|
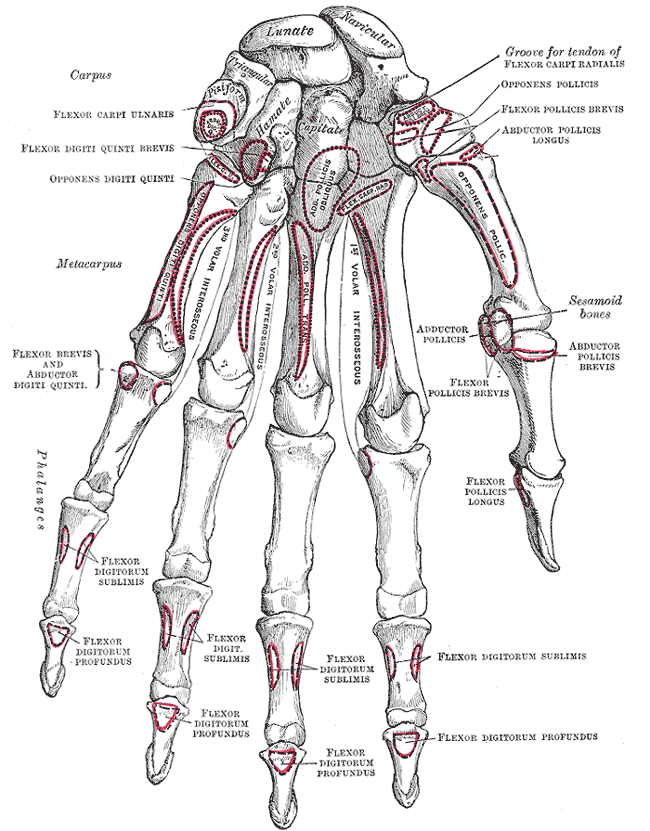
Adductor Pollicis
In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique. It is a fleshy, flat, triangular, and fan-shaped muscle deep in the thenar compartment beneath the long flexor tendons and the lumbrical muscles at the center of the palm. It overlies the metacarpal bones and the interosseous muscles. Structure Oblique head The oblique head (Latin: ''adductor obliquus pollicis'') arises by several slips from the capitate bone, the bases of the second and third metacarpals, the intercarpal ligaments, and the sheath of the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis. Gray's Anatomy 1918. (See infobox) From this origin the greater number of fibers pass obliquely downward and converge to a tendon, which, uniting with the tendons of the medial portion of the flexor pollicis brevis and the transverse head of the adductor pollicis, is inserted into the ulnar side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Metacarpal
The third metacarpal bone (metacarpal bone of the middle finger) is a little smaller than the second. The dorsal aspect of its base presents on its radial side a pyramidal eminence, the styloid process, which extends upward behind the capitate; immediately distal to this is a rough surface for the attachment of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle. The carpal articular facet is concave behind, flat in front, and articulates with the capitate. On the radial side is a smooth, concave facet for articulation with the second metacarpal, and on the ulnar side two small oval facets for the fourth metacarpal. Ossification The ossification process begins in the shaft during prenatal life, and in the head between 11th and 27th months. Additional images File:Third metacarpal bone (left hand) - animation01.gif, Third metacarpal bone of the left hand (shown in red). Animation. File:Third metacarpal bone (left hand) - animation02.gif, Third metacarpal bone of the left hand. Close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thenar Eminence
The thenar eminence is the mound formed at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand by the intrinsic group of muscles of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The word thenar comes . Structure The following three muscles are considered part of the thenar eminence: * Abductor pollicis brevis abducts the thumb. This muscle is the most superficial of the thenar group. * Flexor pollicis brevis, which lies next to the abductor, will flex the thumb, curling it up in the palm. (The Flexor pollicis longus, which is inserted into the distal phalanx of the thumb, is not considered part of the thenar eminence.) * Opponens pollicis lies deep to abductor pollicis brevis. As its name suggests it opposes the thumb, bringing it against the fingers. This is a very important movement, as most of human hand dexterity comes from this action. Another muscle that controls movement of the thumb is adductor pollicis. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abductor Pollicis Brevis
The abductor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that functions as an abductor of the thumb. Structure The abductor pollicis brevis is a flat, thin muscle located just under the skin. It is a thenar muscle, and therefore contributes to the bulk of the palm's thenar eminence. It originates from the flexor retinaculum of the hand, the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, and additionally sometimes from the tubercle of the trapezium. Running lateralward and downward, it is inserted by a thin, flat tendon into the lateral side of the base of the first phalanx of the thumb, and the capsule of the metacarpophalangeal joint. Nerve supply The abductor pollicis brevis is supplied by the recurrent branch of the median nerve (Roots C8-T1). Function Abduction of the thumb is defined as the movement of the thumb anteriorly, a direction perpendicular to the palm. The abductor pollicis brevis does this by acting across both the carpometacarpal joint and the metacarpophalangeal joint The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Pollicis Longus
The flexor pollicis longus (; FPL, Latin ''flexor'', bender; ''pollicis'', of the thumb; ''longus'', long) is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is unique to humans, being either rudimentary or absent in other primates. A meta-analysis indicated accessory flexor pollicis longus is present in around 48% of the population. Human anatomy Origin and insertion It arises from the grooved anterior (side of palm) surface of the body of the radius, extending from immediately below the radial tuberosity and oblique line to within a short distance of the pronator quadratus muscle.Gray 1918, ''Flexor Pollicis Longus'', paras 20, 25 An occasionally present accessory long head of the flexor pollicis longus muscle is called 'Gantzer's muscle'. It may cause compression of the anterior interosseous nerve. It arises also from the adjacent part of the interosseous membrane of the forearm, and gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciculus
''Fasciculus vesanus'' is an extinct species of stem-group ctenophores known from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. It is dated to and belongs to middle Cambrian strata. The species is remarkable for its two sets of long and short comb rows, not seen in similar form elsewhere in the fossil record or among modern species. See also *'' Ctenorhabdotus capulus'' *'' Xanioascus canadensis'' Maotianshan shales The Maotianshan Shales are a series of Early Cambrian deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their '' Konservat Lagerstätten'', deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shale ... ctenophores **'' Maotianoascus octonarius'' **'' Sinoascus paillatus'' **'' Stromatoveris psygmoglena'' References External links * Prehistoric ctenophore genera Burgess Shale animals Monotypic ctenophore genera Fossil taxa described in 1978 Cambrian genus extinctions {{Ctenophore-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
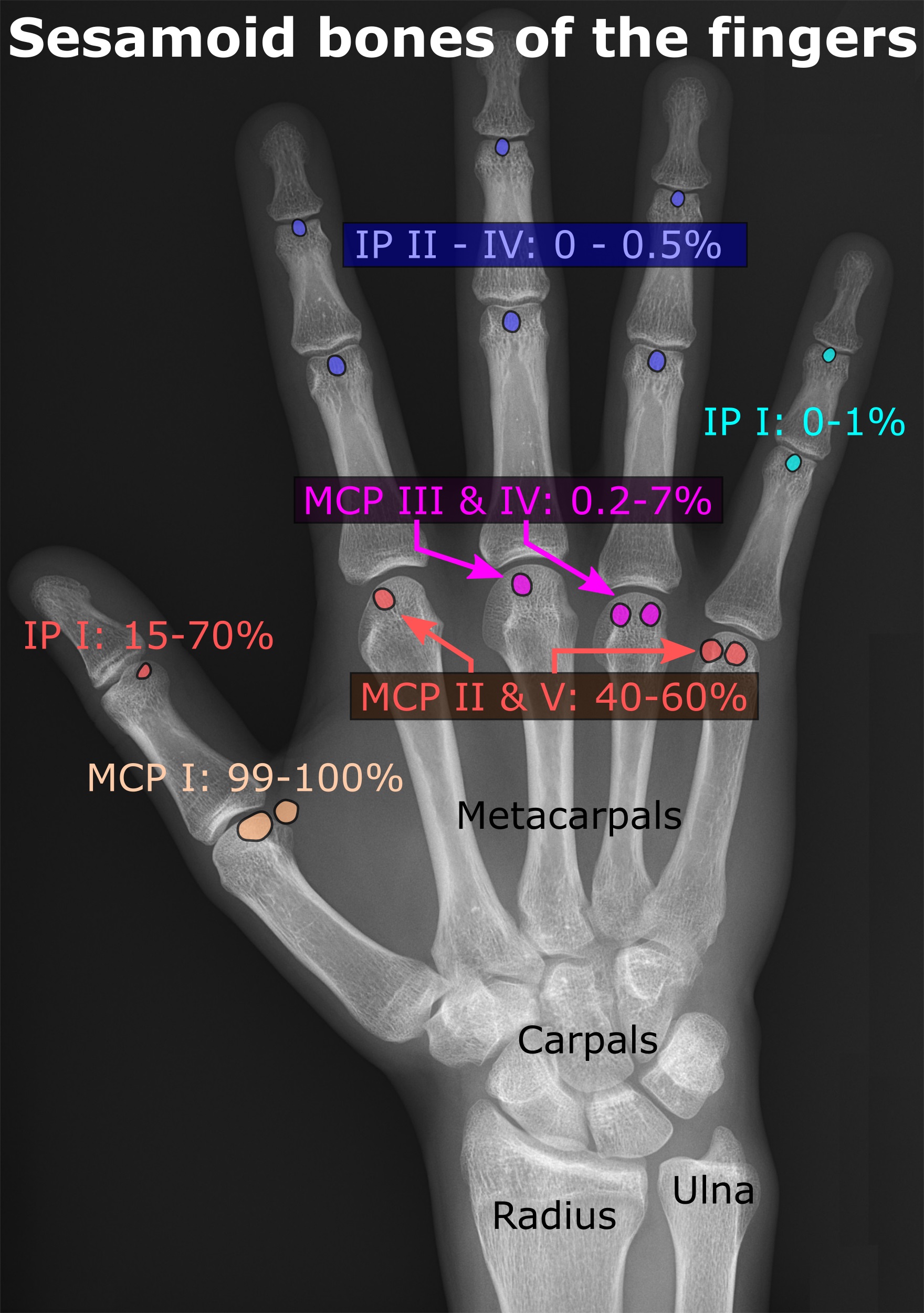
Sesamoid
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a normal variant. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulleys, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit muscular forces. Structure Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the body, including: * In the knee—the patella (within the quadriceps tendon). This is the largest sesamoid bone. * In the hand—two sesamoid bones are commonly found in the distal portions of the first metacarpal bone (within the tendons of adductor pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis). There is also commonly a sesamoid bone in distal portions of the second metacarpal bone. * In the wrist—The pisiform of the wrist is a sesamoid bone (within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx Bones
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Pollicis Brevis
The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part. Origin and insertion The muscle's superficial head arises from the distal edge of the flexor retinaculum and the tubercle of the trapezium, the most lateral bone in the distal row of carpal bones. It passes along the radial side of the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus. The deeper (and medial) head "varies in size and may be absent." It arises from the trapezoid and capitate bones on the floor of the carpal tunnel, as well as the ligaments of the distal carpal row. Both heads become tendinous and insert together into the radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb; at the junction between the tendinous heads there is a sesamoid bone.'' Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox Innervation The superficial head is usually innervated by the lateral terminal branch of the median nerve. The deep part is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray's Anatomy
''Gray's Anatomy'' is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter, and first published in London in 1858. It has gone through multiple revised editions and the current edition, the 42nd (October 2020), remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible". Earlier editions were called ''Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical'', ''Anatomy of the Human Body'' and ''Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied'', but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, ''Gray's Anatomy''. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject. Publication history Origins The English anatomist Henry Gray was born in 1827. He studied the development of the endocrine glands and spleen and in 1853 was appointed Lecturer on Anatomy at St George's Hospital Medical School in London. In 1855, he approached his colleague Henry Vandyke Carter with his idea to produce an inexpensive a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Carpi Radialis
In anatomy, flexor carpi radialis is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (radially) abduct the hand. The Latin ''carpus'' means wrist; hence flexor carpi is a flexor of the wrist. Origin and insertion The flexor carpi radialis is one of four muscles in the superficial layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm. This muscle originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus as part of the common flexor tendon. It runs just laterally of flexor digitorum superficialis and inserts on the anterior aspect of the base of the second metacarpal, and has small slips to both the third metacarpal and trapezium tuberosity. The tendon of the flexor carpi radialis is visible on the anterior surface of the forearm, just proximal to the wrist, when the wrist is flexed. It is the tendon seen most lateral, closest to the thumb. Nerve and artery Like most flexors of the anterior compartment of the forearm, FCR is innervated by the median nerve, specifically by axons from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacarpus
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist, which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones are analogous to the metatarsal bones in the foot. Structure The metacarpals form a transverse arch to which the rigid row of distal carpal bones are fixed. The peripheral metacarpals (those of the thumb and little finger) form the sides of the cup of the palmar gutter and as they are brought together they deepen this concavity. The index metacarpal is the most firmly fixed, while the thumb metacarpal articulates with the trapezium and acts independently from the others. The middle metacarpals are tightly united to the carpus by intrinsic interlocking bone elements at their bases. The ring metacarpal is somewhat more mobile while the fifth metacarpal is semi-independent.Tubiana ''et al'' 1998, p 11 Each metacarpal bone consists of a bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitate Bone
The capitate bone is a bone in the human wrist found in the center of the carpal bone region, located at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone (the middle finger) and forms the third carpometacarpal joint. The capitate bone is the largest of the carpal bones in the human hand. It presents, above, a rounded portion or head, which is received into the concavity formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones; a constricted portion or neck; and below this, the body.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). See infobox. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "third distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians. Structure The capitate is the largest carpal bone found within the hand. The capitate is found within the distal row of carpal bones. The capitate lies directly adjacent to the metacarpal of the ring finger on its distal surface, has the hamate on its ulnar surface and trapezoid on its radial surface, and abuts t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_dorsal_view.png)