|
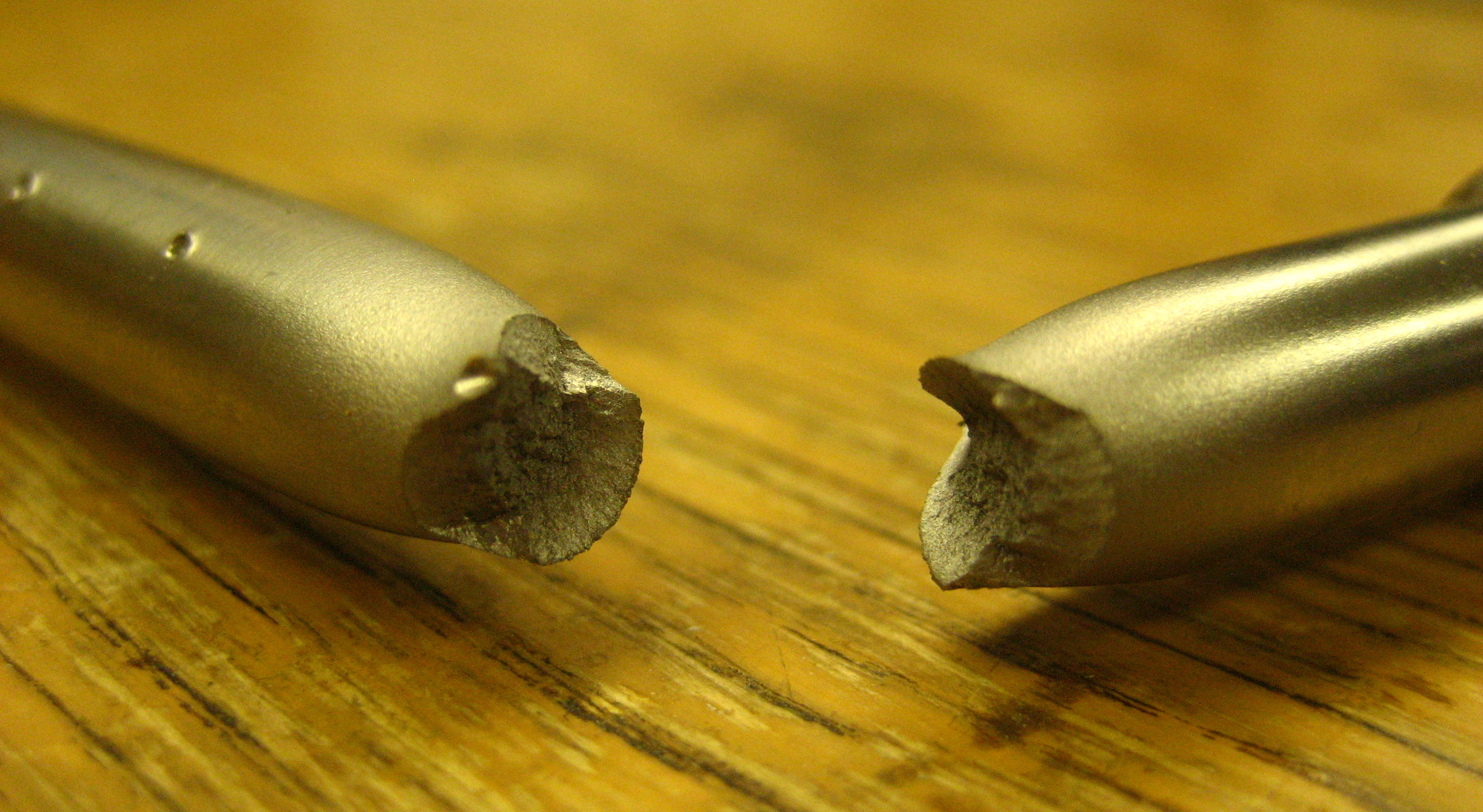
Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is a type of rapidly transient mechanical load. By definition, it is a mechanical load caused by a rapid change of temperature of a certain point. It can be also extended to the case of a thermal gradient, which makes different parts of an object expand by different amounts. This differential expansion can be more directly understood in terms of strain, than in terms of stress, as it is shown in the following. At some point, this stress can exceed the tensile strength of the material, causing a crack to form. If nothing stops this crack from propagating through the material, it will cause the object's structure to fail. Failure due to thermal shock can be prevented by: # Reducing the thermal gradient seen by the object, by changing its temperature more slowly or increasing the material's thermal conductivity # Reducing the material's coefficient of thermal expansion # Increasing its strength # Introducing built-in compressive stress, as for example in tempered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Gradient
A temperature gradient is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the temperature changes the most rapidly around a particular location. The temperature gradient is a Dimensional analysis, dimensional quantity expressed in Units of measurement, units of degrees (on a particular temperature scale) per unit length. The International System of Units, SI unit is kelvin per meter (K/m). Temperature gradients in the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere are important in the atmospheric sciences (meteorology, climatology and related fields). Mathematical description Assuming that the temperature ''T'' is an intensive quantity, i.e., a single-valued, Continuous function, continuous and Derivative, differentiable Function (mathematics), function of three-dimensional space (often called a scalar field), i.e., that :T=T(x,y,z) where ''x'', ''y'' and ''z'' are the Cartesian coordinate system, coordinates of the location of interest, then the temperature gradient is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolated as a metal in 1783. Its important ores include scheelite and wolframite, the latter lending the element its alternate name. The free element is remarkable for its robustness, especially the fact that it has the highest melting point of all known elements barring carbon (which sublimes at normal pressure), melting at . It also has the highest boiling point, at . Its density is , comparable with that of uranium and gold, and much higher (about 1.7 times) than that of lead. Polycrystalline tungsten is an intrinsically brittle and hard material (under standard conditions, when uncombined), making it difficult to work. However, pure single-crystalline tungsten is more ductile and can be cut with a hard-steel hacksaw. Tungsten occurs in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displacement develops perpendicular to the surface, it is called a normal tensile crack or simply a crack; if a displacement develops tangentially, it is called a shear crack, slip band or dislocation. Brittle fractures occur with no apparent deformation before fracture. Ductile fractures occur after visible deformation. Fracture strength, or breaking strength, is the stress when a specimen fails or fractures. The detailed understanding of how a fracture occurs and develops in materials is the object of fracture mechanics. Strength Fracture strength, also known as breaking strength, is the stress at which a specimen fails via fracture. This is usually determined for a given specimen by a tensile test, which charts the stress–strain cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yield (engineering)
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed. Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and non-reversible and is known as plastic deformation. The yield strength or yield stress is a material property and is the stress corresponding to the yield point at which the material begins to deform plastically. The yield strength is often used to determine the maximum allowable load in a mechanical component, since it represents the upper limit to forces that can be applied without producing permanent deformation. In some materials, such as aluminium, there is a gradual onset of non-linear behavior, making the precise yield point difficult to determine. In such a case, the offset yiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damping Ratio
Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. In physical systems, damping is produced by processes that dissipate the energy stored in the oscillation. Examples include viscous drag (a liquid's viscosity can hinder an oscillatory system, causing it to slow down; see viscous damping) in mechanical systems, resistance in electronic oscillators, and absorption and scattering of light in optical oscillators. Damping not based on energy loss can be important in other oscillating systems such as those that occur in biological systems and bikes (ex. Suspension (mechanics)). Not to be confused with friction, which is a dissipative force acting on a system. Friction can cause or be a factor of damping. The damping ratio is a dimensionless measure describing how oscillations in a system decay after a disturbance. Many systems exhibit oscillatory behavior when they are disturbed from their position of sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poisson's Ratio
In materials science and solid mechanics, Poisson's ratio \nu ( nu) is a measure of the Poisson effect, the deformation (expansion or contraction) of a material in directions perpendicular to the specific direction of loading. The value of Poisson's ratio is the negative of the ratio of transverse strain to axial strain. For small values of these changes, \nu is the amount of transversal elongation divided by the amount of axial compression. Most materials have Poisson's ratio values ranging between 0.0 and 0.5. For soft materials, such as rubber, where the bulk modulus is much higher than the shear modulus, Poisson's ratio is near 0.5. For open-cell polymer foams, Poisson's ratio is near zero, since the cells tend to collapse in compression. Many typical solids have Poisson's ratios in the range of 0.2–0.3. The ratio is named after the French mathematician and physicist Siméon Poisson. Origin Poisson's ratio is a measure of the Poisson effect, the phenomenon in which a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Modulus
In materials science, shear modulus or modulus of rigidity, denoted by ''G'', or sometimes ''S'' or ''μ'', is a measure of the elastic shear stiffness of a material and is defined as the ratio of shear stress to the shear strain: :G \ \stackrel\ \frac = \frac = \frac where :\tau_ = F/A \, = shear stress :F is the force which acts :A is the area on which the force acts :\gamma_ = shear strain. In engineering :=\Delta x/l = \tan \theta , elsewhere := \theta :\Delta x is the transverse displacement :l is the initial length of the area. The derived SI unit of shear modulus is the pascal (Pa), although it is usually expressed in gigapascals (GPa) or in thousand pounds per square inch (ksi). Its dimensional form is M1L−1T−2, replacing ''force'' by ''mass'' times ''acceleration''. Explanation The shear modulus is one of several quantities for measuring the stiffness of materials. All of them arise in the generalized Hooke's law: * Young's modulus ''E'' describes the mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impulse Excitation Technique
The impulse excitation technique (IET) is a non-destructive material characterization technique to determine the elastic properties and internal friction of a material of interest. It measures the resonant frequencies in order to calculate the Young's modulus, shear modulus, Poisson's ratio and internal friction of predefined shapes like rectangular bars, cylindrical rods and disc shaped samples. The measurements can be performed at room temperature or at elevated temperatures (up to 1700 °C) under different atmospheres. The measurement principle is based on tapping the sample with a small projectile and recording the induced vibration signal with a piezoelectric sensor, microphone, laser vibrometer or accelerometer. To optimize the results a microphone or a laser vibrometer can be used as there is no contact between the test-piece and the sensor. Laser vibrometers are preferred to measure signals in vacuum. Afterwards, the acquired vibration signal in the time domain is conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon composite, or just carbon, are extremely strong and light fiber-reinforced plastics that contain carbon fibers. CFRPs can be expensive to produce, but are commonly used wherever high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness (rigidity) are required, such as aerospace, superstructures of ships, automotive, civil engineering, sports equipment, and an increasing number of consumer and technical applications. The binding polymer is often a thermoset resin such as epoxy, but other thermoset or thermoplastic polymers, such as polyester, vinyl ester, or nylon, are sometimes used. The properties of the final CFRP product can be affected by the type of additives introduced to the binding matrix (resin). The most common additive is silica, but other addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large scale (300 kton/year, in 1989) for uses in pencils, lubricants, and electrodes. Under high pressures and temperatures it converts to diamond. It is a weak conductor of heat and electricity. Types and varieties Natural graphite The principal types of natural graphite, each occurring in different types of ore deposits, are * Crystalline small flakes of graphite (or flake graphite) occurs as isolated, flat, plate-like particles with hexagonal edges if unbroken. When broken the edges can be irregular or angular; * Amorphous graphite: very fine flake graphite is sometimes called amorphous; * Lump graphite (or vein graphite) occurs in fissure veins or fractures and appears as massive platy intergrowths of fibrous or acicular crystalline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corrosion resistance, resistance to corrosion results from the chromium, which forms a Passivation (chemistry), passive film that can protect the material and self-healing material, self-heal in the presence of oxygen. The alloy's properties, such as luster and resistance to corrosion, are useful in many applications. Stainless steel can be rolled into Sheet metal, sheets, plates, bars, wire, and tubing. These can be used in cookware, cutlery, surgical instruments, major appliances, vehicles, construction material in large buildings, industrial equipment (e.g., in paper mills, chemical plants, water treatment), and storage tanks and tankers for chemicals and food products. The biological cleanability of stainless steel is superior to both alumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |