Software Components on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Component-based software engineering (CBSE), also called component-based development (CBD), is a branch of software engineering that emphasizes the separation of concerns with respect to the wide-ranging functionality available throughout a given
Component-based software engineering (CBSE), also called component-based development (CBD), is a branch of software engineering that emphasizes the separation of concerns with respect to the wide-ranging functionality available throughout a given
 Another important attribute of components is that they are ''substitutable'', so that a component can replace another (at design time or run-time), if the successor component meets the requirements of the initial component (expressed via the interfaces). Consequently, components can be replaced with either an updated version or an alternative without breaking the system in which the component operates.
As a
Another important attribute of components is that they are ''substitutable'', so that a component can replace another (at design time or run-time), if the successor component meets the requirements of the initial component (expressed via the interfaces). Consequently, components can be replaced with either an updated version or an alternative without breaking the system in which the component operates.
As a
Bit
provided a free infrastructure for the development and composition of components into software applications, products, services and systems.
AXCIOMA
(the component framework for distributed, real-time, and embedded systems) b
Remedy IT
*
COHORTE
the cross-platform runtime for executing and managing robust and reliable distributed Service-oriented Component-based applications, b
isandlaTech
**DX-MAN Service Model * Generic programming emphasizes separation of algorithms from data representation * Interface description languages (IDLs) ** Open Service Interface Definitions (OSIDs) ** Part of both
''Why Software Reuse has Failed and How to Make It Work for You''
by Douglas C. Schmidt
''What is the True essence and reality of CBD?''
(Evidence to show existing CBD paradigm is flawed) * comprehensive list o
Component Systems
on SourceForge
''Brief Introduction to Real COP (Component Oriented Programming)''
by Using a small GUI application as an example {{DEFAULTSORT:Component-Based Software Engineering Object-oriented programming Software architecture Software engineering
software system
A software system is a system of intercommunicating components based on software forming part of a computer system (a combination of hardware and software). It "consists of a number of separate programs, configuration files, which are used to se ...
. It is a reuse-based approach to defining, implementing and composing loosely coupled independent components into systems. This practice aims to bring about an equally wide-ranging degree of benefits in both the short-term and the long-term for the software itself and for organizations that sponsor such software.
Software engineering practitioners regard components as part of the starting platform for service-orientation. Components play this role, for example, in web services, and more recently, in service-oriented architectures (SOA), whereby a component is converted by the web service into a ''service'' and subsequently inherits further characteristics beyond that of an ordinary component.
Components can produce or consume events and can be used for event-driven architectures (EDA).
Definition and characteristics of components
An individual software component is asoftware package
Software package may refer to:
* Package (package management system), in which individual files or resources are packed together as a software collection that provides certain functionality as part of a larger system
* Software suite, which provid ...
, a web service, a web resource, or a module that encapsulates a set of related functions (or data).
All system processes are placed into separate components so that all of the data and functions inside each component are semantically related (just as with the contents of classes). Because of this principle, it is often said that components are ''modular'' and ''cohesive''.
With regard to system-wide co-ordination, components communicate with each other via ''interfaces
Interface or interfacing may refer to:
Academic journals
* Interface (journal), ''Interface'' (journal), by the Electrochemical Society
* ''Interface, Journal of Applied Linguistics'', now merged with ''ITL International Journal of Applied Lin ...
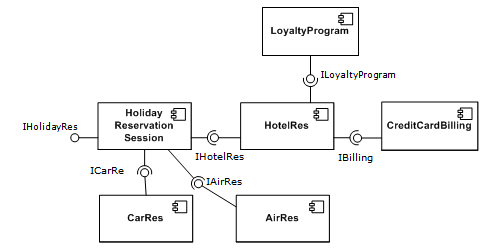
''. When a component offers services to the rest of the system, it adopts a ''provided'' interface that specifies the services that other components can utilize, and how they can do so. This interface can be seen as a signature of the component - the client does not need to know about the inner workings of the component (implementation) in order to make use of it. This principle results in components referred to as ''encapsulated''. The UML illustrations within this article represent provided interfaces by a lollipop-symbol attached to the outer edge of the component.
However, when a component needs to use another component in order to function, it adopts a ''used'' interface that specifies the services that it needs. In the UML illustrations in this article, ''used interfaces'' are represented by an open socket symbol attached to the outer edge of the component.
 Another important attribute of components is that they are ''substitutable'', so that a component can replace another (at design time or run-time), if the successor component meets the requirements of the initial component (expressed via the interfaces). Consequently, components can be replaced with either an updated version or an alternative without breaking the system in which the component operates.
As a
Another important attribute of components is that they are ''substitutable'', so that a component can replace another (at design time or run-time), if the successor component meets the requirements of the initial component (expressed via the interfaces). Consequently, components can be replaced with either an updated version or an alternative without breaking the system in which the component operates.
As a rule of thumb
In English, the phrase ''rule of thumb'' refers to an approximate method for doing something, based on practical experience rather than theory. This usage of the phrase can be traced back to the 17th century and has been associated with various t ...
for engineers substituting components, component B can immediately replace component A, if component B provides at least what component A provided and uses no more than what component A used.
Software components often take the form of objects (not classes) or collections of objects (from object-oriented programming), in some binary or textual form, adhering to some interface description language
interface description language or interface definition language (IDL), is a generic term for a language that lets a program or object written in one language communicate with another program written in an unknown language. IDLs describe an inter ...
(IDL) so that the component may exist autonomously from other components in a computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
. In other words, a component acts without changing its source code. Although the behavior of the component's source code may change based on the application's extensibility, provided by its writer.
When a component is to be accessed or shared across execution contexts or network links, techniques such as serialization
In computing, serialization (or serialisation) is the process of translating a data structure or object state into a format that can be stored (e.g. files in secondary storage devices, data buffers in primary storage devices) or transmitted (e ...
or marshalling are often employed to deliver the component to its destination.
Reusability is an important characteristic of a high-quality software component. Programmers should design and implement software components in such a way that many different programs can reuse them. Furthermore, component-based usability testing should be considered when software components directly interact with users.
It takes significant effort and awareness to write a software component that is effectively reusable. The component needs to be:
* fully documented
* thoroughly tested
** robust - with comprehensive input-validity checking
** able to pass back appropriate error messages or return codes
* designed with an awareness that it ''will'' be put to unforeseen uses
In the 1960s, programmers built scientific subroutine
In computer programming, a function or subroutine is a sequence of program instructions that performs a specific task, packaged as a unit. This unit can then be used in programs wherever that particular task should be performed.
Functions may ...
libraries that were reusable in a broad array of engineering and scientific applications. Though these subroutine libraries reused well-defined algorithms in an effective manner, they had a limited domain of application. Commercial sites routinely created application programs from reusable modules written in assembly language
In computer programming, assembly language (or assembler language, or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as Assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence be ...
, COBOL
COBOL (; an acronym for "common business-oriented language") is a compiled English-like computer programming language designed for business use. It is an imperative, procedural and, since 2002, object-oriented language. COBOL is primarily us ...
, PL/1 and other second- and third-generation languages using both system
A system is a group of Interaction, interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment (systems), environment, is described by its boundaries, ...
and user application libraries.
, modern reusable components encapsulate both data structures and the algorithms that are applied to the data structures. Component-based software engineering builds on prior theories of software objects, software architectures, software framework
In computer programming, a software framework is an abstraction in which software, providing generic functionality, can be selectively changed by additional user-written code, thus providing application-specific software. It provides a standard ...
s and software design patterns, and the extensive theory of object-oriented programming and the object-oriented design of all these. It claims that software components, like the idea of hardware components
Circuit Component may refer to:
•Are devices that perform functions when they are connected in a circuit.
In engineering, science, and technology Generic systems
* System components, an entity with discrete structure, such as an assem ...
, used for example in telecommunications, can ultimately be made interchangeable and reliable. On the other hand, it is argued that it is a mistake to focus on independent components rather than the framework (without which they would not exist).
History
The idea that software should be componentized - built from prefabricated ''components'' - first became prominent with Douglas McIlroy's address at the NATO conference on software engineering in Garmisch, Germany, 1968, titled ''Mass Produced Software Components''. The conference set out to counter the so-called software crisis. McIlroy's subsequent inclusion of pipes and filters into the Unix operating system was the first implementation of an infrastructure for this idea. Brad Cox ofStepstone
Next may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Next'' (1990 film), an animated short about William Shakespeare
* ''Next'' (2007 film), a sci-fi film starring Nicolas Cage
* '' Next: A Primer on Urban Painting'', a 2005 documentary film
Lit ...
largely defined the modern concept of a software component. He called them ''Software ICs'' and set out to create an infrastructure and market for these components by inventing the Objective-C programming language. (He summarizes this view in his book ''Object-Oriented Programming - An Evolutionary Approach'' 1986.)
The software components are used in two different contexts and two kinds: i) using components as parts to build a single executable, or ii) each executable is treated as a component in a distributed environment, where components collaborate with each other using internet or intranet communication protocols for IPC (Inter Process Communications). The above belongs to former kind, while the below belongs to later kind.
IBM led the path with their System Object Model (SOM) in the early 1990s. As a reaction, Microsoft paved the way for actual deployment of component software with Object linking and embedding (OLE) and Component Object Model (COM). many successful software component models exist.
In 2021 open-source toolchaiBit
provided a free infrastructure for the development and composition of components into software applications, products, services and systems.
Architecture
A computer running several software components is often called anapplication server
An application server is a server that hosts applications or software that delivers a business application through a communication protocol.
An application server framework is a service layer model. It includes software components available to a ...
. This combination of application servers and software components is usually called distributed computing. Typical real-world application of this is in, e.g., financial applications or business software.
Component models
A component model is a definition of properties that components must satisfy, methods and mechanisms for the composition of components. During the last decades, researchers and practitioners have proposed several component models with different characteristics. A classification of the existing component models is given in. Examples of component models are: Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) model, Component Object Model (COM) model, .NET model, X-MAN component model, andCommon Object Request Broker Architecture
The Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) is a standard defined by the Object Management Group (OMG) designed to facilitate the communication of systems that are deployed on diverse platforms. CORBA enables collaboration between sys ...
(CORBA) component model.
Technologies
* Business object technologies ** Newi * Component-basedsoftware framework
In computer programming, a software framework is an abstraction in which software, providing generic functionality, can be selectively changed by additional user-written code, thus providing application-specific software. It provides a standard ...
s for specific domains
** Advanced Component Framework
** Earth System Modeling Framework ( ESMF)
** MASH IoT Platform for Asset Management
** KOALA component model developed for software in consumer electronics
** React (JavaScript library)
** Software Communications Architecture
{{inline, date=May 2014
The Software Communications Architecture (SCA) is an open architecture framework that defines a standard way for radios to instantiate, configure, and manage waveform applications running on their platform. The SCA separa ...
(JTRS SCA)
* Component-oriented programming
** Bundles as defined by the OSGi Service Platform
** Component Object Model (OCX/ActiveX/COM) and DCOM from Microsoft
** TASCS - SciDAC Center for Technology for Advanced Scientific Component Software
** Eiffel programming language
** Enterprise JavaBeans from Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. (Sun for short) was an American technology company that sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services and created the Java programming language, the Solaris operating system, ZFS, the ...
(now Oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination.
Description
The word '' ...
)
** Flow-based programming
** Fractal component model from ObjectWeb
** MidCOM component framework for Midgard and PHP
** Oberon, Component Pascal
Component Pascal is a programming language in the tradition of Niklaus Wirth's Pascal, Modula-2, Oberon
and Oberon-2.
It bears the name of the language Pascal and preserves its heritage, but is incompatible with Pascal. Instead, it is a minor var ...
, and BlackBox Component Builder
** rCOS method of component-based model driven design from UNU-IIST
** SOFA component system from ObjectWeb
** The System.ComponentModel namespace in Microsoft .NET
** Unity developed by Unity Technologies
** Unreal Engine developed by Epic Games
Epic Games, Inc. is an American video game and software developer and publisher based in Cary, North Carolina. The company was founded by Tim Sweeney as Potomac Computer Systems in 1991, originally located in his parents' house in Potomac, M ...
** UNO
Uno or UNO may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Television
* "Uno" (''Better Call Saul''), premiere episode of the American TV series ''Better Call Saul''
* ''Uno'' (film), a 2004 Norwegian drama film
* Rai Uno, an Italian TV channel
**' ...
from the OpenOffice.org office suite
** VCL and CLX from Borland
Borland Software Corporation was a computer technology company founded in 1983 by Niels Jensen, Ole Henriksen, Mogens Glad and Philippe Kahn. Its main business was the development and sale of software development and software deployment product ...
and similar free LCL
LCL can mean:
Science, technology, and medicine
* Lateral collateral ligament (disambiguation), one of several ligaments located on the lateral side of a joint:
** Fibular collateral ligament, a ligament of the knee joint
** Lateral collateral ...
library.
** XPCOM from Mozilla Foundation
* Compound document technologies
** Active Documents in Oberon System
The Oberon System is a modular, single-user, single-process, multitasking operating system written in the programming language Oberon. It was originally developed in the late 1980s at ETH Zurich. The Oberon System has an unconventional visual t ...
and BlackBox Component Builder
** KParts, the KDE compound document technology
** Object linking and embedding (OLE)
** OpenDoc
* Distributed computing software components
**.NET Remoting
.NET Remoting is a Microsoft application programming interface (API) for interprocess communication released in 2002 with the 1.0 version of .NET Framework. It is one in a series of Microsoft technologies that began in 1990 with the first version ...
from Microsoft
** 9P distributed protocol developed for Plan 9 Plan 9 or Plan Nine may refer to:
Music
* Plan 9 (band), a psychedelic rock band from Rhode Island
* ''Plan 9'', an album by Big Guitars From Memphis with Rick Lindy
* "Plan 9", a song on the 1993 album ''Gorgeous'' by electronica band 808 Stat ...
, and used by Inferno and other systems.
** CORBA and the CORBA Component Model from the Object Management Group
** D-Bus from the freedesktop.org organization
** DCOM and later versions of COM
Com or COM may refer to:
Computing
* COM (hardware interface), a serial port interface on IBM PC-compatible computers
* COM file, or .com file, short for "command", a file extension for an executable file in MS-DOS
* .com, an Internet top-level d ...
(and COM+) from Microsoft
** DSOM and SOM from IBM (now scrapped)
** Ice from ZeroC
** Java EE from Sun
** Kompics from SICS
RISE SICS (previously Swedish Institute of Computer Science) is a leading research institute for applied information and communication technology in Sweden, founded in 1985.
It explores the digitalization of products, services and businesses.
In ...
** Universal Network Objects (UNO) from OpenOffice.org
** Web services
*** REST
** Zope from Zope Corporation
Zope is a family of free and open-source web application servers written in Python, and their associated online community. Zope stands for "Z Object Publishing Environment", and was the first system using the now common object publishing methodolo ...
*AXCIOMA
(the component framework for distributed, real-time, and embedded systems) b
Remedy IT
*
COHORTE
the cross-platform runtime for executing and managing robust and reliable distributed Service-oriented Component-based applications, b
isandlaTech
**DX-MAN Service Model * Generic programming emphasizes separation of algorithms from data representation * Interface description languages (IDLs) ** Open Service Interface Definitions (OSIDs) ** Part of both
COM
Com or COM may refer to:
Computing
* COM (hardware interface), a serial port interface on IBM PC-compatible computers
* COM file, or .com file, short for "command", a file extension for an executable file in MS-DOS
* .com, an Internet top-level d ...
and CORBA
** Platform-Independent Component Modeling Language
** SIDL - Scientific Interface Definition Language
*** Part of the Babel
Babel is a name used in the Hebrew Bible for the city of Babylon and may refer to:
Arts and media Written works Books
*Babel (book), ''Babel'' (book), by Patti Smith
* Babel (2012 manga), ''Babel'' (2012 manga), by Narumi Shigematsu
* Babel (20 ...
Scientific Programming Language Interoperability System (SIDL and Babel are core technologies of the CCA and the SciDAC TASCS Center - see above.)
** SOAP IDL
IDL may refer to:
Computing
* Interface description language, any computer language used to describe a software component's interface
** IDL specification language, the original IDL created by Lamb, Wulf and Nestor at Queen's University, Canada
...
from World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)
** WDDX
** XML-RPC, the predecessor of SOAP
* Inversion of control (IoC) and Plain Old C++/Java Object (POCO/POJO) component frameworks
* Pipes and filters
** Unix operating system
See also
* Business logic * Modular programming * Service Component Architecture (SCA) *Software Communications Architecture
{{inline, date=May 2014
The Software Communications Architecture (SCA) is an open architecture framework that defines a standard way for radios to instantiate, configure, and manage waveform applications running on their platform. The SCA separa ...
(JTRS SCA)
* Third-party software component
* Web service
* Web components
Web Components are a set of features that provide a standard component model for the Web allowing for encapsulation and interoperability of individual HTML elements.
Primary technologies used to create them include:
* Custom Elements: APIs to ...
References
Further reading
* Brad J. Cox, Andrew J. Novobilski (1991). ''Object-Oriented Programming: An Evolutionary Approach''. 2nd ed. Addison-Wesley, Reading * Bertrand Meyer (1997). ''Object-Oriented Software Construction''. 2nd ed. Prentice Hall. * George T. Heineman, William T. Councill (2001). ''Component-Based Software Engineering: Putting the Pieces Together''. Addison-Wesley Professional, Reading 2001 * Richard Veryard (2001). ''Component-based business : plug and play''. London : Springer. * Clemens Szyperski, Dominik Gruntz, Stephan Murer (2002). ''Component Software: Beyond Object-Oriented Programming''. 2nd ed. ACM Press - Pearson Educational, London 2002External links
''Why Software Reuse has Failed and How to Make It Work for You''
by Douglas C. Schmidt
''What is the True essence and reality of CBD?''
(Evidence to show existing CBD paradigm is flawed) * comprehensive list o
Component Systems
on SourceForge
''Brief Introduction to Real COP (Component Oriented Programming)''
by Using a small GUI application as an example {{DEFAULTSORT:Component-Based Software Engineering Object-oriented programming Software architecture Software engineering