Sulphur Dell In Color on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sulfur (or sulphur in
here
The greatest commercial use of the element is the production of

 Sulfur forms over 30 solid
Sulfur forms over 30 solid
 32S is created inside massive stars, at a depth where the temperature exceeds 2.5×109 K, by the
32S is created inside massive stars, at a depth where the temperature exceeds 2.5×109 K, by the
 This reaction highlights a distinctive property of sulfur: its ability to
This reaction highlights a distinctive property of sulfur: its ability to
File:Allicin skeletal.svg,
Some of the main classes of sulfur-containing organic compounds include the following:
*
 Being abundantly available in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times and is referred to in the
Being abundantly available in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times and is referred to in the
 Sulfur may be found by itself and historically was usually obtained in this form;
Sulfur may be found by itself and historically was usually obtained in this form;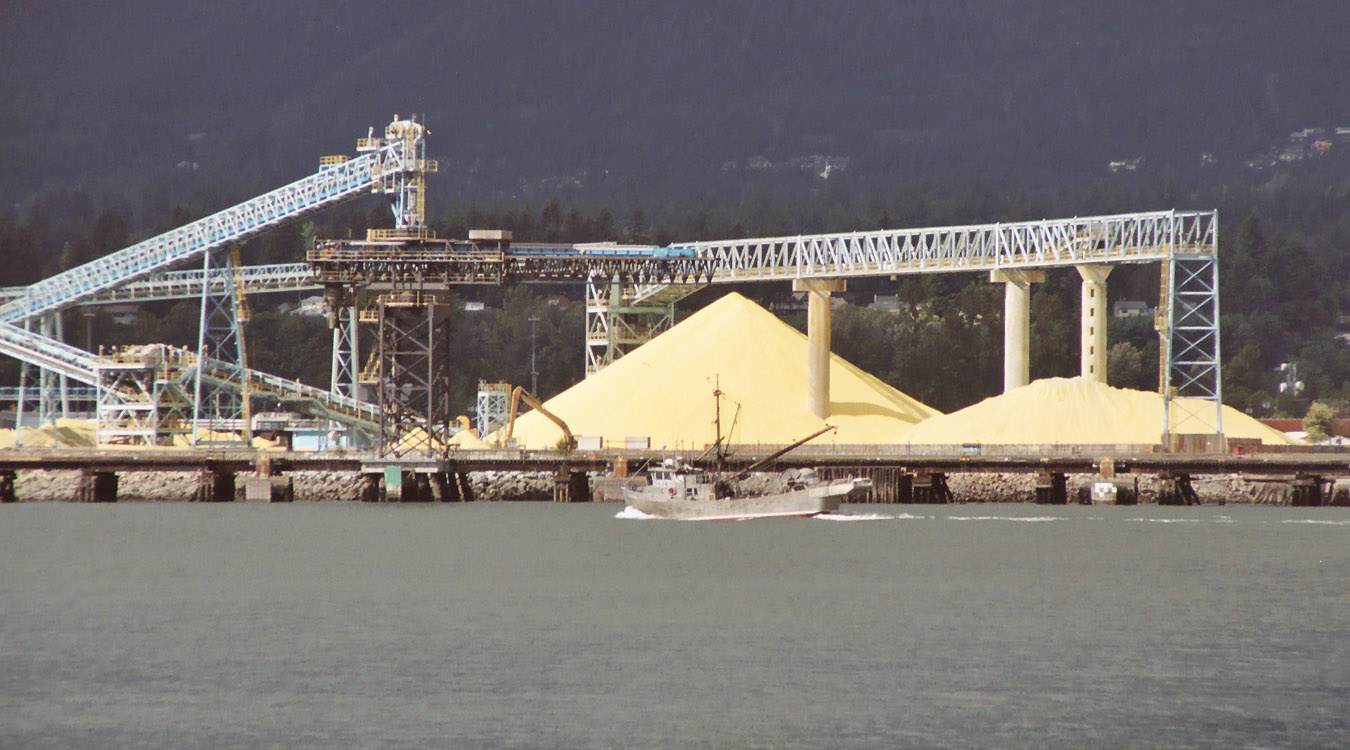  Elemental sulfur was extracted from
Elemental sulfur was extracted from  Owing to the high sulfur content of the Athabasca Oil Sands, stockpiles of elemental sulfur from this process now exist throughout
Owing to the high sulfur content of the Athabasca Oil Sands, stockpiles of elemental sulfur from this process now exist throughout
 In 2010, the United States produced more sulfuric acid than any other inorganic industrial chemical. The principal use for the acid is the extraction of phosphate ores for the production of fertilizer manufacturing. Other applications of sulfuric acid include oil refining, wastewater processing, and mineral extraction.
In 2010, the United States produced more sulfuric acid than any other inorganic industrial chemical. The principal use for the acid is the extraction of phosphate ores for the production of fertilizer manufacturing. Other applications of sulfuric acid include oil refining, wastewater processing, and mineral extraction.
 Elemental sulfur is one of the oldest fungicides and pesticides. "Dusting sulfur", elemental sulfur in powdered form, is a common fungicide for grapes, strawberry, many vegetables and several other crops. It has a good efficacy against a wide range of powdery mildew diseases as well as black spot. In organic production, sulfur is the most important fungicide. It is the only fungicide used in organically farmed apple production against the main disease
Elemental sulfur is one of the oldest fungicides and pesticides. "Dusting sulfur", elemental sulfur in powdered form, is a common fungicide for grapes, strawberry, many vegetables and several other crops. It has a good efficacy against a wide range of powdery mildew diseases as well as black spot. In organic production, sulfur is the most important fungicide. It is the only fungicide used in organically farmed apple production against the main disease
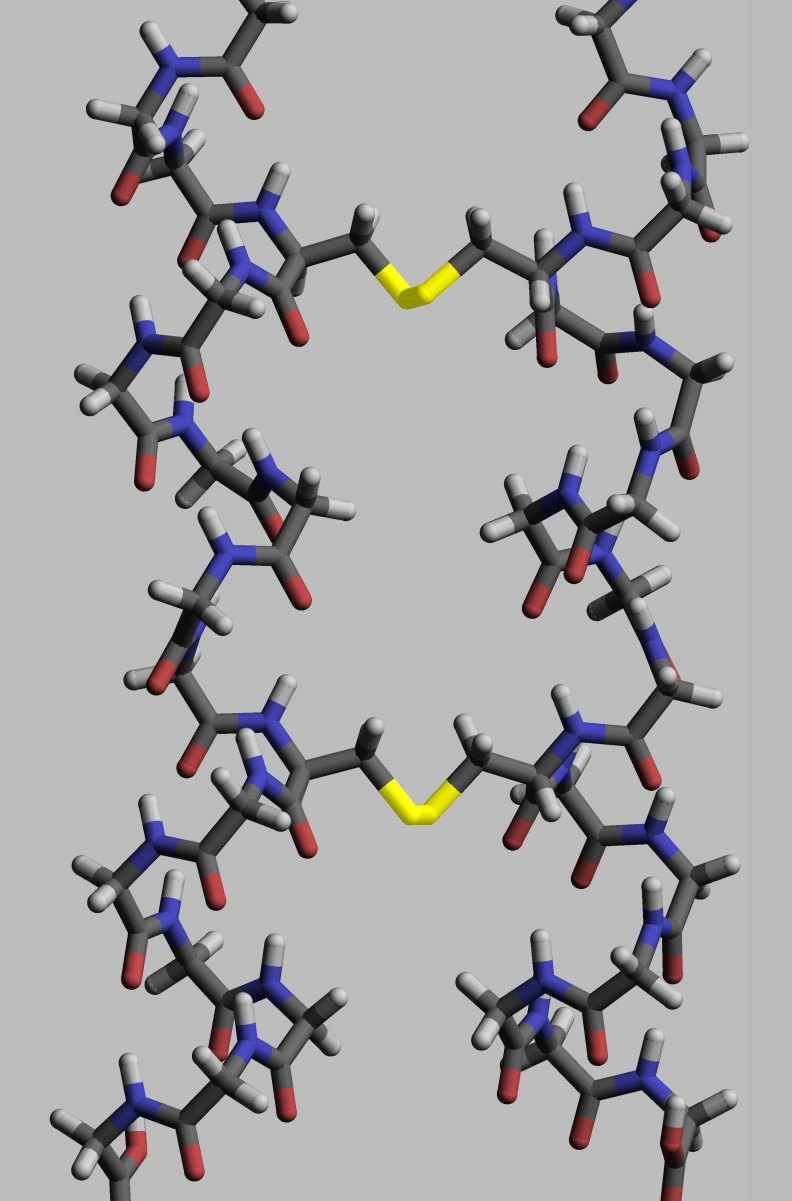 Proteins, to execute their Protein#Cellular functions, biological function, need to have specific space geometry. Formation of this geometry is performed in a process called protein folding, and is provided by intra- and inter-molecular bonds. The process has several stages. While at premier stages a polypeptide chain folds due to hydrogen bonds, at later stages folding is provided (apart from hydrogen bonds) by covalent bonds between two sulfur atoms of two cysteine residues (so called disulfide bridges) at different places of a chain (tertriary protein structure) as well as between two cysteine residues in two separated protein subunits (quaternary protein structure). Both structures easily may be seen in insulin. As the bond energy of a covalent disulfide bridge is higher than the energy of a Coordinate covalent bond, coordinate bond or hydrophylic either hydrophobic interaction, the higher disulfide bridges content leads the higher energy needed for protein Denaturation (biochemistry), denaturation. In general disulfide bonds are necessary in proteins functioning outside cellular space, and they do not change proteins' conformation (geometry), but serve as its stabilizers. Within cytoplasm cysteine residues of proteins are saved in reduced state (i.e. in -SH form) by thioredoxins.
This property manifests in following examples. Lysozyme is stable enough to be applied as a drug. Feathers and hair have relative strength, and consisting in them
Proteins, to execute their Protein#Cellular functions, biological function, need to have specific space geometry. Formation of this geometry is performed in a process called protein folding, and is provided by intra- and inter-molecular bonds. The process has several stages. While at premier stages a polypeptide chain folds due to hydrogen bonds, at later stages folding is provided (apart from hydrogen bonds) by covalent bonds between two sulfur atoms of two cysteine residues (so called disulfide bridges) at different places of a chain (tertriary protein structure) as well as between two cysteine residues in two separated protein subunits (quaternary protein structure). Both structures easily may be seen in insulin. As the bond energy of a covalent disulfide bridge is higher than the energy of a Coordinate covalent bond, coordinate bond or hydrophylic either hydrophobic interaction, the higher disulfide bridges content leads the higher energy needed for protein Denaturation (biochemistry), denaturation. In general disulfide bonds are necessary in proteins functioning outside cellular space, and they do not change proteins' conformation (geometry), but serve as its stabilizers. Within cytoplasm cysteine residues of proteins are saved in reduced state (i.e. in -SH form) by thioredoxins.
This property manifests in following examples. Lysozyme is stable enough to be applied as a drug. Feathers and hair have relative strength, and consisting in them
 Elemental sulfur is non-toxic when one touches it, however it is not harmless. Inhaling sulfur dust, or its contacting to eyes and/or skin may cause irritation. Ingesting sulfur is not safe too. There are reports of cases where people deliberately consumed sulfur (as a folk remedy) that led to life-threatening metabolic acidosis.
Elemental sulfur is non-toxic when one touches it, however it is not harmless. Inhaling sulfur dust, or its contacting to eyes and/or skin may cause irritation. Ingesting sulfur is not safe too. There are reports of cases where people deliberately consumed sulfur (as a folk remedy) that led to life-threatening metabolic acidosis.
Sulfur
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
Atomic Data for Sulfur
NIST Physical Measurement Laboratory
Sulfur phase diagram
, Introduction to Chemistry for Ages 13–17
*[http://extoxnet.orst.edu/pips/sulfur.htm Sulfur and its use as a pesticide]
The Sulphur InstituteNutrient Stewardship and The Sulphur Institute
{{Authority control Sulfur, Chemical elements Chalcogens Reactive nonmetals Polyatomic nonmetals Agricultural chemicals Anti-acne preparations Dietary minerals Industrial minerals Inorganic polymers Native element minerals Orthorhombic minerals Minerals in space group 70 Pyrotechnic fuels Chemical elements with primitive orthorhombic structure
British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
) is a chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
with the symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
S and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
16. It is abundant, multivalent
In chemistry, polyvalency (or polyvalence, multivalency) is the property of chemical species (generally atoms or molecules) that exhibit more than one valence by forming multiple chemical bonds (Fig. 1). A bivalent species can form two bonds; a ...
and nonmetal
In chemistry, a nonmetal is a chemical element that generally lacks a predominance of metallic properties; they range from colorless gases (like hydrogen) to shiny solids (like carbon, as graphite). The electrons in nonmetals behave differentl ...
lic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
line solid at room temperature
Colloquially, "room temperature" is a range of air temperatures that most people prefer for indoor settings. It feels comfortable to a person when they are wearing typical indoor clothing. Human comfort can extend beyond this range depending on ...
.
Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native
Native may refer to:
People
* Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Native Americans (disambiguation)
In arts and entert ...
form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds lar ...
and sulfate minerals
The sulfate minerals are a class of minerals that include the sulfate ion () within their structure. The sulfate minerals occur commonly in primary evaporite depositional environments, as gangue minerals in hydrothermal Vein (geology), veins and as ...
. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
, ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
and petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
.. Downloahere
The greatest commercial use of the element is the production of
sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
for sulfate and phosphate fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s, and other chemical processes. Sulfur is used in match
A match is a tool for starting a fire. Typically, matches are made of small wooden sticks or stiff paper. One end is coated with a material that can be ignited by friction generated by striking the match against a suitable surface. Wooden matc ...
es, insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
s, and fungicide
Fungicides are biocidal chemical compounds or biological organisms used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. A fungistatic inhibits their growth. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in critical losses of yield, quality, ...
s. Many sulfur compounds are odoriferous, and the smells of odorized natural gas, skunk scent, grapefruit, and garlic are due to organosulfur
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur ...
compounds. Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
gives the characteristic odor to rotting eggs and other biological processes.
Sulfur is an essential element
In the context of nutrition, a mineral is a chemical element required as an essential nutrient by organisms to perform functions necessary for life. However, the four major structural elements in the human body by weight (oxygen, hydrogen, carbon ...
for all life, but almost always in the form of organosulfur compounds
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur ...
or metal sulfides. Amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s (two proteinogenic
Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation. The word "proteinogenic" means "protein creating". Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) amino aci ...
: cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
and methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
, and many other non-coded: cystine
Cystine is the oxidized derivative of the amino acid cysteine and has the formula (SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H)2. It is a white solid that is poorly soluble in water. As a residue in proteins, cystine serves two functions: a site of redox reactions and a me ...
, taurine
Taurine (), or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is an organic compound that is widely distributed in animal tissues. It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine, and accounts for up to 0.1% of total human body weight. It ...
, etc.) and two vitamins (biotin
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', bor ...
and thiamine
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient, that cannot be made in the body. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thi ...
) are organosulfur compounds crucial for life. Many cofactors
Cofactor may also refer to:
* Cofactor (biochemistry), a substance that needs to be present in addition to an enzyme for a certain reaction to be catalysed
* A domain parameter in elliptic curve cryptography, defined as the ratio between the order ...
also contain sulfur, including glutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, pero ...
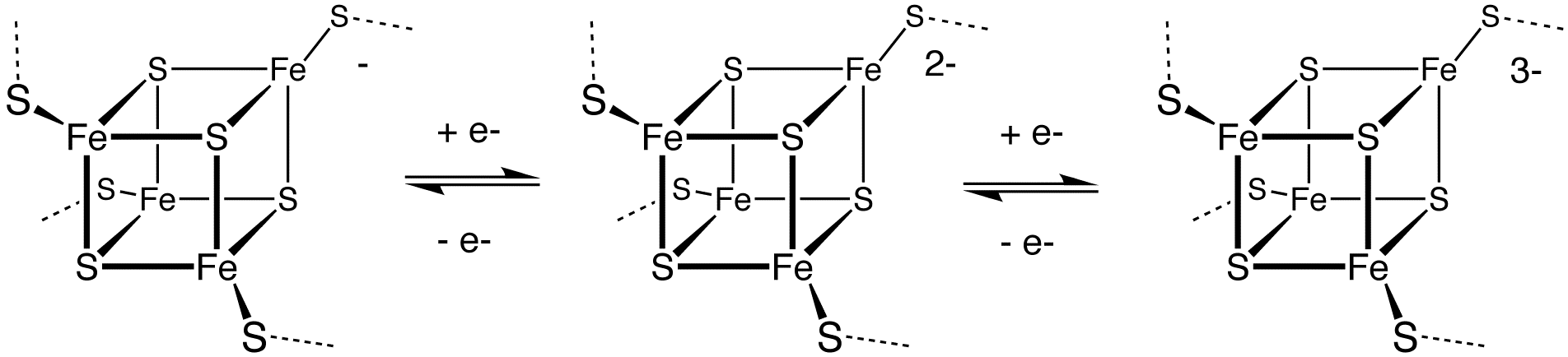
, and iron–sulfur protein
Iron–sulfur proteins (or iron–sulphur proteins in British spelling) are proteins characterized by the presence of iron–sulfur clusters containing sulfide-linked di-, tri-, and tetrairon centers in variable oxidation states. Iron–sulfur clu ...
s. Disulfide
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In ...
s, S–S bonds, confer mechanical strength and insolubility of the (among others) protein keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
, found in outer skin, hair, and feathers. Sulfur is one of the core chemical elements needed for biochemical
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology an ...
functioning and is an elemental macronutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
for all living organisms.
Characteristics

Physical properties
Sulfur forms several polyatomic molecules. The best-known allotrope isoctasulfur
Octasulfur is an inorganic substance with the chemical formula . It is an odourless and tasteless yellow solid, and is a major industrial chemical. It is the most common allotrope of sulfur and occurs widely in nature.Steudel, R., "Homocyclic Sul ...
, cyclo-S8. The point group
In geometry, a point group is a mathematical group of symmetry operations (isometries in a Euclidean space) that have a fixed point in common. The coordinate origin of the Euclidean space is conventionally taken to be a fixed point, and every p ...
of cyclo-S8 is D4d and its dipole moment is 0 D. Octasulfur is a soft, bright-yellow solid that is odorless, but impure samples have an odor similar to that of match
A match is a tool for starting a fire. Typically, matches are made of small wooden sticks or stiff paper. One end is coated with a material that can be ignited by friction generated by striking the match against a suitable surface. Wooden matc ...
es. It melts at , boils at and sublimes more or less between and . At , below its melting temperature, cyclo-octasulfur changes from α-octasulfur to the β- polymorph. The structure of the S8 ring is virtually unchanged by this phase change, which affects the intermolecular interactions. Between its melting and boiling temperatures, octasulfur changes its allotrope again, turning from β-octasulfur to γ-sulfur, again accompanied by a lower density but increased viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
due to the formation of polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
s. At higher temperatures, the viscosity decreases as depolymerization occurs. Molten sulfur assumes a dark red color above . The density of sulfur is about 2 g/cm3, depending on the allotrope; all of the stable allotropes are excellent electrical insulators.
Sulfur is insoluble in water but soluble in carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is a neurotoxic, colorless, volatile liquid with the formula and structure . The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non ...
and, to a lesser extent, in other nonpolar
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
Polar molecules must contain one or more polar ...
organic solvents, such as benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, ...
and toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a colorless, water-insoluble liquid with the smell associated with paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, consisting of a methyl group (CH3) at ...
.
Chemical properties
Under normal conditions, sulfurhydrolyzes
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
very slowly to mainly form hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
and sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
:
: + 4 → 3 +
The reaction involves adsorption of protons onto clusters, followed by disproportionation
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states. More generally, the term can b ...
into the reaction products.
The second, fourth and sixth ionization energies
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule i ...
of sulfur are 2252 kJ/mol−1, 4556 kJ/mol−1 and 8495.8 kJ/mol−1,respectively. A composition of products of sulfur's reactions with oxidants (and its oxidation state) depends on that whether releasing out of a reaction energy overcomes these thresholds. Applying catalysts
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
and / or supply of outer energy may vary sulfur's oxidation state and a composition of reaction products. While reaction between sulfur and oxygen at normal conditions gives sulfur dioxide (oxidation state +4), formation of sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide (alternative spelling sulphur trioxide, also known as ''nisso sulfan'') is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. It has been described as "unquestionably the most important economically" sulfur oxide. It is prepared on an ind ...
(oxidation state +6) requires temperature 400 – 600 °C and presence of a catalyst.
In reactions with elements electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the d ...
of which less than sulfur's, it comes as an oxidant, and forms sulfides with oxidation state –2.
Sulfur reacts with nearly all other elements with the exception of the noble gases, even with the notoriously unreactive metal iridium
Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density of ...
(yielding iridium disulfide
Iridium disulfide is the binary inorganic compound with the formula IrS2. Prepared by the direct reaction of the elements, the compound adopts the Pyrite#Crystallography, pyrite crystal structure at high pressure. At normal atmospheric pressures ...
).
Some of those reactions need elevated temperatures.
Allotropes
 Sulfur forms over 30 solid
Sulfur forms over 30 solid allotropes
Allotropy or allotropism () is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state, known as allotropes of the elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications of an element: th ...
, more than any other element. Besides S8, several other rings are known. Removing one atom from the crown gives S7, which is more of a deep yellow than the S8. HPLC
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture. It relies on pumps to pa ...
analysis of "elemental sulfur" reveals an equilibrium mixture of mainly S8, but with S7 and small amounts of S6. Larger rings have been prepared, including S12 and S18.
Amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal.
Etymology
The term comes from the Greek ''a'' ("wi ...
or "plastic" sulfur is produced by rapid cooling of molten sulfur—for example, by pouring it into cold water. X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
studies show that the amorphous form may have a helical
Helical may refer to:
* Helix, the mathematical concept for the shape
* Helical engine, a proposed spacecraft propulsion drive
* Helical spring, a coilspring
* Helical plc, a British property company, once a maker of steel bar stock
* Helicoil
A t ...
structure with eight atoms per turn. The long coiled polymeric molecules make the brownish substance elastic
Elastic is a word often used to describe or identify certain types of elastomer, elastic used in garments or stretchable fabrics.
Elastic may also refer to:
Alternative name
* Rubber band, ring-shaped band of rubber used to hold objects togeth ...
, and in bulk this form has the feel of crude rubber. This form is metastable
In chemistry and physics, metastability denotes an intermediate Energy level, energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's ground state, state of least energy.
A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of me ...
at room temperature and gradually reverts to crystalline molecular allotrope, which is no longer elastic. This process happens within a matter of hours to days, but can be rapidly catalyzed.
Isotopes
Sulfur has 23 knownisotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) ...
s, four of which are stable: 32S (), 33S (), 34S (), and 36S (). Other than 35S, with a half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
of 87 days and formed in cosmic ray spallation
Cosmic ray spallation, also known as the x-process, is a set of naturally occurring nuclear reactions causing nucleosynthesis; it refers to the formation of chemical elements from the impact of cosmic rays on an object. Cosmic rays are highly energ ...
of 40 Ar, the radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
isotopes of sulfur have half-lives less than 3 hours.
When sulfide mineral
The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S2−) or disulfide (S22−) as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, the ...
s are precipitated, isotopic equilibration among solids and liquid may cause small differences in the δ34S values of co-genetic minerals. The differences between minerals can be used to estimate the temperature of equilibration. The δ13C and δ34S of coexisting carbonate minerals
Carbonate minerals are those minerals containing the carbonate ion, .
Carbonate divisions Anhydrous carbonates
*Calcite group: trigonal
**Calcite CaCO3
**Gaspéite (Ni,Mg,Fe2+)CO3
**Magnesite MgCO3
**Otavite CdCO3
**Rhodochrosite MnCO3
**Sider ...
and sulfides can be used to determine the pH and oxygen fugacity
In chemical thermodynamics, the fugacity of a real gas is an effective partial pressure which replaces the mechanical partial pressure in an accurate computation of the chemical equilibrium constant. It is equal to the pressure of an ideal gas whic ...
of the ore-bearing fluid during ore formation.
In most forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
ecosystems, sulfate is derived mostly from the atmosphere; weathering of ore minerals and evaporites contribute some sulfur. Sulfur with a distinctive isotopic composition has been used to identify pollution sources, and enriched sulfur has been added as a tracer in hydrologic
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is calle ...
studies. Differences in the natural abundance
In physics, natural abundance (NA) refers to the abundance of isotopes of a chemical element as naturally found on a planet. The relative atomic mass (a weighted average, weighted by mole-fraction abundance figures) of these isotopes is the atomi ...
s can be used in systems where there is sufficient variation in the 34S of ecosystem components. Rocky Mountain
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
lakes thought to be dominated by atmospheric sources of sulfate have been found to have characteristic 34S values from lakes believed to be dominated by watershed sources of sulfate.
Natural occurrence
 32S is created inside massive stars, at a depth where the temperature exceeds 2.5×109 K, by the
32S is created inside massive stars, at a depth where the temperature exceeds 2.5×109 K, by the fusion
Fusion, or synthesis, is the process of combining two or more distinct entities into a new whole.
Fusion may also refer to:
Science and technology Physics
*Nuclear fusion, multiple atomic nuclei combining to form one or more different atomic nucl ...
of one nucleus of silicon plus one nucleus of helium. As this nuclear reaction is part of the alpha process
The alpha process, also known as the alpha ladder, is one of two classes of nuclear fusion reactions by which stars convert helium into heavier elements, the other being the triple-alpha process.
The triple-alpha process consumes only helium, an ...
that produces elements in abundance, sulfur is the 10th most common element in the universe.
Sulfur, usually as sulfide, is present in many types of meteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the ...
s. Ordinary chondrites contain on average 2.1% sulfur, and carbonaceous chondrites may contain as much as 6.6%. It is normally present as troilite
Troilite is a rare iron sulfide mineral with the simple formula of FeS. It is the iron-rich endmember of the pyrrhotite group. Pyrrhotite has the formula Fe(1-x)S (x = 0 to 0.2) which is iron deficient. As troilite lacks the iron deficiency whic ...
(FeS), but there are exceptions, with carbonaceous chondrites containing free sulfur, sulfates and other sulfur compounds. The distinctive colors of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
's volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
moon Io are attributed to various forms of molten, solid, and gaseous sulfur.
It is the fifth most common element by mass in the Earth. Elemental sulfur can be found near hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
s and volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
regions in many parts of the world, especially along the Pacific Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions and ...
; such volcanic deposits are currently mined in Indonesia, Chile, and Japan. These deposits are polycrystalline, with the largest documented single crystal measuring 22×16×11 cm. Historically, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
was a major source of sulfur in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
. Lakes of molten sulfur up to ~200 m in diameter have been found on the sea floor, associated with submarine volcano
Submarine volcanoes are underwater vents or fissures in the Earth's surface from which magma can erupt. Many submarine volcanoes are located near areas of tectonic plate formation, known as mid-ocean ridges. The volcanoes at mid-ocean ridges ...
es, at depths where the boiling point of water is higher than the melting point of sulfur.C. E. J. de Ronde, W. W. Chadwick Jr, R. G. Ditchburn, R. W. Embley, V. Tunnicliffe, E. T. Baker. S. L. Walker. V. L. Ferrini, and S. M. Merle (2015): "Molten Sulfur Lakes of Intraoceanic Arc Volcanoes". Chapter of ''Volcanic Lakes'' (Springer), pages 261-288.
Native sulfur is synthesised by anaerobic bacteria
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenate ...
acting on sulfate minerals
The sulfate minerals are a class of minerals that include the sulfate ion () within their structure. The sulfate minerals occur commonly in primary evaporite depositional environments, as gangue minerals in hydrothermal Vein (geology), veins and as ...
such as gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. ...
in salt dome
A salt dome is a type of structural dome formed when salt (or other evaporite minerals) intrudes into overlying rocks in a process known as diapirism. Salt domes can have unique surface and subsurface structures, and they can be discovered using ...
s. Significant deposits in salt domes occur along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
, and in evaporite
An evaporite () is a water-soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocea ...
s in eastern Europe and western Asia. Native sulfur may be produced by geological processes alone. Fossil-based sulfur deposits from salt domes were once the basis for commercial production in the United States, Russia, Turkmenistan, and Ukraine. Currently, commercial production is still carried out in the Osiek mine in Poland. Such sources are now of secondary commercial importance, and most are no longer worked.
Common naturally occurring sulfur compounds include the sulfide minerals
The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S2−) or disulfide (S22−) as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, the ...
, such as pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), lust ...
(iron sulfide), cinnabar
Cinnabar (), or cinnabarite (), from the grc, κιννάβαρι (), is the bright scarlet to brick-red form of Mercury sulfide, mercury(II) sulfide (HgS). It is the most common source ore for refining mercury (element), elemental mercury and ...
(mercury sulfide), galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It cryst ...
(lead sulfide), sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimen ...
(zinc sulfide), and stibnite
Stibnite, sometimes called antimonite, is a sulfide mineral with the formula Sb2 S3. This soft grey material crystallizes in an orthorhombic space group. It is the most important source for the metalloid antimony. The name is derived from the ...
(antimony sulfide); and the sulfate minerals
The sulfate minerals are a class of minerals that include the sulfate ion () within their structure. The sulfate minerals occur commonly in primary evaporite depositional environments, as gangue minerals in hydrothermal Vein (geology), veins and as ...
, such as gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. ...
(calcium sulfate), alunite
Alunite is a hydroxylated aluminium potassium sulfate mineral, formula K Al3( S O4)2(O H)6. It was first observed in the 15th century at Tolfa, near Rome, where it was mined for the manufacture of alum. First called ''aluminilite'' by J.C. Del ...
(potassium aluminium sulfate), and barite
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate ( Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), ...
(barium sulfate). On Earth, just as upon Jupiter's moon Io, elemental sulfur occurs naturally in volcanic emissions, including emissions from hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
s.
The main industrial source of sulfur is now petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
.
Compounds
Commonoxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. C ...
s of sulfur range from −2 to +6. Sulfur forms stable compounds with all elements except the noble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemi ...
es.
Electron transfer reactions
Sulfur polycations, S82+, S42+ and S162+ are produced when sulfur is reacted with oxidising agents in a strongly acidic solution. The colored solutions produced by dissolving sulfur inoleum
Oleum (Latin ''oleum'', meaning oil), or fuming sulfuric acid, is a term referring to solutions of various compositions of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid, or sometimes more specifically to disulfuric acid (also known as pyrosulfuric acid). Ole ...
were first reported as early as 1804 by C.F. Bucholz, but the cause of the color and the structure of the polycations involved was only determined in the late 1960s. S82+ is deep blue, S42+ is yellow and S162+ is red.
Reduction of sulfur gives various polysulfide
Polysulfides are a class of chemical compounds containing chains of sulfur atoms. There are two main classes of polysulfides: inorganic and organic. Among the inorganic polysulfides, there are ones which contain anions, which have the general formu ...
s with the formula Sx2-, many of which have been obtained crystalline form. Illustrative is the production of sodium tetrasulfide:
:
Some of these dianions dissociate to give radical anion
In organic chemistry, a radical anion is a free radical species that carries a negative charge. Radical anions are encountered in organic chemistry as reduced derivatives of polycyclic aromatic compounds, e.g. sodium naphthenide. An example of a ...
s, such as S3− gives the blue color of the rock lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mines, ...
.
