sulfatase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
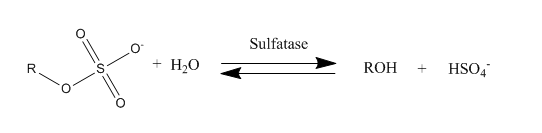
Sulfatases are enzymes of the esterase class that catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters. These may be found on a range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. In the latter case the resultant N-sulfates can also be termed
 The following sulfatases have been shown to be structurally related based on their
The following sulfatases have been shown to be structurally related based on their
Overview at rndsystems.com
{{InterPro content, IPR000917 Transmembrane proteins
sulfamate
Sulfamic acid, also known as amidosulfonic acid, amidosulfuric acid, aminosulfonic acid, sulphamic acid and sulfamidic acid, is a molecular compound with the formula H3NSO3. This colourless, water-soluble compound finds many applications. Sulfami ...
s.
Sulfatases play important roles in the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodelling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. Together with sulfotransferases, sulfatases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of sulfate esters.
Occurrence and importance
Sulfatases are found in lower and higher organisms. In higher organisms they are found in intracellular and extracellular spaces. Steroid sulfatase is distributed in a wide range of tissues throughout the body, enabling sulfated steroids synthesized in the adrenals and gonads to be desulfated following distribution through the circulation system. Many sulfatases are localized in the lysosome, an acidic digestive organelle found within the cell. Lysosomal sulfatases cleave a range of sulfated carbohydrates including sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids. Genetic defects in sulfatase activity can arise through mutations in individual sulfatases and result in certainlysosomal storage disorders
Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs; ) are a group of over 70 rare inherited metabolic disorders that result from defects in lysosomal function. Lysosomes are sacs of enzymes within cells that digest large molecules and pass the fragments on to othe ...
with a spectrum of phenotypes ranging from defects in physical and intellectual development.
Three-dimensional structure
 The following sulfatases have been shown to be structurally related based on their
The following sulfatases have been shown to be structurally related based on their sequence homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a spe ...
:
* cerebroside-sulfatase
* steroid sulfatase
Steroid sulfatase (STS), or steryl-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.2), formerly known as arylsulfatase C, is a sulfatase enzyme involved in the metabolism of steroids. It is encoded by the ''STS'' gene.
Reactions
This enzyme catalysis, catalyses the follow ...
* arylsulfatase A (ASA), a lysosomal enzyme which hydrolyzes cerebroside sulfate
Cerebrosides is the common name for a group of glycosphingolipids called monoglycosylceramides which are important components in animal muscle and neuron, nerve cell cell membrane, membranes.
They consist of a ceramide with a single sugar resid ...
;
*arylsulfatase B
Arylsulfatase B (N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase, chondroitinsulfatase, chondroitinase, acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfatase, N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate sulfohydrolase, ) is an enzyme associated with mucopolysaccharidosis VI (Maroteaux– ...
(ASB) which hydrolyzes the sulfate ester group from N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate residues of dermatan sulfate;
* arylsulfatase C (ASD) and E (ASE); steryl-sulfatase (STS), a membrane bound enzyme which hydrolyzes 3-beta-hydroxy steroid sulfate
Steroid sulfates are endogenous sulfate esters of steroids. They are formed by steroid sulfotransferases via sulfation of endogenous steroids like cholesterol and steroid hormones. Although steroid sulfates do not bind to steroid hormone receptor ...
s;
*iduronate 2-sulfatase
Iduronate 2-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.13; systematic name L-iduronate-2-sulfate 2-sulfohydrolase) is a sulfatase enzyme associated with Hunter syndrome. It catalyses hydrolysis of the 2-sulfate groups of the L-iduronate 2-sulfate units of dermatan sul ...
(IDS), a lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyzes the 2-sulfate groups from iduronic acids in dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate;
* N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase , which hydrolyzes the 6-sulfate groups of the N-acetyl-D-galactosamine of chondroitin sulfate and D-galactose 6-sulfate units of keratan sulfate
Keratan sulfate (KS), also called keratosulfate, is any of several sulfated glycosaminoglycans (structural carbohydrates) that have been found especially in the cornea, cartilage, and bone. It is also synthesized in the central nervous system w ...
;
* N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase , the lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyses N-sulfo-D-glucosamine into glucosamine and sulfate;
* glucosamine-6-sulfatase (G6S), which hydrolyzes the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-sulfate units of heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate;
* N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase , the lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyses N-sulfo-D-glucosamine into glucosamine and sulfate;
*sea urchin embryo arylsulfatase ;
*green algae arylsulfatase , which plays a role in the mineralization
Mineralization may refer to:
* Mineralization (biology), when an inorganic substance precipitates in an organic matrix
** Biomineralization, a form of mineralization
** Mineralization of bone, an example of mineralization
** Mineralized tissues are ...
of sulfates; and
* arylsulfatase from '' Escherichia coli'', ''Klebsiella aerogenes
''Klebsiella aerogenes'', previously known as ''Enterobacter aerogenes,'' is a Gram-negative, Oxidase test, oxidase negative, catalase positive, Citrate test, citrate positive, Indole test, indole negative, Bacillus, rod-shaped bacterium. The ba ...
'' and '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa''.
Human proteins containing this domain
ARSA;ARSB
Arylsulfatase B (N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase, chondroitinsulfatase, chondroitinase, acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfatase, N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate sulfohydrolase, ) is an enzyme associated with mucopolysaccharidosis VI (Maroteaux†...
; ARSD; ARSE; ARSF
The Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) is a British research council that supports research, training and knowledge transfer activities in the environmental sciences.
History
NERC began in 1965 when several environmental (mainly geog ...
; ARSG; ARSH; ARSI;
ARSJ; ARSK; GALNS
N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ''GALNS'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''gener ...
; GNS; IDS; PIGG; SGSH; STS;
SULF1; SULF2
Extracellular sulfatase Sulf-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SULF2'' gene.
Function
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) act as coreceptors for numerous heparin-binding growth factors and cytokines and are involved in cell ...
;
References
External links
*Overview at rndsystems.com
{{InterPro content, IPR000917 Transmembrane proteins