Subtropical cyclone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A subtropical cyclone is a
A subtropical cyclone is a
Atlantic Hurricane Season of 1972.
Monthly Weather Review, April 1973, pp. 323–332. Retrieved on 2008-06-14. and updated the hurricane database to include subtropical cyclones from 1968 through 1971. The term "neutercane" began to be used for small subtropical cyclones below 100 miles in diameter which formed from mesoscale features, and the NHC began issuing public statements during the 1972 Atlantic hurricane season employing that classification. This name was not noted as controversial in contemporary news reports, but it was quickly dropped less than a year later. Recent articles, published after the year 2000, have suggested that the name "neutercane" was considered sexist in the 1970s, but there do not appear to be any published reports from that period making this claim.
 In the north Atlantic basin, subtropical cyclones were initially named from the
In the north Atlantic basin, subtropical cyclones were initially named from the
TROPICAL CYCLONE OPERATIONAL PLAN FOR THE SOUTH-WEST INDIAN OCEAN: 2006 Edition.
pp. I-3, I-9. Retrieved on 2009-02-28. Since 2011, subtropical storms in the western south Atlantic Ocean are named by the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center.
 Subtropical cyclones can form in a wide band of
Subtropical cyclones can form in a wide band of
Subject: A6) What is a sub-tropical cyclone?
Climate Dynamics of the Tropics.
Springer, pp 244. . Retrieved on 2009-02-29. In the southern hemisphere, subtropical cyclones are regularly observed across southern portions of the
"> Another subtropical cyclone was identified at 77.8 degrees longitude in May 2018, just off the coast of Chile. This system was unofficially named ''Lexi'' by researchers. A subtropical cyclone was spotted just off the Chilean coast in January 2022.
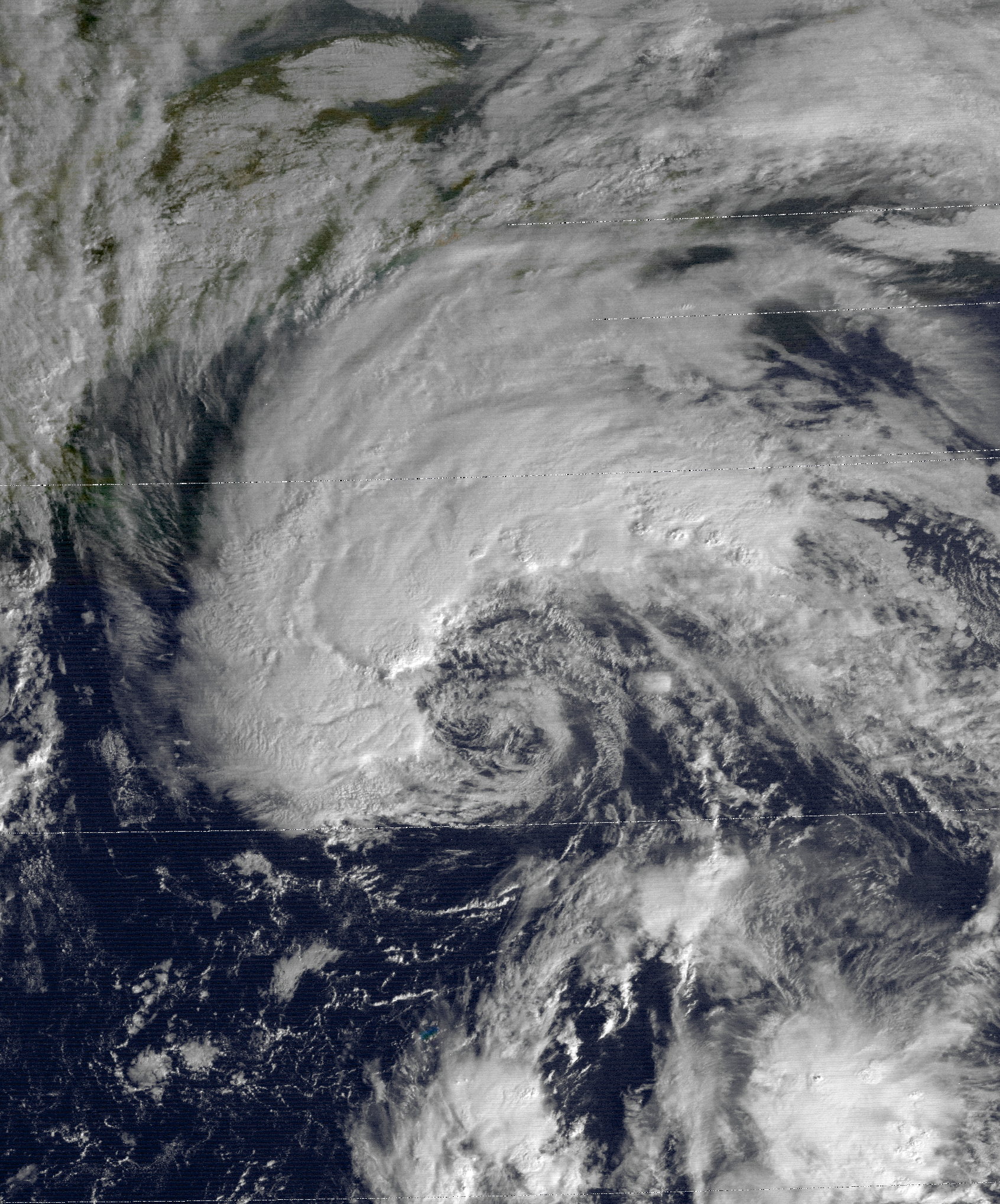
 Subtropical cyclones are more likely than tropical cyclones to form outside of a region's designated hurricane season. Examples during the 21st century in the north Atlantic include:
* Subtropical Storm Ana (which became Tropical Storm Ana) in late-April of the 2003 hurricane season.
Subtropical cyclones are more likely than tropical cyclones to form outside of a region's designated hurricane season. Examples during the 21st century in the north Atlantic include:
* Subtropical Storm Ana (which became Tropical Storm Ana) in late-April of the 2003 hurricane season.
Atlantic Hurricane Database (HURDAT2).
Retrieved on 2017-04-24. * Subtropical Storm Andrea in early-May of the 2007 hurricane season. * Subtropical Storm Olga (which became
 Kona storms (or Kona lows) are deep cyclones that form during the cool winter season of the central Pacific Ocean. A definition change in the term during the early 1970s makes categorization of the systems more complex, as many kona lows are extratropical cyclones, complete with their own weather fronts. Those across the northeast Pacific Ocean consider them subtropical cyclones as long as a weak surface circulation is present. ''Kona'' is a Hawaiian term for ''leeward'', which explains the change in wind direction for the Hawaiian Islands from easterly to southerly when this type of cyclone is present.
Kona storms (or Kona lows) are deep cyclones that form during the cool winter season of the central Pacific Ocean. A definition change in the term during the early 1970s makes categorization of the systems more complex, as many kona lows are extratropical cyclones, complete with their own weather fronts. Those across the northeast Pacific Ocean consider them subtropical cyclones as long as a weak surface circulation is present. ''Kona'' is a Hawaiian term for ''leeward'', which explains the change in wind direction for the Hawaiian Islands from easterly to southerly when this type of cyclone is present.
 Australian east coast lows (known locally as east coast lows and sometimes as east coast cyclones) are
Australian east coast lows (known locally as east coast lows and sometimes as east coast cyclones) are
NOAA FAQ on tropical cyclones
{{DEFAULTSORT:Subtropical Cyclone Subtropics
 A subtropical cyclone is a
A subtropical cyclone is a weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmo ...
system that has some characteristics of both tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
and extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of p ...
s.
As early as the 1950s, meteorologists were uncertain whether they should be characterized as tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
or extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of p ...
s. They were officially recognized and titled by the National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the IERS Reference Meridian, Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian ...
in 1972. Beginning in 2002, subtropical cyclones began receiving names from the official tropical cyclone lists in the North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for ...
basin. Subtropical cyclones are also recognized in the South-West Indian Ocean and South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for ...
basins.
There are two definitions currently used for subtropical cyclones depending on their location. Across the north Atlantic and southwest Indian Ocean, they require some central convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
fairly near the center surrounding a warming core existing in the mid-levels of the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
. Across the eastern half of the northern Pacific however, they require a mid-tropospheric cyclone to be cut off from the main belt of the westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes (about ...
and with only a weak surface circulation. Subtropical cyclones have wider wind fields with the maximum sustained winds located further from the center than typical tropical cyclones, and have no weather fronts
A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For in ...
linked into their center.
Since they form from initially extratropical cyclones which have colder temperatures aloft than normally found in the tropics, the sea surface temperatures required for their formation are lower than the tropical cyclone threshold (around 26.5° C (79.7° F)) by 3° C (5° F), lying around 23 °C (73 °F). This also means that subtropical cyclones are more likely to form outside the traditional bounds of the North Atlantic hurricane season and at higher latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
s. Subtropical cyclones are also observed to form in the South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for ...
, where subtropical cyclones are observed in all months.
History of term
Throughout the 1950s and 1960s, the terms semi-tropical and quasi-tropical were used for what would become known as the subtropical cyclones. The term subtropical cyclone initially merely referred to any cyclone located in the subtropical belt near and just north of thehorse latitudes
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as subtropical ridges or highs. It is a high-pressu ...
. Later, intense debate ensued in the late 1960s, after a number of hybrid cyclones formed in the Atlantic Basin. In 1972, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) finally designated these "hybrid" storms as true subtropical cyclones in real-time,R. H. Simpson and Paul J. Hebert (1973)Atlantic Hurricane Season of 1972.
Monthly Weather Review, April 1973, pp. 323–332. Retrieved on 2008-06-14. and updated the hurricane database to include subtropical cyclones from 1968 through 1971. The term "neutercane" began to be used for small subtropical cyclones below 100 miles in diameter which formed from mesoscale features, and the NHC began issuing public statements during the 1972 Atlantic hurricane season employing that classification. This name was not noted as controversial in contemporary news reports, but it was quickly dropped less than a year later. Recent articles, published after the year 2000, have suggested that the name "neutercane" was considered sexist in the 1970s, but there do not appear to be any published reports from that period making this claim.
Naming
 In the north Atlantic basin, subtropical cyclones were initially named from the
In the north Atlantic basin, subtropical cyclones were initially named from the NATO phonetic alphabet
The International Radiotelephony Spelling Alphabet or simply the Radiotelephony Spelling Alphabet, commonly known as the NATO phonetic alphabet, is the most widely used set of clear-code words for communicating the letters of the Latin/Roman ...
list in the early to mid-1970s. In the intervening years of 1975–2001, subtropical storms were either named from the traditional list and still was considered tropical in real-time, or used a separate numbering system instead. Between 1992 and 2001, two different numbers were given to subtropical depressions or subtropical storms, one for public use, the other one for NRL and NHC reference. For example, Hurricane Karen in 2001 was initially known as Subtropical Storm One as well as AL1301 (or 13L for short). In 2002, the NHC began giving numbers to subtropical depressions and names to subtropical storms from the same sequence as tropical cyclones. From 2002 onward, Subtropical Depression 13L would be known as Subtropical Depression Thirteen instead. Hurricane Gustav of 2002 was the first subtropical storm to receive a name but became tropical shortly after naming. Subtropical Storm Nicole from the 2004 Atlantic hurricane season
The 2004 Atlantic hurricane season was a very deadly, destructive, and active Atlantic hurricane season, with over 3,200 deaths and more than $61 billion (2004 USD, $95.77 billion 2022 USD) in damage. More than half of the 16 trop ...
was the first subtropical storm that did not become tropical since the policy change. A subtropical storm from the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season
The 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was a record-breaking, devastating and deadly Atlantic hurricane season. It is the second-costliest hurricane season, just behind the 2017 season And 2024. It featured 28 tropical and subtropical storms, ...
also did not become tropical, but was not named since it was not recognized until post-season analysis.
In the southern Indian Ocean, subtropical cyclones are also named once winds reach tropical storm or gale
A gale is a strong wind; the word is typically used as a descriptor in nautical contexts. The U.S. National Weather Service defines a gale as sustained surface wind moving at a speed between .
force.World Meteorological Organization (2006)TROPICAL CYCLONE OPERATIONAL PLAN FOR THE SOUTH-WEST INDIAN OCEAN: 2006 Edition.
pp. I-3, I-9. Retrieved on 2009-02-28. Since 2011, subtropical storms in the western south Atlantic Ocean are named by the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center.
Formation
 Subtropical cyclones can form in a wide band of
Subtropical cyclones can form in a wide band of latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
, mainly south of the 50th parallel in the northern hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
, and north of the 50th parallel in the southern hemisphere. Chris LandseaSubject: A6) What is a sub-tropical cyclone?
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the IERS Reference Meridian, Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian ...
. Retrieved on 2008-06-14. Due to the increased frequency of cyclones which cut off from the main belt of the westerlies during the summer and fall, subtropical cyclones are significantly more frequent across the north Atlantic than the northwestern Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
. In the eastern half of the north Pacific Ocean and north Indian Ocean, the older subtropical cyclone definition term is still used, which requires a weak circulation forming underneath a mid to upper-tropospheric low which has cut off from the main belt of the westerlies during the cold season (winter
Winter is the coldest and darkest season of the year in temperate and polar climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Dif ...
), similar to the north Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
and southwest Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
. In the case of the north Indian Ocean, the formation of this type of vortex leads to the onset of monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
rains during the wet season
The wet season (sometimes called the rainy season or monsoon season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Generally, the season lasts at least one month. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used a ...
.S. Hastenrath (1991)Climate Dynamics of the Tropics.
Springer, pp 244. . Retrieved on 2009-02-29. In the southern hemisphere, subtropical cyclones are regularly observed across southern portions of the
Mozambique Channel
The Mozambique Channel (, , ) is an arm of the Indian Ocean located between the Southeast African countries of Madagascar and Mozambique. The channel is about long and across at its narrowest point, and reaches a depth of about off the coa ...
.
Most subtropical cyclones form when a deep cold-core extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of p ...
drops down into the subtropics. The system becomes blocked by a high latitude ridge, and eventually sheds its frontal boundaries as its source of cool and dry air from the high latitudes diverts away from the system, and warms the central circulation, allowing further transition. Temperature differences between the 500 hPa pressure level and the sea surface temperatures initially exceed the dry adiabatic lapse rate
The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. ''Lapse rate'' arises from the word ''lapse'' (in its "becoming less" sense, not its "interruption" sense). In dry air, ...
, which causes an initial round of thunderstorms
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are som ...
to form at a distance east of the center. Due to the initial cold temperatures aloft, sea surface temperatures usually need to reach at least for this initial round of thunderstorms. The initial thunderstorm activity humidifies the environment around the low pressure system, which destabilizes the atmosphere by reducing the lapse rate
The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. ''Lapse rate'' arises from the word ''lapse'' (in its "becoming less" sense, not its "interruption" sense). In dry air, ...
needed for convection. When the next shortwave or upper-level jet streak (wind maximum within the jet stream) moves nearby, the convection reignites closer to the center, which warms the core and develops the system into a true subtropical cyclone. The average sea surface temperature that helps lead to subtropical cyclogenesis is . If the thunderstorm activity becomes deep and persistent, allowing its initial low level warm core to deepen, extension to tropical cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropics, tropical cyclogenesis occur are distinctly different from those through which temperate cyclogenesis occu ...
is possible. The locus of formation for north Atlantic subtropical cyclones is out in the open ocean; the island of Bermuda is regularly impacted by these systems.
The south Atlantic environment for formation of subtropical cyclones has both stronger vertical wind shear
Wind shear (; also written windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical ...
and lower sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature (or ocean surface temperature) is the ocean temperature, temperature of ocean water close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies in the literature and in practice. It is usually between and below the sea ...
s, yet subtropical cyclogenesis is regularly observed in the open ocean in the south Atlantic. A second mechanism for formation has been diagnosed for south Atlantic subtropical cyclones: lee cyclogenesis in the region of the Brazil Current.
Subtropical cyclone formation is extremely rare in the far southeastern Pacific Ocean, due to the cold sea-surface temperatures generated by the Humboldt Current
The Humboldt Current, also called the Peru Current, is a cold, low-salinity ocean current that flows north along the western coast of South America.Montecino, Vivian, and Carina B. Lange. "The Humboldt Current System: Ecosystem components and pro ...
and unfavorable wind shear
Wind shear (; also written windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical ...
. In late April 2015, a rare subtropical cyclone was identified to have formed in this region. This system was unofficially dubbed ''Katie'' by researchers.Katie
Katie is an English female name. It is a form of Katherine, Kate, Caitlin, Kathleen, Katey and their related forms. It is frequently used on its own.
People Sports
* Katie Boulter (born 1996), British tennis player
* Katie Clark (born 1994), ...Transition from extratropical
By gaining tropical characteristics, an extratropical low may transit into a subtropical depression or storm. A subtropical depression/storm may further gain tropical characteristics to become a pure tropical depression or storm, which may eventually develop into a hurricane, and there are at least ten cases of tropical cyclones transforming into a subtropical cyclone ( Tropical Storm Gilda in 1973, Subtropical Storm Four in 1974, Tropical Storm Jose in 1981, Hurricane Klaus in 1984, Tropical Storm Allison in 2001, Tropical Storm Lee in 2011, Hurricane Humberto in 2013, Tropical Storm Ian in 2016, Typhoon Jelawat in 2018, and Typhoon Surigae in 2021). There have also been three recorded cases of a storm transitioning from tropical to extratropical back to a subtropical cyclone; as seen with the Caribbean–Azores hurricane in 1970, Hurricane Georges in 1980, and Hurricane Beryl in 2018. Generally, a tropical storm or tropical depression is not called subtropical while it is becoming extratropical and vice versa, after hitting either land or colder waters. This transition normally requires significant instability through the atmosphere, with temperature differences between the underlying ocean and the mid-levels of thetroposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
requiring over 38 °C, or 68 °F, of contrast in this roughly layer of the lower atmosphere. The mode of the sea surface temperatures that subtropical cyclones form over is . Transition from subtropical cyclones into fully tropical cyclones occurs only in very rare cases over the south Atlantic Ocean, such as Hurricane Catarina in 2004.
Characteristics

Intensity
Subtropical cyclones can have maximumwind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heatin ...
s extending farther from the center than in a purely tropical cyclone and have no weather front
A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For ins ...
s linking directly to the center of circulation. In the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
Basin, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploratio ...
classifies subtropical cyclones similarly to tropical cyclones, based on maximum sustained surface winds. Those with winds below 18 m/s, (65 km/h
The kilometre per hour ( SI symbol: km/h; non-SI abbreviations: kph, kmph, km/hr) is a unit of speed, expressing the number of kilometres travelled in one hour.
History
Although the metre was formally defined in 1799, the term "kilometres per h ...
, 35 knots
A knot is a fastening in rope or interwoven lines.
Knot or knots may also refer to:
Other common meanings
* Knot (unit), of speed
* Knot (wood), a timber imperfection
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Knots'' (film), a 2004 film
* ''Kn ...
, or 39 mph) are called subtropical depressions, while those at or above this speed
In kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a non-negative scalar quantity. Intro ...
are referred to as subtropical storms. Diagrams which depict a cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an ant ...
's phase depict subtropical cyclones with a shallow warm core and as asymmetric systems, similar to tropical cyclones which have begun the transition to an extratropical cyclone.
Subtropical cyclones with hurricane-force winds of 33 m/s, (119 km/h, 64 knots, or 74 mph) or greater are no longer recognized by the National Hurricane Center. Once a subtropical storm intensifies enough to have hurricane-force winds, it is then automatically assumed to have become a fully tropical hurricane even if it still has subtropical characteristics. Despite this however, prior to the start of modern policies in the Atlantic there were two subtropical cyclones, one in 1968
Events January–February
* January 1968, January – The I'm Backing Britain, I'm Backing Britain campaign starts spontaneously.
* January 5 – Prague Spring: Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Cze ...
and another in 1979
Events
January
* January 1
** United Nations Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim heralds the start of the ''International Year of the Child''. Many musicians donate to the ''Music for UNICEF Concert'' fund, among them ABBA, who write the song ...
, that attained hurricane-force winds while subtropical. In addition, one system, Subtropical Depression 11 during the 2000–01 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, was analyzed by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) to have reached hurricane strength as a subtropical cyclone, but Météo-France
Météo-France is the official French meteorological administration, also offering services to Andorra and Monaco. It has the powers of the state and can exercise them in relation to meteorology. Météo-France is in charge of observing, study ...
(MFR) only considers it to have been a subtropical depression.
Examples during the off-season
 Subtropical cyclones are more likely than tropical cyclones to form outside of a region's designated hurricane season. Examples during the 21st century in the north Atlantic include:
* Subtropical Storm Ana (which became Tropical Storm Ana) in late-April of the 2003 hurricane season.
Subtropical cyclones are more likely than tropical cyclones to form outside of a region's designated hurricane season. Examples during the 21st century in the north Atlantic include:
* Subtropical Storm Ana (which became Tropical Storm Ana) in late-April of the 2003 hurricane season.National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the IERS Reference Meridian, Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian ...
(2017)Atlantic Hurricane Database (HURDAT2).
Retrieved on 2017-04-24. * Subtropical Storm Andrea in early-May of the 2007 hurricane season. * Subtropical Storm Olga (which became
Tropical Storm Olga The name Olga has been used seventeen tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that ...
