|
Alunite
Alunite is a hydroxylated aluminium potassium sulfate mineral, formula K Al3( S O4)2(O H)6. It was first observed in the 15th century at Tolfa, near Rome, where it was mined for the manufacture of alum. First called ''aluminilite'' by J.C. Delamétherie in 1797, this name was contracted by François Beudant three decades later to alunite. Alunite crystals morphologically are rhombohedron, rhombohedra with interfacial angles of 90° 50', causing them to resemble cubes. Crystal symmetry is trigonal. Minute glistening crystals have also been found loose in cavities in altered rhyolite. Alunite varies in color from white to yellow gray. The hardness on the Mohs scale is 4 and the specific gravity is between 2.6 and 2.8. It is insoluble in water or weak acids, but soluble in sulfuric acid. Sodium can substitute for potassium in the mineral, and when the sodium content is high, is called natroalunite. Alunite is an analog of jarosite, where aluminium replaces Fe3+. Alunit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarosite
Jarosite is a basic hydrous sulfate of potassium and ferric iron (Fe-III) with a chemical formula of KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6. This sulfate mineral is formed in ore deposits by the oxidation of iron sulfides. Jarosite is often produced as a byproduct during the purification and refining of zinc and is also commonly associated with acid mine drainage and acid sulfate soil environments. Physical properties Jarosite has a trigonal crystal structure and is brittle, with basal cleavage, a hardness of 2.5-3.5, and a specific gravity of 3.15-3.26. It is translucent to opaque with a vitreous to dull luster, and is colored dark yellow to yellowish-brown. It can sometimes be confused with limonite or goethite with which it commonly occurs in the gossan (oxidized cap over an ore body). Jarosite is an iron analogue of the potassium aluminium sulfate, alunite. Solid solution series The alunite supergroup includes the alunite, jarosite, beudantite, crandallite and florencite subgroups. The alu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
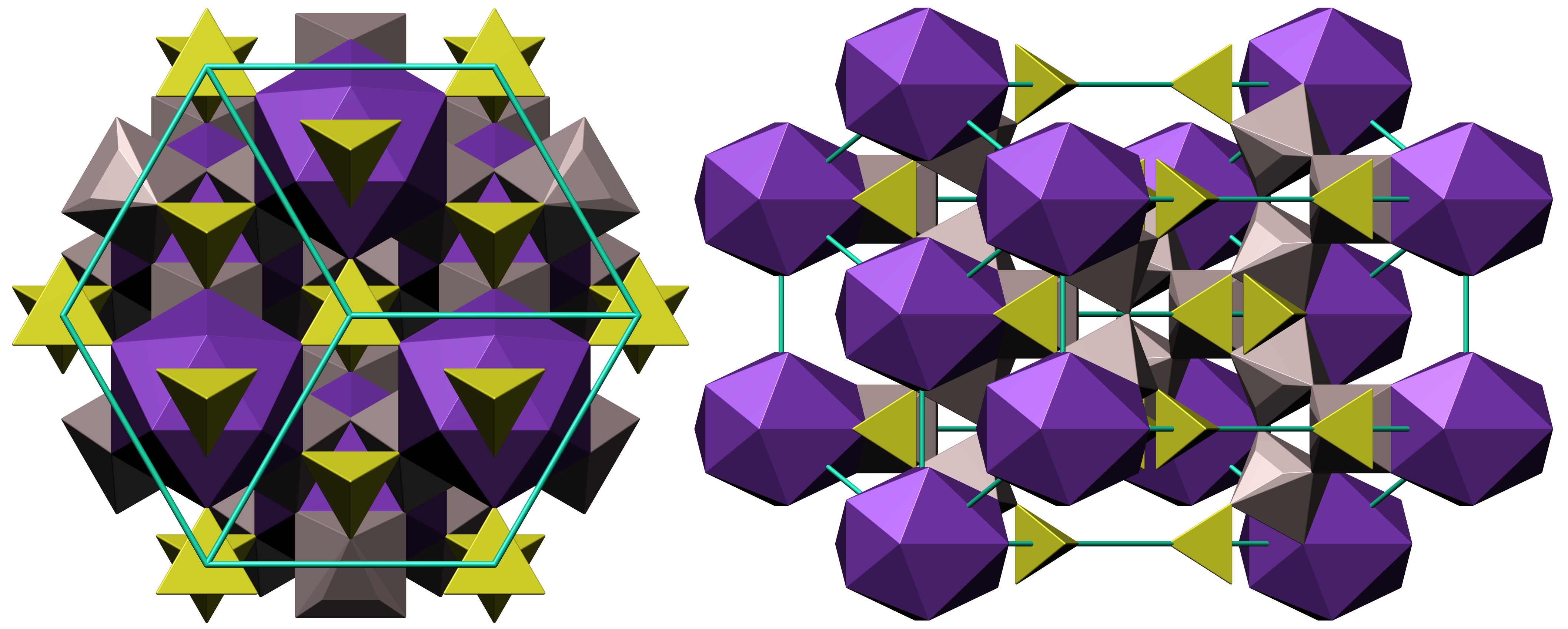
Alunite Crystal Structure
Alunite is a hydroxylated aluminium potassium sulfate mineral, formula K Al3( S O4)2(O H)6. It was first observed in the 15th century at Tolfa, near Rome, where it was mined for the manufacture of alum. First called ''aluminilite'' by J.C. Delamétherie in 1797, this name was contracted by François Beudant three decades later to alunite. Alunite crystals morphologically are rhombohedron, rhombohedra with interfacial angles of 90° 50', causing them to resemble cubes. Crystal symmetry is trigonal. Minute glistening crystals have also been found loose in cavities in altered rhyolite. Alunite varies in color from white to yellow gray. The hardness on the Mohs scale is 4 and the specific gravity is between 2.6 and 2.8. It is insoluble in water or weak acids, but soluble in sulfuric acid. Sodium can substitute for potassium in the mineral, and when the sodium content is high, is called natroalunite. Alunite is an analog of jarosite, where aluminium replaces Fe3+. Alunite o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alunite Basic Hydrous Aluminum Potassium Sulfate Marysvale Piute County Utah 2324
Alunite is a hydroxylated aluminium potassium sulfate mineral, formula K Al3( S O4)2(O H)6. It was first observed in the 15th century at Tolfa, near Rome, where it was mined for the manufacture of alum. First called ''aluminilite'' by J.C. Delamétherie in 1797, this name was contracted by François Beudant three decades later to alunite. Alunite crystals morphologically are rhombohedron, rhombohedra with interfacial angles of 90° 50', causing them to resemble cubes. Crystal symmetry is trigonal. Minute glistening crystals have also been found loose in cavities in altered rhyolite. Alunite varies in color from white to yellow gray. The hardness on the Mohs scale is 4 and the specific gravity is between 2.6 and 2.8. It is insoluble in water or weak acids, but soluble in sulfuric acid. Sodium can substitute for potassium in the mineral, and when the sodium content is high, is called natroalunite. Alunite is an analog of jarosite, where aluminium replaces Fe3+. Alunite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double sulfate salt of aluminium with the general formula , where is a monovalent cation such as potassium or ammonium. By itself, "alum" often refers to potassium alum, with the formula . Other alums are named after the monovalent ion, such as sodium alum and ammonium alum. The name "alum" is also used, more generally, for salts with the same formula and structure, except that aluminium is replaced by another trivalent metal ion like chromium, and/or sulfur is replaced by another chalcogen like selenium. The most common of these analogs is chrome alum . In most industries, the name "alum" (or "papermaker's alum") is used to refer to aluminium sulfate, , which is used for most industrial flocculation (the variable is an integer whose size depends on the amount of water absorbed into the alum). In medicine, "alum" may also refer to aluminium hydroxide gel used as a vaccine adjuvant. History Alum found at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Minerals
The sulfate minerals are a class of minerals that include the sulfate ion () within their structure. The sulfate minerals occur commonly in primary evaporite depositional environments, as gangue minerals in hydrothermal veins and as secondary minerals in the oxidizing zone of sulfide mineral deposits. The chromate and manganate minerals have a similar structure and are often included with the sulfates in mineral classification systems.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy,'' 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 347–354 . Sulfate minerals include: *Anhydrous sulfates **Barite BaSO4 ** Celestite SrSO4 **Anglesite PbSO4 **Anhydrite CaSO4 **Hanksite Na22K(SO4)9(CO3)2Cl *Hydroxide and hydrous sulfates **Gypsum CaSO4·2H2O **Chalcanthite CuSO4·5H2O **Kieserite MgSO4·H2O ** Starkeyite MgSO4·4H2O **Hexahydrite MgSO4·6H2O **Epsomite MgSO4·7H2O **Meridianiite MgSO4·11H2O **Melanterite FeSO4·7H2O **Antlerite Cu3SO4(OH)4 **Brochantite Cu4SO4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Mineral
The sulfate minerals are a class of minerals that include the sulfate ion () within their structure. The sulfate minerals occur commonly in primary evaporite depositional environments, as gangue minerals in hydrothermal veins and as secondary minerals in the oxidizing zone of sulfide mineral deposits. The chromate and manganate minerals have a similar structure and are often included with the sulfates in mineral classification systems.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy,'' 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 347–354 . Sulfate minerals include: *Anhydrous sulfates ** Barite BaSO4 **Celestite SrSO4 ** Anglesite PbSO4 ** Anhydrite CaSO4 ** Hanksite Na22K(SO4)9(CO3)2Cl *Hydroxide and hydrous sulfates **Gypsum CaSO4·2H2O ** Chalcanthite CuSO4·5H2O ** Kieserite MgSO4·H2O ** Starkeyite MgSO4·4H2O ** Hexahydrite MgSO4·6H2O ** Epsomite MgSO4·7H2O ** Meridianiite MgSO4·11H2O ** Melanterite FeSO4·7H2O ** Antlerite Cu3SO4(OH)4 **Broc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonal
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal system and the rhombohedral lattice system are not equivalent (see section crystal systems below). In particular, there are crystals that have trigonal symmetry but belong to the hexagonal lattice (such as α-quartz). The hexagonal crystal family consists of the 12 point groups such that at least one of their space groups has the hexagonal lattice as underlying lattice, and is the union of the hexagonal crystal system and the trigonal crystal system. There are 52 space groups associated with it, which are exactly those whose Bravais lattice is either hexagonal or rhombohedral. __TOC__ Lattice systems The hexagonal crystal family consists of two lattice systems: hexagonal and rhombohedral. Each lattice system consists of one Bravais l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolfa
Tolfa is a town and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Rome, in the Lazio region of central Italy; it lies to the ENE of Civitavecchia by road. It is the main center in the Monti della Tolfa, an extinct volcanic group between Civitavecchia and the Lake of Bracciano. History A town of medieval origin in the orbit of Viterbo, it was assumed into the Papal States and granted first to the Capocci family, and then to the Roman nobles Ludovico and Pietro Frangipani who walled the community. Tolfa achieved sudden importance following the discovery there in 1461 of large deposits of alunite, the source of alum, with the result that direct control was assumed, after some confrontations with the Frangipani, by the Camera Apostolica. Alum was an essential mordant in the textile industry, which was central to the Late Medieval and Early Modern Italian economy. Previously, the only supplies of alum were imported from the East, from sources controlled by the Ottoman Turks, through Venice, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the producti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonal
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal system and the rhombohedral lattice system are not equivalent (see section crystal systems below). In particular, there are crystals that have trigonal symmetry but belong to the hexagonal lattice (such as α-quartz). The hexagonal crystal family consists of the 12 point groups such that at least one of their space groups has the hexagonal lattice as underlying lattice, and is the union of the hexagonal crystal system and the trigonal crystal system. There are 52 space groups associated with it, which are exactly those whose Bravais lattice is either hexagonal or rhombohedral. __TOC__ Lattice systems The hexagonal crystal family consists of two lattice systems: hexagonal and rhombohedral. Each lattice system consists of one Bravais l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not exist naturally on Earth due to its strong affinity to water vapor; it is hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals, since it is an oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid, but to the contrary dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is released; thus the reverse procedure of adding water to the acid should not be performed since the heat released ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |