweden, it has long been used in local and state government, and most of the educational system, but remained only a ''de facto'' primary language with no official status in law until 2009. A bill was proposed in 2005 that would have made Swedish an official language, but failed to pass by the narrowest possible margin (145–147) due to a pairing-off failure. A proposal for a broader language law, designating Swedish as the main language of the country and bolstering the status of the minority languages, was submitted by an expert committee to the Swedish Ministry of Culture in March 2008. It was subsequently enacted by the
Swedish is the official main language of Sweden. Swedish is also one of two official languages of Finland. In Sweden, it has long been used in local and state government, and most of the educational system, but remained only a ''de facto'' primary language with no official status in law until 2009. A bill was proposed in 2005 that would have made Swedish an official language, but failed to pass by the narrowest possible margin (145–147) due to a pairing-off failure. A proposal for a broader language law, designating Swedish as the main language of the country and bolstering the status of the minority languages, was submitted by an expert committee to the Swedish Ministry of Culture in March 2008. It was subsequently enacted by the
 The
The
 Swedish dialects have either 17 or 18 vowel
Swedish dialects have either 17 or 18 vowel
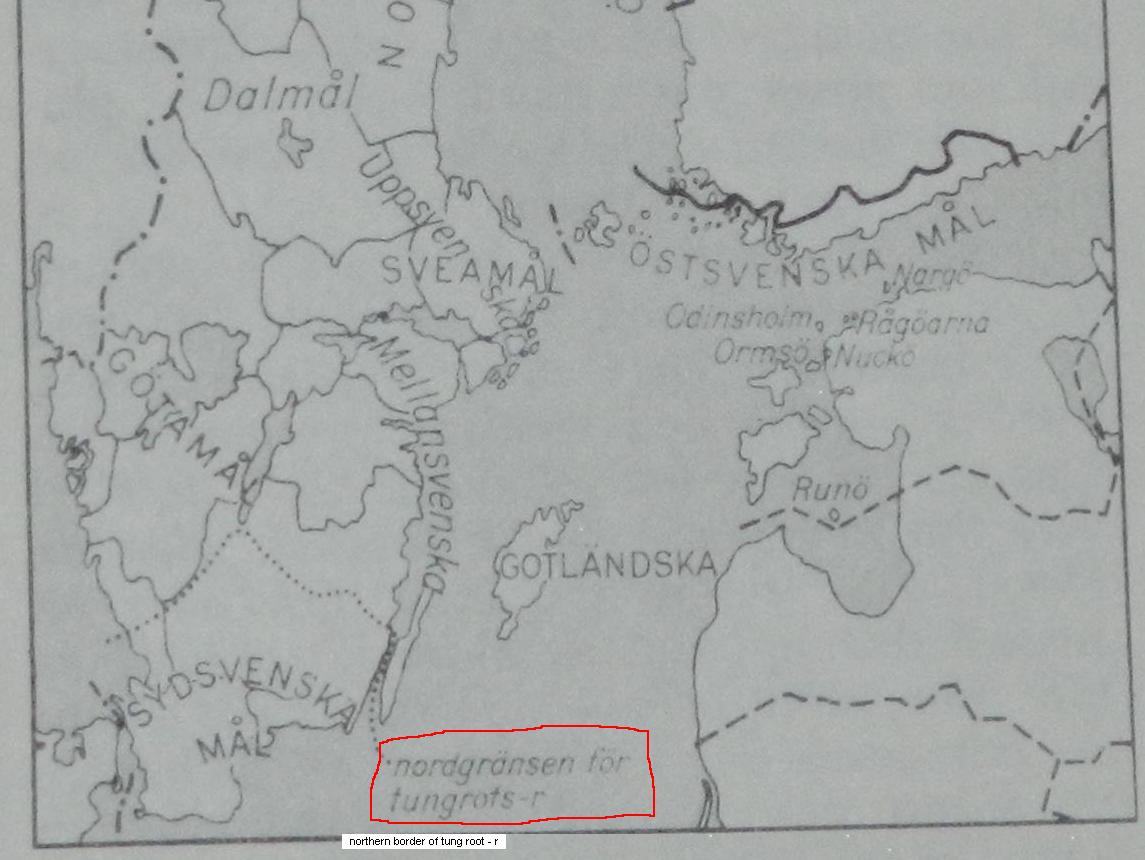 According to a traditional division of Swedish
According to a traditional division of Swedish 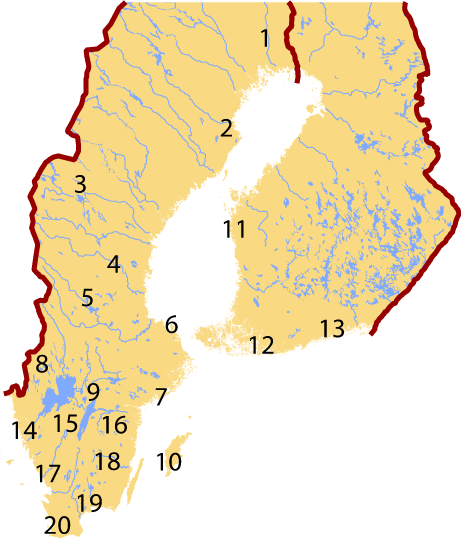 #
#
younger female
#
older female
#
younger female
#
older male
#
older female
traditionally considered a dialect, but now often recognized as
older male
#
younger male
# Köla,
# Viby,
older male
# Sproge,
younger female
# Närpes, Ostrobothnia
younger female
#
older male
#
younger male
# Orust,
older male
#
older female
#
older female
# Årstad-
younger male
# Stenberga,
younger female
#
older female
# Bara,
older male
Handelns Utredningsinstitut
'), the attitudes of Swedes to the use of certain dialects by salesmen revealed that 54% believed that ''rikssvenska'' was the variety they would prefer to hear when speaking with salesmen over the phone, even though dialects such as ''gotländska'' or '' skånska'' were provided as alternatives in the poll.
online edition
* * * * *
Swadesh list of Swedish basic vocabulary words
(from Wiktionary'
Swadesh-list appendix
Dictionaries fro
Språkrådet – Institute for Language and Folklore
Online version
of '' Svenska Akademiens ordbok'' {{Authority control Languages of Finland Languages of Estonia Languages of Sweden East Scandinavian languages North Germanic languages Scandinavian culture Stress-timed languages Subject–verb–object languages Verb-second languages
North Germanic language
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is als ...
spoken predominantly in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
and in parts of Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bot ...
. It has at least 10 million native
Native may refer to:
People
* Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Native Americans (disambiguation)
In arts and entert ...
speakers, the fourth most spoken Germanic language and the first among any other of its type in the Nordic countries overall.
Swedish, like the other Nordic languages, is a descendant of Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
, the common language of the Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
living in Scandinavia during the Viking Era
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the ...
. It is largely mutually intelligible
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as a ...
with Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
and Danish, although the degree of mutual intelligibility is largely dependent on the dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is ...
and accent of the speaker. Written Norwegian and Danish are usually more easily understood by Swedish speakers than the spoken languages, due to the differences in tone, accent, and intonation.
Standard Swedish
Standard Swedish () denotes Swedish as a spoken and written standard language. While Swedish as a written language is uniform and standardized, the spoken standard may vary considerably from region to region. Several prestige dialects have devel ...
, spoken by most Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
, is the national language
A national language is a language (or language variant, e.g. dialect) that has some connection—de facto or de jure—with a nation. There is little consistency in the use of this term. One or more languages spoken as first languages in the te ...
that evolved from the Central Swedish dialects in the 19th century and was well established by the beginning of the 20th century. While distinct regional varieties and rural dialects still exist, the written language is uniform and standardized
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization ...
. Swedish is the most widely spoken second language
A person's second language, or L2, is a language that is not the native language ( first language or L1) of the speaker, but is learned later. A second language may be a neighbouring language, another language of the speaker's home country, or a ...
in Finland where it has status as co-official language.
Swedish was long spoken in parts of Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, an ...
, although the current status of the Estonian Swedish
Estonian Swedish ( sv, estlandssvenska; et, rannarootsi keel, lit=Coastal Swedish) are the eastern varieties of Swedish that were spoken in the formerly Swedish-populated areas of Estonia (locally known as '' Aiboland'') on the islands of Orm ...
speakers is almost extinct. It is also used in the Swedish diaspora, most notably in Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
, with more than 50,000 Swedish residents.
Classification
Swedish is anIndo-European language
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
belonging to the North Germanic
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also r ...
branch of the Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, ...
. In the established classification, it belongs to the East Scandinavian languages
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is als ...
, together with Danish, separating it from the West Scandinavian languages, consisting of Faroese, Icelandic, and Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
. However, more recent analyses divide the North Germanic languages into two groups: ''Insular Scandinavian'' (Faroese and Icelandic), and ''Continental Scandinavian'' (Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish), based on mutual intelligibility due to heavy influence of East Scandinavian (particularly Danish) on Norwegian during the last millennium and divergence from both Faroese and Icelandic.
By many general criteria of mutual intelligibility, the Continental Scandinavian languages could very well be considered dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is ...
s of a common Scandinavian language. However, because of several hundred years of sometimes quite intense rivalry between Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
and Sweden, including a long series of wars from the 16th to 18th centuries, and the nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Th ...
ideas that emerged during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the languages have separate orthographies
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.
Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and ...
, dictionaries, grammars, and regulatory bodies. Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish are thus from a linguistic perspective more accurately described as a dialect continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulate over distance so that widely separated vari ...
of Scandinavian (North Germanic), and some of the dialects, such as those on the border between Norway and Sweden, especially parts of Bohuslän
Bohuslän (; da, Bohuslen; no, Båhuslen) is a Swedish province in Götaland, on the northernmost part of the country's west coast. It is bordered by Dalsland to the northeast, Västergötland to the southeast, the Skagerrak arm of the North ...
, Dalsland, western Värmland
Värmland () also known as Wermeland, is a '' landskap'' (historical province) in west-central Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Dalsland, Dalarna, Västmanland, and Närke, and is bounded by Norway in the west. Latin name versions are '' ...
, western Dalarna
Dalarna () is a '' landskap'' (historical province) in central Sweden. English exonyms for it are Dalecarlia () and the Dales.
Dalarna adjoins Härjedalen, Hälsingland, Gästrikland, Västmanland and Värmland. It is also bordered by Norwa ...
, Härjedalen, Jämtland
Jämtland (; no, Jemtland or , ; Jamtish: ''Jamtlann''; la, Iemptia) is a historical province () in the centre of Sweden in northern Europe. It borders Härjedalen and Medelpad to the south, Ångermanland to the east, Lapland to the nort ...
, and Scania
Scania, also known by its native name of Skåne (, ), is the southernmost of the historical provinces (''landskap'') of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous with Skån ...
, could be described as intermediate dialects of the national standard languages.
Swedish pronunciations also vary greatly from one region to another, a legacy of the vast geographic distances and historical isolation. Even so, the vocabulary is standardized to a level that make dialects within Sweden virtually fully mutually intelligible.
History
Old Norse
In the 8th century, the common Germanic language of Scandinavia,Proto-Norse
Proto-Norse (also called Ancient Nordic, Ancient Scandinavian, Ancient Norse, Primitive Norse, Proto-Nordic, Proto-Scandinavian and Proto-North Germanic) was an Indo-European language spoken in Scandinavia that is thought to have evolved as ...
, evolved into Old Norse. This language underwent more changes that did not spread to all of Scandinavia, which resulted in the appearance of two similar dialects: ''Old West Norse'' (Norway, the Faroe Islands and Iceland) and ''Old East Norse'' (Denmark and Sweden). The dialects of Old East Norse spoken in Sweden are called ''Runic Swedish
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
'', while the dialects of Denmark are referred to as ''Runic Danish''. The dialects are described as "runic" because the main body of text appears in the runic alphabet
Runes are the letters in a set of related alphabets known as runic alphabets native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were used to write various Germanic languages (with some exceptions) before they adopted the Latin alphabet, and for specialised ...
. Unlike Proto-Norse, which was written with the Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark (or Fuþark), also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic alphabets. It was a writing system used by Germanic peoples for Northwest Germanic dialects in the Migration Peri ...
alphabet, Old Norse was written with the Younger Futhark
The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet and a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, with only 16 characters, in use from about the 9th century, after a "transitional period" during the 7th and 8th centuries.
The ...
alphabet, which had only 16 letters. Because the number of runes was limited, some runes were used for a range of phoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
s, such as the rune for the vowel ''u'', which was also used for the vowels ''o'', ''ø'' and ''y'', and the rune for ''i'', also used for ''e''.Lars-Erik Edlund, "Språkhistorisk översikt" in
From 1200 onwards, the dialects in Denmark began to diverge from those of Sweden. The innovations spread unevenly from Denmark, creating a series of minor dialectal boundaries, or isogloss
An isogloss, also called a heterogloss (see Etymology below), is the geographic boundary of a certain linguistic feature, such as the pronunciation of a vowel, the meaning of a word, or the use of some morphological or syntactic feature. Major ...
es, ranging from Zealand
Zealand ( da, Sjælland ) at 7,031 km2 is the largest and most populous island in Denmark proper (thus excluding Greenland and Disko Island, which are larger in size). Zealand had a population of 2,319,705 on 1 January 2020.
It is the 1 ...
in the south to Norrland
Norrland (, "Northland", originally ''Norrlanden'' or "the Northlands") is the northernmost, largest and least populated of the three traditional lands of Sweden, consisting of nine provinces. Although Norrland does not serve any administ ...
, Österbotten and northwestern Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bot ...
in the north.
An early change that separated Runic Danish from the other dialects of Old East Norse was the change of the diphthong
A diphthong ( ; , ), also known as a gliding vowel, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of the speech ...
''æi'' to the monophthong
A monophthong ( ; , ) is a pure vowel sound, one whose articulation at both beginning and end is relatively fixed, and which does not glide up or down towards a new position of articulation. The monophthongs can be contrasted with diphthongs, wh ...
''é'', as in ''stæinn'' to ''sténn'' "stone". This is reflected in runic inscriptions where the older read ''stain'' and the later ''stin''. There was also a change of ''au'' as in ''dauðr'' into a long open ''ø'' as in ''døðr'' "dead". This change is shown in runic inscriptions as a change from ''tauþr'' into ''tuþr''. Moreover, the ''øy'' diphthong changed into a long, close ''ø'', as in the Old Norse word for "island". By the end of the period, these innovations had affected most of the Runic Swedish-speaking area as well, with the exception of the dialects spoken north and east of Mälardalen where the diphthongs still exist in remote areas.
Old Swedish
 Old Swedish (Swedish: ''fornsvenska'') is the term used for the
Old Swedish (Swedish: ''fornsvenska'') is the term used for the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
Swedish language. The start date is usually set to 1225 since this is the year that '' Västgötalagen'' ("the Västgöta Law") is believed to have been compiled for the first time. It is among the most important documents of the period written in Latin script
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern ...
and the oldest Swedish law codes. Old Swedish is divided into ''äldre fornsvenska'' (1225–1375) and ''yngre fornsvenska'' (1375–1526), "older" and "younger" Old Swedish. Important outside influences during this time came with the firm establishment of the Christian church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym fo ...
and various monastic
Monasticism (from Ancient Greek , , from , , 'alone'), also referred to as monachism, or monkhood, is a religion, religious way of life in which one renounces world (theology), worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual work. Monastic ...
orders, introducing many Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
loanwords. With the rise of Hanseatic power in the late 13th and early 14th century, Middle Low German
Middle Low German or Middle Saxon (autonym: ''Sassisch'', i.e. " Saxon", Standard High German: ', Modern Dutch: ') is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented i ...
became very influential. The Hanseatic league provided Swedish commerce and administration with a large number of Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle ...
-speaking immigrants. Many became quite influential members of Swedish medieval society, and brought terms from their native languages into the vocabulary. Besides a great number of loanwords for such areas as warfare, trade and administration, general grammatical suffixes and even conjunctions were imported. The League also brought a certain measure of influence from Danish (at the time much more similar than today's language).Lars-Erik Edlund, "Språkhistorisk översikt" in
Early Old Swedish was markedly different from the modern language in that it had a more complex case
Case or CASE may refer to:
Containers
* Case (goods), a package of related merchandise
* Cartridge case or casing, a firearm cartridge component
* Bookcase, a piece of furniture used to store books
* Briefcase or attaché case, a narrow box to ca ...
structure and also retained the original Germanic three-gender
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most culture ...
system. Noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for:
* Living creatures (including people, alive, ...
s, adjective
In linguistics, an adjective ( abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the ...
s, pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun ( abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not ...
s and certain numerals
A numeral is a figure, symbol, or group of figures or symbols denoting a number. It may refer to:
* Numeral system used in mathematics
* Numeral (linguistics), a part of speech denoting numbers (e.g. ''one'' and ''first'' in English)
* Numerical d ...
were inflected in four cases; besides the extant nominative
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or (in Latin and formal variants of Eng ...
, there were also the genitive
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can a ...
(later possessive
A possessive or ktetic form ( abbreviated or ; from la, possessivus; grc, κτητικός, translit=ktētikós) is a word or grammatical construction used to indicate a relationship of possession in a broad sense. This can include strict ow ...
), dative
In grammar, the dative case ( abbreviated , or sometimes when it is a core argument) is a grammatical case used in some languages to indicate the recipient or beneficiary of an action, as in "Maria Jacobo potum dedit", Latin for "Maria gave Jacob ...
and accusative
The accusative case ( abbreviated ) of a noun is the grammatical case used to mark the direct object of a transitive verb.
In the English language, the only words that occur in the accusative case are pronouns: 'me,' 'him,' 'her,' 'us,' and ‘ ...
. The gender system resembled that of modern German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, having masculine, feminine and neuter genders. The masculine and feminine genders were later merged into a ''common gender'' with the definite suffix ''-en'' and the definite article
An article is any member of a class of dedicated words that are used with noun phrases to mark the identifiability of the referents of the noun phrases. The category of articles constitutes a part of speech.
In English, both "the" and "a(n)" a ...
''den'', in contrast with the neuter gender equivalents ''-et'' and ''det''. The verb system was also more complex: it included subjunctive
The subjunctive (also known as conjunctive in some languages) is a grammatical mood, a feature of the utterance that indicates the speaker's attitude towards it. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unreality s ...
and imperative moods and verbs were conjugated according to person
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of prope ...
as well as number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual number ...
. By the 16th century, the case and gender systems of the colloquial spoken language and the profane literature had been largely reduced to the two cases and two genders of modern Swedish.
A transitional change of the Latin script in the Nordic countries was to spell the letter combination "ae" as æ – and sometimes as a' – though it varied between persons and regions. The combination "ao" was similarly rendered ao, and "oe" became oe. These three were later to evolve into the separate letters ä, å and ö. The first time the new letters were used in print was in ''Aff dyäffwlsens frästilse'' ("By the Devil's temptation") published by Johan Gerson Johan
* Johan (given name)
* ''Johan'' (film), a 1921 Swedish film directed by Mauritz Stiller
* Johan (band), a Dutch pop-group
** ''Johan'' (album), a 1996 album by the group
* Johan Peninsula, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada
* Jo-Han, a man ...
in 1495.
Modern Swedish
 Modern Swedish (Swedish: ''nysvenska'') begins with the advent of the
Modern Swedish (Swedish: ''nysvenska'') begins with the advent of the printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the ...
and the European Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
. After assuming power, the new monarch Gustav Vasa
Gustav I, born Gustav Eriksson of the Vasa noble family and later known as Gustav Vasa (12 May 1496 – 29 September 1560), was King of Sweden from 1523 until his death in 1560, previously self-recognised Protector of the Realm ('' Riksför ...
ordered a Swedish translation of the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
. The New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
was published in 1526, followed by a full Bible translation
The Bible has been translated into many languages from the biblical languages of Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek. all of the Bible has been translated into 724 languages, the New Testament has been translated into an additional 1,617 languages, and ...
in 1541, usually referred to as the '' Gustav Vasa Bible'', a translation deemed so successful and influential that, with revisions incorporated in successive editions, it remained the most common Bible translation until 1917. The main translators were Laurentius Andreæ and the brothers Laurentius
Laurentius is a Latin given name and surname that means "''From Laurentum''" (a city near Rome).
It is possible that the place name ''Laurentum'' is derived from the Latin ''laurus'' (" laurel").
People with the name include:
In Early Christ ...
and Olaus Petri.
The Vasa Bible is often considered to be a reasonable compromise between old and new; while not adhering to the colloquial spoken language of its day, it was not overly conservative in its use of archaic forms. It was a major step towards a more consistent Swedish orthography
Swedish orthography is the set of rules and conventions used for writing Swedish. The primary authority on Swedish orthography is ''Svenska Akademiens ordlista'' (SAOL), a spelling dictionary published annually by the Swedish Academy. The balan ...
. It established the use of the vowels "å", "ä", and "ö", and the spelling "ck" in place of "kk", distinguishing it clearly from the Danish Bible, perhaps intentionally, given the ongoing rivalry between the countries. All three translators came from central Sweden, which is generally seen as adding specific Central Swedish features to the new Bible.
Though it might seem as if the Bible translation set a very powerful precedent for orthographic standards, spelling actually became more inconsistent during the remainder of the century. It was not until the 17th century that spelling began to be discussed, around the time when the first grammars were written. Capitalization
Capitalization (American English) or capitalisation (British English) is writing a word with its first letter as a capital letter (uppercase letter) and the remaining letters in lower case, in writing systems with a case distinction. The term ...
during this time was not standardized. It depended on the authors and their background. Those influenced by German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
capitalized all nouns, while others capitalized more sparsely. It is also not always apparent which letters are capitalized owing to the Gothic or blackletter
Blackletter (sometimes black letter), also known as Gothic script, Gothic minuscule, or Textura, was a script used throughout Western Europe from approximately 1150 until the 17th century. It continued to be commonly used for the Danish, Norwe ...
typeface that was used to print the Bible. This typeface was in use until the mid-18th century, when it was gradually replaced with a Latin typeface (often antiqua).
Some important changes in sound during the Modern Swedish period were the gradual assimilation of several different consonant clusters into the fricative
A fricative is a consonant produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate in ...
and later into . There was also the gradual softening of and into and the fricative
A fricative is a consonant produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate in ...
before front vowel
A front vowel is a class of vowel sounds used in some spoken languages, its defining characteristic being that the highest point of the tongue is positioned as far forward as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would otherw ...
s. The velar fricative
A velar fricative is a fricative consonant produced at the velar place of articulation. It is possible to distinguish the following kinds of velar fricatives:
*Voiced velar fricative, a consonant sound written as in the International Phonetic Alph ...
was also transformed into the corresponding plosive
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or simply a stop, is a pulmonic consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases.
The occlusion may be made with the tongue tip or blade (, ), tongue body (, ), lip ...
.

Contemporary Swedish
 The period that includes Swedish as it is spoken today is termed ''nusvenska'' (lit., "Now-Swedish") in linguistics, and started in the last decades of the 19th century. It saw a democratization of the language with a less formal written form that approached the spoken one. The growth of a public school system also led to the evolution of so-called ''boksvenska'' (literally, "book Swedish"), especially among the working classes, where spelling to some extent influenced pronunciation, particularly in official contexts. With the industrialization and urbanization of Sweden well under way by the last decades of the 19th century, a new breed of authors made their mark on
The period that includes Swedish as it is spoken today is termed ''nusvenska'' (lit., "Now-Swedish") in linguistics, and started in the last decades of the 19th century. It saw a democratization of the language with a less formal written form that approached the spoken one. The growth of a public school system also led to the evolution of so-called ''boksvenska'' (literally, "book Swedish"), especially among the working classes, where spelling to some extent influenced pronunciation, particularly in official contexts. With the industrialization and urbanization of Sweden well under way by the last decades of the 19th century, a new breed of authors made their mark on Swedish literature
Swedish literature () refers to literature written in the Swedish language or by writers from Sweden.
The first literary text from Sweden is the Rök runestone, carved during the Viking Age circa 800 AD. With the conversion of the land to Chri ...
. Many scholars, politicians and other public figures had a great influence on the emerging national language, among them prolific authors like the poet Gustaf Fröding, Nobel laureate Selma Lagerlöf
Selma Ottilia Lovisa Lagerlöf (, , ; 20 November 1858 – 16 March 1940) was a Swedish author. She published her first novel, '' Gösta Berling's Saga'', at the age of 33. She was the first woman to win the Nobel Prize in Literature, which she wa ...
, and radical writer and playwright August Strindberg
Johan August Strindberg (, ; 22 January 184914 May 1912) was a Swedish playwright, novelist, poet, essayist and painter.Lane (1998), 1040. A prolific writer who often drew directly on his personal experience, Strindberg wrote more than sixty p ...
.
It was during the 20th century that a common, standardized national language became available to all Swedes. The orthography finally stabilized and became almost completely uniform, with some minor deviations, by the time of the spelling reform of 1906. With the exception of plural forms of verbs and a slightly different syntax, particularly in the written language, the language was the same as the Swedish of today. The plural verb forms appeared decreasingly in formal writing into the 1950s, when their use was removed from all official recommendations.
A very significant change in Swedish occurred in the late 1960s, with the so-called ''du-reformen
''Du-reformen'' (, "the thou-reform") was the process of popularization of the second-person singular pronoun ''du'' as a universal form of address in Sweden that took place in the late 1960s. The use of '' du'' (cognate with English ''thou'', Fre ...
'', "the you-reform". Previously, the proper way to address people of the same or higher social status had been by title and surname. The use of ''herr'' ("Mr" or "Sir"), ''fru'' ("Mrs" or "Ma'am") or ''fröken'' ("Miss") was considered the only acceptable way to begin conversation with strangers of unknown occupation, academic title or military rank. The fact that the listener should preferably be referred to in the third person tended to further complicate spoken communication between members of society. In the early 20th century, an unsuccessful attempt was made to replace the insistence on titles with ''ni''—the standard second person plural pronoun)—analogous to the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
''vous''. (Cf. T-V distinction.) ''Ni'' wound up being used as a slightly less familiar form of ''du'', the singular second person pronoun, used to address people of lower social status. With the liberalization and radicalization of Swedish society in the 1950s and 1960s, these class distinctions became less important, and ''du'' became the standard, even in formal and official contexts. Though the reform was not an act of any centralized political decree, but rather the result of sweeping change in social attitudes, it was completed in just a few years, from the late 1960s to early 1970s. The use of ''ni'' as a polite form of address is sometimes encountered today in both the written and spoken language, particularly among older speakers.
Geographic distribution
Swedish is the sole official national language ofSweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
, and one of two in Finland (alongside Finnish). As of 2006, it was the sole native language of 83% of Swedish residents. In 2007 around 5.5% (c. 290,000) of the population of Finland were native speakers of Swedish,Population structureStatistics Finland (29 March 2007). Retrieved on 27 November 2007. partially due to a decline following the Russian annexation of Finland after the
Finnish War
The Finnish War ( sv, Finska kriget, russian: Финляндская война, fi, Suomen sota) was fought between the Kingdom of Sweden and the Russian Empire from 21 February 1808 to 17 September 1809 as part of the Napoleonic Wars. As a re ...
1808–1809. The Finland Swedish
Finland Swedish or Fenno-Swedish ( sv, finlandssvenska; fi, suomenruotsi) is a general term for the variety of the Swedish language and a closely related group of Swedish dialects spoken in Finland by the Swedish-speaking population, commonly ...
minority is concentrated in the coastal areas and archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arch ...
s of southern and western Finland. In some of these areas, Swedish is the predominant language; in 19 municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the ...
, 16 of which are located in Åland
Åland ( fi, Ahvenanmaa: ; ; ) is an autonomous and demilitarised region of Finland since 1920 by a decision of the League of Nations. It is the smallest region of Finland by area and population, with a size of 1,580 km2, and a populat ...
, Swedish is the sole official language. Åland county is an autonomous region of Finland.
According to a rough estimation, as of 2010 there were up to 300,000 Swedish-speakers living outside Sweden and Finland. The largest populations were in the United States (up to 100,000), the UK, Spain and Germany (c. 30,000 each) and a large proportion of the remaining 100,000 in the Scandinavian countries, France, Switzerland, Belgium, the Netherlands, Canada and Australia. Over 3 million people speak Swedish as a second language, with about 2,410,000 of those in Finland. According to a survey by the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
, 44% of respondents from Finland who did not have Swedish as a native language considered themselves to be proficient enough in Swedish to hold a conversation. Due to the close relation between the Scandinavian languages, a considerable proportion of speakers of Danish and especially Norwegian are able to understand Swedish.
There is considerable migration between the Nordic countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; lit. 'the North') are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sw ...
, but owing to the similarity between the cultures and languages (with the exception of Finnish), expatriates generally assimilate quickly and do not stand out as a group. According to the 2000 United States Census, some 67,000 people over the age of five were reported as Swedish speakers, though without any information on the degree of language proficiency. Similarly, there were 16,915 reported Swedish speakers in Canada from the 2001 census. Although there are no certain numbers, some 40,000 Swedes are estimated to live in the London area in the United Kingdom. Outside Sweden and Finland, there are about 40,000 active learners enrolled in Swedish language courses.
Official status
Riksdag
The Riksdag (, ; also sv, riksdagen or ''Sveriges riksdag'' ) is the legislature and the supreme decision-making body of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral legislature with 349 members (), elected proportionally and se ...
, and entered into effect on 1 July 2009.
Swedish is the sole official language of Åland
Åland ( fi, Ahvenanmaa: ; ; ) is an autonomous and demilitarised region of Finland since 1920 by a decision of the League of Nations. It is the smallest region of Finland by area and population, with a size of 1,580 km2, and a populat ...
(an autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ow ...
province under the sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
of Finland), where the vast majority of the 26,000 inhabitants speak Swedish as a first language. In Finland as a whole, Swedish is one of the two "national" languages, with the same official status as Finnish (spoken by the majority) at the state level and an official language in some municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the ...
.
Swedish is one of the official languages of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
, and one of the working languages of the Nordic Council
The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomou ...
. Under the Nordic Language Convention The Nordic Language Convention is a convention of linguistic rights that came into force on 1 March 1987, under the auspices of the Nordic Council. Under the Convention, citizens of the Nordic countries have the opportunity to use their native lan ...
, citizens of the Nordic countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; lit. 'the North') are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sw ...
speaking Swedish have the opportunity to use their native language when interacting with official bodies in other Nordic countries without being liable for interpretation or translation costs.
Regulatory bodies
 The
The Swedish Language Council
The Language Council of Sweden ( sv, Språkrådet) is the primary regulatory body for the advancement and cultivation of the Swedish language. The council is a department of the Swedish government's Institute for Language and Folklore ( sv, Inst ...
(''Språkrådet'') is the regulator of Swedish in Sweden but does not attempt to enforce control of the language, as for instance the ''Académie française
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosop ...
'' does for French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
. However, many organizations and agencies require the use of the council's publication ''Svenska skrivregler'' in official contexts, with it otherwise being regarded as a ''de facto'' orthographic standard. Among the many organizations that make up the Swedish Language Council, the Swedish Academy
The Swedish Academy ( sv, Svenska Akademien), founded in 1786 by King Gustav III, is one of the Royal Academies of Sweden. Its 18 members, who are elected for life, comprise the highest Swedish language authority. Outside Scandinavia, it is bes ...
(established 1786) is arguably the most influential. Its primary instruments are the spelling dictionary '' Svenska Akademiens ordlista'' (''SAOL'', currently in its 14th edition) and the dictionary '' Svenska Akademiens Ordbok'', in addition to various books on grammar, spelling and manuals of style. Although the dictionaries have a prescriptive element, they mainly describe current usage.
In Finland, a special branch of the Research Institute for the Languages of Finland has official status as the regulatory body for Swedish in Finland. Among its highest priorities is to maintain intelligibility with the language spoken in Sweden. It has published ''Finlandssvensk ordbok'', a dictionary about the differences between Swedish in Finland and Sweden.
Language minorities in Estonia and Ukraine
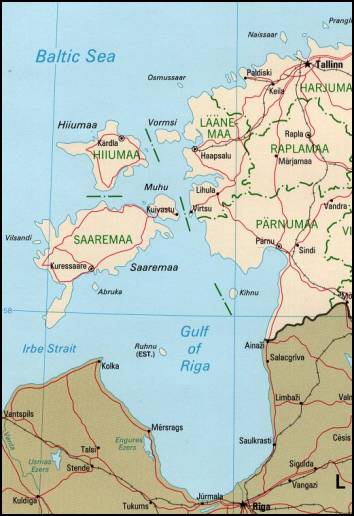
From the 13th to 20th century, there were Swedish-speaking communities in Estonia, particularly on the islands (e. g.,Hiiumaa
Hiiumaa (, ) is the second largest island in Estonia and is part of the West Estonian archipelago, in the Baltic Sea. It has an area of 989 km2 and is 22 km from the Estonian mainland. Its largest town is Kärdla. It is located within ...
, Vormsi, Ruhnu; in Swedish, known as ''Dagö'', ''Ormsö'', ''Runö'', respectively) along the coast of the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
, communities that today have all disappeared. The Swedish-speaking minority was represented in parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
, and entitled to use their native language in parliamentary debates. After the loss of Estonia to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
in the early 18th century, around 1,000 Estonian Swedish
Estonian Swedish ( sv, estlandssvenska; et, rannarootsi keel, lit=Coastal Swedish) are the eastern varieties of Swedish that were spoken in the formerly Swedish-populated areas of Estonia (locally known as '' Aiboland'') on the islands of Orm ...
speakers were forced to march to southern Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
, where they founded a village, ''Gammalsvenskby
Gammalsvenskby ( sv, Gammölsvänskbi, label=Gammalsvenska, lit=Old Swedish Village; uk, Старошведське, translit=Staroshvedske; german: Alt-Schwedendorf) is a former village that is now a neighbourhood of Zmiivka ( uk, Зміїв ...
'' ("Old Swedish Village"). A few elderly people in the village still speak a Swedish dialect and observe the holidays of the Swedish calendar, although their dialect is most likely facing extinction.
From 1918 to 1940, when Estonia was independent, the small Swedish community was well treated. Municipalities with a Swedish majority, mainly found along the coast, used Swedish as the administrative language and Swedish-Estonian culture saw an upswing. However, most Swedish-speaking people fled to Sweden before the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, that is, before the invasion of Estonia by the Soviet army in 1944. Only a handful of speakers remain.
Phonology
phoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
s, 9 long and 9 short. As in the other Germanic languages, including English, most long vowels are phonetically paired with one of the short vowels, and the pairs are such that the two vowels are of similar quality
Quality may refer to:
Concepts
*Quality (business), the ''non-inferiority'' or ''superiority'' of something
*Quality (philosophy), an attribute or a property
*Quality (physics), in response theory
* Energy quality, used in various science discipl ...
, but with the short vowel being slightly lower and slightly centralized. In contrast to e.g. Danish, which has only tense vowels, the short vowels are slightly more lax, but the tense vs. lax contrast is not nearly as pronounced as in English, German or Dutch. In many dialects, the short vowel sound pronounced or has merged with the short (transcribed in the chart below).;
There are 18 consonant phonemes, two of which, and , vary considerably in pronunciation depending on the dialect and social status of the speaker. In many dialects, sequences of (pronounced alveolarly) with a dental consonant result in retroflex consonant
A retroflex ( /ˈɹɛtʃɹoːflɛks/), apico-domal ( /əpɪkoːˈdɔmɪnəl/), or cacuminal () consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the h ...
s; alveolarity of the pronunciation of is a precondition for this retroflexion. has a guttural
Guttural speech sounds are those with a primary place of articulation near the back of the oral cavity, especially where it's difficult to distinguish a sound's place of articulation and its phonation. In popular usage it is an imprecise term fo ...
or "French R" pronunciation in the South Swedish dialects; consequently, these dialects lack retroflex consonant
A retroflex ( /ˈɹɛtʃɹoːflɛks/), apico-domal ( /əpɪkoːˈdɔmɪnəl/), or cacuminal () consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the h ...
s.
Swedish is a stress-timed
Isochrony is the postulated rhythmic division of time into equal portions by a language. Rhythm is an aspect of prosody, others being intonation, stress, and tempo of speech.
Three alternative ways in which a language can divide time are postul ...
language, where the time intervals between stressed syllables are equal. However, when casually spoken, it tends to be syllable-timed. Any stressed syllable carries one of two tones, which gives Swedish much of its characteristic sound. Prosody is often one of the most noticeable differences between dialects.
Grammar
The standard word order is, as in mostGermanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, ...
, V2, which means that the finite verb
Traditionally, a finite verb (from la, fīnītus, past participle of to put an end to, bound, limit) is the form "to which number and person appertain", in other words, those inflected for number and person. Verbs were originally said to be ''fin ...
(V) appears in the second position (2) of a declarative main clause
An independent clause (or main clause) is a clause that can stand by itself as a ''simple sentence''. An independent clause contains a subject and a predicate and makes sense by itself.
Independent clauses can be joined by using a semicolon or ...
. Swedish morphology
Swedish is descended from Old Norse. Compared to its progenitor, Swedish grammar is much less characterized by inflection. Modern Swedish has two genders and no longer conjugates verbs based on person or number. Its nouns have lost the morpholo ...
is similar to English; that is, words have comparatively few inflections. Swedish has two genders
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most cultures us ...
and is generally seen to have two grammatical cases
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers ( determiners, adjectives, participles, and numerals), which corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nom ...
– nominative
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or (in Latin and formal variants of Eng ...
and genitive
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can a ...
(except for pronouns that, as in English, also are inflected in the object
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ...
form) – although it is debated if the genitive in Swedish should be seen as a genitive case or just the nominative plus the so-called genitive ''s'', then seen as a clitic
In morphology and syntax, a clitic (, backformed from Greek "leaning" or "enclitic"Crystal, David. ''A First Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics''. Boulder, CO: Westview, 1980. Print.) is a morpheme that has syntactic characteristics of a ...
. Swedish has two grammatical number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a grammatical category of nouns, pronouns, adjectives and verb agreement that expresses count distinctions (such as "one", "two" or "three or more"). English and other languages present number categories of ...
s – plural
The plural (sometimes list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated pl., pl, or ), in many languages, is one of the values of the grammatical number, grammatical category of number. The plural of a noun typically denotes a quantity greater than the ...
and singular
Singular may refer to:
* Singular, the grammatical number that denotes a unit quantity, as opposed to the plural and other forms
* Singular homology
* SINGULAR, an open source Computer Algebra System (CAS)
* Singular or sounder, a group of boar ...
. Adjectives
In linguistics, an adjective (abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the ...
have discrete comparative and superlative forms and are also inflected according to gender, number and definiteness
In linguistics, definiteness is a semantic feature of noun phrases, distinguishing between referents or senses that are identifiable in a given context (definite noun phrases) and those which are not (indefinite noun phrases). The prototypical ...
. The definiteness of nouns is marked primarily through suffixes
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry g ...
(endings), complemented with separate definite and indefinite articles
Article often refers to:
* Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness
* Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication
Article may also refer to:
...
. The prosody features both stress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
and in most dialects tonal qualities. The language has a comparatively large vowel
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (len ...
inventory. Swedish is also notable for the voiceless dorso-palatal velar fricative
The ''sj''-sound ( sv, sj-ljudet ) is a voiceless fricative phoneme found in most dialects of the sound system of Swedish. It has a variety of realisations, whose precise phonetic characterisation is a matter of debate, but which usually featur ...
, a highly variable consonant phoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
.
Swedish noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for:
* Living creatures (including people, alive, ...
s and adjective
In linguistics, an adjective ( abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the ...
s are declined in genders
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most cultures us ...
as well as number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual number ...
. Nouns are of common gender
In linguistics, grammatical gender system is a specific form of noun class system, where nouns are assigned with gender categories that are often not related to their real-world qualities. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns ...
(''en'' form) or neuter gender
In linguistics, grammatical gender system is a specific form of noun class system, where nouns are assigned with gender categories that are often not related to their real-world qualities. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nou ...
(''ett'' form). The gender determines the declension of the adjective
In linguistics, an adjective ( abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the ...
s. For example, the word ''fisk'' ("fish") is a noun of common gender (''en fisk'') and can have the following forms:
The definite singular form of a noun is created by adding a suffix (''-en'', ''-n'', ''-et'' or ''-t''), depending on its gender and if the noun ends in a vowel or not. The definite articles ''den'', ''det'', and ''de'' are used for variations to the definitiveness of a noun. They can double as demonstrative
Demonstratives ( abbreviated ) are words, such as ''this'' and ''that'', used to indicate which entities are being referred to and to distinguish those entities from others. They are typically deictic; their meaning depending on a particular fram ...
pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun ( abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not ...
s or demonstrative determiners when used with adverb An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, adjective, another adverb, determiner, clause, preposition, or sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, level of certainty, etc., answering ...
s such as ''här'' ("here") or ''där'' ("there") to form ''den/det här (can also be "denna/detta")'' ("this"), ''de här (can also be "dessa")'' ("these"), ''den/det där'' ("that"), and ''de där'' ("those"). For example, ''den där fisken'' means "that fish" and refers to a specific fish; ''den fisken'' is less definite and means "that fish" in a more abstract sense, such as that set of fish; while ''fisken'' means "the fish". In certain cases, the definite form indicates possession, e. g., ''jag måste tvätta håret'' ("I must wash ''my'' hair").
Adjective
In linguistics, an adjective ( abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the ...
s are inflected in two declensions – indefinite and definite – and they must match the noun they modify in gender and number. The indefinite neuter and plural forms of an adjective are usually created by adding a suffix (''-t'' or ''-a'') to the common form of the adjective, e. g., ''en grön stol'' (a green chair), ''ett grönt hus'' (a green house), and ''gröna stolar'' ("green chairs"). The definite form of an adjective is identical to the indefinite plural form, e. g., ''den gröna stolen'' ("the green chair"), ''det gröna huset'' ("the green house"), and ''de gröna stolarna'' ("the green chairs").
Swedish pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun ( abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not ...
s are similar to those of English. Besides the two natural genders ''han'' and ''hon'' ("he" and "she"), there are also the two grammatical gender
In linguistics, grammatical gender system is a specific form of noun class system, where nouns are assigned with gender categories that are often not related to their real-world qualities. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all noun ...
s ''den'' and ''det'', usually termed common and neuter. In recent years, a gender-neutral
Gender neutrality (adjective form: gender-neutral), also known as gender-neutralism or the gender neutrality movement, is the idea that policies, language, and other social institutions ( social structures or gender roles) should avoid disting ...
pronoun ''hen'' has been introduced, particularly in literary Swedish. Unlike the nouns, pronouns have an additional object
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ...
form, derived from the old dative
In grammar, the dative case ( abbreviated , or sometimes when it is a core argument) is a grammatical case used in some languages to indicate the recipient or beneficiary of an action, as in "Maria Jacobo potum dedit", Latin for "Maria gave Jacob ...
form. ''Hon'', for example, has the following nominative, possessive, and object forms:
:''hon'' – ''hennes'' – ''henne''
Swedish also uses third-person possessive reflexive pronoun
A reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that refers to another noun or pronoun (its antecedent) within the same sentence.
In the English language specifically, a reflexive pronoun will end in ''-self'' or ''-selves'', and refer to a previously n ...
s that refer to the subject in a clause, a trait that is restricted to North Germanic languages:
:''Anna gav Maria sin bok.''; "Anna gave Maria her nna'sbook." (reflexive)
:''Anna gav Maria hennes bok.''; "Anna gave Maria her aria'sbook." (not reflexive)
Swedish used to have a genitive
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can a ...
that was placed at the end of the head of a noun phrase. In modern Swedish, it has become an enclitic
In morphology and syntax, a clitic (, backformed from Greek "leaning" or "enclitic"Crystal, David. ''A First Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics''. Boulder, CO: Westview, 1980. Print.) is a morpheme that has syntactic characteristics of a ...
''-s'', which attaches to the end of the noun phrase, rather than the noun itself.
:''hästen''; "the horse" – ''hästens'' "the horse's"
:''hästen på den blommande ängens svarta man''; "the horse in the flowering meadow's black mane"
In formal written language, it used to be considered correct to place the genitive ''-s'' after the head of the noun phrase (''hästen''), though this is today considered dated, and different grammatical constructions are often used.
Verbs are conjugated according to tense. One group of verbs (the ones ending in ''-er'' in present tense) has a special imperative form (generally the verb stem
Stem or STEM may refer to:
Plant structures
* Plant stem, a plant's aboveground axis, made of vascular tissue, off which leaves and flowers hang
* Stipe (botany), a stalk to support some other structure
* Stipe (mycology), the stem of a mushro ...
), but with most verbs the imperative is identical to the infinitive
Infinitive ( abbreviated ) is a linguistics term for certain verb forms existing in many languages, most often used as non-finite verbs. As with many linguistic concepts, there is not a single definition applicable to all languages. The word is de ...
form. Perfect and present
The present (or here'' and ''now) is the time that is associated with the events perceived directly and in the first time, not as a recollection (perceived more than once) or a speculation (predicted, hypothesis, uncertain). It is a period of ...
participle
In linguistics, a participle () (from Latin ' a "sharing, partaking") is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from ...
s as adjectival verbs are very common:
:Perfect participle: ''en stekt fisk''; "a fried fish" (steka = to fry)
:Present participle: ''en stinkande fisk''; "a stinking fish" (stinka = to stink)
In contrast to English and many other languages, Swedish does not use the perfect participle to form the present perfect and past perfect. Rather, the auxiliary verb
An auxiliary verb ( abbreviated ) is a verb that adds functional or grammatical meaning to the clause in which it occurs, so as to express tense, aspect, modality, voice, emphasis, etc. Auxiliary verbs usually accompany an infinitive verb or a ...