 This reaction highlights a distinctive property of sulfur: its ability to
This reaction highlights a distinctive property of sulfur: its ability to catenate
In chemistry, catenation is the bonding of atoms of the same element into a series, called a ''chain''. A chain or a ring shape may be ''open'' if its ends are not bonded to each other (an open-chain compound), or ''closed'' if they are bonded ...
(bind to itself by formation of chains). Protonation
In chemistry, protonation (or hydronation) is the adding of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) to an atom, molecule, or ion, forming a conjugate acid. (The complementary process, when a proton is removed from a Brønsted–Lowry acid, ...
of these polysulfide anions produces the polysulfane
A polysulfane is a chemical compound of formula , where ''n'' > 1 (although disulfane () is sometimes excluded). Polysulfanes consist of unbranched chains of sulfur atoms terminated with hydrogen atoms. Compounds containing 2 – 8 concatenated s ...
s, H2Sx where x= 2, 3, and 4. Ultimately, reduction of sulfur produces sulfide salts:
:16 Na + S8 → 8 Na2S
The interconversion of these species is exploited in the sodium–sulfur battery
A sodium–sulfur battery is a type of molten-salt battery constructed from liquid sodium (Na) and sulfur (S). This type of battery has a high energy density (its energy density is 5 times that of a lead-acid battery), high efficiency of charge/ ...
.
Hydrogenation
Treatment of sulfur with hydrogen giveshydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
. When dissolved in water, hydrogen sulfide is mildly acidic:Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. .
:H2S HS− + H+
Hydrogen sulfide gas and the hydrosulfide anion are extremely toxic to mammals, due to their inhibition of the oxygen-carrying capacity of hemoglobin and certain cytochrome
Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with a central Fe atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in electron transport chain and redox catalysis. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of bin ...
s in a manner analogous to cyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of ...
and azide
In chemistry, azide is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula and structure . It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid . Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula , containing the azide functional group. The dominant applic ...
(see below, under ''precautions'').
Combustion
The two principal sulfur oxides are obtained by burning sulfur: :S + O2 → SO2 (sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activ ...
)
:2 SO2 + O2 → 2 SO3 (sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide (alternative spelling sulphur trioxide, also known as ''nisso sulfan'') is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. It has been described as "unquestionably the most important economically" sulfur oxide. It is prepared on an ind ...
)
Many other sulfur oxides are observed including the sulfur-rich oxides include sulfur monoxide, disulfur monoxide, disulfur dioxides, and higher oxides containing peroxo groups.
Halogenation
Sulfur reacts with fluorine to give the highly reactivesulfur tetrafluoride
Sulfur tetrafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula S F4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous HF upon exposure to water or moisture. Despite these unwelcome characteristics, this compound is a useful reagent for t ...
and the highly inert Sulfur hexafluoride
Sulfur hexafluoride or sulphur hexafluoride (British spelling) is an inorganic compound with the formula SF6. It is a colorless, odorless, non- flammable, and non-toxic gas. has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attached ...
. Whereas fluorine gives S(IV) and S(VI) compounds, chlorine gives S(II) and S(I) derivatives. Thus, sulfur dichloride
Sulfur dichloride is the chemical compound with the formula . This cherry-red liquid is the simplest sulfur chloride and one of the most common, and it is used as a precursor to organosulfur compounds. It is a highly corrosive and toxic substance, ...
, disulfur dichloride
Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the Chemical formula, formula S2Cl2.
Some alternative names for this compound are ''sulfur monochloride'' (the name implied by its empirical formula, SCl), ''disulphur dich ...
, and higher chlorosulfanes arise from the chlorination of sulfur. Sulfuryl chloride
Sulfuryl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula SO2Cl2. At room temperature, it is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Sulfuryl chloride is not found in nature, as can be inferred from its rapid hydrolysis.
Sulfuryl chloride is ...
and chlorosulfuric acid
Chlorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurochloridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula HSO3Cl. It is also known as chlorosulfonic acid, being the sulfonic acid of chlorine. It is a distillable, colorless liquid which is hygroscopic and ...
are derivatives of sulfuric acid; thionyl chloride
Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately per year bein ...
(SOCl2) is a common reagent in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
.
Pseudohalides
Sulfur oxidizescyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of ...
and sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion (or the sulfate(IV) ion, from its correct systematic name), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid ( sulfurous acid) is elusive, its salts are wide ...
to give thiocyanate
Thiocyanate (also known as rhodanide) is the anion . It is the conjugate base of thiocyanic acid. Common derivatives include the colourless salts potassium thiocyanate and sodium thiocyanate. Mercury(II) thiocyanate was formerly used in pyrot ...
and thiosulfate
Thiosulfate ( IUPAC-recommended spelling; sometimes thiosulphate in British English) is an oxyanion of sulfur with the chemical formula . Thiosulfate also refers to the compounds containing this anion, which are the salts of thiosulfuric acid, ...
, respectively.
Metal sulfides
Sulfur reacts with many metals. Electropositive metals give polysulfide salts. Copper, zinc, silver are attacked by sulfur, see tarnishing. Although many metal sulfides are known, most are prepared by high temperature reactions of the elements.Organic compounds
Allicin
Allicin is an organosulfur compound obtained from garlic, a species in the family Alliaceae. It was first isolated and studied in the laboratory by Chester J. Cavallito and John Hays Bailey in 1944. When fresh garlic is chopped or crushed, the ...
, a chemical compound in garlic
File:L-Cystein - L-Cysteine.svg , (''R'')-cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
, an amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
containing a thiol group
File:Methionin - Methionine.svg, Methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
, an amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
containing a thioether
File:Diphenyl disulfide.svg, Diphenyl disulfide
Diphenyl disulfide is the chemical compound with the formula (C6H5S)2. This colorless crystalline material is often abbreviated Ph2S2. It is one of the more commonly encountered organic disulfides in organic synthesis. Minor contamination by thiop ...
, a representative disulfide
File:Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid structure.svg, Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid
Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) (conjugate base perfluorooctanesulfonate) is a chemical compound having an eight-carbon fluorocarbon chain and a sulfonic acid functional group and thus a perfluorosulfonic acid. It is an anthropogenic (man-ma ...
, a surfactant
File:Dibenzothiophen - Dibenzothiophene.svg, Dibenzothiophene
Dibenzothiophene (DBT, diphenylene sulfide) is the organosulfur compound consisting of two benzene rings fused to a central thiophene ring. It is a colourless solid that is chemically somewhat similar to anthracene. This tricyclic heterocycle, and ...
, a component of crude oil
File:Penicillin core.svg, Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
, an antibiotic where "R" is the variable group
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl gro ...
s or mercaptans (so called because they capture mercury as chelators) are the sulfur analogs of alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
s; treatment of thiols with base gives thiolate
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl grou ...
ions.
* Thioether
In organic chemistry, an organic sulfide (British English sulphide) or thioether is an organosulfur functional group with the connectivity as shown on right. Like many other sulfur-containing compounds, volatile sulfides have foul odors. A sul ...
s are the sulfur analogs of ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be c ...
s.
* Sulfonium
In organic chemistry, a sulfonium ion, also known as sulphonium ion or sulfanium ion, is a positively-charged ion (a " cation") featuring three organic substituents attached to sulfur. These organosulfur compounds have the formula . Together wi ...
ions have three groups attached to a cationic sulfur center. Dimethylsulfoniopropionate
Dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2S+CH2CH2COO−. This zwitterionic metabolite can be found in marine phytoplankton, seaweeds, and some species of terrestrial and aquatic vascular plants ...
(DMSP) is one such compound, important in the marine organic sulfur cycle
The sulfur cycle is a biogeochemical cycle in which the sulfur moves between rocks, waterways and living systems. It is important in geology as it affects many minerals and in life because sulfur is an essential element ( CHNOPS), being a const ...
.
* Sulfoxide
In organic chemistry, a sulfoxide, also called a sulphoxide, is an organosulfur compound containing a sulfinyl () functional group attached to two carbon atoms. It is a polar functional group. Sulfoxides are oxidized derivatives of sulfides. E ...
s and sulfone
In organic chemistry, a sulfone is a organosulfur compound containing a sulfonyl () functional group attached to two carbon atoms. The central hexavalent sulfur atom is double-bonded to each of two oxygen atoms and has a single bond to each of ...
s are thioethers with one and two oxygen atoms attached to the sulfur atom, respectively. The simplest sulfoxide, dimethyl sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula ( CH3)2. This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds a ...
, is a common solvent; a common sulfone is sulfolane
Sulfolane (also ''tetramethylene sulfone'', systematic name: 1λ6-thiolane-1,1-dione) is an organosulfur compound, formally a cyclic sulfone, with the formula (CH2)4SO2. It is a colorless liquid commonly used in the chemical industry as a solvent ...
.
* Sulfonic acid
In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid (or sulphonic acid) refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula , where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is kn ...
s are used in many detergents.
Compounds with carbon–sulfur multiple bonds are uncommon, an exception being carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is a neurotoxic, colorless, volatile liquid with the formula and structure . The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non ...
, a volatile colorless liquid that is structurally similar to carbon dioxide. It is used as a reagent to make the polymer rayon
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. It is also called viscose. Many types and grades of viscose f ...
and many organosulfur compounds. Unlike carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
, carbon monosulfide
Carbon monosulfide is a chemical compound with the formula CS. This diatomic molecule is the sulfur analogue of carbon monoxide, and is unstable as a solid or a liquid, but it has been observed as a gas both in the laboratory and in the interstel ...
is stable only as an extremely dilute gas, found between solar systems.
Organosulfur compounds are responsible for some of the unpleasant odors of decaying organic matter. They are widely known as the odorant
An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavoring, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For an individual chemical or class of chemical compounds to impart a smell or fragrance, it must be sufficiently vol ...
in domestic natural gas, garlic odor, and skunk spray. Not all organic sulfur compounds smell unpleasant at all concentrations: the sulfur-containing monoterpenoid
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings (monocyclic and bicyclic). Modified terpenes, such as those containing oxygen funct ...
(grapefruit mercaptan
Grapefruit mercaptan is the common name for a natural organic compound found in grapefruit. It is a monoterpenoid that contains a thiol (also known as a mercaptan) functional group. Structurally a hydroxy group of terpineol is replaced by the th ...
) in small concentrations is the characteristic scent of grapefruit, but has a generic thiol odor at larger concentrations. Sulfur mustard
Mustard gas or sulfur mustard is a chemical compound belonging to a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known as mustard agents. The name ''mustard gas'' is technically incorrect: the substance, when dispersed, is often not actually a gas, b ...
, a potent vesicant
A blister agent (or vesicant), is a chemical compound that causes severe skin, eye and mucosal pain and irritation. They are named for their ability to cause severe chemical burns, resulting in painful water blisters on the bodies of those affec ...
, was used in World War I as a disabling agent.
Sulfur–sulfur bonds are a structural component used to stiffen rubber, similar to the disulfide bridges that rigidify proteins (see biological below). In the most common type of industrial "curing" or hardening and strengthening of natural rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
, elemental sulfur is heated with the rubber to the point that chemical reactions form disulfide
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In ...
bridges between isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)−CH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. Isoprene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. It is produced by many plants and animals ...
units of the polymer. This process, patented in 1843, made rubber a major industrial product, especially in automobile tires. Because of the heat and sulfur, the process was named vulcanization
Vulcanization (British: Vulcanisation) is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to include ...
, after the Roman god of the forge and volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called ...
.
History
Antiquity
 Being abundantly available in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times and is referred to in the
Being abundantly available in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times and is referred to in the Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the s ...
(Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Bible
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of mankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Book of ...
). English translations of the Christian Bible commonly referred to burning sulfur as "brimstone", giving rise to the term " fire-and-brimstone" sermon
A sermon is a religious discourse or oration by a preacher, usually a member of clergy. Sermons address a scriptural, theological, or moral topic, usually expounding on a type of belief, law, or behavior within both past and present contexts. El ...
s, in which listeners are reminded of the fate of eternal damnation
Damnation (from Latin '' damnatio'') is the concept of divine punishment and torment in an afterlife for actions that were committed, or in some cases, not committed on Earth.
In Ancient Egyptian religious tradition, citizens would recite t ...
that await the unbelieving and unrepentant. It is from this part of the Bible that Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hell ...
is implied to "smell of sulfur" (likely due to its association with volcanic activity). According to the Ebers Papyrus, a sulfur ointment was used in ancient Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
to treat granular eyelids. Sulfur was used for fumigation in preclassical Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
; this is mentioned in the ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek Epic poetry, epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by moder ...
''. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
discusses sulfur in book 35 of his '' Natural History'', saying that its best-known source is the island of Melos
Milos or Melos (; el, label=Modern Greek, Μήλος, Mílos, ; grc, Μῆλος, Mêlos) is a volcanic Greek island in the Aegean Sea, just north of the Sea of Crete. Milos is the southwesternmost island in the Cyclades group.
The ''Venus d ...
. He mentions its use for fumigation, medicine, and bleaching cloth.
A natural form of sulfur known as () was known in China since the 6th century BC and found in Hanzhong
Hanzhong (; abbreviation: Han) is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Shaanxi province, China, bordering the provinces of Sichuan to the south and Gansu to the west.
The founder of the Han dynasty, Liu Bang, was once enfeoffed as the ...
. By the 3rd century, the Chinese had discovered that sulfur could be extracted from pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), lust ...
. Chinese Daoists
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Tao ...
were interested in sulfur's flammability and its reactivity with certain metals, yet its earliest practical uses were found in traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of action ...
. A Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
military treatise of 1044 AD described various formulas for Chinese black powder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
, which is a mixture of potassium nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Indian saltpetre (large deposits of which were historically mined in India). It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrat ...
(), charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, cal ...
, and sulfur. It remains an ingredient of black gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
.
Indian alchemists, practitioners of the "science of chemicals" ( sa, रसशास्त्र, rasaśāstra), wrote extensively about the use of sulfur in alchemical operations with mercury, from the eighth century AD onwards. In the tradition, sulfur is called "the smelly" (, ).
Early Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an alchemists
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
gave sulfur a unique alchemical symbol
Alchemical symbols, originally devised as part of alchemy, were used to denote some elements and some compounds until the 18th century. Although notation like this was mostly standardized, style and symbol varied between alchemists, so this pag ...
, a triangle atop a cross (🜍). (This is sometimes confused with the astronomical crossed-spear symbol ⚴ for 2 Pallas
Pallas (minor-planet designation: 2 Pallas) is the second asteroid to have been discovered, after Ceres. It is believed to have a mineral composition similar to carbonaceous chondrite meteorites, like Ceres, though significantly less hyd ...
.) The variation known as brimstone has a symbol combining a two-barred cross
A two-barred cross is similar to a Latin cross but with an extra bar added. The lengths and placement of the bars (or "arms") vary, and most of the variations are interchangeably called the cross of Lorraine, the patriarchal cross, the Orthodox ...
atop a lemniscate
In algebraic geometry, a lemniscate is any of several figure-eight or -shaped curves. The word comes from the Latin "''lēmniscātus''" meaning "decorated with ribbons", from the Greek λημνίσκος meaning "ribbons",. or which alternativel ...
(🜏). In traditional skin treatment, elemental sulfur was used (mainly in creams) to alleviate such conditions as scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious skin infestation by the mite ''Sarcoptes scabiei''. The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the skin ...
, ringworm
Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple a ...
, psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete ...
, eczema
Dermatitis is inflammation of the Human skin, skin, typically characterized by itchiness, erythema, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become lichenification, thick ...
, and acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, black ...
. The mechanism of action is unknown—though elemental sulfur does oxidize slowly to sulfurous acid, which is (through the action of sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion (or the sulfate(IV) ion, from its correct systematic name), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid ( sulfurous acid) is elusive, its salts are wide ...
) a mild reducing and antibacterial agent.
Modern times
Sulfur appears in a column of fixed (non-acidic)alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a ...
in a chemical table of 1718. Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794), When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and th ...
used sulfur in combustion experiments, writing of some of these in 1777.
Sulfur deposits in Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
were the dominant source for more than a century. By the late 18th century, about 2,000 tonnes per year of sulfur were imported into Marseille
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern Franc ...
, France, for the production of sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
for use in the Leblanc process
The Leblanc process (pronounced leh-blaank) was an early industrial process for making ''soda ash'' (sodium carbonate) used throughout the 19th century, named after its inventor, Nicolas Leblanc. It involved two stages: making sodium sulfate from ...
. In industrializing
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
Britain, with the repeal of tariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and poli ...
s on salt in 1824, demand for sulfur from Sicily surged upward. The increasing British control and exploitation of the mining, refining, and transportation of the sulfur, coupled with the failure of this lucrative export to transform Sicily's backward and impoverished economy, led to the Sulfur Crisis of 1840
The Sulphur Crisis of 1840 (also known as the Sulphur War of 1840 or Anglo-Neapolitan Sulphur Crisis) was a conflict between the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies and the United Kingdom. In the 19th century, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies maintained ...
, when King Ferdinand II
Ferdinand II ( an, Ferrando; ca, Ferran; eu, Errando; it, Ferdinando; la, Ferdinandus; es, Fernando; 10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), also called Ferdinand the Catholic (Spanish: ''el Católico''), was King of Aragon and Sardinia from ...
gave a monopoly of the sulfur industry to a French firm, violating an earlier 1816 trade agreement with Britain. A peaceful solution was eventually negotiated by France.
In 1867, elemental sulfur was discovered in underground deposits in Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
and Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
. The highly successful Frasch process was developed to extract this resource.
In the late 18th century, furniture
Furniture refers to movable objects intended to support various human activities such as seating (e.g., stools, chairs, and sofas), eating (tables), storing items, eating and/or working with an item, and sleeping (e.g., beds and hammocks). Fu ...
makers used molten sulfur to produce decorative inlays. Molten sulfur is sometimes still used for setting steel bolts into drilled concrete holes where high shock resistance is desired for floor-mounted equipment attachment points. Pure powdered sulfur was used as a medicinal tonic and laxative.
With the advent of the contact process
The contact process is the current method of producing sulfuric acid in the high concentrations needed for industrial processes. Platinum was originally used as the catalyst for this reaction; however, as it is susceptible to reacting with arsenic ...
, the majority of sulfur today is used to make sulfuric acid for a wide range of uses, particularly fertilizer.
In recent times, the main source of sulfur has become petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
. This is due to the requirement to remove sulfur from fuels in order to prevent acid rain
Acid rain is rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists between 6.5 and 8.5, but acid ...
, and has resulted in a surplus of sulfur.
Spelling and etymology
''Sulfur'' is derived from the Latin word ', which wasHellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in th ...
to ' in the erroneous belief that the Latin word came from Greek. This spelling was later reinterpreted as representing an /f/ sound and resulted in the spelling ', which appears in Latin toward the end of the Classical period. The true Ancient Greek word for sulfur, , ''theîon'' (from earlier , ''théeion''), is the source of the international chemical prefix ''thio-
The prefix thio-, when applied to a chemical, such as an ion, means that an oxygen atom in the compound has been replaced by a sulfur atom. This term is often used in organic chemistry. For example, from the word ''ether,'' referring to an oxyg ...
''. The Modern Standard Greek word for sulfur is θείο, ''theío''.
In 12th-century Anglo-French
Anglo-French (or sometimes Franco-British) may refer to:
*France–United Kingdom relations
*Anglo-Norman language or its decendants, varieties of French used in medieval England
*Anglo-Français and Français (hound), an ancient type of hunting d ...
, it was '. In the 14th century, the erroneously Hellenized Latin ' was restored in Middle English '. By the 15th century, both full Latin spelling variants ''sulfur'' and ''sulphur'' became common in English. The parallel ''f~ph'' spellings continued in Britain until the 19th century, when the word was standardized as ''sulphur''. On the other hand, ''sulfur'' was the form chosen in the United States, whereas Canada uses both.
The IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
adopted the spelling ''sulfur'' in 1990 or 1971, depending on the source cited, as did the Nomenclature Committee of the Royal Society of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Ro ...
in 1992, restoring the spelling ''sulfur'' to Britain. Oxford Dictionaries note that "in chemistry and other technical uses ... the ''-f-'' spelling is now the standard form for this and related words in British as well as US contexts, and is increasingly used in general contexts as well."
Production
 Sulfur may be found by itself and historically was usually obtained in this form;
Sulfur may be found by itself and historically was usually obtained in this form; pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), lust ...
has also been a source of sulfur. In volcanic regions in Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, in ancient times, it was found on the surface of the Earth, and the " Sicilian process" was used: sulfur deposits were piled and stacked in brick kilns built on sloping hillsides, with airspaces between them. Then, some sulfur was pulverized, spread over the stacked ore and ignited, causing the free sulfur to melt down the hills. Eventually the surface-borne deposits played out, and miners excavated veins that ultimately dotted the Sicilian landscape with labyrinthine mines. Mining was unmechanized and labor-intensive, with pickmen freeing the ore from the rock, and mine-boys or '' carusi'' carrying baskets of ore to the surface, often through a mile or more of tunnels. Once the ore was at the surface, it was reduced and extracted in smelting ovens. The conditions in Sicilian sulfur mines were horrific, prompting Booker T. Washington
Booker Taliaferro Washington (April 5, 1856November 14, 1915) was an American educator, author, orator, and adviser to several presidents of the United States. Between 1890 and 1915, Washington was the dominant leader in the African-American c ...
to write "I am not prepared just now to say to what extent I believe in a physical hell in the next world, but a sulphur mine in Sicily is about the nearest thing to hell that I expect to see in this life."
 Elemental sulfur was extracted from
Elemental sulfur was extracted from salt dome
A salt dome is a type of structural dome formed when salt (or other evaporite minerals) intrudes into overlying rocks in a process known as diapirism. Salt domes can have unique surface and subsurface structures, and they can be discovered using ...
s (in which it sometimes occurs in nearly pure form) until the late 20th century. Sulfur is now produced as a side product of other industrial processes such as in oil refining, in which sulfur is undesired. As a mineral, native sulfur under salt domes is thought to be a fossil mineral resource, produced by the action of anaerobic bacteria on sulfate deposits. It was removed from such salt-dome mines mainly by the Frasch process. In this method, superheated water was pumped into a native sulfur deposit to melt the sulfur, and then compressed air returned the 99.5% pure melted product to the surface. Throughout the 20th century this procedure produced elemental sulfur that required no further purification. Due to a limited number of such sulfur deposits and the high cost of working them, this process for mining sulfur has not been employed in a major way anywhere in the world since 2002.
Today, sulfur is produced from petroleum, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, and related fossil resources, from which it is obtained mainly as hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
. Organosulfur compound
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfu ...
s, undesirable impurities in petroleum, may be upgraded by subjecting them to hydrodesulfurization
Hydrodesulfurization (HDS) is a catalytic chemical process widely used to remove sulfur (S) from natural gas and from refined petroleum products, such as gasoline or petrol, jet fuel, kerosene, diesel fuel, and fuel oils. The purpose of remov ...
, which cleaves the C–S bonds:
:R-S-R + 2 H2 → 2 RH + H2S
The resulting hydrogen sulfide from this process, and also as it occurs in natural gas, is converted into elemental sulfur by the Claus process
The Claus process is the most significant gas desulfurizing process, recovering elemental sulfur from gaseous hydrogen sulfide. First patented in 1883 by the chemist Carl Friedrich Claus, the Claus process has become the industry standard.
Th ...
. This process entails oxidation of some hydrogen sulfide to sulfur dioxide and then the comproportionation
Comproportionation or synproportionation is a chemical reaction where two reactants containing the same element but with different oxidation numbers, form a compound having an intermediate oxidation number. It is the opposite of disproportionation. ...
of the two:
:3 O2 + 2 H2S → 2 SO2 + 2 H2O
:SO2 + 2 H2S → 3 S + 2 H2O
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, Canada. Another way of storing sulfur is as a binder for concrete, the resulting product having many desirable properties (see sulfur concrete).
Sulfur is still mined from surface deposits in poorer nations with volcanoes, such as Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, and worker conditions have not improved much since Booker T. Washington
Booker Taliaferro Washington (April 5, 1856November 14, 1915) was an American educator, author, orator, and adviser to several presidents of the United States. Between 1890 and 1915, Washington was the dominant leader in the African-American c ...
's days.
The world production of sulfur in 2011 amounted to 69 million tonnes (Mt), with more than 15 countries contributing more than 1 Mt each. Countries producing more than 5 Mt are China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
(9.6), the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
(8.8), Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
(7.1) and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
(7.1). Production has been slowly increasing from 1900 to 2010; the price was unstable in the 1980s and around 2010.
Applications
Sulfuric acid
Elemental sulfur is used mainly as a precursor to other chemicals. Approximately 85% (1989) is converted tosulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
(H2SO4):
:2 S + 3 O2 + 2 H2O → 2 H2SO4
 In 2010, the United States produced more sulfuric acid than any other inorganic industrial chemical. The principal use for the acid is the extraction of phosphate ores for the production of fertilizer manufacturing. Other applications of sulfuric acid include oil refining, wastewater processing, and mineral extraction.
In 2010, the United States produced more sulfuric acid than any other inorganic industrial chemical. The principal use for the acid is the extraction of phosphate ores for the production of fertilizer manufacturing. Other applications of sulfuric acid include oil refining, wastewater processing, and mineral extraction.
Other important sulfur chemistry
Sulfur reacts directly with methane to givecarbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is a neurotoxic, colorless, volatile liquid with the formula and structure . The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non ...
, which is used to manufacture cellophane
Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. Its low permeability to air, oils, greases, bacteria, and liquid water makes it useful for food packaging. Cellophane is highly permeable to water vapour, but may be coated w ...
and rayon
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. It is also called viscose. Many types and grades of viscose f ...
. One of the uses of elemental sulfur is in vulcanization
Vulcanization (British: Vulcanisation) is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to include ...
of rubber, where polysulfide
Polysulfides are a class of chemical compounds containing chains of sulfur atoms. There are two main classes of polysulfides: inorganic and organic. Among the inorganic polysulfides, there are ones which contain anions, which have the general formu ...
chains crosslink organic polymers. Large quantities of sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion (or the sulfate(IV) ion, from its correct systematic name), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid ( sulfurous acid) is elusive, its salts are wide ...
s are used to bleach
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color (whitening) from a fabric or fiber or to clean or to remove stains in a process called bleaching. It often refers specifically, to ...
paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed ...
and to preserve dried fruit
Dried fruit is fruit from which the majority of the original water content has been removed either naturally, through sun drying, or through the use of specialized dryers or dehydrators. Dried fruit has a long tradition of use dating back to th ...
. Many surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming ...
s and detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are more ...
s (e.g. sodium lauryl sulfate
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) or sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), sometimes written sodium laurilsulfate, is an organic compound with the formula . It is an anionic surfactant used in many cleaning and hygiene products. This compound is the sodium salt ...
) are sulfate derivatives. Calcium sulfate
Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Pari ...
, gypsum, (CaSO4·2H2O) is mined on the scale of 100 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s each year for use in Portland cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19th c ...
and fertilizers.
When silver-based photography
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed ...
was widespread, sodium and ammonium thiosulfate
Thiosulfate ( IUPAC-recommended spelling; sometimes thiosulphate in British English) is an oxyanion of sulfur with the chemical formula . Thiosulfate also refers to the compounds containing this anion, which are the salts of thiosulfuric acid, ...
were widely used as "fixing agents". Sulfur is a component of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). ...
("black powder").
Fertilizer
Amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s synthesized by living organisms
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
such as methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
and cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
contain organosulfur
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur ...
groups (thioester
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the functional group . They are analogous to carboxylate esters () with the sulfur in the thioester playing the role of the linking oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by t ...
and thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl gro ...
respectively). The antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricant ...
glutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, pero ...
protecting many living organisms against free radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing.
Ageing
Ailments of unknown cause
Biogerontology
Biological processes
Causes of death
Cellular processes
Gerontology
Life extension
Metabo ...
s and oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily Detoxification, detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances ...
also contains organic sulfur. Some crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydroponic ...
s such as onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion ...
and garlic
Garlic (''Allium sativum'') is a species of bulbous flowering plant in the genus ''Allium''. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, Allium fistulosum, Welsh onion and Allium chinense, Chinese onion. It is native to South A ...
also produce different organosulfur compounds
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur ...
such as syn-propanethial-S-oxide
''syn''-Propanethial ''S''-oxide (or (''Z'')-propanethial ''S''-oxide), a member of a class of organosulfur compounds known as thiocarbonyl ''S''-oxides (formerly " sulfines"), is a volatile liquid that acts as a lachrymatory agent (triggers tear ...
responsible of lacrymal irritation (onions), or diallyl disulfide
Diallyl disulfide (DADS or 4,5-dithia-1,7-octadiene) is an organosulfur compound derived from garlic and a few other genus ''Allium'' plants. Along with diallyl trisulfide and diallyl tetrasulfide, it is one of the principal components of the dist ...
and allicin
Allicin is an organosulfur compound obtained from garlic, a species in the family Alliaceae. It was first isolated and studied in the laboratory by Chester J. Cavallito and John Hays Bailey in 1944. When fresh garlic is chopped or crushed, the ...
(garlic). Sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ar ...
s, commonly found in soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former te ...
s and groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
s are often a sufficient natural source of sulfur for plants and bacteria. Atmospheric deposition of sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activ ...
(SO2) is also a common artificial source ( coal combustion) of sulfur for the soils. Under normal circumstances, in most agricultural soils, sulfur is not a limiting nutrient
A limiting factor is a variable of a system that causes a noticeable change in output or another measure of a type of system. The limiting factor is in a pyramid shape of organisms going up from the producers to consumers and so on. A factor not l ...
for plants and microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s (see the Liebig's law of the minimum#Liebig's barrel). However, in some circumstance, soils can be depleted in sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ar ...
, e.g. if this later is leached by meteoric water
Meteoric water is the water derived from precipitation (snow and rain). This includes water from lakes, rivers, and icemelts, which all originate from precipitation indirectly. While the bulk of rainwater or meltwater from snow and ice reaches the ...
(rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
) or if the requirements in sulfur for some types of crops are high. This explains that sulfur is increasingly recognized and used as a component of fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s. The most important form of sulfur for fertilizer is the calcium sulfate
Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Pari ...
, commonly found in nature as the mineral gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. ...
(CaSO4·2H2O). Elemental sulfur is hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, th ...
(not soluble in water) and cannot be used directly by plants. Elemental sulfur (ES) is sometimes mixed with bentonite
Bentonite () is an absorbent swelling clay consisting mostly of montmorillonite (a type of smectite) which can either be Na-montmorillonite or Ca-montmorillonite. Na-montmorillonite has a considerably greater swelling capacity than Ca-mon ...
to amend depleted soils for crops with high requirement in organo-sulfur. Over time, oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
abiotic
In biology and ecology, abiotic components or abiotic factors are non-living chemical and physical parts of the environment that affect living organisms and the functioning of ecosystems. Abiotic factors and the phenomena associated with them under ...
processes with atmospheric
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
and soil bacteria can oxidize
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
and convert elemental sulfur to soluble derivatives, which can then be used by microorganisms and plants. Sulfur improves the efficiency of other essential plant nutrients, particularly nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
and phosphorus. Biologically produced sulfur particles are naturally hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are no ...
due to a biopolymer
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, cl ...
coating and are easier to disperse over the land in a spray of diluted slurry, resulting in a faster uptake by plants.
The plants requirement for sulfur equals or exceeds the requirement for phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
. It is an essential nutrient for plant growth, root nodule formation of legumes, and immunity and defense systems. Sulfur deficiency has become widespread in many countries in Europe. Because atmospheric inputs of sulfur continue to decrease, the deficit in the sulfur input/output is likely to increase unless sulfur fertilizers are used. Atmospheric inputs of sulfur decrease because of actions taken to limit acid rain
Acid rain is rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists between 6.5 and 8.5, but acid ...
s.
Fungicide and pesticide
 Elemental sulfur is one of the oldest fungicides and pesticides. "Dusting sulfur", elemental sulfur in powdered form, is a common fungicide for grapes, strawberry, many vegetables and several other crops. It has a good efficacy against a wide range of powdery mildew diseases as well as black spot. In organic production, sulfur is the most important fungicide. It is the only fungicide used in organically farmed apple production against the main disease
Elemental sulfur is one of the oldest fungicides and pesticides. "Dusting sulfur", elemental sulfur in powdered form, is a common fungicide for grapes, strawberry, many vegetables and several other crops. It has a good efficacy against a wide range of powdery mildew diseases as well as black spot. In organic production, sulfur is the most important fungicide. It is the only fungicide used in organically farmed apple production against the main disease apple scab
Apple scab is a common disease of plants in the rose family ( Rosaceae) that is caused by the ascomycete fungus ''Venturia inaequalis''. While this disease affects several plant genera, including ''Sorbus, Cotoneaster,'' and '' Pyrus'', it is m ...
under colder conditions. Biosulfur (biologically produced elemental sulfur with hydrophilic characteristics) can also be used for these applications.
Standard-formulation dusting sulfur is applied to crops with a sulfur duster or from a dusting plane. Wettable sulfur is the commercial name for dusting sulfur formulated with additional ingredients to make it water miscible
Miscibility () is the property of two substances to mix in all proportions (that is, to fully dissolve in each other at any concentration), forming a homogeneous mixture (a solution). The term is most often applied to liquids but also applies ...
. It has similar applications and is used as a fungicide
Fungicides are biocidal chemical compounds or biological organisms used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. A fungistatic inhibits their growth. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in critical losses of yield, quality, ...
against mildew
Mildew is a form of fungus. It is distinguished from its closely related counterpart, mould, largely by its colour: moulds appear in shades of black, blue, red, and green, whereas mildew is white. It appears as a thin, superficial growth consi ...
and other mold-related problems with plants and soil.
Elemental sulfur powder is used as an "organic
Organic may refer to:
* Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity
* Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ
Chemistry
* Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product ...
" (i.e., "green") insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
(actually an acaricide
Acaricides are pesticides that kill members of the arachnid subclass ''Acari'', which includes ticks and mites.
Acaricides are used both in medicine and agriculture, although the desired selective toxicity differs between the two fields.
Termino ...
) against tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s and mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evid ...
s. A common method of application is dusting the clothing or limbs with sulfur powder.
A diluted solution of lime sulfur
In horticulture, lime sulfur (British spelling lime sulphur) is mainly a mixture of calcium polysulfides and thiosulfate (plus other reaction by-products as sulfite and sulfate) formed by reacting calcium hydroxide with elemental sulfur, used in p ...
(made by combining calcium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed or slaked with water. It has m ...
with elemental sulfur in water) is used as a dip for pets to destroy ringworm (fungus), mange
Mange is a type of skin disease caused by parasitic mites. Because various species of mites also infect plants, birds and reptiles, the term "mange", or colloquially "the mange", suggesting poor condition of the skin and fur due to the infection ...
, and other dermatoses
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this s ...
and parasites
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of lif ...
.
Sulfur candles of almost pure sulfur were burned to fumigate structures and wine barrels, but are now considered too toxic for residences.
Pharmaceuticals
Sulfur (specificallyoctasulfur
Octasulfur is an inorganic substance with the chemical formula . It is an odourless and tasteless yellow solid, and is a major industrial chemical. It is the most common allotrope of sulfur and occurs widely in nature.Steudel, R., "Homocyclic Sul ...
, S8) is used in pharmaceutical skin preparations for the treatment of acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, black ...
and other conditions. It acts as a keratolytic
Keratolytic () therapy is a type of medical treatment to remove warts, calluses and other lesions in which the epidermis produces excess skin. In this therapy, acidic topical medicines, such as Whitfield's ointment or Jessner's solution, are ap ...
agent and also kills bacteria, fungi, scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious skin infestation by the mite ''Sarcoptes scabiei''. The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the skin ...
mites, and other parasites. Precipitated sulfur and colloidal sulfur are used, in form of lotion
Lotion is a low-viscosity topical preparation intended for application to the skin. By contrast, creams and gels have higher viscosity, typically due to lower water content. Lotions are applied to external skin with bare hands, a brush, a clean ...
s, creams, powders, soaps, and bath additives, for the treatment of acne vulgaris
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and po ...
, acne rosacea
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and p ...
, and seborrhoeic dermatitis
Seborrhoeic dermatitis, sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea, is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include red, scaly, greasy, itchy, and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the ...
.
Many drugs contain sulfur. Early examples include antibacterial sulfonamides
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. ...
, known as ''sulfa drugs''. A more recent example is mucolytic acetylcysteine
Acetylcysteine, also known as ''N''-acetylcysteine (NAC), is a medication that is used to treat paracetamol overdose and to loosen thick mucus in individuals with chronic bronchopulmonary disorders like pneumonia and bronchitis. It has been used ...
. Sulfur is a part of many bacterial defense molecules. Most β-lactam
A beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring is a four-membered lactam. A ''lactam'' is a cyclic amide, and ''beta''-lactams are named so because the nitrogen atom is attached to the Β carbon, β-carbon atom relative to the carbonyl. The simplest β-lactam p ...
antibiotics, including the penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
s, cephalosporins
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics ...
and monobactam
Monobactams are monocyclic and bacterially-produced β-lactam antibiotics. The β-lactam ring is not fused to another ring, in contrast to most other β-lactams. Monobactams are effective only against aerobic Gram-negative bacteria (e.g., ''Nei ...
s contain sulfur.
Batteries
Due to their high energy density and the availability of sulfur, there is ongoing research in creating rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries. Until now, carbonate electrolytes have caused failures in such batteries after a single cycle. In February 2022, researchers atDrexel University
Drexel University is a private research university with its main campus in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Drexel's undergraduate school was founded in 1891 by Anthony J. Drexel, a financier and philanthropist. Founded as Drexel Institute of Art, S ...
have not only created a prototypical battery that lasted 4000 recharge cycles, but also found the first monoclinic gamma sulfur that remained stable below 95 degrees Celsius.
Biological role
Sulfur is an essential component of all livingcells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
. It is the eighth most abundant element in the human body by weight, about equal in abundance to potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosphe ...
, and slightly greater than sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable iso ...
and chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate betwee ...
. A human body contains about 140 grams of sulfur. The main dietary source of sulfur for humans is sulfur-containing amino-acids, which can be found in plant and animal proteins.
Transferring sulfur between inorganic and biomolecules
In the 1880s, while studying Beggiatoa (a bacterium living in a sulfur rich environment),Sergei Winogradsky
Sergei Nikolaievich Winogradsky (or Vinohradsky; published under the name of Sergius Winogradsky or M. S. Winogradsky from Ukrainian Mykolayovych Serhiy; uk, Сергій Миколайович Виноградський; 1 September 1856 – ...
found that it oxidized hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
(H2S) as an energy source, forming intracellular sulfur droplets. Winogradsky referred to this form of metabolism as inorgoxidation (oxidation of inorganic compounds). Another contributor, who continued to study it was Selman Waksman
Selman Abraham Waksman (July 22, 1888 – August 16, 1973) was a Jewish Russian-born American inventor, Nobel Prize laureate, biochemist and microbiologist whose research into the decomposition of organisms that live in soil enabled the discov ...
. Primitive bacteria that live around deep ocean volcanic vents
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
oxidize hydrogen sulfide for their nutrition, as discovered by Robert Ballard
Robert Duane Ballard (born June 30, 1942) is an American retired Navy officer and a professor of oceanography at the University of Rhode Island who is most noted for his work in underwater archaeology: maritime archaeology and archaeology of ...
.
Sulfur oxidizers can use as energy sources reduced sulfur compounds, including hydrogen sulfide, elemental sulfur, sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion (or the sulfate(IV) ion, from its correct systematic name), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid ( sulfurous acid) is elusive, its salts are wide ...
, thiosulfate
Thiosulfate ( IUPAC-recommended spelling; sometimes thiosulphate in British English) is an oxyanion of sulfur with the chemical formula . Thiosulfate also refers to the compounds containing this anion, which are the salts of thiosulfuric acid, ...
, and various polythionates (e.g., tetrathionate
The tetrathionate anion, , is a sulfur oxoanion derived from the compound tetrathionic acid, H2S4O6. Two of the sulfur atoms present in the ion are in oxidation state 0 and two are in oxidation state +5. Alternatively, the compound can be viewed ...
). They depend on enzymes such as sulfur oxygenase and sulfite oxidase
Sulfite oxidase () is an enzyme in the mitochondria of all eukaryotes, with exception of the yeasts. It oxidizes sulfite to sulfate and, via cytochrome c, transfers the electrons produced to the electron transport chain, allowing generation o ...
to oxidize sulfur to sulfate. Some lithotroph
Lithotrophs are a diverse group of organisms using an inorganic substrate (usually of mineral origin) to obtain reducing equivalents for use in biosynthesis (e.g., carbon dioxide fixation) or energy conservation (i.e., ATP production) via aerobic ...
s can even use the energy contained in sulfur compounds to produce sugars, a process known as chemosynthesis
In biochemistry, chemosynthesis is the biological conversion of one or more carbon-containing molecules (usually carbon dioxide or methane) and nutrients into organic matter using the oxidation of inorganic compounds (e.g., hydrogen gas, hydro ...
. Some bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
and archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
use hydrogen sulfide in place of water as the electron donor
In chemistry, an electron donor is a chemical entity that donates electrons to another compound. It is a reducing agent that, by virtue of its donating electrons, is itself oxidized in the process.
Typical reducing agents undergo permanent chem ...
in chemosynthesis, a process similar to photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
that produces sugars and uses oxygen as the electron acceptor
An electron acceptor is a chemical entity that accepts electrons transferred to it from another compound. It is an oxidizing agent that, by virtue of its accepting electrons, is itself reduced in the process. Electron acceptors are sometimes mista ...
. Sulfur-based chemosynthesis may be simplifiedly compared with photosynthesis:
: H2S +CO2 → sugars + S
: H2O + CO2 → sugars + O2
There are bacteria combining these two ways of nutrition: green sulfur bacteria
The green sulfur bacteria are a phylum of obligately anaerobic photoautotrophic bacteria that metabolize sulfur.
Green sulfur bacteria are nonmotile (except ''Chloroherpeton thalassium'', which may glide) and capable of anoxygenic photosynthesi ...
and purple sulfur bacteria
The purple sulfur bacteria (PSB) are part of a group of Pseudomonadota capable of photosynthesis, collectively referred to as purple bacteria. They are anaerobic or microaerophilic, and are often found in stratified water environments including ...
. Also sulfur-oxidizing bacteria can go into symbiosis with larger organisms, enabling the later to use hydrogen sulfide as food to be oxidized. Example: the giant tube worm
''Riftia pachyptila'', commonly known as the giant tube worm and less commonly known as the Giant beardworm, is a marine invertebrate in the phylum Annelida (formerly grouped in phylum Pogonophora and Vestimentifera) related to tube worms ...
.
There are sulfate-reducing bacteria, that, by contrast, "breathe sulfate" instead of oxygen. They use organic compounds or molecular hydrogen as the energy source. They use sulfur as the electron acceptor, and reduce various oxidized sulfur compounds back into sulfide, often into hydrogen sulfide. They can grow on other partially oxidized sulfur compounds (e.g. thiosulfates, thionates, polysulfides, sulfites).
There are studies pointing that many deposits of native sulfur in places that were the bottom of Tethys Ocean, the ancient oceans have biological origin. These studies indicate that this native sulfur have been obtained through biological activity, but what is responsible for that (sulfur-oxidizing bacteria or sulfate-reducing bacteria) is still unknown for sure.
Sulfur is absorbed by plants roots from soil as sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ar ...
and transported as a phosphate ester. Sulfate is reduced to sulfide via sulfite before it is incorporated into cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
and other organosulfur compounds.
: SO42− → SO32− → H2S → cysteine (thiol) → methionine (thioether)
While the plants' role in transferring sulfur to animals by food chains is more or less understood, the role of sulfur bacteria is just getting investigated.
Protein and organic metabolites
In all forms of life, most of the sulfur is contained in two proteinogenic amino acids (cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
and methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
), thus the element is present in all proteins that contain these amino acids, as well as in respective peptides. Some of the sulfur is comprised in certain metabolites — many of which are Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors, — and sulfated polysaccharides of connective tissue (chondroitin sulfates, heparin).
 Proteins, to execute their Protein#Cellular functions, biological function, need to have specific space geometry. Formation of this geometry is performed in a process called protein folding, and is provided by intra- and inter-molecular bonds. The process has several stages. While at premier stages a polypeptide chain folds due to hydrogen bonds, at later stages folding is provided (apart from hydrogen bonds) by covalent bonds between two sulfur atoms of two cysteine residues (so called disulfide bridges) at different places of a chain (tertriary protein structure) as well as between two cysteine residues in two separated protein subunits (quaternary protein structure). Both structures easily may be seen in insulin. As the bond energy of a covalent disulfide bridge is higher than the energy of a Coordinate covalent bond, coordinate bond or hydrophylic either hydrophobic interaction, the higher disulfide bridges content leads the higher energy needed for protein Denaturation (biochemistry), denaturation. In general disulfide bonds are necessary in proteins functioning outside cellular space, and they do not change proteins' conformation (geometry), but serve as its stabilizers. Within cytoplasm cysteine residues of proteins are saved in reduced state (i.e. in -SH form) by thioredoxins.
This property manifests in following examples. Lysozyme is stable enough to be applied as a drug. Feathers and hair have relative strength, and consisting in them
Proteins, to execute their Protein#Cellular functions, biological function, need to have specific space geometry. Formation of this geometry is performed in a process called protein folding, and is provided by intra- and inter-molecular bonds. The process has several stages. While at premier stages a polypeptide chain folds due to hydrogen bonds, at later stages folding is provided (apart from hydrogen bonds) by covalent bonds between two sulfur atoms of two cysteine residues (so called disulfide bridges) at different places of a chain (tertriary protein structure) as well as between two cysteine residues in two separated protein subunits (quaternary protein structure). Both structures easily may be seen in insulin. As the bond energy of a covalent disulfide bridge is higher than the energy of a Coordinate covalent bond, coordinate bond or hydrophylic either hydrophobic interaction, the higher disulfide bridges content leads the higher energy needed for protein Denaturation (biochemistry), denaturation. In general disulfide bonds are necessary in proteins functioning outside cellular space, and they do not change proteins' conformation (geometry), but serve as its stabilizers. Within cytoplasm cysteine residues of proteins are saved in reduced state (i.e. in -SH form) by thioredoxins.
This property manifests in following examples. Lysozyme is stable enough to be applied as a drug. Feathers and hair have relative strength, and consisting in them keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
is considered indigestible by most organisms. However, there are fungi and bacteria containing keratinase, and are able to destruct keratin.
Many important cellular enzymes use prosthetic groups ending with -SH moieties to handle reactions involving acyl-containing biochemicals: two common examples from basic metabolism are coenzyme A and alpha-lipoic acid. Cysteine-related metabolites homocysteine and taurine
Taurine (), or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is an organic compound that is widely distributed in animal tissues. It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine, and accounts for up to 0.1% of total human body weight. It ...
are other sulfur-containing amino acids that are similar in structure, but not coded by DNA, and are not part of the primary structure of proteins, take part in various locations of mammalian physiology. Two of the 13 classical vitamins, biotin
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', bor ...
, and thiamine
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient, that cannot be made in the body. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thi ...
, contain sulfur, and serve as cofactors to several enzymes.
In intracellular chemistry, sulfur operates as a carrier of reducing hydrogen and its electrons for cellular repair of oxidation. Reduced glutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, pero ...
, a sulfur-containing tripeptide, is a reducing agent through its sulfhydryl (-SH) moiety derived from cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
.
Methanogenesis, the route to most of the world's methane, is a multistep biochemical transformation of carbon dioxide. This conversion requires several organosulfur cofactors. These include coenzyme M, CH3SCH2CH2SO3−, the immediate precursor to methane.
Metalloproteins and inorganic cofactors
Metalloproteins — in which the active site is a transition metal ion (or metal-sulfide cluster) often coordinated by sulfur atoms of cysteine residues — are essential components of enzymes involved in electron transfer processes. Examples include plastocyanin (Cu2+) and nitrous-oxide reductase, nitrous oxide reductase (Cu–S). The function of these enzymes is dependent on the fact that the transition metal ion can undergo redox reactions. Other examples include many zinc proteins, as well as iron–sulfur clusters. Most pervasive are the ferrodoxins, which serve as electron shuttles in cells. In bacteria, the important nitrogenase enzymes contains an Fe–Mo–S cluster and is a catalyst that performs the important function of nitrogen fixation, converting atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia that can be used by microorganisms and plants to make proteins, DNA, RNA, alkaloids, and the other organic nitrogen compounds necessary for life. :
Deficiency
In humans methionine is an essential amino acid, cysteine is conditionally essential and may be synthesized from non-essential serine (sulfur donator would be methionine in this case). Dietary deficiency rarely happens in common conditions. Artificial methionine deficiency is attempted to apply in cancer treatment, but the method is still potentially dangerous. There is a rare fatal genetic disease connected withsulfite oxidase
Sulfite oxidase () is an enzyme in the mitochondria of all eukaryotes, with exception of the yeasts. It oxidizes sulfite to sulfate and, via cytochrome c, transfers the electrons produced to the electron transport chain, allowing generation o ...
impairment an enzyme metabolizing sulfur-containing amino acids.
Precautions
Toxicity of sulfur compounds
Most of the solublesulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ar ...
salts, such as Epsom salts, are non-toxic. Soluble sulfate salts are poorly absorbed and laxative. When injected parenterally, they are freely filtered by the kidneys and eliminated with very little toxicity in multi-gram amounts. Aluminium sulfate is used in the purification of drinking water, wastewater treatment plants and papermaking.
When sulfur burns in air, it produces sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activ ...
. In water, this gas produces sulfurous acid and sulfites; sulfites are antioxidants that inhibit growth of aerobic bacteria and a useful food additive in small amounts. At high concentrations these acids harm the human lungs, lungs, human eyes, eyes, or other biological tissue, tissues. In organisms without lungs such as insects or plants, sulfite in high concentration prevents respiration (physiology), respiration.
Sulfur trioxide (made by catalysis from sulfur dioxide) and sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
are similarly highly acidic and corrosive in the presence of water. Sulfuric acid is a strong dehydrating agent that can strip available water molecules and water components from sugar and organic tissue.
The burning of coal and/or petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
by industry and power plants generates sulfur dioxide (SO2) that reacts with atmospheric water and oxygen to produce sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and sulfurous acid (H2SO3). These acids are components of acid rain
Acid rain is rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists between 6.5 and 8.5, but acid ...
, lowering the pH of soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former te ...
and freshwater bodies, sometimes resulting in substantial damage to the environment (biophysical), environment and chemical weathering of statues and structures. Fuel standards increasingly require that fuel producers extract sulfur from fossil fuels to prevent acid rain formation. This extracted and refined sulfur represents a large portion of sulfur production. In coal-fired power plants, flue gases are sometimes purified. More modern power plants that use synthesis gas extract the sulfur before they burn the gas.
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
is about one-half as toxic as hydrogen cyanide, and intoxicates by the same mechanism (inhibition of the respiratory enzyme cytochrome oxidase), though hydrogen sulfide is less likely to cause sudden poisonings from small inhaled amounts (near its permissible exposure limit — PEL — of 20 ppm) because of its disagreeable odor. However, its presence in ambient air at concentration over 100-150 ppm quickly deadens the sense of smell, and a victim may breathe increasing quantities without noticing until severe symptoms cause death. Dissolved sulfide and hydrosulfide salts are toxic by the same mechanism.
See also
*Blue lava *Stratospheric sulfur aerosols *Sulfur assimilation *Ultra-low sulfur dieselReferences
Further reading
External links
Sulfur
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
Atomic Data for Sulfur
NIST Physical Measurement Laboratory
Sulfur phase diagram
, Introduction to Chemistry for Ages 13–17
*[http://extoxnet.orst.edu/pips/sulfur.htm Sulfur and its use as a pesticide]
The Sulphur Institute
{{Authority control Sulfur, Chemical elements Chalcogens Reactive nonmetals Polyatomic nonmetals Agricultural chemicals Anti-acne preparations Dietary minerals Industrial minerals Inorganic polymers Native element minerals Orthorhombic minerals Minerals in space group 70 Pyrotechnic fuels Chemical elements with primitive orthorhombic structure