|
Iduronate 2-sulfatase
Iduronate 2-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.13; systematic name L-iduronate-2-sulfate 2-sulfohydrolase) is a sulfatase enzyme associated with Hunter syndrome. It catalyses hydrolysis of the 2-sulfate groups of the L-iduronate 2-sulfate units of dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate and heparin. Function Iduronate 2-sulfatase is required for the lysosomal degradation of heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Mutations in this X-chromosome gene that result in enzymatic deficiency lead to the sex-linked mucopolysaccharidosis type II, also known as Hunter syndrome. At least 174 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. Iduronate-2-sulfatase has a strong sequence homology with human arylsulfatase Arylsulfatase (EC 3.1.6.1, sulfatase, nitrocatechol sulfatase, phenolsulfatase, phenylsulfatase, ''p''-nitrophenyl sulfatase, arylsulfohydrolase, 4-methylumbelliferyl sulfatase, estrogen sulfatase) is a type of sulfatase enzyme with systematic name ...s A, B, and C, and human glucosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
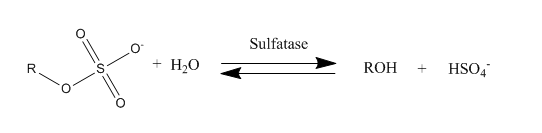
Sulfatase
Sulfatases are enzymes of the esterase class that catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters. These may be found on a range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. In the latter case the resultant N-sulfates can also be termed sulfamates. Sulfatases play important roles in the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodelling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. Together with sulfotransferases, sulfatases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of sulfate esters. Occurrence and importance Sulfatases are found in lower and higher organisms. In higher organisms they are found in intracellular and extracellular spaces. Steroid sulfatase is distributed in a wide range of tissues throughout the body, enabling sulfated steroids synthesized in the adrenals and gonads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunter Syndrome
Hunter syndrome, or mucopolysaccharidosis type II (MPS II), is a rare genetic disorder in which large sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (or GAGs or mucopolysaccharides) build up in body tissues. It is a form of lysosomal storage disease. Hunter syndrome is caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme iduronate-2-sulfatase (I2S). The lack of this enzyme causes heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate to accumulate in all body tissues. Hunter syndrome is the only MPS syndrome to exhibit X-linked recessive inheritance. The symptoms of Hunter syndrome are comparable to those of MPS I. It causes abnormalities in many organs, including the skeleton, heart, and respiratory system. In severe cases, this leads to death during the teenaged years. Unlike MPS I, corneal clouding is not associated with this disease. Signs and symptoms Hunter syndrome may present with a wide variety of phenotypes. It has traditionally been categorized as either "mild" or "severe" depending on the pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heparan Sulfate
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan (HSPG, i.e. Heparan Sulfate ProteoGlycan) in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. It is in this form that HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB (Granzyme B), and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2. Proteoglycans The major cell membrane HSPGs are the transmembrane syndecans and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored glypicans. Other minor forms of membrane HSPG include betaglycan and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatan Sulfate
Dermatan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan (formerly called a mucopolysaccharide) found mostly in skin, but also in blood vessels, heart valves, tendons, and lungs. It is also referred to as chondroitin sulfate B, although it is no longer classified as a form of chondroitin sulfate by most sources. The formula is C14H21NO15S. This carbohydrate is composed of linear polymers of disaccharide units that contain, N-acetyl galactosamine (GalNAc) and iduronic acid (IdoA). These repeating units are sulfated at a variety of positions. Dermatan sulfate is a component of the compound sulodexide. Function Dermatan sulfate may have roles in coagulation, cardiovascular disease, carcinogenesis, infection, wound repair, maintains the shape of galactosamine 4-sulfate skin and fibrosis. Pathology Dermatan sulfate accumulates abnormally in several of the mucopolysaccharidosis disorders. An excess of dermatan sulfate in the mitral valve is characteristic of myxomatous degeneration of the leaflet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucopolysaccharidosis
Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders caused by the absence or malfunctioning of lysosome, lysosomal enzymes needed to break down molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). These long chains of sugar carbohydrates occur within the Cell (biology), cells that help build bone, cartilage, tendons, corneas, skin and connective tissue. GAGs (formerly called mucopolysaccharides) are also found in Synovial fluid, the fluids that lubricate joints. Individuals with mucopolysaccharidosis either do not produce enough of one of the eleven enzymes required to break down these sugar chains into simpler molecules, or they produce enzymes that do not work properly. Over time, these GAGs collect in the cells, blood and connective tissues. The result is permanent, progressive cellular damage which affects appearance, physical abilities, organ and system functioning. The mucopolysaccharidoses are part of the lysosomal storage disease family, a group of more than 40 genetic disord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylsulfatase
Arylsulfatase (EC 3.1.6.1, sulfatase, nitrocatechol sulfatase, phenolsulfatase, phenylsulfatase, ''p''-nitrophenyl sulfatase, arylsulfohydrolase, 4-methylumbelliferyl sulfatase, estrogen sulfatase) is a type of sulfatase enzyme with systematic name ''aryl-sulfate sulfohydrolase''. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction : an aryl sulfate + H2O \rightleftharpoons a phenol + sulfate Types include: *Arylsulfatase A (also known as "cerebroside-sulfatase") *Arylsulfatase B (also known as "''N''-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase") *Steroid sulfatase (formerly known as "arylsulfatase C") * ARSC2 * ARSD *ARSE *ARSF * ARSG * ARSH * ARSI * ARSJ * ARSK See also * Aryl In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used ... References Hydrolases EC 3.1.6 {{biochem-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idursulfase
Idursulfase (brand name Elaprase), manufactured by Takeda, is a drug used to treat Hunter syndrome (also called MPS-II). It is a purified form of the lysosomal enzyme iduronate-2-sulfatase and is produced by recombinant DNA technology Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word ''cloning'' refers to the fact that the metho ... in a human cell line. It is one of the most expensive drugs ever produced, costing US$567,412 per patient per year. Barbara Kollmeyer, Marketwatch, Fed. 3, 2016 References External links *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |