Sesamoid Bones on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
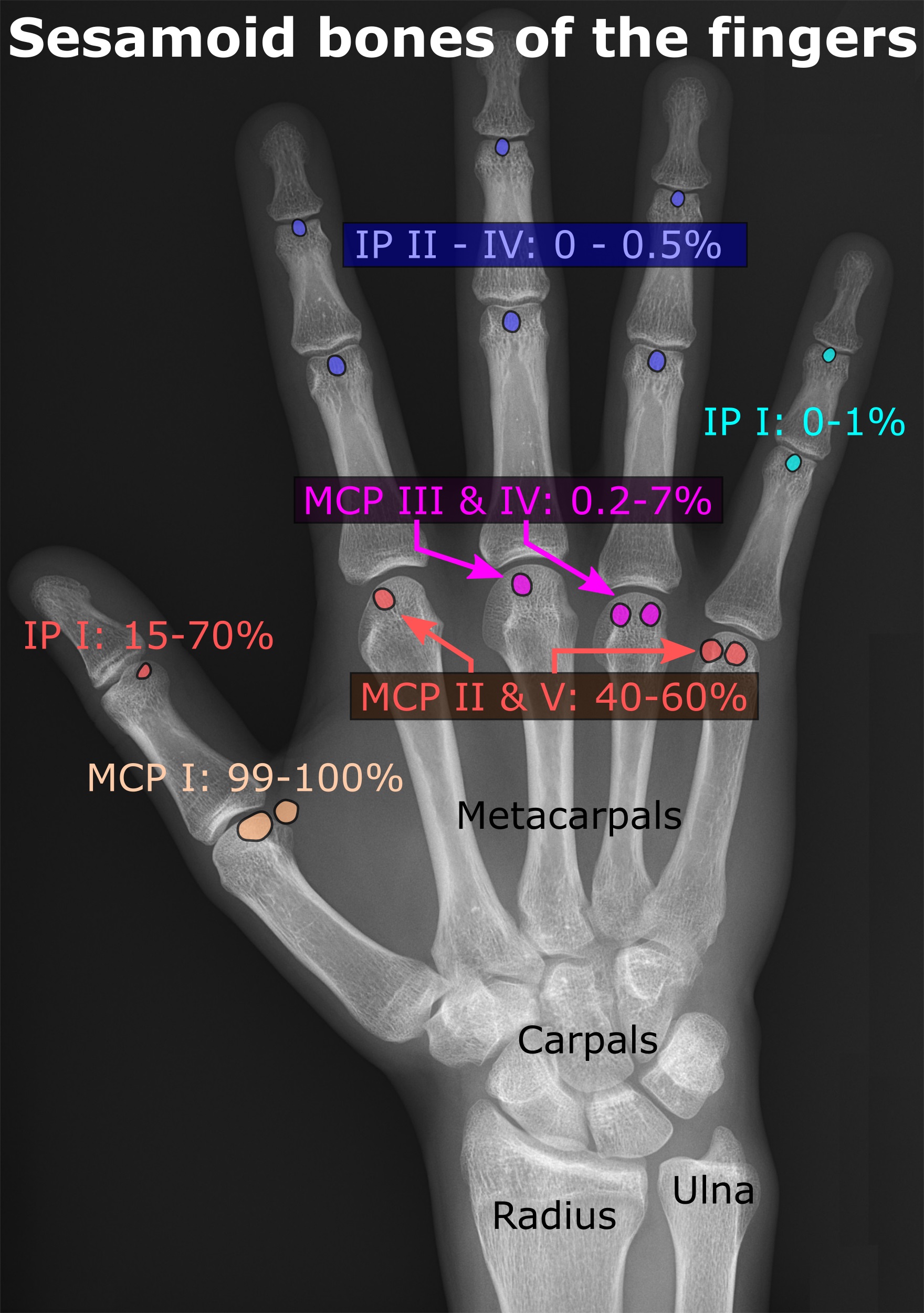 Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the body, including:
* In the
Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the body, including:
* In the
 * One or both of the sesamoid bones under the first
* One or both of the sesamoid bones under the first
File:Accessory and sesamoid bones of the foot - lateral projection.jpg, Lateral view.
File:Pie metatarso-falanges.JPG, Bipartite medial sesamoid bone under the first
''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918)
(Bartleby)
anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
, a sesamoid bone () is a bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
embedded within a tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
or a muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for 'sesame
Sesame ( or ; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a flowering plant in the genus ''Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cu ...
seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a normal variant
Human variability, or human variation, is the range of possible values for any characteristic, physical or mental, of human beings
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipeda ...
. The patella
The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as m ...
is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulley
A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft that is designed to support movement and change of direction of a taut cable or belt, or transfer of power between the shaft and cable or belt. In the case of a pulley supported by a frame or shell that ...
s, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit muscular forces.
Structure
 Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the body, including:
* In the
Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the body, including:
* In the knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
—the patella
The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as m ...
(within the quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
tendon). This is the largest sesamoid bone.
* In the hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "h ...
—two sesamoid bones are commonly found in the distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
portions of the first metacarpal bone
The first metacarpal bone or the metacarpal bone of the thumb is the first bone proximal to the thumb. It is connected to the trapezium of the carpus at the first carpometacarpal joint and to the proximal thumb phalanx at the first metacarpophal ...
(within the tendons of adductor pollicis
In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique.
It is a fleshy, flat, triangular, and fan-shaped muscle deep in the thenar compartment beneath ...
and flexor pollicis brevis
The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part.
Origin and insertion
The muscle's superficial head arises from the distal edge of the fl ...
). There is also commonly a sesamoid bone in distal portions of the second metacarpal bone
The second metacarpal bone (metacarpal bone of the index finger) is the longest, and its base the largest, of all the metacarpal bones.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). See infobox.
Human anatomy
Its base is prolonged upward and medialward, forming a ...
.
* In the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the Carpal bones, carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known ...
—The pisiform
The pisiform bone ( or ), also spelled pisiforme (from the Latin ''pisifomis'', pea-shaped), is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel.
Structure
The pisiform is a sesamoid bone, ...
of the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the Carpal bones, carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known ...
is a sesamoid bone (within the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris
The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a muscle of the forearm that flexes and adducts at the wrist joint.
Structure Origin
The flexor carpi ulnaris has two heads; a humeral head and ulnar head. The humeral head originates from the medial epicondyle o ...
). It begins to ossify
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
in children ages 9–12.
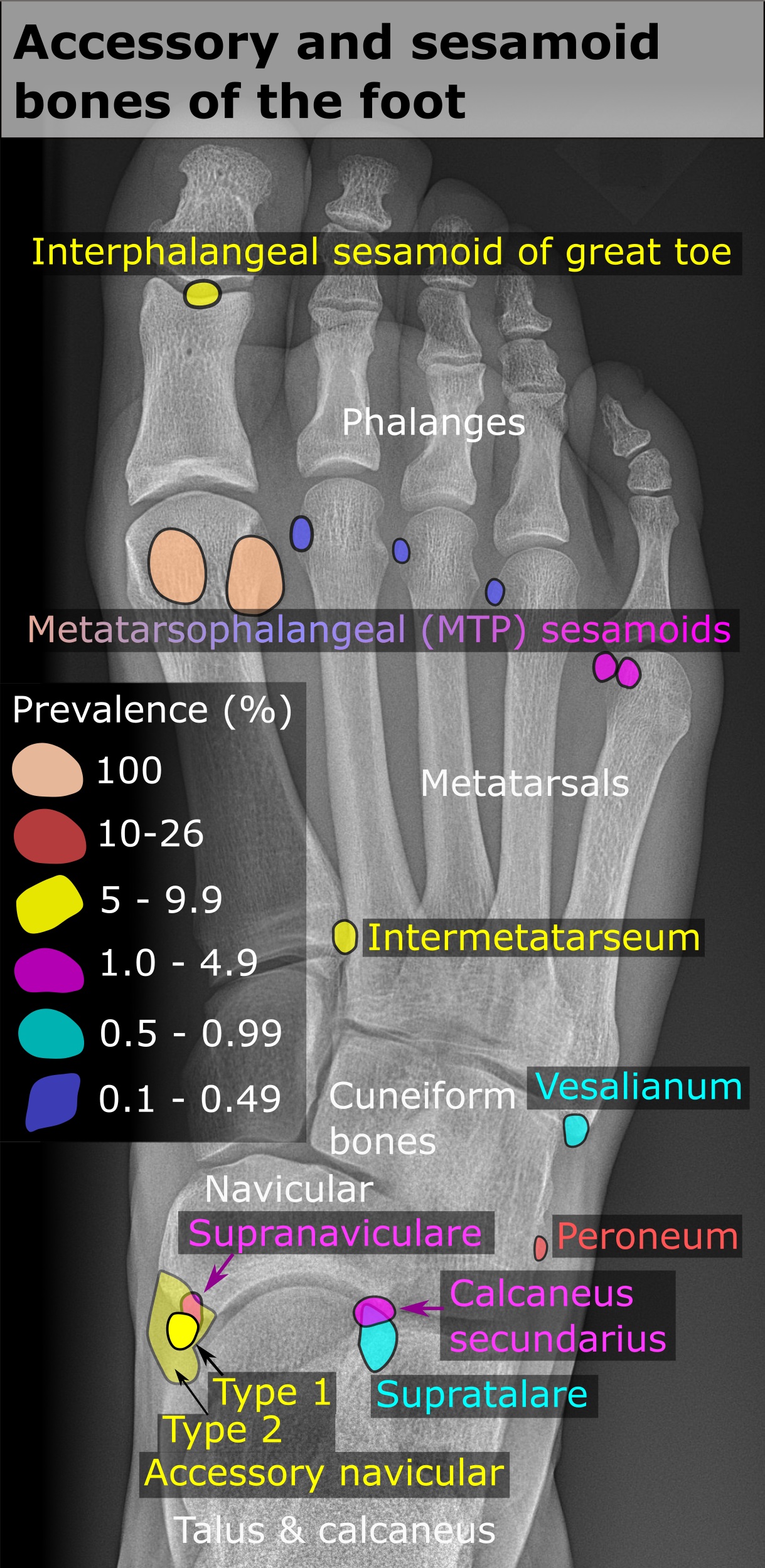
* In the foot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made ...
—the first metatarsal bone
The first metatarsal bone is the bone in the foot just behind the big toe. The first metatarsal bone is the shortest of the metatarsal bones and by far the thickest and strongest of them.
Like the four other metatarsals, it can be divided into ...
usually has two sesamoid bones at its connection to the big toe
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being '' digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being '' pl ...
(both within the tendon of flexor hallucis brevis
A flexor is a muscle that flexes a joint. In anatomy, flexion (from the Latin verb ''flectere'', to bend) is a joint movement that decreases the angle between the bones that converge at the joint. For example, one’s elbow joint flexes when one ...
). One is found on the lateral side of the first metatarsal while the other is found on the medial side. In some people, only a single sesamoid is found on the first metatarsal bone
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the ...
.
Common variants
 * One or both of the sesamoid bones under the first
* One or both of the sesamoid bones under the first metatarsophalangeal joint
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints), also informally known as toe knuckles, are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones (proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an ellipt ...
(of the great toe
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being '' digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being '' pl ...
) can be multipartite – in two or three parts (mostly bipartite – in two parts).
* The fabella
The fabella is a small sesamoid bone found in some mammals embedded in the tendon of the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle behind the lateral condyle of the femur. It is an accessory bone, an anatomical variation present in 39% of h ...
is a small sesamoid bone found in some mammals embedded in the tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
of the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle
The gastrocnemius muscle (plural ''gastrocnemii'') is a superficial two-headed muscle that is in the back part of the lower leg of humans. It runs from its two heads just above the knee to the heel, a three joint muscle (knee, ankle and subtala ...
behind the lateral condyle
A condyle (;Entry "condyle"
in
femur The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with ...
. It is a variant of normal anatomy and present in humans in 10% to 30% of individuals. The fabella can also be mutipartite or bipartite.
* The cyamella is a small sesamoid bone embedded in the tendon of the in
femur The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with ...
popliteus muscle
The popliteus muscle in the leg is used for unlocking the knees when walking, by laterally rotating the femur on the tibia during the closed chain portion of the bipedal gait cycle, gait cycle (one with the foot in contact with the ground). In op ...
. It is a variant of normal anatomy. It is rarely seen in humans, but has been described more often in other primates and certain other animals.
metatarsophalangeal joint
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints), also informally known as toe knuckles, are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones (proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an ellipt ...
of the great toe
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being '' digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being '' pl ...
of the left foot of an adult woman.
Clinical significance
* A common foot ailment in dancers issesamoiditis
Sesamoiditis is inflammation of the sesamoid bones.
Humans
Sesamoiditis occurs on the bottom of the foot, just behind the big toe. There are normally two sesamoid bones on each foot; sometimes sesamoids can be bipartite, which means they each ...
(an inflammation of the sesamoid bones under the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe). This is a form of tendinitis which results from the tendons surrounding the sesamoid becoming inflamed or irritated.
* Sesamoid bones generally have a very limited blood supply, rendering them prone to avascular necrosis
Avascular necrosis (AVN), also called osteonecrosis or bone infarction, is death of bone tissue due to interruption of the blood supply. Early on, there may be no symptoms. Gradually joint pain may develop which may limit the ability to move. Co ...
(bone death from lack of blood supply), which is very difficult to treat.
Other animals
Inequine anatomy
Equine anatomy encompasses the gross and microscopic anatomy of horses, ponies and other equids, including donkeys, mules and zebras. While all anatomical features of equids are described in the same terms as for other animals by the Internatio ...
, the term sesamoid bone usually refers to the two sesamoid bones found at the back of the fetlock
Fetlock is the common name in horses, large animals, and sometimes dogs for the metacarpophalangeal and metatarsophalangeal joints (MCPJ and MTPJ).
Although it somewhat resembles the human ankle in appearance, the joint is homologous to the ba ...
or metacarpophalangeal and metatarsophalangeal joints in both hindlimbs and forelimbs
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the cranial (anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used instead. ...
. Strictly these should be termed the proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
sesamoid bones whereas the navicular bone
The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals.
Human anatomy
The navicular bone in humans is one of the tarsal bones, found in the foot. Its name derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat, caused by the ...
should be referred to as the distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
sesamoid bone. The patella is also a form of sesamoid bone in the horse.
Although many carnivores have radial sesamoid bones, the giant panda
The giant panda (''Ailuropoda melanoleuca''), also known as the panda bear (or simply the panda), is a bear species endemic to China. It is characterised by its bold black-and-white coat and rotund body. The name "giant panda" is sometimes us ...
and red panda
The red panda (''Ailurus fulgens''), also known as the lesser panda, is a small mammal native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. It has dense reddish-brown fur with a black belly and legs, white-lined ears, a mostly white muzzle ...
independently evolved to have an enlarged radial sesamoid bone. This evolution has caused the two species to diverge from other carnivores. The red panda likely originally evolved the "pseudo-thumb" in order to assist in arboreal locomotion. When the red panda later evolved to consume a bamboo diet, the enlarged bone underwent exaptation
Exaptation and the related term co-option describe a shift in the function of a trait during evolution. For example, a trait can evolve because it served one particular function, but subsequently it may come to serve another. Exaptations are common ...
to assist in grasping bamboo. The giant panda, however, evolved the enlarged radial sesamoid bone around the same time as it evolved a bamboo diet. In the giant panda, the bone allows for a pincer-like motion and is used in grasping the bamboo. In these two panda species, ''DYNC2H1'' gene and ''PCNT'' gene have been identified as possible causes for the pseudo-thumb development.
Recently, the enlarged radial sesamoid bone of cotton rat
A cotton rat is any member of the rodent genus ''Sigmodon''. Their name derives from their damaging effects on cotton as well as other plantation crops, such as sugarcane, corn, peanut and rice. Cotton rats have small ears and dark coats, and a ...
s has been studied. Their enlarged radial sesamoid bone and that of the giant panda have a similar morphology and size relative to the rest of the hand. The reason for this evolutionary change is still unknown; however, it may be to assist in grasping small objects and thin branches.
Elephants
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and ...
have similarly enlarged sesamoid bones in both their forelimbs and hindlimbs, referred to as the prepollex and prehallux, respectively. These sesamoids function as "sixth toes", helping to distribute the animals' weight. In contrast to other sesamoids in elephants, which ossify at 3-7 years of age, the ossification of the prepollex and prehallux is delayed and is known to not have yet occurred in animals in excess of 20 years of age. The prehallux is further divided into two elements; the more proximal of these is fixed, whilst the more distal is mobile. Evidence of these "predigits" has also been found in certain fossil proboscideans
The Proboscidea (; , ) are a taxonomic order of afrotherian mammals containing one living family (Elephantidae) and several extinct families. First described by J. Illiger in 1811, it encompasses the elephants and their close relatives. Fro ...
.
The forepaws of moles Moles can refer to:
* Moles de Xert, a mountain range in the Baix Maestrat comarca, Valencian Community, Spain
* The Moles (Australian band)
*The Moles, alter ego of Scottish band Simon Dupree and the Big Sound
People
*Abraham Moles, French engin ...
also possess a prepollex consisting of an enlarged, sickle-shaped sesamoid.
See also
*Accessory bone
An accessory bone or supernumerary bone is a bone that is not normally present in the body, but can be found as a variant in a significant number of people. It poses a risk of being misdiagnosed as bone fractures on radiography.
Wrist and hand
...
Footnotes
References
''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918)
(Bartleby)
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Sesamoid Bone Skeletal system Horse anatomy