) in mid-December of the 2007 hurricane season.
* Subtropical Storm Beryl (which became Tropical Storm Beryl) in late-May of the 2012 hurricane season.
* An unnamed subtropical storm in early-December of the 2013 hurricane season.
* Subtropical Storm Ana (which became Tropical Storm Ana) in early-May of the 2015 hurricane season.
* Subtropical Storm Alex (which became Hurricane Alex) in mid-January of the 2016 hurricane season.
* Subtropical Depression One (which became Tropical Storm Arlene) in mid-April of the 2017 hurricane season.
*Subtropical Storm Alberto (which became Tropical Storm Alberto) in late-May of the 2018 hurricane season.
* Subtropical Storm Andrea in late-May of the 2019 hurricane season.
*Subtropical Storm Ana (which became Tropical Storm Ana) in late-May of the 2021 hurricane season.
*An unnamed subtropical storm in mid-January of the 2023 hurricane season.
Types
Upper-level low
The most common type of subtropical storm is an upper-level cold low with circulation extending to the surface layer and maximum sustained winds generally occurring at a radius of about or more from the center. In comparison totropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
s, such systems have a relatively wide zone of maximum winds that is located further from the center, and typically have a less symmetric wind field and distribution of convection.
Mesoscale low
A second type of subtropical cyclone is a mesoscale low originating in or near a frontolyzing zone of horizontal wind shear, also known as a "dying" frontal zone, with radius of maximum sustained winds generally less than . The entire circulation may initially have a diameter of less than . These generally short-lived systems may be eithercold core
A cold-core low, also known as an upper level low or cold-core cyclone, is a cyclone aloft which has an associated cold pool of air residing at high altitude within the Earth's troposphere, without a weather front, frontal structure. It is a low ...
or warm core, and in 1972 this type of subtropical cyclone was ephemerally referred to as a "neutercane".
Kona storm
 Kona storms (or Kona lows) are deep cyclones that form during the cool winter season of the central Pacific Ocean. A definition change in the term during the early 1970s makes categorization of the systems more complex, as many kona lows are extratropical cyclones, complete with their own weather fronts. Those across the northeast Pacific Ocean consider them subtropical cyclones as long as a weak surface circulation is present. ''Kona'' is a Hawaiian term for ''leeward'', which explains the change in wind direction for the Hawaiian Islands from easterly to southerly when this type of cyclone is present.
Kona storms (or Kona lows) are deep cyclones that form during the cool winter season of the central Pacific Ocean. A definition change in the term during the early 1970s makes categorization of the systems more complex, as many kona lows are extratropical cyclones, complete with their own weather fronts. Those across the northeast Pacific Ocean consider them subtropical cyclones as long as a weak surface circulation is present. ''Kona'' is a Hawaiian term for ''leeward'', which explains the change in wind direction for the Hawaiian Islands from easterly to southerly when this type of cyclone is present.
Australian east coast lows
 Australian east coast lows (known locally as east coast lows and sometimes as east coast cyclones) are
Australian east coast lows (known locally as east coast lows and sometimes as east coast cyclones) are extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of p ...
s, the most intense of these systems have many of the characteristics of subtropical cyclones. They develop between 25° south and 40° south and within 5° of the Australian coastline, also typically during the winter months. Each year there are about ten "significant impact" maritime lows. Explosive cyclogenesis is seen on average just once per year, but these storms cause significant wind and flood damage when they occur. Australian east coast cyclones vary in size from mesoscale (approximately 10 km to 100 km) to synoptic scale (approximately 100 km to 1,000 km). These storms which mostly affect the southeast coast should not be confused with Australian region tropical cyclones which typically affect the northern half of the continent instead.
See also
* Hybrid low (disambiguation) * Extratropical transition technique *Mediterranean tropical-like cyclone
Mediterranean tropical-like cyclones, often referred to as Mediterranean cyclones or Mediterranean hurricanes, and shortened as medicanes, are meteorological phenomena occasionally observed over the Mediterranean Sea. On a few rare occasions, so ...
* Australian east coast low
* Polar low
* Subtropical Cyclone Katie
* Subtropical Storm Alpha (2020)
*Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
*Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of p ...
References
External links
NOAA FAQ on tropical cyclones
{{DEFAULTSORT:Subtropical Cyclone Subtropics