St.Petersburg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), is the second-largest city in

 Swedish colonists built
Swedish colonists built  In 1810,
In 1810,
 On , the
On , the  On 26 January 1924, five days after Lenin's death, Petrograd was renamed ''Leningrad''. Later some streets and other toponyms were renamed accordingly. The city has over 230 places associated with the life and activities of Lenin. Some of them were turned into museums, including the cruiser ''Aurora''—a symbol of the October Revolution and the oldest ship in the Russian Navy.
In the 1920s and 1930s, the poor outskirts were reconstructed into regularly planned boroughs.
On 26 January 1924, five days after Lenin's death, Petrograd was renamed ''Leningrad''. Later some streets and other toponyms were renamed accordingly. The city has over 230 places associated with the life and activities of Lenin. Some of them were turned into museums, including the cruiser ''Aurora''—a symbol of the October Revolution and the oldest ship in the Russian Navy.
In the 1920s and 1930s, the poor outskirts were reconstructed into regularly planned boroughs.
 During
During
The siege lasted 872 days, or almost two and a half years, from 8 September 1941 to 27 January 1944. The
 In October 1946 some territories along the northern coast of the
In October 1946 some territories along the northern coast of the  Leningrad gave its name to the Leningrad Affair (1949–1952), a notable event in the postwar political struggle in the
Leningrad gave its name to the Leningrad Affair (1949–1952), a notable event in the postwar political struggle in the
 On 12 June 1991, simultaneously with the first Russian presidential elections, the city authorities arranged for the mayoral elections and a referendum upon the city's name, when the name reverted to Saint Petersburg. The turnout was 65%; 66.13% of the total count of votes went to Anatoly Sobchak, who became the first directly elected mayor of the city.
Meanwhile, economic conditions started to deteriorate as the country tried to adapt to major changes. For the first time since the 1940s, food
On 12 June 1991, simultaneously with the first Russian presidential elections, the city authorities arranged for the mayoral elections and a referendum upon the city's name, when the name reverted to Saint Petersburg. The turnout was 65%; 66.13% of the total count of votes went to Anatoly Sobchak, who became the first directly elected mayor of the city.
Meanwhile, economic conditions started to deteriorate as the country tried to adapt to major changes. For the first time since the 1940s, food 
 The law on election of the City Governor was changed, breaking the tradition of democratic election by universal suffrage. In 2006 the city legislature re-approved Matviyenko as governor. Residential building had intensified again; real-estate prices inflated greatly, which caused many new problems for the preservation of the historical part of the city.
Although the central part of the city has a
The law on election of the City Governor was changed, breaking the tradition of democratic election by universal suffrage. In 2006 the city legislature re-approved Matviyenko as governor. Residential building had intensified again; real-estate prices inflated greatly, which caused many new problems for the preservation of the historical part of the city.
Although the central part of the city has a
 The area of Saint Petersburg city proper is . The area of the federal subject is , which contains Saint Petersburg proper (consisting of eighty-one municipal ''
The area of Saint Petersburg city proper is . The area of the federal subject is , which contains Saint Petersburg proper (consisting of eighty-one municipal ''
 A 14- to 15-letter-long name, composed of the three roots proved too cumbersome, and many shortened versions were used. The first General Governor of the city Menshikov is maybe also the author of the first nickname of Petersburg which he called Петри (''Petri''). It took some years until the known Russian spelling of this name finally settled. In 1740s
A 14- to 15-letter-long name, composed of the three roots proved too cumbersome, and many shortened versions were used. The first General Governor of the city Menshikov is maybe also the author of the first nickname of Petersburg which he called Петри (''Petri''). It took some years until the known Russian spelling of this name finally settled. In 1740s  After the
After the
 Saint Petersburg is the second largest city in Russia. As of the 2017 Rosstat, the federal subject's population is 5,281,579 or 3.6% of the total population of Russia; up from 4,879,566 (3.4%) recorded in the 2010 Census, and up from 5,023,506 recorded in the 1989 Census.
Saint Petersburg is the second largest city in Russia. As of the 2017 Rosstat, the federal subject's population is 5,281,579 or 3.6% of the total population of Russia; up from 4,879,566 (3.4%) recorded in the 2010 Census, and up from 5,023,506 recorded in the 1989 Census.
 ;Vital statistics for 2016
* Births: 72 879 (13.9 per 1000)
* Deaths: 61 459 (11.7 per 1000)
;
Ethnic composition of Saint Petersburg
During the 20th century, the city experienced dramatic population changes. From 2.4 million residents in 1916, its population dropped to less than 740,000 by 1920 during the
;Vital statistics for 2016
* Births: 72 879 (13.9 per 1000)
* Deaths: 61 459 (11.7 per 1000)
;
Ethnic composition of Saint Petersburg
During the 20th century, the city experienced dramatic population changes. From 2.4 million residents in 1916, its population dropped to less than 740,000 by 1920 during the
Третье сокращение численности населения... и последнее?
''Demoscope Weekly'' 163 – 164, 1–15 August 2004. For the first half of 2007, the birth rate was 9.1 per 1000 and remained lower than the
 Saint Petersburg is a
Saint Petersburg is a  According to the federal law passed in 2004, heads of federal subjects, including the governor of Saint Petersburg, were nominated by the
According to the federal law passed in 2004, heads of federal subjects, including the governor of Saint Petersburg, were nominated by the

 Ten per cent of the world's power
Ten per cent of the world's power
 Saint Petersburg has three skyscrapers: Leader Tower (140 m), Alexander Nevsky (124 m) and Atlantic City (105 m) all far from the historical centre. Regulations forbid the construction of tall buildings in the city centre. The tall
Saint Petersburg has three skyscrapers: Leader Tower (140 m), Alexander Nevsky (124 m) and Atlantic City (105 m) all far from the historical centre. Regulations forbid the construction of tall buildings in the city centre. The tall 
 Unlike in Moscow, the historic architecture of Saint Petersburg's city centre, mostly Baroque and Neoclassical buildings of the 18th and 19th centuries, has been largely preserved; although a number of buildings were demolished after the Bolsheviks' seizure of power, during the
Unlike in Moscow, the historic architecture of Saint Petersburg's city centre, mostly Baroque and Neoclassical buildings of the 18th and 19th centuries, has been largely preserved; although a number of buildings were demolished after the Bolsheviks' seizure of power, during the 

 The
The 
 Many notable landmarks are to the west and south of the Admiralty Building, including the Trinity Cathedral, Mariinsky Palace, Hotel Astoria, famous
Many notable landmarks are to the west and south of the Admiralty Building, including the Trinity Cathedral, Mariinsky Palace, Hotel Astoria, famous  Southern suburbs of the city feature former imperial residences, including
Southern suburbs of the city feature former imperial residences, including
 Saint Petersburg is home to many parks and gardens. Some of the most well-known are in the southern suburbs, including Pavlovsk, one of Europe's largest
Saint Petersburg is home to many parks and gardens. Some of the most well-known are in the southern suburbs, including Pavlovsk, one of Europe's largest
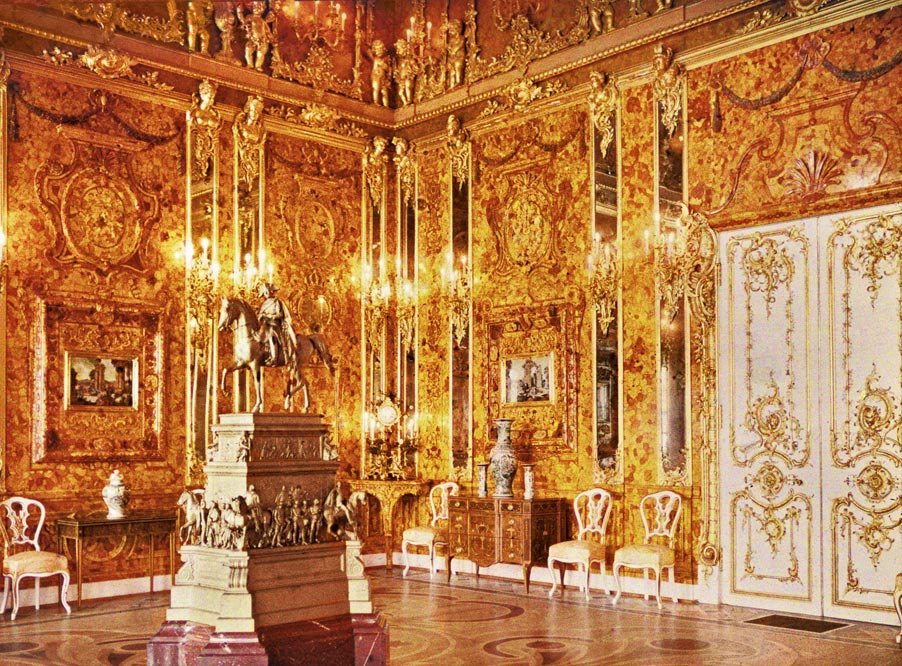
File:Cameron gallery in Tsarskoe Selo 02.jpg, alt=, Cameron gallery in Catherine park of Tsarskoe Selo.
File:Grot pavilion in Tsarskoe Selo.jpg, alt=, Grotto pavilion in Catherine park of Tsarskoe Selo
File:Liceum building in Tsarskoe Selo 03.jpg, alt=, The Imperial Lyceum in Tsarskoye Selo.
File:RUS-2016-Aerial-SPB-Grand Menshikov Palace.jpg, alt=, Grand Menshikov Palace.
 Saint Petersburg is inscribed on the
Saint Petersburg is inscribed on the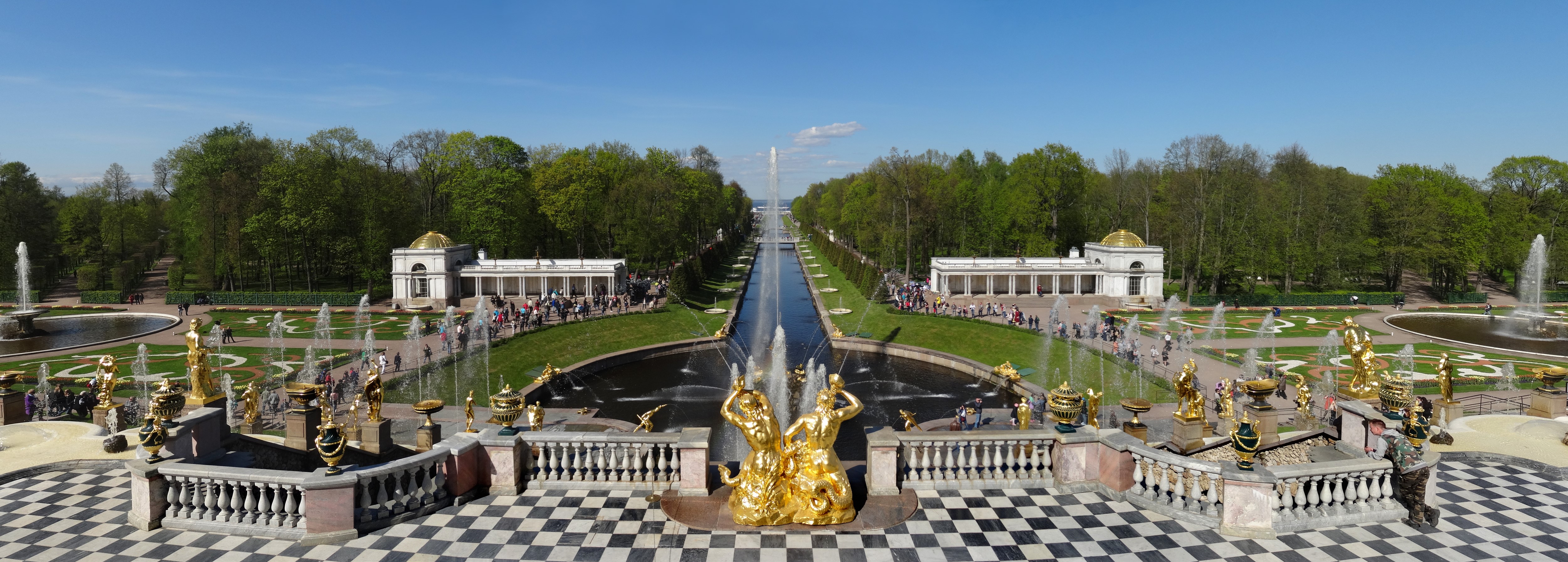  Despite the economic instability of the 1990s, not a single major theatre or museum was closed in Saint Petersburg; on the contrary many new ones opened, for example a private museum of puppets (opened in 1999) is the third museum of its kind in Russia, where collections of more than 2000 dolls are presented including 'The multinational Saint Petersburg' and Pushkin's Petersburg. The museum world of Saint Petersburg is incredibly diverse. The city is not only home to the world-famous
Despite the economic instability of the 1990s, not a single major theatre or museum was closed in Saint Petersburg; on the contrary many new ones opened, for example a private museum of puppets (opened in 1999) is the third museum of its kind in Russia, where collections of more than 2000 dolls are presented including 'The multinational Saint Petersburg' and Pushkin's Petersburg. The museum world of Saint Petersburg is incredibly diverse. The city is not only home to the world-famous  The musical life of Saint Petersburg is rich and diverse, with the city now playing host to a number of annual carnivals. Ballet performances occupy a special place in the cultural life of Saint Petersburg. The Petersburg School of Ballet is named as one of the best in the world. Traditions of the Russian classical school have been passed down from generation to generation among outstanding educators. The art of famous and prominent Saint Petersburg dancers like
The musical life of Saint Petersburg is rich and diverse, with the city now playing host to a number of annual carnivals. Ballet performances occupy a special place in the cultural life of Saint Petersburg. The Petersburg School of Ballet is named as one of the best in the world. Traditions of the Russian classical school have been passed down from generation to generation among outstanding educators. The art of famous and prominent Saint Petersburg dancers like
File:Exterior of Hermitage Museum-2.jpg, alt=, The State Hermitage Museum is the largest art museum in the world by gallery space.
File:Russian museam.JPG, alt=, The State Russian Museum is the world's largest depository of Russian fine art.
File:Этнографический музей (СПБ).jpg, alt=, The Russian Museum of Ethnography is one of the largest ethnographic museums in the world.
A number of museums provide insight into the Soviet history of Saint Petersburg, including the Museum of the Blockade, which describes the

 Among the city's more than fifty theatres is the
Among the city's more than fifty theatres is the  Dmitri Shostakovich, who was born and raised in Saint Petersburg, dedicated his Seventh Symphony to the city, calling it the "Leningrad Symphony". He wrote the symphony while based in the city during the siege of Leningrad. It was premiered in Samara in March 1942; a few months later, it received its first
Dmitri Shostakovich, who was born and raised in Saint Petersburg, dedicated his Seventh Symphony to the city, calling it the "Leningrad Symphony". He wrote the symphony while based in the city during the siege of Leningrad. It was premiered in Samara in March 1942; a few months later, it received its first
 Saint Petersburg has a longstanding and world-famous tradition in literature.
Saint Petersburg has a longstanding and world-famous tradition in literature.
 Over 250 international and Russian movies were filmed in Saint Petersburg. Well over a thousand feature films about tsars, revolution, people and stories set in Saint Petersburg have been produced worldwide but not filmed in the city. The first film studios were founded in Saint Petersburg in the 20th century and since the 1920s
Over 250 international and Russian movies were filmed in Saint Petersburg. Well over a thousand feature films about tsars, revolution, people and stories set in Saint Petersburg have been produced worldwide but not filmed in the city. The first film studios were founded in Saint Petersburg in the 20th century and since the 1920s
Leteiny Theatre
an
Youth Theatre on the Fontanka
 Leningrad hosted part of the association football tournament during the 1980
Leningrad hosted part of the association football tournament during the 1980
 Saint Petersburg is a major transport hub. The first Russian railway was built here in 1837, and since then the city's transport infrastructure has kept pace with the city's growth. Petersburg has an extensive system of local roads and railway services, maintains a large public transport system that includes the
Saint Petersburg is a major transport hub. The first Russian railway was built here in 1837, and since then the city's transport infrastructure has kept pace with the city's growth. Petersburg has an extensive system of local roads and railway services, maintains a large public transport system that includes the

 Saint Petersburg has an extensive city-funded network of public transport (buses,
Saint Petersburg has an extensive city-funded network of public transport (buses,
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
. It is situated on the Neva
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it i ...
River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
on the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
, with a population of roughly 5.4 million residents. Saint Petersburg is the fourth-most populous city in Europe after Istanbul, Moscow and London, the most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As Russia's Imperial capital, and a historically strategic port, it is governed as a federal city.
The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
on 27 May 1703 on the site of a captured Swedish fortress, and was named after apostle Saint Peter
) (Simeon, Simon)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire
, death_date = Between AD 64–68
, death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire
, parents = John (or Jonah; Jona)
, occupa ...
. In Russia, Saint Petersburg is historically and culturally associated with the birth of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
and Russia's entry into modern history as a European great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power inf ...
. It served as a capital of the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
, and the subsequent Russian Empire, from 1713 to 1918 (being replaced by Moscow for a short period of time between 1728 and 1730). After the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
in 1917, the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
moved their government to Moscow.
As Russia's cultural center, Saint Petersburg received over 15 million tourists in 2018. It is considered an important economic, scientific, and tourism centre of Russia and Europe. In modern times, the city has the nickname of being "the Northern Capital of Russia" and is home to notable federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-govern ...
bodies such as the Constitutional Court of Russia
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
and the Heraldic Council of the President of the Russian Federation. It is also a seat for the National Library of Russia
The National Library of Russia (NLR, russian: Российская национальная библиотека}), located in Saint Petersburg, is the first, and one of three national public libraries in Russia. The NLR is currently ranked amo ...
and a planned location for the Supreme Court of Russia
The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation (russian: links=no, Верховный суд Российской Федерации, Verkhovny sud Rossiyskoy Federatsii) is a court within the judiciary of Russia and the court of last resort in R ...
, as well as the home to the headquarters of the Russian Navy, and the Western Military District
The Western Military District (russian: Западный военный округ, Zapadnyy voyennyy okrug) is a military district of Russia.
It is one of the five military districts of the Russian Armed Forces, with its jurisdiction prima ...
of the Russian Armed Forces
The Armed Forces of the Russian Federation (, ), commonly referred to as the Russian Armed Forces, are the military forces of Russia. In terms of active-duty personnel, they are the world's fifth-largest military force, with at least two m ...
. The Historic Centre of Saint Petersburg and Related Groups of Monuments constitute a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
. Saint Petersburg is home to the Hermitage, one of the largest art museum
An art museum or art gallery is a building or space for the display of art, usually from the museum's own Collection (artwork), collection. It might be in public or private ownership and may be accessible to all or have restrictions in place. ...
s in the world, the Lakhta Center
The Lakhta Center () is an 87-story skyscraper built in the northwestern neighbourhood of Lakhta in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Standing tall, it is the tallest building in Russia, the tallest building in Europe, and the sixteenth-tallest bu ...
, the tallest skyscraper in Europe, and was one of the host cities of the 2018 FIFA World Cup
The 2018 FIFA World Cup was the 21st FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial world championship for men's national football teams organized by FIFA. It took place in Russia from 14 June to 15 July 2018, after the country was awarded the hosting righ ...
and the UEFA Euro 2020
The 2020 UEFA European Football Championship, commonly referred to as UEFA Euro 2020 (stylised as UEFA EURO 2020) or simply Euro 2020, was the 16th UEFA European Championship, the quadrennial international men's football championship of Euro ...
.
Toponymy
A proponent ofwesternising
Westernization (or Westernisation), also Europeanisation or occidentalization (from the '' Occident''), is a process whereby societies come under or adopt Western culture in areas such as industry, technology, science, education, politics ...
Russia, Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
, the then Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the te ...
, who established the city, originally named it () in Dutch manner and later its spelling was standardised as Sankt-Peterburg () under German influence. On 1 September 1914, after the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the Imperial government renamed the city ''Petrograd'' ( rus, links=no, Петроград, p=pʲɪtrɐˈgrat), meaning 'Peter's city', in order to expunge the German words and . On 26 January 1924, shortly after the death of Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
, it was renamed to ''Leningrad'' ( rus, links=no, Ленинград, p=lʲɪnʲɪnˈgrat), meaning 'Lenin's City'. On 6 September 1991, the original name, ''Sankt-Peterburg'', was returned by citywide referendum. Today, in English the city is known as ''Saint Petersburg''. Local residents often refer to the city by its shortened nickname, ''Piter'' ( rus, links=no, Питер, p=ˈpʲitʲɪr).
A former spelling of the city's name in English was ''Saint Petersburgh'', under the influence of ''burgh''. This spelling survives in the name of a street in the Bayswater
Bayswater is an area within the City of Westminster in West London. It is a built-up district with a population density of 17,500 per square kilometre, and is located between Kensington Gardens to the south, Paddington to the north-east, and ...
district of London, near St Sophia's Cathedral, named after a visit by the Tsar to London in 1814.
Saint Petersburg has been traditionally called the "Window to Europe" and the "Window to the West" by the Russians. The city is the northernmost metropolis in the world, and is also often described as the "Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
of the North" or the "Russian Venice" due to its many water corridors, as the city is built on swamp and water. Furthermore, it has strongly Western European-inspired architecture and culture, which is combined with the city's Russian heritage. Another nickname of Saint Petersburg is "The City of the White Nights" because of a natural phenomenon which arises due to the closeness to the polar region
The polar regions, also called the frigid zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high latitudes are dominated by flo ...
and ensures that in summer the night skies of the city do not get completely dark for a month. The city is also often called the "Northern Palmyra
Palmyra (; Palmyrene: () ''Tadmor''; ar, تَدْمُر ''Tadmur'') is an ancient city in present-day Homs Governorate, Syria. Archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first mention the city in the early seco ...
", due to its extravagant architecture.
History
Imperial era (1703–1917)

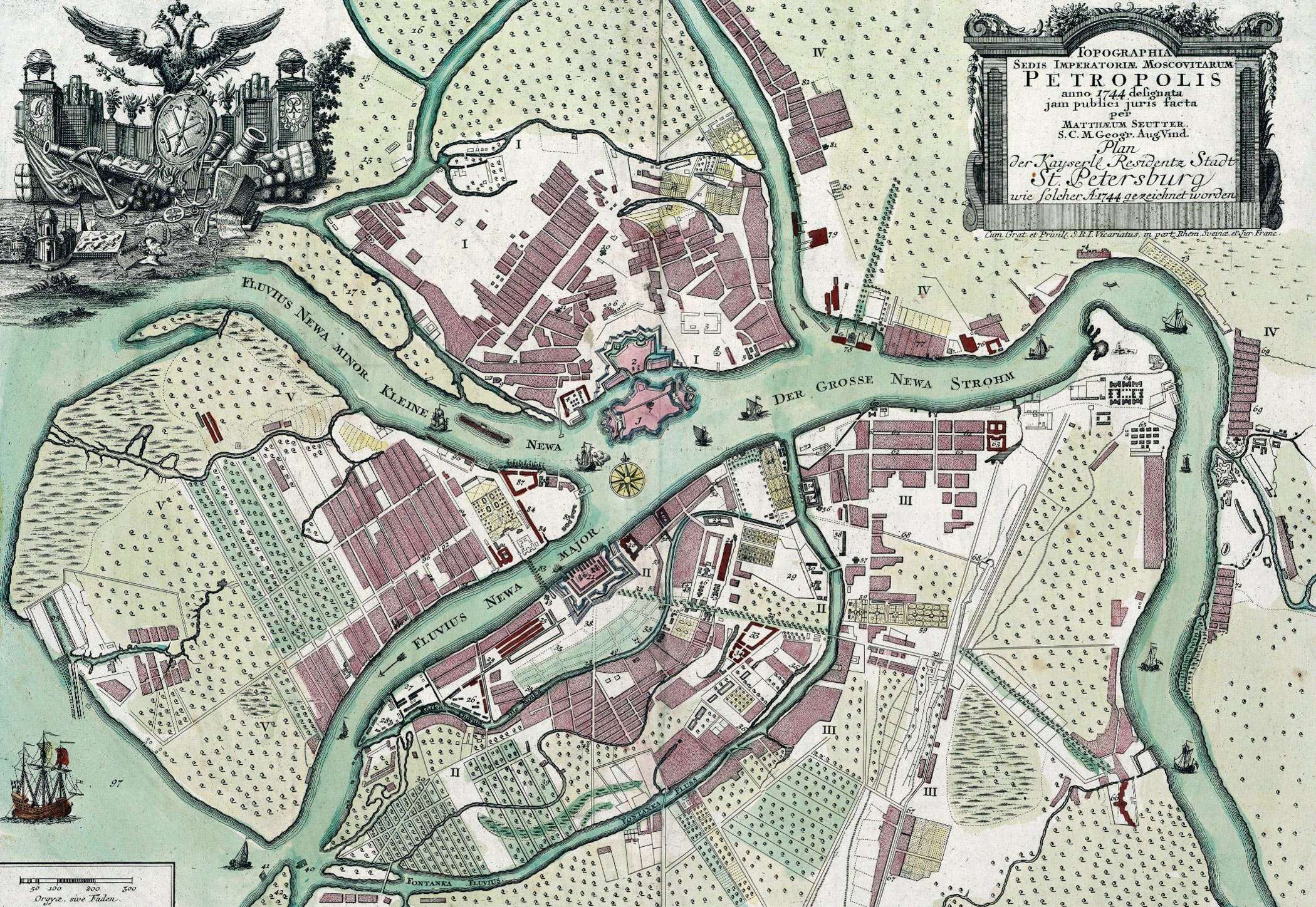
 Swedish colonists built
Swedish colonists built Nyenskans
Nyenschantz (russian: Ниенша́нц, ''Nienshants''; sv, Nyenskans; fi, Nevanlinna) was a Swedish fortress at the confluence of the Neva River and Okhta River, the site of present-day Saint Petersburg, Russia. Nyenschantz was built in 1611 ...
, a fortress at the mouth of the Neva
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it i ...
River in 1611, which was later called Ingermanland. This area was inhabited by a Finnic tribe of Ingrians
The Ingrians ( fi, inkeriläiset, ; russian: Ингерманландцы, translit=Ingermanlandts'i), sometimes called Ingrian Finns, are the Finnish population of Ingria (now the central part of Leningrad Oblast in Russia), descending from Lu ...
. The small town of Nyen grew up around the fort.
At the end of the 17th century, Peter the Great, who was interested in seafaring and maritime affairs, wanted Russia to gain a seaport to trade with the rest of Europe. He needed a better seaport than the country's main one at the time, Arkhangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ; rus, Арха́нгельск, p=ɐrˈxanɡʲɪlʲsk), also known in English as Archangel and Archangelsk, is a city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near i ...
, which was on the White Sea
The White Sea (russian: Белое море, ''Béloye móre''; Karelian and fi, Vienanmeri, lit. Dvina Sea; yrk, Сэрако ямʼ, ''Serako yam'') is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is s ...
in the far north and closed to shipping during the winter.
On , during the Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swed ...
, Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
captured Nyenskans and soon replaced the fortress. On , closer to the estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
( inland from the gulf), on Zayachy (Hare) Island, he laid down the Peter and Paul Fortress
The Peter and Paul Fortress is the original citadel of St. Petersburg, Russia, founded by Peter the Great in 1703 and built to Domenico Trezzini's designs from 1706 to 1740 as a star fortress. Between the first half of the 1700s and early 1920 ...
, which became the first brick and stone building of the new city.
The city was built by conscripted peasants from all over Russia; in some years several Swedish prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
were also involved under the supervision of Alexander Menshikov. Tens of thousands of serfs died while building the city. Later, the city became the centre of the Saint Petersburg Governorate
Saint Petersburg Governorate (russian: Санкт-Петербу́ргская губе́рния, ''Sankt-Peterburgskaya guberniya''), or Government of Saint Petersburg, was an administrative division (a '' guberniya'') of the Tsardom of Russia ...
. Peter moved the capital from Moscow to Saint Petersburg in 1712, 9 years before the Treaty of Nystad
The Treaty of Nystad (russian: Ништадтский мир; fi, Uudenkaupungin rauha; sv, Freden i Nystad; et, Uusikaupunki rahu) was the last peace treaty of the Great Northern War of 1700–1721. It was concluded between the Tsardom of ...
of 1721 ended the war. He referred to Saint Petersburg as the capital (or seat of government) as early as 1704. While the city was being built, Peter lived in a three-room log cabin with his wife Catherine and their children.
During its first few years, the city developed around Trinity Square on the right bank of the Neva, near the Peter and Paul Fortress. However, Saint Petersburg soon started to be built out according to a plan. By 1716 the Swiss Italian
The Italian language in Switzerland or Swiss Italian ( it, italiano svizzero) is the variety of the Italian language taught in the Italian-speaking area of Switzerland. Italian is spoken natively by about 700,000 people in the canton of Ticin ...
Domenico Trezzini had elaborated a project whereby the city centre would be on Vasilyevsky Island
Vasilyevsky Island (russian: Васи́льевский о́стров, Vasilyevsky Ostrov, V.O.) is an island in St. Petersburg, Russia, bordered by the Bolshaya Neva and Malaya Neva Rivers (in the delta of the Neva River) in the south ...
and shaped by a rectangular grid of canals. The project was not completed but is evident in the layout of the streets. In 1716, Peter the Great appointed Frenchman Jean-Baptiste Alexandre Le Blond
Jean-Baptiste Alexandre Le Blond (1679 – 10 March 1719) was a French architect and garden designer who became the chief architect of Saint Petersburg in 1716.
Career in France
He was the son of Jean Le Blond, painter in ordinary to the king, a ...
as the chief architect of Saint Petersburg.
The style of Petrine Baroque, developed by Trezzini and other architects and exemplified by such buildings as the Menshikov Palace, Kunstkamera
The Kunstkamera (russian: Кунсткамера) or Kunstkammer ( German for "Culture Room" (literally) or "Art Chamber", typically used for a " cabinet of curiosities") is a public museum located on the Universitetskaya Embankment in Saint P ...
, Peter and Paul Cathedral, Twelve Collegia, became prominent in the city architecture of the early 18th century. In 1724 the Academy of Sciences
An academy of sciences is a type of learned society or academy (as special scientific institution) dedicated to sciences that may or may not be state funded. Some state funded academies are tuned into national or royal (in case of the Unit ...
, University
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which ...
and Academic Gymnasium were established in Saint Petersburg by Peter the Great.
In 1725, Peter died at age fifty-two. His endeavors to modernize Russia had been opposed by the Russian nobility
The Russian nobility (russian: дворянство ''dvoryanstvo'') originated in the 14th century. In 1914 it consisted of approximately 1,900,000 members (about 1.1% of the population) in the Russian Empire.
Up until the February Revolutio ...
. There were several attempts on his life and a treason case involving his son. In 1728, Peter II of Russia
Peter II Alexeyevich (russian: Пётр II, Пётр Алексеевич, ''Pyotr Vtoroy'', ''Pyotr Alekseyevich'', – ) reigned as Emperor of Russia from 1727 until his untimely death at the age of 14. He was the only son of Tsarevich Alexei ...
moved his seat back to Moscow. But four years later, in 1732, under Empress Anna of Russia
Anna Ioannovna (russian: Анна Иоанновна; ), also russified as Anna Ivanovna and sometimes anglicized as Anne, served as regent of the duchy of Courland from 1711 until 1730 and then ruled as Empress of Russia from 1730 to 1740. Muc ...
, Saint Petersburg was again designated as the capital of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
. It remained the seat of the Romanov dynasty
The House of Romanov (also transcribed Romanoff; rus, Романовы, Románovy, rɐˈmanəvɨ) was the reigning imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after the Tsarina, Anastasia Romanova, was married to th ...
and the Imperial Court of the Russian tsars, as well as the seat of the Russian government, for another 186 years until the communist revolution of 1917.
In 1736–1737 the city suffered from catastrophic fires. To rebuild the damaged boroughs, a committee under Burkhard Christoph von Münnich commissioned a new plan in 1737. The city was divided into five boroughs, and the city centre was moved to the Admiralty borough, on the east bank between the Neva and Fontanka
The Fontanka (russian: Фонтанка), a left branch of the river Neva, flows through the whole of Central Saint Petersburg, Russia – from the Summer Garden to . It is long, with a width up to , and a depth up to . The Moyka River ...
.
It developed along three radial streets, which meet at the Admiralty building and are now known as Nevsky Prospect
Nevsky Prospect ( rus, Не́вский проспе́кт, r=Nevsky Prospekt, p=ˈnʲɛfskʲɪj prɐˈspʲɛkt) is the main street ( high street) in the federal city of St. Petersburg in Russia. It takes its name from the Alexander Nevsk ...
(which is considered the main street of the city), Gorokhovaya Street and Voznesensky Avenue. Baroque architecture
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the early 17th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means t ...
became dominant in the city during the first sixty years, culminating in the Elizabethan Baroque, represented most notably by Italian Bartolomeo Rastrelli with such buildings as the Winter Palace
The Winter Palace ( rus, Зимний дворец, Zimnij dvorets, p=ˈzʲimnʲɪj dvɐˈrʲɛts) is a palace in Saint Petersburg that served as the official residence of the Emperor of all the Russias, Russian Emperor from 1732 to 1917. The p ...
. In the 1760s, Baroque architecture was succeeded by neoclassical architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing sty ...
.
Established in 1762, the Commission of Stone Buildings of Moscow and Saint Petersburg ruled that no structure in the city could be higher than the Winter Palace and prohibited spacing between buildings. During the reign of Catherine the Great in the 1760s–1780s, the banks of the Neva were lined with granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
embankments.
However, it was not until 1850 that the first permanent bridge across the Neva, Annunciation Bridge, was allowed to open. Before that, only pontoon bridge
A pontoon bridge (or ponton bridge), also known as a floating bridge, uses floats or shallow- draft boats to support a continuous deck for pedestrian and vehicle travel. The buoyancy of the supports limits the maximum load that they can carry. ...
s were allowed. Obvodny Canal (dug in 1769–1833) became the southern limit of the city.
The most prominent neoclassical and Empire-style architects in Saint Petersburg included:
* Jean-Baptiste Vallin de la Mothe (Imperial Academy of Arts
The Russian Academy of Arts, informally known as the Saint Petersburg Academy of Arts, was an art academy in Saint Petersburg, founded in 1757 by the founder of the Imperial Moscow University Ivan Shuvalov under the name ''Academy of the T ...
, Small Hermitage
The State Hermitage Museum ( rus, Государственный Эрмитаж, r=Gosudarstvennyj Ermitaž, p=ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)ɨj ɪrmʲɪˈtaʂ, links=no) is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is the largest ...
, Gostiny Dvor
Gostinyi dvor ( rus, гостиный двор, p=ɡɐˈsʲtʲinɨj ˈdvor) is a historic Russian term for an indoor market or shopping centre. It is translated from Russian either as "guest court" or "merchant yard", although both translations a ...
, New Holland Arch, Catholic Church of St. Catherine)
* Antonio Rinaldi (Marble Palace
Marble Palace (Мраморный дворец) is one of the first Neoclassical palaces in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is situated between the Field of Mars and Palace Quay, slightly to the east from New Michael Palace.
Design and pre-1917 o ...
)
* Yury Felten (Old Hermitage
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
*Old, Baranya, Hungary
*Old, Northamptonshire, England
*Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Mai ...
, Chesme Church)
* Giacomo Quarenghi
Giacomo Quarenghi (; rus, Джа́комо Кваре́нги, Džákomo Kvaréngi, ˈdʐakəmə kvɐˈrʲenʲɡʲɪ; 20 or 21 September 1744) was an Italian architect who was the foremost and most prolific practitioner of neoclassical architectu ...
(Academy of Sciences, Hermitage Theatre
The Hermitage Theatre ( rus, Эрмитажный Театр, Èrmitážnyj Teátr, ɪrʲmʲɪˈtaʐnɨj tʲɪˈatər) in Saint Petersburg, Russia is one of five Hermitage buildings lining the Palace Embankment of the Neva River.
The Hermitag ...
, Yusupov Palace)
* Andrey Voronikhin
Andrey (Andrei) Nikiforovich Voronikhin (russian: Андрей Никифорович Воронихин) (28 October 1759, Novoe Usolye, Perm Oblast – 21 February 1814, Saint Petersburg) was a Russian architect and painter. As a representa ...
( Mining Institute, Kazan Cathedral)
* Andreyan Zakharov ( Admiralty building)
* Jean-François Thomas de Thomon (Spit of Vasilievsky Island
The Old Saint Petersburg Stock Exchange (also '' Bourse'') and Rostral Columns, located in Saint Petersburg in the Russian Federation, are significant examples of Greek Revival architecture. Designed by French architect Thomas de Thomon, and i ...
)
* Carlo Rossi ( Yelagin Palace, Mikhailovsky Palace, Alexandrine Theatre
The Alexandrinsky Theatre (russian: Александринский театр) or National Drama Theatre of Russia is a theatre in Saint Petersburg, Russia.
The Alexandrinsky Theatre was built for the Imperial troupe of Petersburg (Imperial trou ...
, Senate and Synod Buildings, General staff Building, design of many streets and squares)
* Vasily Stasov ( Moscow Triumphal Gate, Trinity Cathedral)
* Auguste de Montferrand
Auguste de Montferrand (; January 23, 1786 – July 10, 1858) was a French classicist architect who worked primarily in Russia. His two best known works are the Saint Isaac's Cathedral and the Alexander Column in St. Petersburg.
Ear ...
(Saint Isaac's Cathedral
Saint Isaac's Cathedral or Isaakievskiy Sobor (russian: Исаа́киевский Собо́р) is a large architectural landmark cathedral that currently functions as a museum with occasional church services in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is ...
, Alexander Column)
 In 1810,
In 1810, Alexander I Alexander I may refer to:
* Alexander I of Macedon, king of Macedon 495–454 BC
* Alexander I of Epirus (370–331 BC), king of Epirus
* Pope Alexander I (died 115), early bishop of Rome
* Pope Alexander I of Alexandria (died 320s), patriarch of ...
established the first engineering Higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after compl ...
, the Saint Petersburg Main military engineering School in Saint Petersburg. Many monuments commemorate the Russian victory over Napoleonic France
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Eu ...
in the Patriotic War of 1812
The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign, the Second Polish War, the Army of Twenty nations, and the Patriotic War of 1812 was launched by Napoleon Bonaparte to force the Russian Empire back into the continental block ...
, including the Alexander Column by Montferrand, erected in 1834, and the Narva Triumphal Arch.
In 1825, the suppressed Decembrist revolt
The Decembrist Revolt ( ru , Восстание декабристов, translit = Vosstaniye dekabristov , translation = Uprising of the Decembrists) took place in Russia on , during the interregnum following the sudden death of Emperor Al ...
against Nicholas I took place on the Senate Square in the city, a day after Nicholas assumed the throne.
By the 1840s, neoclassical architecture had given way to various romanticist styles, which dominated until the 1890s, represented by such architects as Andrei Stackenschneider ( Mariinsky Palace, Beloselsky-Belozersky Palace, Nicholas Palace, New Michael Palace) and Konstantin Thon
Konstantin Andreyevich Thon, also spelled Ton (russian: Константи́н Андре́евич Тон; October 26, 1794 – January 25, 1881) was an official architect of Imperial Russia during the reign of Nicholas I. His major works includ ...
( Moskovsky railway station).
With the emancipation of the serfs undertaken by Alexander II in 1861 and an Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, the influx of former peasants into the capital increased greatly. Poor boroughs spontaneously developed on the outskirts of the city. Saint Petersburg surpassed Moscow in population and industrial growth; it became one of the largest industrial cities in Europe, with a major naval base (in Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for " crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city ...
), the Neva River, and a seaport on the Baltic.
The names of Saints Peter and Paul, bestowed upon the original city's citadel and its cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominatio ...
(from 1725—a burial vault of Russian emperors) coincidentally were the names of the first two assassinated Russian emperors, Peter III (1762, supposedly killed in a conspiracy led by his wife, Catherine the Great) and Paul I (1801, Nikolay Alexandrovich Zubov and other conspirators who brought to power Alexander I, the son of their victim). The third emperor's assassination took place in Saint Petersburg in 1881 when Alexander II was murdered by terrorists
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
(see the Church of the Savior on Blood
The Church of the Savior on Spilled Blood (russian: Церковь Спаса на Крови, ''Tserkovʹ Spasa na Krovi'') is a Russian Orthodox church in Saint Petersburg, Russia which currently functions as a secular museum and church at t ...
).
The Revolution of 1905
The Russian Revolution of 1905,. also known as the First Russian Revolution,. occurred on 22 January 1905, and was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. The mass unrest was directed again ...
began in Saint Petersburg and spread rapidly into the provinces.
On 1 September 1914, after the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the Imperial government renamed the city ''Petrograd'', meaning "Peter's City", to remove the German words '' Sankt'' and '' Burg''.
Revolution and Soviet era (1917–1941)
In March 1917, during the February Revolution Nicholas II abdicated for himself and on behalf of his son, ending the Russian monarchy and over three hundred years of Romanovdynastic rule
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A d ...
.
 On , the
On , the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
s, led by Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
, stormed the Winter Palace
The Winter Palace ( rus, Зимний дворец, Zimnij dvorets, p=ˈzʲimnʲɪj dvɐˈrʲɛts) is a palace in Saint Petersburg that served as the official residence of the Emperor of all the Russias, Russian Emperor from 1732 to 1917. The p ...
in an event known thereafter as the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
, which led to the end of the post-Tsarist provisional government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, or a transitional government, is an emergency governmental authority set up to manage a political transition generally in the cases of a newly formed state or f ...
, the transfer of all political power to the Soviets, and the rise of the Communist Party
A communist party is a political party that seeks to realize the socio-economic goals of communism. The term ''communist party'' was popularized by the title of '' The Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (1848) by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. ...
. After that the city acquired a new descriptive name, "the city of three revolutions", referring to the three major developments in the political history of Russia of the early 20th century.
In September and October 1917, German troops invaded the West Estonian archipelago
West Estonian archipelago ( et, Lääne-Eesti saarestik, also Moonsund archipelago) is a group of Estonian islands located in the Baltic Sea around Väinameri. The total area is about . The archipelago is composed of the islands Saaremaa, Hiiu ...
and threatened Petrograd with bombardment and invasion. On 12 March 1918, the Soviets transferred the government to Moscow, to keep it away from the state border. During the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, in mid-1919 Russian anti-communist forces with the help of Estonians
Estonians or Estonian people ( et, eestlased) are a Finnic ethnic group native to Estonia who speak the Estonian language.
The Estonian language is spoken as the first language by the vast majority of Estonians; it is closely related to othe ...
attempted to capture the city, but Leon Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein. ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky; uk, link= no, Лев Давидович Троцький; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trotskij'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky''. (), was a Russian M ...
mobilized the army and forced them to retreat back to Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and t ...
.
 On 26 January 1924, five days after Lenin's death, Petrograd was renamed ''Leningrad''. Later some streets and other toponyms were renamed accordingly. The city has over 230 places associated with the life and activities of Lenin. Some of them were turned into museums, including the cruiser ''Aurora''—a symbol of the October Revolution and the oldest ship in the Russian Navy.
In the 1920s and 1930s, the poor outskirts were reconstructed into regularly planned boroughs.
On 26 January 1924, five days after Lenin's death, Petrograd was renamed ''Leningrad''. Later some streets and other toponyms were renamed accordingly. The city has over 230 places associated with the life and activities of Lenin. Some of them were turned into museums, including the cruiser ''Aurora''—a symbol of the October Revolution and the oldest ship in the Russian Navy.
In the 1920s and 1930s, the poor outskirts were reconstructed into regularly planned boroughs. Constructivist architecture
Constructivist architecture was a constructivist style of modern architecture that flourished in the Soviet Union in the 1920s and early 1930s. Abstract and austere, the movement aimed to reflect modern industrial society and urban space, whil ...
flourished around that time. Housing became a government-provided amenity; many "bourgeois" apartments were so large that numerous families were assigned to what were called "communal" apartments ('' kommunalkas''). By the 1930s, 68% of the population lived in such housing. In 1935 a new general plan was outlined, whereby the city should expand to the south. Constructivism was rejected in favour of a more pompous Stalinist architecture. Moving the city centre further from the border with Finland, Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
adopted a plan to build a new city hall with a huge adjacent square at the southern end of Moskovsky Prospekt, designated as the new main street of Leningrad. After the Winter (Soviet-Finnish) war in 1939–1940, the Soviet–Finnish border moved northwards. Nevsky Prospekt with Palace Square maintained the functions and the role of a city centre.
In December 1931, Leningrad was administratively separated from Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast ( rus, Ленинградская область, Leningradskaya oblast’, lʲɪnʲɪnˈgratskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ, , ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 1 ...
. At that time it included the Leningrad Suburban District, some parts of which were transferred back to Leningrad Oblast in 1936 and turned into Vsevolozhsky District, Krasnoselsky District, Pargolovsky District and Slutsky District (renamed Pavlovsky District in 1944).
On 1 December 1934, Sergey Kirov
Sergei Mironovich Kirov ( né Kostrikov; 27 March 1886 – 1 December 1934) was a Soviet politician and Bolshevik revolutionary whose assassination led to the first Great Purge.
Kirov was an early revolutionary in the Russian Empire and memb ...
, the popular communist leader of Leningrad, was assassinated, which became the pretext for the Great Purge
The Great Purge or the Great Terror (russian: Большой террор), also known as the Year of '37 (russian: 37-й год, translit=Tridtsat sedmoi god, label=none) and the Yezhovshchina ('period of Yezhov'), was Soviet General Secreta ...
. In Leningrad, approximately 40,000 were executed during Stalin's purges.
World War II (1941–1945)
 During
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, German forces besieged Leningrad following the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941.Siege of LeningradThe siege lasted 872 days, or almost two and a half years, from 8 September 1941 to 27 January 1944. The
Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet Union, So ...
proved one of the longest, most destructive, and most lethal sieges of a major city in modern history. It isolated the city from food supplies except those provided through the Road of Life across Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga (; rus, Ла́дожское о́зеро, r=Ladozhskoye ozero, p=ˈladəʂskəjə ˈozʲɪrə or rus, Ла́дога, r=Ladoga, p=ˈladəɡə, fi, Laatokka arlier in Finnish ''Nevajärvi'' ; vep, Ladog, Ladoganjärv) is a fresh ...
, which could not make it through until the lake froze. More than one million civilians were killed, mainly from starvation. Many others escaped or were evacuated, so the city became largely depopulated.
On 1 May 1945 Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
, in his Supreme Commander Order No. 20, named Leningrad, alongside Stalingrad
Volgograd ( rus, Волгогра́д, a=ru-Volgograd.ogg, p=vəɫɡɐˈɡrat), formerly Tsaritsyn (russian: Цари́цын, Tsarítsyn, label=none; ) (1589–1925), and Stalingrad (russian: Сталингра́д, Stalingrád, label=none; ) ...
, Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
, and Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrat ...
, hero cities
A hero (feminine: heroine) is a real person or a main fictional character who, in the face of danger, combats adversity through feats of ingenuity, courage, or strength. Like other formerly gender-specific terms (like ''actor''), ''hero ...
of the war. A law acknowledging the honorary title of "Hero City" passed on 8 May 1965 (the 20th anniversary of the victory in the Great Patriotic War), during the Brezhnev era. The Presidium of the Supreme Soviet
The Presidium of the Supreme Soviet (russian: Президиум Верховного Совета, Prezidium Verkhovnogo Soveta) was a body of state power in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR).Order of Lenin
The Order of Lenin (russian: Орден Ленина, Orden Lenina, ), named after the leader of the Russian October Revolution, was established by the Central Executive Committee on April 6, 1930. The order was the highest civilian decoration ...
and the Gold Star medal "for the heroic resistance of the city and tenacity of the survivors of the Siege". The Hero-City Obelisk bearing the Gold Star sign was installed in April 1985.
Post-war Soviet era (1945–1991)
 In October 1946 some territories along the northern coast of the
In October 1946 some territories along the northern coast of the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
, which had passed to the USSR from Finland in 1940 under the peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surr ...
following the Winter War
The Winter War,, sv, Vinterkriget, rus, Зи́мняя война́, r=Zimnyaya voyna. The names Soviet–Finnish War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финская война́ 1939–1940) and Soviet–Finland War 1 ...
, were transferred from Leningrad Oblast to Leningrad and divided into Sestroretsky District and Kurortny District
Kurortny District (russian: Куро́ртный райо́н) is a district of the federal city of St. Petersburg, Russia, located on the Karelian Isthmus along the northern shore of the Gulf of Finland. As of the 2010 Census, its populati ...
. These included the town of Terijoki (renamed Zelenogorsk in 1948). Leningrad and many of its suburbs were rebuilt over the post-war decades, partially according to pre-war plans. The 1948 general plan for Leningrad featured radial urban development
Urban means "related to a city". In that sense, the term may refer to:
* Urban area, geographical area distinct from rural areas
* Urban culture, the culture of towns and cities
Urban may also refer to:
General
* Urban (name), a list of people ...
in the north as well as in the south. In 1953 Pavlovsky District in Leningrad Oblast was abolished, and parts of its territory, including Pavlovsk, merged with Leningrad. In 1954 the settlements Levashovo, Pargolovo and Pesochny merged with Leningrad.
 Leningrad gave its name to the Leningrad Affair (1949–1952), a notable event in the postwar political struggle in the
Leningrad gave its name to the Leningrad Affair (1949–1952), a notable event in the postwar political struggle in the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
. It was a product of rivalry between Stalin's potential successors where one side was represented by the leaders of the city Communist Party
A communist party is a political party that seeks to realize the socio-economic goals of communism. The term ''communist party'' was popularized by the title of '' The Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (1848) by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. ...
organization—the second most significant one in the country after Moscow. The entire elite leadership of Leningrad was destroyed, including the former mayor Kuznetsov, the acting mayor Pyotr Sergeevich Popkov, and all their deputies; overall 23 leaders were sentenced to the death penalty, 181 to prison or exile (exonerated in 1954). About 2,000 ranking officials across the USSR were expelled from the party and the Komsomol and removed from leadership positions. They were accused of Russian nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
.
The Leningrad Metro
The Saint Petersburg Metro (russian: links=no, Петербургский метрополитен, Peterburgskiy metropoliten) is a rapid transit system in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Construction began in early 1941, but was put on hold due to Wor ...
underground rapid transit system, designed before the war, opened in 1955 with its first eight stations decorated with marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorpho ...
and bronze. However, after Stalin's death in 1953, the perceived ornamental excesses of the Stalinist architecture were abandoned. From the 1960s to the 1980s many new residential boroughs were built on the outskirts; while the functionalist apartment blocks were nearly identical to each other, many families moved there from ''kommunalkas'' in the city centre to live in separate apartments.
Contemporary era (1991–present)
 On 12 June 1991, simultaneously with the first Russian presidential elections, the city authorities arranged for the mayoral elections and a referendum upon the city's name, when the name reverted to Saint Petersburg. The turnout was 65%; 66.13% of the total count of votes went to Anatoly Sobchak, who became the first directly elected mayor of the city.
Meanwhile, economic conditions started to deteriorate as the country tried to adapt to major changes. For the first time since the 1940s, food
On 12 June 1991, simultaneously with the first Russian presidential elections, the city authorities arranged for the mayoral elections and a referendum upon the city's name, when the name reverted to Saint Petersburg. The turnout was 65%; 66.13% of the total count of votes went to Anatoly Sobchak, who became the first directly elected mayor of the city.
Meanwhile, economic conditions started to deteriorate as the country tried to adapt to major changes. For the first time since the 1940s, food rationing
Rationing is the controlled distribution of scarce resources, goods, services, or an artificial restriction of demand. Rationing controls the size of the ration, which is one's allowed portion of the resources being distributed on a particular ...
was introduced, and the city received humanitarian food aid
In international relations, aid (also known as international aid, overseas aid, foreign aid, economic aid or foreign assistance) is – from the perspective of governments – a voluntary transfer of resources from one country to another.
...
from abroad. This dramatic time was depicted in photographic series of Russian photographer Alexey Titarenko. Economic conditions began to improve only at the beginning of the 21st century. In 1995 a northern section of the Kirovsko-Vyborgskaya Line
Line 1 of the Saint Petersburg Metro, also known as ''Kirovsko-Vyborgskaya Line'' (russian: Ки́ровско-Вы́боргская ли́ния) or ''Red Line'', is the oldest rapid transit line in Saint Petersburg, Russia, opened in 1955, wh ...
of the Saint Petersburg Metro
The Saint Petersburg Metro (russian: links=no, Петербургский метрополитен, Peterburgskiy metropoliten) is a rapid transit system in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Construction began in early 1941, but was put on hold due to Wor ...
was cut off by underground flooding, creating a major obstacle to the city development for almost ten years. On 13 June 1996 Saint Petersburg, alongside Leningrad Oblast and Tver Oblast
Tver Oblast (russian: Тверска́я о́бласть, ''Tverskaya oblast'', ), from 1935 to 1990 known as Kalinin Oblast (), is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Tver. It was named after ...
, signed a power-sharing agreement with the federal government, granting it autonomy. This agreement was abolished on 4 April 2002.
In 1996, Vladimir Yakovlev defeated Anatoly Sobchak in the elections for the head of the city administration
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
. The title of the city head was changed from "mayor" to "governor". In 2000 Yakovlev won re-election. His second term expired in 2004; the long-awaited restoration of the broken subway connection was expected to finish by that time. But in 2003 Yakovlev suddenly resigned, leaving the governor's office to Valentina Matviyenko
Valentina Ivanovna Matviyenko (russian: Валентина Ивановна Матвиенко, p=vəlʲɪnˈtʲinə ɪˈvanəvnə mətvʲɪˈjɛnkə, ukr, Валентина Іванівна Матвієнко; née Tyutina (Тютина; , ...
.
 The law on election of the City Governor was changed, breaking the tradition of democratic election by universal suffrage. In 2006 the city legislature re-approved Matviyenko as governor. Residential building had intensified again; real-estate prices inflated greatly, which caused many new problems for the preservation of the historical part of the city.
Although the central part of the city has a
The law on election of the City Governor was changed, breaking the tradition of democratic election by universal suffrage. In 2006 the city legislature re-approved Matviyenko as governor. Residential building had intensified again; real-estate prices inflated greatly, which caused many new problems for the preservation of the historical part of the city.
Although the central part of the city has a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
designation (there are about 8,000 architectural monuments in Petersburg), the preservation of its historical and architectural environment became controversial. After 2005, the demolition of older buildings in the historical centre was permitted. In 2006 Gazprom
PJSC Gazprom ( rus, Газпром, , ɡɐzˈprom) is a Russian majority state-owned multinational energy corporation headquartered in the Lakhta Center in Saint Petersburg. As of 2019, with sales over $120 billion, it was ranked as the largest ...
announced an ambitious project to erect a skyscraper (the Okhta Center) opposite to Smolny
Smolny is a place name in central Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is a compound of historically interrelated buildings erected in 18th and 19th centuries. As the most widely known of the buildings, the Smolny Institute, has been used as the seat of t ...
, which could result in the loss of the unique line of Petersburg landscape. Urgent protests by citizens and prominent public figures of Russia against this project were not considered by Governor Valentina Matviyenko
Valentina Ivanovna Matviyenko (russian: Валентина Ивановна Матвиенко, p=vəlʲɪnˈtʲinə ɪˈvanəvnə mətvʲɪˈjɛnkə, ukr, Валентина Іванівна Матвієнко; née Tyutina (Тютина; , ...
and the city authorities until December 2010, when after the statement of President Dmitry Medvedev, the city decided to find a more appropriate location for this project. In the same year, the new location for the project was relocated to Lakhta, a historical area northwest of the city centre, and the new project would be named Lakhta Center
The Lakhta Center () is an 87-story skyscraper built in the northwestern neighbourhood of Lakhta in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Standing tall, it is the tallest building in Russia, the tallest building in Europe, and the sixteenth-tallest bu ...
. Construction was approved by Gazprom and the city administration and commenced in 2012. The high Lakhta Center has become the first tallest skyscraper in Russia and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
outside of Moscow.
Geography
 The area of Saint Petersburg city proper is . The area of the federal subject is , which contains Saint Petersburg proper (consisting of eighty-one municipal ''
The area of Saint Petersburg city proper is . The area of the federal subject is , which contains Saint Petersburg proper (consisting of eighty-one municipal ''okrug
An ''okrug, ; russian: о́круг, ókrug; sr, округ, okrug, ; uk, о́круг, о́kruh; be, акруга, akruha; pl, okręg; ab, оқрҿс; mhr, йырвел, '' is a type of administrative division in some Slavic states. Th ...
s''), nine municipal towns – ( Kolpino, Krasnoye Selo, Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for " crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city ...
, Lomonosov, Pavlovsk, Petergof
Petergof (russian: Петерго́ф), known as Petrodvorets () from 1944 to 1997, is a municipal town in Petrodvortsovy District of the federal city of St. Petersburg, located on the southern shore of the Gulf of Finland.
The town hos ...
, Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, ...
, Sestroretsk, Zelenogorsk) – and twenty-one municipal settlements.
Petersburg is on the middle taiga
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces ...
lowlands along the shores of the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
, and islands of the river delta. The largest are Vasilyevsky Island
Vasilyevsky Island (russian: Васи́льевский о́стров, Vasilyevsky Ostrov, V.O.) is an island in St. Petersburg, Russia, bordered by the Bolshaya Neva and Malaya Neva Rivers (in the delta of the Neva River) in the south ...
(besides the artificial island
An artificial island is an island that has been constructed by people rather than formed by natural means. Artificial islands may vary in size from small islets reclaimed solely to support a single pillar of a building or structure to those tha ...
between Obvodny canal and Fontanka
The Fontanka (russian: Фонтанка), a left branch of the river Neva, flows through the whole of Central Saint Petersburg, Russia – from the Summer Garden to . It is long, with a width up to , and a depth up to . The Moyka River ...
, and Kotlin in the Neva Bay), Petrogradsky, Dekabristov and Krestovsky. The latter together with Yelagin and Kamenny Island are covered mostly by parks. The Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (russian: Карельский перешеек, Karelsky peresheyek; fi, Karjalankannas; sv, Karelska näset) is the approximately stretch of land, situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern R ...
, North of the city, is a popular resort area. In the south, Saint Petersburg crosses the Baltic-Ladoga Klint
The Baltic Klint (Clint, Glint; et, Balti klint, sv, Baltiska klinten, russian: Балтийско-Ладожский уступ, Глинт) is an erosional limestone escarpment and cuesta on several islands of the Baltic Sea, in Estonia, in ...
and meets the Izhora Plateau.
The elevation of Saint Petersburg ranges from the sea level to its highest point of at the Orekhovaya Hill in the Duderhof Heights in the south. Part of the city's territory west of Liteyny Prospekt
Liteyny Avenue (russian: Лите́йный проспе́кт, ''Liteyny Prospekt'') is a wide avenue in the Central District of Saint Petersburg, Russia. The avenue runs from Liteyny Bridge to Nevsky Avenue.
The avenue originated in 1738 whe ...
is no higher than above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as '' orthometric heights''.
The ...
, and has suffered from numerous floods. Floods in Saint Petersburg are triggered by a long wave in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
, caused by meteorological conditions, winds and shallowness of the Neva Bay. The five most disastrous floods occurred in 1824 ( above sea level, during which over 300 buildings were destroyed); 1924 (); 1777 (); 1955 (); and 1975 (). To prevent floods, the Saint Petersburg Dam has been constructed.
Since the 18th century, the city's terrain has been raised artificially, at some places by more than , making mergers of several islands, and changing the hydrology of the city. Besides the Neva and its tributaries, other important rivers of the federal subject of Saint Petersburg are Sestra, Okhta
The Okhta () is a river in Vsevolozhsky District of Leningrad Oblast and the eastern part of the city of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is the largest right tributary of the river Neva. It joins the Neva upstream of the Neva's mouth, within ...
and Izhora. The largest lake is Sestroretsky Razliv in the north, followed by Lakhtinsky Razliv
Lake Lakhta (Russian: Лахтинский разлив; ''Lakhtinsky razliv''; from Finnish ''lahti'', 'gulf') is a lake (or inlet) in St. Petersburg's Primorsky District connected to the Neva Bay of the Baltic Sea by the 500-meter-long Bobylka ...
, Suzdal Lakes, and other smaller lakes.
Due to its northerly location at c. 60° N latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north po ...
the day length in Petersburg varies across seasons, ranging from 5 hours 53 minutes to 18 hours 50 minutes. A period from mid-May to mid-July during which twilight may last all night is called ''the white nights''.
Saint Petersburg is about from the border with Finland, connected to it via the M10 highway ( E18), along which there is also a connection to the historic city of Vyborg
Vyborg (; rus, Вы́борг, links=1, r=Výborg, p=ˈvɨbərk; fi, Viipuri ; sv, Viborg ; german: Wiborg ) is a town in, and the administrative center of, Vyborgsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Karelian Isthmus n ...
.
Climate
Under theKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
, Saint Petersburg is classified as ''Dfb'', a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
. The distinct moderating influence of Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
cyclones results in warm, humid, and short summers and long, moderately cold wet winters. The climate of Saint Petersburg is close to that of Helsinki
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of U ...
, although colder in winter and warmer in summer because of its more eastern location.
The average maximum temperature in July is , and the average minimum temperature in February is ; an extreme temperature of occurred during the 2010 Northern Hemisphere summer heat wave
The 2010 Northern Hemisphere summer heat waves included severe heat waves that impacted most of the United States, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, China, Hong Kong, North Africa and the European continent as a whole, along with parts of Canada, Russia, Indoc ...
. A winter minimum of was recorded in 1883. The average annual temperature is . The Neva River within the city limits usually freezes up in November–December and break-up occurs in April. From December to March there are 118 days on average with snow cover, which reaches an average snow depth of by February. The frost-free period in the city lasts on average for about 135 days. Despite St. Petersburg's northern location, its winters are warmer than Moscow's due to the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
and some Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Uni ...
influence from Scandinavian winds that can bring temperature slightly above freezing. The city also has a slightly warmer climate than its suburbs. Weather conditions are quite variable all year round.
Average annual precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hai ...
varies across the city, averaging per year and reaching maximum in late summer. Due to the cool climate, soil moisture is almost always high because of lower evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the combined processes by which water moves from the earth’s surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transpir ...
. Air humidity is 78% on average, and there are, on average, 165 overcast days per year.
Toponymy
The first and fairly rich chapter of the history of the localtoponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name o ...
is the story of the city's name. The name day
In Christianity, a name day is a tradition in many countries of Europe and the Americas, among other parts of Christendom. It consists of celebrating a day of the year that is associated with one's baptismal name, which is normatively that of ...
of Peter I Peter I may refer to:
Religious hierarchs
* Saint Peter (c. 1 AD – c. 64–88 AD), a.k.a. Simon Peter, Simeon, or Simon, apostle of Jesus
* Pope Peter I of Alexandria (died 311), revered as a saint
* Peter I of Armenia (died 1058), Catholicos ...
falls on 29 June, when the Russian Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = ru
, image = Moscow July 2011-7a.jpg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Christ the Saviour in Moscow, Russia
, abbreviation = ROC
, type ...
observes the memory of saint apostles Peter and Paul. The consecration of the small wooden church in their names (its construction began at the same time as the citadel) made them the heavenly patrons of the Peter and Paul Fortress
The Peter and Paul Fortress is the original citadel of St. Petersburg, Russia, founded by Peter the Great in 1703 and built to Domenico Trezzini's designs from 1706 to 1740 as a star fortress. Between the first half of the 1700s and early 1920 ...
, while Saint Peter at the same time became the eponym
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
of the whole city. When in June 1703 Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
gave the site a new name after Saint Peter, he did not issue a naming act that established an official spelling; even in his own letters he used diverse spellings, such as Санктьпетерсьбурк (''Sanktpetersburk''), emulating German ''Sankt Petersburg'', and Сантпитербурх (''Santpiterburkh''), emulating Dutch ''Sint-Pietersburgh'', as Peter was multilingual and a Neerlandophile. The name was later normalized and russified
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
to Санкт-Петербург.
 A 14- to 15-letter-long name, composed of the three roots proved too cumbersome, and many shortened versions were used. The first General Governor of the city Menshikov is maybe also the author of the first nickname of Petersburg which he called Петри (''Petri''). It took some years until the known Russian spelling of this name finally settled. In 1740s
A 14- to 15-letter-long name, composed of the three roots proved too cumbersome, and many shortened versions were used. The first General Governor of the city Menshikov is maybe also the author of the first nickname of Petersburg which he called Петри (''Petri''). It took some years until the known Russian spelling of this name finally settled. In 1740s Mikhail Lomonosov
Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov (; russian: Михаил (Михайло) Васильевич Ломоносов, p=mʲɪxɐˈil vɐˈsʲilʲjɪvʲɪtɕ , a=Ru-Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov.ogg; – ) was a Russian polymath, scientist and wri ...
uses a derivative of el, link=no, Πετρόπολις (Петрополис, ''Petropolis'') in a Russified form ''Petropol'' (Петрополь). A combo ''Piterpol'' (Питерпол) also appears at this time.Nesterov, V. ''Знаешь ли ты свой город'' ("Do you know your city?"). Leningrad, 1958, p. 58. In any case, eventually the usage of prefix "''Sankt-''" ceased except for the formal official documents, where a three-letter abbreviation "СПб" (''SPB'') was very widely used as well.
In the 1830s Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, ...
translated the "foreign" city name of "Saint Petersburg" to the more Russian ''Petrograd'' in one of his poems. However, it was only on , after the war with Germany had begun, that Tsar Nicholas II
Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov; spelled in pre-revolutionary script. ( 186817 July 1918), known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer,. was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Polan ...
renamed the capital to Petrograd. Since the prefix "Saint" was omitted, this act also changed the eponym
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
and the "patron" of the city from Saint Peter to Peter the Great, its founder.
 After the
After the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
the name ''Red Petrograd'' (Красный Петроград, ''Krasny Petrograd'') was often used in newspapers and other prints until the city was renamed ''Leningrad'' in January 1924.
A referendum on reversing the renaming of ''Leningrad'' was held on 12 June 1991, with 54.86% of voters (with a turnout of 65%) supporting "''Saint Petersburg''". Renaming the city ''Petrograd'' was not an option. This change officially took effect on 6 September 1991. Meanwhile, the oblast whose administrative center is also in Saint Petersburg is still named Leningrad
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
.
Having passed the role of capital to Petersburg, Moscow never relinquished the title of "capital", being called ''pervoprestolnaya'' ("first-throned") for 200 years. An equivalent name for Petersburg, the "Northern Capital", has re-entered usage today since several federal institutions were recently moved from Moscow to Saint Petersburg. Solemn descriptive names like "the city of three revolutions" and "the cradle of the October revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
" used in the Soviet era are reminders of the pivotal events in national history that occurred here. ''Petropolis'' is a translation of a city name to Greek, and is also a kind of descriptive name: Πέτρ- is a Greek root for "stone", so the "city from stone" emphasizes the material that had been forcibly made obligatory for construction from the first years of the city. (The proper Greek translation is Αγία Πετρούπολη, ''Agia Petroupoli''.)
Demographics
 Saint Petersburg is the second largest city in Russia. As of the 2017 Rosstat, the federal subject's population is 5,281,579 or 3.6% of the total population of Russia; up from 4,879,566 (3.4%) recorded in the 2010 Census, and up from 5,023,506 recorded in the 1989 Census.
Saint Petersburg is the second largest city in Russia. As of the 2017 Rosstat, the federal subject's population is 5,281,579 or 3.6% of the total population of Russia; up from 4,879,566 (3.4%) recorded in the 2010 Census, and up from 5,023,506 recorded in the 1989 Census.
 ;Vital statistics for 2016
* Births: 72 879 (13.9 per 1000)
* Deaths: 61 459 (11.7 per 1000)
;
Ethnic composition of Saint Petersburg
During the 20th century, the city experienced dramatic population changes. From 2.4 million residents in 1916, its population dropped to less than 740,000 by 1920 during the
;Vital statistics for 2016
* Births: 72 879 (13.9 per 1000)
* Deaths: 61 459 (11.7 per 1000)
;
Ethnic composition of Saint Petersburg
During the 20th century, the city experienced dramatic population changes. From 2.4 million residents in 1916, its population dropped to less than 740,000 by 1920 during the Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
and Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
. The minorities of Germans, Poles, Finns, Estonians and Latvians were almost completely transferred from Leningrad during the 1930s. From 1941 to the end of 1943, population dropped from 3 million to less than 600,000, as people died in battles, starved to death or were evacuated during the Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet Union, So ...
. Some evacuees returned after the siege, but most influx was due to migration from other parts of the Soviet Union. The city absorbed about 3 million people in the 1950s and grew to over 5 million in the 1980s. From 1991 to 2006 the city's population decreased to 4.6 million, while the suburban population increased due to privatization of land and massive move to suburbs. Based on the 2010 census results the population is over 4.8 million.Chistyakova, NТретье сокращение численности населения... и последнее?
''Demoscope Weekly'' 163 – 164, 1–15 August 2004. For the first half of 2007, the birth rate was 9.1 per 1000 and remained lower than the
death rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of de ...
(until 2012); people over 65 constitute more than twenty percent of the population; and the median age is about 40 years. Since 2012 the birth rate
The birth rate for a given period is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; populati ...
became higher than the death rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of de ...
. But in 2020 the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified ...
caused a drop in birth rate, and the city population decreased to 5,395,000 people.
;Religion
According to various opinion polls, more than half of the residents of Saint Petersburg "believe in God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
" (up to 67% according to VTsIOM data for 2002).
Among the believers, the overwhelming majority of the residents of the city are Orthodox (57.5%), followed by small minority communities of Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
(0.7%), Protestants
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
(0.6%), and Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
(0.5%), and Buddhists
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and g ...
(0.1%).
In total, roughly 59% of the population of the city is Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
, of which over 90% are Orthodox. Non-Abrahamic religions and other faiths are represented by only 1.2% of the total population.
There are 268 communities of confessions and religious associations in the city: the Russian Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = ru
, image = Moscow July 2011-7a.jpg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Christ the Saviour in Moscow, Russia
, abbreviation = ROC
, type ...
(130 associations), Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestantism, Protestant Charismatic Christianity, Charismatic Christian movementLutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
(19 associations), Baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost inv ...
(13 associations), as well as Old Believers
Old Believers or Old Ritualists, ''starovery'' or ''staroobryadtsy'' are Eastern Orthodox Christians who maintain the liturgical and ritual practices of the Russian Orthodox Church as they were before the reforms of Patriarch Nikon of Moscow ...
, Roman Catholic Church, Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
, Georgian Orthodox Church
The Apostolic Autocephalous Orthodox Church of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამოციქულო ავტოკეფალური მართლმადიდებელი ეკლესია, tr), commonly ...
, Seventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventism, Adventist Protestantism, Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the Names of the days of the week#Numbered days of the week, seventh day of the ...
, Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
, Buddhist, Muslim, Bahá'í and others.
229 religious buildings in the city are owned or run by religious associations. Among them are architectural monuments of federal significance. The oldest cathedral in the city is the Peter and Paul Cathedral, built between 1712–1733, and the largest is the Kazan Cathedral, completed in 1811.
Government
 Saint Petersburg is a
Saint Petersburg is a federal subject
The federal subjects of Russia, also referred to as the subjects of the Russian Federation (russian: субъекты Российской Федерации, subyekty Rossiyskoy Federatsii) or simply as the subjects of the federation (russian ...
of Russia (a federal city). The political life of Saint Petersburg is regulated by the Charter of Saint Petersburg adopted by the city legislature in 1998. The superior executive body is the Saint Petersburg City Administration
Saint Petersburg City Administration (Администрация Санкт-Петербурга) is the superior executive body of Saint Petersburg (formerly Leningrad), Russian Federation. It is located in a historic building, Smolny and known a ...
, led by the city governor (mayor before 1996). Saint Petersburg has a single-chamber legislature, the Saint Petersburg Legislative Assembly, which is the city's regional parliament.
 According to the federal law passed in 2004, heads of federal subjects, including the governor of Saint Petersburg, were nominated by the
According to the federal law passed in 2004, heads of federal subjects, including the governor of Saint Petersburg, were nominated by the President of Russia
The president of the Russian Federation ( rus, Президент Российской Федерации, Prezident Rossiyskoy Federatsii) is the head of state of the Russian Federation. The president leads the executive branch of the federal ...
and approved by local legislatures. Should the legislature disapprove the nominee, the President could dissolve it. The former governor, Valentina Matviyenko
Valentina Ivanovna Matviyenko (russian: Валентина Ивановна Матвиенко, p=vəlʲɪnˈtʲinə ɪˈvanəvnə mətvʲɪˈjɛnkə, ukr, Валентина Іванівна Матвієнко; née Tyutina (Тютина; , ...
, was approved according to the new system in December 2006. She was the only woman governor in the whole of Russia until her resignation on 22 August 2011. Matviyenko stood for elections as member of the Regional Council of Saint Petersburg and won comprehensively with allegations of rigging and ballot stuffing by the opposition. Russian President Dmitry Medvedev has already backed her for the position of Speaker to the Federation Council of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation and her election qualifies her for that job. After her resignation, Georgy Poltavchenko
Georgy Sergeyevich Poltavchenko ( rus, Гео́ргий Серге́евич Полта́вченко, p=ɡʲɪˈorɡʲɪj sʲɪrˈɡʲejɪvʲɪtɕ pɐlˈtaftɕɪnkə; born on 24 February 1953) is a Russian politician.
He became Governor of Sa ...
was appointed as the new acting governor the same day. In 2012, following passage of a new federal law, restoring direct elections of heads of federal subjects, the city charter was again amended to provide for direct elections of governor. On 3 October 2018, Poltavchenko resigned, and Alexander Beglov was appointed acting governor.
Saint Petersburg is also the unofficial but ''de facto'' administrative centre of Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast ( rus, Ленинградская область, Leningradskaya oblast’, lʲɪnʲɪnˈgratskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ, , ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 1 ...
, and of the Northwestern Federal District
Northwestern Federal District,, ''Severo-Zapadny federalny okrug'' is one of the eight federal districts of Russia. It covers most of Northwest Russia. Its population was 13.6 million, of which 83.5% was urban, living in an area of , accordin ...
. The Constitutional Court of Russia
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
moved to Saint Petersburg from Moscow in May 2008.
Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast, being two different federal subjects, share a number of local departments of federal executive agencies and courts, such as court of arbitration, police, FSB, postal service, drug enforcement administration, penitentiary service, federal registration service, and other federal services.
Administrative divisions
Economy
Saint Petersburg is a major trade gateway, serving as the financial and industrial centre of Russia, with specializations in oil and gas trade; shipbuilding yards;aerospace industry
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astro ...
; technology, including radio, electronics, software, and computers; machine building, heavy machinery and transport, including tanks and other military equipment
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
; mining; instrument manufacture; ferrous and nonferrous metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sci ...
(production of aluminium alloys); chemicals, pharmaceuticals
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
, and medical equipment
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assur ...
; publishing and printing; food and catering; wholesale and retail; textile and apparel
Clothing (also known as clothes, apparel, and attire) are items worn on the body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin sheets of materials and natura ...
industries; and many other businesses. It was also home to Lessner, one of Russia's two pioneering automobile manufacturers (along with Russo-Baltic); it was founded by machine tool and boilermaker G.A. Lessner in 1904, with designs by Boris Loutsky, and it survived until 1910.

 Ten per cent of the world's power
Ten per cent of the world's power turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating ...
s are made there at the LMZ, which built over two thousand turbines for power plants across the world. Major local industries are Admiralty Shipyard
The JSC Admiralty Shipyards (russian: link=no, Адмиралтейские верфи) (''formerly Soviet Shipyard No. 194'') is one of the oldest and largest shipyards in Russia, located in Saint Petersburg. The shipyard's building ways can ac ...
, Baltic Shipyard, LOMO
LOMO (russian: Ленинградское Oптико-Mеханическое Oбъединение, Leningradskoye Optiko-Mekhanicheskoye Obyedinenie, Leningrad Optical Mechanical Association) is a manufacturer of medical and motion-picture lens ...
, Kirov Plant
The Kirov Plant, Kirov Factory or Leningrad Kirov Plant (LKZ) ( rus, Кировский завод, Kirovskiy zavod) is a major Russian mechanical engineering and agricultural machinery manufacturing plant in St. Petersburg, Russia. It was esta ...
, Elektrosila, Izhorskiye Zavody; also registered in Saint Petersburg are Sovkomflot, Petersburg Fuel Company
The Petersburg Fuel Company (PTK, in Russian: Петербургская топливная компания, ПТК) is an open joint-stock company of Saint Petersburg, Russia, founded in September 1994, after a fuel supply crisis had hit the cit ...
and SIBUR
SIBUR (PJSC SIBUR Holding) is a Russian petrochemicals company founded in 1995 and headquartered in Moscow.
SIBUR is the largest integrated petrochemicals company in Russia and one of the fastest-growing companies in the global petrochemicals ...
among other major Russian and international companies.
The Port of Saint Petersburg has three large cargo terminals, Bolshoi Port Saint Petersburg, Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for " crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city ...
, and Lomonosov terminal. International cruise liners have been served at the passenger port at Morskoy Vokzal on the south-west of Vasilyevsky Island
Vasilyevsky Island (russian: Васи́льевский о́стров, Vasilyevsky Ostrov, V.O.) is an island in St. Petersburg, Russia, bordered by the Bolshaya Neva and Malaya Neva Rivers (in the delta of the Neva River) in the south ...
. In 2008 the first two berths opened at the New Passenger Port on the west of the island. The new passenger terminal is part of the city's "Marine Facade" development project and was due to have seven berths in operation by 2010.
A complex system of riverports on both banks of the Neva River
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it ...
are interconnected with the system of seaports, thus making Saint Petersburg the main link between the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
and the rest of Russia through the Volga-Baltic Waterway.
The Saint Petersburg Mint
Saint Petersburg Mint (russian: Санкт-Петербу́ргский моне́тный двор) is one of the world's largest mints. It was founded by Peter the Great in 1724 on the territory of Peter and Paul Fortress, so it is one of the ...
(Monetny Dvor), founded in 1724, is one of the largest mints in the world, it mints Russian coins, medals and badges. Saint Petersburg is also home to the oldest and largest Russian foundry, Monumentskulptura, which made thousands of sculptures and statues that now grace the public parks of Saint Petersburg and many other cities. Monuments and bronze statues of the Tsars, as well as other important historic figures and dignitaries, and other world-famous monuments, such as the sculptures by Peter Clodt von Jürgensburg
Peter Jakob Freiherr Clodt von Jürgensburg, known in Russian as Pyotr Karlovich Klodt (russian: Пётр Карлович Клодт; 5 June 1805, Saint Petersburg – 25 November 1867, Klevenoye, Vyborg Governorate), was a favourite sculpto ...
, Paolo Troubetzkoy, Mark Antokolsky
Mark Matveyevich Antokolsky (russian: Марк Матве́евич Антоко́льский; 2 November 18409 July 1902) was a Russian Imperial sculptor of Lithuanian Jewish descent.
Biography
Mordukh Matysovich Antokolsky''Boris Schatz: Th ...
, and others, were made there.
In 2007, Toyota
is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 ...
opened a Camry plant after investing 5 billion roubles (approx. 200 mln dollars) in Shushary, one of the southern suburbs of Saint Petersburg. Opel
Opel Automobile GmbH (), usually shortened to Opel, is a German automobile manufacturer which has been a subsidiary of Stellantis since 16 January 2021. It was owned by the American automaker General Motors from 1929 until 2017 and the PSA ...
, Hyundai Hyundai is a South Korean industrial conglomerate ("chaebol"), which was restructured into the following groups:
* Hyundai Group, parts of the former conglomerate which have not been divested
** Hyundai Mobis, Korean car parts company
** Hyundai As ...
and Nissan have also signed deals with the Russian government
The Government of Russia exercises executive power in the Russian Federation. The members of the government are the prime minister, the deputy prime ministers, and the federal ministers. It has its legal basis in the Constitution of the Russ ...
to build their automotive plants in Saint Petersburg. The automotive and auto-parts industry is on the rise there during the last decade.
Saint Petersburg has a large brewery and distillery industry. Known as Russia's "beer capital" due to the supply and quality of local water, its five large breweries account for over 30% of the country's domestic beer production. They include Europe's second-largest brewery Baltika, Vena (both operated by BBH), Heineken Brewery
Heineken N.V. () is a Dutch multinational brewing company, founded in 1864 by Gerard Adriaan Heineken in Amsterdam. , Heineken owns over 165 breweries in more than 70 countries. It produces 348 international, regional, local and speciality be ...
, Stepan Razin
Stepan Timofeyevich Razin (russian: Степа́н Тимофе́евич Ра́зин, ; 1630 – ), known as Stenka Razin ( ), was a Cossack leader who led a major uprising against the nobility and tsarist bureaucracy in southern Russia in 16 ...
(both by Heineken
Heineken Lager Beer ( nl, Heineken Pilsener), or simply Heineken () is a pale lager beer with 5% alcohol by volume produced by the Dutch brewing company Heineken N.V. Heineken beer is sold in a green bottle with a red star.
History
On 15 Fe ...
) and Tinkoff brewery (SUN- InBev).
The city's many local distilleries
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the heati ...
produce a broad range of vodka
Vodka ( pl, wódka , russian: водка , sv, vodka ) is a clear distilled alcoholic beverage. Different varieties originated in Poland, Russia, and Sweden. Vodka is composed mainly of water and ethanol but sometimes with traces of impuriti ...
brands. The oldest ones is LIVIZ (founded in 1897). Among the youngest is Russian Standard Vodka introduced in Moscow in 1998, which opened in 2006 a new $60 million distillery in Petersburg (an area of , production rate of 22,500 bottles per hour). In 2007, this brand was exported to over 70 countries.
Saint Petersburg has the second-largest construction industry
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and ...
in Russia, including commercial, housing, and road construction.
In 2006, Saint Petersburg's city budget was 180 billion rubles (about 7 billion US$ at 2006 exchange rates),. The federal subject's Gross Regional Product
Gross regional product (GRP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all final goods and services produced in a region or subdivision of a country in a period (quarterly or yearly) of time.
A metropolitan area's GRP (gross metropolitan pro ...
was 3.7 trillion Russian ruble
''hum''; cv, тенкĕ ''tenke''; kv, шайт ''shayt''; Lak: къуруш ''k'urush''; Mari: теҥге ''tenge''; os, сом ''som''; tt-Cyrl, сум ''sum''; udm, манет ''manet''; sah, солкуобай ''solkuobay''
, name_ab ...
s (or around US$70 billion), ranked 2nd in Russia, after Moscow and per capita of US$13,000, ranked 12th among Russia's federal subjects, contributed mostly by wholesale and retail trade and repair services (24.7%) as well as processing industry (20.9%) and transportation and telecommunications (15.1%).
Budget revenues of the city in 2009 amounted to 294.3 billion rubles (about 10.044 billion US$ at 2009 exchange rates), expenses – 336.3 billion rubles (about 11.477 billion US$ at 2009 exchange rates). The budget deficit amounted to about 42 billion rubles. (about 1.433 billion US$ at 2009 exchange rates)
In 2015, St. Petersburg was ranked in 4th place economically amongst all federal subjects of the Russian Federation, surpassed only by Moscow, the Tyumen and Moscow Region.
Cityscape
 Saint Petersburg has three skyscrapers: Leader Tower (140 m), Alexander Nevsky (124 m) and Atlantic City (105 m) all far from the historical centre. Regulations forbid the construction of tall buildings in the city centre. The tall
Saint Petersburg has three skyscrapers: Leader Tower (140 m), Alexander Nevsky (124 m) and Atlantic City (105 m) all far from the historical centre. Regulations forbid the construction of tall buildings in the city centre. The tall Saint Petersburg TV Tower
Saint Petersburg Television Tower is a Russian steel lattice television tower in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Being the first dedicated television tower in the Soviet Union, the Saint Petersburg TV Tower is utilized for transmitting for FM-/ TV ...
is the tallest completed structure in the city. However, there was a controversial project endorsed by the city authorities, and known as the Okhta Center, to build a supertall skyscraper. In 2008, the World Monuments Fund
World Monuments Fund (WMF) is a private, international, non-profit organization dedicated to the preservation of historic architecture and cultural heritage sites around the world through fieldwork, advocacy, grantmaking, education, and traini ...
included the Saint Petersburg historic skyline on the watch list of the 100 most endangered sites due to the expected construction, which threatens to alter it drastically. The Okhta Center project was cancelled at the end of 2010 and the Lakhta Center
The Lakhta Center () is an 87-story skyscraper built in the northwestern neighbourhood of Lakhta in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Standing tall, it is the tallest building in Russia, the tallest building in Europe, and the sixteenth-tallest bu ...
project began in the city's outskirts. The complex includes office skyscraper and several low rise mixed-use buildings. The Lakhta Center project has caused much less controversy. Unlike the previous unbuilt project, it is not seen by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
as a potential threat to the city's cultural heritage because it is far from the historical centre. The skyscraper was completed in 2019, and at 462.5 metres, it is currently the tallest in Russia and Europe.

 Unlike in Moscow, the historic architecture of Saint Petersburg's city centre, mostly Baroque and Neoclassical buildings of the 18th and 19th centuries, has been largely preserved; although a number of buildings were demolished after the Bolsheviks' seizure of power, during the
Unlike in Moscow, the historic architecture of Saint Petersburg's city centre, mostly Baroque and Neoclassical buildings of the 18th and 19th centuries, has been largely preserved; although a number of buildings were demolished after the Bolsheviks' seizure of power, during the Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet Union, So ...
and in recent years. The oldest of the remaining building is a wooden house built for Peter I Peter I may refer to:
Religious hierarchs
* Saint Peter (c. 1 AD – c. 64–88 AD), a.k.a. Simon Peter, Simeon, or Simon, apostle of Jesus
* Pope Peter I of Alexandria (died 311), revered as a saint
* Peter I of Armenia (died 1058), Catholicos ...
in 1703 on the shore of the Neva
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it i ...
near Trinity Square. Since 1991 the Historic Centre of Saint Petersburg and Related Groups of Monuments in Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast have been listed by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
as a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
.
The ensemble of Peter and Paul Fortress
The Peter and Paul Fortress is the original citadel of St. Petersburg, Russia, founded by Peter the Great in 1703 and built to Domenico Trezzini's designs from 1706 to 1740 as a star fortress. Between the first half of the 1700s and early 1920 ...
with the Peter and Paul Cathedral takes a dominant position on Zayachy Island along the right bank of the Neva River
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it ...
. Each noon a cannon fires a blank shot from the fortress. The Saint Petersburg Mosque
The Saint Petersburg Mosque (russian: Санкт-Петербу́ргская мече́ть), when opened in 1913, was the largest mosque in Europe outside Turkey, its minarets 49 meters in height and the dome is 39 meters high. The mosque is situ ...
, the largest mosque in Europe when opened in 1913, is on the right bank nearby. The Spit of Vasilievsky Island
The Old Saint Petersburg Stock Exchange (also '' Bourse'') and Rostral Columns, located in Saint Petersburg in the Russian Federation, are significant examples of Greek Revival architecture. Designed by French architect Thomas de Thomon, and i ...
, which splits the river into two largest armlets, the Bolshaya Neva and Malaya Neva, is connected to the northern bank (Petrogradsky Island
Petrogradsky Island or Petrograd Island ( Russian: Петроградский остров) is the third largest island in the Neva River delta
in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Along with Zayachy Island, Aptekarsky Island, and Petrovsky Island, i ...
) via the Exchange Bridge and occupied by the Old Saint Petersburg Stock Exchange and Rostral Columns. The southern coast of Vasilyevsky Island
Vasilyevsky Island (russian: Васи́льевский о́стров, Vasilyevsky Ostrov, V.O.) is an island in St. Petersburg, Russia, bordered by the Bolshaya Neva and Malaya Neva Rivers (in the delta of the Neva River) in the south ...
along the Bolshaya Neva features some of the city's oldest buildings, dating from the 18th century, including the Kunstkamera
The Kunstkamera (russian: Кунсткамера) or Kunstkammer ( German for "Culture Room" (literally) or "Art Chamber", typically used for a " cabinet of curiosities") is a public museum located on the Universitetskaya Embankment in Saint P ...
, Twelve Collegia, Menshikov Palace and Imperial Academy of Arts
The Russian Academy of Arts, informally known as the Saint Petersburg Academy of Arts, was an art academy in Saint Petersburg, founded in 1757 by the founder of the Imperial Moscow University Ivan Shuvalov under the name ''Academy of the T ...
. It hosts one of two campuses of Saint Petersburg State University
Saint Petersburg State University (SPBU; russian: Санкт-Петербургский государственный университет) is a public research university in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Founded in 1724 by a decree of Peter the G ...
.
On the southern, left bank of the Neva, connected to the spit of Vasilyevsky Island via the Palace Bridge, lie the Admiralty building, the vast Hermitage Museum
The State Hermitage Museum ( rus, Государственный Эрмитаж, r=Gosudarstvennyj Ermitaž, p=ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)ɨj ɪrmʲɪˈtaʂ, links=no) is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is the largest ...
complex stretching along the Palace Embankment
The Palace Embankment or Palace Quay (Russian: Дворцовая набережная, Dvortsovaya naberezhnaya) is a street along the Neva River in Central Saint Petersburg which contains the complex of the Hermitage Museum buildings (includ ...
, which includes the Baroque Winter Palace
The Winter Palace ( rus, Зимний дворец, Zimnij dvorets, p=ˈzʲimnʲɪj dvɐˈrʲɛts) is a palace in Saint Petersburg that served as the official residence of the Emperor of all the Russias, Russian Emperor from 1732 to 1917. The p ...
, former official residence of Russian emperors, as well as the neoclassical Marble Palace
Marble Palace (Мраморный дворец) is one of the first Neoclassical palaces in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is situated between the Field of Mars and Palace Quay, slightly to the east from New Michael Palace.
Design and pre-1917 o ...
. The Winter Palace faces Palace Square, the city's main square with the Alexander Column. 

Nevsky Prospekt
Nevsky Prospect ( rus, Не́вский проспе́кт, r=Nevsky Prospekt, p=ˈnʲɛfskʲɪj prɐˈspʲɛkt) is the main street ( high street) in the federal city of St. Petersburg in Russia. It takes its name from the Alexander Nevsky ...
, also on the left bank of the Neva
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it i ...
, is the city's main avenue. It starts at the Admiralty and runs eastwards next to Palace Square. Nevsky Prospekt crosses the Moika ( Green Bridge), Griboyedov Canal ( Kazansky Bridge), Garden Street
Sadovaya Street or Garden Street is a major thoroughfare in Saint Petersburg, Russia, passing through the historic city center.
From east to west, it begins near the Field of Mars, crosses the Moika River at the First Sadovy Bridge, then pas ...
, the Fontanka
The Fontanka (russian: Фонтанка), a left branch of the river Neva, flows through the whole of Central Saint Petersburg, Russia – from the Summer Garden to . It is long, with a width up to , and a depth up to . The Moyka River ...
( Anichkov Bridge), meets Liteyny Prospekt
Liteyny Avenue (russian: Лите́йный проспе́кт, ''Liteyny Prospekt'') is a wide avenue in the Central District of Saint Petersburg, Russia. The avenue runs from Liteyny Bridge to Nevsky Avenue.
The avenue originated in 1738 whe ...
and proceeds to Uprising Square near the Moskovsky railway station, where it meets Ligovsky Prospekt
Ligovsky Prospekt () is a major street in Saint Petersburg. Before the establishment of the city, it was a street leading to Novgorod, used by the people living in the villages around the Neva delta.
Between 1718-25, when Saint Petersburg wa ...
and turns to the Alexander Nevsky Lavra
Saint Alexander Nevsky Lavra or Saint Alexander Nevsky Monastery was founded by Peter I of Russia in 1710 at the eastern end of the Nevsky Prospekt in Saint Petersburg, in the belief that this was the site of the Neva Battle in 1240 when Ale ...
. The Passage, Catholic Church of St. Catherine, Book House (former Singer Manufacturing Company Building in the Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Moder ...
style), Grand Hotel Europe, Lutheran Church of Saint Peter and Saint Paul
The Lutheran Church of Saint Peter and Saint Paul (in russian: Лютеранская церковь Святых Петра и Павла or in German: Lutherische Kirche der Heiligen Peter und Paul) is a Lutheran church located in Saint Petersb ...
, Great Gostiny Dvor
Great Gostiny Dvor (russian: Большой Гостиный Двор) is a vast department store on Nevsky Avenue in St Petersburg.
This ''Gostiny Dvor
Gostinyi dvor ( rus, гостиный двор, p=ɡɐˈsʲtʲinɨj ˈdvor) is a histor ...
, Russian National Library
The National Library of Russia (NLR, russian: Российская национальная библиотека}), located in Saint Petersburg, is the first, and one of three national public libraries in Russia. The NLR is currently ranked amo ...
, Alexandrine Theatre
The Alexandrinsky Theatre (russian: Александринский театр) or National Drama Theatre of Russia is a theatre in Saint Petersburg, Russia.
The Alexandrinsky Theatre was built for the Imperial troupe of Petersburg (Imperial trou ...
behind Mikeshin's statue of Catherine the Great, Kazan Cathedral, Stroganov Palace, Anichkov Palace and Beloselsky-Belozersky Palace are all along that avenue.

 The
The Alexander Nevsky Lavra
Saint Alexander Nevsky Lavra or Saint Alexander Nevsky Monastery was founded by Peter I of Russia in 1710 at the eastern end of the Nevsky Prospekt in Saint Petersburg, in the belief that this was the site of the Neva Battle in 1240 when Ale ...
, intended to house the relics of St. Alexander Nevsky
Alexander Yaroslavich Nevsky (russian: Александр Ярославич Невский; ; 13 May 1221 – 14 November 1263) served as Prince of Novgorod (1236–40, 1241–56 and 1258–1259), Grand Prince of Kiev (1236–52) and Grand P ...
, is an important centre of Christian education in Russia. It also contains the Tikhvin Cemetery with graves of many notable Petersburgers.
On the territory between the Neva and Nevsky Prospekt the Church of the Savior on Blood
The Church of the Savior on Spilled Blood (russian: Церковь Спаса на Крови, ''Tserkovʹ Spasa na Krovi'') is a Russian Orthodox church in Saint Petersburg, Russia which currently functions as a secular museum and church at t ...
, Mikhailovsky Palace housing the Russian Museum
The State Russian Museum (russian: Государственный Русский музей), formerly the Russian Museum of His Imperial Majesty Alexander III (russian: Русский Музей Императора Александра III), on ...
, Field of Mars The term Field of Mars ( la, Campus Martius) goes back to antiquity, and designates an area, inside or near a city, used as a parade or exercise ground by the military.
Notable examples of places which were used for these purposes include:
* Campus ...
, St. Michael's Castle
Saint Michael's Castle (russian: Миха́йловский за́мок, ''Mikhailovsky zamok''), also called the Mikhailovsky Castle or the Engineers' Castle (russian: Инженерный замок, ''Inzhenerny zamok''), is a former royal ...
, Summer Garden
The Summer Garden (russian: Ле́тний сад, ''Letniy sad'') is a historic public garden that occupies an eponymous island between the Neva, Fontanka, Moika, and the Swan Canal in
downtown Saint Petersburg, Russia and shares its nam ...
, Tauride Palace
Tauride Palace (russian: Таврический дворец, translit=Tavrichesky dvorets) is one of the largest and most historically important palaces in Saint Petersburg, Russia.
Construction and early use
Prince Grigory Potemkin of Taurid ...
, Smolny Institute and Smolny Convent are located.
 Many notable landmarks are to the west and south of the Admiralty Building, including the Trinity Cathedral, Mariinsky Palace, Hotel Astoria, famous
Many notable landmarks are to the west and south of the Admiralty Building, including the Trinity Cathedral, Mariinsky Palace, Hotel Astoria, famous Mariinsky Theatre
The Mariinsky Theatre ( rus, Мариинский театр, Mariinskiy teatr, also transcribed as Maryinsky or Mariyinsky) is a historic theatre of opera and ballet in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Opened in 1860, it became the preeminent music th ...
, New Holland Island, Saint Isaac's Cathedral
Saint Isaac's Cathedral or Isaakievskiy Sobor (russian: Исаа́киевский Собо́р) is a large architectural landmark cathedral that currently functions as a museum with occasional church services in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is ...
, the largest in the city, and Senate Square, with the Bronze Horseman
The ''Bronze Horseman'' (russian: link=no, Медный всадник, literally "copper horseman") is an equestrian statue of Peter the Great in the Senate Square in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It was opened to the public on 7 (18) August ...
, 18th-century equestrian monument to Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
, which is considered among the city's most recognisable symbols.
Other symbols of Saint Petersburg include the weather vane
A wind vane, weather vane, or weathercock is an instrument used for showing the direction of the wind. It is typically used as an architectural ornament to the highest point of a building. The word ''vane'' comes from the Old English word , ...
in the shape of a small ship on top of the Admiralty's golden spire and the golden angel on top of the Peter and Paul Cathedral. The Palace Bridge drawn at night is yet another symbol of the city.
From April to November, 22 bridges across the Neva and main canals are drawn to let ships pass in and out of the Baltic Sea according to a schedule. It was not until 2004 that the first high bridge across the Neva, which does not need to be drawn, Big Obukhovsky Bridge, was opened. The most remarkable bridges of our days are Korabelny and Petrovsky cable-stayed bridges, which form the most spectacular part of the city toll road, Western High-Speed Diameter. There are hundreds of smaller bridges in Saint Petersburg
There are more than 342 bridges in the city limits of Saint Petersburg, Russia. This is a partial list of the most famous ones.
Peter the Great was designing the city as another Amsterdam and Venice, with canals instead of streets and citizens sk ...
spanning numerous canals and distributaries of the Neva, some of the most important of which are the Moika, Fontanka
The Fontanka (russian: Фонтанка), a left branch of the river Neva, flows through the whole of Central Saint Petersburg, Russia – from the Summer Garden to . It is long, with a width up to , and a depth up to . The Moyka River ...
, Griboyedov Canal, Obvodny Canal, Karpovka and Smolenka. Due to the intricate web of canals, Saint Petersburg is often called '' Venice of the North''. The rivers and canals in the city centre are lined with granite embankments. The embankments and bridges are separated from rivers and canals by granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
or cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron– carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impu ...
parapet
A parapet is a barrier that is an extension of the wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/breast'). ...
s.
 Southern suburbs of the city feature former imperial residences, including
Southern suburbs of the city feature former imperial residences, including Petergof
Petergof (russian: Петерго́ф), known as Petrodvorets () from 1944 to 1997, is a municipal town in Petrodvortsovy District of the federal city of St. Petersburg, located on the southern shore of the Gulf of Finland.
The town hos ...
, with majestic fountain cascades and parks, Tsarskoe Selo
Tsarskoye Selo ( rus, Ца́рское Село́, p=ˈtsarskəɪ sʲɪˈlo, a=Ru_Tsarskoye_Selo.ogg, "Tsar's Village") was the town containing a former residence of the Russian imperial family and visiting nobility, located south from the c ...
, with the baroque Catherine Palace
The Catherine Palace (russian: Екатерининский дворец, ) is a Rococo palace in Tsarskoye Selo (Pushkin), 30 km south of St. Petersburg, Russia. It was the summer residence of the Russian tsars. The Palace is part of the ...
and the neoclassical Alexander Palace, and Pavlovsk, which has a domed palace of Emperor Paul and one of Europe's largest English-style parks. Some other residences nearby and making part of the world heritage site, including a castle and park in Gatchina, actually belong to Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast ( rus, Ленинградская область, Leningradskaya oblast’, lʲɪnʲɪnˈgratskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ, , ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 1 ...
rather than Saint Petersburg. Another notable suburb is Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for " crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city ...
with its 19th-century fortifications and naval monuments, occupying the Kotlin Island
Kotlin (russian: Ко́тлин) ( sv, Reitskär) is a Russian island, located near the head of the Gulf of Finland, west of Saint Petersburg in the Baltic Sea. Kotlin separates the Neva Bay from the rest of the gulf. The fortified city of Krons ...
in the Gulf of Finland.
Since around the end of the 20th century a great deal of active building and restoration works have been carried out in a number of the city's older districts.
The authorities have recently been compelled to transfer the ownership of state-owned private residences in the city centre to private lessors.
Many older buildings have been reconstructed to allow their use as apartments and penthouses.
Some of these structures, such as the Saint Petersburg Commodity and Stock Exchange
The Saint Petersburg Commodity and Stock Exchange is based in a housing complex in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Its offices along with the residential buildings were constructed in 2007–2008 on Vasilievsky Island near a recreation center.
After the ...
have been recognised as town-planning errors.
Parks
 Saint Petersburg is home to many parks and gardens. Some of the most well-known are in the southern suburbs, including Pavlovsk, one of Europe's largest
Saint Petersburg is home to many parks and gardens. Some of the most well-known are in the southern suburbs, including Pavlovsk, one of Europe's largest English garden
The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden (french: Jardin à l'anglaise, it, Giardino all'inglese, german: Englischer Landschaftsgarten, pt, Jardim inglês, es, Jardín inglés), is a sty ...
s. Sosnovka
Sosnovka (russian: Сосновка) is the name of several inhabited localities in Russia.
Modern localities Altai Krai
As of 2012, six rural localities in Altai Krai bear this name:
* Sosnovka, Charyshsky District, Altai Krai, a '' selo'' in M ...
is the largest park within the city limits, occupying 240 ha. The Summer Garden
The Summer Garden (russian: Ле́тний сад, ''Letniy sad'') is a historic public garden that occupies an eponymous island between the Neva, Fontanka, Moika, and the Swan Canal in
downtown Saint Petersburg, Russia and shares its nam ...
is the oldest, dating back to the early 18th century and designed in the regular style. It is on the Neva's southern bank at the head of the Fontanka and is famous for its cast iron railing and marble sculptures.
Among other notable parks are the Maritime Victory Park on Krestovsky Island
Krestovsky Island (russian: Крестовский остров) is a 3.4 km2 island in Saint Petersburg, Russia, between several tributaries of the Neva: the Srednyaya Nevka, the Malaya Nevka and the Krestovka. The island is served by ...
and the Moscow Victory Park in the south, both commemorating the victory over Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
in the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, as well as the Central Park of Culture and Leisure occupying Yelagin Island
Yelagin Island () is a park island at the mouth of the Neva River which is part of St. Petersburg, Russia. Yelagin Island is home to the Yelagin Palace but has a few other buildings as well. A former suburban estate of 18 century Russian n ...
and the Tauride Garden around the Tauride Palace
Tauride Palace (russian: Таврический дворец, translit=Tavrichesky dvorets) is one of the largest and most historically important palaces in Saint Petersburg, Russia.
Construction and early use
Prince Grigory Potemkin of Taurid ...
. The most common trees grown in the parks are the English oak, Norway maple, green ash
''Fraxinus pennsylvanica'', the green ash or red ash, is a species of ash native to eastern and central North America, from Nova Scotia west to southeastern Alberta and eastern Colorado, south to northern Florida, and southwest to Oklahoma and ...
, silver birch, Siberian Larch
''Larix sibirica'', the Siberian larch or Russian larch, is a frost-hardy tree native to western Russia, from close to the Finnish border east to the Yenisei valley in central Siberia, where it hybridises with the Dahurian larch ''L. gmelini ...
, blue spruce, crack willow, limes
Limes may refer to:
* the plural form of lime (disambiguation)
* the Latin word for ''limit'' which refers to:
** Limes (Roman Empire)
(Latin, singular; plural: ) is a modern term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimitin ...
, and poplars. Important dendrological collections dating back to the 19th century are hosted by the Saint Petersburg Botanical Garden and the Park of the Forestry Academy.
In order to commemorate 300 years anniversary of Saint Petersburg a new park was laid out. The park is in the northwestern part of the city. The construction was started in 1995. It is planned to connect the park with the pedestrian bridge to the territory of Lakhta Center
The Lakhta Center () is an 87-story skyscraper built in the northwestern neighbourhood of Lakhta in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Standing tall, it is the tallest building in Russia, the tallest building in Europe, and the sixteenth-tallest bu ...
's recreation areas. In the park 300 trees of valuable sorts, 300 decorative apple trees, 70 limes. 300 other trees and bushes were planted. These trees were presented to Saint Petersburg by non-commercial and educational organizations of the city, its sister-cities, the city of Helsinki, heads of other regions of Russia, German Savings Bank and other people and organizations.Tourism
Saint Petersburg has a significant historical and cultural heritage. The city's 18th and 19th-century architectural ensemble and its environs is preserved in virtually unchanged form. For various reasons (including large-scale destruction duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and construction of modern buildings during the postwar period in the largest historical centres of Europe), Saint Petersburg has become a unique reserve of European architectural styles of the past three centuries. Saint Petersburg's loss of capital city status helped it retain many of its pre-revolutionary buildings, as modern architectural 'prestige projects' tended to be built in Moscow; this largely prevented the rise of mid-to-late-20th century architecture and helped maintain the architectural appearance of the historic city centre.
 Saint Petersburg is inscribed on the
Saint Petersburg is inscribed on the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
World Heritage list as an area with 36 historical architectural complexes and around 4000 outstanding individual monuments of architecture, history and culture. New tourist programs and sightseeing tours have been developed for those wishing to see Saint Petersburg's cultural heritage.
The city has 221 museums, 2,000 libraries, more than 80 theatres, 100 concert organizations, 45 galleries and exhibition halls, 62 cinemas, and 80 other cultural establishments. Every year the city hosts around 100 festivals and various competitions of art and culture, including more than 50 international ones.
 Despite the economic instability of the 1990s, not a single major theatre or museum was closed in Saint Petersburg; on the contrary many new ones opened, for example a private museum of puppets (opened in 1999) is the third museum of its kind in Russia, where collections of more than 2000 dolls are presented including 'The multinational Saint Petersburg' and Pushkin's Petersburg. The museum world of Saint Petersburg is incredibly diverse. The city is not only home to the world-famous
Despite the economic instability of the 1990s, not a single major theatre or museum was closed in Saint Petersburg; on the contrary many new ones opened, for example a private museum of puppets (opened in 1999) is the third museum of its kind in Russia, where collections of more than 2000 dolls are presented including 'The multinational Saint Petersburg' and Pushkin's Petersburg. The museum world of Saint Petersburg is incredibly diverse. The city is not only home to the world-famous Hermitage Museum
The State Hermitage Museum ( rus, Государственный Эрмитаж, r=Gosudarstvennyj Ermitaž, p=ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)ɨj ɪrmʲɪˈtaʂ, links=no) is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is the largest ...
and the Russian Museum
The State Russian Museum (russian: Государственный Русский музей), formerly the Russian Museum of His Imperial Majesty Alexander III (russian: Русский Музей Императора Александра III), on ...
with its rich collection of Russian art
Russian culture (russian: Культура России, Kul'tura Rossii) has been formed by the nation's history, its geographical location and its vast expanse, religious and social traditions, and Western influence. Russian writers and phi ...
, but also the palaces of Saint Petersburg and its suburbs, so-called small-town museums and others like the museum of famous Russian writer Dostoyevsky
Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky (, ; rus, Фёдор Михайлович Достоевский, Fyódor Mikháylovich Dostoyévskiy, p=ˈfʲɵdər mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪdʑ dəstɐˈjefskʲɪj, a=ru-Dostoevsky.ogg, links=yes; 11 November 18219 ...
; Museum of Musical Instruments, the museum of decorative arts and the museum of professional orientation. The musical life of Saint Petersburg is rich and diverse, with the city now playing host to a number of annual carnivals. Ballet performances occupy a special place in the cultural life of Saint Petersburg. The Petersburg School of Ballet is named as one of the best in the world. Traditions of the Russian classical school have been passed down from generation to generation among outstanding educators. The art of famous and prominent Saint Petersburg dancers like
The musical life of Saint Petersburg is rich and diverse, with the city now playing host to a number of annual carnivals. Ballet performances occupy a special place in the cultural life of Saint Petersburg. The Petersburg School of Ballet is named as one of the best in the world. Traditions of the Russian classical school have been passed down from generation to generation among outstanding educators. The art of famous and prominent Saint Petersburg dancers like Rudolf Nureyev
Rudolf Khametovich Nureyev ( ; Tatar/ Bashkir: Рудольф Хәмит улы Нуриев; rus, Рудо́льф Хаме́тович Нуре́ев, p=rʊˈdolʲf xɐˈmʲetəvʲɪtɕ nʊˈrʲejɪf; 17 March 19386 January 1993) was a Soviet ...
, Natalia Makarova
Natalia Romanovna Makarova (russian: Ната́лия Рома́новна Мака́рова, born 21 November 1940) is a Russian prima ballerina and choreographer. ''The History of Dance'', published in 1981, notes that "her performances se ...
, Mikhail Baryshnikov
Mikhail Nikolayevich Baryshnikov ( rus, Михаил Николаевич Барышников, p=mʲɪxɐˈil bɐ'rɨʂnʲɪkəf; lv, Mihails Barišņikovs; born January 28, 1948) is a Soviet Latvian-born Russian-American dancer, choreograp ...
was, and is, admired throughout the world. Contemporary Petersburg ballet is made up not only of traditional Russian classical school but also ballets by those like Boris Eifman
Boris Eifman (Борис Яковлевич Эйфман) (born 22 July 1946, in Rubtsovsk) is a Russian choreographer and artistic director. He has done more than fifty ballet productions.
Eifman was born in Siberia, where his engineer father h ...
, who expanded the scope of strict classical Russian ballet
Russian ballet (russian: Русский балет) (french: Ballet russe) is a form of ballet characteristic of or originating from Russia.
Imperial Russian Ballet
Until 1689, ballet in Russia was nonexistent (ballet has its origins in the cour ...
to almost unimaginable limits. Remaining faithful to the classical basis (he was a choreographer at the Vaganova Academy of Russian Ballet
The Vaganova Academy of Russian Ballet is a school of classical ballet in St Petersburg, Russia. Established in 1738 during the reign of Empress Anna, the academy was known as the Imperial Ballet School until the Soviet era, when, after a brief ...
), he combined classical ballet
Classical ballet is any of the traditional, formal styles of ballet that exclusively employ classical ballet technique. It is known for its aesthetics and rigorous technique (such as pointe work, turnout of the legs, and high extensions), its f ...
with the avant-garde style, and then, in turn, with acrobatics, rhythmic gymnastics, dramatic expressiveness, cinema, color, light, and finally with spoken word.
Media and communications
All major Russian newspapers are active in Saint Petersburg. The city has a developed telecommunications system. In 2014,Rostelecom
Rostelecom is Russia’s largest provider of digital services for a wide variety of consumers, households, private businesses, government and municipal authorities, and other telecom providers.
Rostelecom interconnects all local public operators� ...
, the national operator, announced the beginning of a major modernization of the fixed-line network in the city.
Culture
Museums
Saint Petersburg is home to more than two hundred museums, many of them in historic buildings. The largest is theHermitage Museum
The State Hermitage Museum ( rus, Государственный Эрмитаж, r=Gosudarstvennyj Ermitaž, p=ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)ɨj ɪrmʲɪˈtaʂ, links=no) is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is the largest ...
that features the interiors of the former imperial residence and a vast collection of art. The Russian Museum
The State Russian Museum (russian: Государственный Русский музей), formerly the Russian Museum of His Imperial Majesty Alexander III (russian: Русский Музей Императора Александра III), on ...
is a large museum devoted to Russian fine art. The apartments of some famous Petersburgers, including Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, ...
, Fyodor Dostoyevsky
Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky (, ; rus, Фёдор Михайлович Достоевский, Fyódor Mikháylovich Dostoyévskiy, p=ˈfʲɵdər mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪdʑ dəstɐˈjefskʲɪj, a=ru-Dostoevsky.ogg, links=yes; 11 November 18219 ...
, Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov . At the time, his name was spelled Николай Андреевичъ Римскій-Корсаковъ. la, Nicolaus Andreae filius Rimskij-Korsakov. The composer romanized his name as ''Nicolas Rimsk ...
, Feodor Chaliapin
Feodor Ivanovich Chaliapin ( rus, Фёдор Ива́нович Шаля́пин, Fyodor Ivanovich Shalyapin, ˈfʲɵdər ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ ʂɐˈlʲapʲɪn}; April 12, 1938) was a Russian opera singer. Possessing a deep and expressive bass v ...
, Alexander Blok
Alexander Alexandrovich Blok ( rus, Алекса́ндр Алекса́ндрович Бло́к, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ɐlʲɪˈksandrəvʲɪtɕ ˈblok, a=Ru-Alyeksandr Alyeksandrovich Blok.oga; 7 August 1921) was a Russian lyrical poet, writer, publ ...
, Vladimir Nabokov
Vladimir Vladimirovich Nabokov (russian: link=no, Владимир Владимирович Набоков ; 2 July 1977), also known by the pen name Vladimir Sirin (), was a Russian-American novelist, poet, translator, and entomologist. Bor ...
, Anna Akhmatova
Anna Andreyevna Gorenko rus, А́нна Андре́евна Горе́нко, p=ˈanːə ɐnˈdrʲe(j)ɪvnə ɡɐˈrʲɛnkə, a=Anna Andreyevna Gorenko.ru.oga, links=yes; uk, А́нна Андрі́ївна Горе́нко, Ánna Andríyivn ...
, Mikhail Zoshchenko, Joseph Brodsky
Iosif Aleksandrovich Brodsky (; russian: link=no, Иосиф Александрович Бродский ; 24 May 1940 – 28 January 1996) was a Russian and American poet and essayist.
Born in Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg), USSR in 1940, ...
, as well as some palace and park ensembles of the southern suburbs and notable architectural monuments such as St. Isaac's Cathedral, have also been turned into public museums.
The Kunstkamera
The Kunstkamera (russian: Кунсткамера) or Kunstkammer ( German for "Culture Room" (literally) or "Art Chamber", typically used for a " cabinet of curiosities") is a public museum located on the Universitetskaya Embankment in Saint P ...
, with its collection established in 1714 by Peter the Great to collect curiosities from all over the world, is sometimes considered the first museum in Russia, which has evolved into the present-day Peter the Great Museum of Anthropology and Ethnography
The Kunstkamera (russian: Кунсткамера) or Kunstkammer (German for "Culture Room" (literally) or "Art Chamber", typically used for a " cabinet of curiosities") is a public museum located on the Universitetskaya Embankment in Saint Pete ...
. The Russian Ethnography Museum
The Russian Museum of Ethnography (Российский этнографический музей) is a museum in St. Petersburg that houses a collection of about 500,000 items relating to the ethnography, or cultural anthropology, of peoples of t ...
, which has been split from the Russian Museum, is devoted to the cultures of the people of Russia, the former Soviet Union
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet Republics and in Russia as the near abroad (russian: links=no, ближнее зарубежье, blizhneye zarubezhye), are the 15 sovereign states that wer ...
and Russian Empire.
Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet Union, So ...
and the Museum of Political History, which explains many authoritarian features of the USSR.
Other notable museums include the Central Naval Museum, and Zoological Museum
This is a list of natural history museums, also known as museums of natural history, i.e. museums whose exhibits focus on the subject of natural history, including such topics as animals, plants, ecosystems, geology, paleontology, and cl ...
, Central Soil Museum, the Russian Railway Museum, Suvorov Museum, Museum of the Siege of Leningrad, Erarta Museum of Contemporary Art, the largest non-governmental museum of contemporary art in Russia, Saint Petersburg Museum of History in the Peter and Paul Fortress
The Peter and Paul Fortress is the original citadel of St. Petersburg, Russia, founded by Peter the Great in 1703 and built to Domenico Trezzini's designs from 1706 to 1740 as a star fortress. Between the first half of the 1700s and early 1920 ...
and Artillery Museum, which includes not only artillery items, but also a huge collection of other military equipment, uniforms, and decorations. Amongst others, Saint Petersburg also hosts State Museum of the History of Religion, one of the eldest museums in Russia about religion depicting cultural representations from various parts of the globe.
Music

 Among the city's more than fifty theatres is the
Among the city's more than fifty theatres is the Mariinsky Theatre
The Mariinsky Theatre ( rus, Мариинский театр, Mariinskiy teatr, also transcribed as Maryinsky or Mariyinsky) is a historic theatre of opera and ballet in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Opened in 1860, it became the preeminent music th ...
(formerly known as the Kirov Theatre), home to the Mariinsky Ballet
The Mariinsky Ballet (russian: Балет Мариинского театра) is the resident classical ballet company of the Mariinsky Theatre in Saint Petersburg, Russia.
Founded in the 18th century and originally known as the Imperial Russ ...
company and opera. Leading ballet dancers, such as Vaslav Nijinsky, Anna Pavlova
Anna Pavlovna Pavlova ( , rus, Анна Павловна Павлова ), born Anna Matveyevna Pavlova ( rus, Анна Матвеевна Павлова; – 23 January 1931), was a Russian prima ballerina of the late 19th and the early 20t ...
, Rudolph Nureyev
Rudolf Khametovich Nureyev ( ; Tatar/ Bashkir: Рудольф Хәмит улы Нуриев; rus, Рудо́льф Хаме́тович Нуре́ев, p=rʊˈdolʲf xɐˈmʲetəvʲɪtɕ nʊˈrʲejɪf; 17 March 19386 January 1993) was a Sovie ...
, Mikhail Baryshnikov
Mikhail Nikolayevich Baryshnikov ( rus, Михаил Николаевич Барышников, p=mʲɪxɐˈil bɐ'rɨʂnʲɪkəf; lv, Mihails Barišņikovs; born January 28, 1948) is a Soviet Latvian-born Russian-American dancer, choreograp ...
, Galina Ulanova
Galina Sergeyevna Ulanova (russian: Галина Сергеевна Уланова, ; 21 March 1998) was a Russian ballet dancer. She is frequently cited as being one of the greatest ballerinas of the 20th century.
Biography
Ulanova was born ...
and Natalia Makarova
Natalia Romanovna Makarova (russian: Ната́лия Рома́новна Мака́рова, born 21 November 1940) is a Russian prima ballerina and choreographer. ''The History of Dance'', published in 1981, notes that "her performances se ...
, were principal stars of the Mariinsky ballet.
The first music school, the Saint Petersburg Conservatory, was founded in 1862 by the Russian pianist and composer Anton Rubinstein
Anton Grigoryevich Rubinstein ( rus, Антон Григорьевич Рубинштейн, r=Anton Grigor'evič Rubinštejn; ) was a Russian pianist, composer and conductor who became a pivotal figure in Russian culture when he founded the S ...
. The school alumni have included such notable composers as Pyotr Tchaikovsky
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky , group=n ( ; 7 May 1840 – 6 November 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic period. He was the first Russian composer whose music would make a lasting impression internationally. He wrote some of the most pop ...
, Sergei Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''., group=n (27 April .S. 15 April1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, p ...
, Artur Kapp
Artur Kapp (28 February 1878 – 14 January 1952) was an Estonian composer.
Born in Suure-Jaani, Estonia, then part of the Governorate of Livonia, Russian Empire, he was the son of Joosep Kapp, who was also a classically trained musician. Ka ...
, Rudolf Tobias
Rudolf Tobias ( – 29 October 1918) was the first Estonian professional composer, as well as a professional organist. He studied at the Saint Petersburg Conservatory. His compositions include among others piano works, string quartets and an or ...
and Dmitri Shostakovich, who taught at the conservatory during the 1960s, bringing it additional fame. The renowned Russian composer Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov . At the time, his name was spelled Николай Андреевичъ Римскій-Корсаковъ. la, Nicolaus Andreae filius Rimskij-Korsakov. The composer romanized his name as ''Nicolas Rimsk ...
also taught at the conservatory from 1871 to 1905. Among his students were Igor Stravinsky
Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky (6 April 1971) was a Russian composer, pianist and conductor, later of French (from 1934) and American (from 1945) citizenship. He is widely considered one of the most important and influential composers of the ...
, Alexander Glazounov, Anatoly Liadov and others. The former St. Petersburg apartment of Rimsky-Korsakov has been faithfully preserved as the composer's only museum.
 Dmitri Shostakovich, who was born and raised in Saint Petersburg, dedicated his Seventh Symphony to the city, calling it the "Leningrad Symphony". He wrote the symphony while based in the city during the siege of Leningrad. It was premiered in Samara in March 1942; a few months later, it received its first
Dmitri Shostakovich, who was born and raised in Saint Petersburg, dedicated his Seventh Symphony to the city, calling it the "Leningrad Symphony". He wrote the symphony while based in the city during the siege of Leningrad. It was premiered in Samara in March 1942; a few months later, it received its first performance
A performance is an act of staging or presenting a play, concert, or other form of entertainment. It is also defined as the action or process of carrying out or accomplishing an action, task, or function.
Management science
In the work place ...
in the besieged Leningrad at the Bolshoy Philharmonic Hall under the baton of conductor Karl Eliasberg
Karl Ilitch Eliasberg ( be, Карл Ілліч Эліасберг; russian: Карл Ильич Элиасберг) (10 June 1907, in Minsk – 12 February 1978, in Leningrad) was a Soviet conductor.
Eliasberg graduated from the Leningrad Conserv ...
. It was heard over the radio and was said to have lifted the spirits of the surviving population. In 1992, the 7th Symphony was performed by the 14 surviving orchestral players of the Leningrad premiere in the same hall as half a century before. The Leningrad Philharmonic Orchestra remained one of the best known symphony orchestras
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families.
There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, c ...
in the world under the leadership of conductors Yevgeny Mravinsky and Yuri Temirkanov
Yuri Khatuevich Temirkanov (russian: Ю́рий Хату́евич Темирка́нов; kbd, Темыркъан Хьэту и къуэ Юрий; born December 10, 1938) is a Russian conductor of Circassian ( Kabardian) origin.
Early life
B ...
. Mravinsky's term as artistic director of the Leningrad Philharmonic—a term that is possibly the longest of any conductor with any orchestra in modern times—led the orchestra from a little-known provincial ensemble to one of the world's most highly regarded orchestras, especially for the performance of Russian music.
The Imperial Choral Capella was founded and modelled after the royal courts of other European capitals.
Saint Petersburg has been home to the newest movements in popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Funk ...
in the country. The early Soviet jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a majo ...
bands founded here included Leopold Teplitsky's First Concert Jazz Band (1927,) Leonid Utyosov 's TheaJazz (1928, under the patronage of composer Isaak Dunayevsky
Isaak Osipovich Dunayevsky (russian: Исаак Осипович Дунаевский ; also transliterated as Dunaevski or Dunaevskiy; 25 July 1955) was a Soviet film composer and conductor of the 1930s and 1940s, who composed music for operet ...
) and Georgy Landsberg's Jazz Cappella (1929). The first jazz appreciation society in the Soviet Union was founded here in 1958 as J58, and later named jazz club
A jazz club is a venue where the primary entertainment is the performance of live jazz music, although some jazz clubs primarily focus on the study and/or promotion of jazz-music. Jazz clubs are usually a type of nightclub or bar, which is lice ...
Kvadrat. In 1956 the popular ensemble Druzhba was founded by Aleksandr Bronevitsky and Edita Piekha
Edita Piekha (russian: Эди́та Станисла́вовна Пье́ха, ''Edita Stanislavovna Pyekha'', pl, Edyta Piecha, french: Édith-Marie Piecha) is a Soviet and Russian singer and actress of Polish descent. She was the third popular ...
to become the first popular band in the USSR during the 1950s. In the 1960s student rock-groups Argonavty, Kochevniki and others pioneered a series of unofficial and underground rock concerts and festivals. In 1972 Boris Grebenshchikov
Boris Borisovich Grebenshchikov (russian: link=no, Борис Борисович Гребенщиков; born ) is a prominent member of the generation which is widely considered to be the "founding fathers" of Russian rock music. He is the fo ...
founded the band Aquarium, which later grew to huge popularity. Since then "Peter's rock" music style was formed.
In the 1970s many bands came out from the "underground" scene and eventually founded the Leningrad Rock Club, which provided a stage to bands such as DDT, Kino, Alisa, Zemlyane
Zemlyane (russian: link=no, Земляне, lit=Earthlings) is a Soviet and later Russian rock band, formed in Leningrad in 1978. The band achieved great popularity in the early 1980s and remains active.
A key artist in the VIA (vocal-instrumen ...
, Zoopark, Piknik
Piknik (Picnic, russian: Пикни́к) is a Russian rock band known for its unique style which is a mixture of art rock, progressive rock and original Russian rock. The band was formed in 1978 in Leningrad by Sergey Omelnichenko, Evgeny Volos ...
, and Secret
Secrecy is the practice of hiding information from certain individuals or groups who do not have the "need to know", perhaps while sharing it with other individuals. That which is kept hidden is known as the secret.
Secrecy is often controvers ...
. The first Russian-style happening show Pop Mekhanika, mixing over 300 people and animals on stage, was directed by the multi-talented Sergey Kuryokhin in the 1980s. The Sergey Kuryokhin International Festival (SKIF) is named after him. In 2004 the Kuryokhin Center The Kuryokhin Center, or more extended the Sergey Kuryokhin Center for Modern Art, is a non-profit cultural centre in Saint Petersburg, Russia. The centre was founded in 2004 and named after the Russian avant garde composer Sergey Kuryokhin. The mai ...
was founded, where the SKIF and the Electro-Mechanica and Ethnomechanica festivals take place. SKIF focuses on experimental pop music and avant garde music
Avant-garde music is music that is considered to be at the forefront of innovation in its field, with the term "avant-garde" implying a critique of existing aesthetic conventions, rejection of the status quo in favor of unique or original eleme ...
, Electro-Mechanica on electronic music
Electronic music is a Music genre, genre of music that employs electronic musical instruments, digital instruments, or electronics, circuitry-based music technology in its creation. It includes both music made using electronic and electromech ...
, and Ethnomechanica on world music.
Today's Saint Petersburg boasts many notable musicians of various genres, from popular Leningrad's Sergei Shnurov
Sergey Vladimirovich Shnurov (russian: Серге́й Влади́мирович Шну́ров; born 13 April 1973) is a Russian musician and songwriter, best known as ''Shnur'' (lit. cord), of the ska-punk band Leningrad which he formed in ...
, Tequilajazzz, Splean, and Korol i Shut, to rock veterans Yuri Shevchuk, Vyacheslav Butusov, and Mikhail Boyarsky. In the early 2000s the city saw a wave of popularity of metalcore
Metalcore (also known as metallic hardcore) is a fusion music genre that combines elements of extreme metal and hardcore punk. As with other styles blending metal and hardcore, such as crust punk and grindcore, metalcore is noted for its use ...
, rapcore, and emocore, and there are bands such as Amatory, Kirpichi, Psychea, Stigmata
Stigmata ( grc, στίγματα, plural of , 'mark, spot, brand'), in Roman Catholicism, are bodily wounds, scars and pain which appear in locations corresponding to the crucifixion wounds of Jesus Christ: the hands, wrists, and feet.
Sti ...
, Grenouer and Animal Jazz.
The White Nights Festival in Saint Petersburg is famous for spectacular fireworks and a massive show celebrating the end of the school year
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compul ...
.
The rave band Little Big also hails from Saint Petersburg. Their music video for "Skibidi
"Skibidi" is a dance song by Russian rave band Little Big. It was released on 5 October 2018 along with their album ''Antipositive, Pt. 2'' on Warner Music Russia. Ilya Prusikin and the media producer of the group 'Khleb", Lyubim Khomchuk w ...
" was filmed in the city, starting at Akademicheskiy Pereulok.
Literature
 Saint Petersburg has a longstanding and world-famous tradition in literature.
Saint Petersburg has a longstanding and world-famous tradition in literature. Dostoyevsky
Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky (, ; rus, Фёдор Михайлович Достоевский, Fyódor Mikháylovich Dostoyévskiy, p=ˈfʲɵdər mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪdʑ dəstɐˈjefskʲɪj, a=ru-Dostoevsky.ogg, links=yes; 11 November 18219 ...
called it "The most abstract and intentional city in the world", emphasizing its artificiality, but it was also a symbol of modern disorder in a changing Russia. It often appeared to Russian writers
This is a list of authors who have written works of prose and poetry in the Russian language.
For separate lists by literary field:
*List of Russian-language novelists
*List of Russian-language playwrights
* List of Russian-language poets
A ...
as a menacing and inhuman mechanism. The grotesque and often nightmarish image of the city is featured in Pushkin's last poems, the Petersburg stories of Gogol
Nikolai Vasilyevich Gogol; uk, link=no, Мико́ла Васи́льович Го́голь, translit=Mykola Vasyliovych Hohol; (russian: Яновский; uk, Яновський, translit=Yanovskyi) ( – ) was a Russian novelist, ...
, the novels of Dostoyevsky
Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky (, ; rus, Фёдор Михайлович Достоевский, Fyódor Mikháylovich Dostoyévskiy, p=ˈfʲɵdər mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪdʑ dəstɐˈjefskʲɪj, a=ru-Dostoevsky.ogg, links=yes; 11 November 18219 ...
, the verse of Alexander Blok
Alexander Alexandrovich Blok ( rus, Алекса́ндр Алекса́ндрович Бло́к, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ɐlʲɪˈksandrəvʲɪtɕ ˈblok, a=Ru-Alyeksandr Alyeksandrovich Blok.oga; 7 August 1921) was a Russian lyrical poet, writer, publ ...
and Osip Mandelshtam
Osip Emilyevich Mandelstam ( rus, Осип Эмильевич Мандельштам, p=ˈosʲɪp ɨˈmʲilʲjɪvʲɪtɕ mənʲdʲɪlʲˈʂtam; – 27 December 1938) was a Russian and Soviet poet. He was one of the foremost members of the Acm ...
, and in the symbolist novel ''Petersburg
Petersburg, or Petersburgh, may refer to:
Places Australia
*Petersburg, former name of Peterborough, South Australia
Canada
* Petersburg, Ontario
Russia
*Saint Petersburg, sometimes referred to as Petersburg
United States
*Peterborg, U.S. Virg ...
'' by Andrey Bely. According to Lotman in his chapter, 'The Symbolism of Saint Petersburg' in ''Universe and the Mind'', these writers were inspired by symbolism from within the city itself. The effect of life in Saint Petersburg on the plight of the poor clerk in a society obsessed with hierarchy and status also became an important theme for authors such as Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, ...
, Gogol, and Dostoyevsky. Another important feature of early Saint Petersburg literature is its mythical element, which incorporates urban legend
An urban legend (sometimes contemporary legend, modern legend, urban myth, or urban tale) is a genre of folklore comprising stories or fallacious claims circulated as true, especially as having happened to a "friend of a friend" or a family m ...
s and popular ghost stories, as the stories of Pushkin and Gogol included ghosts returning to Saint Petersburg to haunt other characters as well as other fantastical elements, creating a surreal and abstract image of Saint Petersburg.
20th-century writers from Saint Petersburg, such as Vladimir Nabokov
Vladimir Vladimirovich Nabokov (russian: link=no, Владимир Владимирович Набоков ; 2 July 1977), also known by the pen name Vladimir Sirin (), was a Russian-American novelist, poet, translator, and entomologist. Bor ...
, Ayn Rand
Alice O'Connor (born Alisa Zinovyevna Rosenbaum;, . Most sources transliterate her given name as either ''Alisa'' or ''Alissa''. , 1905 – March 6, 1982), better known by her pen name Ayn Rand (), was a Russian-born American writer and p ...
, Andrey Bely and Yevgeny Zamyatin
Yevgeny Ivanovich Zamyatin ( rus, Евге́ний Ива́нович Замя́тин, p=jɪvˈɡʲenʲɪj ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ zɐˈmʲætʲɪn; – 10 March 1937), sometimes anglicized as Eugene Zamyatin, was a Russian author of science fictio ...
, along with his apprentices, The Serapion Brothers created entirely new styles in literature and contributed new insights to the understanding of society through their experience in this city. Anna Akhmatova
Anna Andreyevna Gorenko rus, А́нна Андре́евна Горе́нко, p=ˈanːə ɐnˈdrʲe(j)ɪvnə ɡɐˈrʲɛnkə, a=Anna Andreyevna Gorenko.ru.oga, links=yes; uk, А́нна Андрі́ївна Горе́нко, Ánna Andríyivn ...
became an important leader for Russian poetry
This is a list of authors who have written poetry in the Russian language.
Alphabetical list
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
I
K
L
M
N
O
P
R
S
T
U
V
Y
Z
Sources
See also
* List of Russian archite ...
. Her poem ''Requiem'' adumbrates the perils encountered during the Stalinist era. Another notable 20th-century writer from Saint Petersburg is Joseph Brodsky
Iosif Aleksandrovich Brodsky (; russian: link=no, Иосиф Александрович Бродский ; 24 May 1940 – 28 January 1996) was a Russian and American poet and essayist.
Born in Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg), USSR in 1940, ...
, recipient of the Nobel Prize in Literature
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, caption =
, awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in literature
, presenter = Swedish Academy
, holder = Annie Ernaux (2022)
, location = Stockholm, Sweden
, year = 1901 ...
(1987). While living in the United States, his writings in English reflected on life in Saint Petersburg from the unique perspective of being both an insider and an outsider to the city in essays such as, "A Guide to a Renamed City" and the nostalgic "In a Room and a Half".
Film
 Over 250 international and Russian movies were filmed in Saint Petersburg. Well over a thousand feature films about tsars, revolution, people and stories set in Saint Petersburg have been produced worldwide but not filmed in the city. The first film studios were founded in Saint Petersburg in the 20th century and since the 1920s
Over 250 international and Russian movies were filmed in Saint Petersburg. Well over a thousand feature films about tsars, revolution, people and stories set in Saint Petersburg have been produced worldwide but not filmed in the city. The first film studios were founded in Saint Petersburg in the 20th century and since the 1920s Lenfilm
Lenfilm (russian: link=no, Ленфильм) is a Russian production company with its own film studio located in Saint Petersburg (the city was called Leningrad from 1924 to 1991, thus the name). It is a corporation with its stakes shared betwe ...
has been the largest film studio based in Saint Petersburg. The first foreign feature movie filmed entirely in Saint Petersburg was the 1997 production of Tolstoy's ''Anna Karenina
''Anna Karenina'' ( rus, «Анна Каренина», p=ˈanːə kɐˈrʲenʲɪnə) is a novel by the Russian author Leo Tolstoy, first published in book form in 1878. Widely considered to be one of the greatest works of literature ever writte ...
'', starring Sophie Marceau and Sean Bean
Sean Bean (born Shaun Mark Bean on 17 April 1959) is an English actor. After graduating from the Royal Academy of Dramatic Art, Bean made his professional debut in a theatre production of '' Romeo and Juliet'' in 1983. Retaining his Yorkshire ...
and made by an international team of British, American, French and Russian filmmakers.
The cult comedy '' Irony of Fate'' (also Ирония судьбы, или С лёгким паром!) is set in Saint Petersburg and pokes fun at Soviet city planning. The 1985 film '' White Nights'' received considerable Western attention for having captured genuine Leningrad street scenes at a time when filming in the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
by Western production companies was generally unheard of. Other movies include '' GoldenEye'' (1995), '' Midnight in Saint Petersburg'' (1996), ''Brother
A brother is a man or boy who shares one or more parents with another; a male sibling. The female counterpart is a sister. Although the term typically refers to a familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to refer to non-famil ...
'' (1997) and Tamil romantic thriller film
Thriller film, also known as suspense film or suspense thriller, is a broad film genre that evokes excitement and suspense in the audience. The suspense element found in most films' plots is particularly exploited by the filmmaker in this genre. ...
-'' Dhaam Dhoom'' (2008). '' Onegin'' (1999) is based on the Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, ...
poem and showcases many tourist attraction
A tourist attraction is a place of interest that tourists visit, typically for its inherent or an exhibited natural or cultural value, historical significance, natural or built beauty, offering leisure and amusement.
Types
Places of natural ...
s. In addition, the Russian romantic comedy, ''Piter FM
Piter FM is a 2006 Russian romantic comedy-drama film directed by Oksana Bychkova and starring Ekaterina Fedulova, Evgeniy Tsyganov and Alexey Barabash. The plot revolves around the serendipitous and unexpected romance between a young man and w ...
'', intricately showcases the cityscape, almost as if it were a main character in the film.
Several international film festivals are held annually, such as the Festival of Festivals, Saint Petersburg, as well as the Message to Man International Documentary Film Festival, since its inauguration in 1988 during the White Nights.
Dramatic theatre
St Petersburg has a number of dramatic theatres and drama schools. These include the Student Theatre onMokhovaya Street
Mokhovaya Street (russian: Моховая улица) is a one-way street in central Moscow, Russia, a part of Moscow's innermost ring road - Central Squares of Moscow. Between 1961 and 1990 it formed part of Karl Marx Avenue (Проспек ...
. Учебный театр «На Моховой»Leteiny Theatre
an
Youth Theatre on the Fontanka
Education
–2007, there were 1,024 kindergartens, 716public schools
Public school may refer to:
*State school (known as a public school in many countries), a no-fee school, publicly funded and operated by the government
*Public school (United Kingdom), certain elite fee-charging independent schools in England and ...
and 80 vocational
A vocation () is an occupation to which a person is especially drawn or for which they are suited, trained or qualified. People can be given information about a new occupation through student orientation. Though now often used in non-religious ...
schools in Saint Petersburg. The largest of the public higher education institutions is Saint Petersburg State University
Saint Petersburg State University (SPBU; russian: Санкт-Петербургский государственный университет) is a public research university in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Founded in 1724 by a decree of Peter the G ...
, enrolling approximately 32,000 undergraduate students; and the largest non-governmental higher education institutions is the Institute of International Economic Relations, Economics, and Law. Other famous universities are Saint Petersburg Polytechnic University, Herzen University, Saint Petersburg State University of Economics and Finance and Saint Petersburg Military engineering-technical university. However, the public universities are all federal property and do not belong to the city.
Sports
 Leningrad hosted part of the association football tournament during the 1980
Leningrad hosted part of the association football tournament during the 1980 Summer Olympics
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The ina ...
. The 1994 Goodwill Games
The Goodwill Games were an international sports competition created by Ted Turner in reaction to the political troubles surrounding the Olympic Games of the 1980s. In 1979, the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan caused the United States and other W ...
were also held here.
In boating, the first competition here was the 1703 rowing event initiated by Peter the Great, after the victory over the Swedish fleet
The Swedish Navy ( sv, Svenska marinen) is the naval branch of the Swedish Armed Forces. It is composed of surface and submarine naval units – the Fleet () – as well as marine units, the Amphibious Corps ().
In Swedish, vessels of ...
. The Russian Navy held Yachting
Yachting is the use of recreational boats and ships called '' yachts'' for racing or cruising. Yachts are distinguished from working ships mainly by their leisure purpose. "Yacht" derives from the Dutch word '' jacht'' ("hunt"). With sailboat ...
events since the foundation of the city. Yacht club
A yacht club is a sports club specifically related to yachting.
Description
Yacht clubs are mostly located by the sea, although there some that have been established at a lake or riverside locations. Yacht or sailing clubs have either a mar ...
s: St. Petersburg River Yacht Club
The St. Petersburg River Yacht Club, also known as St. Petersburg Central River Yacht Club or simply Central River Yacht Club, is a sailing club in Saint Petersburg. It is located on Petrovsky Island, off Peter's Passage, between the mouths of Mala ...
, Neva Yacht Club, the latter is the oldest yacht club in the world. In the winter, when the sea and lake surfaces are frozen and yachts and dinghies cannot be used, local people sail ice boat
An iceboat (occasionally spelled ice boat or traditionally called an ice yacht) is a recreational or competition sailing craft supported on metal runners for traveling over ice. One of the runners is steerable. Originally, such craft were boats ...
s.
Equestrianism has been a long tradition, popular among the Tsars and aristocracy, as well as part of military training
Military education and training is a process which intends to establish and improve the capabilities of military personnel in their respective roles. Military training may be voluntary or compulsory duty. It begins with recruit training, proceed ...
. Several historic sports arenas were built for equestrianism since the 18th century to maintain training all year round, such as the Zimny Stadion and Konnogvardeisky Manezh.
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to dist ...
tradition was highlighted by the 1914 international tournament, partially funded by the Tsar, in which the title "Grandmaster" was first formally conferred by Russian Tsar Nicholas II
Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov; spelled in pre-revolutionary script. ( 186817 July 1918), known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer,. was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Pola ...
to five players: Lasker, Capablanca, Alekhine
Alexander Aleksandrovich Alekhine, ''Aleksándr Aleksándrovich Alékhin''; (March 24, 1946) was a Russian and French chess player and the fourth World Chess Champion, a title he held for two reigns.
By the age of 22, Alekhine was already a ...
, Tarrasch and Marshall.
Kirov Stadium with a capacity of 70 thousand seats (now a modern Gazprom Arena since 2017) which hosted matches for the 2018 FIFA World Cup is one of the largest stadiums in the world and home to FC Zenit Saint Petersburg
Football Club Zenit (russian: link=no, Футбольный клуб «Зенит» ), also known as Zenit Saint Petersburg or simply Zenit, is a Russian professional football club based in Saint Petersburg. Founded in 1925 (or in 1914, acco ...
from 1950 to 1993 and again in 1995. In 1951 a crowd of 110,000 set the single-game attendance record for Soviet football. Zenit have been champions of the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
and Russian league nine times, most notably claiming the RPL title in four consecutive seasons from 2018-19 to 2021-22. The club has also won the Soviet/Russian Cup on five occasions. One of Zenit's most successful players was Andrei Arshavin, who led the team to claim the UEFA Cup 2007–08 season and the 2008 UEFA Super Cup.
Hockey teams in the city include SKA Saint Petersburg in the KHL, HC VMF St. Petersburg in the VHL, and junior clubs SKA-1946
The Hockey Club SKA-1946 Saint Petersburg (russian: link=no, Хоккейный клуб "СКА-1946" Санкт-Петербург), is a Russian junior ice hockey club based in Saint Petersburg, Russia. They are members of the Western Conf ...
and Silver Lions
The 1st Battalion, 68th Armor Regiment (1–68 Armor) is a battalion of the 68th Armor Regiment, United States Army.
Operation Iraqi Freedom
Upon return from deployment to Operation Iraqi Freedom (OIF) 1, the 4th Infantry Division immediately ...
in the Russian Major League
The Supreme Hockey League (SHL) (russian: Высшая хоккейная лига (ВХЛ), links=no, ''Vysshaya hokkeinaya liga (VHL)''), also known as the Major Hockey League or Higher Hockey League (HHL), is a professional ice hockey league i ...
. SKA Saint Petersburg is one of the most popular in the KHL, consistently being at or near the top of the league in attendance. Along with their popularity, they are one of the best teams in the KHL right now, as they have won the Gagarin Cup
The Gagarin Cup (russian: Кубок Гагарина, Kubok Gagarina) is the trophy presented to the winner of the Kontinental Hockey League (KHL) playoffs, and is named after Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, the first human in space. The Cup was ...
twice. Well-known players on the team include Pavel Datsyuk
Pavel Valerievich Datsyuk (, ; born 20 July 1978) is a Russian former professional ice hockey player. Datsyuk was nicknamed the "Magic Man" honoring his incredible stickhandling and creativity with the puck. From 2001 to 2016, he played for the ...
, Ilya Kovalchuk
Ilya Valeryevich Kovalchuk (russian: Илья Валерьевич Ковальчук; born 15 April 1983) is a Russian former professional ice hockey winger. He played for the Atlanta Thrashers, New Jersey Devils, Los Angeles Kings, Montreal ...
, Nikita Gusev, Sergei Shirokov and Viktor Tikhonov. During the NHL lockout, stars Ilya Kovalchuk, Sergei Bobrovsky and Vladimir Tarasenko also played for the team. They play their home games at Ice Palace Saint Petersburg.
The city's long-time basketball team is BC Spartak Saint Petersburg, which launched the career of Andrei Kirilenko. BC Spartak Saint Petersburg won two championships in the USSR Premier League (1975 and 1992), two USSR Cups (1978 and 1987), and a Russian Cup title (2011). They also won the Saporta Cup twice (1973 and 1975). Legends of the club include Alexander Belov and Vladimir Kondrashin. The city also has a new basketball team, BC Zenit Saint Petersburg.
Citing the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, UEFA removed St Petersburg as host for the 2022 UEFA Champions League Final in February 2022.
Transport
 Saint Petersburg is a major transport hub. The first Russian railway was built here in 1837, and since then the city's transport infrastructure has kept pace with the city's growth. Petersburg has an extensive system of local roads and railway services, maintains a large public transport system that includes the
Saint Petersburg is a major transport hub. The first Russian railway was built here in 1837, and since then the city's transport infrastructure has kept pace with the city's growth. Petersburg has an extensive system of local roads and railway services, maintains a large public transport system that includes the Saint Petersburg tram
Trams in Saint Petersburg are a major mode of public transit in the city of Saint Petersburg, Russia. Saint Petersburg once had the second-largest tram network in the world, consisting of about of unduplicated track in the late 1980s. Howeve ...
and the Saint Petersburg Metro
The Saint Petersburg Metro (russian: links=no, Петербургский метрополитен, Peterburgskiy metropoliten) is a rapid transit system in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Construction began in early 1941, but was put on hold due to Wor ...
, and is home to several riverine services that convey passengers around the city efficiently and in relative comfort.
The city is connected to the rest of Russia and the wider world by several federal highways and national and international rail routes. Pulkovo Airport
Pulkovo ( rus, links=no, Пулково, p=ˈpulkəvə) is an international airport serving St. Petersburg, Russia. It consists of one terminal which is located south of the city centre. The airport serves as a hub for Rossiya Airlines an ...
serves most of the air passengers departing from or arriving to the city.
Roads and public transport

 Saint Petersburg has an extensive city-funded network of public transport (buses,
Saint Petersburg has an extensive city-funded network of public transport (buses, trams
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
, trolleybus
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or trol ...
es) and several hundred routes served by ''marshrutka
''Marshrutka''Trams in Saint Petersburg used to be the main means of transport; in the 1980s this was the largest tram network globally, but many tracks were dismantled in the 2000s.
 Buses carry up to three million passengers daily, serving over 250 urban and a number of suburban bus routes.
Buses carry up to three million passengers daily, serving over 250 urban and a number of suburban bus routes.
 Buses carry up to three million passengers daily, serving over 250 urban and a number of suburban bus routes.
Buses carry up to three million passengers daily, serving over 250 urban and a number of suburban bus routes. Saint Petersburg Metro
The Saint Petersburg Metro (russian: links=no, Петербургский метрополитен, Peterburgskiy metropoliten) is a rapid transit system in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Construction began in early 1941, but was put on hold due to Wor ...
underground rapid transit system was opened in 1955; it now has 5 lines with 72 stations, connecting all five railway terminals, and carrying 2.3 million passengers daily. Metro stations are often elaborately decorated with materials such as marble and bronze.
As of 2018, the Saint Petersburg Metro will include new stations: Prospekt Slavy, Dunayskaya, Shushary, Begovaya, and Novokrestovskaya, the latter built specifically to offer convenient access to the stadium during the 2018 FIFA World Cup
The 2018 FIFA World Cup was the 21st FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial world championship for men's national football teams organized by FIFA. It took place in Russia from 14 June to 15 July 2018, after the country was awarded the hosting righ ...
games and games played by FC Zenit.
Traffic jams are common in the city due to daily commuter traffic volumes, intercity traffic and excessive winter snow. The construction of freeways
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms i ...
such as the Saint Petersburg Ring Road, completed in 2011, and the Western High-Speed Diameter, completed in 2017, helped reduce the traffic in the city. The M11 Neva, also known as the Moscow-Saint Petersburg Motorway, is a federal highway, and connects Saint Petersburg to Moscow by a freeway.
Saint Petersburg is an important transport corridor
A transport corridor is a generally linear area that is defined by one or more modes of transportation crossing the limits of more than one city or county like highways, railroads or public transit which share a common destination. Development ...
linking Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
to Russia and Eastern Europe. The city is a node of the international European routes E18 towards Helsinki
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of U ...
, E20 E20 or E-20 may refer to:
* E20 fuel, a mixture of 20% ethanol and 80% gasoline
* European route E20
* Tandberg E20, a videoconferencing system
* E20, a postcode district in the E postcode area, announced in March 2011 for use on the site of the 20 ...
towards Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju '' ...
, E95 towards Pskov, Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
and Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrat ...
and E105 towards Petrozavodsk
Petrozavodsk (russian: Петрозаводск, p=pʲɪtrəzɐˈvotsk; Karelian, Vepsian and fi, Petroskoi) is the capital city of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, which stretches along the western shore of Lake Onega for some . The populati ...
, Murmansk
Murmansk ( Russian: ''Мурманск'' lit. " Norwegian coast"; Finnish: ''Murmansk'', sometimes ''Muurmanski'', previously ''Muurmanni''; Norwegian: ''Norskekysten;'' Northern Sámi: ''Murmánska;'' Kildin Sámi: ''Мурман ланнҍ ...
and Kirkenes
Kirkenes (; ; Skolt Sami: ''Ǩeârkknjargg;'' fi, Kirkkoniemi; ; russian: Киркенес) is a town in Sør-Varanger Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, in the far northeastern part of Norway. The town lies on a peninsula along the Bøk ...
(north) and towards Moscow and Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, wikt:Харків, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine.
The city is also served by passenger and cargo seaports in the Neva Bay of the
 The city is the final destination for a web of intercity and suburban railways, served by five different railway terminals ( Baltiysky, Finlyandsky, Ladozhsky, Moskovsky and Vitebsky), as well as dozens of non-terminal
The city is the final destination for a web of intercity and suburban railways, served by five different railway terminals ( Baltiysky, Finlyandsky, Ladozhsky, Moskovsky and Vitebsky), as well as dozens of non-terminal
"Murderers, you bombed it": a schoolgirl was detained in St. Petersburg for writing on an installation about Mariupol
/ref>
Travel to the Baltic Hansa
. The European Union and its enlargement to the East) Book in Italian. * George, Arthur L. & Elena George. ''St. Petersburg: Russia's Window to the Future, The First Three Centuries''. Lanham: Taylor Trade Publishing, 2003. . * Glantz, David M. ''The Battle for Leningrad, 1941–1944''. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 2002. . * Hellberg-Hirn, Elena. ''Imperial Imprints: Post-Soviet St. Petersburg''. Helsinki: SKS Finnish literature Society, 2003. . * * Duncan Fallowell, ''One Hot Summer in St Petersburg'' (London, Jonathan Cape,1995) * ''Knopf Guide: Sat. Petersburg''. New York: Knopf, 1995. . * Eyewitness Guide: St. Petersburg. * Lincoln, W. Bruce. ''Sunlight at Midnight: St. Petersburg and the Rise of Modern Russia''. New York: Basic Books, 2000. . * Orttung, Robert W. ''From Leningrad to St. Petersburg: Democratization in a Russian City''. New York: St. Martin's, 1995. . * * Ruble, Blair A. ''Leningrad: Shaping a Soviet City''. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1990. . * Shvidkovsky, Dmitry O. & Alexander Orloff. ''St. Petersburg: Architecture of the Tsars''. New York: Abbeville Press, 1996. . * Volkov, Solomon. ''St. Petersburg: A Cultural History''. New York: Free Press, 1995. . * St. Petersburg:Architecture of the Tsars. 360 pages. Abbeville Press, 1996. * Saint Petersburg: Museums, Palaces, and Historic Collections: A Guide to the Lesser Known Treasures of St. Petersburg. 2003. . * . * *
City Tourist Portal
* by FIFA *
St-Petersburg, Virtual Tour • 360° Aerial Panorama
* 50 photographs of St. Petersburg from "Travel literature, Travelogues" of Burton Holmes (Vol. 8, 1914) and other sources * * 3500 entries, 9200 personalities, 3500 addresses, 2000 pictures and 40 geographical maps, 3800 bibliographical references from the original "Encyclopaedia of Saint Petersburg" (SPb., Rosspen, 2004) *
Байков В.Д. Ленинградские хроники: от послевоенных 50-х до "лихих 90-х". М. Карамзин, 2017. – 486 с., илл. – in English: Leningrad Chronicles: from the postwar fifties to the "wild nineties"
site {{Authority control Saint Petersburg, 1703 establishments in Russia 1703 establishments in Europe Federal cities of Russia Former national capitals Planned capitals Populated coastal places in Russia Populated places established in 1703 Port cities and towns in Russia Port cities and towns of the Baltic Sea Sankt-Peterburgsky Uyezd World Heritage Sites in Russia
Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
, Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
, the river port higher up the Neva and tens of smaller passenger stations on both banks of the Neva river. It is a terminus of both the Volga-Baltic and White Sea-Baltic waterways.
The first high bridge that does not need to be drawn, the Big Obukhovsky Bridge opened in 2004. Meteor hydrofoils link the city centre to the coastal towns of Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for " crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city ...
and Shlisselburg
Shlisselburg ( rus, Шлиссельбу́рг, p=ʂlʲɪsʲɪlʲˈburk; german: Schlüsselburg; fi, Pähkinälinna; sv, Nöteborg), formerly Oreshek (Орешек) (1323–1611) and Petrokrepost (Петрокрепость) (1944–1992), is ...
from May through October. In the warmer months many smaller boats and water-taxis navigate the city's canals.
The shipping company St. Peter Line
St. Peter Line is water transport company owned by Moby SPL Limited, a Maltese-registered shipping company, which operated services from Helsinki, St. Petersburg, Stockholm and Tallinn. The company was founded in 2010 with it starting operation ...
operates two ferries that sail from Helsinki
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of U ...
to Saint Petersburg and from Stockholm to Saint Petersburg.
Rail
 The city is the final destination for a web of intercity and suburban railways, served by five different railway terminals ( Baltiysky, Finlyandsky, Ladozhsky, Moskovsky and Vitebsky), as well as dozens of non-terminal
The city is the final destination for a web of intercity and suburban railways, served by five different railway terminals ( Baltiysky, Finlyandsky, Ladozhsky, Moskovsky and Vitebsky), as well as dozens of non-terminal railway stations
A train station, railway station, railroad station or depot is a railway facility where trains stop to load or unload passengers, freight or both. It generally consists of at least one platform, one track and a station building providing su ...
within the federal subject. Saint Petersburg has international railway connections to Helsinki
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of U ...
, Finland, Berlin, Germany, and many former republics of the USSR. The Helsinki railway, built in 1870 and long, has trains running five times a day, in a journey lasting about three and a half hours with the Allegro train.
The Moscow – Saint Petersburg Railway opened in 1851, and is long; the commute to Moscow now requires from three and a half to nine hours.
In 2009 Russian Railways
Russian Railways (russian: link=no, ОАО «Российские железные дороги» (ОАО «РЖД»), OAO Rossiyskie zheleznye dorogi (OAO RZhD)) is a Russian fully state-owned vertically integrated railway company, both managi ...
launched a high speed service for the Moscow–Saint Petersburg route. The new train, known as Sapsan
The ''Sapsan'' (russian: Сапсан, lit=Peregrine Falcon, known as Velaro RUS EVS) is a Russian gauge high speed electric express train. The train is a Siemens Velaro model, which in turn is based on the ICE 3M/F high-speed trains manufac ...
, is a derivative of the popular Siemens Velaro train; various versions of this already operate in some European countries. It set records for the fastest train in Russia on 2 May 2009, travelling at and on 7 May 2009, traveling at .
Since 12 December 2010 Karelian Trains, a joint venture between Russian Railways
Russian Railways (russian: link=no, ОАО «Российские железные дороги» (ОАО «РЖД»), OAO Rossiyskie zheleznye dorogi (OAO RZhD)) is a Russian fully state-owned vertically integrated railway company, both managi ...
and VR (Finnish Railways), has been running Alstom Pendolino operated high-speed services between Saint Petersburg's Finlyandsky and Helsinki's Central railway stations. These services are branded as "Allegro" trains. "Allegro" is known for suffering some big technical problems from time to time, which sometimes result in significant delays and even cancellation of tourists' trips.
Air
Saint Petersburg is served by Pulkovo International Airport. Pulkovo airport was opened to passengers as a small aerodrome in 1931. , the Pulkovo airport, which handles over 12 million passengers annually, is the 3rd busiest in Russia after Moscow's Sheremetyevo and Domodedovo International Airport, Domodedovo. As a result, the steadily increasing passenger traffic has triggered a massive modernization of the entire airport infrastructure. A newly built Terminal 1 of the Pulkovo airport was put into operation on 4 December 2013 and integrated international flights of the former terminal Pulkovo-2. The renovated terminal Pulkovo-1 has been opened for domestic flights as an extension of Terminal 1 in 2015. One of the oldest air carriers of the Russian Federation Rossiya is registered in Saint Petersburg and is the largest and the base carrier of Pulkovo Airport. There is a regular rapid-bus connection (buses 39, 39E, K39) between Pulkovo airport and the Moskovskaya (Saint Petersburg Metro), Moskovskaya metro station as well as 24/7 taxi service.Notable people
International relations
List of sister cities to Saint Petersburg as it appears on the official portal of the City Government, listing both sister cities and partnership ties: Non CIS/Baltic states sister cities of Saint Petersburg (from official government list) Sister cities in the Commonwealth of Independent States and Baltic states Sister cities of Saint Petersburg (not included on official government list)Former twin towns
Milan andVenice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
were formerly twin cities of Saint Petersburg, but suspended this link due to St Petersburg's ban on "gay propaganda". Milan suspended the relationship with Saint Petersburg on 23 November 2012 and Venice did so on 28 January 2013.
In March 2022, Gdańsk, Warsaw, Aarhus and Melbourne terminated or suspended the cooperation, affiliation or sister city relationship with Saint Petersburg as a response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, Russian invasion of Ukraine..
Twinning with occupied Mariupol
Some Russian cities are twinned with ones in occupied Ukraine, in particular, Saint Petersburg is twinned with Mariupol. An art symbol of the twinning was unveiled on Palace Square in Saint Petersburg, defaced and removed./ref>
See also
* Fences in Saint Petersburg * Hotels in Saint Petersburg * List of buildings and structures in Saint Petersburg * List of museums in Saint Petersburg * List of people from Saint Petersburg, List of notable people from Saint Petersburg * List of Saint Petersburg Metro stations * List of sister cities to Saint Petersburg, List of Saint Petersburg sister cities * List of theatres in Saint Petersburg * Outline of Saint Petersburg * Timeline of Saint PetersburgNotes
References
Citations
Sources
* Amery, Colin, Brian Curran & Yuri Molodkovets. ''St. Petersburg''. London: Frances Lincoln, 2006. . * Bater, James H. ''St. Petersburg: Industrialization and Change''. Montreal: McGuill-Queen's University Press, 1976. . * Berelowitch, Wladimir & Olga Medvedkova. ''Histoire de Saint-Pétersbourg''. Paris: Fayard, 1996. . * Brumfield, William Craft. ''The Origins of Modernism in Russian Architecture''. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1991. . * Buckler, Julie. ''Mapping St. Petersburg: Imperial Text and Cityshape''. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2005 . * Clark, Katerina, ''Petersburg, Crucible of Revolution''. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1995. * Cross, Anthony (ed.). ''St. Petersburg, 1703–1825''. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan, 2003. . * "San Pietroburgo, la capitale del nord" by Giuseppe D'Amato in ''Viaggio nell'Hansa baltica.'' L'Unione europea e l'allargamento ad Est. Greco&Greco editori, Milano, 2004. pp. 27–46. .Travel to the Baltic Hansa
. The European Union and its enlargement to the East) Book in Italian. * George, Arthur L. & Elena George. ''St. Petersburg: Russia's Window to the Future, The First Three Centuries''. Lanham: Taylor Trade Publishing, 2003. . * Glantz, David M. ''The Battle for Leningrad, 1941–1944''. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 2002. . * Hellberg-Hirn, Elena. ''Imperial Imprints: Post-Soviet St. Petersburg''. Helsinki: SKS Finnish literature Society, 2003. . * * Duncan Fallowell, ''One Hot Summer in St Petersburg'' (London, Jonathan Cape,1995) * ''Knopf Guide: Sat. Petersburg''. New York: Knopf, 1995. . * Eyewitness Guide: St. Petersburg. * Lincoln, W. Bruce. ''Sunlight at Midnight: St. Petersburg and the Rise of Modern Russia''. New York: Basic Books, 2000. . * Orttung, Robert W. ''From Leningrad to St. Petersburg: Democratization in a Russian City''. New York: St. Martin's, 1995. . * * Ruble, Blair A. ''Leningrad: Shaping a Soviet City''. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1990. . * Shvidkovsky, Dmitry O. & Alexander Orloff. ''St. Petersburg: Architecture of the Tsars''. New York: Abbeville Press, 1996. . * Volkov, Solomon. ''St. Petersburg: A Cultural History''. New York: Free Press, 1995. . * St. Petersburg:Architecture of the Tsars. 360 pages. Abbeville Press, 1996. * Saint Petersburg: Museums, Palaces, and Historic Collections: A Guide to the Lesser Known Treasures of St. Petersburg. 2003. . * . * *
External links
City Tourist Portal
* by FIFA *
St-Petersburg, Virtual Tour • 360° Aerial Panorama
* 50 photographs of St. Petersburg from "Travel literature, Travelogues" of Burton Holmes (Vol. 8, 1914) and other sources * * 3500 entries, 9200 personalities, 3500 addresses, 2000 pictures and 40 geographical maps, 3800 bibliographical references from the original "Encyclopaedia of Saint Petersburg" (SPb., Rosspen, 2004) *
Байков В.Д. Ленинградские хроники: от послевоенных 50-х до "лихих 90-х". М. Карамзин, 2017. – 486 с., илл. – in English: Leningrad Chronicles: from the postwar fifties to the "wild nineties"
site {{Authority control Saint Petersburg, 1703 establishments in Russia 1703 establishments in Europe Federal cities of Russia Former national capitals Planned capitals Populated coastal places in Russia Populated places established in 1703 Port cities and towns in Russia Port cities and towns of the Baltic Sea Sankt-Peterburgsky Uyezd World Heritage Sites in Russia