Solid Pseudopapillary Tumour - High Mag on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Solid is one of the
Solid is one of the
 The atoms, molecules or ions that make up solids may be arranged in an orderly repeating pattern, or irregularly. Materials whose constituents are arranged in a regular pattern are known as
The atoms, molecules or ions that make up solids may be arranged in an orderly repeating pattern, or irregularly. Materials whose constituents are arranged in a regular pattern are known as
 Metals typically are strong, dense, and good conductors of both
Metals typically are strong, dense, and good conductors of both
 Minerals are naturally occurring solids formed through various geological processes under high pressures. To be classified as a true mineral, a substance must have a
Minerals are naturally occurring solids formed through various geological processes under high pressures. To be classified as a true mineral, a substance must have a
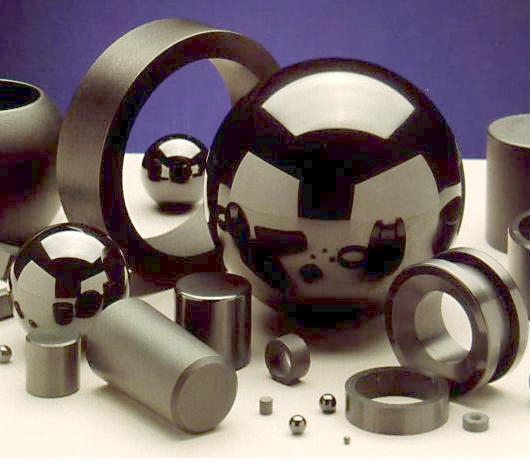 Ceramic solids are composed of inorganic compounds, usually oxides of chemical elements. They are chemically inert, and often are capable of withstanding chemical erosion that occurs in an acidic or caustic environment. Ceramics generally can withstand high temperatures ranging from 1000 to 1600 °C (1800 to 3000 °F). Exceptions include non-oxide inorganic materials, such as
Ceramic solids are composed of inorganic compounds, usually oxides of chemical elements. They are chemically inert, and often are capable of withstanding chemical erosion that occurs in an acidic or caustic environment. Ceramics generally can withstand high temperatures ranging from 1000 to 1600 °C (1800 to 3000 °F). Exceptions include non-oxide inorganic materials, such as
 Solid is one of the
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter
In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many intermediate states are known to exist, such as liquid crystal, ...
(the others being liquid, gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural rigidity
In discrete geometry and mechanics, structural rigidity is a combinatorial theory for predicting the flexibility of ensembles formed by rigid bodies connected by flexible linkages or hinges.
Definitions
Rigidity is the property of a struct ...
and resistance to a force applied to the surface. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. The atoms in a solid are bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice
In the mathematics of matroids and lattices, a geometric lattice is a finite atomistic semimodular lattice, and a matroid lattice is an atomistic semimodular lattice without the assumption of finiteness. Geometric lattices and matroid lattices, r ...
( crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaqu ...
), or irregularly (an amorphous solid
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal.
Etymology
The term comes from the Greek ''a'' ("wi ...
such as common window glass). Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because the molecules in a gas are loosely packed.
The branch of physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science is primarily concerned with the physical and chemical properties
A chemical property is any of a material's properties that becomes evident during, or after, a chemical reaction; that is, any quality that can be established only by changing a substance's chemical identity.William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley, ...
of solids. Solid-state chemistry Solid-state chemistry, also sometimes referred as materials chemistry, is the study of the synthesis, structure, and properties of solid phase materials, particularly, but not necessarily exclusively of, non-molecular solids. It therefore has a str ...
is especially concerned with the synthesis of novel materials, as well as the science of identification and chemical composition.
Microscopic description
 The atoms, molecules or ions that make up solids may be arranged in an orderly repeating pattern, or irregularly. Materials whose constituents are arranged in a regular pattern are known as
The atoms, molecules or ions that make up solids may be arranged in an orderly repeating pattern, or irregularly. Materials whose constituents are arranged in a regular pattern are known as crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
s. In some cases, the regular ordering can continue unbroken over a large scale, for example diamonds, where each diamond is a single crystal
In materials science, a single crystal (or single-crystal solid or monocrystalline solid) is a material in which the crystal lattice of the entire sample is continuous and unbroken to the edges of the sample, with no grain boundaries.RIWD. "Re ...
. Solid objects that are large enough to see and handle are rarely composed of a single crystal, but instead are made of a large number of single crystals, known as crystallite
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains.
Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel longulites.
Stru ...
s, whose size can vary from a few nanometers to several meters. Such materials are called polycrystal
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains.
Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel longulites.
Stru ...
line. Almost all common metals, and many ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
s, are polycrystalline.
In other materials, there is no long-range order in the position of the atoms. These solids are known as amorphous solid
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal.
Etymology
The term comes from the Greek ''a'' ("wi ...
s; examples include polystyrene and glass.
Whether a solid is crystalline or amorphous depends on the material involved, and the conditions in which it was formed. Solids that are formed by slow cooling will tend to be crystalline, while solids that are frozen rapidly are more likely to be amorphous. Likewise, the specific crystal structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns ...
adopted by a crystalline solid depends on the material involved and on how it was formed.
While many common objects, such as an ice cube or a coin, are chemically identical throughout, many other common materials comprise a number of different substances packed together. For example, a typical rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
is an aggregate of several different minerals and mineraloids, with no specific chemical composition. Wood is a natural organic material consisting primarily of cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell w ...
fibers embedded in a matrix of organic lignin. In materials science, composites of more than one constituent material can be designed to have desired properties.
Classes of solids
The forces between the atoms in a solid can take a variety of forms. For example, a crystal of sodium chloride (common salt) is made up ofion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
ic sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
and chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
, which are held together by ionic bond
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply different electronegativities, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds ...
s. In diamond or silicon, the atoms share electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s and form covalent bonds. In metals, electrons are shared in metallic bond
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions. It may be des ...
ing. Some solids, particularly most organic compounds, are held together with van der Waals force
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and th ...
s resulting from the polarization of the electronic charge cloud on each molecule. The dissimilarities between the types of solid result from the differences between their bonding.
Metals
 Metals typically are strong, dense, and good conductors of both
Metals typically are strong, dense, and good conductors of both electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
and heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is ...
.
The bulk of the elements in the periodic table, those to the left of a diagonal line drawn from boron to polonium
Polonium is a chemical element with the symbol Po and atomic number 84. Polonium is a chalcogen. A rare and highly radioactive metal with no stable isotopes, polonium is chemically similar to selenium and tellurium, though its metallic character ...
, are metals.
Mixtures of two or more elements in which the major component is a metal are known as alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
s.
People have been using metals for a variety of purposes since prehistoric times.
The strength
Strength may refer to:
Physical strength
*Physical strength, as in people or animals
* Hysterical strength, extreme strength occurring when people are in life-and-death situations
*Superhuman strength, great physical strength far above human c ...
and reliability
Reliability, reliable, or unreliable may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Computing
* Data reliability (disambiguation), a property of some disk arrays in computer storage
* High availability
* Reliability (computer networking), a ...
of metals has led to their widespread use in construction of buildings and other structures, as well as in most vehicles, many appliances and tools, pipes, road signs and railroad tracks. Iron and aluminium are the two most commonly used structural metals. They are also the most abundant metals in the Earth's crust. Iron is most commonly used in the form of an alloy, steel, which contains up to 2.1% carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
, making it much harder than pure iron.
Because metals are good conductors of electricity, they are valuable in electrical appliances and for carrying an electric current over long distances with little energy loss or dissipation. Thus, electrical power grids rely on metal cables to distribute electricity. Home electrical systems, for example, are wired with copper for its good conducting properties and easy machinability. The high thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
of most metals also makes them useful for stovetop cooking utensils.
The study of metallic elements and their alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
s makes up a significant portion of the fields of solid-state chemistry, physics, materials science and engineering.
Metallic solids are held together by a high density of shared, delocalized electrons, known as "metallic bond
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions. It may be des ...
ing". In a metal, atoms readily lose their outermost ("valence") electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s, forming positive ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
s. The free electrons are spread over the entire solid, which is held together firmly by electrostatic interactions between the ions and the electron cloud. The large number of free electrons gives metals their high values of electrical and thermal conductivity. The free electrons also prevent transmission of visible light, making metals opaque, shiny and lustrous
Lustre (British English) or luster (American English; see spelling differences) is the way light interacts with the surface of a crystal, rock, or mineral. The word traces its origins back to the Latin ''lux'', meaning "light", and generally ...
.
More advanced models of metal properties consider the effect of the positive ions cores on the delocalised electrons. As most metals have crystalline structure, those ions are usually arranged into a periodic lattice. Mathematically, the potential of the ion cores can be treated by various models, the simplest being the nearly free electron model
In solid-state physics, the nearly free electron model (or NFE model) or quasi-free electron model is a quantum mechanical model of physical properties of electrons that can move almost freely through the crystal lattice of a solid. The model i ...
.
Minerals
 Minerals are naturally occurring solids formed through various geological processes under high pressures. To be classified as a true mineral, a substance must have a
Minerals are naturally occurring solids formed through various geological processes under high pressures. To be classified as a true mineral, a substance must have a crystal structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns ...
with uniform physical properties throughout. Minerals range in composition from pure elements and simple salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
s to very complex silicates with thousands of known forms. In contrast, a rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
sample is a random aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids, and has no specific chemical composition. The vast majority of the rocks of the Earth's crust consist of quartz (crystalline SiO2), feldspar, mica, chlorite, kaolin
Kaolinite ( ) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is an important industrial mineral. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral ...
, calcite, epidote
Epidote is a calcium aluminium iron sorosilicate mineral.
Description
Well developed crystals of epidote, Ca2Al2(Fe3+;Al)(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH), crystallizing in the monoclinic system, are of frequent occurrence: they are commonly prismatic in hab ...
, olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickl ...
, augite, hornblende
Hornblende is a complex inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common in igneous and metamorphic rock ...
, magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With th ...
, hematite, limonite and a few other minerals. Some minerals, like quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
, mica or feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) felds ...
are common, while others have been found in only a few locations worldwide. The largest group of minerals by far is the silicates
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name i ...
(most rocks are ≥95% silicates), which are composed largely of silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ta ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
, with the addition of ions of aluminium, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
, iron, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
and other metals.
Ceramics
 Ceramic solids are composed of inorganic compounds, usually oxides of chemical elements. They are chemically inert, and often are capable of withstanding chemical erosion that occurs in an acidic or caustic environment. Ceramics generally can withstand high temperatures ranging from 1000 to 1600 °C (1800 to 3000 °F). Exceptions include non-oxide inorganic materials, such as
Ceramic solids are composed of inorganic compounds, usually oxides of chemical elements. They are chemically inert, and often are capable of withstanding chemical erosion that occurs in an acidic or caustic environment. Ceramics generally can withstand high temperatures ranging from 1000 to 1600 °C (1800 to 3000 °F). Exceptions include non-oxide inorganic materials, such as nitride
In chemistry, a nitride is an inorganic compound of nitrogen. The "nitride" anion, N3- ion, is very elusive but compounds of nitride are numerous, although rarely naturally occuring. Some nitrides have a find applications, such as wear-resistant ...
s, boride A boride is a compound between boron and a less electronegative element, for example silicon boride (SiB3 and SiB6). The borides are a very large group of compounds that are generally high melting and are covalent more than ionic in nature. Some bo ...
s and carbide
In chemistry, a carbide usually describes a compound composed of carbon and a metal. In metallurgy, carbiding or carburizing is the process for producing carbide coatings on a metal piece.
Interstitial / Metallic carbides
The carbides of th ...
s.
Traditional ceramic raw materials include clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
minerals such as kaolinite, more recent materials include aluminium oxide ( alumina). The modern ceramic materials, which are classified as advanced ceramics, include silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal s ...
and tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: WC) is a chemical compound (specifically, a carbide) containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into ...
. Both are valued for their abrasion resistance, and hence find use in such applications as the wear plates of crushing equipment in mining operations.
Most ceramic materials, such as alumina and its compounds, are formed from fine powders, yielding a fine grained polycrystalline
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains.
Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel longulites.
Stru ...
microstructure
Microstructure is the very small scale structure of a material, defined as the structure of a prepared surface of material as revealed by an optical microscope above 25× magnification. The microstructure of a material (such as metals, polymers ...
that is filled with light-scattering centers comparable to the wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
of visible light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
. Thus, they are generally opaque materials, as opposed to transparent materials
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions ...
. Recent nanoscale (e.g. sol-gel) technology has, however, made possible the production of polycrystalline transparent ceramics
Many ceramic materials, both glassy and crystalline, have found use as optically transparent materials in various forms from bulk solid-state components to high surface area forms such as thin films, coatings, and fibers. Such devices have found ...
such as transparent alumina and alumina compounds for such applications as high-power lasers. Advanced ceramics are also used in the medicine, electrical and electronics industries.
Ceramic engineering
Ceramic engineering is the science and technology of creating objects from inorganic, non-metallic materials. This is done either by the action of heat, or at lower temperatures using precipitation reactions from high-purity chemical solutions ...
is the science and technology of creating solid-state ceramic materials, parts and devices. This is done either by the action of heat, or, at lower temperatures, using precipitation reactions from chemical solutions. The term includes the purification of raw materials, the study and production of the chemical compounds concerned, their formation into components, and the study of their structure, composition and properties.
Mechanically speaking, ceramic materials are brittle, hard, strong in compression and weak in shearing and tension. Brittle
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength. Br ...
materials may exhibit significant tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials t ...
by supporting a static load. Toughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.fracture toughness (denoted KIc ) describes the ability of a material with inherent microstructural flaws to resist fracture via crack growth and propagation. If a material has a large value of fracture toughness, the basic principles of fracture mechanics suggest that it will most likely undergo ductile fracture. Brittle fracture is very characteristic of most
 Glass-ceramic materials share many properties with both non-crystalline glasses and
Glass-ceramic materials share many properties with both non-crystalline glasses and
 Organic chemistry studies the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation by synthesis (or other means) of chemical compounds of
Organic chemistry studies the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation by synthesis (or other means) of chemical compounds of
 One important property of carbon in organic chemistry is that it can form certain compounds, the individual molecules of which are capable of attaching themselves to one another, thereby forming a chain or a network. The process is called polymerization and the chains or networks polymers, while the source compound is a monomer. Two main groups of polymers exist: those artificially manufactured are referred to as industrial polymers or synthetic polymers (plastics) and those naturally occurring as biopolymers.
Monomers can have various chemical substituents, or functional groups, which can affect the chemical properties of organic compounds, such as solubility and chemical reactivity, as well as the physical properties, such as hardness, density, mechanical or tensile strength, abrasion resistance, heat resistance, transparency, color, etc.. In proteins, these differences give the polymer the ability to adopt a biologically active conformation in preference to others (see
One important property of carbon in organic chemistry is that it can form certain compounds, the individual molecules of which are capable of attaching themselves to one another, thereby forming a chain or a network. The process is called polymerization and the chains or networks polymers, while the source compound is a monomer. Two main groups of polymers exist: those artificially manufactured are referred to as industrial polymers or synthetic polymers (plastics) and those naturally occurring as biopolymers.
Monomers can have various chemical substituents, or functional groups, which can affect the chemical properties of organic compounds, such as solubility and chemical reactivity, as well as the physical properties, such as hardness, density, mechanical or tensile strength, abrasion resistance, heat resistance, transparency, color, etc.. In proteins, these differences give the polymer the ability to adopt a biologically active conformation in preference to others (see  People have been using natural organic polymers for centuries in the form of waxes and
People have been using natural organic polymers for centuries in the form of waxes and
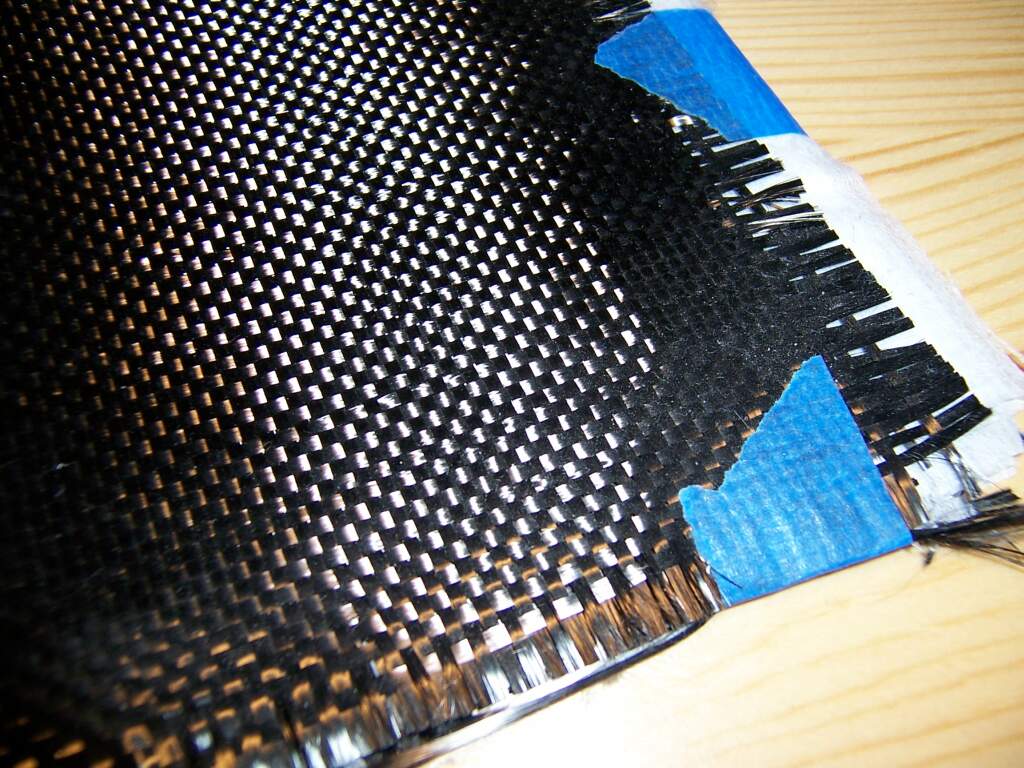


 Many traditional solids exhibit different properties when they shrink to nanometer sizes. For example,
Many traditional solids exhibit different properties when they shrink to nanometer sizes. For example,
 Many natural (or biological) materials are complex composites with remarkable mechanical properties. These complex structures, which have risen from hundreds of million years of evolution, are inspiring materials scientists in the design of novel materials. Their defining characteristics include structural hierarchy, multifunctionality and self-healing capability. Self-organization is also a fundamental feature of many biological materials and the manner by which the structures are assembled from the molecular level up. Thus,
Many natural (or biological) materials are complex composites with remarkable mechanical properties. These complex structures, which have risen from hundreds of million years of evolution, are inspiring materials scientists in the design of novel materials. Their defining characteristics include structural hierarchy, multifunctionality and self-healing capability. Self-organization is also a fundamental feature of many biological materials and the manner by which the structures are assembled from the molecular level up. Thus,
 The mechanical properties of materials describe characteristics such as their
The mechanical properties of materials describe characteristics such as their
 Because solids have
Because solids have
ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
and glass-ceramic
Glass-ceramics are polycrystalline materials produced through controlled crystallization of base glass, producing a fine uniform dispersion of crystals throughout the bulk material. Crystallization is accomplished by subjecting suitable glasses to ...
materials that typically exhibit low (and inconsistent) values of KIc.
For an example of applications of ceramics, the extreme hardness of zirconia
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral baddeleyite. A dopant sta ...
is utilized in the manufacture of knife blades, as well as other industrial cutting tools. Ceramics such as alumina, boron carbide and silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal s ...
have been used in bulletproof vests to repel large-caliber rifle fire. Silicon nitride
Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term "silicon nitride" commonly refers to this specific composition. It ...
parts are used in ceramic ball bearings, where their high hardness makes them wear resistant. In general, ceramics are also chemically resistant and can be used in wet environments where steel bearings would be susceptible to oxidation (or rust).
As another example of ceramic applications, in the early 1980s, Toyota
is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 ...
researched production of an adiabatic ceramic engine with an operating temperature of over 6000 °F (3300 °C). Ceramic engines do not require a cooling system and hence allow a major weight reduction and therefore greater fuel efficiency. In a conventional metallic engine, much of the energy released from the fuel must be dissipated as waste heat
Waste heat is heat that is produced by a machine, or other process that uses energy, as a byproduct of doing work. All such processes give off some waste heat as a fundamental result of the laws of thermodynamics. Waste heat has lower utility ...
in order to prevent a meltdown of the metallic parts. Work is also being done in developing ceramic parts for gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directio ...
engines
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power g ...
. Turbine engines made with ceramics could operate more efficiently, giving aircraft greater range and payload for a set amount of fuel. Such engines are not in production, however, because the manufacturing of ceramic parts in the sufficient precision and durability is difficult and costly. Processing methods often result in a wide distribution of microscopic flaws that frequently play a detrimental role in the sintering process, resulting in the proliferation of cracks, and ultimate mechanical failure.
