|
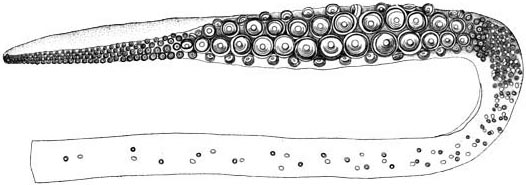
Taningia Danae
''Taningia danae'', the Dana octopus squid, is a species of squid in the family Octopoteuthidae. It is one of the largest known squid species, reaching a mantle length of and total length of . The largest known specimen, a mature female, weighed .Roper, C.F.E. & P. Jereb 2010. Family Octopoteuthidae. In: P. Jereb & C.F.E. Roper (eds.) Cephalopods of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of species known to date. Volume 2. Myopsid and Oegopsid Squids'. FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes No. 4, Vol. 2. FAO, Rome. pp. 262–268. ''Taningia danae'' is named after Danish fisheries biologist Åge Vedel Tåning (1890–1958), who often traveled on the research vessel ''Dana''. Ecology ''Taningia danae'' possesses bioluminescence, like other octopoteuthids. Its photophores are some of the largest such organs known to science, the organs being compared in size to fists or lemons. They possess a black membrane over the photophore that may conceal the organs, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taningia Danae7
''Taningia'' is a genus of squid in the family Octopoteuthidae. For over 150 years, it has been believed to comprise a single species known as ''Taningia danae.'' Recently it has been shown to contain at least two new species ('' T. fimbria'', ''T. rubea''). Another species, ''Taningia persica'', has historically been referred to but has been questioned. This genus is named after Danish fisheries Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both ... biologist Åge Vedel Tåning (1890-1958). References External links Tree of Life web project: ''Taningia'' Squid Cephalopod genera Bioluminescent molluscs {{Squid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taningia Danae Hunting
''Taningia'' is a genus of squid in the family Octopoteuthidae. For over 150 years, it has been believed to comprise a single species known as ''Taningia danae.'' Recently it has been shown to contain at least two new species ('' T. fimbria'', ''T. rubea''). Another species, ''Taningia persica'', has historically been referred to but has been questioned. This genus is named after Danish fisheries biologist Åge Vedel Tåning Åge Vedel Tåning (27 July 1890 – 26 September 1958 in Copenhagen) was a Danish ichthyologist. He was a director of the Carlsberg Laboratory, the Dana collection and the Danish Fisheries Research Station. Lanternfish genus ''Taaningichthys'' ... (1890-1958). References External links Tree of Life web project: ''Taningia'' Squid Cephalopod genera Bioluminescent molluscs {{Squid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod Size
Cephalopods vary enormously in size. The smallest are only about long and weigh less than at maturity, while the largest—the giant and colossal squids—can exceed in length and weigh close to half a tonne (), making them the largest living invertebrates. Living species range in mass more than three-billion-fold, or across nine orders of magnitude, from the lightest hatchlings to the heaviest adults. Certain cephalopod species are also noted for having individual body parts of exceptional size. The giant and colossal squids, for example, have the largest known eyes among living animals. Nilsson ''et al.'', 2012:683 Cephalopods were at one time the largest of all organisms on Earth, and numerous species of comparable size to the largest present day squids are known from the fossil record, including enormous examples of ammonoids, belemnoids, nautiloids, orthoceratoids, teuthids, and vampyromorphids. In terms of mass, the largest of all known cephalopods were likely th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The IUCN Red List Of Threatened Species
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit. The aim of the IUCN Red List is to convey the urgency of conservation issues to the public and policy makers, as well as help the international community to reduce species extinction. According to IUCN the formally stated goals of the Red List are to provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyelid
An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. The human eyelid features a row of eyelashes along the eyelid margin, which serve to heighten the protection of the eye from dust and foreign debris, as well as from perspiration. "Palpebral" (and "blepharal") means relating to the eyelids. Its key function is to regularly spread the tears and other secretions on the eye surface to keep it moist, since the cornea must be continuously moist. They keep the eyes from drying out when asleep. Moreover, the blink reflex protects the eye from foreign bodies. The appearance of the human upper eyelid often varies between different populations. The prevalence of an epicanthic fold covering the inner corner of the eye account for the majority of East Asian and Southeast Asian populations, and is also found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discovery Channel
Discovery Channel (known as The Discovery Channel from 1985 to 1995, and often referred to as simply Discovery) is an American cable channel owned by Warner Bros. Discovery, a publicly traded company run by CEO David Zaslav. , Discovery Channel was the third most widely distributed subscription channel in the United States, behind now-sibling channel TBS and The Weather Channel; it is available in 409 million households worldwide, through its U.S. flagship channel and its various owned or licensed television channels internationally. It initially provided documentary television programming focused primarily on popular science, technology, and history, but by the 2010s had expanded into reality television and pseudo-scientific entertainment. , Discovery Channel is available to approximately 88,589,000 pay television households in the United States. History John Hendricks founded the channel and its parent company, Cable Educational Network Inc., in 1982. Several inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Squid
The giant squid (''Architeuthis dux'') is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family (biology), family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of deep-sea gigantism, abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around Dianne Tracey, Tracey, D. M., O. F. Anderson & J. R. Naylor (2011)''A guide to common deepsea invertebrates in New Zealand waters. Third edition.''National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research, Wellington. 317 pp.Yukhov, V. L. (2014)Гигантские кальмары рода ''Architeuthis'' в Южном океане / Giant calmaries ''Аrchiteuthis'' in the Southern ocean [Gigantskiye kalmary roda ''Architeuthis'' v Yuzhnom okeane.] ''Ukrainian Antarctic Journal'' no. 13: 242–253. for females and for males, from the cephalopod fin, posterior fins to the tip of the two long cephalopod limb, tentacles (longer than the colossal squid at an estimated , but substantially lighter, due to the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ritualized Aggression
Ritualized aggression is when animals use a range of behaviours as posture or warning but without engaging in actual aggression, which is expensive in terms of energy and the risk of injury. Ritualized aggression involves a graded series of behaviours or displays that include threatening gestures (such as vocalizations, spreading of wings or gill covers, lifting and presentation of claws, head bobbing, tail beating, lunging, etc.) and occasionally posturing physical actions such as inhibited (non-injurious) bites. Examples Cats Domestic cats (''Felis catus'') are very territorial and defend their territories with ritualized body posturing, stalking, staring, spitting, yowling and howling. Spider monkeys Spider monkeys (genus ''Ateles'') defend their territory by screams, barks, rattling or dropping branches, and urinating and defecating on intruders below. Oscar cichlids Oscar cichlids (''Astronotus ocellatus'') are able to rapidly alter their colouration, a trait whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtship Display
A courtship display is a set of display behaviors in which an animal, usually a male, attempts to attract a mate; the mate exercises choice, so sexual selection acts on the display. These behaviors often include ritualized movement ("dances"), vocalizations, mechanical sound production, or displays of beauty, strength, or agonistic ability. Male display In some species, males will perform ritualized movements to attract females. The male six-plumed bird-of-paradise ( ''Parotia lawesii'') exemplifies male courtship display with its ritualized "ballerina dance" and unique occipital and breast feathers that serve to stimulate the female visual system. In ''Drosophila subobscura,'' male courtship display is seen through the male's intricate wing scissoring patterns and rapid sidestepping. These stimulations, along with many other factors, result in subsequent copulation or rejection. In other species, males may exhibit courtship displays that serve as both visual and auditory sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod Arm
All cephalopods possess flexible limbs extending from their heads and surrounding their beaks. These appendages, which function as muscular hydrostats, have been variously termed arms, legs or tentacles. Description In the scientific literature, a cephalopod ''arm'' is often treated as distinct from a ''tentacle'', though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, often with the latter acting as an umbrella term for cephalopod limbs. Generally, arms have suckers along most of their length, as opposed to tentacles, which have suckers only near their ends.Young, R.E., M. Vecchione & K.M. Mangold 1999Cephalopoda Glossary Tree of Life web project. Barring a few exceptions, octopuses have eight arms and no tentacles, while squid and cuttlefish have eight arms (or two "legs" and six "arms") and two tentacles.Norman, M. 2000. ''Cephalopods: A World Guide''. ConchBooks, Hackenheim. p. 15. "There is some confusion around the terms ''arms'' versus ''tentacles''. The numerous lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photophore
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, however unlike an eye it is optimized to produce light, not absorb it. The bioluminescence can variously be produced from compounds during the digestion of prey, from specialized mitochondrial cells in the organism called photocytes ("light producing" cells), or, similarly, associated with symbiotic bacteria in the organism that are cultured. The character of photophores is important in the identification of deep sea fishes. Photophores on fish are used for attracting food or for camouflage from predators by counter-illumination. Photophores are found on some cephalopods including the firefly squid, which can create impressive light displays, as well as numerous other deep sea organisms such as the pocket shark Mollisquama mississipp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus '' Vibrio''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves. In a general sense, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves a light-emitting molecule and an enzyme, generally called luciferin and luciferase, respectively. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of the luciferin. In some species, the luciferase requires other cofactors, such as calcium or magnesium ions, and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |