Squid Jiggin' Ground on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
True squid are
File:Rhomboteuthis lehmani (cropped).jpg, Fossil ''
 Squid are soft-bodied molluscs whose forms evolved to adopt an active predatory lifestyle. The head and foot of the squid are at one end of a long body, and this end is functionally
Squid are soft-bodied molluscs whose forms evolved to adopt an active predatory lifestyle. The head and foot of the squid are at one end of a long body, and this end is functionally
File:Chromatophores.jpg, upright=1.25, Controllable chromatophores of different colours in the skin of a squid allow it to change its coloration and patterns rapidly, whether for camouflage or signalling.
File:Squid Counterillumination.png, Principle of counter-illumination camouflage of the firefly squid, ''
 Squid distract attacking predators by ejecting a cloud of ink, giving themselves an opportunity to escape. The ink gland and its associated ink sac empties into the rectum close to the anus, allowing the squid to rapidly discharge black ink into the mantle cavity and surrounding water. The ink is a suspension of melanin particles and quickly disperses to form a dark cloud that obscures the escape manoeuvres of the squid. Predatory fish may also be deterred by the alkaloid nature of the discharge which may interfere with their chemoreceptors.
Squid distract attacking predators by ejecting a cloud of ink, giving themselves an opportunity to escape. The ink gland and its associated ink sac empties into the rectum close to the anus, allowing the squid to rapidly discharge black ink into the mantle cavity and surrounding water. The ink is a suspension of melanin particles and quickly disperses to form a dark cloud that obscures the escape manoeuvres of the squid. Predatory fish may also be deterred by the alkaloid nature of the discharge which may interfere with their chemoreceptors.
 The sexes are separate in squid, there being a single
The sexes are separate in squid, there being a single  The female has a large translucent
The female has a large translucent
 Like all cephalopods, squids are predators and have complex digestive systems. The mouth is equipped with a sharp, horny beak mainly made of chitin and cross-linked proteins, which is used to kill and tear prey into manageable pieces. The beak is very robust, but does not contain minerals, unlike the teeth and jaws of many other organisms; the cross-linked proteins are histidine- and glycine-rich and give the beak a stiffness and hardness greater than most equivalent synthetic organic materials. The stomachs of captured whales often have indigestible squid beaks inside. The mouth contains the
Like all cephalopods, squids are predators and have complex digestive systems. The mouth is equipped with a sharp, horny beak mainly made of chitin and cross-linked proteins, which is used to kill and tear prey into manageable pieces. The beak is very robust, but does not contain minerals, unlike the teeth and jaws of many other organisms; the cross-linked proteins are histidine- and glycine-rich and give the beak a stiffness and hardness greater than most equivalent synthetic organic materials. The stomachs of captured whales often have indigestible squid beaks inside. The mouth contains the
 Unlike nautiloids which have gas-filled chambers inside their shells which provide buoyancy, and octopuses which live near and rest on the seabed and do not require to be buoyant, many squid have a fluid-filled receptacle, equivalent to the
Unlike nautiloids which have gas-filled chambers inside their shells which provide buoyancy, and octopuses which live near and rest on the seabed and do not require to be buoyant, many squid have a fluid-filled receptacle, equivalent to the
 The majority of squid are no more than long, although the giant squid may reach . The smallest species are probably the benthic pygmy squids '' Idiosepius'', which grow to a mantle length of , and have short bodies and stubby arms.
In 1978, sharp, curved claws on the suction cups of squid tentacles cut up the rubber coating on the hull of the USS ''Stein''. The size suggested the largest squid known at the time.
In 2003, a large specimen of an abundant but poorly understood species, ''Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni'' (the colossal squid), was discovered. This species may grow to in length, making it the largest invertebrate. In February 2007, a New Zealand fishing vessel caught the largest squid ever documented, weighing and measuring around off the coast of Antarctica. Dissection showed that the eyes, used to detect prey in the deep Southern Ocean, exceeded the size of footballs; these may be among the largest eyes ever to exist in the animal kingdom.
The majority of squid are no more than long, although the giant squid may reach . The smallest species are probably the benthic pygmy squids '' Idiosepius'', which grow to a mantle length of , and have short bodies and stubby arms.
In 1978, sharp, curved claws on the suction cups of squid tentacles cut up the rubber coating on the hull of the USS ''Stein''. The size suggested the largest squid known at the time.
In 2003, a large specimen of an abundant but poorly understood species, ''Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni'' (the colossal squid), was discovered. This species may grow to in length, making it the largest invertebrate. In February 2007, a New Zealand fishing vessel caught the largest squid ever documented, weighing and measuring around off the coast of Antarctica. Dissection showed that the eyes, used to detect prey in the deep Southern Ocean, exceeded the size of footballs; these may be among the largest eyes ever to exist in the animal kingdom.
 In a well-studied bioluminescent species, the Hawaiian bobtail squid, a special light organ in the squid's mantle is rapidly colonized with '' Aliivibrio fischeri'' bacteria within hours of hatching. This light-organ colonization requires this particular bacterial species for a symbiotic relationship; no colonization occurs in the absence of ''A. fischeri''. Colonization occurs in a horizontal manner, such that the hosts acquires its bacterial partners from the environment. The symbiosis is
In a well-studied bioluminescent species, the Hawaiian bobtail squid, a special light organ in the squid's mantle is rapidly colonized with '' Aliivibrio fischeri'' bacteria within hours of hatching. This light-organ colonization requires this particular bacterial species for a symbiotic relationship; no colonization occurs in the absence of ''A. fischeri''. Colonization occurs in a horizontal manner, such that the hosts acquires its bacterial partners from the environment. The symbiosis is
 Squid can move about in several different ways. Slow movement is achieved by a gentle undulation of the muscular lateral fins on either side of the trunk which drives the animal forward. A more common means of locomotion providing sustained movement is achieved using jetting, during which contraction of the muscular wall of the mantle cavity provides jet propulsion.
Slow jetting is used for ordinary locomotion, and ventilation of the gills is achieved at the same time. The circular muscles in the mantle wall contract; this causes the inhalant valve to close, the exhalant valve to open and the mantle edge to lock tightly around the head. Water is forced out through the funnel which is pointed in the opposite direction to the required direction of travel. The inhalant phase is initiated by the relaxation of the circular muscles causes them to stretch, the connective tissue in the mantle wall recoils elastically, the mantle cavity expands causing the inhalant valve to open, the exhalant valve to close and water to flow into the cavity. This cycle of exhalation and inhalation is repeated to provide continuous locomotion.
Fast jetting is an escape response. In this form of locomotion, radial muscles in the mantle wall are involved as well as circular ones, making it possible to hyper-inflate the mantle cavity with a larger volume of water than during slow jetting. On contraction, water flows out with great force, the funnel always being pointed anteriorly, and travel is backwards. During this means of locomotion, some squid exit the water in a similar way to flying fish, gliding through the air for up to , and occasionally ending up on the decks of ships.
Squid can move about in several different ways. Slow movement is achieved by a gentle undulation of the muscular lateral fins on either side of the trunk which drives the animal forward. A more common means of locomotion providing sustained movement is achieved using jetting, during which contraction of the muscular wall of the mantle cavity provides jet propulsion.
Slow jetting is used for ordinary locomotion, and ventilation of the gills is achieved at the same time. The circular muscles in the mantle wall contract; this causes the inhalant valve to close, the exhalant valve to open and the mantle edge to lock tightly around the head. Water is forced out through the funnel which is pointed in the opposite direction to the required direction of travel. The inhalant phase is initiated by the relaxation of the circular muscles causes them to stretch, the connective tissue in the mantle wall recoils elastically, the mantle cavity expands causing the inhalant valve to open, the exhalant valve to close and water to flow into the cavity. This cycle of exhalation and inhalation is repeated to provide continuous locomotion.
Fast jetting is an escape response. In this form of locomotion, radial muscles in the mantle wall are involved as well as circular ones, making it possible to hyper-inflate the mantle cavity with a larger volume of water than during slow jetting. On contraction, water flows out with great force, the funnel always being pointed anteriorly, and travel is backwards. During this means of locomotion, some squid exit the water in a similar way to flying fish, gliding through the air for up to , and occasionally ending up on the decks of ships.
 Although squid can catch large prey, the mouth is relatively small, and the food must be cut into pieces by the chitinous beak with its powerful muscles before being swallowed. The radula is located in the buccal cavity and has multiple rows of tiny teeth that draw the food backwards and grind it in pieces. The deep sea squid '' Mastigoteuthis'' has the whole length of its whip-like tentacles covered with tiny suckers; it probably catches small organisms in the same way that
Although squid can catch large prey, the mouth is relatively small, and the food must be cut into pieces by the chitinous beak with its powerful muscles before being swallowed. The radula is located in the buccal cavity and has multiple rows of tiny teeth that draw the food backwards and grind it in pieces. The deep sea squid '' Mastigoteuthis'' has the whole length of its whip-like tentacles covered with tiny suckers; it probably catches small organisms in the same way that
 Courtship in squid takes place in the open water and involves the male selecting a female, the female responding, and the transfer by the male of spermatophores to the female. In many instances, the male may display to identify himself to the female and drive off any potential competitors. Elaborate changes in body patterning take place in some species in both agonistic and courtship behaviour. The Caribbean reef squid (''Sepioteuthis sepioidea''), for example, employs a complex array of colour changes during courtship and social interactions and has a range of about 16 body patterns in its repertoire.
The pair adopt a head-to-head position, and "jaw locking" may take place, in a similar manner to that adopted by some
Courtship in squid takes place in the open water and involves the male selecting a female, the female responding, and the transfer by the male of spermatophores to the female. In many instances, the male may display to identify himself to the female and drive off any potential competitors. Elaborate changes in body patterning take place in some species in both agonistic and courtship behaviour. The Caribbean reef squid (''Sepioteuthis sepioidea''), for example, employs a complex array of colour changes during courtship and social interactions and has a range of about 16 body patterns in its repertoire.
The pair adopt a head-to-head position, and "jaw locking" may take place, in a similar manner to that adopted by some  The sperm may be used immediately or may be stored. As the eggs pass down the oviduct, they are wrapped in a gelatinous coating, before continuing to the mantle cavity, where they are fertilised. In '' Loligo'', further coatings are added by the nidimental glands in the walls of the cavity and the eggs leave through a funnel formed by the arms. The female attaches them to the substrate in strings or groups, the coating layers swelling and hardening after contact with sea water. ''Loligo'' sometimes forms breeding aggregations which may create a "community pile" of egg strings. Some pelagic and deep sea squid do not attach their egg masses, which float freely.
The sperm may be used immediately or may be stored. As the eggs pass down the oviduct, they are wrapped in a gelatinous coating, before continuing to the mantle cavity, where they are fertilised. In '' Loligo'', further coatings are added by the nidimental glands in the walls of the cavity and the eggs leave through a funnel formed by the arms. The female attaches them to the substrate in strings or groups, the coating layers swelling and hardening after contact with sea water. ''Loligo'' sometimes forms breeding aggregations which may create a "community pile" of egg strings. Some pelagic and deep sea squid do not attach their egg masses, which float freely.
 Squid form a major food resource and are used in cuisines around the world, notably in Japan where it is eaten as ika sōmen, sliced into vermicelli-like strips; as sashimi; and as tempura. Three species of ''Loligo'' are used in large quantities, '' L. vulgaris'' in the Mediterranean (known as ''Calamar'' in Spanish, ''Calamaro'' in Italian); '' L. forbesii'' in the Northeast Atlantic; and '' L. pealei'' on the American East Coast. Among the Ommastrephidae, '' Todarodes pacificus'' is the main commercial species, harvested in large quantities across the North Pacific in Canada, Japan and China.
In English-speaking countries, squid as food is often called '' calamari'', adopted from Italian into English in the 17th century. Squid are found abundantly in certain areas, and provide large catches for
Squid form a major food resource and are used in cuisines around the world, notably in Japan where it is eaten as ika sōmen, sliced into vermicelli-like strips; as sashimi; and as tempura. Three species of ''Loligo'' are used in large quantities, '' L. vulgaris'' in the Mediterranean (known as ''Calamar'' in Spanish, ''Calamaro'' in Italian); '' L. forbesii'' in the Northeast Atlantic; and '' L. pealei'' on the American East Coast. Among the Ommastrephidae, '' Todarodes pacificus'' is the main commercial species, harvested in large quantities across the North Pacific in Canada, Japan and China.
In English-speaking countries, squid as food is often called '' calamari'', adopted from Italian into English in the 17th century. Squid are found abundantly in certain areas, and provide large catches for
 Prototype chromatophores that mimic the squid's adaptive camouflage have been made by
Prototype chromatophores that mimic the squid's adaptive camouflage have been made by
CephBase: Teuthida
Colossal Squid at the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa
Market squid mating, laying eggs (video)
Scientific American – Giant Squid
The Cephalopod Page
The Octopus News Magazine Online
{{Authority control Commercial molluscs Cenozoic cephalopods Cretaceous cephalopods Extant Devonian first appearances Mollusc common names
mollusc
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is esti ...
s with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms
Arms or ARMS may refer to:
*Arm or arms, the upper limbs of the body
Arm, Arms, or ARMS may also refer to:
People
* Ida A. T. Arms (1856–1931), American missionary-educator, temperance leader
Coat of arms or weapons
*Armaments or weapons
**Fi ...
, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, an ...
, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, take the face of a human being which has a pla ...
, and a mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttle ...
es, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
.
Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar role to teleost fish as open water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swallowing. Squid are rapid swimmers, moving by jet propulsion, and largely locate their prey by sight. They are among the most intelligent of invertebrates, with groups of Humboldt squid having been observed hunting cooperatively. They are preyed on by sharks, other fish, sea birds, seals and cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel them ...
ns, particularly sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the sperm whale famil ...
s.
Squid can change colour for camouflage and signalling. Some species are bioluminescent
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some Fungus, fungi, microorganisms including ...
, using their light for counter-illumination camouflage, while many species can eject a cloud of ink to distract predators.
Squid are used for human consumption with commercial fisheries in Japan, the Mediterranean, the southwestern Atlantic, the eastern Pacific and elsewhere. They are used in cuisines around the world, often known as " calamari". Squid have featured in literature since classical times, especially in tales of giant squid and sea monsters.
Taxonomy and phylogeny
Squid are members of the classCephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...
a, subclass Coleoidea. The squid orders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
Myopsida and Oegopsida
Oegopsida is one of the two orders of squid in the superorder Decapodiformes, in the class Cephalopoda. Together with the Myopsina, it was formerly considered to be a suborder of the order Teuthida, in which case it was known as Oegopsina. This ...
are in the superorder Decapodiformes (from the Greek for "ten-legged"). Two other orders of decapodiform cephalopods are also called squid, although they are taxonomically
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are gi ...
distinct from squids and differ recognizably in their gross anatomical features. They are the bobtail squid of order Sepiolida and the ram's horn squid
''Spirula spirula'' is a species of deep-water squid-like cephalopod mollusc, mollusk. It is the only extant taxon, extant member of the genus ''Spirula'', the Family (biology), family Spirulidae, and the order (biology), order Spirulida. Because ...
of the monotypic order Spirulida. The vampire squid ('' Vampyroteuthis infernalis''), however, is more closely related to the octopus than to any squid.
The cladogram, not fully resolved, is based on Sanchez et al., 2018. Their molecular phylogeny used mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
l and nuclear DNA marker sequences; they comment that a robust phylogeny "has proven very challenging to obtain". If it is accepted that Sepiidae
Sepiidae is a family of cephalopods in the order Sepiida.
Classification
*Order Sepiida: cuttlefish
**Family Sepiadariidae
**Family Sepiidae
***Genus '' Metasepia''
****'' Metasepia pfefferi'', flamboyant cuttlefish
****''Metasepia tullbergi ...
cuttlefish are a kind of squid, then the squids, excluding the vampire squid, form a clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
as illustrated. Orders are shown in boldface; all the families not included in those orders are in the paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
order "Oegopsida", except Sepiadariidae and Sepiidae that are in the paraphyletic order "Sepiida",
Evolution
Crown coleoids (the common ancestor of octopuses and squid) diverged in the late Paleozoic (Mississippian
Mississippian may refer to:
* Mississippian (geology), a subperiod of the Carboniferous period in the geologic timescale, roughly 360 to 325 million years ago
*Mississippian culture, a culture of Native American mound-builders from 900 to 1500 AD ...
), according to fossils of ''Syllipsimopodi
''Syllipsimopodi'' is an extinct member of the cephalopod subclass Coleoidea belonging to the clade Vampyropoda, which includes octopuses (Octopoda) and vampire squids (Vampyromorphida). The type and only known species is ''Syllipsimopodi bid ...
'', an early relative of vampire squids and octopuses. True squid diverged during the Jurassic, but many squid families appeared in or after the Cretaceous. Both the coleoids and the teleost fish were involved in much adaptive radiation at this time, and the two modern groups resemble each other in size, ecology, habitat, morphology and behaviour, however some fish moved into fresh water while the coleoids remained in marine environments.
The ancestral coleoid was probably nautiloid-like with a strait septate shell that became immersed in the mantle and was used for buoyancy control. Four lines diverged from this, Spirulida (with one living member), the cuttlefish
Cuttlefish or cuttles are marine molluscs of the order Sepiida. They belong to the class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of ...
es, the squids and the octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttle ...
es. Squid have differentiated from the ancestral mollusc
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is esti ...
such that the body plan has been condensed antero-posteriorly and extended dorso-ventrally. What may have been the foot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made ...
of the ancestor is modified into a complex set of appendages around the mouth. The sense organs are highly developed and include advanced eyes similar to those of vertebrates.
The ancestral shell has been lost, with only an internal gladius, or pen, remaining. The pen, made of a chitin-like material, is a feather-shaped internal structure that supports the squid's mantle and serves as a site for muscle attachment. The cuttlebone or sepion of the Sepiidae is calcareous and appears to have evolved afresh in the Tertiary.
Rhomboteuthis
''Rhomboteuthis'' is an extinct species of squid, with '' Rhomboteuthis lehmani'' currently being the only described member of the genus. ''Rhomboteuthis'' is known from during the Mid-Jurassic of Voulte-sur-Rhône, Ardèche, France
...
'' from the Lower Callovian (, middle Jurassic) of La Voulte-sur-Rhône, France
File:Plesioteuthis prisca 01.jpg, Fossil '' Plesioteuthis'' from the Tithonian
In the geological timescale, the Tithonian is the latest age of the Late Jurassic Epoch and the uppermost stage of the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 152.1 ± 4 Ma and 145.0 ± 4 Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the K ...
(, upper Jurassic), Solnhofen
Solnhofen is a municipality in the district of Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen in the region of Middle Franconia in the ' of Bavaria in Germany. It is in the Altmühl valley.
The local area is famous in geology and palaeontology for Solnhofen limesto ...
, Germany
Description
 Squid are soft-bodied molluscs whose forms evolved to adopt an active predatory lifestyle. The head and foot of the squid are at one end of a long body, and this end is functionally
Squid are soft-bodied molluscs whose forms evolved to adopt an active predatory lifestyle. The head and foot of the squid are at one end of a long body, and this end is functionally anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
, leading the animal as it moves through the water. A set of eight arms and two distinctive tentacles surround the mouth; each appendage takes the form of a muscular hydrostat and is flexible and prehensile, usually bearing disc-like suckers.
The suckers may lie directly on the arm or be stalked. Their rims are stiffened with chitin and may contain minute toothlike denticles. These features, as well as strong musculature, and a small ganglion beneath each sucker to allow individual control, provide a very powerful adhesion to grip prey. Hooks are present on the arms and tentacles in some species, but their function is unclear. The two tentacles are much longer than the arms and are retractile. Suckers are limited to the spatulate tip of the tentacle, known as the manus
Manus may refer to:
* Manus (anatomy), the zoological term for the distal portion of the forelimb of an animal (including the human hand)
* ''Manus'' marriage, a type of marriage during Roman times
Relating to locations around New Guinea
* Man ...
.
In the mature male, the outer half of one of the left arms is hectocotylised
A hectocotylus (plural: ''hectocotyli'') is one of the arms of male cephalopods that is specialized to store and transfer spermatophores to the female. Structurally, hectocotyli are muscular hydrostats. Depending on the species, the male may use i ...
– and ends in a copulatory pad rather than suckers. This is used for depositing a spermatophore inside the mantle cavity of a female. A ventral part of the foot has been converted into a funnel through which water exits the mantle cavity.
The main body mass is enclosed in the mantle, which has a swimming fin along each side. These fins are not the main source of locomotion in most species. The mantle wall is heavily muscled and internal. The visceral mass, which is covered by a thin, membranous epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
, forms a cone-shaped posterior region known as the "visceral hump". The mollusc shell is reduced to an internal, longitudinal chitinous "pen" in the functionally dorsal part of the animal; the pen acts to stiffen the squid and provides attachments for muscles.
On the functionally ventral part of the body is an opening to the mantle cavity, which contains the gills (ctenidia) and openings from the excretory, digestive and reproductive systems. An inhalant siphon behind the funnel draws water into the mantle cavity via a valve. The squid uses the funnel for locomotion via precise jet propulsion. In this form of locomotion, water is sucked into the mantle cavity and expelled out of the funnel in a fast, strong jet. The direction of travel is varied by the orientation of the funnel. Squid are strong swimmers and certain species can "fly" for short distances out of the water.
Camouflage
Squid make use of different kinds of camouflage, namely active camouflage for background matching (in shallow water) and counter-illumination. This helps to protect them from their predators and allows them to approach their prey. The skin is covered in controllable chromatophores of different colours, enabling the squid to match its coloration to its surroundings. The play of colours may in addition distract prey from the squid's approaching tentacles. The skin also contains light reflectors callediridophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, ...
s and leucophores that, when activated, in millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds.
A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called ...
s create changeable skin patterns of polarized light. Such skin camouflage may serve various functions, such as communication with nearby squid, prey detection, navigation, and orientation during hunting or seeking shelter. Neural control of the iridophores enabling rapid changes in skin iridescence
Iridescence (also known as goniochromism) is the phenomenon of certain surfaces that appear to gradually change color as the angle of view or the angle of illumination changes. Examples of iridescence include soap bubbles, feathers, butterfl ...
appears to be regulated by a cholinergic process affecting reflectin proteins.
Some mesopelagic squid such as the firefly squid (''Watasenia scintillans'') and the midwater squid
''Abralia veranyi'' is a species of squid in the family Enoploteuthidae. Common names include the eye-flash squid, Verany's enope squid and the midwater squid. It is found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It undergoes a daily ver ...
(''Abralia veranyi'') use counter-illumination camouflage, generating light to match the downwelling light from the ocean surface. This creates the effect of countershading, making the underside lighter than the upperside.
Counter-illumination is also used by the Hawaiian bobtail squid
__NOTOC__
''Euprymna scolopes'', also known as the Hawaiian bobtail squid, is a species of bobtail squid in the family Sepiolidae native to the central Pacific Ocean, where it occurs in shallow coastal waters off the Hawaiian Islands and Midway Is ...
(''Euprymna scolopes''), which has symbiotic bacteria Symbiotic bacteria are bacteria living in symbiosis with another organism or each other. For example, rhizobia living in root nodules of legumes provide nitrogen fixing activity for these plants. Symbiosis was first defined by Marko de Bary in 186 ...
(''Aliivibrio fischeri'') that produce light to help the squid avoid nocturnal predators. This light shines through the squid's skin on its underside and is generated by a large and complex two-lobed light organ inside the squid's mantle cavity. From there, it escapes downwards, some of it travelling directly, some coming off a reflector at the top of the organ (dorsal side). Below there is a kind of iris, which has branches (diverticula) of its ink sac
An ink sac is an anatomical feature that is found in many cephalopod mollusks used to produce the defensive cephalopod ink. With the exception of nocturnal and very deep water cephalopods, all Coleoidea (squid, octopus and cuttlefish) which dwell ...
, with a lens below that; both the reflector and lens are derived from mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical E ...
. The squid controls light production by changing the shape of its iris or adjusting the strength of yellow filters on its underside, which presumably change the balance of wavelengths emitted. Light production shows a correlation with intensity of down-welling light, but it is about one third as bright; the squid can track repeated changes in brightness. Because the Hawaiian bobtail squid hides in sand during the day to avoid predators, it does not use counter-illumination during daylight hours.
Watasenia scintillans
The firefly squid (''Watasenia scintillans''), also commonly known as the sparkling enope squid or hotaru-ika in Japan, is a species of squid in the family Enoploteuthidae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus ''Watasenia''. These tiny ...
''. When seen from below by a predator, the animal's light helps to match its brightness and colour to the sea surface above.
Predator distraction with ink
 Squid distract attacking predators by ejecting a cloud of ink, giving themselves an opportunity to escape. The ink gland and its associated ink sac empties into the rectum close to the anus, allowing the squid to rapidly discharge black ink into the mantle cavity and surrounding water. The ink is a suspension of melanin particles and quickly disperses to form a dark cloud that obscures the escape manoeuvres of the squid. Predatory fish may also be deterred by the alkaloid nature of the discharge which may interfere with their chemoreceptors.
Squid distract attacking predators by ejecting a cloud of ink, giving themselves an opportunity to escape. The ink gland and its associated ink sac empties into the rectum close to the anus, allowing the squid to rapidly discharge black ink into the mantle cavity and surrounding water. The ink is a suspension of melanin particles and quickly disperses to form a dark cloud that obscures the escape manoeuvres of the squid. Predatory fish may also be deterred by the alkaloid nature of the discharge which may interfere with their chemoreceptors.
Nervous system and sense organs
Cephalopods have the most highly developed nervous systems among invertebrates. Squids have a complex brain in the form of a nerve ring encircling the oesophagus, enclosed in a cartilaginouscranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
. Paired cerebral ganglia
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system there are both sympatheti ...
above the oesophagus receive sensory information from the eyes and statocysts, and further ganglia below control the muscles of the mouth, foot, mantle and viscera. Giant axons up to in diameter convey nerve messages with great rapidity to the circular muscles of the mantle wall, allowing a synchronous, powerful contraction and maximum speed in the jet propulsion system.
The paired eyes, on either side of the head, are housed in capsules fused to the cranium. Their structure is very similar to that of a fish eye, with a globular lens that has a depth of focus from to infinity. The image is focused by changing the position of the lens, as in a camera or telescope, rather than changing the shape of the lens, as in the human eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm.
...
. Squid adjust to changes in light intensity by expanding and contracting the slit-shaped pupil. Deep sea squids in the family Histioteuthidae
Histioteuthidae is a family of Oegopsid squid. The family was previously considered to be monotypic but the World Register of Marine Species assigns two genera to this family.
The species classified under Histioteuthidae are mostly weakly mu ...
have eyes of two different types and orientation. The large left eye is tubular in shape and looks upwards, presumably searching for the silhouettes of animals higher in the water column. The normally-shaped right eye points forwards and downwards to detect prey.
The statocysts are involved in maintaining balance and are analogous to the inner ear of fish. They are housed in cartilaginous capsules on either side of the cranium. They provide the squid with information on its body position in relation to gravity, its orientation, acceleration and rotation, and are able to perceive incoming vibrations. Without the statocysts, the squid cannot maintain equilibrium. Squid appear to have limited hearing, but the head and arms bear lines of hair-cells that are weakly sensitive to water movements and changes in pressure, and are analogous in function to the lateral line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial ...
system of fish.
Reproductive system
 The sexes are separate in squid, there being a single
The sexes are separate in squid, there being a single gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sper ...
in the posterior part of the body with fertilisation being external, and usually taking place in the mantle cavity of the female. The male has a testis from which sperm pass into a single gonoduct where they are rolled together into a long bundle, or spermatophore. The gonoduct is elongated into a "penis" that extends into the mantle cavity and through which spermatophores are ejected. In shallow water species, the penis is short, and the spermatophore is removed from the mantle cavity by a tentacle of the male, which is specially adapted for the purpose and known as a hectocotylus, and placed inside the mantle cavity of the female during mating.
 The female has a large translucent
The female has a large translucent ovary
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. ...
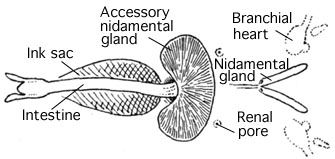
, situated towards the posterior of the visceral mass. From here, eggs travel along the gonocoel, where there are a pair of white nidamental gland
Nidamental glands are internal organs found in some elasmobranchs and certain molluscs, including cephalopods (specifically Decapodiformes and nautiluses) and gastropods.Young, R.E., M. Vecchione & K.M. Mangold (1999)Cephalopoda Glossary Tree of Li ...
s, which lie anterior to the gills. Also present are red-spotted accessory nidamental glands containing symbiotic
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
bacteria; both organs are associated with nutrient manufacture and forming shells for the eggs. The gonocoel enters the mantle cavity at the gonopore, and in some species, receptacles for storing spermatophores are located nearby, in the mantle wall.
In shallow-water species of the continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
and epipelagic or mesopelagic zone
The mesopelagic zone (Greek μέσον, middle), also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone, is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light, and begins ...
s, it is frequently one or both of arm pair IV of males that are modified into hectocotyli. However, most deep-sea squid lack hectocotyl arms and have longer penises; Ancistrocheiridae and Cranchiinae are exceptions. Giant squid of the genus ''Architeuthis'' are unusual in that they possess both a large penis and modified arm tips, although whether the latter are used for spermatophore transfer is uncertain. Penis elongation has been observed in the deep-water species ''Onykia ingens
''Onykia ingens'', the greater hooked squid, is a species of squid in the family Onychoteuthidae. It occurs worldwide in subantarctic oceans.
Although ''O. ingens'' was long attributed to the genus ''Moroteuthis'', several authors have recently ...
''; when erect, the penis may be as long as the mantle, head, and arms combined. As such, deep-water squid have the greatest known penis length relative to body size of all mobile animals, second in the entire animal kingdom only to certain sessile barnacle
A barnacle is a type of arthropod constituting the subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacea, and is hence related to crabs and lobsters. Barnacles are exclusively marine, and tend to live in shallow and tidal waters, typically in eros ...
s.
Digestive system
 Like all cephalopods, squids are predators and have complex digestive systems. The mouth is equipped with a sharp, horny beak mainly made of chitin and cross-linked proteins, which is used to kill and tear prey into manageable pieces. The beak is very robust, but does not contain minerals, unlike the teeth and jaws of many other organisms; the cross-linked proteins are histidine- and glycine-rich and give the beak a stiffness and hardness greater than most equivalent synthetic organic materials. The stomachs of captured whales often have indigestible squid beaks inside. The mouth contains the
Like all cephalopods, squids are predators and have complex digestive systems. The mouth is equipped with a sharp, horny beak mainly made of chitin and cross-linked proteins, which is used to kill and tear prey into manageable pieces. The beak is very robust, but does not contain minerals, unlike the teeth and jaws of many other organisms; the cross-linked proteins are histidine- and glycine-rich and give the beak a stiffness and hardness greater than most equivalent synthetic organic materials. The stomachs of captured whales often have indigestible squid beaks inside. The mouth contains the radula
The radula (, ; plural radulae or radulas) is an anatomical structure used by molluscs for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food ...
, the rough tongue common to all molluscs except bivalvia, which is equipped with multiple rows of teeth. In some species, toxic saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
helps to control large prey; when subdued, the food can be torn in pieces by the beak, moved to the oesophagus by the radula, and swallowed.
The food bolus
Bolus may refer to:
Geography
* Bolus, Iran, a village in Ardabil Province, Iran
* Bolus, or Baulus, an Anatolian village on the site of ancient Berissa
Medicine
* Bolus (digestion), a ball-shaped mass moving through the digestive tract
* Bolus ...
is moved along the gut by waves of muscular contractions ( peristalsis). The long oesophagus leads to a muscular stomach roughly in the middle of the visceral mass. The digestive gland, which is equivalent to a vertebrate liver, diverticulates here, as does the pancreas, and both of these empty into the caecum, a pouch-shaped sac where most of the absorption of nutrients takes place. Indigestible food can be passed directly from the stomach to the rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the s ...
where it joins the flow from the caecum and is voided through the anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, d ...
into the mantle cavity. Cephalopods are short-lived, and in mature squid, priority is given to reproduction; the female ''Onychoteuthis banksii
''Onychoteuthis banksii'', the common clubhook squid, is a species of squid in the family Onychoteuthidae. It is the type species of the genus ''Onychoteuthis''. This species was thought to have a worldwide distribution but with the revision of ...
'' for example, sheds its feeding tentacles on reaching maturity, and becomes flaccid and weak after spawning.
Cardiovascular and excretory systems
The squid mantle cavity is a seawater-filled sac containing three hearts and other organs supporting circulation, respiration, and excretion. Squid have a mainsystemic
Systemic fundamental to a predominant social, economic, or political practice. This refers to:
In medicine
In medicine, ''systemic'' means affecting the whole body, or at least multiple organ systems. It is in contrast with ''topical'' or ''loc ...
heart that pumps blood around the body as part of the general circulatory system, and two branchial hearts. The systemic heart consists of three chambers, a lower ventricle and two upper atria, all of which can contract to propel the blood. The branchial hearts pump blood specifically to the gills for oxygenation, before returning it to the systemic heart. The blood contains the copper-rich protein hemocyanin, which is used for oxygen transport
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the ci ...
at low ocean temperatures and low oxygen concentrations, and makes the oxygenated blood a deep, blue color. As systemic blood returns via two vena cavae to the branchial hearts, excretion of urine, carbon dioxide, and waste solutes occurs through outpockets (called nephridial appendages) in the vena cavae walls that enable gas exchange and excretion via the mantle cavity seawater.
Buoyancy
 Unlike nautiloids which have gas-filled chambers inside their shells which provide buoyancy, and octopuses which live near and rest on the seabed and do not require to be buoyant, many squid have a fluid-filled receptacle, equivalent to the
Unlike nautiloids which have gas-filled chambers inside their shells which provide buoyancy, and octopuses which live near and rest on the seabed and do not require to be buoyant, many squid have a fluid-filled receptacle, equivalent to the swim bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled Organ (anatomy), organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their curren ...
of a fish, in the coelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in most animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, it r ...
or connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
. This reservoir acts as a chemical buoyancy chamber, with the heavy metallic cations typical of seawater replaced by low molecular-weight ammonium
The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary a ...
ions, a product of excretion. The small difference in density provides a small contribution to buoyancy per unit volume, so the mechanism requires a large buoyancy chamber to be effective. Since the chamber is filled with liquid, it has the advantage over a swim bladder of not changing significantly in volume with pressure. Glass squids in the family Cranchiidae
The family Cranchiidae comprises the approximately 60 species of glass squid, also known as cockatoo squid, cranchiid, cranch squid, or bathyscaphoid squid. Cranchiid squid occur in surface and midwater depths of open oceans around the world. The ...
for example, have an enormous transparent coelom containing ammonium ions and occupying about two-thirds the volume of the animal, allowing it to float at the required depth. About half of the 28 families of squid use this mechanism to solve their buoyancy issues.
Largest and smallest
 The majority of squid are no more than long, although the giant squid may reach . The smallest species are probably the benthic pygmy squids '' Idiosepius'', which grow to a mantle length of , and have short bodies and stubby arms.
In 1978, sharp, curved claws on the suction cups of squid tentacles cut up the rubber coating on the hull of the USS ''Stein''. The size suggested the largest squid known at the time.
In 2003, a large specimen of an abundant but poorly understood species, ''Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni'' (the colossal squid), was discovered. This species may grow to in length, making it the largest invertebrate. In February 2007, a New Zealand fishing vessel caught the largest squid ever documented, weighing and measuring around off the coast of Antarctica. Dissection showed that the eyes, used to detect prey in the deep Southern Ocean, exceeded the size of footballs; these may be among the largest eyes ever to exist in the animal kingdom.
The majority of squid are no more than long, although the giant squid may reach . The smallest species are probably the benthic pygmy squids '' Idiosepius'', which grow to a mantle length of , and have short bodies and stubby arms.
In 1978, sharp, curved claws on the suction cups of squid tentacles cut up the rubber coating on the hull of the USS ''Stein''. The size suggested the largest squid known at the time.
In 2003, a large specimen of an abundant but poorly understood species, ''Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni'' (the colossal squid), was discovered. This species may grow to in length, making it the largest invertebrate. In February 2007, a New Zealand fishing vessel caught the largest squid ever documented, weighing and measuring around off the coast of Antarctica. Dissection showed that the eyes, used to detect prey in the deep Southern Ocean, exceeded the size of footballs; these may be among the largest eyes ever to exist in the animal kingdom.
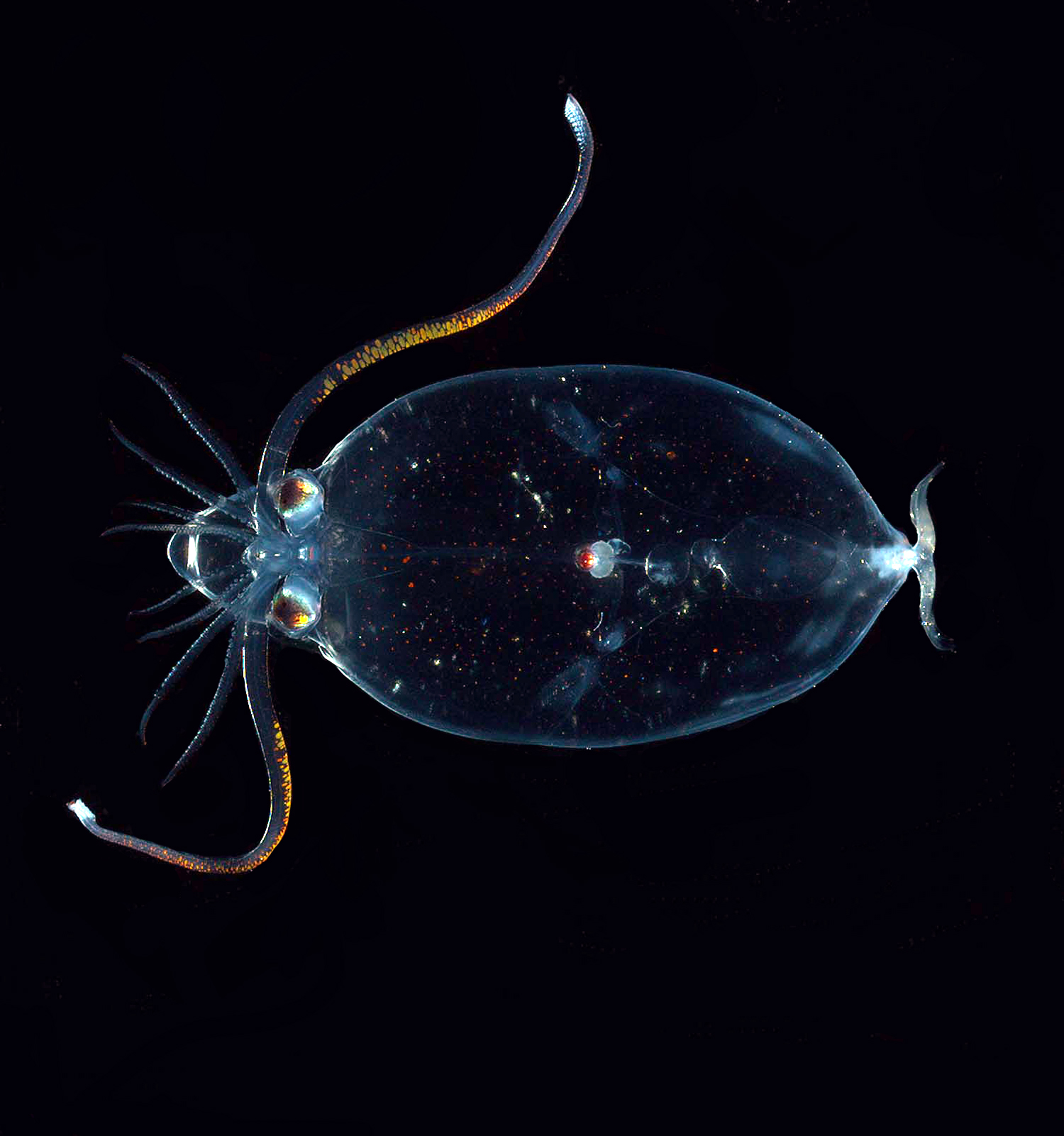
Development
The eggs of squid are large for a mollusc, containing a large amount of yolk to nourish the embryo as it develops directly, without an intervening veliger larval stage. The embryo grows as a disc of cells on top of the yolk. During thegastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. Be ...
stage, the margins of the disc grow to surround the yolk, forming a yolk sac, which eventually forms part of the animal's gut. The dorsal side of the disc grows upwards and forms the embryo, with a shell gland on its dorsal surface, gills, mantle and eyes. The arms and funnel develop as part of the foot on the ventral side of the disc. The arms later migrate upwards, coming to form a ring around the funnel and mouth. The yolk is gradually absorbed as the embryo grows. Some juvenile squid live higher in the water column than do adults. Squids tend to be short-lived; '' Loligo'' for example lives from one to three years according to species, typically dying soon after spawning.
obligate {{wiktionary, obligate
As an adjective, obligate means "by necessity" (antonym ''facultative'') and is used mainly in biology in phrases such as:
* Obligate aerobe, an organism that cannot survive without oxygen
* Obligate anaerobe, an organism that ...
for the squid, but facultative for the bacteria. Once the bacteria enter the squid, they colonize interior epithelial cells in the light organ, living in crypts with complex microvilli
Microvilli (singular: microvillus) are microscopic cellular membrane protrusions that increase the surface area for diffusion and minimize any increase in volume, and are involved in a wide variety of functions, including absorption, secretion, ...
protrusions. The bacteria also interact with hemocyte
A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), a ...
s, macrophage-like blood cells that migrate between epithelial cells, but the mechanism and function of this process is not well understood. Bioluminescence reaches its highest levels during the early evening hours and bottoms out before dawn; this occurs because at the end of each day, the contents of the squid's crypts are expelled into the surrounding environment. Approximately 95% of the bacteria are voided each morning before the bacterial population builds up again by nightfall.
Behaviour
Locomotion
 Squid can move about in several different ways. Slow movement is achieved by a gentle undulation of the muscular lateral fins on either side of the trunk which drives the animal forward. A more common means of locomotion providing sustained movement is achieved using jetting, during which contraction of the muscular wall of the mantle cavity provides jet propulsion.
Slow jetting is used for ordinary locomotion, and ventilation of the gills is achieved at the same time. The circular muscles in the mantle wall contract; this causes the inhalant valve to close, the exhalant valve to open and the mantle edge to lock tightly around the head. Water is forced out through the funnel which is pointed in the opposite direction to the required direction of travel. The inhalant phase is initiated by the relaxation of the circular muscles causes them to stretch, the connective tissue in the mantle wall recoils elastically, the mantle cavity expands causing the inhalant valve to open, the exhalant valve to close and water to flow into the cavity. This cycle of exhalation and inhalation is repeated to provide continuous locomotion.
Fast jetting is an escape response. In this form of locomotion, radial muscles in the mantle wall are involved as well as circular ones, making it possible to hyper-inflate the mantle cavity with a larger volume of water than during slow jetting. On contraction, water flows out with great force, the funnel always being pointed anteriorly, and travel is backwards. During this means of locomotion, some squid exit the water in a similar way to flying fish, gliding through the air for up to , and occasionally ending up on the decks of ships.
Squid can move about in several different ways. Slow movement is achieved by a gentle undulation of the muscular lateral fins on either side of the trunk which drives the animal forward. A more common means of locomotion providing sustained movement is achieved using jetting, during which contraction of the muscular wall of the mantle cavity provides jet propulsion.
Slow jetting is used for ordinary locomotion, and ventilation of the gills is achieved at the same time. The circular muscles in the mantle wall contract; this causes the inhalant valve to close, the exhalant valve to open and the mantle edge to lock tightly around the head. Water is forced out through the funnel which is pointed in the opposite direction to the required direction of travel. The inhalant phase is initiated by the relaxation of the circular muscles causes them to stretch, the connective tissue in the mantle wall recoils elastically, the mantle cavity expands causing the inhalant valve to open, the exhalant valve to close and water to flow into the cavity. This cycle of exhalation and inhalation is repeated to provide continuous locomotion.
Fast jetting is an escape response. In this form of locomotion, radial muscles in the mantle wall are involved as well as circular ones, making it possible to hyper-inflate the mantle cavity with a larger volume of water than during slow jetting. On contraction, water flows out with great force, the funnel always being pointed anteriorly, and travel is backwards. During this means of locomotion, some squid exit the water in a similar way to flying fish, gliding through the air for up to , and occasionally ending up on the decks of ships.
Feeding
Squid are carnivores, and, with their strong arms and suckers, can overwhelm relatively large animals efficiently. Prey is identified by sight or by touch, grabbed by the tentacles which can be shot out with great rapidity, brought back to within reach of the arms, and held by the hooks and suckers on their surface. In some species, the squid's saliva contains toxins which act to subdue the prey. These are injected into its bloodstream when the prey is bitten, along with vasodilators and chemicals to stimulate the heart, and quickly circulate to all parts of its body. The deep sea squid ''Taningia danae
''Taningia danae'', the Dana octopus squid, is a species of squid in the family Octopoteuthidae. It is one of the largest known squid species, reaching a mantle length of and total length of . The largest known specimen, a mature female, weig ...
'' has been filmed releasing blinding flashes of light from large photophores on its arms to illuminate and disorientate potential prey.
 Although squid can catch large prey, the mouth is relatively small, and the food must be cut into pieces by the chitinous beak with its powerful muscles before being swallowed. The radula is located in the buccal cavity and has multiple rows of tiny teeth that draw the food backwards and grind it in pieces. The deep sea squid '' Mastigoteuthis'' has the whole length of its whip-like tentacles covered with tiny suckers; it probably catches small organisms in the same way that
Although squid can catch large prey, the mouth is relatively small, and the food must be cut into pieces by the chitinous beak with its powerful muscles before being swallowed. The radula is located in the buccal cavity and has multiple rows of tiny teeth that draw the food backwards and grind it in pieces. The deep sea squid '' Mastigoteuthis'' has the whole length of its whip-like tentacles covered with tiny suckers; it probably catches small organisms in the same way that flypaper
Flypaper (also known as a fly ribbon, fly strip, fly capture tape, or fly catcher) is a fly-killing device made of paper coated with a sweetly fragrant, but extremely sticky and sometimes poisonous substance that traps flies and other flying inse ...
traps flies. The tentacles of some bathypelagic
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagic ...
squids bear photophores which may bring food within its reach by attracting prey.
Squid are among the most intelligent invertebrates. For example, groups of Humboldt squid hunt cooperatively, spiralling up through the water at night and coordinating their vertical and horizontal movements while foraging.
Reproduction
 Courtship in squid takes place in the open water and involves the male selecting a female, the female responding, and the transfer by the male of spermatophores to the female. In many instances, the male may display to identify himself to the female and drive off any potential competitors. Elaborate changes in body patterning take place in some species in both agonistic and courtship behaviour. The Caribbean reef squid (''Sepioteuthis sepioidea''), for example, employs a complex array of colour changes during courtship and social interactions and has a range of about 16 body patterns in its repertoire.
The pair adopt a head-to-head position, and "jaw locking" may take place, in a similar manner to that adopted by some
Courtship in squid takes place in the open water and involves the male selecting a female, the female responding, and the transfer by the male of spermatophores to the female. In many instances, the male may display to identify himself to the female and drive off any potential competitors. Elaborate changes in body patterning take place in some species in both agonistic and courtship behaviour. The Caribbean reef squid (''Sepioteuthis sepioidea''), for example, employs a complex array of colour changes during courtship and social interactions and has a range of about 16 body patterns in its repertoire.
The pair adopt a head-to-head position, and "jaw locking" may take place, in a similar manner to that adopted by some cichlid
Cichlids are fish from the family Cichlidae in the order Cichliformes. Cichlids were traditionally classed in a suborder, the Labroidei, along with the wrasses ( Labridae), in the order Perciformes, but molecular studies have contradicted this ...
fish. The heterodactylus of the male is used to transfer the spermatophore and deposit it in the female's mantle cavity in the position appropriate for the species; this may be adjacent to the gonopore or in a seminal receptacle.
 The sperm may be used immediately or may be stored. As the eggs pass down the oviduct, they are wrapped in a gelatinous coating, before continuing to the mantle cavity, where they are fertilised. In '' Loligo'', further coatings are added by the nidimental glands in the walls of the cavity and the eggs leave through a funnel formed by the arms. The female attaches them to the substrate in strings or groups, the coating layers swelling and hardening after contact with sea water. ''Loligo'' sometimes forms breeding aggregations which may create a "community pile" of egg strings. Some pelagic and deep sea squid do not attach their egg masses, which float freely.
The sperm may be used immediately or may be stored. As the eggs pass down the oviduct, they are wrapped in a gelatinous coating, before continuing to the mantle cavity, where they are fertilised. In '' Loligo'', further coatings are added by the nidimental glands in the walls of the cavity and the eggs leave through a funnel formed by the arms. The female attaches them to the substrate in strings or groups, the coating layers swelling and hardening after contact with sea water. ''Loligo'' sometimes forms breeding aggregations which may create a "community pile" of egg strings. Some pelagic and deep sea squid do not attach their egg masses, which float freely.
Ecology
Squid mostly have an annual life cycle, growing fast and dying soon after spawning. The diet changes as they grow but mostly consists of large zooplankton and small nekton. In Antarctica for example, krill is the main constituent of the diet, with other food items being amphipods, other small crustaceans, and large arrow worms. Fish are also eaten, and some squid are cannibalistic. As well as occupying a key role in the food chain, squid are an important prey for predators including sharks, sea birds, seals and whales. Juvenile squid provide part of the diet for worms and small fish. When researchers studied the contents of the stomachs of elephant seals in South Georgia, they found 96% squid by weight. In a single day, a sperm whale can eat 700 to 800 squid, and a Risso's dolphin entangled in a net in the Mediterranean was found to have eatenangel clubhook squid
''Ancistroteuthis lichtensteinii'', also known as the angel clubhook squid or simply angel squid, is a species of squid in the family Onychoteuthidae and the sole member of the genus ''Ancistroteuthis''. It grows to a mantle length of 30 cm. ...
, umbrella squid, reverse jewel squid and European flying squid
The European flying squid (''Todarodes sagittatus'') is a species of squid from the continental slope and oceanic waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It is the type species of the genus ''Todarodes'', the type genus o ...
, all identifiable from their indigestible beaks. ''Ornithoteuthis volatilis
''Ornithoteuthis volatilis'', the shiny bird squid, is a squid from the subfamily Ommastrephinae, the flying squids, of the family Ommastrephidae part of the pelagic squid order Oegopsida. It is a tropical and sub-tropical species which is wide ...
'', a common squid from the tropical Indo-Pacific, is predated by yellowfin tuna, longnose lancetfish
''Alepisaurus ferox'', the long snouted lancetfish, longnose lancetfish, or cannibal fish, is a species of lancetfish found in the ocean depths down to 1,830 m (6,000 ft). This species grows to in total length and a weight of .
It is ...
, common dolphinfish
The mahi-mahi () or common dolphinfish (''Coryphaena hippurus'') is a surface-dwelling ray-finned fish found in off-shore temperate, tropical, and subtropical waters worldwide. Also widely called dorado (not to be confused with '' Salminus br ...
and swordfish
Swordfish (''Xiphias gladius''), also known as broadbills in some countries, are large, highly migratory predatory fish characterized by a long, flat, pointed bill. They are a popular sport fish of the billfish category, though elusive. Swordfis ...
, the tiger shark, the scalloped hammerhead shark and the smooth hammerhead shark. Sperm whales also hunt this species extensively as does the brown fur seal. In the Southern Ocean, penguin
Penguins (order (biology), order List of Sphenisciformes by population, Sphenisciformes , family (biology), family Spheniscidae ) are a group of Water bird, aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: on ...
s and wandering albatrosses are major predators of ''Gonatus antarcticus
''Gonatus antarcticus'' is a squid in the family Gonatidae. The species is known with certainty only from southern Atlantic waters but it may have a circum- Antarctic distribution.Xavier, J.C. & Rodhouse, P.G. & Trathan, P.N. & Wood, A.G. 1999. ...
''.
Human uses

In literature and art
Giant squid have featured as monsters of the deep since classical times. Giant squid were described by Aristotle (4th century BC) in his '' History of Animals'' and Pliny the Elder (1st century AD) in his '' Natural History''. The Gorgon of Greek mythology may have been inspired by squid or octopus, the animal itself representing the severed head of Medusa, the beak as the protruding tongue and fangs, and its tentacles as the snakes. The six-headed sea monster of the '' Odyssey'',Scylla
In Greek mythology, Scylla), is obsolete. ( ; grc-gre, Σκύλλα, Skúlla, ) is a legendary monster who lives on one side of a narrow channel of water, opposite her counterpart Charybdis. The two sides of the strait are within an arrow's r ...
, may have had a similar origin. The Nordic legend of the kraken may also have derived from sightings of large cephalopods.
In literature, H. G. Wells' short story "The Sea Raiders
"The Sea Raiders" is a short story by H. G. Wells, first published in 1896 in ''The Weekly Sun Literary Supplement''. It was included in ''The Plattner Story and Others'', a collection of short stories by Wells published by Methuen & Co. in 1897. ...
" featured a man-eating squid species ''Haploteuthis ferox''. The science fiction writer Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne (;''Longman Pronunciation Dictionary''. ; 8 February 1828 – 24 March 1905) was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the ''Voyages extraor ...
told a tale of a kraken
The kraken () is a legendary sea monster of enormous size said to appear off the coasts of Norway.
Kraken, the subject of sailors' superstitions and mythos, was first described in the modern age at the turn of the 18th century, in a travelogu ...
-like monster in his 1870 novel '' Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea''.
As food
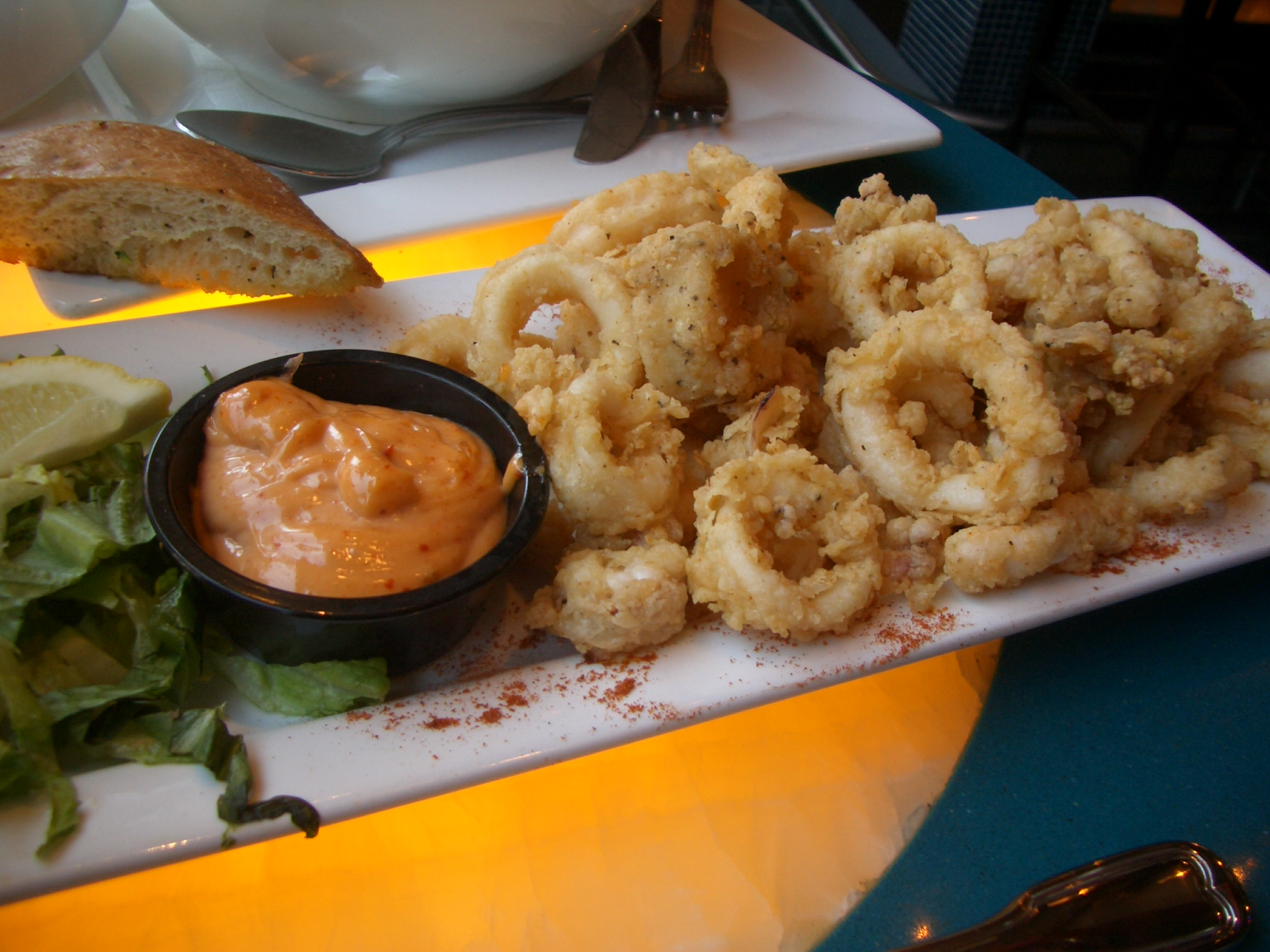
 Squid form a major food resource and are used in cuisines around the world, notably in Japan where it is eaten as ika sōmen, sliced into vermicelli-like strips; as sashimi; and as tempura. Three species of ''Loligo'' are used in large quantities, '' L. vulgaris'' in the Mediterranean (known as ''Calamar'' in Spanish, ''Calamaro'' in Italian); '' L. forbesii'' in the Northeast Atlantic; and '' L. pealei'' on the American East Coast. Among the Ommastrephidae, '' Todarodes pacificus'' is the main commercial species, harvested in large quantities across the North Pacific in Canada, Japan and China.
In English-speaking countries, squid as food is often called '' calamari'', adopted from Italian into English in the 17th century. Squid are found abundantly in certain areas, and provide large catches for
Squid form a major food resource and are used in cuisines around the world, notably in Japan where it is eaten as ika sōmen, sliced into vermicelli-like strips; as sashimi; and as tempura. Three species of ''Loligo'' are used in large quantities, '' L. vulgaris'' in the Mediterranean (known as ''Calamar'' in Spanish, ''Calamaro'' in Italian); '' L. forbesii'' in the Northeast Atlantic; and '' L. pealei'' on the American East Coast. Among the Ommastrephidae, '' Todarodes pacificus'' is the main commercial species, harvested in large quantities across the North Pacific in Canada, Japan and China.
In English-speaking countries, squid as food is often called '' calamari'', adopted from Italian into English in the 17th century. Squid are found abundantly in certain areas, and provide large catches for fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both ...
. The body can be stuffed whole, cut into flat pieces, or sliced into rings. The arms, tentacles, and ink are also edible; the only parts not eaten are the beak and gladius (pen). Squid is a good food source for zinc and manganese, and high in copper, selenium, vitamin B12, and riboflavin
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is a vitamin found in food and sold as a dietary supplement. It is essential to the formation of two major coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide. These coenzymes are involved in ...
.
Commercial fishing
According to the FAO, the cephalopod catch for 2002 was . Of this, 2,189,206 tonnes, or 75.8 percent, was squid. The following table lists squid species fishery catches that exceeded in 2002.In biomimicry
Bristol University
, mottoeng = earningpromotes one's innate power (from Horace, ''Ode 4.4'')
, established = 1595 – Merchant Venturers School1876 – University College, Bristol1909 – received royal charter
, type ...
researchers using an electroactive dielectric elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic p ...
, a flexible "smart" material that changes its colour and texture in response to electrical signals. The researchers state that their goal is to create an artificial skin that provides rapid active camouflage.
The squid giant axon inspired Otto Schmitt to develop a comparator circuit with hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of ...
now called the Schmitt trigger, replicating the axon's propagation of nerve impulses.
See also
*Paralarva
Paralarvae (singular: ''paralarva'') are young cephalopods in the planktonic stages between hatchling and subadult. This stage differs from the larval stage of animals that undergo true metamorphosis. Paralarvae have been observed only in membe ...
Notes
References
Sources
*External links
CephBase: Teuthida
Colossal Squid at the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa
Market squid mating, laying eggs (video)
Scientific American – Giant Squid
The Cephalopod Page
The Octopus News Magazine Online
{{Authority control Commercial molluscs Cenozoic cephalopods Cretaceous cephalopods Extant Devonian first appearances Mollusc common names