Subject side parameter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The subject-side parameter, also called the specifier–head parameter, is a proposed parameter within
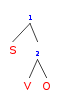 In this sentence, the
In this sentence, the
 Above, the
Above, the

 One of the explanations for such word order is that there is a
One of the explanations for such word order is that there is a
 Desmond C. Derbyshire suggested that this word order in Hixkaryana is based on its native-speakers' intuitions and
Desmond C. Derbyshire suggested that this word order in Hixkaryana is based on its native-speakers' intuitions and
generative linguistics
Generative grammar, or generativism , is a linguistic theory that regards linguistics as the study of a hypothesised innate grammatical structure. It is a biological or biologistic modification of earlier structuralist theories of linguistic ...
which states that the position of the subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
may precede or follow the head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may ...
. In the world's languages, Specifier-first order (i.e., subject-initial order) is more common than Specifier-final order (i.e., subject-final order). For example, in the World Atlas of Linguistic Structures (WALS), 76% of the languages in their sample Specifier-first (either SOV or SVO). In this respect, the subject-side parameter contrasts with the head-directionality parameter
In linguistics, head directionality is a proposed parameter that classifies languages according to whether they are head-initial (the head of a phrase precedes its complements) or head-final (the head follows its complements). The head is th ...
. The latter, which classifies languages according to whether the head precedes or follows its complement, shows a roughly 50-50 split: in languages that have a fixed word order, about half have a Head-Complement order, and half have a Complement-Head order.
History
First developed in the late 1960s and later introduced in his '' Lectures on Government and Binding'' (1981), Noam Chomsky presented his work onprinciples and parameters
Principles and parameters is a framework within generative linguistics in which the syntax of a natural language is described in accordance with general ''principles'' (i.e. abstract rules or grammars) and specific ''parameters'' (i.e. markers, sw ...
. Originally, it was not understood if word order was distinct from head order, but this was later proven by Flynn and Espinal using the case of Chinese and English showing the need for a subject side parameter.
Statistics
The following are 6 possible word orders that we can find across human languages.WALS
WALS (102.1 FM) is an American radio station broadcasting a country music format. Licensed to Oglesby, Illinois, United States, the station serves the LaSalle-Peru area. Branded as WALLS 102, the station is currently owned by Laco Radio and fe ...
, the World Atlas of Language Structures, presents a statistical estimation on languages with their own word orders.
The WALS database indicates that languages with the order subject-object-verb (SOV) and subject-verb-object (SVO) are overwhelmingly the most numerous. WALS
WALS (102.1 FM) is an American radio station broadcasting a country music format. Licensed to Oglesby, Illinois, United States, the station serves the LaSalle-Peru area. Branded as WALLS 102, the station is currently owned by Laco Radio and fe ...
cites there are 189 languages that have no dominant word order. However, taking this data into account as it is the most complete source of language structure data, X-bar Theory states that underlying structure Deep structure and surface structure (also D-structure and S-structure although those abbreviated forms are sometimes used with distinct meanings) are concepts used in linguistics, specifically in the study of syntax in the Noam Chomsky, Chomskyan t ...
will differ from surface structure, especially in languages that have seemingly non-dominant structures. Additionally, WALS
WALS (102.1 FM) is an American radio station broadcasting a country music format. Licensed to Oglesby, Illinois, United States, the station serves the LaSalle-Peru area. Branded as WALLS 102, the station is currently owned by Laco Radio and fe ...
data appears to lack any data on Amerindian languages or signed languages
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign l ...
.
Theories in word ordering
Subject-initial order
SVO
UsingWALS
WALS (102.1 FM) is an American radio station broadcasting a country music format. Licensed to Oglesby, Illinois, United States, the station serves the LaSalle-Peru area. Branded as WALLS 102, the station is currently owned by Laco Radio and fe ...
data, subject-verb-object languages, such as English, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
, are the second most populous languages in the world at 35.44% of the world's languages. SVO word order is thought to be derived from SOV word order to avoid the possible ambiguity caused by the topicalization of the objects. For example, the topicalization in SVO word order would result in OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
, which leaves the same sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
as in P NP VP
P, or p, is the sixteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''pee'' (pronounced ), plural ''pees''.
History
Th ...
One example of SVO language is an Old French example:
 In this sentence, the
In this sentence, the subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
noun phrase ''je'' comes at the beginning of the sentence, the verb ''croi'' comes the next and then the object noun phrase ''qu'elle...'' follows to form SVO word order. If we were to topicalize the object, then we would have two noun phrases before the verb, which will cause the ambiguity on which of the two noun phrases is the subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
and which is the object.
SOV
Subject-object-verb is another commonsentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
found in many languages. SOV has been thought to be the most "unmarked" word order and assumed to be the base of the other word orders according to X-bar Theory. Similarly, in two well-known studies done by Li and Thompson (1975), it is suggested that SOV word order codes definite
In linguistics, definiteness is a semantic feature of noun phrases, distinguishing between referents or senses that are identifiable in a given context (definite noun phrases) and those which are not (indefinite noun phrases). The prototypical d ...
object. Japanese and Korean are some languages that use SOV word order. In Korean, the subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
comes at the beginning of the sentence, followed by the object and then the verb. For example:
 Above, the
Above, the subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
''na'' comes at the beginning of the sentence, the object ''Yenghi'' follows and then the verb ''po-ass-e'' comes at the end. This forms SOV word order.
Subject-medial order
VSO
Verb-subject-objectstructure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
is thought to be derived from the SVO structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
. Examples of VSO languages are Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
and Arabic. The rarity of this word order may be occur as a result of this language occurring when V-fronting moves the verb out of the verb phrase in the SVO structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
and places it before the subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
This modification disrupts the underlying X-bar structure and thus makes VSO rarer due to the complexity of grammar. Thus, there is no X-bar Theory tree form for this. The subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
position in VSO languages is not properly governed, in that it can sway between VSO and SVO.
Alternately, there is evidence that many languages with a VSO word order can take on SVO as an alternate word order. There is evidence of the underlying structure Deep structure and surface structure (also D-structure and S-structure although those abbreviated forms are sometimes used with distinct meanings) are concepts used in linguistics, specifically in the study of syntax in the Noam Chomsky, Chomskyan t ...
in VSO languages being SVO. For example, in Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
, there is a SVO structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
occurring after auxiliaries but otherwise the sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
is VSO.
Below are two synonymous examples from Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
. Example 5 shows a sentence with VSO structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
and example 6 shows a sentence with SVO structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
:

OSV
Object-subject-verb is the rarestsentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
compared with the above sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
s. No languages are identified as having a basic OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
, however it thought that some Amazonian languages do. There are some languages that are identified as having some OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
s. Some of these languages are American Sign Language
American Sign Language (ASL) is a natural language that serves as the predominant sign language of Deaf communities in the United States of America and most of Anglophone Canadians, Anglophone Canada. ASL is a complete and organized visual lang ...
(ASL), English and German. However, ASL
American Sign Language (ASL) is a natural language that serves as the predominant sign language of Deaf communities in the United States of America and most of Anglophone Canada. ASL is a complete and organized visual language that is express ...
, like many others, does not consistently utilize an OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
. Sometimes if the verb is relating to aspect, it can adopt an SOV structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
. Here is an example of the order in which someone would sign:
One possibility that can explain the rarity of these languages, is that, in general, objects do not occur in initial position often. Subjects occur more often in initial position. This is why SVO and SOV are more common than both OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
and OVS.
The word order of OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
does not fit with the current X-bar Theory and therefore we can not draw a tree. There is some undetermined movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
that occurs or the tree structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
may be altered so that the subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
may be the sister of the verb.
Subject-final order
VOS
Verb-object-subject is an uncommonsentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
. Languages being classified to this structure are Malagasy and Ch'ol.
In these languages, it is mainly divided into two parts: subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
and predicate. In Malagasy, the position in a sentence is related to the degree of topicalization. The normal word order is that subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
is preceded by predicate. The following example is in Malagasy.
 One of the explanations for such word order is that there is a
One of the explanations for such word order is that there is a movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
occurred in the sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
. Specifically, the movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
is phrasal fronting as proposed by Jessica Coon in her paper focusing on Ch'ol, but it is very likely to be used to explain other languages having VOS word order. This proposal is a result of moving the verb phrase to a higher position in a syntactic tree form. The verb phrase is assumed to move to the specifier position of tense phrase. The reasons why there is a verb phrase movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
based on two main factors: agreement Agreement may refer to:
Agreements between people and organizations
* Gentlemen's agreement, not enforceable by law
* Trade agreement, between countries
* Consensus, a decision-making process
* Contract, enforceable in a court of law
** Meeting of ...
features
Feature may refer to:
Computing
* Feature (CAD), could be a hole, pocket, or notch
* Feature (computer vision), could be an edge, corner or blob
* Feature (software design) is an intentional distinguishing characteristic of a software item ...
on tense phrase and restriction on head movement
Syntactic movement is the means by which some theories of syntax address discontinuities. Movement was first postulated by structuralist linguists who expressed it in terms of ''discontinuous constituents'' or ''displacement''. Some constituen ...
. The whole verb phrase movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
acts as the last resort because the language disallow only the head to move. It must take the whole phrase to move instead.
In addition, Diana Massam also proposed that the Extended Projection Principle can be taken in account for the verb phrase movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
, given the predicate feature on the tense phrase.
OVS
Object-verb-subject is a minoritysentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
. There are some South American languages such as Hixkaryana and Urarina that have this uncommon structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
. The following example is from Hixkaryana:
 Desmond C. Derbyshire suggested that this word order in Hixkaryana is based on its native-speakers' intuitions and
Desmond C. Derbyshire suggested that this word order in Hixkaryana is based on its native-speakers' intuitions and statistical evidence
Scientific evidence is evidence that serves to either support or counter a scientific theory or hypothesis, although scientists also use evidence in other ways, such as when applying theories to practical problems. "Discussions about empirical ev ...
. These two pieces of evidence show that the object is followed by a verb and the subject
Subject ( la, subiectus "lying beneath") may refer to:
Philosophy
*''Hypokeimenon'', or ''subiectum'', in metaphysics, the "internal", non-objective being of a thing
**Subject (philosophy), a being that has subjective experiences, subjective cons ...
occurs in final position. On the other hand, Laura Kalin proposed there are three factors to make movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
occur in the sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
: focus, contrastive topic
Topic, topics, TOPIC, topical, or topicality may refer to:
Topic / Topics
* Topić, a Slavic surname
* ''Topics'' (Aristotle), a work by Aristotle
* Topic (chocolate bar), a brand of confectionery bar
* Topic (DJ), German musician
* Topic ...
and wh-questions. This is the driving force to make the verb phrase move to initial position.
Why are some word orders more common?
Though there are logically 6 possible word orders — namely SVO, SOV, VOS, OVS, VSO andOSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
— some orders are more common than others. There are research and studies been done in order to account for such phenomenon; a few of the possible reasons are as follows:
In Matthew Hall, Victor Ferreira and Rachel Mayberry’s paper, they argue that because there are three constraints — being efficient, keeping subjects before objects, avoiding SOV for reversible events — that the SVO word order can allow its users, it becomes more popular than others. Moreover, they clam that when gestural consistency and a passive interlocutor were both present, the SVO word order will appear significantly. Meanwhile, according to Luke Maurits, Amy Perfors and Daniel Navarro, the reason for object-initial languages to be less common than other word orders could be explained by the effects of Uniform Information Density (UID). They suggest that “object-first word orders lead to the least uniform information density in all three of heir
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officiall ...
estimated event distributions”(Maurits et al., 2010, p. 7), and was therefore least common. On the other hand, a stimulation study on word order bias also demonstrates that local syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
is one of the triggers of bias towards SOV/ SVO word orders; furthermore, the global syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
is also constrained by language encoded semantic structures.
Principle of Semantic Interpretation
Keenan (1978) postulates a Principle of Semantic Interpretation, which aims to explain why subject–predicate order is more common than predicate–subject order among the languages of the world. : ''Principle of Semantic Interpretation: The meaning of the predicate phrase often depends on the reference of the subject.'' Whereas a noun has a relatively fixed meaning (usually referring to a specific object in space), the meaning of a verb or adjective is sometimes disambiguated by the noun upon which it is predicated. One example of this phenomenon is the verb ''run''. This verb has a different meaning in each of the following sentences, determined by the respective subject: : ''The children are running.'' : ''The fish are running.'' : ''The buses are running today.'' : ''This watch is running.'' : ''The colors are running.'' : ''The water is running.'' : ''The stockings are running.'' : ''My nose is running.'' In a language with predicate–subject order, a listener must wait for the subject in order to correctly disambiguate the intended meaning of the predicate. Thus, Keenan proposes that subject–predicate order is intuitively preferable to predicate–subject order. Keenan also suggests that this principle has an ontological basis rather than a purely semantic one: objects can exist independently of properties that are ascribed to them, but properties cannot exist independently of objects that exemplify them.Changes over time
In some languages, there is evidence that the dominant word order has changed over time. For example, the dominant word order in Mandarin Chinese and German shifted from SOV to SVO. In Modern Chinese, one factor for this shift is the productivity of compound verbs. This increase in compound verbs lead to an increase in post-positions such as ''le'', ''bei'' and ''ba'', which are used as aspect markers. Li. C, Thompson. S. An Explanation of Word Order Change SVO→SOV Charles N. Springer Article, Vol. 12, No. 2 (Nov., 1974), pp. 201-214 https://www.jstor.org/stable/25000832See also
* Extended Projection Principle *Principles and parameters
Principles and parameters is a framework within generative linguistics in which the syntax of a natural language is described in accordance with general ''principles'' (i.e. abstract rules or grammars) and specific ''parameters'' (i.e. markers, sw ...
* Word Order
* X-bar theory
* Head-directionality parameter
In linguistics, head directionality is a proposed parameter that classifies languages according to whether they are head-initial (the head of a phrase precedes its complements) or head-final (the head follows its complements). The head is th ...
* Head (linguistics)
* Generative linguistics
Generative grammar, or generativism , is a linguistic theory that regards linguistics as the study of a hypothesised innate grammatical structure. It is a biological or biologistic modification of earlier structuralist theories of linguistic ...
* Noam Chomsky
* Transformational grammar
Further reading
* *References
{{Reflist, 30em Generative linguistics Generative syntax Syntax