''har'' ("have"), ''hade'' ("had") is followed by a special form, called the supine
In grammar, a supine is a form of verbal noun used in some languages. The term is most often used for Latin, where it is one of the four principal parts of a verb. The word refers to a position of lying on one's back (as opposed to ' prone', l ...
, used solely for this purpose (although often identical to the neuter form of the perfect participle):
:Perfect participle: ''målad'', "painted" – supine ''målat'', present perfect ''har målat''; "have painted"
:Perfect participle: ''stekt'', "fried" – supine ''stekt'', present perfect ''har stekt''; "have fried"
:Perfect participle: ''skriven'', "written" – supine ''skrivit'', present perfect ''har skrivit''; "have written"
When building the compound passive voice using the verb ''att bli'', the past participle is used:
:''den blir målad''; "it's being painted"
:''den blev målad''; "it was painted"
There exists also an inflected passive voice formed by adding ''-s'', replacing the final ''r'' in the present tense:
:''den målas''; "it's being painted"
:''den målades''; "it was painted"
In a subordinate clause
In language, a clause is a constituent that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject and a syntactic predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb wit ...
, the auxiliary ''har'' is optional and often omitted, particularly in written Swedish.
:''Jag ser att han (har) stekt fisken''; "I see that he has fried the fish"
Subjunctive mood
The subjunctive (also known as conjunctive in some languages) is a grammatical mood, a feature of the utterance that indicates the speaker's attitude towards it. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unreality ...
is occasionally used for some verbs, but its use is in sharp decline and few speakers perceive the handful of commonly used verbs (as for instance: ''vore, månne'') as separate conjugations, most of them remaining only as set of idiomatic expressions.
Where other languages may use grammatical cases
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers ( determiners, adjectives, participles, and numerals), which corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nom ...
, Swedish uses numerous preposition
Prepositions and postpositions, together called adpositions (or broadly, in traditional grammar, simply prepositions), are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in'', ''under'', ''towards'', ''before'') or mark various ...
s, similar to those found in English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
. As in modern German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, prepositions formerly determined case in Swedish, but this feature can only be found in certain idiomatic expressions like ''till fots'' ("on foot", genitive).
As Swedish is a Germanic language, the syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituenc ...
shows similarities to both English and German. Like English, Swedish has a subject–verb–object basic word order, but like German it utilizes verb-second word order in main clauses, for instance after adverbs An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, adjective, another adverb, determiner, clause, preposition, or sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, level of certainty, etc., answering que ...
and adverbial phrases, and dependent clauses. (Adverbial phrases denoting time are usually placed at the beginning of a main clause that is at the head of a sentence.) Prepositional phrase
An adpositional phrase, in linguistics, is a syntactic category that includes ''prepositional phrases'', ''postpositional phrases'', and ''circumpositional phrases''. Adpositional phrases contain an adposition (preposition, postposition, or ci ...
s are placed in a place–manner–time order, as in English (but not German). Adjectives precede the noun they modify. Verb-second (inverted) word order is also used for questions.
Vocabulary
Thevocabulary
A vocabulary is a set of familiar words within a person's language. A vocabulary, usually developed with age, serves as a useful and fundamental tool for communication and acquiring knowledge. Acquiring an extensive vocabulary is one of the ...
of Swedish is mainly Germanic, either through common Germanic heritage or through loans from German, Middle Low German, and to some extent, English. Examples of Germanic words in Swedish are ''mus'' ("mouse"), ''kung'' ("king"), and ''gås'' ("goose"). A significant part of the religious and scientific vocabulary is of Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
or Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
origin, often borrowed from French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and, lately, English. Some 1–200 words are also borrowed from Scandoromani or Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
, often as slang varieties; a commonly used word from Romani is '' tjej'' ("girl").
A large number of French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
words were imported into Sweden around the 18th century. These words have been transcribed to the Swedish spelling system and are therefore pronounced recognizably to a French-speaker. Most of them are distinguished by a "French accent", characterized by emphasis on the last syllable. For example, ''nivå'' (fr. ''niveau'', "level"), ''fåtölj'' (fr. ''fauteuil'', "armchair") and ''affär'' ("shop; affair"), etc. Cross-borrowing from other Germanic languages has also been common, at first from Middle Low German, the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
of the Hanseatic league
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label= Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
and later from Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
. Some compounds are translations of the elements (calque
In linguistics, a calque () or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language ...
s) of German original compounds into Swedish, like ' from German ' ("cotton"; literally, ''tree-wool'').
As with many Germanic languages, new words can be formed by compounding, e. g., nouns like ' ("nail polish remover") or verbs like ' ("to eavesdrop"). Compound nouns take their gender
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most culture ...
from the head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals ...
, which in Swedish is always the last morpheme. New words can also be coined by derivation
Derivation may refer to:
Language
* Morphological derivation, a word-formation process
* Parse tree or concrete syntax tree, representing a string's syntax in formal grammars
Law
* Derivative work, in copyright law
* Derivation proceeding, a proc ...
from other established words, such as the verbification
In linguistics, conversion, also called zero derivation or null derivation, is a kind of word formation involving the creation of a word (of a new word class) from an existing word (of a different word class) without any change in form, which ...
of noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for:
* Living creatures (including people, alive, ...
s by the adding of the suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carr ...
''-a'', as in ' ("car") and ' ("travel (recreationally) by car"). The opposite, making nouns of verbs, is also possible, as in ' ("way of thinking; concept") from ' ("to think").
Writing system
TheSwedish alphabet
The Swedish alphabet ( sv, Svenska alfabetet) is a basic element of the Latin writing system used for the Swedish language. The 29 letters of this alphabet are the modern 26-letter basic Latin alphabet (A through Z) plus Å, Ä, and Ö, in ...
is a 29-letter alphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllab ...
, using the 26-letter ISO basic Latin alphabet
The ISO basic Latin alphabet is an international standard (beginning with ISO/IEC 646) for a Latin-script alphabet that consists of two sets ( uppercase and lowercase) of 26 letters, codified in various national and international standards and ...
plus the three additional letters '' Å''/''å'', '' Ä''/''ä'', and '' Ö''/''ö'' constructed in the 16th century by writing "o" and "e" on top of an "a", and an "e" on top of an "o". Though these combinations are historically modified versions of A and O according to the English range of usage for the term diacritic
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacrit ...
, these three characters are not considered to be diacritics within the Swedish application, but rather separate letters, and are independent letters following ''z''. Before the release of the 13th edition of '' Svenska Akademiens ordlista'' in April 2006, ''w'' was treated as merely a variant of ''v'' used only in names (such as "Wallenberg") and foreign words ("bowling"), and so was both sorted and pronounced as a ''v''. Other diacritic
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacrit ...
s (to use the broader English term usage referenced here) are unusual in Swedish; é is sometimes used to indicate that the stress falls on a terminal syllable containing ''e'', especially when the stress changes the meaning (''ide'' vs. ''idé'', "winter lair" vs. "idea") as well as in some names, like ''Kastrén''; occasionally other acute accent
The acute accent (), , is a diacritic used in many modern written languages with alphabets based on the Latin, Cyrillic, and Greek scripts. For the most commonly encountered uses of the accent in the Latin and Greek alphabets, precomposed ...
s and, less often, grave accent
The grave accent () ( or ) is a diacritical mark used to varying degrees in French, Dutch, Portuguese, Italian and many other western European languages, as well as for a few unusual uses in English. It is also used in other languages usin ...
s can be seen in names and some foreign words. The letter à is used to refer to unit cost (a loan from the French), equivalent to the at sign (@) in English.
The German '' ü'' is treated as a variant of '' y'' and sometimes retained in foreign names and words, e. g., ''müsli'' ("muesli/granola"). A proper diaeresis may very exceptionally be seen in elaborated style (for instance: "Aïda"). The German convention of writing ''ä'' and ''ö'' as ''ae'' and ''oe'' if the characters are unavailable is an unusual convention for speakers of modern Swedish. Despite the availability of all these characters in the Swedish national top-level Internet domain and other such domains, Swedish sites are frequently labelled using ''a'' and ''o'', based on visual similarity, though Swedish domains could be registered using the characters å, ä, and ö from 2003.
In Swedish orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.
Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and ...
, the colon is used in a similar manner as in English, with some exceptions: the colon is used for some abbreviations, such as ''3:e'' for ''tredje'' ("third") and ''S:t'' for ''Sankt'' ("Saint"), and for all types of endings
End, END, Ending, or variation, may refer to:
End
*In mathematics:
**End (category theory)
** End (topology)
**End (graph theory)
** End (group theory) (a subcase of the previous)
**End (endomorphism)
*In sports and games
** End (gridiron footbal ...
that can be added to numbers, letters and abbreviations, such as ''a:et'' ("the a") and ''CD:n'' ("the CD"), or the genitive form ''USA:s'' ("USA's").
Dialects
dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is ...
s, there are six main groups of dialects:
* Norrland dialects
* Finland Swedish
Finland Swedish or Fenno-Swedish ( sv, finlandssvenska; fi, suomenruotsi) is a general term for the variety of the Swedish language and a closely related group of Swedish dialects spoken in Finland by the Swedish-speaking population, commonly ...
* Svealand dialects
Svealand Swedish ( sv, Sveamål) is one of the six major groupings of Swedish dialects, spoken in Svealand.
A major characteristic of ''Svealand Swedish'' is the coalescence of the alveolar trill with following dental and alveolar consonants&mda ...
* Gotland dialects
* Götaland dialects
* South Swedish dialects
The traditional definition of a Swedish dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is ...
has been a local variant that has not been heavily influenced by the standard language and that can trace a separate development all the way back to Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
. Many of the genuine rural dialects, such as those of Orsa in Dalarna
Dalarna () is a '' landskap'' (historical province) in central Sweden. English exonyms for it are Dalecarlia () and the Dales.
Dalarna adjoins Härjedalen, Hälsingland, Gästrikland, Västmanland and Värmland. It is also bordered by Norwa ...
or Närpes in Österbotten, have very distinct phonetic and grammatical features, such as plural forms of verbs or archaic case
Case or CASE may refer to:
Containers
* Case (goods), a package of related merchandise
* Cartridge case or casing, a firearm cartridge component
* Bookcase, a piece of furniture used to store books
* Briefcase or attaché case, a narrow box to ca ...
inflections. These dialects can be near-incomprehensible to a majority of Swedes, and most of their speakers are also fluent in Standard Swedish. The different dialects are often so localized that they are limited to individual parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or ...
es and are referred to by Swedish linguists as ''sockenmål'' (lit., "parish speech"). They are generally separated into six major groups, with common characteristics of prosody, grammar and vocabulary. One or several examples from each group are given here. Though each example is intended to be also representative of the nearby dialects, the actual number of dialects is several hundred if each individual community is considered separately.
This type of classification, however, is based on a somewhat romanticized nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Th ...
view of ethnicity and language. The idea that only rural variants of Swedish should be considered "genuine" is not generally accepted by modern scholars. No dialects, no matter how remote or obscure, remained unchanged or undisturbed by a minimum of influences from surrounding dialects or the standard language, especially not from the late 19th century onwards with the advent of mass media
Mass media refers to a diverse array of media technologies that reach a large audience via mass communication. The technologies through which this communication takes place include a variety of outlets.
Broadcast media transmit informati ...
and advanced forms of transport. The differences are today more accurately described by a scale that runs from "standard language" to "rural dialect" where the speech even of the same person may vary from one extreme to the other depending on the situation. All Swedish dialects with the exception of the highly diverging forms of speech in Dalarna
Dalarna () is a '' landskap'' (historical province) in central Sweden. English exonyms for it are Dalecarlia () and the Dales.
Dalarna adjoins Härjedalen, Hälsingland, Gästrikland, Västmanland and Värmland. It is also bordered by Norwa ...
, Norrbotten
Norrbotten (), known in English as North Bothnia, is a Swedish province (''landskap'') in northernmost Sweden. It borders south to Västerbotten, west to Swedish Lapland, and east to Finland.
Administration
The traditional provinces of ...
and, to some extent, Gotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to ...
can be considered to be part of a common, mutually intelligible dialect continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulate over distance so that widely separated vari ...
. This continuum may also include Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
and some Danish dialects
The Danish language has a number of regional and local dialect varieties. These can be divided into the traditional dialects, which differ from modern Standard Danish in both phonology and grammar, and the Danish accents, which are local varieties ...
.
The samples linked below have been taken from SweDia, a research project on Swedish modern dialects available for download (though with information in Swedish only), with many more samples from 100 different dialects with recordings from four different speakers: older female, older male, younger female and younger male. The dialect groups are those traditionally used by dialectologists.
 #
# Överkalix
Överkalix (; fi, Ylikainuu) is a Urban areas in Sweden, locality and the seat of Överkalix Municipality in Norrbotten County, Sweden with 975 inhabitants in 2010.
Climate
Överkalix has a subarctic climate with significant temperature differenc ...
, Norrbotten
Norrbotten (), known in English as North Bothnia, is a Swedish province (''landskap'') in northernmost Sweden. It borders south to Västerbotten, west to Swedish Lapland, and east to Finland.
Administration
The traditional provinces of ...
younger female
#
Burträsk
Burträsk is a locality situated in Skellefteå Municipality, Västerbotten County, Sweden with 1,575 inhabitants in 2010. It is notable as the only place where Västerbotten cheese
Västerbotten cheese ( sv, Västerbottensost ) is a cheese f ...
, Västerbotten
Västerbotten (), known in English as West Bothnia or Westrobothnia, is a province (''landskap'') in the north of Sweden, bordering Ångermanland, Lapland, North Bothnia, and the Gulf of Bothnia. It is known for the cheese named after the pro ...
older female
#
Aspås
Aspås (from Old Norse ''Öspáss'' 'aspen ridge') is a locality situated in Krokom Municipality, Jämtland County, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the ...
, Jämtland
Jämtland (; no, Jemtland or , ; Jamtish: ''Jamtlann''; la, Iemptia) is a historical province () in the centre of Sweden in northern Europe. It borders Härjedalen and Medelpad to the south, Ångermanland to the east, Lapland to the nort ...
younger female
#
Färila
Färila () is a locality situated in Ljusdal Municipality, Gävleborg County, Sweden with 1,293 inhabitants in 2010. Färila is situated in a valley near the river Ljusnan. People to commute to and from Ljusdal
Ljusdal () is a locality and the ...
, Hälsinglandolder male
#
Älvdalen
Älvdalen (Elfdalian: ''Övdaln'' or ''Tjyörtjbynn''; literally meaning ''The River Valley'') is a locality and the seat of Älvdalen Municipality in Dalarna County, Sweden, with 1,810 inhabitants in 2010.
The parish is widely known for being th ...
, Dalarna
Dalarna () is a '' landskap'' (historical province) in central Sweden. English exonyms for it are Dalecarlia () and the Dales.
Dalarna adjoins Härjedalen, Hälsingland, Gästrikland, Västmanland and Värmland. It is also bordered by Norwa ...
older female
traditionally considered a dialect, but now often recognized as
Elfdalian
Elfdalian or Övdalian ( or , pronounced in Elfdalian, or in Swedish) is a North Germanic language spoken by up to 3,000 people who live or have grown up in the locality of Älvdalen ('), which is located in the southeastern part of Älvd ...
, a separate language
# Gräsö, Uppland
Uppland () is a historical province or ' on the eastern coast of Sweden, just north of Stockholm, the capital. It borders Södermanland, Västmanland and Gästrikland. It is also bounded by lake Mälaren and the Baltic Sea. On the small uninhab ...
older male
#
Sorunda
Sorunda is a locality situated in Nynäshamn Municipality, Stockholm County, Sweden with 1,307 inhabitants in 2010. It is the hometown of Ulla Akselson, Moa Martinsson, and Harry Martinsson.
Sorunda church
Sorunda church is an unusually large, ...
, Södermanland
Södermanland ( or ), locally Sörmland, sometimes referred to under its Latin form ''Sudermannia'' or ''Sudermania'', is a historical province or ''landskap'' on the south eastern coast of Sweden. It borders Östergötland, Närke, Västm ...
younger male
# Köla,
Värmland
Värmland () also known as Wermeland, is a '' landskap'' (historical province) in west-central Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Dalsland, Dalarna, Västmanland, and Närke, and is bounded by Norway in the west. Latin name versions are '' ...
br>younger female# Viby,
Närke
Närke () is a Swedish traditional province, or ''landskap'', situated in Svealand in south central Sweden. It is bordered by Västmanland to the north, Södermanland to the east, Östergötland to the southeast, Västergötland to the southwe ...
older male
# Sproge,
Gotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to ...
younger female
# Närpes, Ostrobothnia
younger female
#
Dragsfjärd
Dragsfjärd is a former municipality of Finland. On 1 January 2009 it was consolidated with Kimito and Västanfjärd to form the new municipality of Kimitoön.
It is located in the province of Western Finland and is part of the Southwest Finla ...
, Southwest Finland
Southwest Finland, calqued as Finland Proper ( fi, Varsinais-Suomi ; sv, Egentliga Finland), is a region in the southwest of Finland. It borders the regions of Satakunta, Pirkanmaa, Tavastia Proper (Kanta-Häme), Uusimaa, and Åland. The reg ...
older male
#
Borgå
Porvoo (; sv, Borgå ; la, Borgoa) is a city and a municipality in the Uusimaa region of Finland, situated on the southern coast about east of the city border of Helsinki and about from the city centre. Porvoo was one of the six medieval t ...
, Eastern Uusimaayounger male
# Orust,
Bohuslän
Bohuslän (; da, Bohuslen; no, Båhuslen) is a Swedish province in Götaland, on the northernmost part of the country's west coast. It is bordered by Dalsland to the northeast, Västergötland to the southeast, the Skagerrak arm of the North ...
older male
#
Floby
Floby is a locality situated in Falköping Municipality, Västra Götaland County, Sweden. It had 1,499 inhabitants in 2010.
History
In 1858 the first portion of the railway line connecting Stockholm and Gothenburg was opened, and a railway statio ...
, Västergötland
Västergötland (), also known as West Gothland or the Latinized version Westrogothia in older literature, is one of the 25 traditional non-administrative provinces of Sweden (''landskap'' in Swedish), situated in the southwest of Sweden.
Väs ...
older female
#
Rimforsa
Rimforsa is a locality situated in Kinda Municipality, Östergötland County, Sweden with 2,238 inhabitants in 2010.
It is surrounded by a lot of forest and is approximately 40 km south of the city of Linköping
Linköping () is a city i ...
, Östergötland
Östergötland (; English exonym: East Gothland) is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap'' in Swedish) in the south of Sweden. It borders Småland, Västergötland, Närke, Södermanland and the Baltic Sea. In older English ...
older female
# Årstad-
Heberg
Heberg is a locality situated in Falkenberg Municipality
Falkenberg Municipality (''Falkenbergs kommun'') is a municipality in Halland County on the Swedish west coast. The town Falkenberg is the municipal seat.
The municipality was created in ...
, Halland
Halland () is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap''), on the western coast of Götaland, southern Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Småland, Scania and the sea of Kattegat. Until 1645 and the Second Treaty of Brömseb ...
younger male
# Stenberga,
Småland
Småland () is a historical province () in southern Sweden.
Småland borders Blekinge, Scania, Halland, Västergötland, Östergötland and the island Öland in the Baltic Sea. The name Småland literally means ''Small Lands''. The Latinized f ...
younger female
#
Jämshög
Jämshög is a locality situated in Olofström Municipality, Blekinge County, Sweden with 1,494 inhabitants in 2010.
It is the site of Jämshög Church (''Jämshögs kyrka'') in the Diocese of Lund. During the Northern Seven Years' War (1563 - ...
, Blekinge
Blekinge (, old da, Bleking) is one of the traditional Swedish provinces (), situated in the southern coast of the geographic region of Götaland, in southern Sweden. It borders Småland, Scania and the Baltic Sea. It is the country's sec ...
older female
# Bara,
Skåne
Scania, also known by its native name of Skåne (, ), is the southernmost of the historical provinces (''landskap'') of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous with Skån ...
older male
Standard Swedish
Standard Swedish
Standard Swedish () denotes Swedish as a spoken and written standard language. While Swedish as a written language is uniform and standardized, the spoken standard may vary considerably from region to region. Several prestige dialects have devel ...
is the language used by virtually all Swedes and most Swedish-speaking Finns
The Swedish-speaking population of Finland (whose members are called by many names; fi, suomenruotsalainen) can be used as an attribute., group=Note—see below; sv, finlandssvenskar; fi, suomenruotsalaiset) is a linguistic minority in Finl ...
. It is called ''rikssvenska'' or ''standardsvenska'' ("Standard Swedish") in Sweden. In Finland, ''högsvenska'' ("High Swedish") is used for the Finnish variant of standard Swedish and ''rikssvenska'' refers to Swedish as spoken in Sweden in general.
In a poll conducted in 2005 by the Swedish Retail Institute
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
(Handelns Utredningsinstitut
'), the attitudes of Swedes to the use of certain dialects by salesmen revealed that 54% believed that ''rikssvenska'' was the variety they would prefer to hear when speaking with salesmen over the phone, even though dialects such as ''gotländska'' or '' skånska'' were provided as alternatives in the poll.
Finland Swedish
Finland was a part of Sweden from the 13th century until the loss of the Finnish territories toRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
in 1809. Swedish was the sole administrative language until 1902 as well as the dominant language of culture and education until Finnish independence in 1917. The percentage of Swedish speakers in Finland has steadily decreased since then. The Swedish-speaking population is mainly concentrated in the coastal areas of Ostrobothnia, Southwest Finland
Southwest Finland, calqued as Finland Proper ( fi, Varsinais-Suomi ; sv, Egentliga Finland), is a region in the southwest of Finland. It borders the regions of Satakunta, Pirkanmaa, Tavastia Proper (Kanta-Häme), Uusimaa, and Åland. The reg ...
and Nyland where the percentage of Finland Swedes partly is high, with Swedish being spoken by more than 90% of the population in several municipalities, and on Åland, where Swedish is spoken by a vast majority of the population and is the only official language. Swedish is an official language also in the rest of Finland, though, with the same official status as Finnish. The country's public broadcaster, Yle, provides two Swedish-language radio stations, Yle Vega and Yle X3M
Yle X3M ( kstrẹ:m ''Radio Extrem'') is a Finnish Swedish-language radio station, owned and operated by Yle. It is generally aimed at the youth audience, and the target audience is 15- to 30-year-olds. It was established in 1997.
In 1998, X3M ...
, as well a TV channel, Yle Fem
Yle Fem (''Yle Five'') was Yle's Finland-Swedish national television channel, providing television programmes in the Swedish language in Finland. It was a public-service channel principally intended for Finland's Swedish-speaking minority. Crea ...
.
Immigrant variants
Rinkeby Swedish
Rinkeby Swedish () is any of a number of varieties of Swedish spoken mainly in urban districts with a high proportion of immigrant residents which emerged as a linguistic phenomenon in the 1980s. Rinkeby in Stockholm is one such suburb, but the ...
(after Rinkeby
Rinkeby () is a district in the Rinkeby-Kista borough, Stockholm, Sweden. Rinkeby had 19,349 inhabitants in 2016. The neighbourhood was part of the Million Programme.
The Stockholm metro station Rinkeby was also opened in 1975.
Rinkeby is note ...
, a suburb of northern Stockholm with a large immigrant population) is a common name among linguists for varieties of Swedish spoken by young people of foreign heritage in certain suburbs and urban districts in the major cities of Stockholm, Gothenburg
Gothenburg (; abbreviated Gbg; sv, Göteborg ) is the second-largest city in Sweden, fifth-largest in the Nordic countries, and capital of the Västra Götaland County. It is situated by the Kattegat, on the west coast of Sweden, and has ...
and Malmö
Malmö (, ; da, Malmø ) is the largest city in the Swedish county (län) of Scania (Skåne). It is the third-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm and Gothenburg, and the sixth-largest city in the Nordic region, with a municipal popul ...
. These varieties could alternatively be classified as sociolect
In sociolinguistics, a sociolect is a form of language (non-standard dialect, restricted register) or a set of lexical items used by a socioeconomic class, profession, an age group, or other social group.
Sociolects involve both passive acquisiti ...
s, because the immigrant dialects share common traits independent of their geographical spread or the native country of the speakers. However, some studies have found distinctive features and led to terms such as Rosengård Swedish (after Rosengård
Rosengård (literally "Rose Manor") was a city district ( sv, stadsdel) in the center of Malmö Municipality, Sweden. On 1 July 2013, it was merged with Husie, forming Öster. In 2012, Rosengård had a population of 23,563 of the municipality' ...
in Malmö), a variant of Scanian. A survey made by the Swedish linguist Ulla-Britt Kotsinas showed that foreign learners had difficulties in guessing the origins of Rinkeby Swedish speakers in Stockholm. The greatest difficulty proved to be identifying the speech of a boy speaking Rinkeby Swedish whose parents were both Swedish; only 1.8% guessed his native language correctly.
New linguistic practices in multilingual urban contexts in fiction and hip-hop culture and rap lyrics have been introduced that go beyond traditional socio-linguistic domains. See also Källström (Chapter 12) and Knudsen (Chapter 13).
Sample
Excerpt from '' Barfotabarn'' (1933), by Nils Ferlin (1898–1961):See also
* Languages of Sweden * Languages of Finland *Swedish as a foreign language
Swedish as a foreign language is studied by about 40,000 people worldwide at the university level and by over one million people on Duolingo. It is taught at over two hundred universities and colleges in 38 countries. Swedish is the Scandinavian ...
* Swenglish
Swenglish is a colloquial term referring to the English language heavily influenced by Swedish in terms of vocabulary, grammar, or pronunciation.
English heavily influenced by Swedish
The name ''Swenglish'' is a portmanteau term of the name ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Nationalencyklopedin
''Nationalencyklopedin'' (; "The National Encyclopedia" in English), abbreviated NE, is a comprehensive contemporary Swedish-language encyclopedia, initiated by a favourable loan from the Government of Sweden of 17 million Swedish kronor in 1 ...
online edition
* * * * *
Further reading
* ''Swedish Essentials of Grammar'' Viberg, Åke; et al. (1991) Chicago: Passport Books. * ''Swedish: An Essential Grammar''. Holmes, Philip; Hinchliffe, Ian; (2000). London; New York: Routledge. . * ''Swedish: A Comprehensive Grammar Second Edition''. Holmes, Philip; Hinchliffe, Ian; (2003). London; New York: Routledge. . * ''Svenska utifrån. Schematic grammar-Swedish structures and everyday phrases'' Byrman, Gunilla; Holm, Britta; (1998) .External links
Swadesh list of Swedish basic vocabulary words
(from Wiktionary'
Swadesh-list appendix
Dictionaries fro
Språkrådet – Institute for Language and Folklore
Online version
of '' Svenska Akademiens ordbok'' {{Authority control Languages of Finland Languages of Estonia Languages of Sweden East Scandinavian languages North Germanic languages Scandinavian culture Stress-timed languages Subject–verb–object languages Verb-second languages