Glass ceramics
 Glass-ceramic materials share many properties with both non-crystalline glasses and
Glass-ceramic materials share many properties with both non-crystalline glasses and crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
. They are formed as a glass, and then partially crystallized by heat treatment, producing both amorphous and crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
phases so that crystalline grains are embedded within a non-crystalline intergranular phase.
Glass-ceramics are used to make cookware (originally known by the brand name CorningWare
Corning Ware, also written CorningWare, was originally a brand name for a unique glass-ceramic ( Pyroceram) cookware resistant to thermal shock. It was first introduced in 1958 by Corning Glass Works (later Corning Inc.) in the United States. The ...
) and stovetops that have both high resistance to thermal shock
Thermal shock is a type of rapidly transient mechanical load.
By definition, it is a mechanical load caused by a rapid change of temperature of a certain point.
It can be also extended to the case of a thermal gradient, which makes different pa ...
and extremely low permeability to liquids. The negative coefficient of thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.
Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kineti ...
of the crystalline ceramic phase can be balanced with the positive coefficient of the glassy phase. At a certain point (~70% crystalline) the glass-ceramic has a net coefficient of thermal expansion close to zero. This type of glass-ceramic exhibits excellent mechanical properties and can sustain repeated and quick temperature changes up to 1000 °C.
Glass ceramics may also occur naturally when lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous release of an avera ...
strikes the crystalline (e.g. quartz) grains found in most beach sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class o ...
. In this case, the extreme and immediate heat of the lightning (~2500 °C) creates hollow, branching rootlike structures called fulgurite
Fulgurites (), commonly known as "fossilized lightning", are natural tubes, clumps, or masses of sintered, vitrified, and/or fused soil, sand, rock, organic debris and other sediments that sometimes form when lightning discharges into ground. ...
via fusion
Fusion, or synthesis, is the process of combining two or more distinct entities into a new whole.
Fusion may also refer to:
Science and technology Physics
*Nuclear fusion, multiple atomic nuclei combining to form one or more different atomic nucl ...
.
Organic solids
 Organic chemistry studies the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation by synthesis (or other means) of chemical compounds of
Organic chemistry studies the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation by synthesis (or other means) of chemical compounds of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
and hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
, which may contain any number of other elements such as nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
and the halogens: fluorine, chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
, bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
and iodine. Some organic compounds may also contain the elements phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
or sulfur. Examples of organic solids include wood, paraffin wax
Paraffin wax (or petroleum wax) is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum, coal, or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between 20 and 40 carbon atoms. It is solid at room temperature and begins to ...
, naphthalene and a wide variety of polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
s and plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
s.
Wood
Wood is a natural organic material consisting primarily ofcellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell w ...
fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin. Regarding mechanical properties, the fibers are strong in tension, and the lignin matrix resists compression. Thus wood has been an important construction material since humans began building shelters and using boats. Wood to be used for construction work is commonly known as ''lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
'' or ''timber''. In construction, wood is not only a structural material, but is also used to form the mould for concrete.
Wood-based materials are also extensively used for packaging (e.g. cardboard) and paper, which are both created from the refined pulp. The chemical pulping processes use a combination of high temperature and alkaline (kraft) or acidic (sulfite) chemicals to break the chemical bonds of the lignin before burning it out.
Polymers
self-assembly
Self-assembly is a process in which a disordered system of pre-existing components forms an organized structure or pattern as a consequence of specific, local interactions among the components themselves, without external direction. When the ...
).
 People have been using natural organic polymers for centuries in the form of waxes and
People have been using natural organic polymers for centuries in the form of waxes and shellac
Shellac () is a resin secreted by the female lac bug on trees in the forests of India and Thailand. It is processed and sold as dry flakes and dissolved in alcohol to make liquid shellac, which is used as a brush-on colorant, food glaze and ...
, which is classified as a thermoplastic polymer. A plant polymer named cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell w ...
provided the tensile strength for natural fibers and ropes, and by the early 19th century natural rubber was in widespread use. Polymers are the raw materials (the resins) used to make what are commonly called plastics. Plastics are the final product, created after one or more polymers or additives have been added to a resin during processing, which is then shaped into a final form. Polymers that have been around, and that are in current widespread use, include carbon-based polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging ( plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including b ...
, polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins a ...
, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, nylons, polyesters, acrylics, polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from ...
, and polycarbonates, and silicon-based silicones. Plastics are generally classified as "commodity", "specialty" and "engineering" plastics.
Composite materials


Composite material
A composite material (also called a composition material or shortened to composite, which is the common name) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or ...
s contain two or more macroscopic phases, one of which is often ceramic. For example, a continuous matrix, and a dispersed phase of ceramic particles or fibers.
Applications of composite materials range from structural elements such as steel-reinforced concrete, to the thermally insulative tiles that play a key and integral role in NASA's Space Shuttle thermal protection system
The Space Shuttle thermal protection system (TPS) is the barrier that protected the Space Shuttle Orbiter during the searing heat of atmospheric reentry. A secondary goal was to protect from the heat and cold of space while in orbit.
Material ...
, which is used to protect the surface of the shuttle from the heat of re-entry into the Earth's atmosphere. One example is Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC), the light gray material that withstands reentry temperatures up to 1510 °C (2750 °F) and protects the nose cap and leading edges of Space Shuttle's wings. RCC is a laminated
Lamination is the technique/process of manufacturing a material in multiple layers, so that the composite material achieves improved strength, stability, sound insulation, appearance, or other properties from the use of the differing materia ...
composite material made from graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
rayon cloth and impregnated with a phenolic resin
Phenol formaldehyde resins (PF) or phenolic resins (also infrequently called phenoplasts) are synthetic polymers obtained by the reaction of phenol or substituted phenol with formaldehyde. Used as the basis for Bakelite, PFs were the first commerc ...
. After curing at high temperature in an autoclave, the laminate is pyrolized to convert the resin to carbon, impregnated with furfural alcohol in a vacuum chamber, and cured/pyrolized to convert the furfural alcohol to carbon. In order to provide oxidation resistance for reuse capability, the outer layers of the RCC are converted to silicon carbide.
Domestic examples of composites can be seen in the "plastic" casings of television sets, cell-phones and so on. These plastic casings are usually a composite made up of a thermoplastic matrix such as acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) in which calcium carbonate chalk, talc
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral, composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thickening agent a ...
, glass fibers or carbon fibers have been added for strength, bulk, or electro-static dispersion. These additions may be referred to as reinforcing fibers, or dispersants, depending on their purpose.
Thus, the matrix material surrounds and supports the reinforcement materials by maintaining their relative positions. The reinforcements impart their special mechanical and physical properties to enhance the matrix properties. A synergism produces material properties unavailable from the individual constituent materials, while the wide variety of matrix and strengthening materials provides the designer with the choice of an optimum combination.
Semiconductors
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
s are materials that have an electrical resistivity (and conductivity) between that of metallic conductors and non-metallic insulators. They can be found in the periodic table moving diagonally downward right from boron. They separate the electrical conductors (or metals, to the left) from the insulators (to the right).
Devices made from semiconductor materials are the foundation of modern electronics, including radio, computers, telephones, etc. Semiconductor devices include the transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
, solar cell
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
s, diodes and integrated circuits. Solar photovoltaic panels are large semiconductor devices that directly convert light into electrical energy.
In a metallic conductor, current is carried by the flow of electrons, but in semiconductors, current can be carried either by electrons or by the positively charged " holes" in the electronic band structure
In solid-state physics, the electronic band structure (or simply band structure) of a solid describes the range of energy levels that electrons may have within it, as well as the ranges of energy that they may not have (called ''band gaps'' or ' ...
of the material. Common semiconductor materials include silicon, germanium and gallium arsenide.
Nanomaterials
 Many traditional solids exhibit different properties when they shrink to nanometer sizes. For example,
Many traditional solids exhibit different properties when they shrink to nanometer sizes. For example, nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 10 ...
s of usually yellow gold and gray silicon are red in color; gold nanoparticles melt at much lower temperatures (~300 °C for 2.5 nm size) than the gold slabs (1064 °C); and metallic nanowires are much stronger than the corresponding bulk metals. The high surface area of nanoparticles makes them extremely attractive for certain applications in the field of energy. For example, platinum metals may provide improvements as automotive fuel catalysts
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
, as well as proton exchange membrane
A proton-exchange membrane, or polymer-electrolyte membrane (PEM), is a semipermeable membrane generally made from ionomers and designed to conduct protons while acting as an electronic insulator and reactant barrier, e.g. to oxygen and hydrogen ...
(PEM) fuel cells. Also, ceramic oxides (or cermets) of lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lant ...
, cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. Cerium is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the +3 ...
, manganese and nickel are now being developed as solid oxide fuel cell
A solid oxide fuel cell (or SOFC) is an electrochemical conversion device that produces electricity directly from oxidizing a fuel. Fuel cells are characterized by their electrolyte material; the SOFC has a solid oxide or ceramic electrolyte.
A ...
s (SOFC). Lithium, lithium-titanate and tantalum nanoparticles are being applied in lithium ion batteries. Silicon nanoparticles have been shown to dramatically expand the storage capacity of lithium ion batteries during the expansion/contraction cycle. Silicon nanowires cycle without significant degradation and present the potential for use in batteries with greatly expanded storage times. Silicon nanoparticles are also being used in new forms of solar energy cells. Thin film deposition of silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ta ...
quantum dots on the polycrystalline silicon substrate of a photovoltaic (solar) cell increases voltage output as much as 60% by fluorescing the incoming light prior to capture. Here again, surface area of the nanoparticles (and thin films) plays a critical role in maximizing the amount of absorbed radiation.
Biomaterials
 Many natural (or biological) materials are complex composites with remarkable mechanical properties. These complex structures, which have risen from hundreds of million years of evolution, are inspiring materials scientists in the design of novel materials. Their defining characteristics include structural hierarchy, multifunctionality and self-healing capability. Self-organization is also a fundamental feature of many biological materials and the manner by which the structures are assembled from the molecular level up. Thus,
Many natural (or biological) materials are complex composites with remarkable mechanical properties. These complex structures, which have risen from hundreds of million years of evolution, are inspiring materials scientists in the design of novel materials. Their defining characteristics include structural hierarchy, multifunctionality and self-healing capability. Self-organization is also a fundamental feature of many biological materials and the manner by which the structures are assembled from the molecular level up. Thus, self-assembly
Self-assembly is a process in which a disordered system of pre-existing components forms an organized structure or pattern as a consequence of specific, local interactions among the components themselves, without external direction. When the ...
is emerging as a new strategy in the chemical synthesis of high performance biomaterials.
Physical properties
Physical properties of elements and compounds that provide conclusive evidence of chemical composition include odor, color, volume, density (mass per unit volume), melting point, boiling point, heat capacity, physical form and shape at room temperature (solid, liquid or gas; cubic, trigonal crystals, etc.), hardness, porosity, index of refraction and many others. This section discusses some physical properties of materials in the solid state.Mechanical
 The mechanical properties of materials describe characteristics such as their
The mechanical properties of materials describe characteristics such as their strength
Strength may refer to:
Physical strength
*Physical strength, as in people or animals
* Hysterical strength, extreme strength occurring when people are in life-and-death situations
*Superhuman strength, great physical strength far above human c ...
and resistance to deformation. For example, steel beams are used in construction because of their high strength, meaning that they neither break nor bend significantly under the applied load.
Mechanical properties include elasticity and plasticity, tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials t ...
, compressive strength, shear strength
In engineering, shear strength is the strength of a material or component against the type of yield or structural failure when the material or component fails in shear. A shear load is a force that tends to produce a sliding failure on a materi ...
, fracture toughness, ductility
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile str ...
(low in brittle materials), and indentation hardness
Indentation hardness tests are used in mechanical engineering to determine the hardness of a material to deformation. Several such tests exist, wherein the examined material is indented until an impression is formed; these tests can be performed on ...
. Solid mechanics
Solid mechanics, also known as mechanics of solids, is the branch of continuum mechanics that studies the behavior of solid materials, especially their motion and deformation under the action of forces, temperature changes, phase changes, and ...
is the study of the behavior of solid matter under external actions such as external forces and temperature changes.
A solid does not exhibit macroscopic flow, as fluids do. Any degree of departure from its original shape is called deformation
Deformation can refer to:
* Deformation (engineering), changes in an object's shape or form due to the application of a force or forces.
** Deformation (physics), such changes considered and analyzed as displacements of continuum bodies.
* Defor ...
. The proportion of deformation to original size is called strain. If the applied stress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
is sufficiently low, almost all solid materials behave in such a way that the strain is directly proportional to the stress (Hooke's law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance () scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of ...
). The coefficient of the proportion is called the modulus of elasticity
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity) is the unit of measurement of an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it. The elastic modulus of an object is ...
or Young's modulus
Young's modulus E, the Young modulus, or the modulus of elasticity in tension or compression (i.e., negative tension), is a mechanical property that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness of a solid material when the force is applied le ...
. This region of deformation is known as the linearly elastic region. Three models can describe how a solid responds to an applied stress:
* Elasticity – When an applied stress is removed, the material returns to its undeformed state.
*Viscoelasticity
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist shear flow and strain linearl ...
– These are materials that behave elastically, but also have damping
Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. In physical systems, damping is produced by processes that dissipate the energy stored in the oscillation. Examples in ...
. When the applied stress is removed, work has to be done against the damping effects and is converted to heat within the material. This results in a hysteresis loop
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of ...
in the stress–strain curve. This implies that the mechanical response has a time-dependence.
* Plasticity – Materials that behave elastically generally do so when the applied stress is less than a yield value. When the stress is greater than the yield stress, the material behaves plastically and does not return to its previous state. That is, irreversible plastic deformation (or viscous flow) occurs after yield that is permanent.
Many materials become weaker at high temperatures. Materials that retain their strength at high temperatures, called refractory materials
In materials science, a refractory material or refractory is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat, pressure, or chemical attack, and retains strength and form at high temperatures. Refractories are polycrystalline, polyphase, ...
, are useful for many purposes. For example, glass-ceramic
Glass-ceramics are polycrystalline materials produced through controlled crystallization of base glass, producing a fine uniform dispersion of crystals throughout the bulk material. Crystallization is accomplished by subjecting suitable glasses to ...
s have become extremely useful for countertop cooking, as they exhibit excellent mechanical properties and can sustain repeated and quick temperature changes up to 1000 °C.
In the aerospace industry, high performance materials used in the design of aircraft and/or spacecraft exteriors must have a high resistance to thermal shock. Thus, synthetic fibers spun out of organic polymers and polymer/ceramic/metal composite materials and fiber-reinforced polymers are now being designed with this purpose in mind.
Thermal
 Because solids have
Because solids have thermal energy
The term "thermal energy" is used loosely in various contexts in physics and engineering. It can refer to several different well-defined physical concepts. These include the internal energy or enthalpy of a body of matter and radiation; heat, de ...
, their atoms vibrate about fixed mean positions within the ordered (or disordered) lattice. The spectrum of lattice vibrations in a crystalline or glassy network provides the foundation for the kinetic theory of solids
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phonon is an excited state in the quantum mechanical ...
. This motion occurs at the atomic level, and thus cannot be observed or detected without highly specialized equipment, such as that used in spectroscopy.
Thermal properties of solids include thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
, which is the property of a material that indicates its ability to conduct heat. Solids also have a specific heat capacity
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat t ...
, which is the capacity of a material to store energy in the form of heat (or thermal lattice vibrations).
Electrical
Electrical properties include both electrical resistivity and conductivity,dielectric strength
In physics, the term dielectric strength has the following meanings:
*for a pure electrically insulating material, the maximum electric field that the material can withstand under ideal conditions without undergoing electrical breakdown and beco ...
, electromagnetic permeability, and permittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter ''ε'' (epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in ...
. Electrical conductors such as metals and alloys are contrasted with electrical insulators such as glasses and ceramics. Semiconductors behave somewhere in between. Whereas conductivity in metals is caused by electrons, both electrons and holes contribute to current in semiconductors. Alternatively, ions support electric current in ionic conductors.
Many materials also exhibit superconductivity at low temperatures; they include metallic elements such as tin and aluminium, various metallic alloys, some heavily doped semiconductors, and certain ceramics. The electrical resistivity of most electrical (metallic) conductors generally decreases gradually as the temperature is lowered, but remains finite. In a superconductor, however, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing in a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.
A dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the mate ...
, or electrical insulator, is a substance that is highly resistant to the flow of electric current. A dielectric, such as plastic, tends to concentrate an applied electric field within itself, which property is used in capacitors. A capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of ...
is an electrical device that can store energy in the electric field between a pair of closely spaced conductors (called 'plates'). When voltage is applied to the capacitor, electric charges of equal magnitude, but opposite polarity, build up on each plate. Capacitors are used in electrical circuits as energy-storage devices, as well as in electronic filters to differentiate between high-frequency and low-frequency signals.
Electro-mechanical
Piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The word ''p ...
is the ability of crystals to generate a voltage in response to an applied mechanical stress. The piezoelectric effect is reversible in that piezoelectric crystals, when subjected to an externally applied voltage, can change shape by a small amount. Polymer materials like rubber, wool, hair, wood fiber, and silk often behave as electret
An electret (formed as a portmanteau of ''electr-'' from "electricity" and ''-et'' from "magnet") is a dielectric material that has a quasi-permanent electric charge or dipole polarization (electrostatics), polarisation. An electret generates int ...
s. For example, the polymer polyvinylidene fluoride
Polyvinylidene fluoride or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive thermoplastic fluoropolymer produced by the polymerization of vinylidene difluoride.
PVDF is a specialty plastic used in applications requiring the highest pur ...
(PVDF) exhibits a piezoelectric response several times larger than the traditional piezoelectric material quartz (crystalline SiO2). The deformation (~0.1%) lends itself to useful technical applications such as high-voltage sources, loudspeakers, lasers, as well as chemical, biological, and acousto-optic sensors and/or transducers.
Optical
Materials can transmit (e.g. glass) or reflect (e.g. metals) visible light. Many materials will transmit some wavelengths while blocking others. For example, window glass is transparent tovisible light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
, but much less so to most of the frequencies of ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
light that cause sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and animals include: red or reddish skin that is h ...
. This property is used for frequency-selective optical filters, which can alter the color of incident light.
For some purposes, both the optical and mechanical properties of a material can be of interest. For example, the sensors on an infrared homing ("heat-seeking") missile must be protected by a cover that is transparent to infrared radiation
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
. The current material of choice for high-speed infrared-guided missile domes is single-crystal sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sa ...
. The optical transmission of sapphire does not actually extend to cover the entire mid-infrared range (3–5 µm), but starts to drop off at wavelengths greater than approximately 4.5 µm at room temperature. While the strength of sapphire is better than that of other available mid-range infrared dome materials at room temperature, it weakens above 600 °C. A long-standing trade-off exists between optical bandpass and mechanical durability; new materials such as transparent ceramics
Many ceramic materials, both glassy and crystalline, have found use as optically transparent materials in various forms from bulk solid-state components to high surface area forms such as thin films, coatings, and fibers. Such devices have found ...
or optical nanocomposites may provide improved performance.
Guided lightwave transmission involves the field of fiber optics and the ability of certain glasses to transmit, simultaneously and with low loss of intensity, a range of frequencies (multi-mode optical waveguides) with little interference between them. Optical waveguides are used as components in integrated optical circuits or as the transmission medium in optical communication systems.
Opto-electronic
A solar cell or photovoltaic cell is a device that converts light energy into electrical energy. Fundamentally, the device needs to fulfill only two functions: photo-generation of charge carriers (electrons and holes) in a light-absorbing material, and separation of the charge carriers to a conductive contact that will transmit the electricity (simply put, carrying electrons off through a metal contact into an external circuit). This conversion is called thephotoelectric effect
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, and solid sta ...
, and the field of research related to solar cells is known as photovoltaics.
Solar cells have many applications. They have long been used in situations where electrical power from the grid is unavailable, such as in remote area power systems, Earth-orbiting satellites and space probes, handheld calculators, wrist watches, remote radiotelephones and water pumping applications. More recently, they are starting to be used in assemblies of solar modules (photovoltaic arrays) connected to the electricity grid through an inverter, that is not to act as a sole supply but as an additional electricity source.
All solar cells require a light absorbing material contained within the cell structure to absorb photons and generate electrons via the photovoltaic effect
The photovoltaic effect is the generation of voltage and electric current in a material upon exposure to light. It is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
The photovoltaic effect is closely related to the photoelectric effect. For both phenomena, ...
. The materials used in solar cells tend to have the property of preferentially absorbing the wavelengths of solar light that reach the earth surface. Some solar cells are optimized for light absorption beyond Earth's atmosphere, as well.
References
External links
{{Portal bar, Science, Chemistry, Water, Underwater diving , Outer space, Physics, Geophysics *Solid Articles containing video clips