|
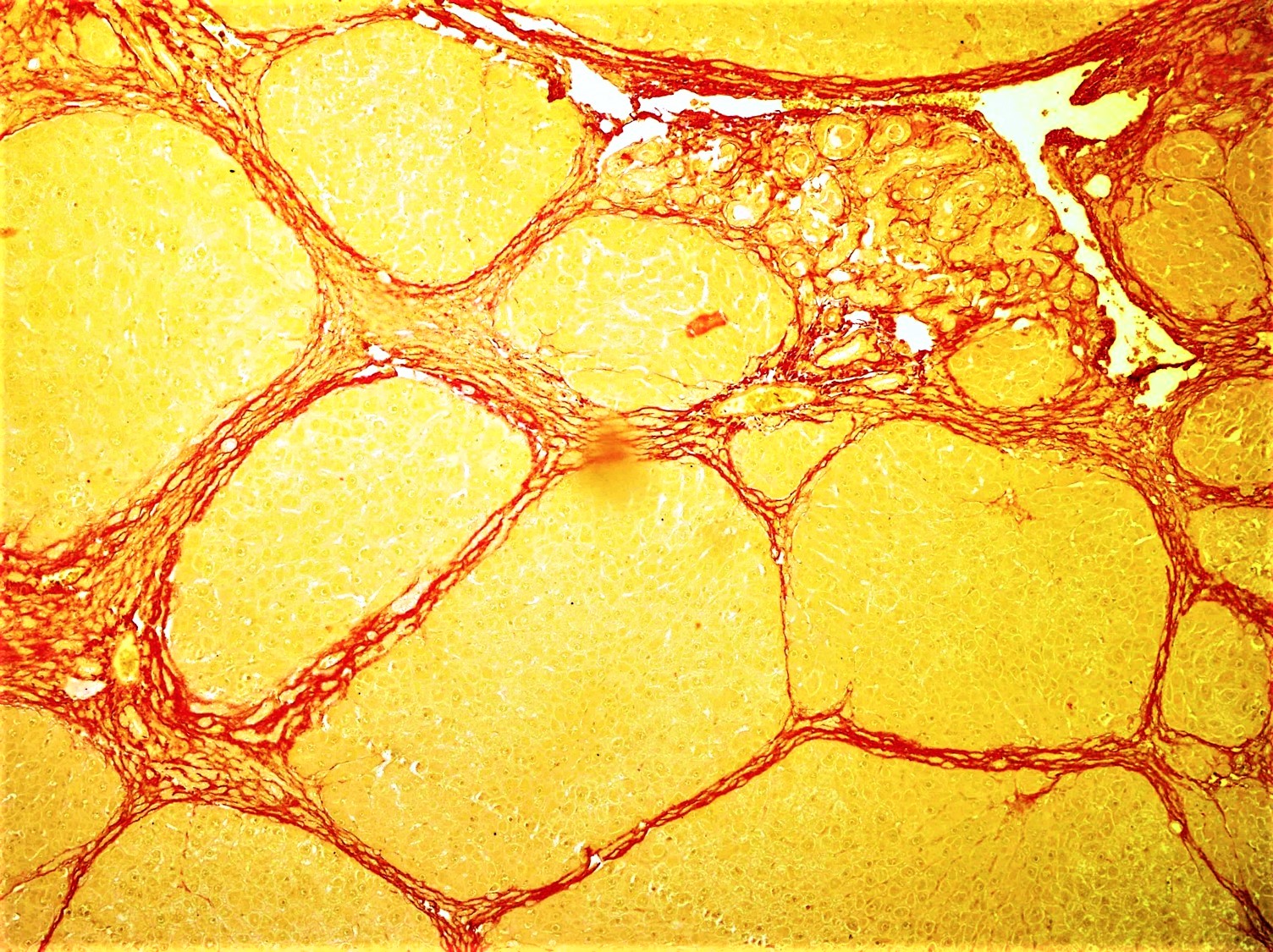
Dermatan Sulfate
Dermatan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan (formerly called a mucopolysaccharide) found mostly in skin, but also in blood vessels, heart valves, tendons, and lungs. It is also referred to as chondroitin sulfate B, although it is no longer classified as a form of chondroitin sulfate by most sources. The formula is C14H21NO15S. This carbohydrate is composed of linear polymers of disaccharide units that contain, N-acetyl galactosamine (GalNAc) and iduronic acid (IdoA). These repeating units are sulfated at a variety of positions. Dermatan sulfate is a component of the compound sulodexide. Function Dermatan sulfate may have roles in coagulation, cardiovascular disease, carcinogenesis, infection, wound repair, maintains the shape of galactosamine 4-sulfate skin and fibrosis. Pathology Dermatan sulfate accumulates abnormally in several of the mucopolysaccharidosis disorders. An excess of dermatan sulfate in the mitral valve is characteristic of myxomatous degeneration of the leaflet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosaminoglycan
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers. Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders in which abnormal accumulations of glycosaminoglycans occur due to enzyme deficiencies. Production Glycosaminoglycans vary greatly in molecular mass, disaccharide structure, and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not template driven, as are proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes. GAGs are classified into four groups, based on their core disaccharide structures. Hepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of permanent scar tissue. Repeated injuries, chronic inflammation and repair are susceptible to fibrosis where an accidental excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, such as the collagen is produced by fibroblasts, leading to the formation of a permanent fibrotic scar. In response to injury, this is called scarring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iduronic Acid
-Iduronic acid (IUPAC abbr.: IdoA) is the major uronic acid component of the glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) dermatan sulfate, and heparin. It is also present in heparan sulfate, although here in a minor amount relative to its carbon-5 epimer glucuronic acid. IdoA is a hexapyranose sugar. Most hexapyranoses are stable in one of two chair conformations 1C4 or 4C1. -iduronate is different and adopts more than one solution conformation, with an equilibrium existing between three low-energy conformers. These are the 1C4 and 4C1 chair forms and an additional 2S0 skew-boat conformation. IdoA may be modified by the addition of an ''O''-sulfate group at carbon position 2 to form 2-''O''-sulfo--iduronic acid (IdoA2S). In 2000, LK Hallak described the importance of this sugar in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. Dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate were the only GAGs containing IdoA, and they were the only ones that inhibited RSV infection in cell culture. When internally position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
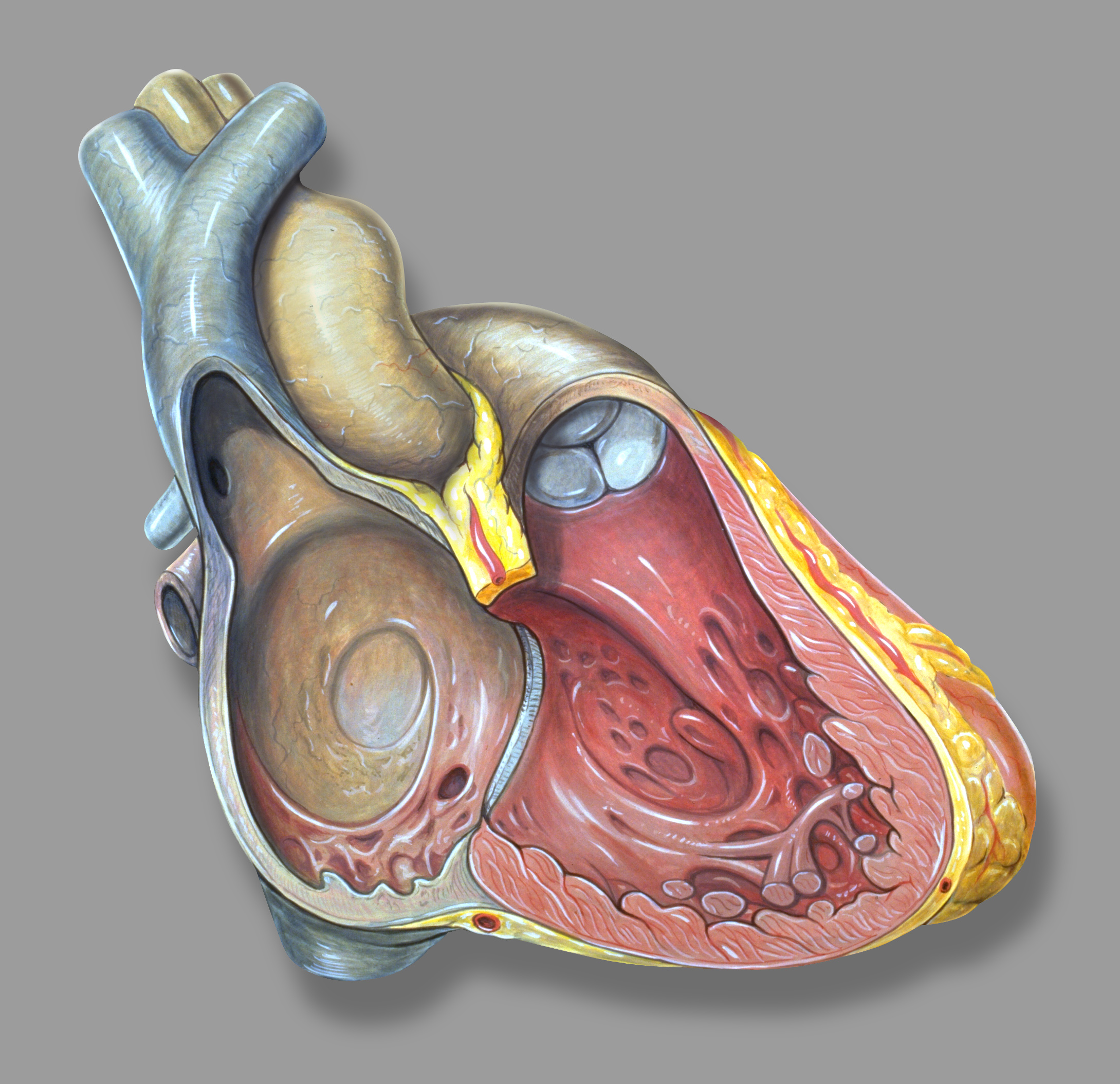
Left Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which the heart becomes thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ventricles. This results in the heart being less able to pump blood effectively and also may cause electrical conduction problems. People who have HCM may have a range of symptoms. People may be asymptomatic, or may have fatigue, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Symptoms may be worse when the person is dehydrated. Complications may include heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, and sudden cardiac death. HCM is most commonly inherited from a person's parents in an autosomal dominant pattern. It is often due to mutations in certain genes involved with making heart muscle proteins. Other inherited causes of left ventricular hypertrophy may include Fabry disease, Friedreich's ataxia, and certain medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitral Insufficiency
Mitral regurgitation (MR), also known as mitral insufficiency or mitral incompetence, is a form of valvular heart disease in which the mitral valve is insufficient and does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood.Mitral valve regurgitation at Mount Sinai Hospital It is the abnormal leaking of blood backwards – regurgitation from the , through the mitral valve, into the |
Mitral Annular Calcification
Mitral annular calcification (MAC) is a multifactorial chronic degenerative process in which calcium with lipid is deposited (calcified) in the annular fibrosa ring of the heart's mitral valve. MAC was first discovered and described in 1908 by M. Bonninger in the journal Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift. In the majority of cases, affected patients are asymptomatic and the condition is only noted incidentally on echocardiography or computed tomography (CT) scans. However, mitral annular calcification remains clinically significant because while in many cases the calcification is limited to the annulus and proximal leaflet bases, it may also extend further into the valve structure. This may potentially cause mitral regurgitation (MR) or more rarely mitral stenosis (MS), which may produce the classic symptoms of these conditions over time. In addition, calcification of the annulus can inhibit electrical conduction of the AV node, consequently causing various degrees of heart bloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health care provider. Etymology The word patient originally meant 'one who suffers'. This English noun comes from the Latin word ', the present participle of the deponent verb, ', meaning 'I am suffering,' and akin to the Greek verb (', to suffer) and its cognate noun (). This language has been construed as meaning that the role of patients is to passively accept and tolerate the suffering and treatments prescribed by the healthcare providers, without engaging in shared decision-making about their care. Outpatients and inpatients An outpatient (or out-patient) is a patient who attends an outpatient clinic with no plan to stay beyond the duration of the visit. Even if the patient will not be formally admitted with a note as an outpatient, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitral Valve Prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole. It is the primary form of myxomatous degeneration of the valve. There are various types of MVP, broadly classified as classic and nonclassic. In severe cases of classic MVP, complications include mitral regurgitation, infective endocarditis, congestive heart failure, and, in rare circumstances, cardiac arrest. The diagnosis of MVP depends upon echocardiography, which uses ultrasound to visualize the mitral valve. MVP is the most common valvular abnormality and is estimated to affect 2–3% of the population and 1 in 40 people might have it. The condition was first described by John Brereton Barlow in 1966. It was subsequently termed ''mitral valve prolapse'' by J. Michael Criley. Although mid-systolic click (sound of prolapsing mitral leaflet) and systolic murmur have been noticed earlier with stethoscope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue (biology)
In biology, tissue is a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" derives from the French word "tissu", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is studied in both plant anatomy and physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the histological stain, and the optical microscope. Developments in electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, and the use of frozen tissue-sections have enhanced the detail that can be observed in tissues. With these tools, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitral Valve
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one-way valves allowing blood flow in just one direction. The mitral valve and the tricuspid valve are known as the atrioventricular valves because they lie between the atria and the ventricles. In normal conditions, blood flows through an open mitral valve during diastole with contraction of the left atrium, and the mitral valve closes during systole with contraction of the left ventricle. The valve opens and closes because of pressure differences, opening when there is greater pressure in the left atrium than ventricle and closing when there is greater pressure in the left ventricle than atrium. In abnormal conditions, blood may flow backward through the valve ( mitral regurgitation) or the mitral valve may be narrowed (mitral stenosis). Rh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |