|
Web Components
Web Components are a set of features that provide a standard component model for the web allowing for encapsulation and interoperability of individual HTML elements. Web Components are a popular approach when building microfrontends. Primary technologies used to create Web Components include: ; Custom Elements : APIs to define new HTML elements ; Shadow DOM : encapsulated DOM and styling, with composition ; HTML Templates : HTML fragments that are not rendered, but stored until instantiated via JavaScript Features Custom Elements There are two parts to Custom Elements: autonomous custom elements and customized built-in elements. Autonomous custom elements are HTML elements that are entirely separated from native HTML elements; they are essentially built from the bottom up using the Custom Elements API. Customized built-in elements are elements that are built upon native HTML elements to reuse their functionality. Shadow DOM The Shadow DOM is a functionality that allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Encapsulation (object-oriented Programming)
In software systems, encapsulation refers to the bundling of data with the mechanisms or methods that operate on the data. It may also refer to the limiting of direct access to some of that data, such as an object's components. Essentially, encapsulation prevents external code from being concerned with the internal workings of an object. Encapsulation allows developers to present a consistent interface that is independent of its internal implementation. As one example, encapsulation can be used to hide the values or state of a structured data object inside a class. This prevents clients from directly accessing this information in a way that could expose hidden implementation details or violate state invariance maintained by the methods. Encapsulation also encourages programmers to put all the code that is concerned with a certain set of data in the same class, which organizes it for easy comprehension by other programmers. Encapsulation is a technique that encourages decoupling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polymer (library)
Polymer is an open-source JavaScript library for building web applications using Web Components. The library is being developed by Google developers and contributors on GitHub. Modern design principles are implemented as a separate project using Google's Material Design design principles. Polymer is used by a number of Google services and websites, including YouTube, YouTube Gaming, the redesigned Google Earth (since 2017), Google I/O 2015 and 2016 websites, Google Play Music, redesign of Google Sites and Allo for web (until its shutdown in 2019). Other notable users include Netflix, Electronics Arts, Comcast, Nuxeo, Coca-Cola, McDonald's, BBVA, IBM, Interxion and General Electric. History Public development of Polymer began in November 2013 with the release of a Promises Polyfill. This steadily expanded into a web design library covering visual styling guidelines (via Material Design), data binding, and a large number of "Core" and "Paper" Web Components. ''Core'' comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Web Framework
A web framework (WF) or web application framework (WAF) is a software framework that is designed to support the development of web applications including web services, web resources, and web APIs. Web frameworks provide a standard way to build and deploy web applications on the World Wide Web. Web frameworks aim to automate the overhead associated with common activities performed in web development. For example, many web frameworks provide libraries for database access, templating frameworks, and session management, and they often promote code reuse. Although they often target development of dynamic web sites, they are also applicable to static websites. History As the design of the World Wide Web was not inherently dynamic, early hypertext consisted of hand-coded HTML text files that were published on web servers. Any modifications to published pages needed to be performed by the pages' author. In 1993, the Common Gateway Interface (CGI) standard was introduced for i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
HTML Components
HTML Components (HTCs) are a legacy technology used to implement components in script as Dynamic HTML (DHTML) "behaviors" in the Microsoft Internet Explorer web browser. Such files typically use an .htc extension and the "text/x-component" MIME type. An HTC is typically an HTML file (with JScript / VBScript) and a set of elements that define the component. This helps to organize behavior encapsulated in script modules that can be attached to parts of a Webpage DOM. Example Example In this example, the li element is given the behavior defined by "hilite.htc" (a file that contains JScript code defining highlight/lowlight actions on mouse over). The same hilite.htc can then be given to any element in the HTML page - thus encapsulating the behavior defined by this file. See also *Web components Web Components are a set of features that provide a standard component model for the web allowing for encapsulation and interoperability of individual HTML elements. Web Compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
LitElement
Polymer is an open-source JavaScript library for building web applications using Web Components. The library is being developed by Google developers and contributors on GitHub. Modern design principles are implemented as a separate project using Google's Material Design design principles. Polymer is used by a number of Google services and websites, including YouTube, YouTube Gaming, the redesigned Google Earth (since 2017), Google I/O 2015 and 2016 websites, Google Play Music, redesign of Google Sites and Allo for web (until its shutdown in 2019). Other notable users include Netflix, Electronics Arts, Comcast, Nuxeo, Coca-Cola, McDonald's, BBVA, IBM, Interxion and General Electric. History Public development of Polymer began in November 2013 with the release of a Promises Polyfill. This steadily expanded into a web design library covering visual styling guidelines (via Material Design), data binding, and a large number of "Core" and "Paper" Web Components. ''Core'' compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. Firefox is available for Windows 10 or later versions of Windows, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, and other operating systems, such as ReactOS. Firefox is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser. Firefox is the spiritual successor of Netscape Navigator, as the Mozilla community was created by Netscape in 1998, before its acqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
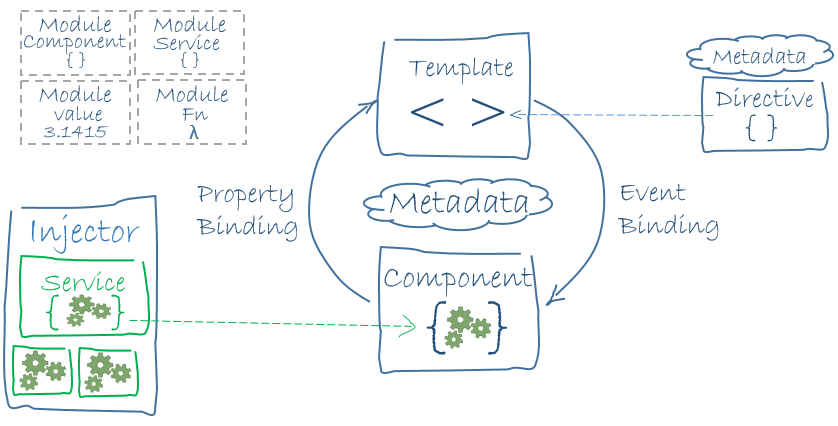
Angular (web Framework)
Angular (also referred to as Angular 2+) is a TypeScript-based Free and open-source software, free and open-source Single-page application, single-page Web framework, web application framework. It is developed by Google and by a community of individuals and corporations. Angular is a complete rewrite from the same team that built AngularJS. The Angular ecosystem consists of a diverse group of over 1.7 million developers, library authors, and content creators. According to the Stack Overflow Developer Survey, Angular is one of the most commonly used web frameworks. Differences between Angular and AngularJS Google designed Angular as a ground-up rewrite of AngularJS. Unlike AngularJS, Angular does not have a concept of "scope" or controllers; instead, it uses a hierarchy of components as its primary architectural characteristic. Angular has a different expression syntax, focusing on "[ ]" for Property (programming), property binding, and "( )" for Event (computing), event binding. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ionic (mobile App Framework)
Ionic is an open-source UI toolkit for building cross-platform mobile, web, and desktop applications using web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript/TypeScript. It provides a set of pre-designed UI components and tools for building high-quality, interactive applications. Ionic was originally built as a complete open-source SDK for hybrid mobile app development created by Max Lynch, Ben Sperry, and Adam Bradley of Drifty Co. in 2013. The original version was released in 2013 and built on top of AngularJS and Apache Cordova. However, the latest release was re-built as a set of Web Components using StencilJS, allowing the user to choose any user interface framework, such as Angular, React or Vue.js. It also allows the use of Ionic components with no user interface framework at all. Ionic provides tools and services for developing hybrid mobile, desktop, and progressive web apps based on modern web development technologies and practices, using Web technologies like CS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Asynchronous Module Definition
Asynchronous module definition (AMD) is a Specification (technical standard), specification for the programming language JavaScript. It defines an application programming interface (API) that defines modular programming, code modules and their Coupling (computer programming), dependencies, and loads them asynchronously if desired. Implementations of AMD provide the following benefits: * Website performance improvements. AMD implementations load smaller JavaScript files, and then only when they are needed. * Fewer page errors. AMD implementations allow developers to define dependencies that must load before a module is executed, so the module does not try to use outside code that is not available yet. In addition to loading multiple JavaScript files at runtime, AMD implementations allow developers to encapsulate code in smaller, more logically-organized files, in a way similar to other programming languages such as Java (programming language), Java. For production and deployment, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Material Design
Material Design (codename Quantum Paper) is a design language developed by Google in 2014. Expanding on the "cards" UI that debuted in Google Now, Material Design uses more grid-based layouts, responsive animations and transitions, padding, and depth effects such as lighting and shadows. Google announced the initial version of Material Design on June 25, 2014, at the 2014 Google I/O conference. The purpose of developing Material Design was to create a novel visual language, synthesizing the classic principles of good design with the innovation and possibility of technology and science. Head designer Matías Duarte explained that "unlike real paper, our digital material expands and reforms intelligently. Material has physical surfaces and edges. Seams and shadows provide meaning about what you can touch." Material Design is based on paper-and-ink as well as skeuomorphic interaction concepts, but implementation happens in a more advanced manner. In 2018, Google revamped the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |