Sauripteridae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rhizodontida is an extinct group of predatory
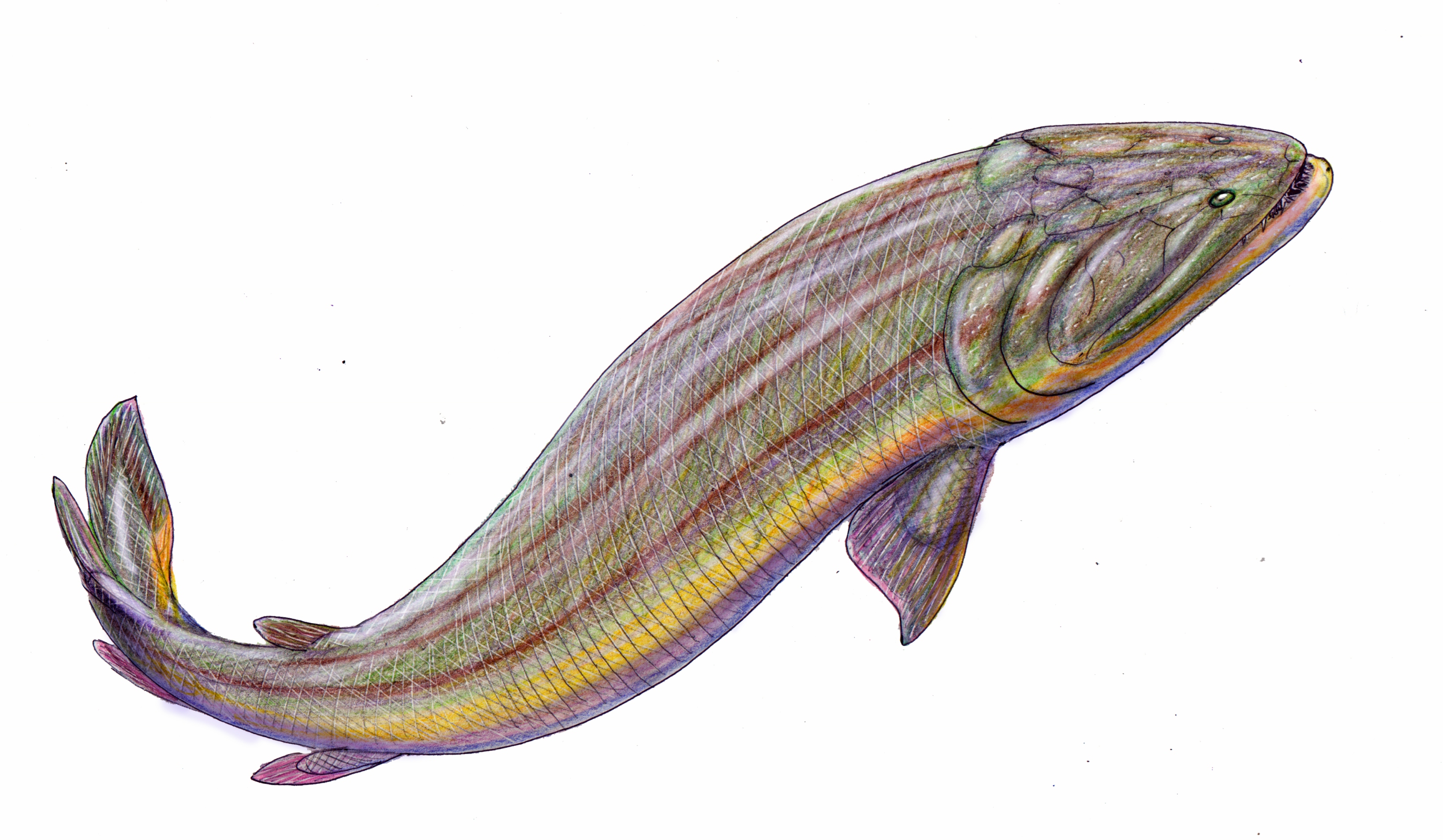 The upper jaw had a marginal row of small teeth on the
The upper jaw had a marginal row of small teeth on the
tetrapodomorph
The Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) are a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advance ...
s known from many areas of the world from the Givetian
The Givetian is one of two faunal stages in the Middle Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Eifelian Stage and followed by the Frasnian Stage. It is named after the town of Givet in Fra ...
through to the Pennsylvanian - the earliest known species is about 377 million years ago (Mya), the latest around 310 Mya. Rhizodonts lived in tropical rivers and freshwater lakes and were the dominant predators of their age. They reached huge sizes - the largest known species, '' Rhizodus hibberti'' from Europe and North America, was an estimated 7 m in length, making it the largest freshwater fish known.
Description
 The upper jaw had a marginal row of small teeth on the
The upper jaw had a marginal row of small teeth on the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
and premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has b ...
, medium-sized fangs on the ectopterygoid and dermopalatine bones, and large tusks on the vomer
The vomer (; lat, vomer, lit=ploughshare) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxill ...
s and premaxillae. On the lower jaw were marginal teeth on the dentary
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movabl ...
, with fangs on the three coronoids and a huge tusk at the symphysial tip of the dentary. Apparently, the left and right mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movabl ...
s rotated inwards towards each other on biting. This may have been a kinetic mechanism to dig the marginal teeth more deeply into the prey, to help grip slippery or struggling items.
The trunk was elongated, with pelvic
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
, two dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
* Dorsal c ...
and anal fin
A fin is a thin component or appendage attached to a larger body or structure. Fins typically function as foils that produce lift or thrust, or provide the ability to steer or stabilize motion while traveling in water, air, or other fluids. Fin ...
s much reduced and placed posteriorly The anal and second dorsal fins formed a functional part of the tail. The lateral line system
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial ...
was elaborated on the skull and pectoral girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of t ...
- in ''Strepsodus
''Strepsodus'' is a genus of rhizodont lobe-finned fish
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. T ...
'' the main trunk lateral line also had several subsidiary lines running parallel to it. This probably helped rhizodonts detect prey in the turbid, swampy environments where they lived.
Rhizodont pelvic fins are known only from external morphology. They are smaller than the pectoral fins and positioned toward the rear of the body. In comparison to the other fins, the pectoral fins were much enlarged. They had a well-developed internal skeleton surrounded by robust, largely unsegmented lepidotrichia
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as see ...
; the whole fin was then covered in deeply overlapping scales. This turned the pectoral fin into a broad paddle.
Phylogeny
The cladogram presented below is based on a 2021 study by Clement and colleagues:Ecology
Judging from their anatomy, rhizodonts had an extremely powerful bite. They probably employed a 'grip and drag' hunting technique, where prey was ambushed, the tusks sunk in to secure it, and then depending on its size, either thrashed on the surface to subdue it, or dragged to where the rhizodont could consume it without being disturbed. Their prey probably included largeshark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimo ...
s, lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, i ...
, and other lobe-finned fishes, and even tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct theraps ...
s, because all tetrapods at this time still had to lay their eggs in water.
References
*Johanson, Z. & Ahlberg, P.E. (1998) A complete primitive rhizodont from Australia. ''Nature'' 394: 569-573. *Johanson, Z., and Ahlberg, P. E. (2001) Devonian rhizodontids and tristichopterids (Sarcopterygii; Tetrapodomorpha) from East Gondwana. ''Trans. R. Soc. Earth Sci.'' 92: 43–74. Classification after Benton, M.J. (2005) ''Vertebrate Palaeontology'', 3rd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. . .External links
*http://www.palaeos.com/Vertebrates/Units/140Sarcopterygii/140.700.html#Rhizodontiformes *https://web.archive.org/web/20121212033229/http://www.donnasaxby.com/rhizodonts/ {{Taxonbar, from1=Q3934109, from2=Q143827 Prehistoric fish orders Carboniferous bony fish