Safety Coffin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A safety coffin or security coffin is a
A safety coffin or security coffin is a
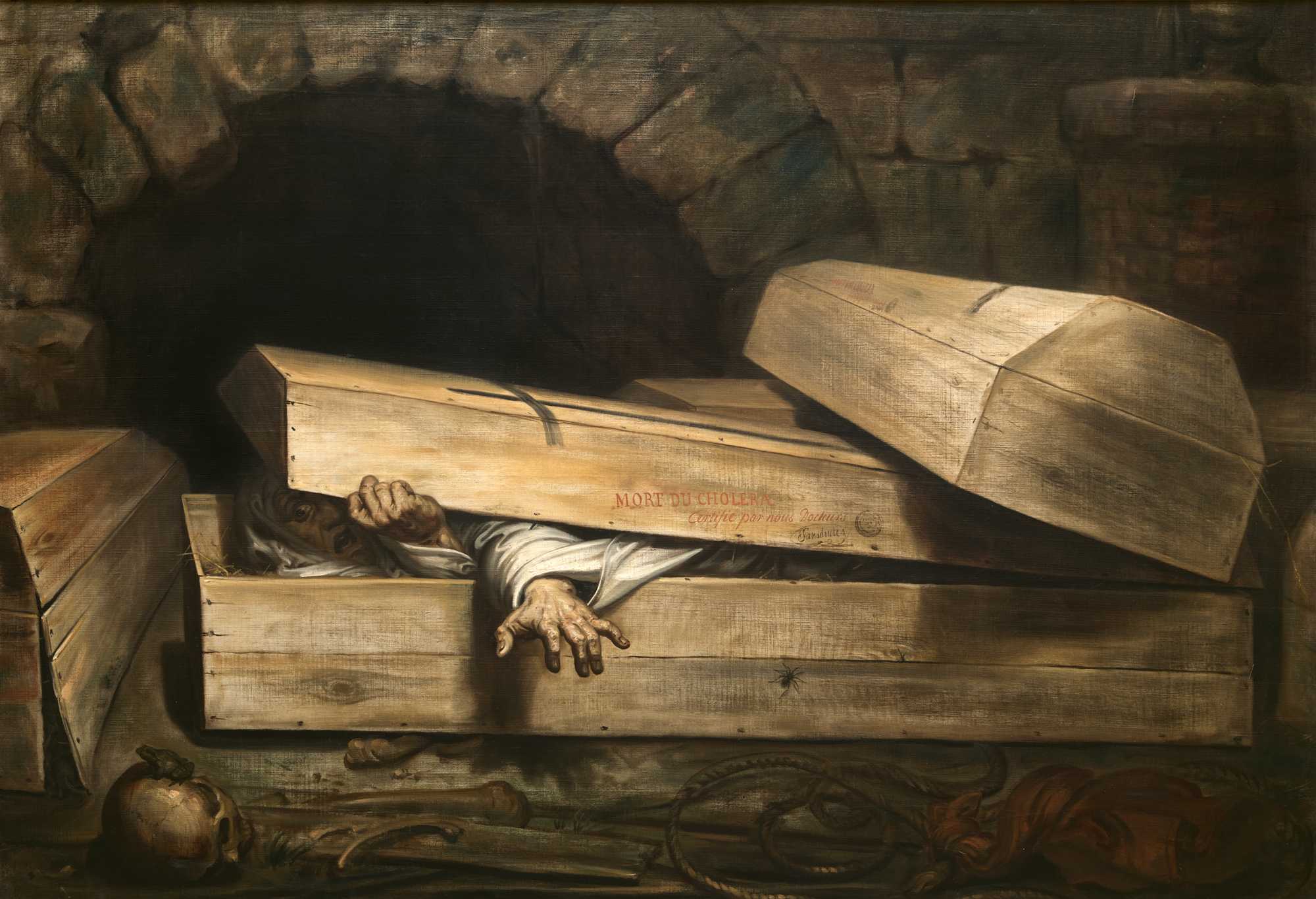 The general fear of premature burial led to the invention of many safety devices which could be incorporated into coffins. Most consisted of some type of device for communication to the outside world such as a cord attached to a bell that the interred person could ring should they revive after the burial. A safety coffin of this type appears in the 1978 film '' The First Great Train Robbery'', and more recently in the 2018 film '' The Nun''. Other variations on the bell included flags and
The general fear of premature burial led to the invention of many safety devices which could be incorporated into coffins. Most consisted of some type of device for communication to the outside world such as a cord attached to a bell that the interred person could ring should they revive after the burial. A safety coffin of this type appears in the 1978 film '' The First Great Train Robbery'', and more recently in the 2018 film '' The Nun''. Other variations on the bell included flags and 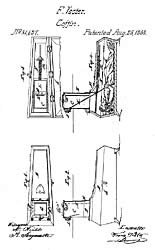 The systems using cords tied to the body suffered from the drawback that the natural processes of decay often caused the body to swell or shift position, causing accidental tension on the cords and a "false positive"
The systems using cords tied to the body suffered from the drawback that the natural processes of decay often caused the body to swell or shift position, causing accidental tension on the cords and a "false positive"
Franz Vester's 1868 "Burial Case"
overcame this problem by adding a tube through which the face of the "corpse" could be viewed. If the interred person came to, they could ring the bell (if not strong enough to ascend the tube by means of a supplied ladder) and the watchmen could check to see if the person had genuinely returned to life or whether it was merely a movement of the corpse. Vester's design allowed the viewing tube to be removed and reused once death was assured. Count Michel de Karnice-Karnicki, a chamberlain to the
Patents related to alarms/signals used in connection with coffins for indicating life in persons supposed to be dead.
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Safety Coffin Coffins
 A safety coffin or security coffin is a
A safety coffin or security coffin is a coffin
A coffin is a funerary box used for viewing or keeping a corpse, either for burial or cremation.
Sometimes referred to as a casket, any box in which the dead are buried is a coffin, and while a casket was originally regarded as a box for j ...
fitted with a mechanism to prevent premature burial
Premature burial, also known as live burial, burial alive, or vivisepulture, means to be buried while still alive.
Animals or humans may be buried alive accidentally on the mistaken assumption that they are dead, or intentionally as a form of t ...
or allow the occupant to signal that they have been buried alive. A large number of designs for safety coffins were patented during the 18th and 19th centuries and variations on the idea are still available today.
History
Thefear of being buried alive
Taphophobia (from Greek τάφος - ''taphos'', "grave, tomb" and φόβος - ''phobos'', "fear") is an abnormal (psychopathological) fear of being buried alive as a result of being incorrectly pronounced dead.
Before the era of modern medi ...
peaked during the cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium '' Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting an ...
epidemics of the 19th century, but accounts of unintentional live burial have been recorded even earlier. The fears of being buried alive were heightened by reports of doctors and accounts in literature and the newspapers. As well as dealing with the subject in "The Fall of the House of Usher
"The Fall of the House of Usher" is a short story by American writer Edgar Allan Poe, first published in 1839 in ''Burton's Gentleman's Magazine'', then included in the collection ''Tales of the Grotesque and Arabesque'' in 1840. The short story ...
" and " The Cask of Amontillado", Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wid ...
wrote " The Premature Burial", which was published in 1844. It contained accounts of supposedly genuine cases of premature burial as well as detailing the narrator's own (perceived) interment while still alive.
 The general fear of premature burial led to the invention of many safety devices which could be incorporated into coffins. Most consisted of some type of device for communication to the outside world such as a cord attached to a bell that the interred person could ring should they revive after the burial. A safety coffin of this type appears in the 1978 film '' The First Great Train Robbery'', and more recently in the 2018 film '' The Nun''. Other variations on the bell included flags and
The general fear of premature burial led to the invention of many safety devices which could be incorporated into coffins. Most consisted of some type of device for communication to the outside world such as a cord attached to a bell that the interred person could ring should they revive after the burial. A safety coffin of this type appears in the 1978 film '' The First Great Train Robbery'', and more recently in the 2018 film '' The Nun''. Other variations on the bell included flags and pyrotechnics
Pyrotechnics is the science and craft of creating such things as fireworks, safety matches, oxygen candles, explosive bolts and other fasteners, parts of automotive airbags, as well as gas-pressure blasting in mining, quarrying, and demolition ...
. Some designs included ladders, escape hatches, and even feeding tubes, but many forgot a method for providing air.
Robert Robinson died in Manchester in 1791. A movable glass pane was inserted in his coffin, and the mausoleum had a door for purposes of inspection by a watchman, who was to see if he breathed on the glass. He instructed his relatives to visit his grave periodically to check that he was still dead.
The first recorded safety coffin was constructed on the orders of Duke Ferdinand of Brunswick before his death in 1792. He had a window installed to allow light in, an air tube to provide a supply of fresh air, and instead of having the lid nailed down he had a lock fitted. In a special pocket of his shroud he had two keys, one for the coffin lid and a second for the tomb door.
P.G. Pessler, a German priest, suggested in 1798 that all coffins have a tube inserted from which a cord would run to the church bells. If an individual had been buried alive they could draw attention to themselves by ringing the bells. This idea, while highly impractical, led to the first designs of safety coffins equipped with signalling systems. Pessler's colleague, Pastor Beck, suggested that coffins should have a small trumpet-like tube attached. Each day the local priest could check the state of putrefaction of the corpse by sniffing the odours emanating from the tube. If no odour was detected or the priest heard cries for help the coffin could be dug up and the occupant rescued.
Dr. Adolf Gutsmuth was buried alive several times to demonstrate a safety coffin of his own design, and in 1822 he stayed underground for several hours and even ate a meal of soup
Soup is a primarily liquid food, generally served warm or hot (but may be cool or cold), that is made by combining ingredients of meat or vegetables with stock, milk, or water. Hot soups are additionally characterized by boiling soli ...
, bratwurst
Bratwurst () is a type of German sausage made from pork or, less commonly, beef or veal. The name is derived from the Old High German ''Brätwurst'', from ''brät-'', finely chopped meat, and ''Wurst'', sausage, although in modern German it is o ...
, marzipan
Marzipan is a confection consisting primarily of sugar, honey, and almond meal (ground almonds), sometimes augmented with almond oil or extract.
It is often made into sweets; common uses are chocolate-covered marzipan and small marzipan imit ...
, sauerkraut
Sauerkraut (; , "sour cabbage") is finely cut raw cabbage that has been fermented by various lactic acid bacteria. It has a long shelf life and a distinctive sour flavor, both of which result from the lactic acid formed when the bacteria ...
, spätzle
Spätzle (or spaetzle; ) is a type of pasta or dumpling made with eggs, typically serving as a side for meat dishes with gravy. Commonly associated with Swabia, it is also found in the cuisines of southern Germany and Austria, Switzerland, Hung ...
, beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
, and for dessert, prinzregententorte
Prinzregententorte () is a Bavarian torte consisting of at least six, usually seven, thin layers of sponge cake interlaid with chocolate buttercream. The exterior is covered in a dark chocolate glaze. Prinzregententorte is very popular in Ba ...
, delivered to him through the coffin's feeding tube.
The 1820s also saw the use of "portable death chambers" in Germany. A small chamber, equipped with a bell for signalling and a window for viewing the body, was constructed over an empty grave. Watchmen would check each day for signs of life or decomposition in each of the chambers. If the bell was rung the "body" could be immediately removed, but if the watchman observed signs of putrefaction in the corpse, a door in the floor of the chamber could be opened and the body would drop down into the grave. A panel could then be slid in to cover the grave and the upper chamber removed and reused.
In 1829, Dr. Johann Gottfried Taberger designed a system using a bell which would alert the cemetery nightwatchman. The corpse would have strings attached to its hands, head and feet. A housing around the bell above ground prevented it ringing accidentally. An improvement over previous designs, the housing prevented rainwater from running down the tube and netting prevented insects from entering the coffin. If the bell rang the watchman had to insert a second tube and pump air into the coffin with a bellows
A bellows or pair of bellows is a device constructed to furnish a strong blast of air. The simplest type consists of a flexible bag comprising a pair of rigid boards with handles joined by flexible leather sides enclosing an approximately airtig ...
to allow the occupant to survive until the casket could be dug up.
 The systems using cords tied to the body suffered from the drawback that the natural processes of decay often caused the body to swell or shift position, causing accidental tension on the cords and a "false positive"
The systems using cords tied to the body suffered from the drawback that the natural processes of decay often caused the body to swell or shift position, causing accidental tension on the cords and a "false positive"Franz Vester's 1868 "Burial Case"
overcame this problem by adding a tube through which the face of the "corpse" could be viewed. If the interred person came to, they could ring the bell (if not strong enough to ascend the tube by means of a supplied ladder) and the watchmen could check to see if the person had genuinely returned to life or whether it was merely a movement of the corpse. Vester's design allowed the viewing tube to be removed and reused once death was assured. Count Michel de Karnice-Karnicki, a chamberlain to the
Tsar of Russia
This is a list of all reigning monarchs in the history of Russia. It includes the princes of medieval Rus′ state (both centralised, known as Kievan Rus′ and feudal, when the political center moved northeast to Vladimir and finally to Mos ...
, patented his own safety coffin, called Le Karnice, in 1897 and demonstrated it at the Sorbonne the following year. His design detected movement in the coffin and opened a tube to supply air while simultaneously raising a flag and ringing a bell. Le Karnice never caught on: it was too sensitive to allow for even a slight movement in a decaying corpse, and a demonstration in which one of Karnice-Karnicki's assistants had been buried alive ended badly when the signalling systems failed. Luckily, the breathing tube had activated and the assistant was disinterred unharmed, but the reputation of Le Karnice was damaged beyond repair.
In 1995 a modern safety coffin was patented by Fabrizio Caselli. His design included an emergency alarm, intercom
An intercom, also called an intercommunication device, intercommunicator, or interphone, is a stand-alone voice communications system for use within a building or small collection of buildings which functions independently of the public telephon ...
system, a torch (flashlight), breathing apparatus, and both a heart monitor
A heart rate monitor (HRM) is a personal monitoring device that allows one to measure/display heart rate in real time or record the heart rate for later study. It is largely used to gather heart rate data while performing various types of phy ...
and stimulator.*
Despite the fear of burial while still alive, there are no documented cases of anybody being saved by a safety coffin.
It is worth noting that the practice of modern-day embalming as practiced in some countries (notably in North America) has, for the most part, eliminated the fear of "premature burial", as no one has ever survived that process once completed.
See also
* Burial vault *Lazarus phenomenon
Lazarus syndrome (the Lazarus heart), also known as autoresuscitation after failed cardiopulmonary resuscitation, is the spontaneous return of a normal cardiac rhythm after failed attempts at resuscitation. It is also the spontaneous return o ...
*Tomb
A tomb ( grc-gre, τύμβος ''tumbos'') is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called ''immureme ...
Notes
References
Patents related to alarms/signals used in connection with coffins for indicating life in persons supposed to be dead.
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Safety Coffin Coffins