Sea And River Gods on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the
 The sea is the interconnected system of all the Earth's oceanic waters, including the
The sea is the interconnected system of all the Earth's oceanic waters, including the https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/sea . Accessed 14 March 2021. However, the word "sea" can also be used for many specific, much smaller bodies of seawater, such as the

Lesson 7: The Water Cycle
" in ''Ocean Explorer''. The

Drinking Seawater Can Be Deadly to Humans
".
. USGS. By Richard Z. Poore, Richard S. Williams, Jr., and Christopher Tracey. For at least the last 100 years, Sea level rise, sea level has been rising at an average rate of about per year. Most of this rise can be attributed to an increase in the temperature of the sea due to climate change, and the resulting slight thermal expansion of the upper of water. Additional contributions, as much as one quarter of the total, come from water sources on land, such as Retreat of glaciers since 1850, melting snow and glaciers and extraction of groundwater for irrigation and other agricultural and human needs.
''Essentials of Oceanography''
. 6th ed. pp. 204 ff. Brooks/Cole, Belmont, California, Belmont. . Most waves are less than high and it is not unusual for strong storms to double or triple that height; offshore construction such as offshore wind farm, wind farms and oil platforms use metocean statistics from measurements in computing the wave forces (due to for instance the hundred-year wave) they are designed against. Rogue waves, however, have been documented at heights above . The top of a wave is known as the crest, the lowest point between waves is the trough and the distance between the crests is the wavelength. The wave is pushed across the surface of the sea by the wind, but this represents a transfer of energy and not a horizontal movement of water. As waves approach land and waves and shallow water, move into shallow water, they change their behavior. If approaching at an angle, waves may bend (refraction) or wrap rocks and headlands (diffraction). When the wave reaches a point where its deepest oscillations of the water contact the seabed, they begin to slow down. This pulls the crests closer together and increases the wave height, waves' height, which is called wave shoaling. When the ratio of the wave's height to the water depth increases above a certain limit, it "wave breaking, breaks", toppling over in a mass of foaming water. This rushes in a sheet up the beach before retreating into the sea under the influence of gravity.
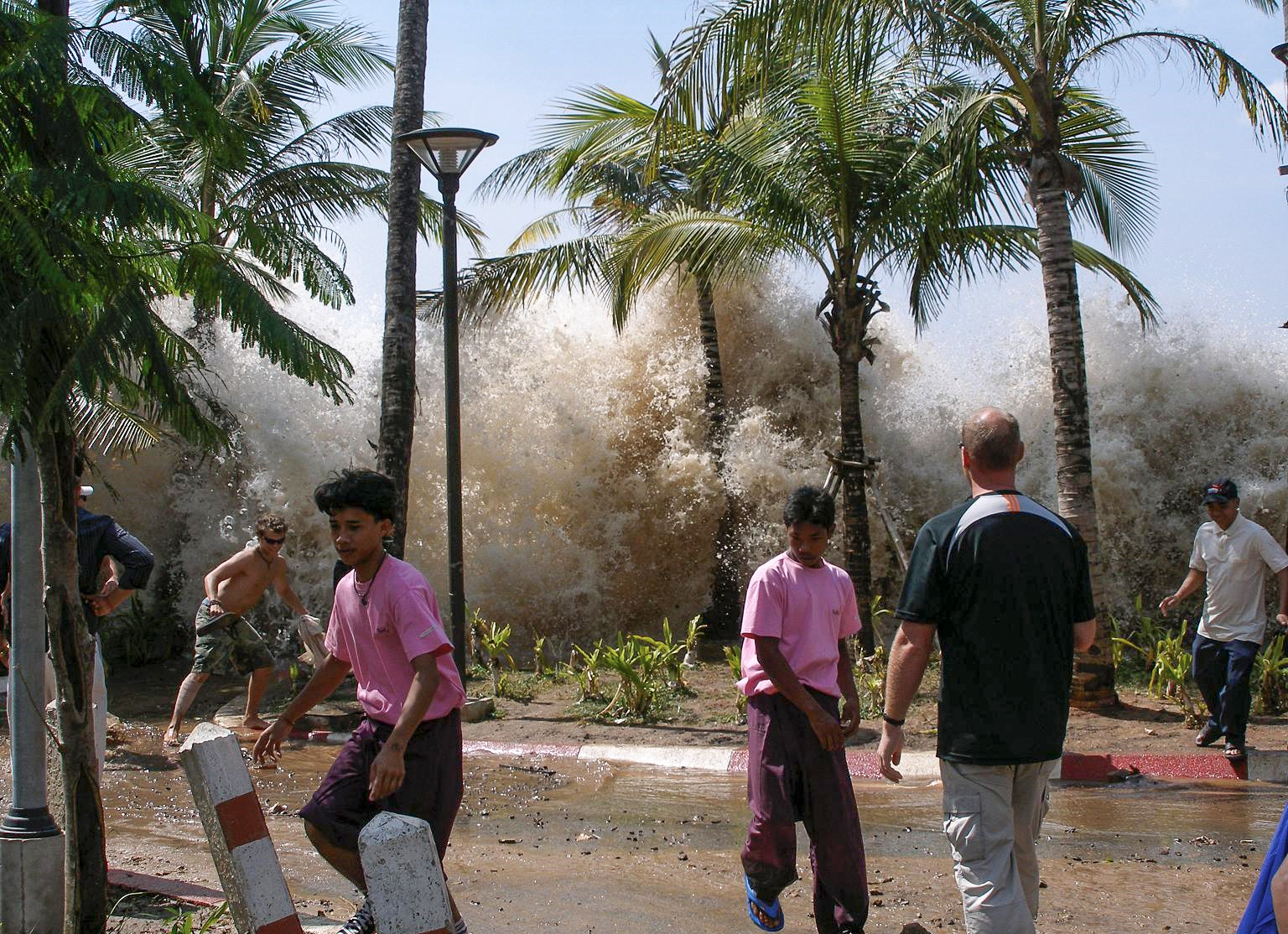 A tsunami is an unusual form of wave caused by an infrequent powerful event such as an underwater earthquake or landslide, a meteorite impact, a volcanic eruption or a collapse of land into the sea. These events can temporarily lift or lower the surface of the sea in the affected area, usually by a few feet. The potential energy of the displaced seawater is turned into kinetic energy, creating a shallow wave, a tsunami, radiating outwards at a velocity proportional to the square root of the depth of the water and which therefore travels much faster in the open ocean than on a continental shelf. In the deep open sea, tsunamis have wavelengths of around , travel at speeds of over 600 miles per hour (970 km/hr) and usually have a height of less than three feet, so they often pass unnoticed at this stage. In contrast, ocean surface waves caused by winds have wavelengths of a few hundred feet, travel at up to and are up to high.
As a tsunami Wave shoaling, moves into shallower water its speed decreases, its wavelength shortens and its amplitude increases enormously, behaving in the same way as a wind-generated wave in shallow water, but on a vastly greater scale. Either the trough or the crest of a tsunami can arrive at the coast first. In the former case, the sea draws back and leaves subtidal areas close to the shore exposed which provides a useful warning for people on land. When the crest arrives, it does not usually break but rushes inland, flooding all in its path. Much of the destruction may be caused by the flood water draining back into the sea after the tsunami has struck, dragging debris and people with it. Often several tsunami are caused by a single geological event and arrive at intervals of between eight minutes and two hours. The first wave to arrive on shore may not be the biggest or most destructive.
A tsunami is an unusual form of wave caused by an infrequent powerful event such as an underwater earthquake or landslide, a meteorite impact, a volcanic eruption or a collapse of land into the sea. These events can temporarily lift or lower the surface of the sea in the affected area, usually by a few feet. The potential energy of the displaced seawater is turned into kinetic energy, creating a shallow wave, a tsunami, radiating outwards at a velocity proportional to the square root of the depth of the water and which therefore travels much faster in the open ocean than on a continental shelf. In the deep open sea, tsunamis have wavelengths of around , travel at speeds of over 600 miles per hour (970 km/hr) and usually have a height of less than three feet, so they often pass unnoticed at this stage. In contrast, ocean surface waves caused by winds have wavelengths of a few hundred feet, travel at up to and are up to high.
As a tsunami Wave shoaling, moves into shallower water its speed decreases, its wavelength shortens and its amplitude increases enormously, behaving in the same way as a wind-generated wave in shallow water, but on a vastly greater scale. Either the trough or the crest of a tsunami can arrive at the coast first. In the former case, the sea draws back and leaves subtidal areas close to the shore exposed which provides a useful warning for people on land. When the crest arrives, it does not usually break but rushes inland, flooding all in its path. Much of the destruction may be caused by the flood water draining back into the sea after the tsunami has struck, dragging debris and people with it. Often several tsunami are caused by a single geological event and arrive at intervals of between eight minutes and two hours. The first wave to arrive on shore may not be the biggest or most destructive.
 Wind blowing over the surface of the sea causes friction at the interface between air and sea. Not only does this cause waves to form but it also makes the surface seawater move in the same direction as the wind. Although winds are variable, in any one place they predominantly blow from a single direction and thus a surface current can be formed. Westerly winds are most frequent in the mid-latitudes while easterlies dominate the tropics. When water moves in this way, other water flows in to fill the gap and a circular movement of surface currents known as a Ocean gyre, gyre is formed. There are five main gyres in the world's oceans: two in the Pacific, two in the Atlantic and one in the Indian Ocean. Other smaller gyres are found in lesser seas and a single gyre flows around
Wind blowing over the surface of the sea causes friction at the interface between air and sea. Not only does this cause waves to form but it also makes the surface seawater move in the same direction as the wind. Although winds are variable, in any one place they predominantly blow from a single direction and thus a surface current can be formed. Westerly winds are most frequent in the mid-latitudes while easterlies dominate the tropics. When water moves in this way, other water flows in to fill the gap and a circular movement of surface currents known as a Ocean gyre, gyre is formed. There are five main gyres in the world's oceans: two in the Pacific, two in the Atlantic and one in the Indian Ocean. Other smaller gyres are found in lesser seas and a single gyre flows around  Surface currents only affect the top few hundred metres of the sea, but there are also large-scale flows in the ocean depths caused by the movement of deep water masses. A main deep ocean current flows through all the world's oceans and is known as the thermohaline circulation or global conveyor belt. This movement is slow and is driven by differences in density of the water caused by variations in salinity and temperature. At high latitudes the water is chilled by the low atmospheric temperature and becomes saltier as sea ice crystallizes out. Both these factors make it denser, and the water sinks. From the deep sea near Greenland, such water flows southwards between the continental landmasses on either side of the Atlantic. When it reaches the Antarctic, it is joined by further masses of cold, sinking water and flows eastwards. It then splits into two streams that move northwards into the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Here it is gradually warmed, becomes less dense, rises towards the surface and loops back on itself. It takes a thousand years for this circulation pattern to be completed.
Besides gyres, there are temporary surface currents that occur under specific conditions. When waves meet a shore at an angle, a Longshore drift, longshore current is created as water is pushed along parallel to the coastline. The water swirls up onto the beach at right angles to the approaching waves but drains away straight down the slope under the effect of gravity. The larger the breaking waves, the longer the beach and the more oblique the wave approach, the stronger is the longshore current. These currents can shift great volumes of sand or pebbles, create Spit (landform), spits and make beaches disappear and water channels silt up. A rip current can occur when water piles up near the shore from advancing waves and is funnelled out to sea through a channel in the seabed. It may occur at a gap in a Shoal, sandbar or near a man-made structure such as a groyne. These strong currents can have a velocity of per second, can form at different places at different stages of the tide and can carry away unwary bathers. Temporary upwelling currents occur when the wind pushes water away from the land and deeper water rises to replace it. This cold water is often rich in nutrients and creates blooms of phytoplankton and a great increase in the productivity of the sea.
Surface currents only affect the top few hundred metres of the sea, but there are also large-scale flows in the ocean depths caused by the movement of deep water masses. A main deep ocean current flows through all the world's oceans and is known as the thermohaline circulation or global conveyor belt. This movement is slow and is driven by differences in density of the water caused by variations in salinity and temperature. At high latitudes the water is chilled by the low atmospheric temperature and becomes saltier as sea ice crystallizes out. Both these factors make it denser, and the water sinks. From the deep sea near Greenland, such water flows southwards between the continental landmasses on either side of the Atlantic. When it reaches the Antarctic, it is joined by further masses of cold, sinking water and flows eastwards. It then splits into two streams that move northwards into the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Here it is gradually warmed, becomes less dense, rises towards the surface and loops back on itself. It takes a thousand years for this circulation pattern to be completed.
Besides gyres, there are temporary surface currents that occur under specific conditions. When waves meet a shore at an angle, a Longshore drift, longshore current is created as water is pushed along parallel to the coastline. The water swirls up onto the beach at right angles to the approaching waves but drains away straight down the slope under the effect of gravity. The larger the breaking waves, the longer the beach and the more oblique the wave approach, the stronger is the longshore current. These currents can shift great volumes of sand or pebbles, create Spit (landform), spits and make beaches disappear and water channels silt up. A rip current can occur when water piles up near the shore from advancing waves and is funnelled out to sea through a channel in the seabed. It may occur at a gap in a Shoal, sandbar or near a man-made structure such as a groyne. These strong currents can have a velocity of per second, can form at different places at different stages of the tide and can carry away unwary bathers. Temporary upwelling currents occur when the wind pushes water away from the land and deeper water rises to replace it. This cold water is often rich in nutrients and creates blooms of phytoplankton and a great increase in the productivity of the sea.
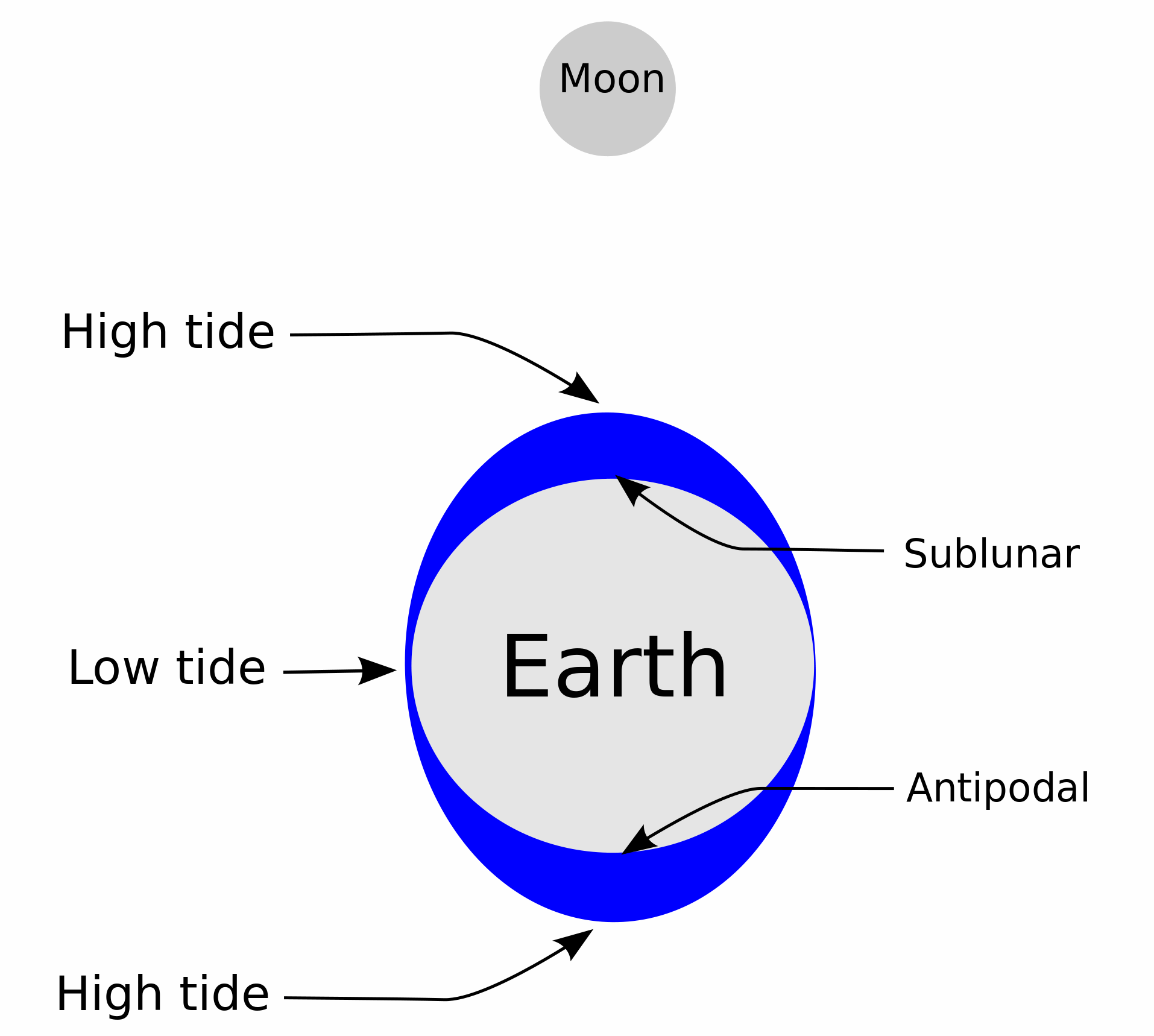 Tides are the regular rise and fall in water level experienced by seas and oceans in response to the Gravity, gravitational influences of the Moon and the Sun, and the effects of the Earth's rotation. During each tidal cycle, at any given place the water rises to a maximum height known as "high tide" before ebbing away again to the minimum "low tide" level. As the water recedes, it uncovers more and more of the foreshore, also known as the intertidal zone. The difference in height between the high tide and low tide is known as the tidal range or tidal amplitude.
Most places experience two high tides each day, occurring at intervals of about 12 hours and 25 minutes. This is half the 24 hours and 50 minute period that it takes for the Earth to make a complete revolution and return the Moon to its previous position relative to an observer. The Moon's mass is some 27 million times smaller than the Sun, but it is 400 times closer to the Earth. Tidal force or tide-raising force decreases rapidly with distance, so the moon has more than twice as great an effect on tides as the Sun. A bulge is formed in the ocean at the place where the Earth is closest to the Moon, because it is also where the effect of the Moon's gravity is stronger. On the opposite side of the Earth, the lunar force is at its weakest and this causes another bulge to form. As the Moon rotates around the Earth, so do these ocean bulges move around the Earth. The gravitational attraction of the Sun is also working on the seas, but its effect on tides is less powerful than that of the Moon, and when the Sun, Moon and Earth are all aligned (full moon and new moon), the combined effect results in the high "spring tides". In contrast, when the Sun is at 90° from the Moon as viewed from Earth, the combined gravitational effect on tides is less causing the lower "neap tides".
A storm surge can occur when high winds pile water up against the coast in a shallow area and this, coupled with a low pressure system, can raise the surface of the sea at high tide dramatically.
Tides are the regular rise and fall in water level experienced by seas and oceans in response to the Gravity, gravitational influences of the Moon and the Sun, and the effects of the Earth's rotation. During each tidal cycle, at any given place the water rises to a maximum height known as "high tide" before ebbing away again to the minimum "low tide" level. As the water recedes, it uncovers more and more of the foreshore, also known as the intertidal zone. The difference in height between the high tide and low tide is known as the tidal range or tidal amplitude.
Most places experience two high tides each day, occurring at intervals of about 12 hours and 25 minutes. This is half the 24 hours and 50 minute period that it takes for the Earth to make a complete revolution and return the Moon to its previous position relative to an observer. The Moon's mass is some 27 million times smaller than the Sun, but it is 400 times closer to the Earth. Tidal force or tide-raising force decreases rapidly with distance, so the moon has more than twice as great an effect on tides as the Sun. A bulge is formed in the ocean at the place where the Earth is closest to the Moon, because it is also where the effect of the Moon's gravity is stronger. On the opposite side of the Earth, the lunar force is at its weakest and this causes another bulge to form. As the Moon rotates around the Earth, so do these ocean bulges move around the Earth. The gravitational attraction of the Sun is also working on the seas, but its effect on tides is less powerful than that of the Moon, and when the Sun, Moon and Earth are all aligned (full moon and new moon), the combined effect results in the high "spring tides". In contrast, when the Sun is at 90° from the Moon as viewed from Earth, the combined gravitational effect on tides is less causing the lower "neap tides".
A storm surge can occur when high winds pile water up against the coast in a shallow area and this, coupled with a low pressure system, can raise the surface of the sea at high tide dramatically.
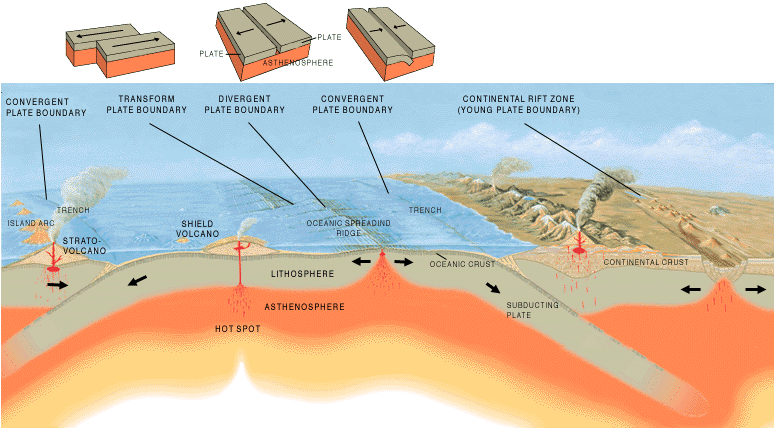 The Earth is composed of a magnetic central Planetary core, core, a mostly liquid Mantle (geology), mantle and a hard rigid outer shell (or lithosphere), which is composed of the Earth's rocky Crust (geology), crust and the deeper mostly solid outer layer of the mantle. On land the crust is known as the continental crust while under the sea it is known as the oceanic crust. The latter is composed of relatively dense basalt and is some five to ten kilometres (three to six miles) thick. The relatively thin lithosphere floats on the weaker and hotter mantle below and is fractured into a number of tectonic plates. In mid-ocean, magma is constantly being thrust through the seabed between adjoining plates to form mid-oceanic ridges and here convection currents within the mantle tend to drive the two plates apart. Parallel to these ridges and nearer the coasts, one oceanic plate may slide beneath another oceanic plate in a process known as subduction. Deep Oceanic trench, trenches are formed here and the process is accompanied by friction as the plates grind together. The movement proceeds in jerks which cause earthquakes, heat is produced and magma is forced up creating underwater mountains, some of which may form chains of volcanic islands near to deep trenches. Near some of the boundaries between the land and sea, the slightly denser oceanic plates slide beneath the continental plates and more subduction trenches are formed. As they grate together, the continental plates are deformed and buckle causing mountain building and seismic activity.
The Earth's deepest trench is the Mariana Trench which extends for about across the seabed. It is near the Mariana Islands, a volcanic archipelago in the West Pacific. Its deepest point is 10.994 kilometres (nearly 7 miles) below the surface of the sea.
The Earth is composed of a magnetic central Planetary core, core, a mostly liquid Mantle (geology), mantle and a hard rigid outer shell (or lithosphere), which is composed of the Earth's rocky Crust (geology), crust and the deeper mostly solid outer layer of the mantle. On land the crust is known as the continental crust while under the sea it is known as the oceanic crust. The latter is composed of relatively dense basalt and is some five to ten kilometres (three to six miles) thick. The relatively thin lithosphere floats on the weaker and hotter mantle below and is fractured into a number of tectonic plates. In mid-ocean, magma is constantly being thrust through the seabed between adjoining plates to form mid-oceanic ridges and here convection currents within the mantle tend to drive the two plates apart. Parallel to these ridges and nearer the coasts, one oceanic plate may slide beneath another oceanic plate in a process known as subduction. Deep Oceanic trench, trenches are formed here and the process is accompanied by friction as the plates grind together. The movement proceeds in jerks which cause earthquakes, heat is produced and magma is forced up creating underwater mountains, some of which may form chains of volcanic islands near to deep trenches. Near some of the boundaries between the land and sea, the slightly denser oceanic plates slide beneath the continental plates and more subduction trenches are formed. As they grate together, the continental plates are deformed and buckle causing mountain building and seismic activity.
The Earth's deepest trench is the Mariana Trench which extends for about across the seabed. It is near the Mariana Islands, a volcanic archipelago in the West Pacific. Its deepest point is 10.994 kilometres (nearly 7 miles) below the surface of the sea.

 The zone where land meets sea is known as the coast and the part between the lowest spring tides and the upper limit reached by splashing waves is the shore. A beach is the accumulation of sand or Shingle beach, shingle on the shore. A headland is a point of land jutting out into the sea and a larger promontory is known as a Cape (geography), cape. The indentation of a coastline, especially between two headlands, is a bay, a small bay with a narrow inlet is a cove and a large bay may be referred to as a List of gulfs, gulf. Coastlines are influenced by a number of factors including the strength of the waves arriving on the shore, the gradient of the land margin, the composition and hardness of the coastal rock, the inclination of the off-shore slope and the changes of the level of the land due to local uplift or submergence. Normally, waves roll towards the shore at the rate of six to eight per minute and these are known as constructive waves as they tend to move material up the beach and have little erosive effect. Storm waves arrive on shore in rapid succession and are known as destructive waves as the swash moves beach material seawards. Under their influence, the sand and shingle on the beach is ground together and abraded. Around high tide, the power of a storm wave impacting on the foot of a cliff has a shattering effect as air in cracks and crevices is compressed and then expands rapidly with release of pressure. At the same time, sand and pebbles have an erosive effect as they are thrown against the rocks. This tends to undercut the cliff, and normal weathering processes such as the action of frost follows, causing further destruction. Gradually, a wave-cut platform develops at the foot of the cliff and this has a protective effect, reducing further wave-erosion.
Material worn from the margins of the land eventually ends up in the sea. Here it is subject to Attrition (erosion), attrition as currents flowing parallel to the coast scour out channels and transport sand and pebbles away from their place of origin. Sediment carried to the sea by rivers settles on the seabed causing River delta, deltas to form in estuaries. All these materials move back and forth under the influence of waves, tides and currents. Dredging removes material and deepens channels but may have unexpected effects elsewhere on the coastline. Governments make efforts to prevent flooding of the land by the building of Breakwater (structure), breakwaters, seawalls, levee, dykes and levees and other sea defences. For instance, the Thames Barrier is designed to protect London from a storm surge, while the failure of the dykes and levees around New Orleans during Hurricane Katrina created a humanitarian crisis in the United States.
The zone where land meets sea is known as the coast and the part between the lowest spring tides and the upper limit reached by splashing waves is the shore. A beach is the accumulation of sand or Shingle beach, shingle on the shore. A headland is a point of land jutting out into the sea and a larger promontory is known as a Cape (geography), cape. The indentation of a coastline, especially between two headlands, is a bay, a small bay with a narrow inlet is a cove and a large bay may be referred to as a List of gulfs, gulf. Coastlines are influenced by a number of factors including the strength of the waves arriving on the shore, the gradient of the land margin, the composition and hardness of the coastal rock, the inclination of the off-shore slope and the changes of the level of the land due to local uplift or submergence. Normally, waves roll towards the shore at the rate of six to eight per minute and these are known as constructive waves as they tend to move material up the beach and have little erosive effect. Storm waves arrive on shore in rapid succession and are known as destructive waves as the swash moves beach material seawards. Under their influence, the sand and shingle on the beach is ground together and abraded. Around high tide, the power of a storm wave impacting on the foot of a cliff has a shattering effect as air in cracks and crevices is compressed and then expands rapidly with release of pressure. At the same time, sand and pebbles have an erosive effect as they are thrown against the rocks. This tends to undercut the cliff, and normal weathering processes such as the action of frost follows, causing further destruction. Gradually, a wave-cut platform develops at the foot of the cliff and this has a protective effect, reducing further wave-erosion.
Material worn from the margins of the land eventually ends up in the sea. Here it is subject to Attrition (erosion), attrition as currents flowing parallel to the coast scour out channels and transport sand and pebbles away from their place of origin. Sediment carried to the sea by rivers settles on the seabed causing River delta, deltas to form in estuaries. All these materials move back and forth under the influence of waves, tides and currents. Dredging removes material and deepens channels but may have unexpected effects elsewhere on the coastline. Governments make efforts to prevent flooding of the land by the building of Breakwater (structure), breakwaters, seawalls, levee, dykes and levees and other sea defences. For instance, the Thames Barrier is designed to protect London from a storm surge, while the failure of the dykes and levees around New Orleans during Hurricane Katrina created a humanitarian crisis in the United States.
 The oceans are home to a diverse collection of life forms that use it as a habitat. Since sunlight illuminates only the upper layers, the major part of the ocean exists in permanent darkness. As the different depth and temperature zones each provide habitat for a unique set of species, the marine environment as a whole encompasses an immense diversity of life. Marine habitats range from surface water to the deepest oceanic trenches, including coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky seabeds, and the open pelagic zone. The organisms living in the sea range from cetaceans, whales 30 metres (100 ft) long to microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton, fungi, and bacteria. Marine life plays an important part in the carbon cycle as photosynthetic organisms convert dissolved carbon dioxide into organic carbon and it is economically important to humans for providing fishery, fish for use as food.
Life may have originated in the sea and all the Phylum, major groups of animals are represented there. Scientists differ as to precisely where in the sea life arose: the Miller-Urey experiments suggested a dilute chemical "soup" in open water, but more recent suggestions include volcanic hot springs, fine-grained clay sediments, or deep-sea "black smoker" vents, all of which would have provided protection from damaging ultraviolet radiation which was not blocked by the early Earth's atmosphere.
The oceans are home to a diverse collection of life forms that use it as a habitat. Since sunlight illuminates only the upper layers, the major part of the ocean exists in permanent darkness. As the different depth and temperature zones each provide habitat for a unique set of species, the marine environment as a whole encompasses an immense diversity of life. Marine habitats range from surface water to the deepest oceanic trenches, including coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky seabeds, and the open pelagic zone. The organisms living in the sea range from cetaceans, whales 30 metres (100 ft) long to microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton, fungi, and bacteria. Marine life plays an important part in the carbon cycle as photosynthetic organisms convert dissolved carbon dioxide into organic carbon and it is economically important to humans for providing fishery, fish for use as food.
Life may have originated in the sea and all the Phylum, major groups of animals are represented there. Scientists differ as to precisely where in the sea life arose: the Miller-Urey experiments suggested a dilute chemical "soup" in open water, but more recent suggestions include volcanic hot springs, fine-grained clay sediments, or deep-sea "black smoker" vents, all of which would have provided protection from damaging ultraviolet radiation which was not blocked by the early Earth's atmosphere.
 There is a broader spectrum of higher animal taxon, taxa in the sea than on land, many marine species have yet to be discovered and the number known to science is expanding annually. Some vertebrates such as seabirds, Pinniped, seals and sea turtles return to the land to breed but fish, cetaceans and sea snakes have a completely aquatic lifestyle and many invertebrate Phylum, phyla are entirely marine. In fact, the oceans teem with life and provide many varying microhabitats. One of these is the surface film which, even though tossed about by the movement of waves, provides a rich environment and is home to bacteria, Marine fungi, fungi, microalgae, protozoa, fish eggs and various larvae.
The pelagic zone contains Fauna#Macrofauna, macro- and microfauna and myriad zooplankton which drift with the currents. Most of the smallest organisms are the larvae of fish and marine invertebrates which liberate Egg (biology), eggs in vast numbers because the chance of any one embryo surviving to maturity is so minute. The zooplankton feed on phytoplankton and on each other and form a basic part of the complex food chain that extends through variously sized fish and other nektonic organisms to large squid, sharks, porpoises, dolphins and whales. Some marine creatures make large migrations, either to other regions of the ocean on a seasonal basis or vertical migrations daily, often ascending to feed at night and descending to safety by day. Ships can introduce or spread invasive species through the discharge of ballast water or the transport of organisms that have accumulated as part of the fouling community on the hulls of vessels.
The demersal zone supports many animals that feed on benthic organisms or seek protection from predators and the seabed provides a range of habitats on or under the surface of the Substrate (biology), substrate which are used by creatures adapted to these conditions. The tidal zone with its periodic exposure to the dehydrating air is home to barnacles, molluscs and crustaceans. The neritic zone has many organisms that need light to flourish. Here, among algal encrusted rocks live sponges, echinoderms, polychaete worms, sea anemones and other invertebrates. Corals often contain photosynthetic Symbiosis, symbionts and live in shallow waters where light penetrates. The extensive calcareous skeletons they extrude build up into coral reefs which are an important feature of the seabed. These provide a Biodiversity, biodiverse habitat for reef dwelling organisms. There is less sea life on the floor of deeper seas but marine life also flourishes around seamounts that rise from the depths, where fish and other animals congregate to spawn and feed. Close to the seabed live demersal fish that feed largely on pelagic organisms or Benthos, benthic invertebrates. Exploration of the deep sea by submersibles revealed a new world of creatures living on the seabed that scientists had not previously known to exist. Some like the Detritivore, detrivores rely on organic material falling to the ocean floor. Others cluster round deep sea hydrothermal vents where mineral-rich flows of water emerge from the seabed, supporting communities whose primary producers are sulphide-oxidising chemoautotrophic bacteria, and whose consumers include specialised bivalves, sea anemones, barnacles, crabs, worms and fish, often found nowhere else. A dead whale sinking to the bottom of the ocean provides food for an assembly of organisms which similarly rely largely on the actions of sulphur-reducing bacteria. Such places support unique biomes where many new microbes and other lifeforms have been discovered.
There is a broader spectrum of higher animal taxon, taxa in the sea than on land, many marine species have yet to be discovered and the number known to science is expanding annually. Some vertebrates such as seabirds, Pinniped, seals and sea turtles return to the land to breed but fish, cetaceans and sea snakes have a completely aquatic lifestyle and many invertebrate Phylum, phyla are entirely marine. In fact, the oceans teem with life and provide many varying microhabitats. One of these is the surface film which, even though tossed about by the movement of waves, provides a rich environment and is home to bacteria, Marine fungi, fungi, microalgae, protozoa, fish eggs and various larvae.
The pelagic zone contains Fauna#Macrofauna, macro- and microfauna and myriad zooplankton which drift with the currents. Most of the smallest organisms are the larvae of fish and marine invertebrates which liberate Egg (biology), eggs in vast numbers because the chance of any one embryo surviving to maturity is so minute. The zooplankton feed on phytoplankton and on each other and form a basic part of the complex food chain that extends through variously sized fish and other nektonic organisms to large squid, sharks, porpoises, dolphins and whales. Some marine creatures make large migrations, either to other regions of the ocean on a seasonal basis or vertical migrations daily, often ascending to feed at night and descending to safety by day. Ships can introduce or spread invasive species through the discharge of ballast water or the transport of organisms that have accumulated as part of the fouling community on the hulls of vessels.
The demersal zone supports many animals that feed on benthic organisms or seek protection from predators and the seabed provides a range of habitats on or under the surface of the Substrate (biology), substrate which are used by creatures adapted to these conditions. The tidal zone with its periodic exposure to the dehydrating air is home to barnacles, molluscs and crustaceans. The neritic zone has many organisms that need light to flourish. Here, among algal encrusted rocks live sponges, echinoderms, polychaete worms, sea anemones and other invertebrates. Corals often contain photosynthetic Symbiosis, symbionts and live in shallow waters where light penetrates. The extensive calcareous skeletons they extrude build up into coral reefs which are an important feature of the seabed. These provide a Biodiversity, biodiverse habitat for reef dwelling organisms. There is less sea life on the floor of deeper seas but marine life also flourishes around seamounts that rise from the depths, where fish and other animals congregate to spawn and feed. Close to the seabed live demersal fish that feed largely on pelagic organisms or Benthos, benthic invertebrates. Exploration of the deep sea by submersibles revealed a new world of creatures living on the seabed that scientists had not previously known to exist. Some like the Detritivore, detrivores rely on organic material falling to the ocean floor. Others cluster round deep sea hydrothermal vents where mineral-rich flows of water emerge from the seabed, supporting communities whose primary producers are sulphide-oxidising chemoautotrophic bacteria, and whose consumers include specialised bivalves, sea anemones, barnacles, crabs, worms and fish, often found nowhere else. A dead whale sinking to the bottom of the ocean provides food for an assembly of organisms which similarly rely largely on the actions of sulphur-reducing bacteria. Such places support unique biomes where many new microbes and other lifeforms have been discovered.
 Humans have Navigation, travelled the seas since they first built sea-going craft. Ubaid period, Mesopotamians were using bitumen#ancient times, bitumen to caulking, caulk their reed boat#History, reed boats and, a little later, masted sails.Carter, Robert (2012). ''A Companion to the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East''. Ch. 19: "Watercraft", pp. 347 ff. Wiley-Blackwell. . By c. 3000 BC, Austronesian people, Austronesians on Taiwan had begun spreading into maritime Southeast Asia. Subsequently, the Austronesian "Lapita" peoples displayed great feats of navigation, reaching out from the Bismarck Archipelago to as far away as Fiji, Tonga, and Samoa. Their descendants Polynesian navigation, continued to travel thousands of miles between tiny islands on outrigger canoe#History, outrigger canoes, and in the process they found many new islands, including Hawaii, Easter Island (Rapa Nui), and New Zealand.
The Ancient Egyptians and Phoenicians explored the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Red Sea with the Egyptian Hannu reaching the Arabian Peninsula and the African Coast around 2750 BC. In the first millennium BC, Phoenicians and Greeks established colonies throughout the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. Around 500 BC, the Carthage, Carthaginian navigator Hanno the Navigator, Hanno left a detailed periplus of an Atlantic journey that reached at least Senegal and possibly Mount Cameroon. In the Dark Ages (historiography), early Mediaeval period, the Vikings crossed the North Atlantic and even reached the northeastern fringes of North America. Novgorod Republic, Novgorodians had also been sailing the White Sea since the 13th century or before. Meanwhile, the seas along the eastern and southern Asian coast were used by Arab and Chinese traders. The Chinese Ming Dynasty had a fleet of 317 ships with 37,000 men under Zheng He in the early fifteenth century, sailing the Indian and Pacific Oceans. In the late fifteenth century, Western European mariners started making longer voyages of exploration in search of trade. Bartolomeu Dias rounded the Cape of Good Hope in 1487 and Vasco da Gama reached India via the Cape in 1498. Christopher Columbus sailed from Cadiz in 1492, attempting to reach the eastern lands of India and Japan by the novel means of travelling westwards. He made landfall instead on an island in the Caribbean Sea and a few years later, the Venetian navigator John Cabot reached Newfoundland. The Italian Amerigo Vespucci, after whom America was named, explored the South American coastline in voyages made between 1497 and 1502, discovering the mouth of the Amazon River. In 1519 the Portugal, Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan led the Spanish Timeline of the Magellan–Elcano circumnavigation, Magellan-Elcano expedition which would be the first to sail around the world.
Humans have Navigation, travelled the seas since they first built sea-going craft. Ubaid period, Mesopotamians were using bitumen#ancient times, bitumen to caulking, caulk their reed boat#History, reed boats and, a little later, masted sails.Carter, Robert (2012). ''A Companion to the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East''. Ch. 19: "Watercraft", pp. 347 ff. Wiley-Blackwell. . By c. 3000 BC, Austronesian people, Austronesians on Taiwan had begun spreading into maritime Southeast Asia. Subsequently, the Austronesian "Lapita" peoples displayed great feats of navigation, reaching out from the Bismarck Archipelago to as far away as Fiji, Tonga, and Samoa. Their descendants Polynesian navigation, continued to travel thousands of miles between tiny islands on outrigger canoe#History, outrigger canoes, and in the process they found many new islands, including Hawaii, Easter Island (Rapa Nui), and New Zealand.
The Ancient Egyptians and Phoenicians explored the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Red Sea with the Egyptian Hannu reaching the Arabian Peninsula and the African Coast around 2750 BC. In the first millennium BC, Phoenicians and Greeks established colonies throughout the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. Around 500 BC, the Carthage, Carthaginian navigator Hanno the Navigator, Hanno left a detailed periplus of an Atlantic journey that reached at least Senegal and possibly Mount Cameroon. In the Dark Ages (historiography), early Mediaeval period, the Vikings crossed the North Atlantic and even reached the northeastern fringes of North America. Novgorod Republic, Novgorodians had also been sailing the White Sea since the 13th century or before. Meanwhile, the seas along the eastern and southern Asian coast were used by Arab and Chinese traders. The Chinese Ming Dynasty had a fleet of 317 ships with 37,000 men under Zheng He in the early fifteenth century, sailing the Indian and Pacific Oceans. In the late fifteenth century, Western European mariners started making longer voyages of exploration in search of trade. Bartolomeu Dias rounded the Cape of Good Hope in 1487 and Vasco da Gama reached India via the Cape in 1498. Christopher Columbus sailed from Cadiz in 1492, attempting to reach the eastern lands of India and Japan by the novel means of travelling westwards. He made landfall instead on an island in the Caribbean Sea and a few years later, the Venetian navigator John Cabot reached Newfoundland. The Italian Amerigo Vespucci, after whom America was named, explored the South American coastline in voyages made between 1497 and 1502, discovering the mouth of the Amazon River. In 1519 the Portugal, Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan led the Spanish Timeline of the Magellan–Elcano circumnavigation, Magellan-Elcano expedition which would be the first to sail around the world.
 As for the history of navigational instrument, a compass was first used by the ancient Greeks and Chinese to show where north lies and the direction in which the ship is heading. The latitude (an angle which ranges from 0° at the equator to 90° at the poles) was determined by measuring the angle between the Sun, Moon or a specific star and the horizon by the use of an astrolabe, Jacob's staff or Sextant (astronomical), sextant. The longitude (a line on the globe joining the two poles) could only be calculated with an accurate Marine chronometer, chronometer to show the exact time difference between the ship and a fixed point such as the Prime meridian (Greenwich), Greenwich Meridian. In 1759, John Harrison, a clockmaker, designed such an instrument and James Cook used it in his voyages of exploration. Nowadays, the Global Positioning System (GPS) using over thirty satellites enables accurate navigation worldwide.
With regards to maps that are vital for navigation, in the second century, Ptolemy mapped the whole known world from the "Fortunatae Insulae", Cape Verde or Canary Islands, eastward to the Gulf of Thailand. This map was used in 1492 when Christopher Columbus set out on his voyages of discovery. Subsequently, Gerardus Mercator made a practical map of the world in 1538, his map projection conveniently making rhumb lines straight. By the eighteenth century better maps had been made and part of the objective of James Cook on his voyages was to further map the ocean. Scientific study has continued with the depth recordings of the ''USS Tuscarora (1861), Tuscarora'', the oceanic research of the Challenger expedition, Challenger voyages (1872–1876), the work of the Scandinavian seamen Roald Amundsen and Fridtjof Nansen, the Michael Sars expedition in 1910, the German Meteor expedition of 1925, the Antarctic survey work of ''RRS Discovery II, Discovery II'' in 1932, and others since. Furthermore, in 1921, the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) was set up, and it constitutes the world authority on Hydrography, hydrographic surveying and nautical charting. A fourth edition draft was published in 1986 but so far several naming disputes (such as the one over the Sea of Japan naming dispute, Sea of Japan) have prevented its ratification.
As for the history of navigational instrument, a compass was first used by the ancient Greeks and Chinese to show where north lies and the direction in which the ship is heading. The latitude (an angle which ranges from 0° at the equator to 90° at the poles) was determined by measuring the angle between the Sun, Moon or a specific star and the horizon by the use of an astrolabe, Jacob's staff or Sextant (astronomical), sextant. The longitude (a line on the globe joining the two poles) could only be calculated with an accurate Marine chronometer, chronometer to show the exact time difference between the ship and a fixed point such as the Prime meridian (Greenwich), Greenwich Meridian. In 1759, John Harrison, a clockmaker, designed such an instrument and James Cook used it in his voyages of exploration. Nowadays, the Global Positioning System (GPS) using over thirty satellites enables accurate navigation worldwide.
With regards to maps that are vital for navigation, in the second century, Ptolemy mapped the whole known world from the "Fortunatae Insulae", Cape Verde or Canary Islands, eastward to the Gulf of Thailand. This map was used in 1492 when Christopher Columbus set out on his voyages of discovery. Subsequently, Gerardus Mercator made a practical map of the world in 1538, his map projection conveniently making rhumb lines straight. By the eighteenth century better maps had been made and part of the objective of James Cook on his voyages was to further map the ocean. Scientific study has continued with the depth recordings of the ''USS Tuscarora (1861), Tuscarora'', the oceanic research of the Challenger expedition, Challenger voyages (1872–1876), the work of the Scandinavian seamen Roald Amundsen and Fridtjof Nansen, the Michael Sars expedition in 1910, the German Meteor expedition of 1925, the Antarctic survey work of ''RRS Discovery II, Discovery II'' in 1932, and others since. Furthermore, in 1921, the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) was set up, and it constitutes the world authority on Hydrography, hydrographic surveying and nautical charting. A fourth edition draft was published in 1986 but so far several naming disputes (such as the one over the Sea of Japan naming dispute, Sea of Japan) have prevented its ratification.
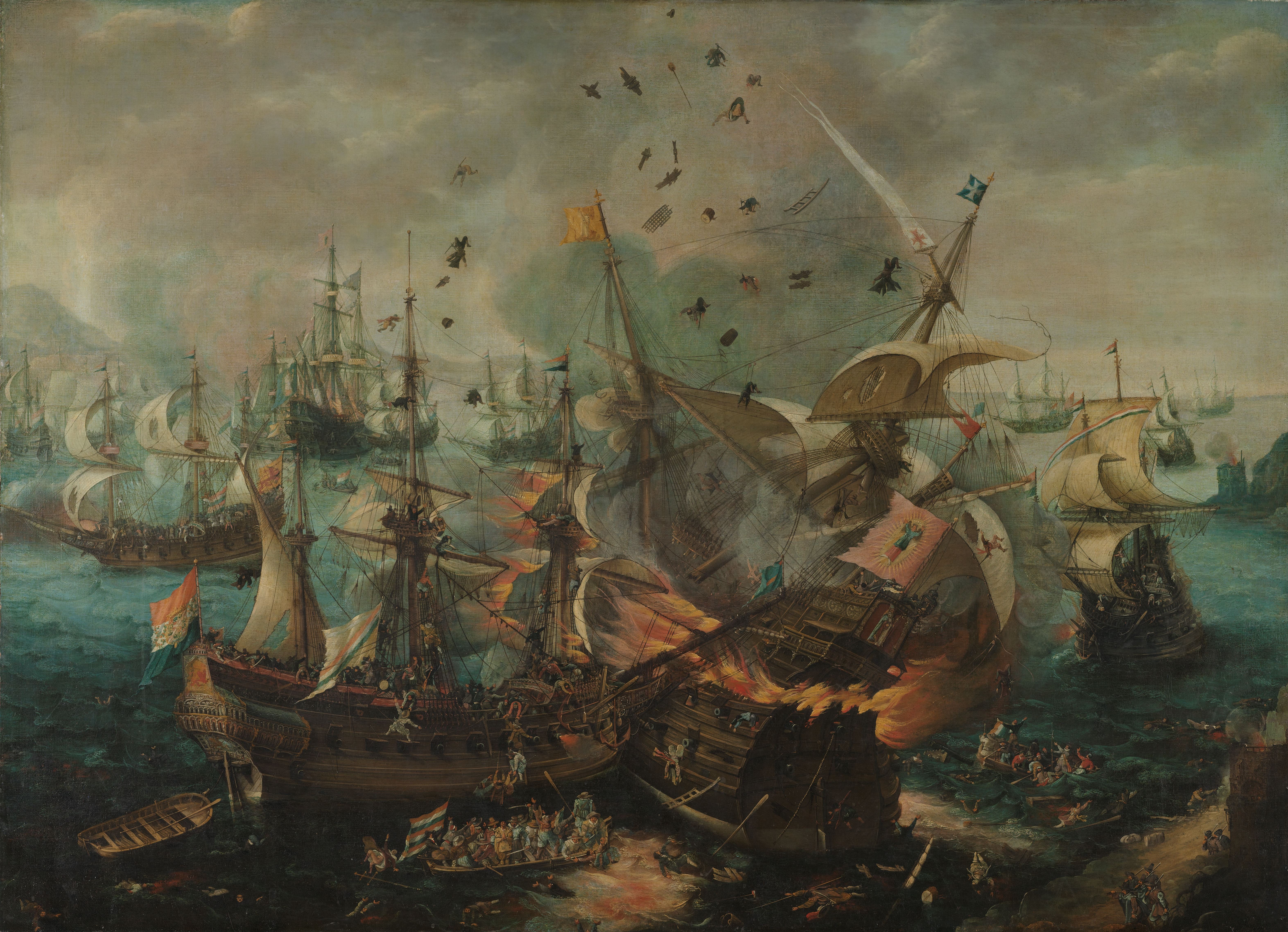 Control of the sea is important to the security of a maritime nation, and the naval blockade of a port can be used to cut off food and supplies in time of war. Battles have been fought on the sea for more than 3,000 years. In about 1210 B.C., Suppiluliuma II, the king of the Hittites, defeated and burned a fleet from Alashiya (modern Cyprus). In the decisive 480 B.C. Battle of Salamis, the Greek general Themistocles trapped the far larger fleet of the Persian king Xerxes II of Persia, Xerxes in a narrow channel and attacked vigorously, destroying 200 Persian ships for the loss of 40 Greek vessels. At the end of the Age of Sail, the British Royal Navy, led by Horatio Nelson, broke the power of the combined French and Spanish fleets at the 1805 Battle of Trafalgar.
With steam and the industrial production of steel plate came greatly increased firepower in the shape of the dreadnought battleships armed with long-range guns. In 1905, the Japanese fleet decisively defeated the Russian fleet, which had travelled over , at the Battle of Tsushima. Dreadnoughts fought inconclusively in the First World War at the 1916 Battle of Jutland between the Royal Navy's Grand Fleet and the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet. In the Second World War, the British victory at the 1940 Battle of Taranto showed that naval air power was sufficient to overcome the largest warships, foreshadowing the decisive sea-battles of the Pacific War including the Battles of the Battle of the Coral Sea, Coral Sea, Battle of Midway, Midway, Battle of the Philippine Sea, the Philippine Sea, and the climactic Battle of Leyte Gulf, in all of which the dominant ships were aircraft carriers.
Submarines became important in naval warfare in World War I, when German submarines, known as U-boats, sank nearly 5,000 Allied merchant ships, including the RMS Lusitania, which helped to bring the United States into the war. In World War II, almost 3,000 Allied ships were sunk by U-boats attempting to block the flow of supplies to Britain, but the Allies broke the blockade in the Battle of the Atlantic, which lasted the whole length of the war, sinking 783 U-boats. Since 1960, several nations have maintained fleets of nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines, vessels equipped to launch ballistic missiles with nuclear warheads from under the sea. Some of these are kept permanently on patrol.
Control of the sea is important to the security of a maritime nation, and the naval blockade of a port can be used to cut off food and supplies in time of war. Battles have been fought on the sea for more than 3,000 years. In about 1210 B.C., Suppiluliuma II, the king of the Hittites, defeated and burned a fleet from Alashiya (modern Cyprus). In the decisive 480 B.C. Battle of Salamis, the Greek general Themistocles trapped the far larger fleet of the Persian king Xerxes II of Persia, Xerxes in a narrow channel and attacked vigorously, destroying 200 Persian ships for the loss of 40 Greek vessels. At the end of the Age of Sail, the British Royal Navy, led by Horatio Nelson, broke the power of the combined French and Spanish fleets at the 1805 Battle of Trafalgar.
With steam and the industrial production of steel plate came greatly increased firepower in the shape of the dreadnought battleships armed with long-range guns. In 1905, the Japanese fleet decisively defeated the Russian fleet, which had travelled over , at the Battle of Tsushima. Dreadnoughts fought inconclusively in the First World War at the 1916 Battle of Jutland between the Royal Navy's Grand Fleet and the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet. In the Second World War, the British victory at the 1940 Battle of Taranto showed that naval air power was sufficient to overcome the largest warships, foreshadowing the decisive sea-battles of the Pacific War including the Battles of the Battle of the Coral Sea, Coral Sea, Battle of Midway, Midway, Battle of the Philippine Sea, the Philippine Sea, and the climactic Battle of Leyte Gulf, in all of which the dominant ships were aircraft carriers.
Submarines became important in naval warfare in World War I, when German submarines, known as U-boats, sank nearly 5,000 Allied merchant ships, including the RMS Lusitania, which helped to bring the United States into the war. In World War II, almost 3,000 Allied ships were sunk by U-boats attempting to block the flow of supplies to Britain, but the Allies broke the blockade in the Battle of the Atlantic, which lasted the whole length of the war, sinking 783 U-boats. Since 1960, several nations have maintained fleets of nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines, vessels equipped to launch ballistic missiles with nuclear warheads from under the sea. Some of these are kept permanently on patrol.
 Maritime trade has existed for millennia. The Ptolemaic dynasty had developed trade with India using the Red Sea ports and in the first millennium BC the Arabs, Phoenicians, Israelites and Indians traded in luxury goods such as spices, gold, and precious stones. The Phoenicians were noted sea traders and under the Greeks and Romans, commerce continued to thrive. With the collapse of the Roman Empire, European trade dwindled but it continued to flourish among the kingdoms of Africa, the Middle East, India, China and southeastern Asia. From the 16th to the 19th centuries, over a period of 400 years, about 12–13 million Africans were shipped across the Atlantic to be sold as slaves in the Americas as part of the Atlantic slave trade.
Large quantities of goods are transported by sea, especially across the Atlantic and around the Pacific Rim. A major trade route passes through the Pillars of Hercules, across the Mediterranean and the Suez Canal to the Indian Ocean and through the Straits of Malacca; much trade also passes through the English Channel. Shipping lanes are the routes on the open sea used by cargo vessels, traditionally making use of trade winds and currents. Over 60 percent of the world's container traffic is conveyed on the top twenty trade routes. Increased melting of Arctic ice since 2007 enables ships to travel the Northwest Passage for some weeks in summertime, avoiding the longer routes via the Suez Canal or the Panama Canal.
Shipping is supplemented by air freight, a more expensive process mostly used for particularly valuable or perishable cargoes. Seaborne trade carries more than US$4 trillion worth of goods each year. Bulk cargo in the form of liquids, powder or particles are carried loose in the Hold (ship), holds of bulk carriers and include Petroleum, crude oil, grain, coal, ore, Scrap, scrap metal, sand and gravel. Other cargo, such as manufactured goods, is usually transported within Shipping container, standard sized, lockable containers, loaded on purpose-built container ships at Container port, dedicated terminals. Before the rise of containerization in the 1960s, these goods were loaded, transported and unloaded piecemeal as Breakbulk cargo, break-bulk cargo. Containerization greatly increased the efficiency and decreased the cost of moving goods by sea, and was a major factor leading to the rise of globalization and exponential increases in international trade in the mid-to-late 20th century.
Maritime trade has existed for millennia. The Ptolemaic dynasty had developed trade with India using the Red Sea ports and in the first millennium BC the Arabs, Phoenicians, Israelites and Indians traded in luxury goods such as spices, gold, and precious stones. The Phoenicians were noted sea traders and under the Greeks and Romans, commerce continued to thrive. With the collapse of the Roman Empire, European trade dwindled but it continued to flourish among the kingdoms of Africa, the Middle East, India, China and southeastern Asia. From the 16th to the 19th centuries, over a period of 400 years, about 12–13 million Africans were shipped across the Atlantic to be sold as slaves in the Americas as part of the Atlantic slave trade.
Large quantities of goods are transported by sea, especially across the Atlantic and around the Pacific Rim. A major trade route passes through the Pillars of Hercules, across the Mediterranean and the Suez Canal to the Indian Ocean and through the Straits of Malacca; much trade also passes through the English Channel. Shipping lanes are the routes on the open sea used by cargo vessels, traditionally making use of trade winds and currents. Over 60 percent of the world's container traffic is conveyed on the top twenty trade routes. Increased melting of Arctic ice since 2007 enables ships to travel the Northwest Passage for some weeks in summertime, avoiding the longer routes via the Suez Canal or the Panama Canal.
Shipping is supplemented by air freight, a more expensive process mostly used for particularly valuable or perishable cargoes. Seaborne trade carries more than US$4 trillion worth of goods each year. Bulk cargo in the form of liquids, powder or particles are carried loose in the Hold (ship), holds of bulk carriers and include Petroleum, crude oil, grain, coal, ore, Scrap, scrap metal, sand and gravel. Other cargo, such as manufactured goods, is usually transported within Shipping container, standard sized, lockable containers, loaded on purpose-built container ships at Container port, dedicated terminals. Before the rise of containerization in the 1960s, these goods were loaded, transported and unloaded piecemeal as Breakbulk cargo, break-bulk cargo. Containerization greatly increased the efficiency and decreased the cost of moving goods by sea, and was a major factor leading to the rise of globalization and exponential increases in international trade in the mid-to-late 20th century.
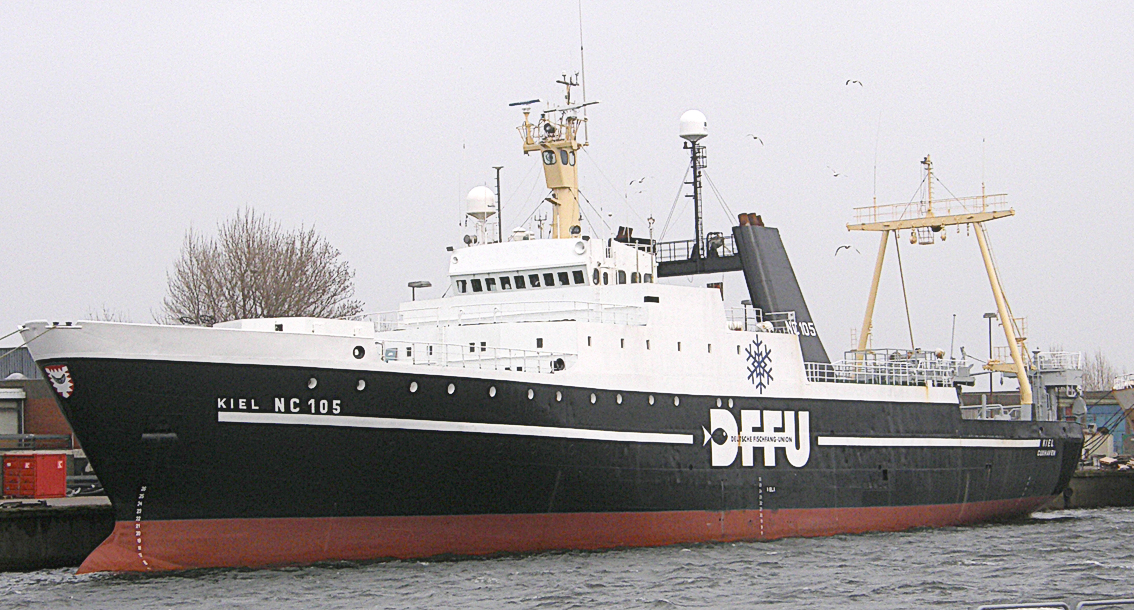 Fish and other fishery products are among the most widely consumed sources of protein and other essential nutrients. In 2009, 16.6% of the world's intake of animal protein and 6.5% of all protein consumed came from fish. In order to fulfill this need, coastal countries have exploited marine resources in their exclusive economic zone, although fishing vessels are increasingly venturing further afield to exploit stocks in international waters. In 2011, the total world production of fish, including aquaculture, was estimated to be 154 million tonnes, of which most was for human consumption. The harvesting of wild fish accounted for 90.4 million tonnes, while annually increasing aquaculture contributes the rest. The north west Pacific is by far the most productive area with 20.9 million tonnes (27 percent of the global marine catch) in 2010. In addition, the number of fishing vessels in 2010 reached 4.36 million, whereas the number of people employed in the primary sector of fish production in the same year amounted to 54.8 million.
Modern fishing vessels include fishing trawlers with a small crew, stern trawlers, purse seiners, long-line factory vessels and large factory ships which are designed to stay at sea for weeks, processing and freezing great quantities of fish. The equipment used to capture the fish may be purse seines, other seines, Trawling, trawls, dredges, gillnets and Longline fishing, long-lines and the fish species most frequently targeted are herring, cod, anchovy, tuna, flounder, Mullet (fish), mullet, squid and salmon. Overexploitation has become a serious concern; it does not only cause the depletion of fish stocks, but also substantially reduce the size of predatory fish populations. It has been estimated that "industrialized fisheries typically reduced community biomass by 80% within 15 years of exploitation." In order to avoid overexploitation, many countries have introduced Individual fishing quota, quotas in their own waters. However, recovery efforts often entail substantial costs to local economies or food provision.
Fish and other fishery products are among the most widely consumed sources of protein and other essential nutrients. In 2009, 16.6% of the world's intake of animal protein and 6.5% of all protein consumed came from fish. In order to fulfill this need, coastal countries have exploited marine resources in their exclusive economic zone, although fishing vessels are increasingly venturing further afield to exploit stocks in international waters. In 2011, the total world production of fish, including aquaculture, was estimated to be 154 million tonnes, of which most was for human consumption. The harvesting of wild fish accounted for 90.4 million tonnes, while annually increasing aquaculture contributes the rest. The north west Pacific is by far the most productive area with 20.9 million tonnes (27 percent of the global marine catch) in 2010. In addition, the number of fishing vessels in 2010 reached 4.36 million, whereas the number of people employed in the primary sector of fish production in the same year amounted to 54.8 million.
Modern fishing vessels include fishing trawlers with a small crew, stern trawlers, purse seiners, long-line factory vessels and large factory ships which are designed to stay at sea for weeks, processing and freezing great quantities of fish. The equipment used to capture the fish may be purse seines, other seines, Trawling, trawls, dredges, gillnets and Longline fishing, long-lines and the fish species most frequently targeted are herring, cod, anchovy, tuna, flounder, Mullet (fish), mullet, squid and salmon. Overexploitation has become a serious concern; it does not only cause the depletion of fish stocks, but also substantially reduce the size of predatory fish populations. It has been estimated that "industrialized fisheries typically reduced community biomass by 80% within 15 years of exploitation." In order to avoid overexploitation, many countries have introduced Individual fishing quota, quotas in their own waters. However, recovery efforts often entail substantial costs to local economies or food provision.
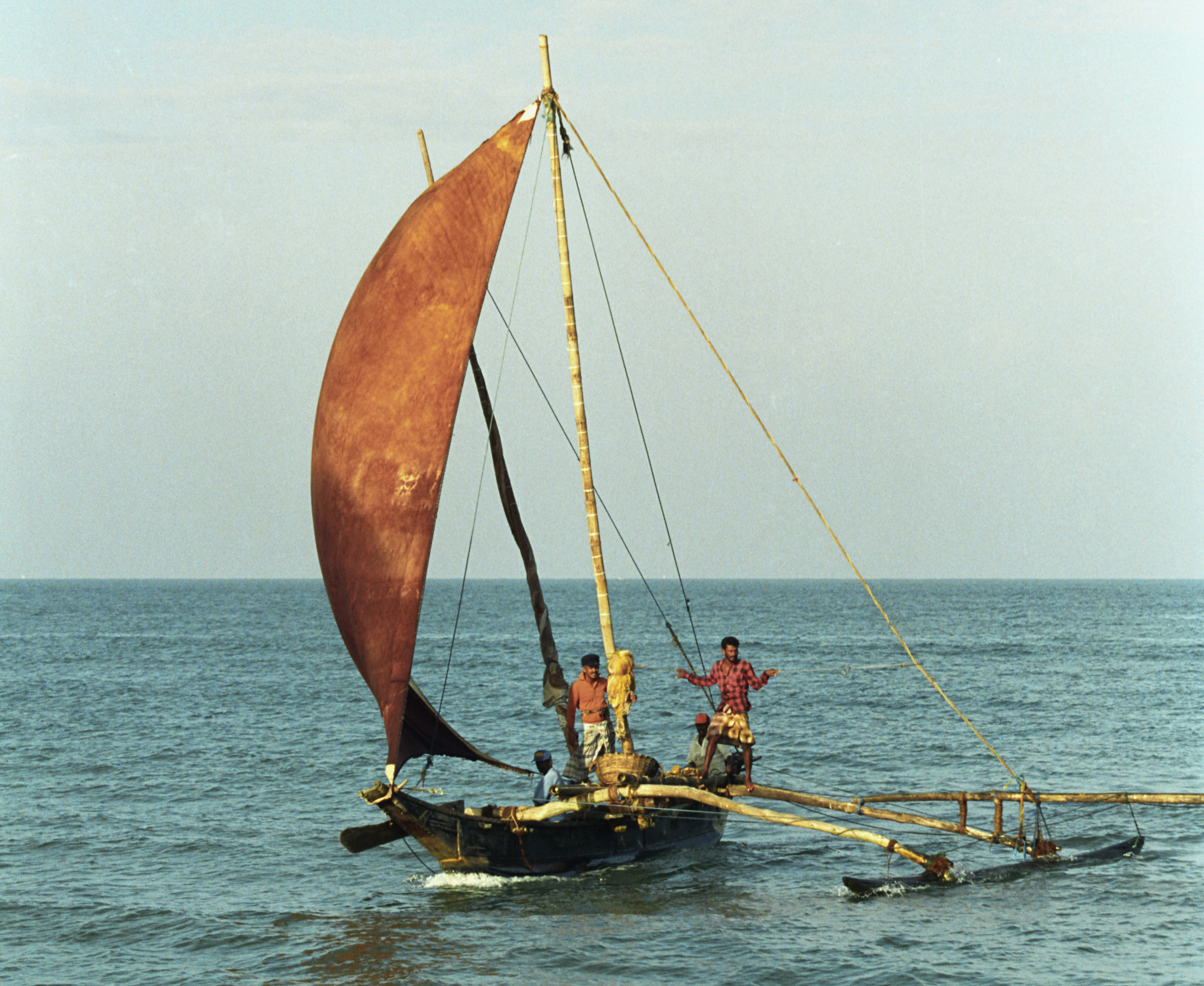 Artisan fishing methods include rod and line, harpoons, skin diving, traps, throw nets and drag nets. Traditional fishing boats are powered by paddle, wind or outboard motors and operate in near-shore waters. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Food and Agriculture Organization is encouraging the development of local fisheries to provide food security to coastal communities and help alleviate poverty.
Artisan fishing methods include rod and line, harpoons, skin diving, traps, throw nets and drag nets. Traditional fishing boats are powered by paddle, wind or outboard motors and operate in near-shore waters. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Food and Agriculture Organization is encouraging the development of local fisheries to provide food security to coastal communities and help alleviate poverty.
 Sea bathing became the vogue in Europe in the 18th century after William Buchan (physician), Dr. William Buchan advocated the practice for health reasons. Surfing is a sport in which a wave is ridden by a surfer, with or without a surfboard. Other marine Surface water sports, water sports include kite surfing, where a power kite propels a rider on a board across the water, windsurfing, where the power is provided by a fixed, manoeuvrable sail and water skiing, where a powerboat is used to pull a skier.
Beneath the surface, freediving is necessarily restricted to shallow descents. Pearl hunting, Pearl divers can dive to with baskets to collect oysters. Human eyes are not adapted for use underwater but vision can be improved by wearing a diving mask. Other useful equipment includes Swimfin, fins and Snorkel (swimming), snorkels, and Scuba set, scuba equipment allows underwater breathing and hence a longer time can be spent beneath the surface. The depths that can be reached by divers and the length of time they can stay underwater is limited by the increase of pressure they experience as they descend and the need to prevent decompression sickness as they return to the surface. Recreational divers restrict themselves to depths of beyond which the danger of nitrogen narcosis increases. Deep diving, Deeper dives can be made with specialised equipment and training.
Sea bathing became the vogue in Europe in the 18th century after William Buchan (physician), Dr. William Buchan advocated the practice for health reasons. Surfing is a sport in which a wave is ridden by a surfer, with or without a surfboard. Other marine Surface water sports, water sports include kite surfing, where a power kite propels a rider on a board across the water, windsurfing, where the power is provided by a fixed, manoeuvrable sail and water skiing, where a powerboat is used to pull a skier.
Beneath the surface, freediving is necessarily restricted to shallow descents. Pearl hunting, Pearl divers can dive to with baskets to collect oysters. Human eyes are not adapted for use underwater but vision can be improved by wearing a diving mask. Other useful equipment includes Swimfin, fins and Snorkel (swimming), snorkels, and Scuba set, scuba equipment allows underwater breathing and hence a longer time can be spent beneath the surface. The depths that can be reached by divers and the length of time they can stay underwater is limited by the increase of pressure they experience as they descend and the need to prevent decompression sickness as they return to the surface. Recreational divers restrict themselves to depths of beyond which the danger of nitrogen narcosis increases. Deep diving, Deeper dives can be made with specialised equipment and training.
 Tidal power uses generators to produce electricity from tidal flows, sometimes by using a dam to store and then release seawater. The Rance barrage, long, near St Malo in Brittany opened in 1967; it generates about 0.5 GW, but it has been followed by few similar schemes.
The large and highly variable energy of waves gives them enormous destructive capability, making affordable and reliable wave machines problematic to develop. A small 2 MW commercial wave power plant, "Osprey", was built in Northern Scotland in 1995 about 300 metres (1000 ft) offshore. It was soon damaged by waves, then destroyed by a storm.
Offshore wind power is captured by wind turbines placed out at sea; it has the advantage that wind speeds are higher than on land, though wind farms are more costly to construct offshore. The first offshore wind farm was installed in Denmark in 1991, and the installed capacity of worldwide offshore wind farms reached 34 GW in 2020, mainly situated in Europe.
Tidal power uses generators to produce electricity from tidal flows, sometimes by using a dam to store and then release seawater. The Rance barrage, long, near St Malo in Brittany opened in 1967; it generates about 0.5 GW, but it has been followed by few similar schemes.
The large and highly variable energy of waves gives them enormous destructive capability, making affordable and reliable wave machines problematic to develop. A small 2 MW commercial wave power plant, "Osprey", was built in Northern Scotland in 1995 about 300 metres (1000 ft) offshore. It was soon damaged by waves, then destroyed by a storm.
Offshore wind power is captured by wind turbines placed out at sea; it has the advantage that wind speeds are higher than on land, though wind farms are more costly to construct offshore. The first offshore wind farm was installed in Denmark in 1991, and the installed capacity of worldwide offshore wind farms reached 34 GW in 2020, mainly situated in Europe.
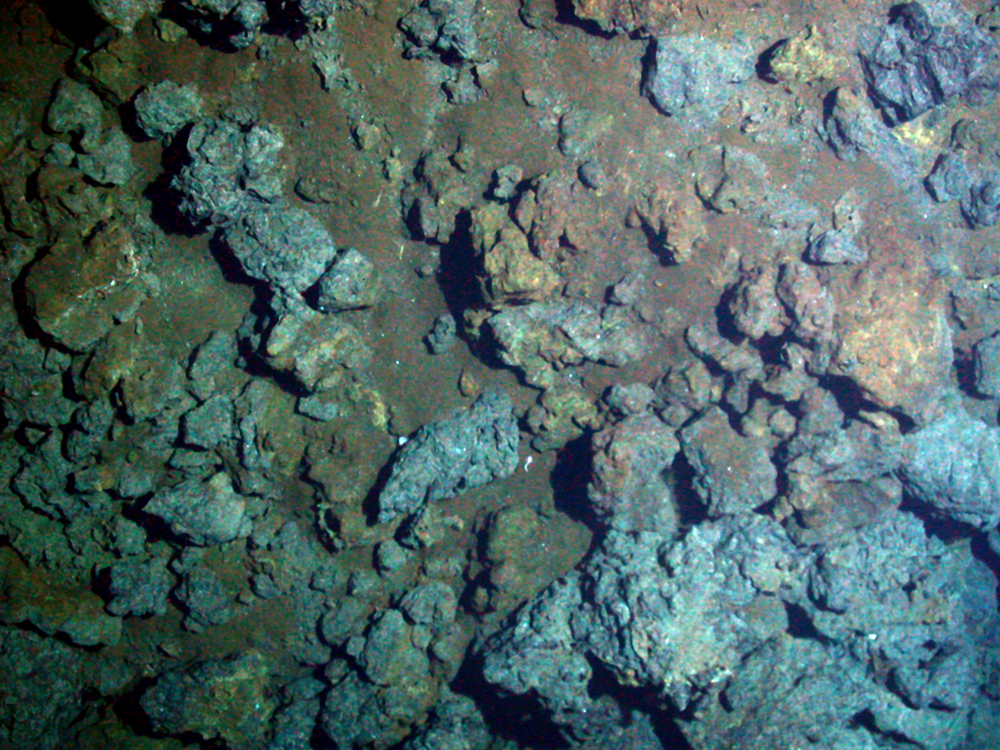 Seafloor massive sulfide deposits, Seafloor massive sulphide deposits are potential sources of silver, gold, copper, lead and zinc and trace metals since their discovery in the 1960s. They form when Geothermal gradient, geothermally heated water is emitted from deep sea hydrothermal vents known as "black smokers". The ores are of high quality but prohibitively costly to extract.
There are large deposits of petroleum, as oil and natural gas, in rocks beneath the seabed. Oil platform, Offshore platforms and drilling rigs Offshore drilling, extract the oil or gas and store it for transport to land. Offshore oil and gas production can be difficult due to the remote, harsh environment. Drilling for oil in the sea has environmental impacts. Animals may be disorientated by seismic waves used to locate deposits, and there is debate as to whether this causes the Beached whale, beaching of whales. Toxic substances such as mercury (element), mercury, lead and arsenic may be released. The infrastructure may cause damage, and oil may be spilt.
Large quantities of methane clathrate exist on the seabed and in ocean sediment, of interest as a potential energy source. Also on the seabed are manganese nodules formed of layers of iron, manganese and other hydroxides around a core. In the Pacific these may cover up to 30 percent of the deep ocean floor. The minerals precipitate from seawater and grow very slowly. Their commercial extraction for nickel was investigated in the 1970s but abandoned in favour of more convenient sources. In suitable locations, diamonds are gathered from the seafloor using suction hoses to bring gravel ashore. In deeper waters, mobile seafloor crawlers are used and the deposits are pumped to a vessel above. In Namibia, more diamonds are now collected from marine sources than by conventional methods on land.
Seafloor massive sulfide deposits, Seafloor massive sulphide deposits are potential sources of silver, gold, copper, lead and zinc and trace metals since their discovery in the 1960s. They form when Geothermal gradient, geothermally heated water is emitted from deep sea hydrothermal vents known as "black smokers". The ores are of high quality but prohibitively costly to extract.
There are large deposits of petroleum, as oil and natural gas, in rocks beneath the seabed. Oil platform, Offshore platforms and drilling rigs Offshore drilling, extract the oil or gas and store it for transport to land. Offshore oil and gas production can be difficult due to the remote, harsh environment. Drilling for oil in the sea has environmental impacts. Animals may be disorientated by seismic waves used to locate deposits, and there is debate as to whether this causes the Beached whale, beaching of whales. Toxic substances such as mercury (element), mercury, lead and arsenic may be released. The infrastructure may cause damage, and oil may be spilt.
Large quantities of methane clathrate exist on the seabed and in ocean sediment, of interest as a potential energy source. Also on the seabed are manganese nodules formed of layers of iron, manganese and other hydroxides around a core. In the Pacific these may cover up to 30 percent of the deep ocean floor. The minerals precipitate from seawater and grow very slowly. Their commercial extraction for nickel was investigated in the 1970s but abandoned in favour of more convenient sources. In suitable locations, diamonds are gathered from the seafloor using suction hoses to bring gravel ashore. In deeper waters, mobile seafloor crawlers are used and the deposits are pumped to a vessel above. In Namibia, more diamonds are now collected from marine sources than by conventional methods on land.
 The sea holds large quantities of valuable dissolved minerals. The most important, Sea salt, Salt for table and industrial use has been harvested by solar evaporation from shallow ponds since prehistoric times. Bromine, accumulated after being leached from the land, is economically recovered from the Dead Sea, where it occurs at 55,000 parts per million (ppm).
The sea holds large quantities of valuable dissolved minerals. The most important, Sea salt, Salt for table and industrial use has been harvested by solar evaporation from shallow ponds since prehistoric times. Bromine, accumulated after being leached from the land, is economically recovered from the Dead Sea, where it occurs at 55,000 parts per million (ppm).
 The sea appears in human culture in contradictory ways, as both powerful but serene and as beautiful but dangerous. It has its place in literature, art, poetry, film, theatre, classical music, mythology and dream interpretation. The Ancient history, Ancients personified it, believing it to be under the control of a List of water deities, being who needed to be appeased, and symbolically, it has been perceived as a hostile environment populated by fantastic creatures; the Leviathan of the Bible, Scylla in Greek mythology, Isonade in Japanese mythology, and the kraken of late Norse mythology.
The sea appears in human culture in contradictory ways, as both powerful but serene and as beautiful but dangerous. It has its place in literature, art, poetry, film, theatre, classical music, mythology and dream interpretation. The Ancient history, Ancients personified it, believing it to be under the control of a List of water deities, being who needed to be appeased, and symbolically, it has been perceived as a hostile environment populated by fantastic creatures; the Leviathan of the Bible, Scylla in Greek mythology, Isonade in Japanese mythology, and the kraken of late Norse mythology.
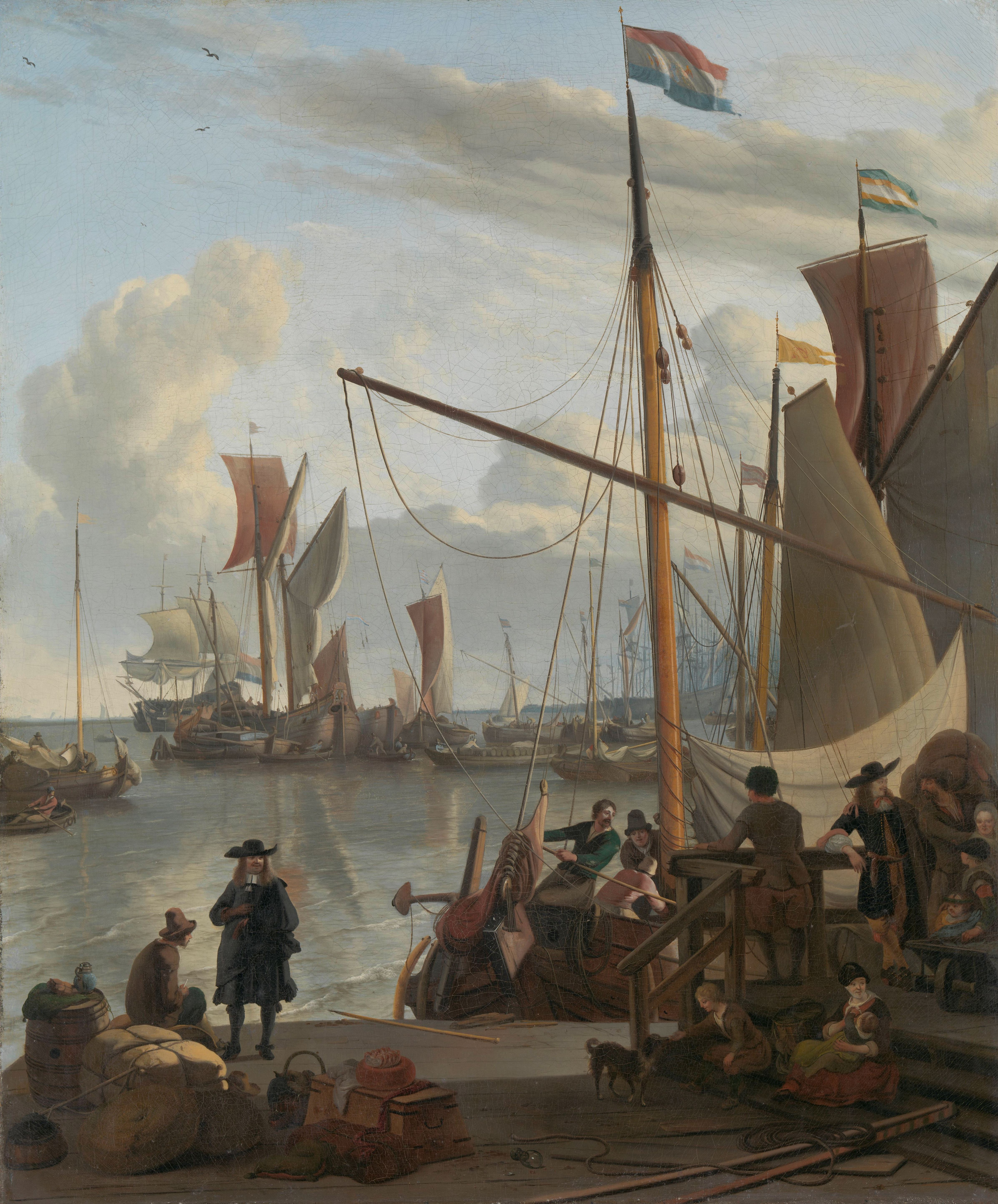 The sea and ships have been Marine art, depicted in art ranging from simple drawings on the walls of huts in Lamu Archipelago, Lamu to seascapes by J. M. W. Turner, Joseph Turner. In Dutch Golden Age painting, artists such as Jan Porcellis, Hendrick Dubbels, Willem van de Velde the Elder and Willem van de Velde the Younger, his son, and Ludolf Bakhuizen celebrated the sea and the Dutch navy at the peak of its military prowess. The Japanese artist Katsushika Hokusai created colour Printmaking, prints of the moods of the sea, including ''The Great Wave off Kanagawa''.
Music too has been inspired by the ocean, sometimes by composers who lived or worked near the shore and saw its many different aspects. Sea shanty, Sea shanties, songs that were chanted by mariners to help them perform arduous tasks, have been woven into compositions and impressions in music have been created of calm waters, crashing waves and storms at sea.
The sea and ships have been Marine art, depicted in art ranging from simple drawings on the walls of huts in Lamu Archipelago, Lamu to seascapes by J. M. W. Turner, Joseph Turner. In Dutch Golden Age painting, artists such as Jan Porcellis, Hendrick Dubbels, Willem van de Velde the Elder and Willem van de Velde the Younger, his son, and Ludolf Bakhuizen celebrated the sea and the Dutch navy at the peak of its military prowess. The Japanese artist Katsushika Hokusai created colour Printmaking, prints of the moods of the sea, including ''The Great Wave off Kanagawa''.
Music too has been inspired by the ocean, sometimes by composers who lived or worked near the shore and saw its many different aspects. Sea shanty, Sea shanties, songs that were chanted by mariners to help them perform arduous tasks, have been woven into compositions and impressions in music have been created of calm waters, crashing waves and storms at sea.
 As a symbol, the sea has for centuries played a role in literature, poetry and dreams. Sometimes it is there just as a gentle background but often it introduces such themes as storm, shipwreck, battle, hardship, disaster, the dashing of hopes and death. In his epic poetry, epic poem the ''Odyssey'', written in the eighth century BC, Homer describes the ten-year voyage of the Greek hero Odysseus who struggles to return home across the sea's many hazards after the war described in the ''Iliad''. The sea is a recurring theme in the Haiku poems of the Japanese Edo period poet Matsuo Bashō (松尾 芭蕉) (1644–1694). In the works of psychiatrist Carl Jung, the sea symbolizes the personal and the collective unconscious in dream interpretation, the depths of the sea symbolizing the depths of the unconscious mind.
As a symbol, the sea has for centuries played a role in literature, poetry and dreams. Sometimes it is there just as a gentle background but often it introduces such themes as storm, shipwreck, battle, hardship, disaster, the dashing of hopes and death. In his epic poetry, epic poem the ''Odyssey'', written in the eighth century BC, Homer describes the ten-year voyage of the Greek hero Odysseus who struggles to return home across the sea's many hazards after the war described in the ''Iliad''. The sea is a recurring theme in the Haiku poems of the Japanese Edo period poet Matsuo Bashō (松尾 芭蕉) (1644–1694). In the works of psychiatrist Carl Jung, the sea symbolizes the personal and the collective unconscious in dream interpretation, the depths of the sea symbolizing the depths of the unconscious mind.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
{{Featured article Seas, Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Lists of landforms Oceans, * Articles containing video clips
 The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
, is the body
Body may refer to:
In science
* Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space
* Body (biology), the physical material of an organism
* Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of anima ...
of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, as well as certain large, entirely landlocked, saltwater lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre). ...
s, such as the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
. The sea moderates Earth's climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
and has important roles in the water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
, carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
, and nitrogen cycles. Humans harnessing and studying the sea have been recorded since ancient times, and evidenced well into prehistory
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
, while its modern scientific study is called oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamic ...
. The most abundant solid dissolved in seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appro ...
is sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g ...
. The water also contains salts
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively cha ...
of magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
, potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosphe ...
, and mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
, amongst many other elements, some in minute concentrations. Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
varies widely, being lower near the surface and the mouths of large rivers
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
and higher in the depths of the ocean; however, the relative proportions of dissolved salts vary little across the oceans.
Winds blowing over the surface of the sea produce waves
Waves most often refers to:
*Waves, oscillations accompanied by a transfer of energy that travel through space or mass.
* Wind waves, surface waves that occur on the free surface of bodies of water.
Waves may also refer to:
Music
* Waves (ban ...
, which break
Break or Breaks or The Break may refer to:
Time off from duties
* Recess (break), time in which a group of people is temporarily dismissed from its duties
* Break (work), time off during a shift/recess
** Coffee break, a short mid-morning rest ...
when they enter the shallow water near land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various islan ...
. Winds also create surface currents
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, ...
through friction, setting up slow but stable circulations of water throughout the oceans. The directions of the circulation are governed by several factors including the shapes of the continents and Earth's rotation
Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own Rotation around a fixed axis, axis, as well as changes in the orientation (geometry), orientation of the rotation axis in space. Earth rotates eastward, in retrograd ...
(through the Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
). Deep-sea currents, known as the global conveyor belt
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The adjective ''thermohaline'' derives from '' thermo-'' referring to tempe ...
, carry cold water from near the poles to every ocean. Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravity, gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide t ...
s, the generally twice-daily rise and fall of sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
s, are caused by Earth's rotation and the gravitational effects of the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
and, to a lesser extent, of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
. Tides may have a very high range
Range may refer to:
Geography
* Range (geographic), a chain of hills or mountains; a somewhat linear, complex mountainous or hilly area (cordillera, sierra)
** Mountain range, a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
* Range, a term used to i ...
in bays
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narr ...
or estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
. Submarine earthquake
A submarine, undersea, or underwater earthquake is an earthquake that occurs underwater at the bottom of a body of water, especially an ocean. They are the leading cause of tsunamis. The magnitude can be measured scientifically by the use of the ...
s arising from tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
movements under the oceans can lead to destructive tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explo ...
s, as can volcanoes, huge landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of ...
s, or the impact of large meteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the ...
s.
A wide variety of organisms, including bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
, protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s, algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, plants, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, and animals, lives in the sea, which offers a wide range of marine habitat
Marine habitats are habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term ''marine'' comes from the Latin ''mare'', meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental a ...
s and ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
, ranging vertically from the sunlit surface and shoreline
A shore or a shoreline is the fringe of land at the edge of a large body of water, such as an ocean, sea, or lake. In physical oceanography, a shore is the wider fringe that is geologically modified by the action of the body of water past a ...
to the great depths and pressures of the cold, dark abyssal zone
The abyssal zone or abyssopelagic zone is a layer of the pelagic zone of the ocean. "Abyss" derives from the Greek word , meaning bottomless. At depths of , this zone remains in perpetual darkness. It covers 83% of the total area of the ocean a ...
, and in latitude from the cold waters under polar ice cap
A polar ice cap or polar cap is a high-latitude region of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite that is covered in ice.
There are no requirements with respect to size or composition for a body of ice to be termed a polar ice cap, nor a ...
s to the warm waters of coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
s in tropical regions
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred t ...
. Many of the major groups of organisms evolved in the sea and life may have started there.
The sea provides substantial supplies of food for humans, mainly fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, but also shellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater envir ...
, mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
and seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
, whether caught by fishermen or farmed
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
underwater. Other human uses of the sea include trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct excha ...
, travel, mineral extraction
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic via ...
, power generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its stor ...
, warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular ...
, and leisure activities such as swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, or other liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs and the body to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that r ...
, sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, windsurfer, or kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (land yacht) over a chosen cour ...
, and scuba diving
Scuba diving is a mode of underwater diving whereby divers use breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface air supply. The name "scuba", an acronym for "Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus", was coined by Chris ...
. Many of these activities create marine pollution
Marine pollution occurs when substances used or spread by humans, such as industrial waste, industrial, agricultural pollution, agricultural and municipal solid waste, residential waste, particle (ecology), particles, noise, excess carbon dioxid ...
. The sea has been an integral element for humans throughout history and culture.
Definition
 The sea is the interconnected system of all the Earth's oceanic waters, including the
The sea is the interconnected system of all the Earth's oceanic waters, including the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
, Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
, Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
s. "Sea." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
or the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
. There is no sharp distinction between seas and ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
s, though generally seas are smaller, and are often partly (as marginal sea
This is a list of seas of the World Ocean, including marginal seas, areas of water, various gulfs, bights, bays, and straits.
Terminology
* Ocean – the four to seven largest named bodies of water in the World Ocean, all of which have "Ocean ...
s or particularly as the Mediterranean sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
) or wholly (as inland seas
An inland sea (also known as an epeiric sea or an epicontinental sea) is a continental body of water which is very large and is either completely surrounded by dry land or connected to an ocean by a river, strait, or "arm of the sea". An inland se ...
) enclosed by land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various islan ...
. However, an exception to this is the Sargasso Sea
The Sargasso Sea () is a region of the Atlantic Ocean bounded by four currents forming an ocean gyre. Unlike all other regions called seas, it has no land boundaries. It is distinguished from other parts of the Atlantic Ocean by its charac ...
which has no coastline and lies within a circular current, the North Atlantic Gyre
The North Atlantic Gyre of the Atlantic Ocean is one of five great oceanic gyres. It is a circular ocean current, with offshoot eddies and sub-gyres, across the North Atlantic from the Intertropical Convergence Zone (calms or doldrums) to the part ...
. Seas are generally larger than lakes and contain salt water, but the Sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee ( he, יָם כִּנֶּרֶת, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ar, بحيرة طبريا), also called Lake Tiberias, Kinneret or Kinnereth, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest ...
is a freshwater lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 167 c ...
states that all of the ocean is "sea".
Physical science

Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
is the only known planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
with seas of liquid water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
on its surface, although Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
possesses ice caps
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets.
Description
Ice caps are not constrained by topographical features ...
and similar planets in other solar systems may have oceans. Earth's of sea contain about 97.2 percent of its known water and cover approximately 71 percent of its surface. Another 2.15% of Earth's water is frozen, found in the sea ice covering the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
, the ice cap covering Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
and its adjacent seas, and various glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires dis ...
s and surface deposits around the world. The remainder (about 0.65% of the whole) form underground reservoirs or various stages of the water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
, containing the freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
encountered and used by most terrestrial life: vapor
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (British English and Canadian English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critic ...
in the air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
, the cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may co ...
s it slowly forms, the rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
falling from them, and the lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
s and river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
s spontaneously formed as its waters flow again and again to the sea.NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
.Lesson 7: The Water Cycle
" in ''Ocean Explorer''. The
scientific study
Scientific study is a kind of study that involves scientific theory, scientific models, experiments and physical situations. It may refer to:
*Scientific method, a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, based on empirical or measurabl ...
of water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
and Earth's water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
is hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is calle ...
; hydrodynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and ...
studies the physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
of water in motion. The more recent study of the sea in particular is oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamic ...
. This began as the study of the shape of the ocean's currents
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
but has since expanded into a large and multidisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several other fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, ec ...
field:Monkhouse, F.J. (1975) ''Principles of Physical Geography''. pp. 327–28. Hodder & Stoughton. . it examines the properties of seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appro ...
; studies waves
Waves most often refers to:
*Waves, oscillations accompanied by a transfer of energy that travel through space or mass.
* Wind waves, surface waves that occur on the free surface of bodies of water.
Waves may also refer to:
Music
* Waves (ban ...
, tides
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables can ...
, and currents
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
; charts coastlines
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in n ...
and maps the seabeds; and studies marine life
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. M ...
. The subfield dealing with the sea's motion, its forces, and the forces acting upon it is known as physical oceanography
Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.
Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divi ...
. Marine biology
Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life, organisms in the sea. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies s ...
(biological oceanography) studies the plants
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
, animals
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
, and other organisms inhabiting marine ecosystems
Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 70% of the surf ...
. Both are informed by chemical oceanography
Marine chemistry, also known as ocean chemistry or chemical oceanography, is influenced by plate tectonics and seafloor spreading, turbidity currents, sediments, pH levels, atmospheric constituents, metamorphic activity, and ecology. The field ...
, which studies the behavior of elements and molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
within the oceans: particularly, at the moment, the ocean's role in the carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as ...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
's role in the increasing acidification of seawater. Marine and maritime geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ...
charts the shape and shaping of the sea, while marine geology
Marine geology or geological oceanography is the study of the history and structure of the ocean floor. It involves geophysical, geochemical, sedimentological and paleontological investigations of the ocean floor and coastal zone. Marine geolog ...
(geological oceanography) has provided evidence of continental drift
Continental drift is the hypothesis that the Earth's continents have moved over geologic time relative to each other, thus appearing to have "drifted" across the ocean bed. The idea of continental drift has been subsumed into the science of pla ...
and the composition
Composition or Compositions may refer to:
Arts and literature
*Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography
*Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include v ...
and structure of the Earth
The internal structure of Earth is the solid portion of the Earth, excluding its atmosphere and hydrosphere. The structure consists of an outer silicate solid crust, a highly viscous asthenosphere and solid mantle, a liquid outer core whos ...
, clarified the process of sedimentation
Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to the ...
, and assisted the study of volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called ...
and earthquakes
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
.
Seawater

Salinity
A characteristic of seawater is that it is salty. Salinity is usually measured in parts per thousand (‰
Per mille (from Latin , "in each thousand") is an expression that means parts per thousand. Other recognised spellings include per mil, per mill, permil, permill, or permille.
The associated sign is written , which looks like a percent si ...
or per mil), and the open ocean has about solids per litre, a salinity of 35 ‰. The Mediterranean Sea is slightly higher at 38 ‰, while the salinity of the northern Red Sea can reach 41‰. In contrast, some landlocked hypersaline lake
A hypersaline lake is a landlocked body of water that contains significant concentrations of sodium chloride, brines, and other salts, with saline levels surpassing that of ocean water (3.5%, i.e. ).
Specific microbial species can thrive in ...
s have a much higher salinity, for example the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank ...
has dissolved solids per litre (300 ‰).
While the constituents of table salt (sodium and chloride) make up about 85 percent of the solids in solution, there are also other metal ions such as magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
and calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
, and negative ions including sulphate, carbonate, and bromide. Despite variations in the levels of salinity in different seas, the relative composition of the dissolved salts is stable throughout the world's oceans. Seawater is too saline for humans to drink safely, as the kidneys cannot excrete urine as salty as seawater.
Although the amount of salt in the ocean remains relatively constant within the scale of millions of years, various factors affect the salinity of a body of water. Evaporation and by-product of ice formation (known as "brine rejection") increase salinity, whereas precipitation, sea ice melt, and runoff from land reduce it. The Baltic Sea, for example, has many rivers flowing into it, and thus the sea could be considered as brackish. Meanwhile, the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
is very salty due to its high evaporation rate.NOAA (11 Jan 2013).Drinking Seawater Can Be Deadly to Humans
".
Temperature
Sea temperature depends on the amount of solar radiation falling on its surface. In the tropics, with the sun nearly overhead, the temperature of the surface layers can rise to over while near the poles the temperature in equilibrium with the sea ice is about . There is a continuous circulation of water in the oceans. Warm surface currents cool as they move away from the tropics, and the water becomes denser and sinks. The cold water moves back towards the equator as a deep sea current, driven by changes in the temperature and density of the water, before eventually welling up again towards the surface. Deep seawater has a temperature between and in all parts of the globe. Seawater with a typical salinity of 35 ‰ has a freezing point of about −1.8 °C (28.8 °F). When its temperature becomes low enough, ice crystals form on the surface. These break into small pieces and coalesce into flat discs that form a thick suspension known as frazil. In calm conditions this freezes into a thin flat sheet known as nilas, which thickens as new ice forms on its underside. In more turbulent seas, frazil crystals join into flat discs known as pancakes. These slide under each other and coalesce to form Drift ice, floes. In the process of freezing, salt water and air are trapped between the ice crystals. Nilas may have a salinity of 12–15 ‰, but by the time the sea ice is one year old, this falls to 4–6 ‰.Oxygen concentration
The amount of oxygen found in seawater depends primarily on the plants growing in it. These are mainly algae, including phytoplankton, with some vascular plants such as seagrasses. In daylight the photosynthesis, photosynthetic activity of these plants produces oxygen, which dissolves in the seawater and is used by marine animals. At night, photosynthesis stops, and the amount of dissolved oxygen declines. In the deep sea, where insufficient light penetrates for plants to grow, there is very little dissolved oxygen. In its absence, organic material is broken down by anaerobic organism, anaerobic bacteria producing hydrogen sulphide. Climate change is likely to reduce levels of oxygen in surface waters, since the solubility of oxygen in water falls at higher temperatures. Ocean deoxygenation is projected to increase Hypoxia (environmental), hypoxia by 10%, and triple suboxic waters (oxygen concentrations 98% less than the mean surface concentrations), for each 1 °C of upper ocean warming.Light
The amount of light that penetrates the sea depends on the angle of the sun, the weather conditions and the turbidity of the water. Much light gets reflected at the surface, and red light gets absorbed in the top few metres. Yellow and green light reach greater depths, and blue and violet light may penetrate as deep as . There is insufficient light for photosynthesis and plant growth beyond a depth of about .Sea level
Over most of geologic time, the sea level has been higher than it is today. The main factor affecting sea level over time is the result of changes in the oceanic crust, with a downward trend expected to continue in the very long term. At the last glacial maximum, some 20,000 years ago, the sea level was about lower than in present times (2012).Sea Level and Climate. USGS. By Richard Z. Poore, Richard S. Williams, Jr., and Christopher Tracey. For at least the last 100 years, Sea level rise, sea level has been rising at an average rate of about per year. Most of this rise can be attributed to an increase in the temperature of the sea due to climate change, and the resulting slight thermal expansion of the upper of water. Additional contributions, as much as one quarter of the total, come from water sources on land, such as Retreat of glaciers since 1850, melting snow and glaciers and extraction of groundwater for irrigation and other agricultural and human needs.
Waves
Wind blowing over the surface of a body of water forms Wind wave, waves that are perpendicular to the direction of the wind. The friction between air and water caused by a gentle breeze on a pond causes Capillary wave, ripples to form. A strong blow over the ocean causes larger waves as the moving air pushes against the raised ridges of water. The waves reach their maximum height when the rate at which they are travelling nearly matches the speed of the wind. In open water, when the wind blows continuously as happens in the Southern Hemisphere in the Roaring Forties, long, organised masses of water called Swell (ocean), swell roll across the ocean. If the wind dies down, the wave formation is reduced, but already-formed waves continue to travel in their original direction until they meet land. The size of the waves depends on the Fetch (geography), fetch, the distance that the wind has blown over the water and the strength and duration of that wind. When waves meet others coming from different directions, interference between the two can produce broken, irregular seas. Constructive interference can cause individual (unexpected) rogue waves much higher than normal.Garrison, Tom (2012)''Essentials of Oceanography''
. 6th ed. pp. 204 ff. Brooks/Cole, Belmont, California, Belmont. . Most waves are less than high and it is not unusual for strong storms to double or triple that height; offshore construction such as offshore wind farm, wind farms and oil platforms use metocean statistics from measurements in computing the wave forces (due to for instance the hundred-year wave) they are designed against. Rogue waves, however, have been documented at heights above . The top of a wave is known as the crest, the lowest point between waves is the trough and the distance between the crests is the wavelength. The wave is pushed across the surface of the sea by the wind, but this represents a transfer of energy and not a horizontal movement of water. As waves approach land and waves and shallow water, move into shallow water, they change their behavior. If approaching at an angle, waves may bend (refraction) or wrap rocks and headlands (diffraction). When the wave reaches a point where its deepest oscillations of the water contact the seabed, they begin to slow down. This pulls the crests closer together and increases the wave height, waves' height, which is called wave shoaling. When the ratio of the wave's height to the water depth increases above a certain limit, it "wave breaking, breaks", toppling over in a mass of foaming water. This rushes in a sheet up the beach before retreating into the sea under the influence of gravity.
Tsunami
 A tsunami is an unusual form of wave caused by an infrequent powerful event such as an underwater earthquake or landslide, a meteorite impact, a volcanic eruption or a collapse of land into the sea. These events can temporarily lift or lower the surface of the sea in the affected area, usually by a few feet. The potential energy of the displaced seawater is turned into kinetic energy, creating a shallow wave, a tsunami, radiating outwards at a velocity proportional to the square root of the depth of the water and which therefore travels much faster in the open ocean than on a continental shelf. In the deep open sea, tsunamis have wavelengths of around , travel at speeds of over 600 miles per hour (970 km/hr) and usually have a height of less than three feet, so they often pass unnoticed at this stage. In contrast, ocean surface waves caused by winds have wavelengths of a few hundred feet, travel at up to and are up to high.
As a tsunami Wave shoaling, moves into shallower water its speed decreases, its wavelength shortens and its amplitude increases enormously, behaving in the same way as a wind-generated wave in shallow water, but on a vastly greater scale. Either the trough or the crest of a tsunami can arrive at the coast first. In the former case, the sea draws back and leaves subtidal areas close to the shore exposed which provides a useful warning for people on land. When the crest arrives, it does not usually break but rushes inland, flooding all in its path. Much of the destruction may be caused by the flood water draining back into the sea after the tsunami has struck, dragging debris and people with it. Often several tsunami are caused by a single geological event and arrive at intervals of between eight minutes and two hours. The first wave to arrive on shore may not be the biggest or most destructive.
A tsunami is an unusual form of wave caused by an infrequent powerful event such as an underwater earthquake or landslide, a meteorite impact, a volcanic eruption or a collapse of land into the sea. These events can temporarily lift or lower the surface of the sea in the affected area, usually by a few feet. The potential energy of the displaced seawater is turned into kinetic energy, creating a shallow wave, a tsunami, radiating outwards at a velocity proportional to the square root of the depth of the water and which therefore travels much faster in the open ocean than on a continental shelf. In the deep open sea, tsunamis have wavelengths of around , travel at speeds of over 600 miles per hour (970 km/hr) and usually have a height of less than three feet, so they often pass unnoticed at this stage. In contrast, ocean surface waves caused by winds have wavelengths of a few hundred feet, travel at up to and are up to high.
As a tsunami Wave shoaling, moves into shallower water its speed decreases, its wavelength shortens and its amplitude increases enormously, behaving in the same way as a wind-generated wave in shallow water, but on a vastly greater scale. Either the trough or the crest of a tsunami can arrive at the coast first. In the former case, the sea draws back and leaves subtidal areas close to the shore exposed which provides a useful warning for people on land. When the crest arrives, it does not usually break but rushes inland, flooding all in its path. Much of the destruction may be caused by the flood water draining back into the sea after the tsunami has struck, dragging debris and people with it. Often several tsunami are caused by a single geological event and arrive at intervals of between eight minutes and two hours. The first wave to arrive on shore may not be the biggest or most destructive.
Currents
 Wind blowing over the surface of the sea causes friction at the interface between air and sea. Not only does this cause waves to form but it also makes the surface seawater move in the same direction as the wind. Although winds are variable, in any one place they predominantly blow from a single direction and thus a surface current can be formed. Westerly winds are most frequent in the mid-latitudes while easterlies dominate the tropics. When water moves in this way, other water flows in to fill the gap and a circular movement of surface currents known as a Ocean gyre, gyre is formed. There are five main gyres in the world's oceans: two in the Pacific, two in the Atlantic and one in the Indian Ocean. Other smaller gyres are found in lesser seas and a single gyre flows around
Wind blowing over the surface of the sea causes friction at the interface between air and sea. Not only does this cause waves to form but it also makes the surface seawater move in the same direction as the wind. Although winds are variable, in any one place they predominantly blow from a single direction and thus a surface current can be formed. Westerly winds are most frequent in the mid-latitudes while easterlies dominate the tropics. When water moves in this way, other water flows in to fill the gap and a circular movement of surface currents known as a Ocean gyre, gyre is formed. There are five main gyres in the world's oceans: two in the Pacific, two in the Atlantic and one in the Indian Ocean. Other smaller gyres are found in lesser seas and a single gyre flows around Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
. These gyres have followed the same routes for millennia, guided by the topography of the land, the wind direction and the Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
. The surface currents flow in a clockwise direction in the Northern Hemisphere and anticlockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. The water moving away from the equator is warm, and that flowing in the reverse direction has lost most of its heat. These currents tend to moderate the Earth's climate, cooling the equatorial region and warming regions at higher latitudes. Global climate and weather forecasting, weather forecasts are powerfully affected by the world ocean, so global climate modelling makes use of List of ocean circulation models, ocean circulation models as well as models of other major components such as the atmosphere, land surfaces, aerosols and sea ice. Ocean models make use of a branch of physics, geophysical fluid dynamics, that describes the large-scale flow of fluids such as seawater.
 Surface currents only affect the top few hundred metres of the sea, but there are also large-scale flows in the ocean depths caused by the movement of deep water masses. A main deep ocean current flows through all the world's oceans and is known as the thermohaline circulation or global conveyor belt. This movement is slow and is driven by differences in density of the water caused by variations in salinity and temperature. At high latitudes the water is chilled by the low atmospheric temperature and becomes saltier as sea ice crystallizes out. Both these factors make it denser, and the water sinks. From the deep sea near Greenland, such water flows southwards between the continental landmasses on either side of the Atlantic. When it reaches the Antarctic, it is joined by further masses of cold, sinking water and flows eastwards. It then splits into two streams that move northwards into the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Here it is gradually warmed, becomes less dense, rises towards the surface and loops back on itself. It takes a thousand years for this circulation pattern to be completed.
Besides gyres, there are temporary surface currents that occur under specific conditions. When waves meet a shore at an angle, a Longshore drift, longshore current is created as water is pushed along parallel to the coastline. The water swirls up onto the beach at right angles to the approaching waves but drains away straight down the slope under the effect of gravity. The larger the breaking waves, the longer the beach and the more oblique the wave approach, the stronger is the longshore current. These currents can shift great volumes of sand or pebbles, create Spit (landform), spits and make beaches disappear and water channels silt up. A rip current can occur when water piles up near the shore from advancing waves and is funnelled out to sea through a channel in the seabed. It may occur at a gap in a Shoal, sandbar or near a man-made structure such as a groyne. These strong currents can have a velocity of per second, can form at different places at different stages of the tide and can carry away unwary bathers. Temporary upwelling currents occur when the wind pushes water away from the land and deeper water rises to replace it. This cold water is often rich in nutrients and creates blooms of phytoplankton and a great increase in the productivity of the sea.
Surface currents only affect the top few hundred metres of the sea, but there are also large-scale flows in the ocean depths caused by the movement of deep water masses. A main deep ocean current flows through all the world's oceans and is known as the thermohaline circulation or global conveyor belt. This movement is slow and is driven by differences in density of the water caused by variations in salinity and temperature. At high latitudes the water is chilled by the low atmospheric temperature and becomes saltier as sea ice crystallizes out. Both these factors make it denser, and the water sinks. From the deep sea near Greenland, such water flows southwards between the continental landmasses on either side of the Atlantic. When it reaches the Antarctic, it is joined by further masses of cold, sinking water and flows eastwards. It then splits into two streams that move northwards into the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Here it is gradually warmed, becomes less dense, rises towards the surface and loops back on itself. It takes a thousand years for this circulation pattern to be completed.
Besides gyres, there are temporary surface currents that occur under specific conditions. When waves meet a shore at an angle, a Longshore drift, longshore current is created as water is pushed along parallel to the coastline. The water swirls up onto the beach at right angles to the approaching waves but drains away straight down the slope under the effect of gravity. The larger the breaking waves, the longer the beach and the more oblique the wave approach, the stronger is the longshore current. These currents can shift great volumes of sand or pebbles, create Spit (landform), spits and make beaches disappear and water channels silt up. A rip current can occur when water piles up near the shore from advancing waves and is funnelled out to sea through a channel in the seabed. It may occur at a gap in a Shoal, sandbar or near a man-made structure such as a groyne. These strong currents can have a velocity of per second, can form at different places at different stages of the tide and can carry away unwary bathers. Temporary upwelling currents occur when the wind pushes water away from the land and deeper water rises to replace it. This cold water is often rich in nutrients and creates blooms of phytoplankton and a great increase in the productivity of the sea.
Tides
 Tides are the regular rise and fall in water level experienced by seas and oceans in response to the Gravity, gravitational influences of the Moon and the Sun, and the effects of the Earth's rotation. During each tidal cycle, at any given place the water rises to a maximum height known as "high tide" before ebbing away again to the minimum "low tide" level. As the water recedes, it uncovers more and more of the foreshore, also known as the intertidal zone. The difference in height between the high tide and low tide is known as the tidal range or tidal amplitude.
Most places experience two high tides each day, occurring at intervals of about 12 hours and 25 minutes. This is half the 24 hours and 50 minute period that it takes for the Earth to make a complete revolution and return the Moon to its previous position relative to an observer. The Moon's mass is some 27 million times smaller than the Sun, but it is 400 times closer to the Earth. Tidal force or tide-raising force decreases rapidly with distance, so the moon has more than twice as great an effect on tides as the Sun. A bulge is formed in the ocean at the place where the Earth is closest to the Moon, because it is also where the effect of the Moon's gravity is stronger. On the opposite side of the Earth, the lunar force is at its weakest and this causes another bulge to form. As the Moon rotates around the Earth, so do these ocean bulges move around the Earth. The gravitational attraction of the Sun is also working on the seas, but its effect on tides is less powerful than that of the Moon, and when the Sun, Moon and Earth are all aligned (full moon and new moon), the combined effect results in the high "spring tides". In contrast, when the Sun is at 90° from the Moon as viewed from Earth, the combined gravitational effect on tides is less causing the lower "neap tides".
A storm surge can occur when high winds pile water up against the coast in a shallow area and this, coupled with a low pressure system, can raise the surface of the sea at high tide dramatically.
Tides are the regular rise and fall in water level experienced by seas and oceans in response to the Gravity, gravitational influences of the Moon and the Sun, and the effects of the Earth's rotation. During each tidal cycle, at any given place the water rises to a maximum height known as "high tide" before ebbing away again to the minimum "low tide" level. As the water recedes, it uncovers more and more of the foreshore, also known as the intertidal zone. The difference in height between the high tide and low tide is known as the tidal range or tidal amplitude.
Most places experience two high tides each day, occurring at intervals of about 12 hours and 25 minutes. This is half the 24 hours and 50 minute period that it takes for the Earth to make a complete revolution and return the Moon to its previous position relative to an observer. The Moon's mass is some 27 million times smaller than the Sun, but it is 400 times closer to the Earth. Tidal force or tide-raising force decreases rapidly with distance, so the moon has more than twice as great an effect on tides as the Sun. A bulge is formed in the ocean at the place where the Earth is closest to the Moon, because it is also where the effect of the Moon's gravity is stronger. On the opposite side of the Earth, the lunar force is at its weakest and this causes another bulge to form. As the Moon rotates around the Earth, so do these ocean bulges move around the Earth. The gravitational attraction of the Sun is also working on the seas, but its effect on tides is less powerful than that of the Moon, and when the Sun, Moon and Earth are all aligned (full moon and new moon), the combined effect results in the high "spring tides". In contrast, when the Sun is at 90° from the Moon as viewed from Earth, the combined gravitational effect on tides is less causing the lower "neap tides".
A storm surge can occur when high winds pile water up against the coast in a shallow area and this, coupled with a low pressure system, can raise the surface of the sea at high tide dramatically.
Ocean basins
 The Earth is composed of a magnetic central Planetary core, core, a mostly liquid Mantle (geology), mantle and a hard rigid outer shell (or lithosphere), which is composed of the Earth's rocky Crust (geology), crust and the deeper mostly solid outer layer of the mantle. On land the crust is known as the continental crust while under the sea it is known as the oceanic crust. The latter is composed of relatively dense basalt and is some five to ten kilometres (three to six miles) thick. The relatively thin lithosphere floats on the weaker and hotter mantle below and is fractured into a number of tectonic plates. In mid-ocean, magma is constantly being thrust through the seabed between adjoining plates to form mid-oceanic ridges and here convection currents within the mantle tend to drive the two plates apart. Parallel to these ridges and nearer the coasts, one oceanic plate may slide beneath another oceanic plate in a process known as subduction. Deep Oceanic trench, trenches are formed here and the process is accompanied by friction as the plates grind together. The movement proceeds in jerks which cause earthquakes, heat is produced and magma is forced up creating underwater mountains, some of which may form chains of volcanic islands near to deep trenches. Near some of the boundaries between the land and sea, the slightly denser oceanic plates slide beneath the continental plates and more subduction trenches are formed. As they grate together, the continental plates are deformed and buckle causing mountain building and seismic activity.
The Earth's deepest trench is the Mariana Trench which extends for about across the seabed. It is near the Mariana Islands, a volcanic archipelago in the West Pacific. Its deepest point is 10.994 kilometres (nearly 7 miles) below the surface of the sea.
The Earth is composed of a magnetic central Planetary core, core, a mostly liquid Mantle (geology), mantle and a hard rigid outer shell (or lithosphere), which is composed of the Earth's rocky Crust (geology), crust and the deeper mostly solid outer layer of the mantle. On land the crust is known as the continental crust while under the sea it is known as the oceanic crust. The latter is composed of relatively dense basalt and is some five to ten kilometres (three to six miles) thick. The relatively thin lithosphere floats on the weaker and hotter mantle below and is fractured into a number of tectonic plates. In mid-ocean, magma is constantly being thrust through the seabed between adjoining plates to form mid-oceanic ridges and here convection currents within the mantle tend to drive the two plates apart. Parallel to these ridges and nearer the coasts, one oceanic plate may slide beneath another oceanic plate in a process known as subduction. Deep Oceanic trench, trenches are formed here and the process is accompanied by friction as the plates grind together. The movement proceeds in jerks which cause earthquakes, heat is produced and magma is forced up creating underwater mountains, some of which may form chains of volcanic islands near to deep trenches. Near some of the boundaries between the land and sea, the slightly denser oceanic plates slide beneath the continental plates and more subduction trenches are formed. As they grate together, the continental plates are deformed and buckle causing mountain building and seismic activity.
The Earth's deepest trench is the Mariana Trench which extends for about across the seabed. It is near the Mariana Islands, a volcanic archipelago in the West Pacific. Its deepest point is 10.994 kilometres (nearly 7 miles) below the surface of the sea.
Coasts

 The zone where land meets sea is known as the coast and the part between the lowest spring tides and the upper limit reached by splashing waves is the shore. A beach is the accumulation of sand or Shingle beach, shingle on the shore. A headland is a point of land jutting out into the sea and a larger promontory is known as a Cape (geography), cape. The indentation of a coastline, especially between two headlands, is a bay, a small bay with a narrow inlet is a cove and a large bay may be referred to as a List of gulfs, gulf. Coastlines are influenced by a number of factors including the strength of the waves arriving on the shore, the gradient of the land margin, the composition and hardness of the coastal rock, the inclination of the off-shore slope and the changes of the level of the land due to local uplift or submergence. Normally, waves roll towards the shore at the rate of six to eight per minute and these are known as constructive waves as they tend to move material up the beach and have little erosive effect. Storm waves arrive on shore in rapid succession and are known as destructive waves as the swash moves beach material seawards. Under their influence, the sand and shingle on the beach is ground together and abraded. Around high tide, the power of a storm wave impacting on the foot of a cliff has a shattering effect as air in cracks and crevices is compressed and then expands rapidly with release of pressure. At the same time, sand and pebbles have an erosive effect as they are thrown against the rocks. This tends to undercut the cliff, and normal weathering processes such as the action of frost follows, causing further destruction. Gradually, a wave-cut platform develops at the foot of the cliff and this has a protective effect, reducing further wave-erosion.
Material worn from the margins of the land eventually ends up in the sea. Here it is subject to Attrition (erosion), attrition as currents flowing parallel to the coast scour out channels and transport sand and pebbles away from their place of origin. Sediment carried to the sea by rivers settles on the seabed causing River delta, deltas to form in estuaries. All these materials move back and forth under the influence of waves, tides and currents. Dredging removes material and deepens channels but may have unexpected effects elsewhere on the coastline. Governments make efforts to prevent flooding of the land by the building of Breakwater (structure), breakwaters, seawalls, levee, dykes and levees and other sea defences. For instance, the Thames Barrier is designed to protect London from a storm surge, while the failure of the dykes and levees around New Orleans during Hurricane Katrina created a humanitarian crisis in the United States.
The zone where land meets sea is known as the coast and the part between the lowest spring tides and the upper limit reached by splashing waves is the shore. A beach is the accumulation of sand or Shingle beach, shingle on the shore. A headland is a point of land jutting out into the sea and a larger promontory is known as a Cape (geography), cape. The indentation of a coastline, especially between two headlands, is a bay, a small bay with a narrow inlet is a cove and a large bay may be referred to as a List of gulfs, gulf. Coastlines are influenced by a number of factors including the strength of the waves arriving on the shore, the gradient of the land margin, the composition and hardness of the coastal rock, the inclination of the off-shore slope and the changes of the level of the land due to local uplift or submergence. Normally, waves roll towards the shore at the rate of six to eight per minute and these are known as constructive waves as they tend to move material up the beach and have little erosive effect. Storm waves arrive on shore in rapid succession and are known as destructive waves as the swash moves beach material seawards. Under their influence, the sand and shingle on the beach is ground together and abraded. Around high tide, the power of a storm wave impacting on the foot of a cliff has a shattering effect as air in cracks and crevices is compressed and then expands rapidly with release of pressure. At the same time, sand and pebbles have an erosive effect as they are thrown against the rocks. This tends to undercut the cliff, and normal weathering processes such as the action of frost follows, causing further destruction. Gradually, a wave-cut platform develops at the foot of the cliff and this has a protective effect, reducing further wave-erosion.
Material worn from the margins of the land eventually ends up in the sea. Here it is subject to Attrition (erosion), attrition as currents flowing parallel to the coast scour out channels and transport sand and pebbles away from their place of origin. Sediment carried to the sea by rivers settles on the seabed causing River delta, deltas to form in estuaries. All these materials move back and forth under the influence of waves, tides and currents. Dredging removes material and deepens channels but may have unexpected effects elsewhere on the coastline. Governments make efforts to prevent flooding of the land by the building of Breakwater (structure), breakwaters, seawalls, levee, dykes and levees and other sea defences. For instance, the Thames Barrier is designed to protect London from a storm surge, while the failure of the dykes and levees around New Orleans during Hurricane Katrina created a humanitarian crisis in the United States.
Water cycle
The sea plays a part in the water cycle, water or hydrological cycle, in which water evaporation, evaporates from the ocean, travels through the atmosphere as vapour, condensation, condenses, falls as Precipitation (meteorology), rain or snow, thereby sustaining life on land, and largely returns to the sea. Even in the Atacama Desert, where little rain ever falls, dense clouds of fog known as the camanchaca blow in from the sea and support plant life. In central Asia and other large land masses, there are endorheic basins which have no outlet to the sea, separated from the ocean by mountains or other natural geologic features that prevent the water draining away. TheCaspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
is the largest one of these. Its main inflow is from the River Volga, there is no outflow and the evaporation of water makes it saline as dissolved minerals accumulate. The Aral Sea in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, and Pyramid Lake (Nevada), Pyramid Lake in the western United States are further examples of large, inland saline water-bodies without drainage. Some endorheic lakes are less salty, but all are sensitive to variations in the quality of the inflowing water.
Carbon cycle
Oceans contain the greatest quantity of actively cycled carbon in the world and are second only to the lithosphere in the amount of carbon they store. The oceans' surface layer holds large amounts of dissolved organic carbon that is exchanged rapidly with the atmosphere. The deep layer's concentration of Total inorganic carbon, dissolved inorganic carbon is about 15 percent higher than that of the surface layer and it remains there for much longer periods of time. Thermohaline circulation exchanges carbon between these two layers. Carbon enters the ocean as atmospheric carbon dioxide dissolves in the surface layers and is converted into carbonic acid, carbonate, and bicarbonate: :CO2 (gas) CO2 (aq) :CO2 (aq) + H2O H2CO3 :H2CO3 HCO3− + H+ :HCO3− CO32− + H+ It can also enter through rivers as dissolved organic carbon and is converted by photosynthetic organisms into organic carbon. This can either be exchanged throughout the food chain or precipitated into the deeper, more carbon rich layers as dead soft tissue or in shells and bones as calcium carbonate. It circulates in this layer for long periods of time before either being deposited as sediment or being returned to surface waters through thermohaline circulation.Life in the sea
Marine habitats
Marine habitats can be divided horizontally into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats extend from the shoreline to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only 7 percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf. Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided vertically into Pelagic zone, pelagic (open water), Demersal zone, demersal (just above the seabed) and Benthic zone, benthic (sea bottom) habitats. A third division is by latitude: from polar seas with ice shelves, sea ice and icebergs, to temperate and tropical waters. Coral reefs, the so-called "rainforests of the sea", occupy less than 0.1 percent of the world's ocean surface, yet their ecosystems include 25 percent of all marine species. The best-known are tropical coral reefs such as Australia's Great Barrier Reef, but cold water reefs harbour a wide array of species including corals (only six of which contribute to reef formation).Algae and plants
Marine primary producers — plants and microscopic organisms in the plankton — are widespread and very essential for the ecosystem. It has been estimated that half of the world's oxygen is produced by phytoplankton. About 45 percent of the sea's primary production of living material is contributed by diatoms. Much larger algae, commonly known asseaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
s, are important locally; ''Sargassum'' forms floating drifts, while kelp form seabed forests. Flowering plants in the form of seagrasses grow in "meadows" in sandy shallows, mangroves line the coast in tropical and subtropical regions and Halophyte, salt-tolerant plants thrive in regularly inundated salt marshes. All of these habitats are able to sequester large quantities of carbon and support a Marine biology, biodiverse range of larger and smaller animal life.
Light is only able to penetrate the top so this is the only part of the sea where plants can grow. The surface layers are often deficient in biologically active nitrogen compounds. The marine nitrogen cycle consists of complex microbial transformations which include the Nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen, its assimilation, nitrification, anammox and denitrification. Some of these processes take place in deep water so that where there is an upwelling of cold waters, and also near estuaries where land-sourced nutrients are present, plant growth is higher. This means that the most productive areas, rich in plankton and therefore also in fish, are mainly coastal.
Animals and other marine life
 There is a broader spectrum of higher animal taxon, taxa in the sea than on land, many marine species have yet to be discovered and the number known to science is expanding annually. Some vertebrates such as seabirds, Pinniped, seals and sea turtles return to the land to breed but fish, cetaceans and sea snakes have a completely aquatic lifestyle and many invertebrate Phylum, phyla are entirely marine. In fact, the oceans teem with life and provide many varying microhabitats. One of these is the surface film which, even though tossed about by the movement of waves, provides a rich environment and is home to bacteria, Marine fungi, fungi, microalgae, protozoa, fish eggs and various larvae.
The pelagic zone contains Fauna#Macrofauna, macro- and microfauna and myriad zooplankton which drift with the currents. Most of the smallest organisms are the larvae of fish and marine invertebrates which liberate Egg (biology), eggs in vast numbers because the chance of any one embryo surviving to maturity is so minute. The zooplankton feed on phytoplankton and on each other and form a basic part of the complex food chain that extends through variously sized fish and other nektonic organisms to large squid, sharks, porpoises, dolphins and whales. Some marine creatures make large migrations, either to other regions of the ocean on a seasonal basis or vertical migrations daily, often ascending to feed at night and descending to safety by day. Ships can introduce or spread invasive species through the discharge of ballast water or the transport of organisms that have accumulated as part of the fouling community on the hulls of vessels.
The demersal zone supports many animals that feed on benthic organisms or seek protection from predators and the seabed provides a range of habitats on or under the surface of the Substrate (biology), substrate which are used by creatures adapted to these conditions. The tidal zone with its periodic exposure to the dehydrating air is home to barnacles, molluscs and crustaceans. The neritic zone has many organisms that need light to flourish. Here, among algal encrusted rocks live sponges, echinoderms, polychaete worms, sea anemones and other invertebrates. Corals often contain photosynthetic Symbiosis, symbionts and live in shallow waters where light penetrates. The extensive calcareous skeletons they extrude build up into coral reefs which are an important feature of the seabed. These provide a Biodiversity, biodiverse habitat for reef dwelling organisms. There is less sea life on the floor of deeper seas but marine life also flourishes around seamounts that rise from the depths, where fish and other animals congregate to spawn and feed. Close to the seabed live demersal fish that feed largely on pelagic organisms or Benthos, benthic invertebrates. Exploration of the deep sea by submersibles revealed a new world of creatures living on the seabed that scientists had not previously known to exist. Some like the Detritivore, detrivores rely on organic material falling to the ocean floor. Others cluster round deep sea hydrothermal vents where mineral-rich flows of water emerge from the seabed, supporting communities whose primary producers are sulphide-oxidising chemoautotrophic bacteria, and whose consumers include specialised bivalves, sea anemones, barnacles, crabs, worms and fish, often found nowhere else. A dead whale sinking to the bottom of the ocean provides food for an assembly of organisms which similarly rely largely on the actions of sulphur-reducing bacteria. Such places support unique biomes where many new microbes and other lifeforms have been discovered.
There is a broader spectrum of higher animal taxon, taxa in the sea than on land, many marine species have yet to be discovered and the number known to science is expanding annually. Some vertebrates such as seabirds, Pinniped, seals and sea turtles return to the land to breed but fish, cetaceans and sea snakes have a completely aquatic lifestyle and many invertebrate Phylum, phyla are entirely marine. In fact, the oceans teem with life and provide many varying microhabitats. One of these is the surface film which, even though tossed about by the movement of waves, provides a rich environment and is home to bacteria, Marine fungi, fungi, microalgae, protozoa, fish eggs and various larvae.
The pelagic zone contains Fauna#Macrofauna, macro- and microfauna and myriad zooplankton which drift with the currents. Most of the smallest organisms are the larvae of fish and marine invertebrates which liberate Egg (biology), eggs in vast numbers because the chance of any one embryo surviving to maturity is so minute. The zooplankton feed on phytoplankton and on each other and form a basic part of the complex food chain that extends through variously sized fish and other nektonic organisms to large squid, sharks, porpoises, dolphins and whales. Some marine creatures make large migrations, either to other regions of the ocean on a seasonal basis or vertical migrations daily, often ascending to feed at night and descending to safety by day. Ships can introduce or spread invasive species through the discharge of ballast water or the transport of organisms that have accumulated as part of the fouling community on the hulls of vessels.
The demersal zone supports many animals that feed on benthic organisms or seek protection from predators and the seabed provides a range of habitats on or under the surface of the Substrate (biology), substrate which are used by creatures adapted to these conditions. The tidal zone with its periodic exposure to the dehydrating air is home to barnacles, molluscs and crustaceans. The neritic zone has many organisms that need light to flourish. Here, among algal encrusted rocks live sponges, echinoderms, polychaete worms, sea anemones and other invertebrates. Corals often contain photosynthetic Symbiosis, symbionts and live in shallow waters where light penetrates. The extensive calcareous skeletons they extrude build up into coral reefs which are an important feature of the seabed. These provide a Biodiversity, biodiverse habitat for reef dwelling organisms. There is less sea life on the floor of deeper seas but marine life also flourishes around seamounts that rise from the depths, where fish and other animals congregate to spawn and feed. Close to the seabed live demersal fish that feed largely on pelagic organisms or Benthos, benthic invertebrates. Exploration of the deep sea by submersibles revealed a new world of creatures living on the seabed that scientists had not previously known to exist. Some like the Detritivore, detrivores rely on organic material falling to the ocean floor. Others cluster round deep sea hydrothermal vents where mineral-rich flows of water emerge from the seabed, supporting communities whose primary producers are sulphide-oxidising chemoautotrophic bacteria, and whose consumers include specialised bivalves, sea anemones, barnacles, crabs, worms and fish, often found nowhere else. A dead whale sinking to the bottom of the ocean provides food for an assembly of organisms which similarly rely largely on the actions of sulphur-reducing bacteria. Such places support unique biomes where many new microbes and other lifeforms have been discovered.
Humans and the sea
History of navigation and exploration
 As for the history of navigational instrument, a compass was first used by the ancient Greeks and Chinese to show where north lies and the direction in which the ship is heading. The latitude (an angle which ranges from 0° at the equator to 90° at the poles) was determined by measuring the angle between the Sun, Moon or a specific star and the horizon by the use of an astrolabe, Jacob's staff or Sextant (astronomical), sextant. The longitude (a line on the globe joining the two poles) could only be calculated with an accurate Marine chronometer, chronometer to show the exact time difference between the ship and a fixed point such as the Prime meridian (Greenwich), Greenwich Meridian. In 1759, John Harrison, a clockmaker, designed such an instrument and James Cook used it in his voyages of exploration. Nowadays, the Global Positioning System (GPS) using over thirty satellites enables accurate navigation worldwide.
With regards to maps that are vital for navigation, in the second century, Ptolemy mapped the whole known world from the "Fortunatae Insulae", Cape Verde or Canary Islands, eastward to the Gulf of Thailand. This map was used in 1492 when Christopher Columbus set out on his voyages of discovery. Subsequently, Gerardus Mercator made a practical map of the world in 1538, his map projection conveniently making rhumb lines straight. By the eighteenth century better maps had been made and part of the objective of James Cook on his voyages was to further map the ocean. Scientific study has continued with the depth recordings of the ''USS Tuscarora (1861), Tuscarora'', the oceanic research of the Challenger expedition, Challenger voyages (1872–1876), the work of the Scandinavian seamen Roald Amundsen and Fridtjof Nansen, the Michael Sars expedition in 1910, the German Meteor expedition of 1925, the Antarctic survey work of ''RRS Discovery II, Discovery II'' in 1932, and others since. Furthermore, in 1921, the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) was set up, and it constitutes the world authority on Hydrography, hydrographic surveying and nautical charting. A fourth edition draft was published in 1986 but so far several naming disputes (such as the one over the Sea of Japan naming dispute, Sea of Japan) have prevented its ratification.
As for the history of navigational instrument, a compass was first used by the ancient Greeks and Chinese to show where north lies and the direction in which the ship is heading. The latitude (an angle which ranges from 0° at the equator to 90° at the poles) was determined by measuring the angle between the Sun, Moon or a specific star and the horizon by the use of an astrolabe, Jacob's staff or Sextant (astronomical), sextant. The longitude (a line on the globe joining the two poles) could only be calculated with an accurate Marine chronometer, chronometer to show the exact time difference between the ship and a fixed point such as the Prime meridian (Greenwich), Greenwich Meridian. In 1759, John Harrison, a clockmaker, designed such an instrument and James Cook used it in his voyages of exploration. Nowadays, the Global Positioning System (GPS) using over thirty satellites enables accurate navigation worldwide.
With regards to maps that are vital for navigation, in the second century, Ptolemy mapped the whole known world from the "Fortunatae Insulae", Cape Verde or Canary Islands, eastward to the Gulf of Thailand. This map was used in 1492 when Christopher Columbus set out on his voyages of discovery. Subsequently, Gerardus Mercator made a practical map of the world in 1538, his map projection conveniently making rhumb lines straight. By the eighteenth century better maps had been made and part of the objective of James Cook on his voyages was to further map the ocean. Scientific study has continued with the depth recordings of the ''USS Tuscarora (1861), Tuscarora'', the oceanic research of the Challenger expedition, Challenger voyages (1872–1876), the work of the Scandinavian seamen Roald Amundsen and Fridtjof Nansen, the Michael Sars expedition in 1910, the German Meteor expedition of 1925, the Antarctic survey work of ''RRS Discovery II, Discovery II'' in 1932, and others since. Furthermore, in 1921, the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) was set up, and it constitutes the world authority on Hydrography, hydrographic surveying and nautical charting. A fourth edition draft was published in 1986 but so far several naming disputes (such as the one over the Sea of Japan naming dispute, Sea of Japan) have prevented its ratification.
History of oceanography and deep sea exploration
Scientific oceanography began with the voyages of Captain James Cook from 1768 to 1779, describing the Pacific with unprecedented precision from 71 degrees South to 71 degrees North. John Harrison's chronometers supported Cook's accurate navigation and charting on two of these voyages, permanently improving the standard attainable for subsequent work. Other expeditions followed in the nineteenth century, from Russia, France, the Netherlands and the United States as well as Britain. On HMS Beagle, HMS ''Beagle'', which provided Charles Darwin with ideas and materials for his 1859 book ''On the Origin of Species'', the ship's captain, Robert FitzRoy, charted the seas and coasts and published his four-volume report of the ship's three voyages in 1839. Edward Forbes's 1854 book, ''Distribution of Marine Life'' argued that no life could exist below around 600 metres (2000 feet). This was proven wrong by the British biologists W. B. Carpenter and C. Wyville Thomson, who in 1868 discovered life in deep water by dredging. Wyville Thompson became chief scientist on the Challenger expedition of 1872–1876, which effectively created the science of oceanography. On her journey round the globe, ''HMS Challenger'' discovered about 4,700 new marine species, and made 492 deep sea soundings, 133 bottom dredges, 151 open water trawls and 263 serial water temperature observations. In the southern Atlantic in 1898/1899, Carl Chun on the ''Valdivia'' brought many new life forms to the surface from depths of over . The first observations of deep-sea animals in their natural environment were made in 1930 by William Beebe and Otis Barton who descended to in the spherical steel Bathysphere. This was lowered by cable but by 1960 a self-powered submersible, Bathyscaphe Trieste, Trieste developed by Jacques Piccard, took Piccard and Don Walsh to the deepest part of theEarth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
's oceans, the Mariana Trench in the Pacific, reaching a record depth of about , a feat not repeated until 2012 when James Cameron piloted the Deepsea Challenger to similar depths. An atmospheric diving suit can be worn for deep sea operations, with a new world record being set in 2006 when a US Navy diver descended to in one of these articulated, pressurized suits.
At great depths, no light penetrates through the water layers from above and the pressure is extreme. For deep sea exploration it is necessary to use specialist vehicles, either remotely operated underwater vehicles with lights and cameras or crewed submersibles. The battery-operated Mir (submersible), Mir submersibles have a three-person crew and can descend to 20,000 feet (6,000 m). They have viewing ports, 5,000-watt lights, video equipment and manipulator arms for collecting samples, placing probes or pushing the vehicle across the sea bed when the thrusters would stir up excessive sediment.
Bathymetry is the mapping and study of the topography of the ocean floor. Methods used for measuring the depth of the sea include single or multibeam echosounders, laser airborne depth sounders and the calculation of depths from satellite remote sensing data. This information is used for determining the routes of undersea cables and pipelines, for choosing suitable locations for siting oil rigs and offshore wind turbines and for identifying possible new fisheries.
Ongoing oceanographic research includes marine lifeforms, conservation, the marine environment, the chemistry of the ocean, the studying and modelling of climate dynamics, the air-sea boundary, weather patterns, ocean resources, renewable energy, waves and currents, and the design and development of new tools and technologies for investigating the deep. Whereas in the 1960s and 1970s research could focus on taxonomy and basic biology, in the 2010s attention has shifted to larger topics such as climate change. Researchers make use of satellite-based remote sensing for surface waters, with research ships, moored observatories and autonomous underwater vehicles to study and monitor all parts of the sea.
Law
"Freedom of the seas" is a principle in international law dating from the seventeenth century. It stresses freedom to navigate the oceans and disapproves of war fought in international waters. Today, this concept is enshrined in the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), the third version of which came into force in 1994. Article 87(1) states: "The high seas are open to all sovereign state, states, whether coastal or landlocked country, land-locked." Article 87(1) (a) to (f) gives a non-exhaustive list of freedoms including navigation, overflight, the laying of submarine communications cable, submarine cables, building artificial islands, fishing and scientific research. The safety of shipping is regulated by the International Maritime Organization. Its objectives include developing and maintaining a regulatory framework for shipping, maritime safety, environmental concerns, legal matters, technical co-operation and maritime security. UNCLOS defines various areas of water. "Internal waters" are on the landward side of a Baseline (sea), baseline and foreign vessels have no right of passage in these. "Territorial waters" extend to 12 nautical miles (22 kilometres; 14 miles) from the coastline and in these waters, the coastal state is free to set laws, regulate use and exploit any resource. A "contiguous zone" extending a further 12 nautical miles allows for hot pursuit of vessels suspected of infringing laws in four specific areas: customs, taxation, immigration and pollution. An "exclusive economic zone" extends for 200 nautical miles (370 kilometres; 230 miles) from the baseline. Within this area, the coastal nation has sole exploitation rights over all natural resources. The "continental shelf" is the natural prolongation of the land territory to the continental margin's outer edge, or 200 nautical miles from the coastal state's baseline, whichever is greater. Here the coastal nation has the exclusive right to harvest minerals and also living resources "attached" to the seabed.War
 Control of the sea is important to the security of a maritime nation, and the naval blockade of a port can be used to cut off food and supplies in time of war. Battles have been fought on the sea for more than 3,000 years. In about 1210 B.C., Suppiluliuma II, the king of the Hittites, defeated and burned a fleet from Alashiya (modern Cyprus). In the decisive 480 B.C. Battle of Salamis, the Greek general Themistocles trapped the far larger fleet of the Persian king Xerxes II of Persia, Xerxes in a narrow channel and attacked vigorously, destroying 200 Persian ships for the loss of 40 Greek vessels. At the end of the Age of Sail, the British Royal Navy, led by Horatio Nelson, broke the power of the combined French and Spanish fleets at the 1805 Battle of Trafalgar.
With steam and the industrial production of steel plate came greatly increased firepower in the shape of the dreadnought battleships armed with long-range guns. In 1905, the Japanese fleet decisively defeated the Russian fleet, which had travelled over , at the Battle of Tsushima. Dreadnoughts fought inconclusively in the First World War at the 1916 Battle of Jutland between the Royal Navy's Grand Fleet and the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet. In the Second World War, the British victory at the 1940 Battle of Taranto showed that naval air power was sufficient to overcome the largest warships, foreshadowing the decisive sea-battles of the Pacific War including the Battles of the Battle of the Coral Sea, Coral Sea, Battle of Midway, Midway, Battle of the Philippine Sea, the Philippine Sea, and the climactic Battle of Leyte Gulf, in all of which the dominant ships were aircraft carriers.
Submarines became important in naval warfare in World War I, when German submarines, known as U-boats, sank nearly 5,000 Allied merchant ships, including the RMS Lusitania, which helped to bring the United States into the war. In World War II, almost 3,000 Allied ships were sunk by U-boats attempting to block the flow of supplies to Britain, but the Allies broke the blockade in the Battle of the Atlantic, which lasted the whole length of the war, sinking 783 U-boats. Since 1960, several nations have maintained fleets of nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines, vessels equipped to launch ballistic missiles with nuclear warheads from under the sea. Some of these are kept permanently on patrol.
Control of the sea is important to the security of a maritime nation, and the naval blockade of a port can be used to cut off food and supplies in time of war. Battles have been fought on the sea for more than 3,000 years. In about 1210 B.C., Suppiluliuma II, the king of the Hittites, defeated and burned a fleet from Alashiya (modern Cyprus). In the decisive 480 B.C. Battle of Salamis, the Greek general Themistocles trapped the far larger fleet of the Persian king Xerxes II of Persia, Xerxes in a narrow channel and attacked vigorously, destroying 200 Persian ships for the loss of 40 Greek vessels. At the end of the Age of Sail, the British Royal Navy, led by Horatio Nelson, broke the power of the combined French and Spanish fleets at the 1805 Battle of Trafalgar.
With steam and the industrial production of steel plate came greatly increased firepower in the shape of the dreadnought battleships armed with long-range guns. In 1905, the Japanese fleet decisively defeated the Russian fleet, which had travelled over , at the Battle of Tsushima. Dreadnoughts fought inconclusively in the First World War at the 1916 Battle of Jutland between the Royal Navy's Grand Fleet and the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet. In the Second World War, the British victory at the 1940 Battle of Taranto showed that naval air power was sufficient to overcome the largest warships, foreshadowing the decisive sea-battles of the Pacific War including the Battles of the Battle of the Coral Sea, Coral Sea, Battle of Midway, Midway, Battle of the Philippine Sea, the Philippine Sea, and the climactic Battle of Leyte Gulf, in all of which the dominant ships were aircraft carriers.
Submarines became important in naval warfare in World War I, when German submarines, known as U-boats, sank nearly 5,000 Allied merchant ships, including the RMS Lusitania, which helped to bring the United States into the war. In World War II, almost 3,000 Allied ships were sunk by U-boats attempting to block the flow of supplies to Britain, but the Allies broke the blockade in the Battle of the Atlantic, which lasted the whole length of the war, sinking 783 U-boats. Since 1960, several nations have maintained fleets of nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines, vessels equipped to launch ballistic missiles with nuclear warheads from under the sea. Some of these are kept permanently on patrol.
Travel
Sailing ships or Packet boat, packets carried mail overseas, one of the earliest being the Dutch service to Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia in the 1670s. These added passenger accommodation, but in cramped conditions. Later, scheduled services were offered but the time journeys took depended much on the weather. When steamships replaced sailing vessels, Ocean liner, ocean-going liners took over the task of carrying people. By the beginning of the twentieth century, crossing the Atlantic took about five days and shipping companies competed to own the largest and fastest vessels. The Blue Riband was an unofficial accolade given to the fastest liner crossing the Atlantic in regular service. The ''RMS Mauretania (1906), Mauretania'' held the title with 26.06 knots (48.26 km/h) for twenty years from 1909. The Hales Trophy, another award for the fastest commercial crossing of the Atlantic, was won by the ''SS United States, United States'' in 1952 for a crossing that took three days, ten hours and forty minutes. The great liners were comfortable but expensive in fuel and staff. The age of the trans-Atlantic liners waned as cheap intercontinental flights became available. In 1958, a regular scheduled air service between New York and Paris taking seven hours doomed the Atlantic ferry service to oblivion. One by one the vessels were laid up, some were scrapped, others became cruise ships for the leisure industry and still others floating hotels.Trade
 Maritime trade has existed for millennia. The Ptolemaic dynasty had developed trade with India using the Red Sea ports and in the first millennium BC the Arabs, Phoenicians, Israelites and Indians traded in luxury goods such as spices, gold, and precious stones. The Phoenicians were noted sea traders and under the Greeks and Romans, commerce continued to thrive. With the collapse of the Roman Empire, European trade dwindled but it continued to flourish among the kingdoms of Africa, the Middle East, India, China and southeastern Asia. From the 16th to the 19th centuries, over a period of 400 years, about 12–13 million Africans were shipped across the Atlantic to be sold as slaves in the Americas as part of the Atlantic slave trade.
Large quantities of goods are transported by sea, especially across the Atlantic and around the Pacific Rim. A major trade route passes through the Pillars of Hercules, across the Mediterranean and the Suez Canal to the Indian Ocean and through the Straits of Malacca; much trade also passes through the English Channel. Shipping lanes are the routes on the open sea used by cargo vessels, traditionally making use of trade winds and currents. Over 60 percent of the world's container traffic is conveyed on the top twenty trade routes. Increased melting of Arctic ice since 2007 enables ships to travel the Northwest Passage for some weeks in summertime, avoiding the longer routes via the Suez Canal or the Panama Canal.
Shipping is supplemented by air freight, a more expensive process mostly used for particularly valuable or perishable cargoes. Seaborne trade carries more than US$4 trillion worth of goods each year. Bulk cargo in the form of liquids, powder or particles are carried loose in the Hold (ship), holds of bulk carriers and include Petroleum, crude oil, grain, coal, ore, Scrap, scrap metal, sand and gravel. Other cargo, such as manufactured goods, is usually transported within Shipping container, standard sized, lockable containers, loaded on purpose-built container ships at Container port, dedicated terminals. Before the rise of containerization in the 1960s, these goods were loaded, transported and unloaded piecemeal as Breakbulk cargo, break-bulk cargo. Containerization greatly increased the efficiency and decreased the cost of moving goods by sea, and was a major factor leading to the rise of globalization and exponential increases in international trade in the mid-to-late 20th century.
Maritime trade has existed for millennia. The Ptolemaic dynasty had developed trade with India using the Red Sea ports and in the first millennium BC the Arabs, Phoenicians, Israelites and Indians traded in luxury goods such as spices, gold, and precious stones. The Phoenicians were noted sea traders and under the Greeks and Romans, commerce continued to thrive. With the collapse of the Roman Empire, European trade dwindled but it continued to flourish among the kingdoms of Africa, the Middle East, India, China and southeastern Asia. From the 16th to the 19th centuries, over a period of 400 years, about 12–13 million Africans were shipped across the Atlantic to be sold as slaves in the Americas as part of the Atlantic slave trade.
Large quantities of goods are transported by sea, especially across the Atlantic and around the Pacific Rim. A major trade route passes through the Pillars of Hercules, across the Mediterranean and the Suez Canal to the Indian Ocean and through the Straits of Malacca; much trade also passes through the English Channel. Shipping lanes are the routes on the open sea used by cargo vessels, traditionally making use of trade winds and currents. Over 60 percent of the world's container traffic is conveyed on the top twenty trade routes. Increased melting of Arctic ice since 2007 enables ships to travel the Northwest Passage for some weeks in summertime, avoiding the longer routes via the Suez Canal or the Panama Canal.
Shipping is supplemented by air freight, a more expensive process mostly used for particularly valuable or perishable cargoes. Seaborne trade carries more than US$4 trillion worth of goods each year. Bulk cargo in the form of liquids, powder or particles are carried loose in the Hold (ship), holds of bulk carriers and include Petroleum, crude oil, grain, coal, ore, Scrap, scrap metal, sand and gravel. Other cargo, such as manufactured goods, is usually transported within Shipping container, standard sized, lockable containers, loaded on purpose-built container ships at Container port, dedicated terminals. Before the rise of containerization in the 1960s, these goods were loaded, transported and unloaded piecemeal as Breakbulk cargo, break-bulk cargo. Containerization greatly increased the efficiency and decreased the cost of moving goods by sea, and was a major factor leading to the rise of globalization and exponential increases in international trade in the mid-to-late 20th century.
Food
 Fish and other fishery products are among the most widely consumed sources of protein and other essential nutrients. In 2009, 16.6% of the world's intake of animal protein and 6.5% of all protein consumed came from fish. In order to fulfill this need, coastal countries have exploited marine resources in their exclusive economic zone, although fishing vessels are increasingly venturing further afield to exploit stocks in international waters. In 2011, the total world production of fish, including aquaculture, was estimated to be 154 million tonnes, of which most was for human consumption. The harvesting of wild fish accounted for 90.4 million tonnes, while annually increasing aquaculture contributes the rest. The north west Pacific is by far the most productive area with 20.9 million tonnes (27 percent of the global marine catch) in 2010. In addition, the number of fishing vessels in 2010 reached 4.36 million, whereas the number of people employed in the primary sector of fish production in the same year amounted to 54.8 million.
Modern fishing vessels include fishing trawlers with a small crew, stern trawlers, purse seiners, long-line factory vessels and large factory ships which are designed to stay at sea for weeks, processing and freezing great quantities of fish. The equipment used to capture the fish may be purse seines, other seines, Trawling, trawls, dredges, gillnets and Longline fishing, long-lines and the fish species most frequently targeted are herring, cod, anchovy, tuna, flounder, Mullet (fish), mullet, squid and salmon. Overexploitation has become a serious concern; it does not only cause the depletion of fish stocks, but also substantially reduce the size of predatory fish populations. It has been estimated that "industrialized fisheries typically reduced community biomass by 80% within 15 years of exploitation." In order to avoid overexploitation, many countries have introduced Individual fishing quota, quotas in their own waters. However, recovery efforts often entail substantial costs to local economies or food provision.
Fish and other fishery products are among the most widely consumed sources of protein and other essential nutrients. In 2009, 16.6% of the world's intake of animal protein and 6.5% of all protein consumed came from fish. In order to fulfill this need, coastal countries have exploited marine resources in their exclusive economic zone, although fishing vessels are increasingly venturing further afield to exploit stocks in international waters. In 2011, the total world production of fish, including aquaculture, was estimated to be 154 million tonnes, of which most was for human consumption. The harvesting of wild fish accounted for 90.4 million tonnes, while annually increasing aquaculture contributes the rest. The north west Pacific is by far the most productive area with 20.9 million tonnes (27 percent of the global marine catch) in 2010. In addition, the number of fishing vessels in 2010 reached 4.36 million, whereas the number of people employed in the primary sector of fish production in the same year amounted to 54.8 million.
Modern fishing vessels include fishing trawlers with a small crew, stern trawlers, purse seiners, long-line factory vessels and large factory ships which are designed to stay at sea for weeks, processing and freezing great quantities of fish. The equipment used to capture the fish may be purse seines, other seines, Trawling, trawls, dredges, gillnets and Longline fishing, long-lines and the fish species most frequently targeted are herring, cod, anchovy, tuna, flounder, Mullet (fish), mullet, squid and salmon. Overexploitation has become a serious concern; it does not only cause the depletion of fish stocks, but also substantially reduce the size of predatory fish populations. It has been estimated that "industrialized fisheries typically reduced community biomass by 80% within 15 years of exploitation." In order to avoid overexploitation, many countries have introduced Individual fishing quota, quotas in their own waters. However, recovery efforts often entail substantial costs to local economies or food provision.
 Artisan fishing methods include rod and line, harpoons, skin diving, traps, throw nets and drag nets. Traditional fishing boats are powered by paddle, wind or outboard motors and operate in near-shore waters. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Food and Agriculture Organization is encouraging the development of local fisheries to provide food security to coastal communities and help alleviate poverty.
Artisan fishing methods include rod and line, harpoons, skin diving, traps, throw nets and drag nets. Traditional fishing boats are powered by paddle, wind or outboard motors and operate in near-shore waters. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Food and Agriculture Organization is encouraging the development of local fisheries to provide food security to coastal communities and help alleviate poverty.
Aquaculture
About 79 million tonnes (78M long tons; 87M short tons) of food and non-food products were produced by aquaculture in 2010, an all-time high. About six hundred species of plants and animals were cultured, some for use in seeding wild populations. The animals raised included finfish, aquatic reptiles, crustaceans, molluscs, sea cucumbers, sea urchins, sea squirts and jellyfish. Integrated mariculture has the advantage that there is a readily available supply of planktonic food in the ocean, and waste is removed naturally. Various methods are employed. Mesh enclosures for finfish can be suspended in the open seas, cages can be used in more sheltered waters or ponds can be refreshed with water at each high tide. Marine shrimp farming, Shrimps can be reared in shallow ponds connected to the open sea. Ropes can be hung in water to grow algae, oysters and mussels. Oysters can be reared on trays or in mesh tubes. Sea cucumbers can be ranched on the seabed. Captive breeding programmes have raised lobster larvae for release of juveniles into the wild resulting in an increased lobster harvest in Maine. At least 145 species of seaweed – red, green, and brown algae – are eaten worldwide, and some have long been farmed in Japan and other Asian countries; there is great potential for additional algaculture. Few maritime flowering plants are widely used for food but one example is marsh samphire which is eaten both raw and cooked. A major difficulty for aquaculture is the tendency towards monoculture and the associated risk of widespread Fish diseases and parasites, disease. Aquaculture is also associated with environmental risks; for instance, shrimp farming has caused the destruction of important mangrove forests throughout southeast Asia.Leisure
Use of the sea for leisure developed in the nineteenth century, and became a significant industry in the twentieth century. Maritime leisure activities are varied, and include self-organized trips Cruising (maritime), cruising, yachting, Offshore powerboat racing, powerboat racing and Recreational boat fishing, fishing; commercially organized voyages on cruise ships; and trips on smaller vessels for ecotourism such as whale watching and coastal birdwatching. Sea bathing became the vogue in Europe in the 18th century after William Buchan (physician), Dr. William Buchan advocated the practice for health reasons. Surfing is a sport in which a wave is ridden by a surfer, with or without a surfboard. Other marine Surface water sports, water sports include kite surfing, where a power kite propels a rider on a board across the water, windsurfing, where the power is provided by a fixed, manoeuvrable sail and water skiing, where a powerboat is used to pull a skier.
Beneath the surface, freediving is necessarily restricted to shallow descents. Pearl hunting, Pearl divers can dive to with baskets to collect oysters. Human eyes are not adapted for use underwater but vision can be improved by wearing a diving mask. Other useful equipment includes Swimfin, fins and Snorkel (swimming), snorkels, and Scuba set, scuba equipment allows underwater breathing and hence a longer time can be spent beneath the surface. The depths that can be reached by divers and the length of time they can stay underwater is limited by the increase of pressure they experience as they descend and the need to prevent decompression sickness as they return to the surface. Recreational divers restrict themselves to depths of beyond which the danger of nitrogen narcosis increases. Deep diving, Deeper dives can be made with specialised equipment and training.
Sea bathing became the vogue in Europe in the 18th century after William Buchan (physician), Dr. William Buchan advocated the practice for health reasons. Surfing is a sport in which a wave is ridden by a surfer, with or without a surfboard. Other marine Surface water sports, water sports include kite surfing, where a power kite propels a rider on a board across the water, windsurfing, where the power is provided by a fixed, manoeuvrable sail and water skiing, where a powerboat is used to pull a skier.
Beneath the surface, freediving is necessarily restricted to shallow descents. Pearl hunting, Pearl divers can dive to with baskets to collect oysters. Human eyes are not adapted for use underwater but vision can be improved by wearing a diving mask. Other useful equipment includes Swimfin, fins and Snorkel (swimming), snorkels, and Scuba set, scuba equipment allows underwater breathing and hence a longer time can be spent beneath the surface. The depths that can be reached by divers and the length of time they can stay underwater is limited by the increase of pressure they experience as they descend and the need to prevent decompression sickness as they return to the surface. Recreational divers restrict themselves to depths of beyond which the danger of nitrogen narcosis increases. Deep diving, Deeper dives can be made with specialised equipment and training.
Industry
Power generation
The sea offers a very large supply of energy carried by ocean waves, tides, salinity differences, and ocean thermal energy, ocean temperature differences which can be harnessed to electricity generation, generate electricity. Forms of Sustainable energy, sustainable marine energy include tidal power, ocean thermal energy conversion, ocean thermal energy and wave power. Electricity power stations are often located on the coast or beside an estuary so that the sea can be used as a heat sink. A colder heat sink enables more efficient power generation, which is important for expensive nuclear power plants in particular. Tidal power uses generators to produce electricity from tidal flows, sometimes by using a dam to store and then release seawater. The Rance barrage, long, near St Malo in Brittany opened in 1967; it generates about 0.5 GW, but it has been followed by few similar schemes.
The large and highly variable energy of waves gives them enormous destructive capability, making affordable and reliable wave machines problematic to develop. A small 2 MW commercial wave power plant, "Osprey", was built in Northern Scotland in 1995 about 300 metres (1000 ft) offshore. It was soon damaged by waves, then destroyed by a storm.
Offshore wind power is captured by wind turbines placed out at sea; it has the advantage that wind speeds are higher than on land, though wind farms are more costly to construct offshore. The first offshore wind farm was installed in Denmark in 1991, and the installed capacity of worldwide offshore wind farms reached 34 GW in 2020, mainly situated in Europe.
Tidal power uses generators to produce electricity from tidal flows, sometimes by using a dam to store and then release seawater. The Rance barrage, long, near St Malo in Brittany opened in 1967; it generates about 0.5 GW, but it has been followed by few similar schemes.
The large and highly variable energy of waves gives them enormous destructive capability, making affordable and reliable wave machines problematic to develop. A small 2 MW commercial wave power plant, "Osprey", was built in Northern Scotland in 1995 about 300 metres (1000 ft) offshore. It was soon damaged by waves, then destroyed by a storm.
Offshore wind power is captured by wind turbines placed out at sea; it has the advantage that wind speeds are higher than on land, though wind farms are more costly to construct offshore. The first offshore wind farm was installed in Denmark in 1991, and the installed capacity of worldwide offshore wind farms reached 34 GW in 2020, mainly situated in Europe.
Extractive industries
The seabed contains large reserves of minerals which can be exploited by dredging. This has advantages over land-based mining in that equipment can be built at specialised shipyards and infrastructure costs are lower. Disadvantages include problems caused by waves and tides, the tendency for excavations to silt up and the washing away of Spoil tip, spoil heaps. There is a risk of coastal erosion and environmental damage. Seafloor massive sulfide deposits, Seafloor massive sulphide deposits are potential sources of silver, gold, copper, lead and zinc and trace metals since their discovery in the 1960s. They form when Geothermal gradient, geothermally heated water is emitted from deep sea hydrothermal vents known as "black smokers". The ores are of high quality but prohibitively costly to extract.
There are large deposits of petroleum, as oil and natural gas, in rocks beneath the seabed. Oil platform, Offshore platforms and drilling rigs Offshore drilling, extract the oil or gas and store it for transport to land. Offshore oil and gas production can be difficult due to the remote, harsh environment. Drilling for oil in the sea has environmental impacts. Animals may be disorientated by seismic waves used to locate deposits, and there is debate as to whether this causes the Beached whale, beaching of whales. Toxic substances such as mercury (element), mercury, lead and arsenic may be released. The infrastructure may cause damage, and oil may be spilt.
Large quantities of methane clathrate exist on the seabed and in ocean sediment, of interest as a potential energy source. Also on the seabed are manganese nodules formed of layers of iron, manganese and other hydroxides around a core. In the Pacific these may cover up to 30 percent of the deep ocean floor. The minerals precipitate from seawater and grow very slowly. Their commercial extraction for nickel was investigated in the 1970s but abandoned in favour of more convenient sources. In suitable locations, diamonds are gathered from the seafloor using suction hoses to bring gravel ashore. In deeper waters, mobile seafloor crawlers are used and the deposits are pumped to a vessel above. In Namibia, more diamonds are now collected from marine sources than by conventional methods on land.
Seafloor massive sulfide deposits, Seafloor massive sulphide deposits are potential sources of silver, gold, copper, lead and zinc and trace metals since their discovery in the 1960s. They form when Geothermal gradient, geothermally heated water is emitted from deep sea hydrothermal vents known as "black smokers". The ores are of high quality but prohibitively costly to extract.
There are large deposits of petroleum, as oil and natural gas, in rocks beneath the seabed. Oil platform, Offshore platforms and drilling rigs Offshore drilling, extract the oil or gas and store it for transport to land. Offshore oil and gas production can be difficult due to the remote, harsh environment. Drilling for oil in the sea has environmental impacts. Animals may be disorientated by seismic waves used to locate deposits, and there is debate as to whether this causes the Beached whale, beaching of whales. Toxic substances such as mercury (element), mercury, lead and arsenic may be released. The infrastructure may cause damage, and oil may be spilt.
Large quantities of methane clathrate exist on the seabed and in ocean sediment, of interest as a potential energy source. Also on the seabed are manganese nodules formed of layers of iron, manganese and other hydroxides around a core. In the Pacific these may cover up to 30 percent of the deep ocean floor. The minerals precipitate from seawater and grow very slowly. Their commercial extraction for nickel was investigated in the 1970s but abandoned in favour of more convenient sources. In suitable locations, diamonds are gathered from the seafloor using suction hoses to bring gravel ashore. In deeper waters, mobile seafloor crawlers are used and the deposits are pumped to a vessel above. In Namibia, more diamonds are now collected from marine sources than by conventional methods on land.
Fresh water production
Desalination is the technique of removing salts from seawater to leave Drinking water, fresh water suitable for drinking or irrigation. The two main processing methods, vacuum distillation and reverse osmosis, use large quantities of energy. Desalination is normally only undertaken where fresh water from other sources is in short supply or energy is plentiful, as in the excess heat generated by power stations. The brine produced as a by-product contains some toxic materials and is returned to the sea.Indigenous sea peoples
Several nomadic indigenous groups in Maritime Southeast Asia live in boats and derive nearly all they need from the sea. The Moken people live on the coasts of Thailand and Burma and islands in the Andaman Sea. The Bajau people are originally from the Sulu Archipelago, Mindanao and northern Borneo. Some Sea Gypsies are accomplished Free-diving, free-divers, able to descend to depths of , though many are adopting a more settled, land-based way of life. The indigenous peoples of the Arctic such as the Chukchi people, Chukchi, Inuit, Inuvialuit and Yupik peoples, Yup'iit hunt marine mammals including seals and whales, and the Torres Strait Islanders of Australia include the Great Barrier Reef among their possessions. They live a traditional life on the islands involving hunting, fishing, gardening and trading with neighbouring peoples in Papua and mainland Aboriginal Australians.In culture
 The sea appears in human culture in contradictory ways, as both powerful but serene and as beautiful but dangerous. It has its place in literature, art, poetry, film, theatre, classical music, mythology and dream interpretation. The Ancient history, Ancients personified it, believing it to be under the control of a List of water deities, being who needed to be appeased, and symbolically, it has been perceived as a hostile environment populated by fantastic creatures; the Leviathan of the Bible, Scylla in Greek mythology, Isonade in Japanese mythology, and the kraken of late Norse mythology.
The sea appears in human culture in contradictory ways, as both powerful but serene and as beautiful but dangerous. It has its place in literature, art, poetry, film, theatre, classical music, mythology and dream interpretation. The Ancient history, Ancients personified it, believing it to be under the control of a List of water deities, being who needed to be appeased, and symbolically, it has been perceived as a hostile environment populated by fantastic creatures; the Leviathan of the Bible, Scylla in Greek mythology, Isonade in Japanese mythology, and the kraken of late Norse mythology.
 The sea and ships have been Marine art, depicted in art ranging from simple drawings on the walls of huts in Lamu Archipelago, Lamu to seascapes by J. M. W. Turner, Joseph Turner. In Dutch Golden Age painting, artists such as Jan Porcellis, Hendrick Dubbels, Willem van de Velde the Elder and Willem van de Velde the Younger, his son, and Ludolf Bakhuizen celebrated the sea and the Dutch navy at the peak of its military prowess. The Japanese artist Katsushika Hokusai created colour Printmaking, prints of the moods of the sea, including ''The Great Wave off Kanagawa''.
Music too has been inspired by the ocean, sometimes by composers who lived or worked near the shore and saw its many different aspects. Sea shanty, Sea shanties, songs that were chanted by mariners to help them perform arduous tasks, have been woven into compositions and impressions in music have been created of calm waters, crashing waves and storms at sea.
The sea and ships have been Marine art, depicted in art ranging from simple drawings on the walls of huts in Lamu Archipelago, Lamu to seascapes by J. M. W. Turner, Joseph Turner. In Dutch Golden Age painting, artists such as Jan Porcellis, Hendrick Dubbels, Willem van de Velde the Elder and Willem van de Velde the Younger, his son, and Ludolf Bakhuizen celebrated the sea and the Dutch navy at the peak of its military prowess. The Japanese artist Katsushika Hokusai created colour Printmaking, prints of the moods of the sea, including ''The Great Wave off Kanagawa''.
Music too has been inspired by the ocean, sometimes by composers who lived or worked near the shore and saw its many different aspects. Sea shanty, Sea shanties, songs that were chanted by mariners to help them perform arduous tasks, have been woven into compositions and impressions in music have been created of calm waters, crashing waves and storms at sea.
 As a symbol, the sea has for centuries played a role in literature, poetry and dreams. Sometimes it is there just as a gentle background but often it introduces such themes as storm, shipwreck, battle, hardship, disaster, the dashing of hopes and death. In his epic poetry, epic poem the ''Odyssey'', written in the eighth century BC, Homer describes the ten-year voyage of the Greek hero Odysseus who struggles to return home across the sea's many hazards after the war described in the ''Iliad''. The sea is a recurring theme in the Haiku poems of the Japanese Edo period poet Matsuo Bashō (松尾 芭蕉) (1644–1694). In the works of psychiatrist Carl Jung, the sea symbolizes the personal and the collective unconscious in dream interpretation, the depths of the sea symbolizing the depths of the unconscious mind.
As a symbol, the sea has for centuries played a role in literature, poetry and dreams. Sometimes it is there just as a gentle background but often it introduces such themes as storm, shipwreck, battle, hardship, disaster, the dashing of hopes and death. In his epic poetry, epic poem the ''Odyssey'', written in the eighth century BC, Homer describes the ten-year voyage of the Greek hero Odysseus who struggles to return home across the sea's many hazards after the war described in the ''Iliad''. The sea is a recurring theme in the Haiku poems of the Japanese Edo period poet Matsuo Bashō (松尾 芭蕉) (1644–1694). In the works of psychiatrist Carl Jung, the sea symbolizes the personal and the collective unconscious in dream interpretation, the depths of the sea symbolizing the depths of the unconscious mind.
Environmental issues
Human activities affect marine life andmarine habitat
Marine habitats are habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term ''marine'' comes from the Latin ''mare'', meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental a ...
s through overfishing, habitat loss, the introduction of invasive species, Marine pollution, ocean pollution, ocean acidification and ocean warming. These impact marine ecosystems and Marine food web, food webs and may result in consequences as yet unrecognised for the biodiversity and continuation of marine life forms.
Acidification
Seawater is slightly alkalinity, alkaline and had an average pH of about 8.2 over the past 300 million years. More recently, climate change has resulted in an increase of the #The carbon cycle, carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere; about 30–40% of the added CO2 is absorbed by the oceans, forming carbonic acid and lowering the pH (now below 8.1) through a process called ocean acidification. The pH is expected to reach 7.7 (representing a 3-fold increase in hydrogen ion concentration) by the year 2100, which is a significant change in a century. One important element for the formation of skeleton, skeletal material in marine animals iscalcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
, but calcium carbonate becomes more soluble with pressure, so carbonate shells and skeletons dissolve below its carbonate compensation depth, compensation depth. Calcium carbonate also becomes more soluble at lower pH, so ocean acidification is likely to have profound effects on marine organisms with calcareous shells, such as oysters, clams, sea urchins, and corals, because their ability to form shells will be reduced, and the carbonate compensation depth will rise closer to the sea surface. Affected planktonic organisms will include the snail-like molluscs known as pteropods, and single-celled algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
called coccolithophorids and foraminifera. All of these are important parts of the food chain and a diminution in their numbers will have significant consequences. In tropical regions, corals are likely to be severely affected as it becomes more difficult to build their calcium carbonate skeletons, in turn adversely impacting other Coral reef, reef dwellers.
The current rate of ocean chemistry change appears to be without precedent in Earth's geological history, making it unclear how well marine ecosystems will be able to adapt to the shifting conditions of the near future. Of particular concern is the manner in which the combination of acidification with the expected additional stressors of higher temperatures and anoxic event, lower oxygen levels will impact the seas.
Marine pollution
Many substances enter the sea as a result of human activities. Combustion products are transported in the air and deposited into the sea by precipitation. Industrial outflows and sewage treatment plant, sewage contribute Heavy metal (chemistry), heavy metals, pesticides, Polychlorinated biphenyl, PCBs, disinfectants, household cleaning products and other synthetic chemicals. These become concentrated in the surface film and in marine sediment, especially estuarine mud. The result of all this contamination is largely unknown because of the large number of substances involved and the lack of information on their biological effects. The heavy metals of greatest concern are copper, lead, mercury, cadmium and zinc which may be Bio-accumulation, bio-accumulated by marine organisms and are passed up the food chain. Much floating plastic rubbish does not Biodegradation, biodegrade, instead disintegrating over time and eventually breaking down to the molecular level. Rigid plastics may float for years. In the centre of the Pacific gyre there is a permanent Great Pacific garbage patch, floating accumulation of mostly plastic waste and there is a similar North Atlantic garbage patch, garbage patch in the Atlantic. Foraging sea birds such as the albatross and petrel may mistake debris for food, and accumulate indigestible plastic in their digestive systems. Turtles and whales have been found with plastic bags and fishing line in their stomachs. Microplastics may sink, threatening filter feeders on the seabed. Most oil pollution in the sea comes from cities and industry. Oil is dangerous for marine animals. It can clog the feathers of sea birds, reducing their insulating effect and the birds' buoyancy, and be ingested when they preen themselves in an attempt to remove the contaminant. Marine mammals are less seriously affected but may be chilled through the removal of their insulation, blinded, dehydrated or poisoned. Benthos, Benthic invertebrates are swamped when the oil sinks, fish are poisoned and the food chain is disrupted. In the short term, oil spills result in wildlife populations being decreased and unbalanced, leisure activities being affected and the livelihoods of people dependent on the sea being devastated. The marine environment has self-cleansing properties and naturally occurring bacteria will act over time to remove oil from the sea. In the Gulf of Mexico, where oil-eating bacteria are already present, they take only a few days to consume spilt oil. Run-off of fertilisers from agricultural land is a major source of pollution in some areas and the discharge of raw sewage has a similar effect. The extra nutrients provided by these sources can cause eutrophication, excessive plant growth. Nitrogen is often the limiting factor in marine systems, and with added nitrogen, algal blooms and red tides can lower the oxygen level of the water and kill marine animals. Such events have created dead zones in the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. Some algal blooms are caused by cyanobacteria that makeshellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater envir ...
that Filter feeder, filter feed on them toxic, harming animals like sea otters. Nuclear facilities too can pollute. The Irish Sea was contaminated by radioactive caesium-137 from the former Sellafield nuclear fuel processing plant and nuclear accidents may also cause radioactive material to seep into the sea, as did the disaster at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011.
The dumping of waste (including oil, noxious liquids, sewage and garbage) at sea is governed by international law. The Convention on the Prevention of Marine Pollution by Dumping of Wastes and Other Matter, London Convention (1972) is a United Nations agreement to control ocean dumping which had been ratified by 89 countries by 8 June 2012. MARPOL 73/78 is a convention to minimize pollution of the seas by ships. By May 2013, 152 maritime nations had ratified MARPOL.
See also
* *List of seas *Bay *GulfNotes
References
External links
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
{{Featured article Seas, Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Lists of landforms Oceans, * Articles containing video clips