Siracusa, Italy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Syracuse ( ; it, Siracusa ; scn, Sarausa ), ; grc-att, ΣÏ
ÏάκοÏ
Ïαι, Syrákousai, ; grc-dor, ΣÏ
ÏάκοÏαι, SyrÄÌkosai, ; grc-x-medieval, ΣÏ
ÏακοῊÏαι, Syrakoûsai, ; el, label= Modern Greek, ΣÏ
ÏακοÏÏεÏ, Syrakoúses, . is a historic city on the Italian island of Sicily, the capital of the Italian province of Syracuse. The city is notable for its rich Greek and Roman history, culture, amphitheatres, architecture, and as the birthplace of the pre-eminent mathematician and engineer



 Syracuse and its surrounding area have been inhabited since ancient times, as shown by the findings in the villages of Stentinello, Ognina, Plemmirio, Matrensa, Cozzo Pantano and ''Thapsos'', which already had a relationship with
Syracuse and its surrounding area have been inhabited since ancient times, as shown by the findings in the villages of Stentinello, Ognina, Plemmirio, Matrensa, Cozzo Pantano and ''Thapsos'', which already had a relationship with
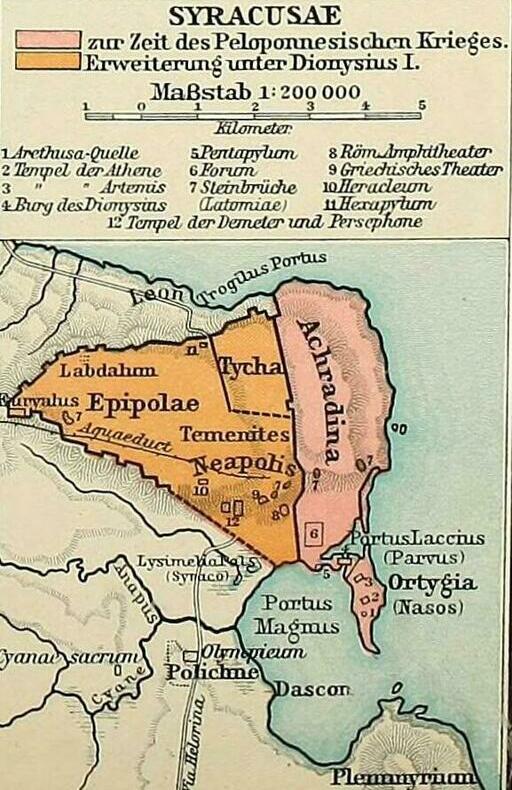 The descendants of the first colonists, called ''Gamoroi'', held power until they were expelled by the lower class of the city assisted by Cyllyrians, identified as enslaved natives similar in status to the helots of Sparta. The former, however, returned to power in 485 BC, thanks to the help of Gelo, ruler of Gela. Gelo himself became the despot of the city, and moved many inhabitants of Gela, Kamarina and
The descendants of the first colonists, called ''Gamoroi'', held power until they were expelled by the lower class of the city assisted by Cyllyrians, identified as enslaved natives similar in status to the helots of Sparta. The former, however, returned to power in 485 BC, thanks to the help of Gelo, ruler of Gela. Gelo himself became the despot of the city, and moved many inhabitants of Gela, Kamarina and
 After Timoleon's death the struggle among the city's parties restarted and ended with the rise of another tyrant, Agathocles, who seized power with a coup in 317 BC. He resumed the war against Carthage, with alternate fortunes. He was besieged in Syracuse by the Carthaginians in 311 BC, but he escaped from the city with a small fleet. He scored a moral success, bringing the war to the Carthaginians' native African soil, inflicting heavy losses to the enemy. The defenders of Syracuse destroyed the Carthaginian army which besieged them. However, Agathocles was eventually defeated in Africa as well. The war ended with another treaty of peace which did not prevent the Carthaginians from interfering in the politics of Syracuse after the death of Agathocles (289 BC). They laid siege to Syracuse for the fourth and last time in 278 BC. They retreated at the arrival of king Pyrrhus of Epirus, whom Syracuse had asked for help. After a brief period under the rule of Epirus,
After Timoleon's death the struggle among the city's parties restarted and ended with the rise of another tyrant, Agathocles, who seized power with a coup in 317 BC. He resumed the war against Carthage, with alternate fortunes. He was besieged in Syracuse by the Carthaginians in 311 BC, but he escaped from the city with a small fleet. He scored a moral success, bringing the war to the Carthaginians' native African soil, inflicting heavy losses to the enemy. The defenders of Syracuse destroyed the Carthaginian army which besieged them. However, Agathocles was eventually defeated in Africa as well. The war ended with another treaty of peace which did not prevent the Carthaginians from interfering in the politics of Syracuse after the death of Agathocles (289 BC). They laid siege to Syracuse for the fourth and last time in 278 BC. They retreated at the arrival of king Pyrrhus of Epirus, whom Syracuse had asked for help. After a brief period under the rule of Epirus,



 Though declining slowly through the years, Syracuse maintained the status of capital of the Roman government of Sicily and seat of the praetor. It remained an important port for trade between the Eastern and the Western parts of the Empire. Christianity spread in the city through the efforts of
Though declining slowly through the years, Syracuse maintained the status of capital of the Roman government of Sicily and seat of the praetor. It remained an important port for trade between the Eastern and the Western parts of the Empire. Christianity spread in the city through the efforts of
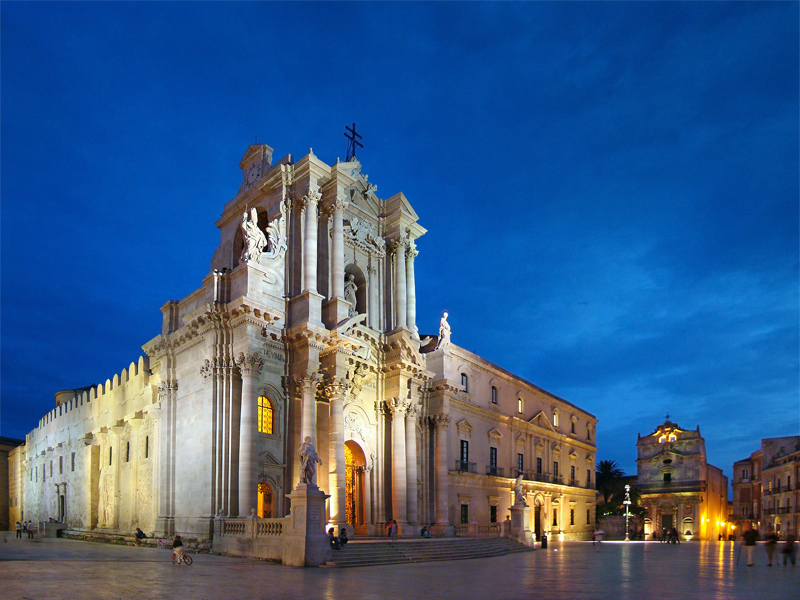
 * Cathedral of Syracuse ( it, Duomo): built by bishop Zosimo in the 7th-century over the great ''Temple of Athena'' (5th century BC), on Ortygia island. This was a
* Cathedral of Syracuse ( it, Duomo): built by bishop Zosimo in the 7th-century over the great ''Temple of Athena'' (5th century BC), on Ortygia island. This was a
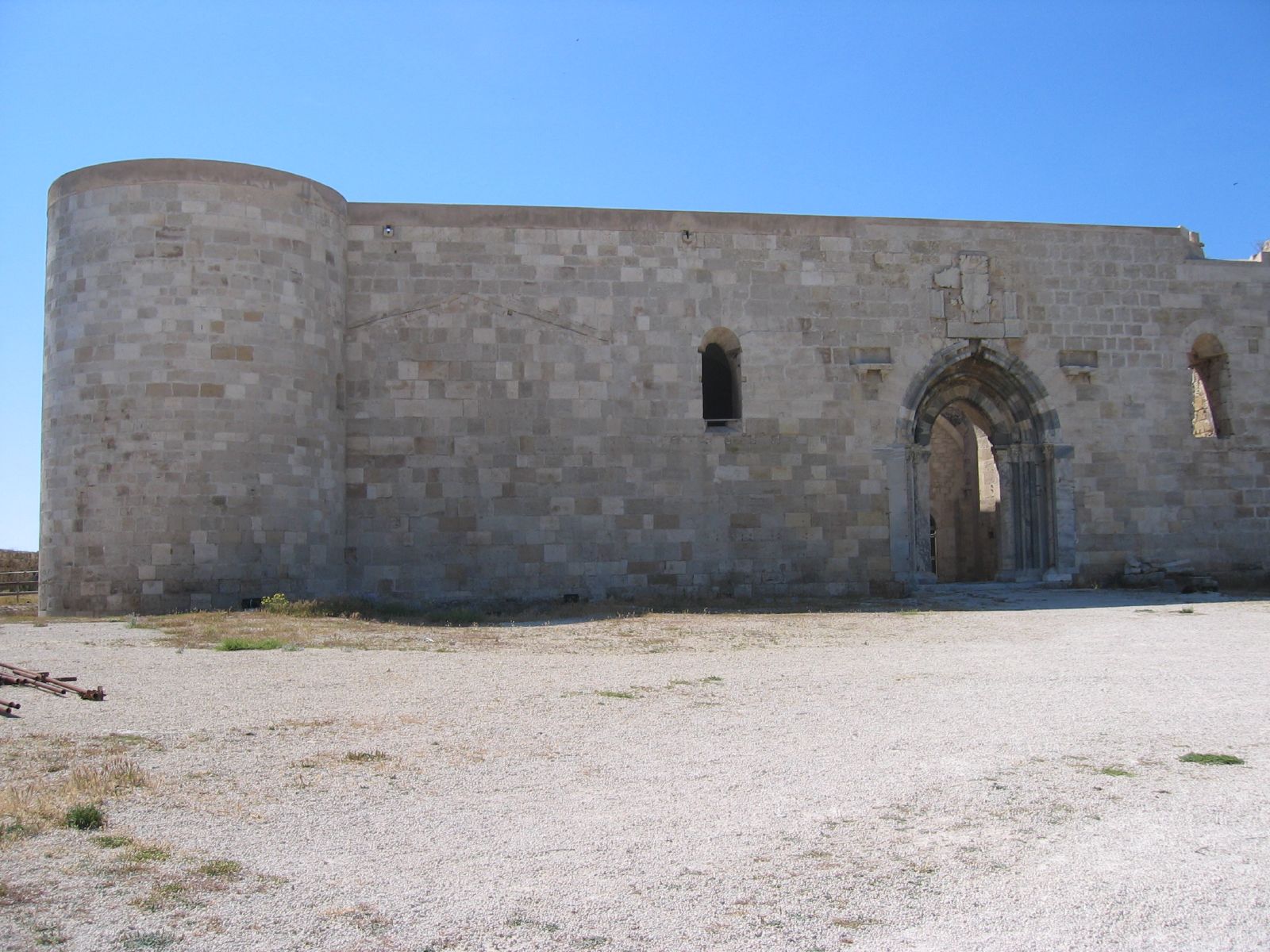


 * Castello Maniace, constructed between 1232 and 1240, is an example of the military architecture of Frederick II's reign. It is a square structure with circular towers at each of the four corners. The most striking feature is the pointed portal, decorated with polychrome marbles.
* ''Archaeological Museum'' with collections including findings from the mid-Bronze Age to 5th century BC.
* ''Palazzo Lanza Buccheri'' (16th century).
* '' Palazzo Bellomo'' (12th century), which contains an art museum that houses Antonello da Messina's ''
* Castello Maniace, constructed between 1232 and 1240, is an example of the military architecture of Frederick II's reign. It is a square structure with circular towers at each of the four corners. The most striking feature is the pointed portal, decorated with polychrome marbles.
* ''Archaeological Museum'' with collections including findings from the mid-Bronze Age to 5th century BC.
* ''Palazzo Lanza Buccheri'' (16th century).
* '' Palazzo Bellomo'' (12th century), which contains an art museum that houses Antonello da Messina's ''
Coins from ancient Syracuse and Sicily
Photos of Ortigia in Syracuse
{{Authority control 8th-century BC establishments in Italy Archaeological sites in Sicily Cities and towns in Sicily Coastal towns in Sicily Corinthian colonies Dorian colonies in Magna Graecia Mediterranean port cities and towns in Italy Municipalities of the Province of Syracuse Populated places established in the 8th century BC Sicilian Baroque World Heritage Sites in Italy Greek city-states
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists ...
. This 2,700-year-old city played a key role in ancient times, when it was one of the major powers of the Mediterranean world. Syracuse is located in the southeast corner of the island of Sicily, next to the Gulf of Syracuse beside the Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea ( el, ÎÏΜιο Î ÎλαγοÏ, ''Iónio Pélagos'' ; it, Mar Ionio ; al, Deti Jon ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including C ...
. It is situated in a drastic rise of land with depths being close to the city offshore although the city itself is generally not so hilly in comparison.
The city was founded by Ancient Greek Corinthians and Teneans and became a very powerful city-state. Syracuse was allied with Sparta and Corinth and exerted influence over the entirety of Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia (, ; , , grc, Îεγάλη áŒÎ»Î»Î¬Ï, ', it, Magna Grecia) was the name given by the Romans to the coastal areas of Southern Italy in the present-day Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania and Sicily; these re ...
, of which it was the most important city. Described by Cicero as "the greatest Greek city and the most beautiful of them all", it equaled Athens in size during the fifth century BC. It later became part of the Roman Republic and the Byzantine Empire. Under Emperor Constans II
Constans II ( grc-gre, ÎÏÎœÏÏαÏ, KÅnstas; 7 November 630 â 15 July 668), nicknamed "the Bearded" ( la, Pogonatus; grc-gre, ᜠΠÏγÏΜ៶ÏοÏ, ho PÅgÅnãtos), was the Eastern Roman emperor from 641 to 668. Constans was the last ...
, it served as the capital of the Byzantine Empire (663â669). Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
later overtook it in importance, as the capital of the Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
. Eventually the kingdom would be united with the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
to form the Two Sicilies until the Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
of 1860.
In the modern day, the city is listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site along with the Necropolis of Pantalica. In the central area, the city itself has a population of around 125,000 people. Syracuse is mentioned in the Bible in the Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Î ÏÎ¬ÎŸÎµÎ¹Ï áŒÏοÏÏÏλÏÎœ, ''Práxeis ApostólÅn''; la, ActÅ«s ApostolÅrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its messag ...
book at 28:12 as Paul stayed there. The patron saint of the city is Saint Lucy; she was born in Syracuse and her feast day, Saint Lucy's Day, is celebrated on 13 December.
History
Archaic period



 Syracuse and its surrounding area have been inhabited since ancient times, as shown by the findings in the villages of Stentinello, Ognina, Plemmirio, Matrensa, Cozzo Pantano and ''Thapsos'', which already had a relationship with
Syracuse and its surrounding area have been inhabited since ancient times, as shown by the findings in the villages of Stentinello, Ognina, Plemmirio, Matrensa, Cozzo Pantano and ''Thapsos'', which already had a relationship with Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in ...
.
Syracuse was founded in 734 or 733 BC by Greek settlers from Corinth and Tenea, led by the ''oecist
The ''oikistes'' ( gr, οጰκιÏÏήÏ), often anglicized as oekist or oecist, was the individual chosen by an ancient Greek polis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, ÏÏλιÏ, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancien ...
'' (colonizer) Archias. There are many attested variants of the name of the city including ''Syrakousai'', ''Syrakosai'' and ''SyrakÅ''. The most acceptable theory is that the Phoenicians called it Sour-ha-Koussim, which means "Stone of the seagulls" from which would come the name of Syracuse. A possible origin of the city's name was given by Vibius Sequester citing first Stephanus Byzantius
Stephanus or Stephan of Byzantium ( la, Stephanus Byzantinus; grc-gre, ΣÏÎÏÎ±ÎœÎ¿Ï ÎÏ
ζάΜÏιοÏ, ''Stéphanos Byzántios''; centuryAD), was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethni ...
''Ethnika'' 592.18â21,593.1â8, i.e. Stephanus Byzantinus
Stephanus or Stephan of Byzantium ( la, Stephanus Byzantinus; grc-gre, ΣÏÎÏÎ±ÎœÎ¿Ï ÎÏ
ζάΜÏιοÏ, ''Stéphanos Byzántios''; centuryAD), was a Byzantine grammarian and the author of an important geographical dictionary entitled ''Ethni ...
' ''Ethnika'' (kat'epitomen), lemma in that there was a Syracusian marsh () called ''Syrako'' and secondly Marcian's ''Periegesis'' wherein Archias gave the city the name of a nearby marsh; hence one gets ''Syrako'' (and thereby ''Syrakousai'' and other variants) for the name of Syracuse, a name also attested by Epicharmus. The settlement of Syracuse was a planned event, as a strong central leader, Arkhias the aristocrat, laid out how property would be divided up for the settlers, as well as plans for how the streets of the settlement should be arranged, and how wide they should be. The nucleus of the ancient city was the small island of Ortygia. The settlers found the land fertile and the native tribes to be reasonably well-disposed to their presence. The city grew and prospered, and for some time stood as the most powerful Greek city anywhere in the Mediterranean. Colonies were founded at Akrai (664 BC), Kasmenai (643 BC), Akrillai (7th century BC), Helorus
Helorus, Heloros, Helorum, or Elorus (Greek: or , Ptol., Steph. B. or , Scyl.; it, Eloro), was an ancient Greek city of Sicily, situated near the east coast, about 40 km south of Syracuse and on the banks of the river of the same name. ...
(7th century BC) and Kamarina (598 BC).
Classical period
 The descendants of the first colonists, called ''Gamoroi'', held power until they were expelled by the lower class of the city assisted by Cyllyrians, identified as enslaved natives similar in status to the helots of Sparta. The former, however, returned to power in 485 BC, thanks to the help of Gelo, ruler of Gela. Gelo himself became the despot of the city, and moved many inhabitants of Gela, Kamarina and
The descendants of the first colonists, called ''Gamoroi'', held power until they were expelled by the lower class of the city assisted by Cyllyrians, identified as enslaved natives similar in status to the helots of Sparta. The former, however, returned to power in 485 BC, thanks to the help of Gelo, ruler of Gela. Gelo himself became the despot of the city, and moved many inhabitants of Gela, Kamarina and Megara
Megara (; el, ÎÎγαÏα, ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, befo ...
to Syracuse, building the new quarters of Tyche and Neapolis outside the walls. His program of new constructions included a new theatre, designed by Damocopos, which gave the city a flourishing cultural life: this in turn attracted personalities as Aeschylus, Ario of Methymna and Eumelos of Corinth. The enlarged power of Syracuse made unavoidable the clash against the Carthaginians, who ruled western Sicily. In the Battle of Himera, Gelo, who had allied with Theron of Agrigento, decisively defeated the African force led by Hamilcar. A temple dedicated to Athena (on the site of today's Cathedral), was erected in the city to commemorate the event.
Syracuse grew considerably during this time. Its walls encircled in the fifth century, but as early as the 470s BC the inhabitants started building outside the walls. The complete population of its territory approximately numbered 250,000 in 415 BC and the population size of the city itself was probably similar to Athens.
Gelo was succeeded by his brother Hiero, who fought against the Etruscans at Cumae in 474 BC. His rule was eulogized by poets like Simonides of Ceos, Bacchylides and Pindar, who visited his court. A democratic regime was introduced by Thrasybulos (467 BC). The city continued to expand in Sicily, fighting against the rebellious Siculi
The Sicels (; la, Siculi; grc, wikt:Σικελοί, Σικελοί ''Sikeloi'') were an Italic people, Italic tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily during the Iron Age. Their neighbours to the west were the Sicani. The Sicels gave Sicily the na ...
, and on the Tyrrhenian Sea, making expeditions up to Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
and Elba. In the late 5th century BC, Syracuse found itself at war with Athens, which sought more resources to fight the Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431â404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
. The Syracusans enlisted the aid of a general from Sparta, Athens' foe in the war, to defeat the Athenians, destroy their ships, and leave them to starve on the island (see Sicilian Expedition). In 401 BC, Syracuse contributed a force of 300 hoplites and a general to Cyrus the Younger
Cyrus the Younger ( peo, ð€ð¢ðœð¢ð ''KÅ«ruÅ¡''; grc-gre, Îá¿ŠÏÎ¿Ï ; died 401 BC) was an Achaemenid prince and general. He ruled as satrap of Lydia and Ionia from 408 to 401 BC. Son of Darius II and Parysatis, he died in 401 BC i ...
's Army of the Ten Thousand.
Then in the early 4th century BC, the tyrant Dionysius the Elder was again at war against Carthage and, although losing Gela and Camarina, kept that power from capturing the whole of Sicily. After the end of the conflict Dionysius built a massive fortress on Ortygia and 22 km-long walls around all of Syracuse. Another period of expansion saw the destruction of Naxos, Catania
Catania (, , Sicilian and ) is the second largest municipality in Sicily, after Palermo. Despite its reputation as the second city of the island, Catania is the largest Sicilian conurbation, among the largest in Italy, as evidenced also by ...
and Lentini; then Syracuse entered again in war against Carthage (397 BC). After various changes of fortune, the Carthaginians managed to besiege Syracuse itself, but were eventually pushed back by a pestilence. A treaty in 392 BC allowed Syracuse to enlarge further its possessions, founding the cities of Adranon, Tyndarion and Tauromenos, and conquering Rhegion on the continent. In the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ...
, to facilitate trade, Dionysius the Elder founded Ancona, Adria and Issa. Apart from his battle deeds, Dionysius was famous as a patron of art, and Plato himself visited Syracuse several times, where Dionysius, offended by Plato's daring to disagree with the king, imprisoned the philosopher and sold him into slavery.
His successor was Dionysius the Younger, who was however expelled by Dion in 356 BC. But the latter's despotic rule led in turn to his expulsion, and Dionysius reclaimed his throne in 347 BC. Dionysius was besieged in Syracuse by the Syracusan general Hicetas in 344 BC. The following year the Corinthian Timoleon installed a democratic regime in the city after he exiled Dionysius and defeated Hicetas. The long series of internal struggles had weakened Syracuse's power on the island, and Timoleon tried to remedy this, defeating the Carthaginians in the Battle of the Crimissus (339 BC).
Hellenistic period
 After Timoleon's death the struggle among the city's parties restarted and ended with the rise of another tyrant, Agathocles, who seized power with a coup in 317 BC. He resumed the war against Carthage, with alternate fortunes. He was besieged in Syracuse by the Carthaginians in 311 BC, but he escaped from the city with a small fleet. He scored a moral success, bringing the war to the Carthaginians' native African soil, inflicting heavy losses to the enemy. The defenders of Syracuse destroyed the Carthaginian army which besieged them. However, Agathocles was eventually defeated in Africa as well. The war ended with another treaty of peace which did not prevent the Carthaginians from interfering in the politics of Syracuse after the death of Agathocles (289 BC). They laid siege to Syracuse for the fourth and last time in 278 BC. They retreated at the arrival of king Pyrrhus of Epirus, whom Syracuse had asked for help. After a brief period under the rule of Epirus,
After Timoleon's death the struggle among the city's parties restarted and ended with the rise of another tyrant, Agathocles, who seized power with a coup in 317 BC. He resumed the war against Carthage, with alternate fortunes. He was besieged in Syracuse by the Carthaginians in 311 BC, but he escaped from the city with a small fleet. He scored a moral success, bringing the war to the Carthaginians' native African soil, inflicting heavy losses to the enemy. The defenders of Syracuse destroyed the Carthaginian army which besieged them. However, Agathocles was eventually defeated in Africa as well. The war ended with another treaty of peace which did not prevent the Carthaginians from interfering in the politics of Syracuse after the death of Agathocles (289 BC). They laid siege to Syracuse for the fourth and last time in 278 BC. They retreated at the arrival of king Pyrrhus of Epirus, whom Syracuse had asked for help. After a brief period under the rule of Epirus, Hiero II
Hiero II ( el, ጹÎÏÏÎœ ÎÎ; c. 308 BC â 215 BC) was the Greek tyrant of Syracuse from 275 to 215 BC, and the illegitimate son of a Syracusan noble, Hierocles, who claimed descent from Gelon. He was a former general of Pyrrhus of Epirus a ...
seized power in 275 BC.
Hiero inaugurated a period of 50 years of peace and prosperity, in which Syracuse became one of the most renowned capitals of Antiquity. He issued the so-called '' Lex Hieronica'', which was later adopted by the Romans for their administration of Sicily; he also had the theatre enlarged and a new immense altar, the "Hiero's Ara", built. Under his rule lived the most famous Syracusan, the mathematician and natural philosopher Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists ...
. Among his many inventions were various military engines including the claw of Archimedes
The Claw of Archimedes ( grc, áŒÏÏάγη, translit=harpágÄ, lit=snatcher; also known as the iron hand) was an ancient weapon devised by Archimedes to defend the seaward portion of Syracuse's city wall against amphibious assault. Although i ...
, later used to resist the Roman siege of 214â212 BC. Literary figures included Theocritus and others.
Hiero's successor, the young Hieronymus (ruled from 215 BC), broke the alliance with the Romans after their defeat at the Battle of Cannae
The Battle of Cannae () was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginians and their allies, led by ...
and accepted Carthage's support. The Romans, led by consul Marcus Claudius Marcellus, besieged the city in 214 BC. The city held out for three years, but fell in 212 BC. The successes of the Syracusians in repelling the Roman siege had made them overconfident. In 212 BC, the Romans received information that the city's inhabitants were to participate in the annual festival to their goddess Artemis. A small party of Roman soldiers approached the city under the cover of night and managed to scale the walls to get into the outer city and with reinforcements soon took control, killing Archimedes in the process, but the main fortress remained firm. After an eight-month siege and with parleys in progress, an Iberian captain named Moeriscus is believed to have let the Romans in near the Fountains of Arethusa. On the agreed signal, during a diversionary attack, he opened the gate. After setting guards on the houses of the pro-Roman faction, Marcellus gave Syracuse to plunder.
Imperial Roman and Byzantine period


 Though declining slowly through the years, Syracuse maintained the status of capital of the Roman government of Sicily and seat of the praetor. It remained an important port for trade between the Eastern and the Western parts of the Empire. Christianity spread in the city through the efforts of
Though declining slowly through the years, Syracuse maintained the status of capital of the Roman government of Sicily and seat of the praetor. It remained an important port for trade between the Eastern and the Western parts of the Empire. Christianity spread in the city through the efforts of Paul of Tarsus
Paul; grc, ΠαῊλοÏ, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡâ²â²©â²â²â²¥; hbo, ×€××××ס ×ש××× (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, ØšÙÙس اÙطرسÙسÙ; grc, Î£Î±á¿ŠÎ»Î¿Ï Î€Î±ÏÏεÏÏ, SaÅ©los Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
and Saint Marziano, the first bishop of the city, who made it one of the main centres of proselytism in the West. In the age of Christian persecutions massive catacomb
Catacombs are man-made subterranean passageways for religious practice. Any chamber used as a burial place is a catacomb, although the word is most commonly associated with the Roman Empire.
Etymology and history
The first place to be referred ...
s were carved, whose size is second only to those of Rome.
After a period of Vandal rule, 469â477, Syracuse and the island was recovered for Roman rule under Odoacer, 476â491 and Theodoric the Great, 491â526, by Belisarius for the Byzantine Empire (31 December 535). From 663 to 668 Syracuse was the seat of the Greek-speaking Emperor Constans II
Constans II ( grc-gre, ÎÏÎœÏÏαÏ, KÅnstas; 7 November 630 â 15 July 668), nicknamed "the Bearded" ( la, Pogonatus; grc-gre, ᜠΠÏγÏΜ៶ÏοÏ, ho PÅgÅnãtos), was the Eastern Roman emperor from 641 to 668. Constans was the last ...
, as well as a capital of the Byzantine (Eastern Roman) Empire and metropolis of the whole Sicilian Church. Constans II was assassinated when his plans to permanently replace the Byzantine capital of Constantinople with Syracuse became suspected.
Emirate of Sicily
The city was besieged by the Aghlabids for almost a year in 827â828, but Byzantine reinforcements prevented its fall. It remained the center of Byzantine resistance to the gradual Muslim conquest of Sicily until it fell to the Aghlabids after another siege on 20/21 May 878. During the two centuries ofMuslim
Muslims ( ar, اÙÙ
سÙÙ
ÙÙ, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
rule, the capital of the Emirate of Sicily
The Emirate of Sicily ( ar, Ø¥ÙÙ
ÙارÙØ© صÙÙÙÙÙÙÙÙØ©, ÊŸImÄrat á¹¢iqilliya) was an Islamic kingdom that ruled the island of Sicily from 831 to 1091. Its capital was Palermo (Arabic: ''Balarm''), which during this period became a ...
was moved from Syracuse to Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
. The cathedral was converted into a mosque and the quarter on the Ortygia island was gradually rebuilt along Islamic styles. The city, nevertheless, maintained important trade relationships, and housed a relatively flourishing cultural and artistic life: several Arab poets, including Ibn Hamdis, the most important Sicilian Arab
Siculo-Arabic ( ar, اÙÙÙÙجÙØ© اÙÙعÙرÙØšÙÙÙØ© اÙÙصÙÙÙÙÙÙØ©), also known as Sicilian Arabic, is the term used for varieties of Arabic that were spoken in the Emirate of Sicily (which included Malta) from the 9th century, ...
poet of the 12th century, flourished in the city.
Norman kingdom of Sicily
In 1038, the Byzantine general George Maniakes reconquered the city, sending the relics of St. Lucy to Constantinople. The eponymous castle on the cape of Ortygia bears his name, although it was built under the Hohenstaufen rule. In 1085 the Normans entered Syracuse, one of the last Arab strongholds, after a summer-long siege by Roger I of Sicily and his son Jordan of Hauteville, who was given the city as count. New quarters were built, and the cathedral was restored, as well as other churches.High medieval period
In 1194, Emperor Henry VI occupied the Sicilian kingdom, including Syracuse. After a short period ofGenoese
Genoese may refer to:
* a person from Genoa
* Genoese dialect, a dialect of the Ligurian language
* Republic of Genoa (â1805), a former state in Liguria
See also
* Genovese, a surname
* Genovesi, a surname
*
*
*
*
* Genova (disambiguati ...
rule (1205â1220) under the notorious admiral and pirate Alamanno da Costa, which favoured a rise of trades, royal authority was re-asserted in the city by Frederick II. He began the construction of the Castello Maniace, the Bishops' Palace and the Bellomo Palace. Frederick's death brought a period of unrest and feudal anarchy. In the War of the Sicilian Vespers between the Angevin and Aragonese dynasties for control of Sicily, Syracuse sided with the Aragonese and expelled the Angevins in 1298, receiving from the Spanish sovereigns great privileges in reward. The preeminence of baronial families is also shown by the construction of the palaces of Abela Abela is a surname.
Notable people with the surname include:
* Anthony Abela (1954â2006), Maltese sociologist
* Carmelo Abela (born 1972), Maltese Labour MP
* Deborah Abela (born 1966), Australian children's writer
* Eduardo Abela (1889â196 ...
, Chiaramonte, Nava, Montalto.
16thâ20th centuries
The city was struck by two ruinous earthquakes in 1542 and1693
Events
JanuaryâMarch
* January 11 â 1693 Sicily earthquake: Mount Etna erupts, causing a devastating earthquake that affects parts of Sicily and Malta.
* January 22 â A total lunar eclipse is visible across North and South Ameri ...
, and a plague in 1729. The 17th century destruction changed the appearance of Syracuse forever, as well as the entire Val di Noto, whose cities were rebuilt along the typical lines of Sicilian Baroque, considered one of the most typical expressions of the architecture of Southern Italy. The spread of cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
in 1837 led to a revolt against the Bourbon government. The punishment was the move of the province capital seat to Noto, but the unrest had not been totally choked, as the Siracusani took part in the Sicilian revolution of 1848
The Sicilian revolution of independence of 1848 ( scn, Rivuluzzioni nnipinnintista siciliana dû 1848) occurred in a year replete with revolutions and popular revolts. It commenced on 12 January 1848, and therefore was the first of the numerous ...
.
After the Unification of Italy of 1865, Syracuse regained its status of provincial capital. In the late 19th century, the walls (including Porta Ligny
Porta Ligny or Porta Ligne was the main city gate of the island of Ortygia in Syracuse, Sicily. It was constructed in 1673 and demolished in 1893.
History
Porta Ligny was constructed in 1673 and it was named after Claude Lamoral, 3rd Prince of ...
) were demolished and a bridge connecting the mainland to Ortygia island was built. In the following year a railway link was constructed.
Modern history
BothAllied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
and German bombings in 1943 caused heavy destruction during World War II. ''Operation Husky'', the codename for the Allied invasion of Sicily, was launched on the night between 9â10 July 1943 with British forces attacking the southeast of the island. The plan was for the British 5th Infantry Division
The 5th Infantry Division was a regular army infantry division of the British Army. It was established by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington for service in the Peninsular War, as part of the Anglo-Portuguese Army, and was active for most o ...
, part of General Sir Bernard Montgomery's Eighth Army, to capture Syracuse on the first day of the invasion. This part of the operation went completely according to plan, and British forces captured Syracuse on the first night of the operation. The port was then used as a base for the British Royal Navy. To the west of the city is a Commonwealth War Graves cemetery where about 1,000 men are buried. After the end of the war the northern quarters of Syracuse experienced a heavy, often chaotic, expansion, favoured by the quick process of industrialization.
Syracuse today has about 125,000 inhabitants and numerous attractions for the visitor interested in historical sites (such as the Ear of Dionysius). A process of recovering and restoring the historical centre has been ongoing since the 1990s. Nearby places of note include Catania
Catania (, , Sicilian and ) is the second largest municipality in Sicily, after Palermo. Despite its reputation as the second city of the island, Catania is the largest Sicilian conurbation, among the largest in Italy, as evidenced also by ...
, Noto, Modica and Ragusa Ragusa is the historical name of Dubrovnik. It may also refer to:
Places Croatia
* the Republic of Ragusa (or Republic of Dubrovnik), the maritime city-state of Ragusa
* Cavtat (historically ' in Italian), a town in Dubrovnik-Neretva County, Cro ...
.
Geography
Climate
Syracuse experiences a hot-summer Mediterranean climate ( Köppen climate classification ''Csa'') with mild, wet winters and warm to hot, dry summers. Snow is infrequent; the last heavy snowfall in the city occurred in December 2014. Frosts are very rare, with the last one also happening in December 2014 when the temperature dropped to the all-time record low of 0 °C. A temperature of was registered in Syracuse by the Sicilian Agrometeorological Information Service (SAIS) on 11 August 2021, if recognized by the World Meteorological Organization, this would be the highest temperature ever recorded in Europe. Guido Guidi, lieutenant colonel of the Italian Meteorological Service, however, says the highest temperature registered in the organizations' stations during the heatwave was , at Naval Air Station Sigonella. Guidi underlines that the reported data by SAIS "is produced directly by the stations and is not subject to any control and validation procedure, neither automatic nor manual. It can therefore report errors due to sensor malfunctions as well as maintenance interventions".Government
Demographics
In 2016, there were 122,051 people residing in Syracuse, located in the province of Syracuse, Sicily, of whom 48.7% were male and 51.3% were female. Minors (children ages 18 and younger) totalled 18.9 percent of the population compared to pensioners who number 16.9 percent. This compares with the Italian average of 18.1 percent (minors) and 19.9 percent (pensioners). The average age of Syracuse resident is 40 compared to the Italian average of 42. In the five years between 2002 and 2007, the population of Syracuse declined by 0.5 percent, while Italy as a whole grew by 3.6 percent. The reason for decline is a population flight to the suburbs, andnorthern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
. The current birth rate of Syracuse is 9.75 births per 1,000 inhabitants compared to the Italian average of 9.45 births.
, 97.9% of the population was of Italian descent. The largest immigrant group came from other European nations (particularly those from Poland, and the United Kingdom): 0.6%, North Africa (mostly Tunisian): 0.5%, and South Asia: 0.4%.
Tourism
Since 2005, the entire city of Syracuse, along with the Necropolis of Pantalica which falls within the province of Syracuse, has been listed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. This programme aims to catalogue, name, and conserve sites of outstanding cultural or natural importance to the common heritage ofhumanity
Humanity most commonly refers to:
* Humankind the total population of humans
* Humanity (virtue)
Humanity may also refer to:
Literature
* Humanity (journal), ''Humanity'' (journal), an academic journal that focuses on human rights
* ''Humanity: A ...
. The deciding committee which evaluates potential candidates described their reasons for choosing Syracuse because "monuments and archeological sites situated in Syracuse are the finest example of outstanding architectural creation spanning several cultural aspects; Greek, Roman and Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
", following on that Ancient Syracuse was "directly linked to events, ideas and literary works of outstanding universal significance".
Buildings of the Greek and Roman periods
* The city walls * The '' Temple of Apollo'', at Piazza Emanuele Pancali, adapted to a church in Byzantine times and to a mosque under Arab rule. * The ''Fountain of Arethusa
The Fountain of Arethusa ( it, Fonte Aretusa, grc, áŒÏÎΞοÏ
Ïα) is a natural fountain on the island of Ortygia in the historical centre of the city of Syracuse in Sicily. According to Greek mythology, the fresh water fountain is the place ...
'', on the Ortygia island. According to a legend, the nymph Arethusa, hunted by Alpheus, took shelter here.
* The '' Greek Theatre'', whose cavea is one of the largest ever built by the ancient Greeks: it has 67 rows, divided into nine sections with eight aisles. Only traces of the scene and the orchestra remain. The edifice (still used today) was modified by the Romans, who adapted it to their different style of spectacles, including also circus games. Near the theatre are the ''latomìe'', stone quarries, also used as prisons in ancient times. The most famous ''latomìa'' is the '' Orecchio di Dionisio'' ("Ear of Dionysius").
* The Roman amphitheatre. It was partly carved out from the rock. In the centre of the area is a rectangular space which was used for the scenic machinery.
* The ''Tomb of Archimede'', in the Grotticelli Necropolis. Decorated with two Doric columns.
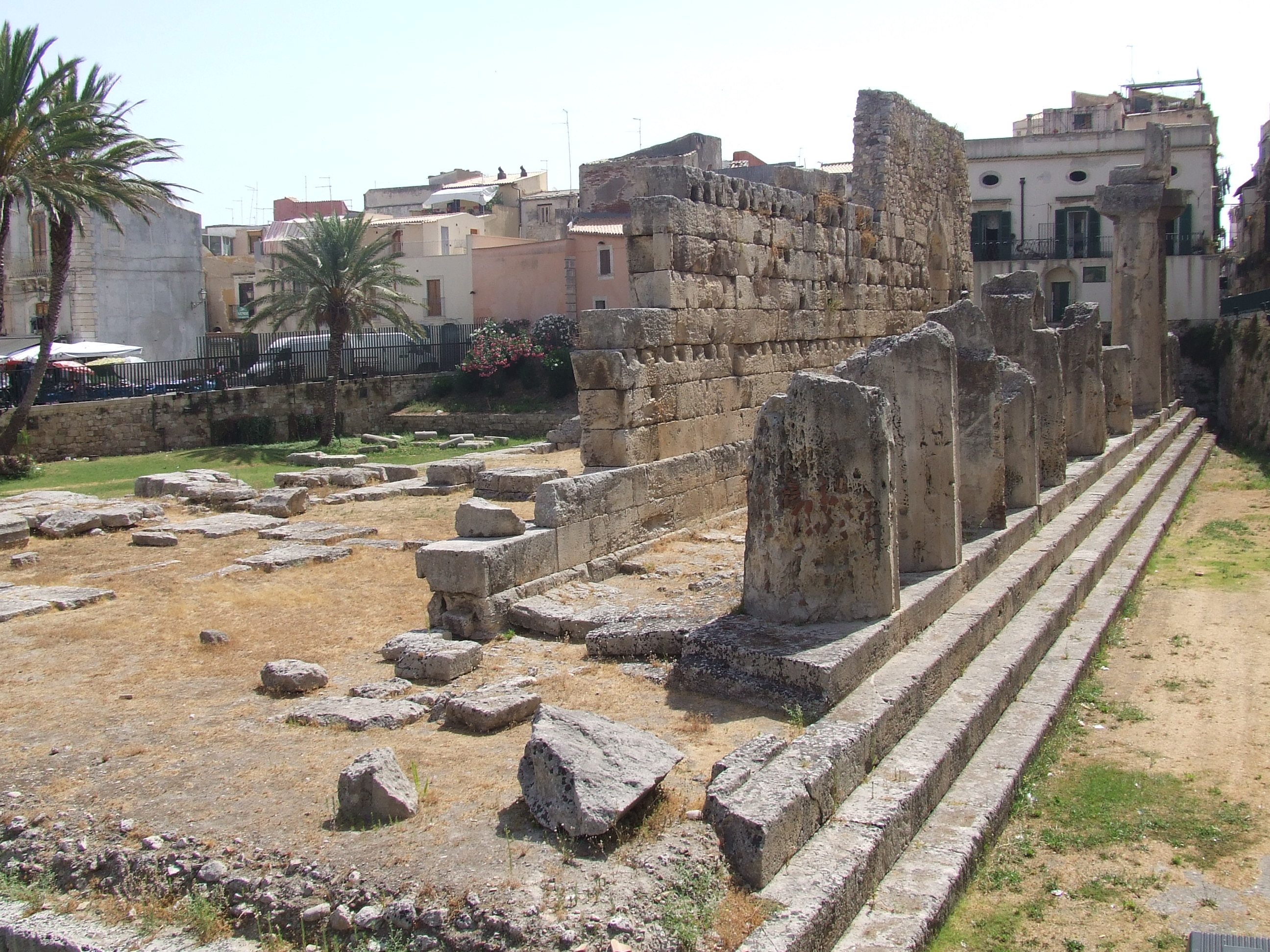
* The ''Temple of Olympian Zeus'', about outside the city, built around the 6th century BC.
Buildings of the Christian period
Doric Doric may refer to:
* Doric, of or relating to the Dorians of ancient Greece
** Doric Greek, the dialects of the Dorians
* Doric order, a style of ancient Greek architecture
* Doric mode, a synonym of Dorian mode
* Doric dialect (Scotland)
* Doric ...
edifice with six columns on the short sides and 14 on the long sides: these are still incorporated into the walls of the cathedral. The base of the temple had three steps. The interior of the church has a nave and two aisles. The roof of the nave is from Norman times, as well as the mosaics in the apses. The façade was rebuilt by Andrea Palma in 1725â1753, with a double order of Corinthian column
The Corinthian order (Greek: ÎοÏιΜΞιακÏÏ ÏÏ
ΞΌÏÏ, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order ...
s, and statues by Ignazio Marabitti. The interior houses a 12th-13th-century marble font, a silver statue of ''St Lucy'' by Pietro Rizzo
Pietro is an Italian masculine given name. Notable people with the name include:
People
* Pietro I Candiano (c. 842â887), briefly the 16th Doge of Venice
* Pietro Tribuno (died 912), 17th Doge of Venice, from 887 to his death
* Pietro II Can ...
(1599), a ciborium by Luigi Vanvitelli, and a statue of the ''Madonna della Neve'' ("Madonna of the Snow", 1512) by Antonello Gagini
Antonello Gagini (1478â1536) was an Italian sculptor of the Renaissance, mainly active in Sicily and Calabria.
Antonello belonged to a family of sculptors and artisans, originally from Northern Italy, but active throughout Italy, including Gen ...
.
* Basilica of ''Santa Lucia Extra moenia'': a Byzantine church built (after Norman rebuilt), according to tradition, in the same place of the martyrdom of the saint in 303 AD. The current appearance is from the 15thâ16th centuries. The most ancient parts still preserved include the portal, the three half-circular apses and the first two orders of the belfry. Under the church are the ''Catacombs of St. Lucy''. For this church Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 â 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of hi ...
painted the Burial of St. Lucy.
* '' Madonna delle Lacrime'': (Our Lady of Tears Shrine) 20th century shrine church.
* ''San Benedetto San Benedetto may refer to:
* Saint Benedict (c. 480-543/547), Italian saint
* Saint Benedict (disambiguation), a number of other Italian saints called San Benedetto (Saint Benedict)
Places of Italy
* San Benedetto Belbo, a municipality in the Pro ...
'': 16th century church, restored after 1693. It houses a painting depicting ''Death of Saint Benedict'' by the Caravaggisti Mario Minniti
Mario Minniti (8 December 1577 â 22 November 1640) was an Italian artist active in Sicily after 1606.
Born in Syracuse, Sicily, he arrived in Rome in 1593, where he became the friend, collaborator, and model of the key Baroque painter Miche ...
.
* Chiesa della Concezione (14th century, rebuilt in the 18th century), with the annexed Benedictine convent.
* ''San Cristoforo
San Cristoforo (in local dialect San Cristòfi) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Alessandria in the Italian region Piedmont, located about southeast of Turin and about southeast of Alessandria. As of 31 December 2004, it had a p ...
'': 14th century church, rebuilt in 18th-century.
* ''San Giovanni Battista'': 14th century church.
* '' San Filippo Apostolo'': 18th-century church with stairs down to a Jewish ritual bath (Mikvah
Mikveh or mikvah (, ''mikva'ot'', ''mikvoth'', ''mikvot'', or (Yiddish) ''mikves'', lit., "a collection") is a bath used for the purpose of ritual immersion in Judaism to achieve ritual purity.
Most forms of ritual impurity can be purifi ...
) dating to prior to the expulsion of Jews in 1492
* '' San Filippo Neri: 17th-century facade and interior reconstructed in 18th-century
* '' San Francesco all'Immacolata'': church with a convex façade intermingled by columns and pilaster strips. It housed an ancient celebration, the Svelata ("Revelation"), in which an image of the Madonna was unveiled at dawn of 29 November.
* ''San Giovanni Evangelista'': basilica church built by the Normans and destroyed in 1693. Only partially restored, it was erected over an ancient crypt of the martyr San Marciano, later destroyed by the Arabs. The main altar is Byzantine. It includes the ''Catacombs of San Giovanni'', featuring a maze of tunnels and passages, with thousands of tombs and several frescoes.
* '' San Giuseppe'': 18th-century octagonal church, in disrepair
* '' Santa Lucia alla Badia'': Baroque sanctuary church built after the 1693 earthquake.
* '' Santa Maria dei Miracoli'': 14th century church.
* '' San Martino'': 6th-century church, 14th-century facade, 18th-century interiors
* '' San Paolo Apostolo'': 18th century church.
* '' Spirito Santo'': 18th-century church.
* Church of the Jesuit College, a majestic, Baroque building.
Other notable buildings


 * Castello Maniace, constructed between 1232 and 1240, is an example of the military architecture of Frederick II's reign. It is a square structure with circular towers at each of the four corners. The most striking feature is the pointed portal, decorated with polychrome marbles.
* ''Archaeological Museum'' with collections including findings from the mid-Bronze Age to 5th century BC.
* ''Palazzo Lanza Buccheri'' (16th century).
* '' Palazzo Bellomo'' (12th century), which contains an art museum that houses Antonello da Messina's ''
* Castello Maniace, constructed between 1232 and 1240, is an example of the military architecture of Frederick II's reign. It is a square structure with circular towers at each of the four corners. The most striking feature is the pointed portal, decorated with polychrome marbles.
* ''Archaeological Museum'' with collections including findings from the mid-Bronze Age to 5th century BC.
* ''Palazzo Lanza Buccheri'' (16th century).
* '' Palazzo Bellomo'' (12th century), which contains an art museum that houses Antonello da Messina's ''Annunciation
The Annunciation (from Latin '), also referred to as the Annunciation to the Blessed Virgin Mary, the Annunciation of Our Lady, or the Annunciation of the Lord, is the Christian celebration of the biblical tale of the announcement by the ange ...
'' (1474).
* '' Palazzo Montalto'' (14th century), which conserves the old façade from the 14th century, with a pointed portal.
* ''Archbishop's Palace'' (17th century, modified in the following century). It houses the ''Alagonian Library'', founded in the late 18th century.
* ''Palazzo Vermexio
Palazzo Vermexio is a 17th-century Baroque monumental building, located facing Piazza Duomo in the island of Ortigia in Siracusa, region of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_ti ...
'': current Town Hall, includes fragments of an Ionic temple of the 5th century BC.
* ''Palazzo Francica Nava'', with parts of the original 16th century building surviving.
* '' Palazzo Beneventano del Bosco'', originally built in the Middle Ages but extensively modified between 1779 and 1788. It has a pleasant internal court.
* ''Palazzo Migliaccio'' (15th century), with notable lava inlay decorations.
* The ''Senate Palace'', housing in the court an 18th-century coach
Coach may refer to:
Guidance/instruction
* Coach (sport), a director of athletes' training and activities
* Coaching, the practice of guiding an individual through a process
** Acting coach, a teacher who trains performers
Transportation
* Co ...
.
* ''Castle of Euryalos'', built outside the city by Dionysius the Elder and which was one of the most powerful fortresses of ancient times. It had three moats with a series of underground galleries which allowed the defenders to remove the materials the attackers could use to fill them.
* ''Mikveh'': a bath used for the purpose of ritual immersion in Judaism, built during the Byzantine era. It is situated in the ''Giudecca'': the ancient Jewish Ghetto of Syracuse.
* Monument to the Italians Fallen in Africa, Siracusa
The Monument to the Fallen Italians in Africa (Monumento ai Caduti italiani d'Africa) is a Fascist era monument, dedicated to the Italians who died during the Ethiopian War (1935-1936), and assembled only in the 1960s on the seashore in Siracusa, ...
Famous people
*Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists ...
, classical Greek mathematician, physicist and engineer
* Antiochus of Syracuse, a Greek historian
* Achaeus of Syracuse
Achaeus of Syracuse ( grc, áŒÏαιÏÏ áœ Î£Ï
ÏακοÏÏιοÏ; lived 4th century BC) was an ancient Greek tragedian native of Syracuse. The '' Suda'' ascribes to him 10 plays, while the Pseudo-Eudocia 14. He may be the "Achaios" who won a v ...
, a Greek tragedian
* Themistogenes
''Anabasis'' (; grc-gre, áŒÎœÎ¬Î²Î±ÏÎ¹Ï ; an "expedition up from") is the most famous work of the Ancient Greek professional soldier and writer Xenophon. It narrates the expedition of a large army of Greek mercenaries hired by Cyrus the You ...
, Greek historian. He wrote about the Anabasis and some other works about the Syracuse.
* Saint Lucy, Roman martyr
* Pope Stephen III
* Ibn Hamdis, Sicilian Arab poet
* Vincenzo Mirabella (1570- 1624), humanist and pioneer of archaeology
* Claudio Schifano (born 1953), contemporary artist of informal painting
Sports
Syracuse is home to association football clubA.S.D. Città di Siracusa
Siracusa Calcio 1924 SSD, commonly referred to as Siracusa, is an Italian football club based in Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse, Sicily. ( it, Siracusa, Sicilia) The club currently plays in Serie D, the fourth-tier of football in Italy.
History
For ...
, the latest reincarnation of several clubs dating back to 1924. The common feature is the azure shirts, hence the nickname ''Azzurri''. Siracusa play at the Stadio Nicola De Simone
Stadio Nicola de Simone (commonly known as La Fossa dei Leoni) is a football stadium in Syracuse, Sicily. It is the home of Siracusa football team and has a capacity of 5,946 spectators.
The stadium was built in 1930 and was inaugurated in 193 ...
with an approximate capacity between 5,000 and 6,000.
See also
*Cassibile (village)
Cassibile ( Sicilian: ''Cassìbbili'') is an Italian village and civil parish (''frazione'') of the city and municipality (''comune'') of Syracuse (''Siracusa''), in Sicily. As of 2006 its population was of 5,800.
History
The Necropolis of Cass ...
* Greek coinage of Italy and Sicily
* '' MalÚna'' â a 2000 romantic comedy-drama film starring Monica Bellucci and Giuseppe Sulfaro was mostly produced in Syracuse
* Peloponnesian League
The Peloponnesian League was an alliance of ancient Greek city-states, dominated by Sparta and centred on the Peloponnese, which lasted from c.550 to 366 BC. It is known mainly for being one of the two rivals in the Peloponnesian War (431â404 BC ...
* Sicilian Wars
* Siracusa International Institute for Criminal Justice and Human Rights
The Siracusa International Institute for Criminal Justice and Human Rights, until 2017 Istituto Superiore Internazionale di Scienze Criminali (ISISC) (in English, International Institute of Higher Studies in Criminal Sciences) is a not-for-profit ...
* Siracusa railway station
Notes
References
Further reading
*External links
*Coins from ancient Syracuse and Sicily
Photos of Ortigia in Syracuse
{{Authority control 8th-century BC establishments in Italy Archaeological sites in Sicily Cities and towns in Sicily Coastal towns in Sicily Corinthian colonies Dorian colonies in Magna Graecia Mediterranean port cities and towns in Italy Municipalities of the Province of Syracuse Populated places established in the 8th century BC Sicilian Baroque World Heritage Sites in Italy Greek city-states