|
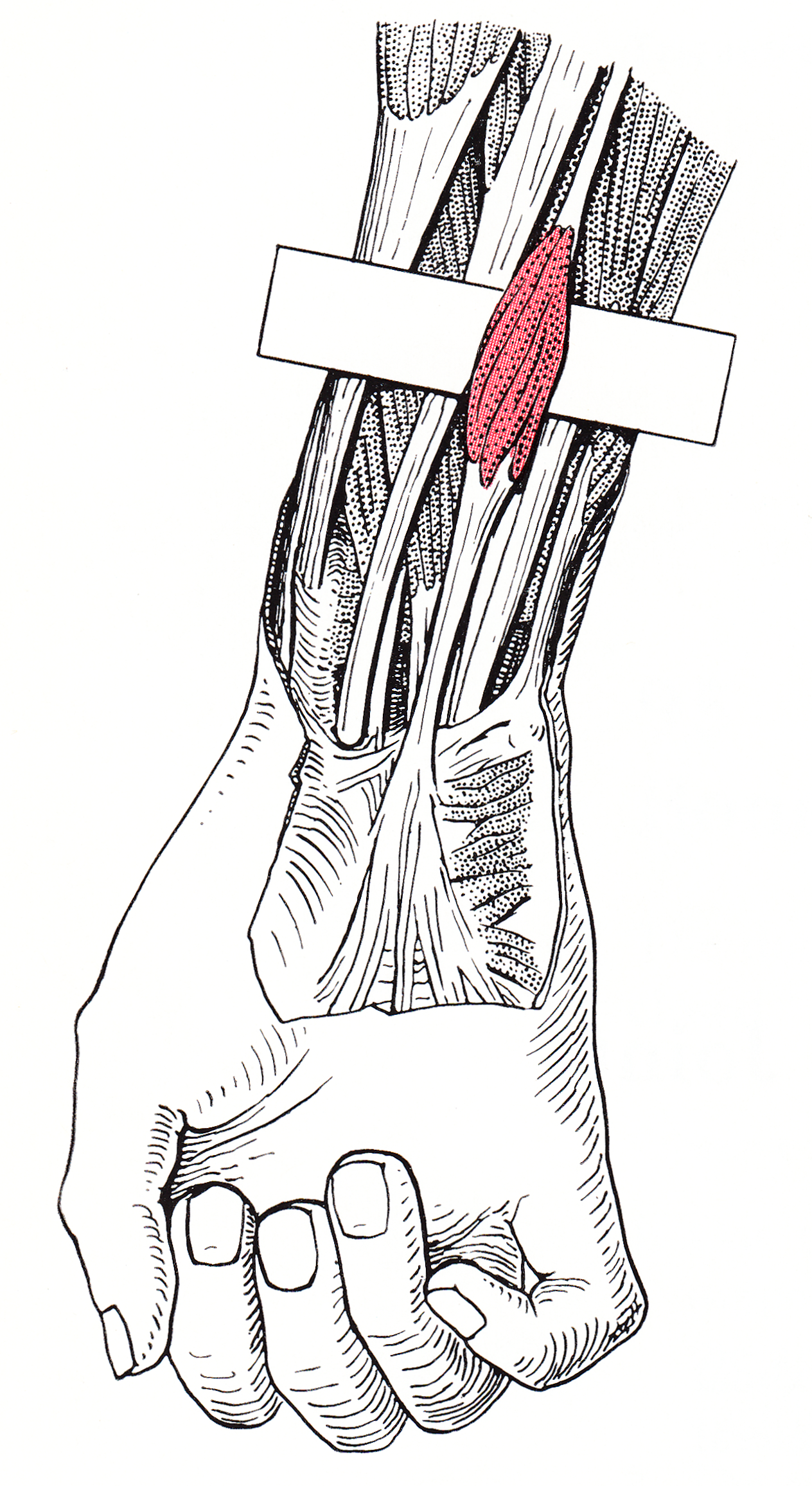
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a muscle of the forearm that flexes and adducts at the wrist joint. Structure Origin The flexor carpi ulnaris has two heads; a humeral head and ulnar head. The humeral head originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus via the common flexor tendon. The ulnar head originates from the medial margin of the olecranon of the ulnar and the upper two-thirds of the dorsal border of the ulnar by an aponeurosis. Between the two heads passes the ulnar nerve and ulnar artery. Insertion The flexor carpi ulnaris inserts onto the pisiform, hook of the hamate (via the pisohamate ligament) and the anterior surface of the base of the fifth metacarpal (via the pisometacarpal ligament). Action The flexor carpi ulnaris flexes and adducts at the wrist joint. Innervation The flexor carpi ulnaris is innervated by the ulnar nerve. The corresponding spinal nerves are C8 and T1. Tendon The tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris can be seen on the anterior surface of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Epicondyle Of The Humerus
The medial epicondyle of the humerus is an epicondyle of the humerus bone of the upper arm in humans. It is larger and more prominent than the lateral epicondyle and is directed slightly more posteriorly in the anatomical position. In birds, where the arm is somewhat rotated compared to other tetrapods, it is called the ventral epicondyle of the humerus. In comparative anatomy, the more neutral term entepicondyle is used. The medial epicondyle gives attachment to the ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint, to the pronator teres, and to a common tendon of origin (the common flexor tendon) of some of the flexor muscles of the forearm: the flexor carpi radialis, the flexor carpi ulnaris, the flexor digitorum superficialis, and the palmaris longus. The medial epicondyle is located on the distal end of the humerus. Additionally, the medial epicondyle is inferior to the medial supracondylar ridge. It is also proximal to the olecranon fossa. The medial epicondyle protects the uln ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Collateral Ligament Of Elbow Joint
The ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) or internal lateral ligament is a thick triangular ligament at the medial aspect of the elbow uniting the distal aspect of the humerus to the proximal aspect of the ulna. Structure It consists of two portions, an anterior and posterior united by a thinner intermediate portion. Note that this ligament is also referred to as the medial collateral ligament and should not be confused with the lateral ulnar collateral ligament (LUCL). The ''anterior portion'', directed obliquely forward, is attached, above, by its apex, to the front part of the medial epicondyle of the humerus; and, below, by its broad base to the medial margin of the coronoid process of the ulna. The ''posterior portion'', also of triangular form, is attached, above, by its apex, to the lower and back part of the medial epicondyle; below, to the medial margin of the olecranon. Between these two bands a few intermediate fibers descend from the medial epicondyle to blend with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumbbell
The dumbbell, a type of free weight, is a piece of equipment used in weight training. It can be used individually or in pairs, with one in each hand. History The forerunner of the dumbbell, halteres, were used in ancient Greece as lifting weights and also as weights in the ancient Greek version of the long jump. A kind of dumbbell was also used in India for more than a millennium, shaped like a club – so it was named Indian club. The design of the "Nal", as the equipment was referred to, can be seen as a halfway point between a barbell and a dumbbell. It was generally used in pairs, in workouts by wrestlers, bodybuilders, sports players, and others wishing to increase strength and muscle size. Etymology The term "dumbbell" or "dumb bell" originated in late Stuart England. In 1711 the poet Joseph Addison mentioned exercising with a "dumb bell" in an essay published in ''The Spectator''. Although Addison elsewhere in the same publication describes having used equipment sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist Curls
The wrist curl is a weight training exercise for developing just the wrist flexor muscles of the forearm. It is therefore an isolation exercise. Ideally, it should be done in combination with the "reverse wrist curl" (also called wrist extension) to ensure equal development of the wrist flexor and wrist extensor muscles. Wrist curls can be performed with a dumbbell or with both hands holding a barbell. To perform a seated wrist curl, the lifter should be seated on a bench with knees bent and the forearm(s) resting on the thigh, or with forearms on a bench and hands hanging off the edge. The palm should be facing up and the hand should be free to move completely up and down. At the starting point, the wrist should be bent back so that the finger A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers ( Pentadactyly). C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist Roller
The wrist roller is a device designed for strengthening the forearm muscles together in a rolling-pulling motion. It consists of a bar of varying lengths, with a cord or rope attached, which the user rolls and unrolls. This is resisted by the weight of a mass at the bottom of the cord. Rolled and unrolled, it has a concentric and eccentric proportion. Different forearm muscles, specifically the flexors and extensors can be targeted by rolling the bar in opposite directions; that is by having the rope either on your side or on the opposite one respectively. It can even be performed (with lighter weights) manipulated by the fingertips to develop dexterity. The length of the rope determines the length of time one will take to vary between the concentric and eccentric portions (though it will always be the same length, if rolled and unrolled at the same pace). Strength is built by using a larger weight. The focus on gripping muscles versus wrist extensor muscles can be varied based upo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strength Training
Strength training or resistance training involves the performance of physical exercises that are designed to improve strength and endurance. It is often associated with the lifting of weights. It can also incorporate a variety of training techniques such as bodyweight exercises, isometrics, and plyometrics. Training works by progressively increasing the force output of the muscles and uses a variety of exercises and types of equipment. Strength training is primarily an anaerobic activity, although circuit training also is a form of aerobic exercise. Strength training can increase muscle, tendon, and ligament strength as well as bone density, metabolism, and the lactate threshold; improve joint and cardiac function; and reduce the risk of injury in athletes and the elderly. For many sports and physical activities, strength training is central or is used as part of their training regimen. Principles and training methods The basic principles of strength training involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmaris Longus
The palmaris longus is a muscle visible as a small tendon located between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris, although it is not always present. It is absent in about 14 percent of the population; this number can vary in African, Asian, and Native American populations, however. Absence of the palmaris longus does not have an effect on grip strength. The lack of palmaris longus muscle does result in decreased pinch strength in fourth and fifth fingers. The absence of palmaris longus muscle is more prevalent in females than males. The palmaris longus muscle can be seen by touching the pads of the fourth finger and thumb and flexing the wrist. The tendon, if present, will be visible in the midline of the anterior wrist. Structure Palmaris longus is a slender, elongated, spindle shaped muscle, lying on the medial side of the flexor carpi radialis. It is widest in the middle, and narrowest at the proximal and distal attachments.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918), see infob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Carpi Radialis Muscle
In anatomy, flexor carpi radialis is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (radially) abduct the hand. The Latin ''carpus'' means wrist; hence flexor carpi is a flexor of the wrist. Origin and insertion The flexor carpi radialis is one of four muscles in the superficial layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm. This muscle originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus as part of the common flexor tendon. It runs just laterally of flexor digitorum superficialis and inserts on the anterior aspect of the base of the second metacarpal, and has small slips to both the third metacarpal and trapezium tuberosity. The tendon of the flexor carpi radialis is visible on the anterior surface of the forearm, just proximal to the wrist, when the wrist is flexed. It is the tendon seen most lateral, closest to the thumb. Nerve and artery Like most flexors of the anterior compartment of the forearm, FCR is innervated by the median nerve, specifically by axons from c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Nerve
In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds. This nerve can cause an electric shock-like sensation by striking the medial epicondyle of the humerus posteriorly, or inferiorly with the elbow flexed. The ulnar nerve is trapped between the bone and the overlying skin at this point. This is commonly referred to as bumping one's "funny bone". This name is thought to be a pun, based on the sound resemblance between the name of the bone of the upper arm, the humerus, and the word "humorous". Alternatively, according to the Oxford English Dictionary, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the Carpal bones, carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius (bone), radius and the Carpal bones, carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the Flexor retinaculum of the hand, flexor retinaculum, and the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisometacarpal Ligament
The pisometacarpal ligament joins the pisiform to the base of the fifth metacarpal bone. It is a continuation of the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a muscle of the forearm that flexes and adducts at the wrist joint. Structure Origin The flexor carpi ulnaris has two heads; a humeral head and ulnar head. The humeral head originates from the medial epicondyle o .... Additional images Image:Ligamentumpisometacarpeum.png, Ligaments of wrist. Anterior view. (Pisometacarpal labeled at right, second from bottom.) References External links * https://web.archive.org/web/20070806224310/http://classes.kumc.edu/sah/resources/handkines/ligaments/wvdpisometa.htm Ligaments of the upper limb {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |