Spectrogram -iua- on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
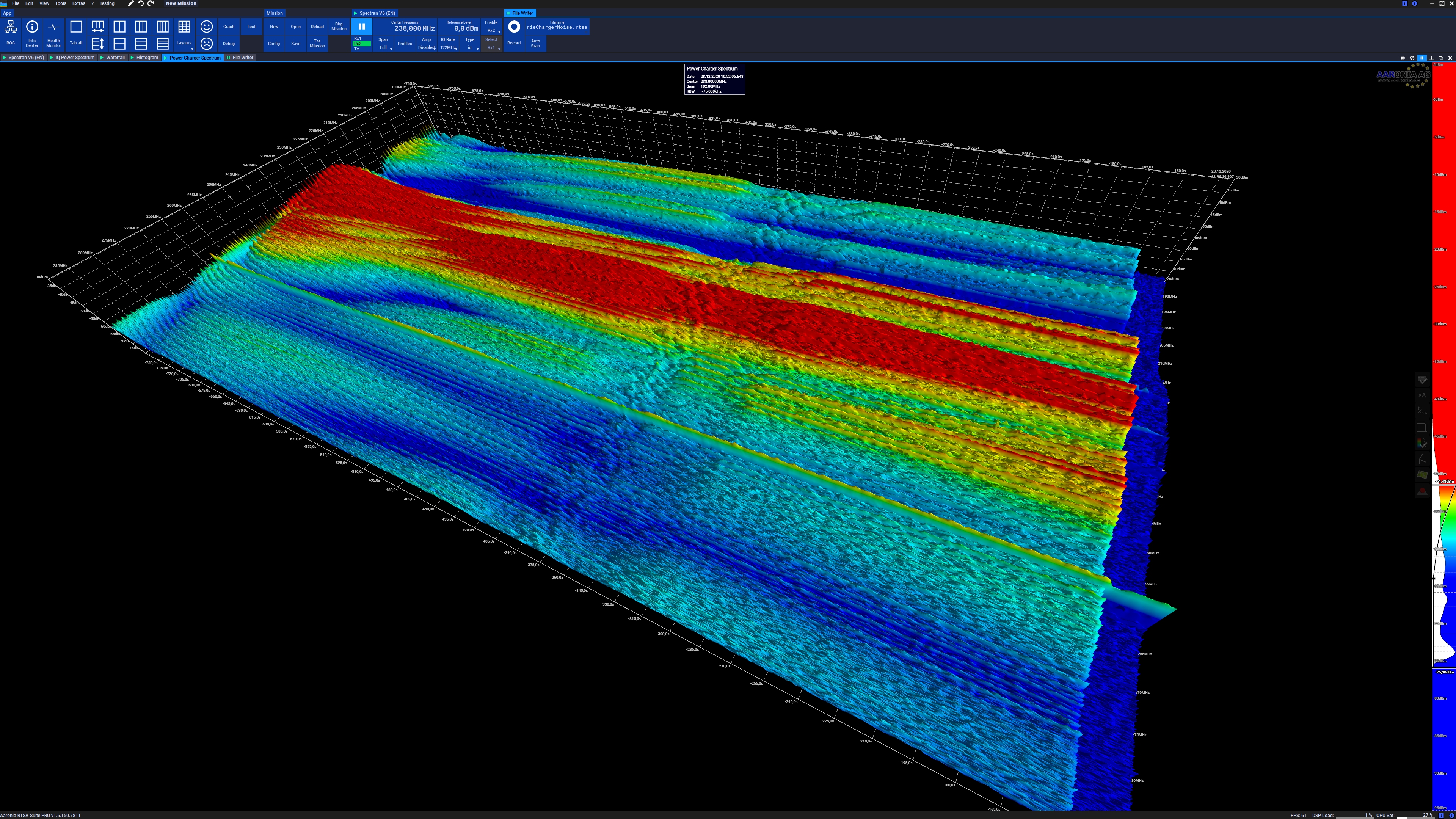 A spectrogram is a visual representation of the
A spectrogram is a visual representation of the
See an online spectrogram of speech or other sounds captured by your computer's microphone.
Generating a tone sequence whose spectrogram matches an arbitrary text, online
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20120331164713/https://kdenlive.org/users/granjow/introducing-scopes-audio-spectrum-and-spectrogram Article describing the development of a software spectrogram
History of spectrograms & development of instrumentation
from a linguistic professor's ''Monthly Mystery Spectrogram'' publication.
Sonogram Visible Speech
GPL Licensed freeware for the Spectrogram generation of Signal Files. Acoustic measurement Signal processing Time–frequency analysis
 A spectrogram is a visual representation of the
A spectrogram is a visual representation of the spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors i ...
of frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
of a signal as it varies with time.
When applied to an audio signal
An audio signal is a representation of sound, typically using either a changing level of electrical voltage for analog signals, or a series of binary numbers for digital signals. Audio signals have frequencies in the audio frequency range of r ...
, spectrograms are sometimes called sonographs, voiceprints, or voicegrams. When the data are represented in a 3D plot they may be called ''waterfall display
Waterfall plots are often used to show how two-dimensional phenomena change over time. A three-dimensional ''spectral waterfall plot'' is a plot in which multiple curves of data, typically spectra, are displayed simultaneously. Typically the cu ...
s''.
Spectrograms are used extensively in the fields of music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
, linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis ...
, sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigation, navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect o ...
, radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
, speech processing
Speech processing is the study of speech signals and the processing methods of signals. The signals are usually processed in a digital representation, so speech processing can be regarded as a special case of digital signal processing, applied t ...
, seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
, and others. Spectrograms of audio can be used to identify spoken words phonetic
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds, or in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. ...
ally, and to analyse the various calls of animals.
A spectrogram can be generated by an optical spectrometer
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
, a bank of band-pass filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects (attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
Description
In electronics and signal processing, a filter is usually a two-por ...
s, by Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...
or by a wavelet transform (in which case it is also known as a scaleogram or scalogram).
A spectrogram is usually depicted as a heat map, i.e., as an image with the intensity shown by varying the colour or brightness.
Format
A common format is a graph with two geometric dimensions: one axis represents time, and the other axis represents frequency; a third dimension indicating the amplitude of a particular frequency at a particular time is represented by theintensity
Intensity may refer to:
In colloquial use
*Strength (disambiguation)
*Amplitude
* Level (disambiguation)
* Magnitude (disambiguation)
In physical sciences
Physics
*Intensity (physics), power per unit area (W/m2)
*Field strength of electric, ma ...
or color of each point in the image.
There are many variations of format: sometimes the vertical and horizontal axes are switched, so time runs up and down; sometimes as a waterfall plot where the amplitude is represented by height of a 3D surface instead of color or intensity. The frequency and amplitude axes can be either linear or logarithmic, depending on what the graph is being used for. Audio would usually be represented with a logarithmic amplitude axis (probably in decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a po ...
s, or dB), and frequency would be linear to emphasize harmonic relationships, or logarithmic to emphasize musical, tonal relationships.
Generation
Spectrograms of light may be created directly using anoptical spectrometer
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
over time.
Spectrograms may be created from a time-domain signal in one of two ways: approximated as a filterbank that results from a series of band-pass filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects (attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
Description
In electronics and signal processing, a filter is usually a two-por ...
s (this was the only way before the advent of modern digital signal processing), or calculated from the time signal using the Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...
. These two methods actually form two different time–frequency representations, but are equivalent under some conditions.
The bandpass filters method usually uses analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analo ...
processing to divide the input signal into frequency bands; the magnitude of each filter's output controls a transducer that records the spectrogram as an image on paper.
Creating a spectrogram using the FFT is a digital process. Digitally sampled data, in the time domain, is broken up into chunks, which usually overlap, and Fourier transformed to calculate the magnitude of the frequency spectrum for each chunk. Each chunk then corresponds to a vertical line in the image; a measurement of magnitude versus frequency for a specific moment in time (the midpoint of the chunk). These spectrums or time plots are then "laid side by side" to form the image or a three-dimensional surface, or slightly overlapped in various ways, i.e. windowing. This process essentially corresponds to computing the squared magnitude of the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) of the signal — that is, for a window width , .
Limitations and resynthesis
From the formula above, it appears that a spectrogram contains no information about the exact, or even approximate,phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
* Phase space, a mathematic ...
of the signal that it represents. For this reason, it is not possible to reverse the process and generate a copy of the original signal from a spectrogram, though in situations where the exact initial phase is unimportant it may be possible to generate a useful approximation of the original signal. The Analysis & Resynthesis Sound Spectrograph is an example of a computer program that attempts to do this. The Pattern Playback was an early speech synthesizer, designed at Haskins Laboratories in the late 1940s, that converted pictures of the acoustic patterns of speech (spectrograms) back into sound.
In fact, there is some phase information in the spectrogram, but it appears in another form, as time delay (or group delay
In signal processing, group delay and phase delay are delay times experienced by a signal's various frequency components when the signal passes through a system that is linear time-invariant (LTI), such as a microphone, coaxial cable, amplifier, l ...
) which is the dual
Dual or Duals may refer to:
Paired/two things
* Dual (mathematics), a notion of paired concepts that mirror one another
** Dual (category theory), a formalization of mathematical duality
*** see more cases in :Duality theories
* Dual (grammatical ...
of the instantaneous frequency.
The size and shape of the analysis window can be varied. A smaller (shorter) window will produce more accurate results in timing, at the expense of precision of frequency representation. A larger (longer) window will provide a more precise frequency representation, at the expense of precision in timing representation. This is an instance of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
In quantum mechanics, the uncertainty principle (also known as Heisenberg's uncertainty principle) is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the accuracy with which the values for certain pairs of physic ...
, that the product of the precision in two conjugate variables
Conjugate variables are pairs of variables mathematically defined in such a way that they become Fourier transform duals, or more generally are related through Pontryagin duality. The duality relations lead naturally to an uncertainty relation— ...
is greater than or equal to a constant (B*T>=1 in the usual notation).
Applications
* Early analog spectrograms were applied to a wide range of areas including the study of bird calls (such as that of the great tit), with current research continuing using modern digital equipment and applied to all animal sounds. Contemporary use of the digital spectrogram is especially useful for studying frequency modulation (FM) in animal calls. Specifically, the distinguishing characteristics of FM chirps, broadband clicks, and social harmonizing are most easily visualized with the spectrogram. * Spectrograms are useful in assisting in overcoming speech deficits and in speech training for the portion of the population that is profoundly deaf * The studies of phonetics andspeech synthesis
Speech synthesis is the artificial production of human speech. A computer system used for this purpose is called a speech synthesizer, and can be implemented in software or hardware products. A text-to-speech (TTS) system converts normal languag ...
are often facilitated through the use of spectrograms.
* In deep learning-keyed speech synthesis, spectrogram (or spectrogram in mel scale
The mel scale (after the word ''melody'')
is a perceptual scale of pitches judged by listeners to be equal in distance from one another. The reference point between this scale and normal frequency measurement is defined by assigning a perce ...
) is first predicted by a seq2seq model, then the spectrogram is fed to a neural vocoder to derive the synthesized raw waveform.
* By reversing the process of producing a spectrogram, it is possible to create a signal whose spectrogram is an arbitrary image. This technique can be used to hide a picture in a piece of audio and has been employed by several electronic music artists. See also steganography.
* Some modern music is created using spectrograms as an intermediate medium; changing the intensity of different frequencies over time, or even creating new ones, by drawing them and then inverse transforming. See Audio timescale-pitch modification
Time stretching is the process of changing the speed or duration of an audio signal without affecting its pitch. Pitch scaling is the opposite: the process of changing the pitch without affecting the speed. Pitch shift is pitch scaling implement ...
and Phase vocoder.
* Spectrograms can be used to analyze the results of passing a test signal through a signal processor such as a filter in order to check its performance.
* High definition spectrograms are used in the development of RF and microwave systems
* Spectrograms are now used to display scattering parameters measured with vector network analyzers
* The US Geological Survey and the IRIS Consortium provide near real-time spectrogram displays for monitoring seismic stations
* Spectrograms can be used with recurrent neural networks for speech recognition.
See also
* Acoustic signature * Chromagram *Fourier analysis
In mathematics, Fourier analysis () is the study of the way general functions may be represented or approximated by sums of simpler trigonometric functions. Fourier analysis grew from the study of Fourier series, and is named after Josep ...
for computing periodicity in evenly spaced data
* Generalized spectrogram
In order to view a signal (taken to be a function of time) represented over both time and frequency axis, time–frequency representation is used. Spectrogram is one of the most popular time-frequency representation, and generalized spectrogram, a ...
* Least-squares spectral analysis for computing periodicity in unevenly spaced data
* List of unexplained sounds
* Reassignment method
* Spectral music
* Spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the ...
* Strobe tuner
In music, an electronic tuner is a device that detects and displays the pitch of musical notes played on a musical instrument. "Pitch" is the perceived fundamental frequency of a musical note, which is typically measured in Hertz. Simple tuner ...
* Waveform
References
External links
{{WiktionarySee an online spectrogram of speech or other sounds captured by your computer's microphone.
Generating a tone sequence whose spectrogram matches an arbitrary text, online
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20120331164713/https://kdenlive.org/users/granjow/introducing-scopes-audio-spectrum-and-spectrogram Article describing the development of a software spectrogram
History of spectrograms & development of instrumentation
from a linguistic professor's ''Monthly Mystery Spectrogram'' publication.
Sonogram Visible Speech
GPL Licensed freeware for the Spectrogram generation of Signal Files. Acoustic measurement Signal processing Time–frequency analysis