Saturn's Moons on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The moons of Saturn are numerous and diverse, ranging from tiny moonlets only tens of meters across to enormous
 Study of Saturn's moons has also been aided by advances in telescope instrumentation, primarily the introduction of digital charge-coupled devices which replaced photographic plates. For the 20th century, Phoebe stood alone among Saturn's known moons with its highly irregular orbit. Then in 2000, three dozen additional irregular moons have been discovered using ground-based telescopes. A survey starting in late 2000 and conducted using three medium-size telescopes found thirteen new moons orbiting Saturn at a great distance, in eccentric orbits, which are highly inclined to both the equator of Saturn and the ecliptic. They are probably fragments of larger bodies captured by Saturn's gravitational pull. In 2005, astronomers using the Mauna Kea Observatory announced the discovery of twelve more small outer moons, in 2006, astronomers using the Subaru 8.2 m telescope reported the discovery of nine more irregular moons, in ,
Study of Saturn's moons has also been aided by advances in telescope instrumentation, primarily the introduction of digital charge-coupled devices which replaced photographic plates. For the 20th century, Phoebe stood alone among Saturn's known moons with its highly irregular orbit. Then in 2000, three dozen additional irregular moons have been discovered using ground-based telescopes. A survey starting in late 2000 and conducted using three medium-size telescopes found thirteen new moons orbiting Saturn at a great distance, in eccentric orbits, which are highly inclined to both the equator of Saturn and the ecliptic. They are probably fragments of larger bodies captured by Saturn's gravitational pull. In 2005, astronomers using the Mauna Kea Observatory announced the discovery of twelve more small outer moons, in 2006, astronomers using the Subaru 8.2 m telescope reported the discovery of nine more irregular moons, in , 
 In 2007, the discovery of 150 more moonlets revealed that they (with the exception of two that have been seen outside the Encke gap) are confined to three narrow bands in the A Ring between 126,750 and 132,000 km from Saturn's center. Each band is about a thousand kilometers wide, which is less than 1% the width of Saturn's rings. This region is relatively free from the disturbances caused by resonances with larger satellites, although other areas of the A Ring without disturbances are apparently free of moonlets. The moonlets were probably formed from the breakup of a larger satellite. It is estimated that the A Ring contains 7,000–8,000 propellers larger than 0.8 km in size and millions larger than 0.25 km. In April 2014, NASA scientists reported the possible consolidation of a new moon within the A Ring, implying that Saturn's present moons may have formed in a similar process in the past when Saturn's ring system was much more massive.
Similar moonlets may reside in the F Ring. There, "jets" of material may be due to collisions, initiated by perturbations from the nearby small moon Prometheus, of these moonlets with the core of the F Ring. One of the largest F Ring moonlets may be the as-yet unconfirmed object S/2004 S 6. The F Ring also contains transient "fans" which are thought to result from even smaller moonlets, about 1 km in diameter, orbiting near the F Ring core.
One of the recently discovered moons, Aegaeon, resides within the bright arc of G Ring and is trapped in the 7:6 mean-motion resonance with Mimas. This means that it makes exactly seven revolutions around Saturn while Mimas makes exactly six. The moon is the largest among the population of bodies that are sources of dust in this ring.
In 2007, the discovery of 150 more moonlets revealed that they (with the exception of two that have been seen outside the Encke gap) are confined to three narrow bands in the A Ring between 126,750 and 132,000 km from Saturn's center. Each band is about a thousand kilometers wide, which is less than 1% the width of Saturn's rings. This region is relatively free from the disturbances caused by resonances with larger satellites, although other areas of the A Ring without disturbances are apparently free of moonlets. The moonlets were probably formed from the breakup of a larger satellite. It is estimated that the A Ring contains 7,000–8,000 propellers larger than 0.8 km in size and millions larger than 0.25 km. In April 2014, NASA scientists reported the possible consolidation of a new moon within the A Ring, implying that Saturn's present moons may have formed in a similar process in the past when Saturn's ring system was much more massive.
Similar moonlets may reside in the F Ring. There, "jets" of material may be due to collisions, initiated by perturbations from the nearby small moon Prometheus, of these moonlets with the core of the F Ring. One of the largest F Ring moonlets may be the as-yet unconfirmed object S/2004 S 6. The F Ring also contains transient "fans" which are thought to result from even smaller moonlets, about 1 km in diameter, orbiting near the F Ring core.
One of the recently discovered moons, Aegaeon, resides within the bright arc of G Ring and is trapped in the 7:6 mean-motion resonance with Mimas. This means that it makes exactly seven revolutions around Saturn while Mimas makes exactly six. The moon is the largest among the population of bodies that are sources of dust in this ring.


 The innermost large moons of Saturn orbit within its tenuous E Ring, along with three smaller moons of the Alkyonides group.
*
The innermost large moons of Saturn orbit within its tenuous E Ring, along with three smaller moons of the Alkyonides group.
*
 Irregular moons are small satellites with large-radii, inclined, and frequently retrograde orbits, believed to have been acquired by the parent planet through a capture process. They often occur as collisional families or groups. The precise size as well as albedo of the irregular moons are not known for sure because the moons are very small to be resolved by a telescope, although the latter is usually assumed to be quite low—around 6% (albedo of Phoebe) or less. The irregulars generally have featureless visible and near infrared spectra dominated by water absorption bands. They are neutral or moderately red in color—similar to C-type, P-type, or D-type asteroids, though they are much less red than
Irregular moons are small satellites with large-radii, inclined, and frequently retrograde orbits, believed to have been acquired by the parent planet through a capture process. They often occur as collisional families or groups. The precise size as well as albedo of the irregular moons are not known for sure because the moons are very small to be resolved by a telescope, although the latter is usually assumed to be quite low—around 6% (albedo of Phoebe) or less. The irregulars generally have featureless visible and near infrared spectra dominated by water absorption bands. They are neutral or moderately red in color—similar to C-type, P-type, or D-type asteroids, though they are much less red than

Saturn Moons
* * * *
at '' The New York Times'' * Planetary Societybr>blog post
(2017-05-17) by
Outer Moons of Saturn
{{DEFAULTSORT:Moons Of Saturn Lists of moons
Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, which is larger than the planet Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
. Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
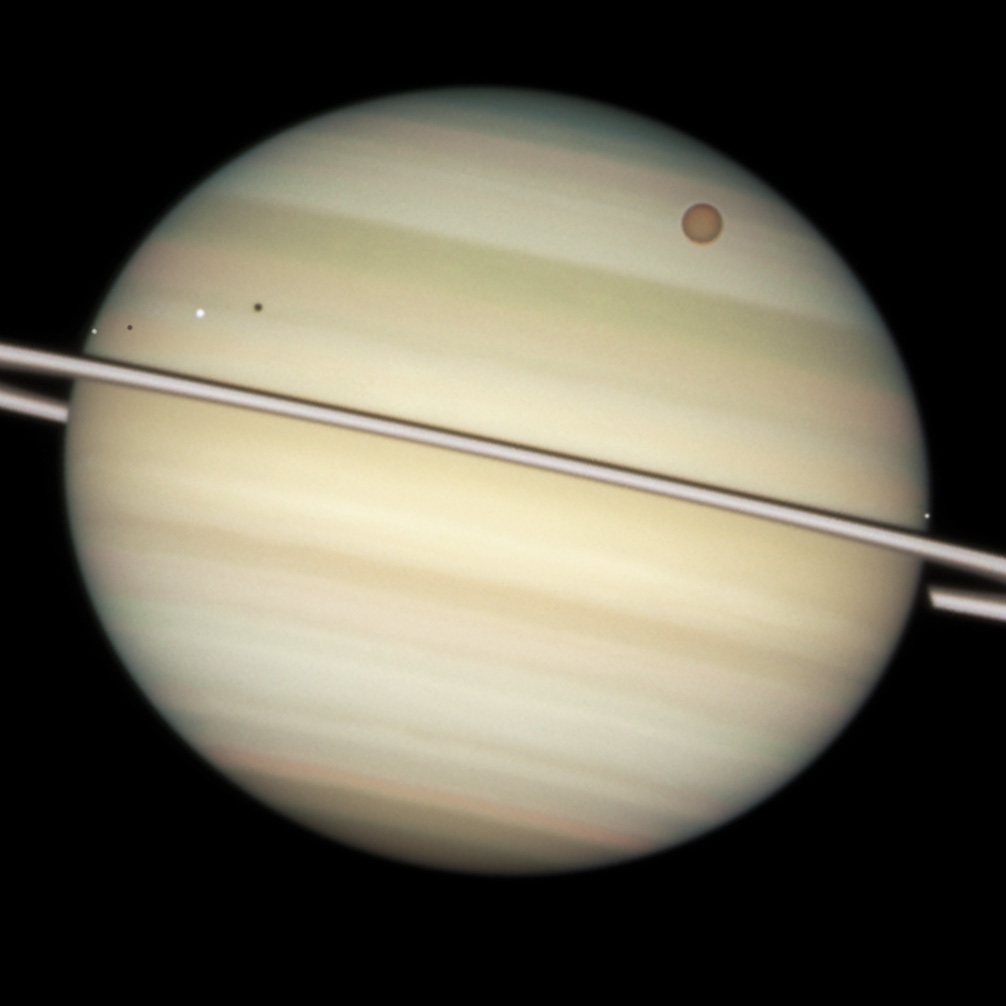
has 83 moons with confirmed orbits that are not embedded in its rings—of which only 13 have diameters greater than 50 kilometers—as well as dense rings that contain millions of embedded moonlets and innumerable smaller ring particles. Seven Saturnian moons are large enough to have collapsed into a relaxed, ellipsoidal shape, though only one or two of those, Titan and possibly Rhea, are currently in hydrostatic equilibrium. Particularly notable among Saturn's moons are Titan, the second- largest moon in the Solar System (after Jupiter's Ganymede), with a nitrogen-rich Earth-like atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
and a landscape featuring dry river networks and hydrocarbon lakes, Enceladus, which emits jets of gas and dust from its south-polar region, and Iapetus
In Greek mythology, Iapetus (; ; grc, Ἰαπετός, Iapetós), also Japetus, is a Titan, the son of Uranus and Gaia and father of Atlas, Prometheus, Epimetheus, and Menoetius. He was also called the father of Buphagus and Anchiale in other ...
, with its contrasting black and white hemispheres.
Twenty-four of Saturn's moons are ''regular satellites''; they have prograde orbits not greatly inclined
Incline, inclined, inclining, or inclination may refer to:
*Grade (slope), the tilt, steepness, or angle from horizontal of a topographic feature (hillside, meadow, etc.) or constructed element (road, railway, field, etc.)
*Slope, the tilt, steepn ...
to Saturn's equatorial plane. They include the seven major satellites, four small moons that exist in a trojan orbit with larger moons, two mutually co-orbital moon
In astronomy, a co-orbital configuration is a configuration of two or more astronomical objects (such as asteroids, moons, or planets) orbiting at the same, or very similar, distance from their primary, i.e. they are in a 1:1 mean-motion resonan ...
s and two moons that act as shepherds of Saturn's F Ring. Two other known regular satellites orbit within gaps in Saturn's rings. The relatively large Hyperion
Hyperion may refer to:
Greek mythology
* Hyperion (Titan), one of the twelve Titans
* ''Hyperion'', a byname of the Sun, Helios
* Hyperion of Troy or Yperion, son of King Priam
Science
* Hyperion (moon), a moon of the planet Saturn
* ''Hyp ...
is locked in a resonance with Titan. The remaining regular moons orbit near the outer edge of the A Ring, within the G Ring and between the major moons Mimas
Mimas may refer to:
*Mimas (Giant), son of Gaia in Greek mythology, one of the Gigantes
* Mimas (''Aeneid''), a son of Amycus and Theono, born the same night as Paris, who escorted Aeneas to Italy
*Karaburun, a town and district in Turkey, formerl ...
and Enceladus. The regular satellites are traditionally named after Titans and Titanesses or other figures associated with the mythological Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
.
The remaining fifty-nine, with mean diameters ranging from 4 to 213 km, are ''irregular satellites'', whose orbits are much farther from Saturn, have high inclinations
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Earth ...
, and are mixed between prograde and retrograde. These moons are probably captured minor planets, or debris from the breakup of such bodies after they were captured, creating collisional families. The irregular satellites have been classified by their orbital characteristics into the Inuit, Norse
Norse is a demonym for Norsemen, a medieval North Germanic ethnolinguistic group ancestral to modern Scandinavians, defined as speakers of Old Norse from about the 9th to the 13th centuries.
Norse may also refer to:
Culture and religion
* Nor ...
, and Gallic groups, and their names are chosen from the corresponding mythologies (with the Gallic group corresponding to Celtic mythology
Celtic mythology is the body of myths belonging to the Celtic peoples.Cunliffe, Barry, (1997) ''The Ancient Celts''. Oxford, Oxford University Press , pp. 183 (religion), 202, 204–8. Like other Iron Age Europeans, Celtic peoples followed a ...
). The sole exception is Phoebe Phoebe or Phœbe may refer to:
__NOTOC__ People and characters
* Phoebe (given name), a list of people, mythological, biblical and fictional characters
* Phoebe (Greek myth), several characters
* Phoebe, an epithet of Artemis/ Diana and Selene/ L ...
, the ninth moon of Saturn and largest irregular, discovered at the end of the 19th century; it is part of the Norse group but named for a Greek Titaness.
The rings of Saturn are made up of objects ranging in size from microscopic to moonlets hundreds of meters across, each in its own orbit around Saturn. Thus a precise number of Saturnian moons cannot be given, because there is no objective boundary between the countless small anonymous objects that form Saturn's ring system and the larger objects that have been named as moons. Over 150 moonlets embedded in the rings have been detected by the disturbance they create in the surrounding ring material, though this is thought to be only a small sample of the total population of such objects.
There are still twenty unnamed moons (), of which all but one is irregular. If named, they will receive names from Gallic, Norse
Norse is a demonym for Norsemen, a medieval North Germanic ethnolinguistic group ancestral to modern Scandinavians, defined as speakers of Old Norse from about the 9th to the 13th centuries.
Norse may also refer to:
Culture and religion
* Nor ...
and Inuit mythology based on the orbital groups of the moons.
Discovery

Early observations
Before the advent of telescopic photography, eight moons of Saturn were discovered by direct observation using optical telescopes. Saturn's largest moon,Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, was discovered in 1655 by Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists of ...
using a objective lens on a refracting telescope of his own design. Tethys, Dione Dione may refer to:
Astronomy
*106 Dione, a large main belt asteroid
*Dione (moon), a moon of Saturn
*Helene (moon), a moon of Saturn sometimes referred to as "Dione B"
Mythology
*Dione (Titaness), a Titaness in Greek mythology
*Dione (mythology) ...
, Rhea and Iapetus
In Greek mythology, Iapetus (; ; grc, Ἰαπετός, Iapetós), also Japetus, is a Titan, the son of Uranus and Gaia and father of Atlas, Prometheus, Epimetheus, and Menoetius. He was also called the father of Buphagus and Anchiale in other ...
(the " Sidera Lodoicea") were discovered between 1671 and 1684 by Giovanni Domenico Cassini. Mimas
Mimas may refer to:
*Mimas (Giant), son of Gaia in Greek mythology, one of the Gigantes
* Mimas (''Aeneid''), a son of Amycus and Theono, born the same night as Paris, who escorted Aeneas to Italy
*Karaburun, a town and district in Turkey, formerl ...
and Enceladus were discovered in 1789 by William Herschel. Hyperion
Hyperion may refer to:
Greek mythology
* Hyperion (Titan), one of the twelve Titans
* ''Hyperion'', a byname of the Sun, Helios
* Hyperion of Troy or Yperion, son of King Priam
Science
* Hyperion (moon), a moon of the planet Saturn
* ''Hyp ...
was discovered in 1848 by W. C. Bond, G. P. Bond and William Lassell.
The use of long-exposure photographic plates made possible the discovery of additional moons. The first to be discovered in this manner, Phoebe Phoebe or Phœbe may refer to:
__NOTOC__ People and characters
* Phoebe (given name), a list of people, mythological, biblical and fictional characters
* Phoebe (Greek myth), several characters
* Phoebe, an epithet of Artemis/ Diana and Selene/ L ...
, was found in 1899 by W. H. Pickering
William Henry Pickering (February 15, 1858 – January 16, 1938) was an American astronomer. Pickering constructed and established several observatories or astronomical observation stations, notably including Percival Lowell's Flagstaff Observ ...
. In 1966 the tenth satellite of Saturn was discovered by Audouin Dollfus
Audouin Charles Dollfus (12 November 1924 – 1 October 2010) was a French astronomer and aeronaut, specialist in studies of the Solar System and discoverer of Janus, a moon of Saturn.
Life and career
Dollfus was born in Paris to aeronaut Charl ...
, when the rings were observed edge-on near an equinox. It was later named Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; la, Ianvs ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janu ...
. A few years later it was realized that all observations of 1966 could only be explained if another satellite had been present and that it had an orbit similar to that of Janus. This object is now known as Epimetheus, the eleventh moon of Saturn. It shares the same orbit with Janus—the only known example of co-orbitals in the Solar System. In 1980, three additional Saturnian moons were discovered from the ground and later confirmed by the ''Voyager
Voyager may refer to:
Computing and communications
* LG Voyager, a mobile phone model manufactured by LG Electronics
* NCR Voyager, a computer platform produced by NCR Corporation
* Voyager (computer worm), a computer worm affecting Oracle ...
'' probes. They are trojan moons of Dione ( Helene) and Tethys ( Telesto and Calypso).
Observations by spacecraft
The study of the outer planets has since been revolutionized by the use of unmanned space probes. The arrival of the ''Voyager
Voyager may refer to:
Computing and communications
* LG Voyager, a mobile phone model manufactured by LG Electronics
* NCR Voyager, a computer platform produced by NCR Corporation
* Voyager (computer worm), a computer worm affecting Oracle ...
'' spacecraft at Saturn in 1980–1981 resulted in the discovery of three additional moons – Atlas, Prometheus and Pandora
In Greek mythology, Pandora (Greek: , derived from , ''pān'', i.e. "all" and , ''dōron'', i.e. "gift", thus "the all-endowed", "all-gifted" or "all-giving") was the first human woman created by Hephaestus on the instructions of Zeus. As Hes ...
, bringing the total to 17. In addition, Epimetheus was confirmed as distinct from Janus. In 1990, Pan was discovered in archival ''Voyager'' images.
The '' Cassini'' mission, which arrived at Saturn in the summer of 2004, initially discovered three small inner moons including Methone and Pallene between Mimas and Enceladus as well as the second trojan moon of Dione – Polydeuces. It also observed three suspected but unconfirmed moons in the F Ring. In Cassini scientists announced that the structure of Saturn's rings indicates the presence of several more moons orbiting within the rings, although only one, Daphnis, had been visually confirmed at the time. In 2007 Anthe was announced. In 2008 it was reported that ''Cassini'' observations of a depletion of energetic electrons in Saturn's magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior dynam ...
near Rhea might be the signature of a tenuous ring system around Saturn's second largest moon. In , Aegaeon, a moonlet within the G Ring, was announced. In July of the same year, S/2009 S 1, the first moonlet within the B Ring, was observed. In April 2014, the possible beginning of a new moon, within the A Ring, was reported. ( related image)
Outer moons
 Study of Saturn's moons has also been aided by advances in telescope instrumentation, primarily the introduction of digital charge-coupled devices which replaced photographic plates. For the 20th century, Phoebe stood alone among Saturn's known moons with its highly irregular orbit. Then in 2000, three dozen additional irregular moons have been discovered using ground-based telescopes. A survey starting in late 2000 and conducted using three medium-size telescopes found thirteen new moons orbiting Saturn at a great distance, in eccentric orbits, which are highly inclined to both the equator of Saturn and the ecliptic. They are probably fragments of larger bodies captured by Saturn's gravitational pull. In 2005, astronomers using the Mauna Kea Observatory announced the discovery of twelve more small outer moons, in 2006, astronomers using the Subaru 8.2 m telescope reported the discovery of nine more irregular moons, in ,
Study of Saturn's moons has also been aided by advances in telescope instrumentation, primarily the introduction of digital charge-coupled devices which replaced photographic plates. For the 20th century, Phoebe stood alone among Saturn's known moons with its highly irregular orbit. Then in 2000, three dozen additional irregular moons have been discovered using ground-based telescopes. A survey starting in late 2000 and conducted using three medium-size telescopes found thirteen new moons orbiting Saturn at a great distance, in eccentric orbits, which are highly inclined to both the equator of Saturn and the ecliptic. They are probably fragments of larger bodies captured by Saturn's gravitational pull. In 2005, astronomers using the Mauna Kea Observatory announced the discovery of twelve more small outer moons, in 2006, astronomers using the Subaru 8.2 m telescope reported the discovery of nine more irregular moons, in , Tarqeq
Tarqeq, also known as Saturn LII (provisional designation S/2007 S 1) is a natural satellite of Saturn. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, Jan Kleyna, and Brian G. Marsden on 13 April 2007 from observations taken ...
(S/2007 S 1) was announced and in May of the same year S/2007 S 2 and S/2007 S 3
S/2007 S 3 is a natural satellite of Saturn. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, Jan Kleyna, and Brian G. Marsden on 1 May 2007 from observations taken between 18 January and 19 April 2007.
S/2007 S 3 is about 5 k ...
were reported. In 2019, twenty new irregular satellites of Saturn were reported, resulting in Saturn overtaking Jupiter as the planet with the most known moons for the first time since 2000. Yet another was reported in 2021, after a survey for Saturnian moons took place in 2019.
Naming
The modern names for Saturnian moons were suggested byJohn Herschel
Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet (; 7 March 1792 – 11 May 1871) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor, experimental photographer who invented the blueprint and did botanical wor ...
in 1847. He proposed to name them after mythological figures associated with the Roman titan of time, Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
(equated to the Greek Cronus
In Ancient Greek religion and mythology, Cronus, Cronos, or Kronos ( or , from el, Κρόνος, ''Krónos'') was the leader and youngest of the first generation of Titans, the divine descendants of the primordial Gaia (Mother Earth) and ...
). In particular, the then known seven satellites were named after Titans, Titanesses and Giants—brothers and sisters of Cronus. In 1848, Lassell proposed that the eighth satellite of Saturn be named Hyperion after another Titan. When in the 20th century the names of Titans were exhausted, the moons were named after different characters of the Greco-Roman mythology or giants from other mythologies. All the irregular moons (except Phoebe, discovered about a century before the others) are named after Inuit and Gallic gods and after Norse
Norse is a demonym for Norsemen, a medieval North Germanic ethnolinguistic group ancestral to modern Scandinavians, defined as speakers of Old Norse from about the 9th to the 13th centuries.
Norse may also refer to:
Culture and religion
* Nor ...
ice giants.
Some asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
s share the same names as moons of Saturn: 55 Pandora
Pandora (minor planet designation: 55 Pandora) is a fairly large and very bright asteroid in the asteroid belt. Pandora was discovered by American astronomer and Catholic priest George Mary Searle on September 10, 1858, from the Dudley Observato ...
, 106 Dione
Dione (minor planet designation: 106 Dione) is a large main-belt asteroid. It probably has a composition similar to 1 Ceres. It was discovered by J. C. Watson on October 10, 1868, and named after Dione, a Titaness in Greek mythology who was som ...
, 577 Rhea
Rhea (minor planet designation: 577 Rhea) is a minor planet orbiting the sun. It is named after Rhea, one of the Titans in Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the A ...
, 1809 Prometheus
1809 Prometheus is an asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 14 kilometers in diameter. Discovered during the Palomar–Leiden survey in 1960, it was given the provisional designation and named after Prometheus fr ...
, 1810 Epimetheus
1810 Epimetheus , provisional designation , is a stony Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 8 kilometers in diameter.
It was discovered on 24 September 1960, by Dutch astronomer couple Ingrid and Cornelis ...
, and 4450 Pan
4450 Pan ('' prov. designation:'' ) is a highly eccentric asteroid and contact binary, classified as a potentially hazardous asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 1.1 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 25 Se ...
. In addition, three more asteroids would share the names of Saturnian moons but for spelling differences made permanent by the International Astronomical Union (IAU): Calypso and asteroid 53 Kalypso
Kalypso (minor planet designation: 53 Kalypso) is a large and very dark main belt asteroid that was discovered by German astronomer Robert Luther on April 4, 1858, at Düsseldorf. It is named after Calypso, a sea nymph in Greek mythology, a name ...
; Helene and asteroid 101 Helena
Helena (minor planet designation: 101 Helena) is a large, rocky main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by Canadian-American astronomer J. C. Watson on August 15, 1868, and was named after Helen of Troy in Greek mythology.
This object is orbitin ...
; and Gunnlod and asteroid 657 Gunlöd
657 Gunlöd is a dark background asteroid orbiting in the intermediate asteroid belt, approximately in diameter. It was discovered on 23 January 1908, by astronomer August Kopff at the Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. It has an ...
.
Sizes
Saturn's satellite system is very lopsided: one moon, Titan, comprises more than 96% of the mass in orbit around the planet. The six other planemo (ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation.
An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the ...
al) moons constitute roughly 4% of the mass, and the remaining 76 small moons, together with the rings, comprise only 0.04%.
Orbital groups
Although the boundaries may be somewhat vague, Saturn's moons can be divided into ten groups according to their orbital characteristics. Many of them, such as Pan and Daphnis, orbit within Saturn's ring system and have orbital periods only slightly longer than the planet's rotation period. The innermost moons and most regular satellites all have mean orbital inclinations ranging from less than a degree to about 1.5 degrees (exceptIapetus
In Greek mythology, Iapetus (; ; grc, Ἰαπετός, Iapetós), also Japetus, is a Titan, the son of Uranus and Gaia and father of Atlas, Prometheus, Epimetheus, and Menoetius. He was also called the father of Buphagus and Anchiale in other ...
, which has an inclination of 7.57 degrees) and small orbital eccentricities. On the other hand, irregular satellites in the outermost regions of Saturn's moon system, in particular the Norse group, have orbital radii of millions of kilometers and orbital periods lasting several years. The moons of the Norse group also orbit in the opposite direction to Saturn's rotation.
Ring moonlets
During late July 2009, a moonlet, S/2009 S 1, was discovered in the B Ring, 480 km from the outer edge of the ring, by the shadow it cast. It is estimated to be 300 m in diameter. Unlike the A Ring moonlets (see below), it does not induce a 'propeller' feature, probably due to the density of the B Ring. In 2006, four tiny moonlets were found in ''Cassini'' images of the A Ring. Before this discovery only two larger moons had been known within gaps in the A Ring: Pan and Daphnis. These are large enough to clear continuous gaps in the ring. In contrast, a moonlet is only massive enough to clear two small—about 10 km across—partial gaps in the immediate vicinity of the moonlet itself creating a structure shaped like an airplanepropeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
. The moonlets themselves are tiny, ranging from about 40 to 500 meters in diameter, and are too small to be seen directly.
 In 2007, the discovery of 150 more moonlets revealed that they (with the exception of two that have been seen outside the Encke gap) are confined to three narrow bands in the A Ring between 126,750 and 132,000 km from Saturn's center. Each band is about a thousand kilometers wide, which is less than 1% the width of Saturn's rings. This region is relatively free from the disturbances caused by resonances with larger satellites, although other areas of the A Ring without disturbances are apparently free of moonlets. The moonlets were probably formed from the breakup of a larger satellite. It is estimated that the A Ring contains 7,000–8,000 propellers larger than 0.8 km in size and millions larger than 0.25 km. In April 2014, NASA scientists reported the possible consolidation of a new moon within the A Ring, implying that Saturn's present moons may have formed in a similar process in the past when Saturn's ring system was much more massive.
Similar moonlets may reside in the F Ring. There, "jets" of material may be due to collisions, initiated by perturbations from the nearby small moon Prometheus, of these moonlets with the core of the F Ring. One of the largest F Ring moonlets may be the as-yet unconfirmed object S/2004 S 6. The F Ring also contains transient "fans" which are thought to result from even smaller moonlets, about 1 km in diameter, orbiting near the F Ring core.
One of the recently discovered moons, Aegaeon, resides within the bright arc of G Ring and is trapped in the 7:6 mean-motion resonance with Mimas. This means that it makes exactly seven revolutions around Saturn while Mimas makes exactly six. The moon is the largest among the population of bodies that are sources of dust in this ring.
In 2007, the discovery of 150 more moonlets revealed that they (with the exception of two that have been seen outside the Encke gap) are confined to three narrow bands in the A Ring between 126,750 and 132,000 km from Saturn's center. Each band is about a thousand kilometers wide, which is less than 1% the width of Saturn's rings. This region is relatively free from the disturbances caused by resonances with larger satellites, although other areas of the A Ring without disturbances are apparently free of moonlets. The moonlets were probably formed from the breakup of a larger satellite. It is estimated that the A Ring contains 7,000–8,000 propellers larger than 0.8 km in size and millions larger than 0.25 km. In April 2014, NASA scientists reported the possible consolidation of a new moon within the A Ring, implying that Saturn's present moons may have formed in a similar process in the past when Saturn's ring system was much more massive.
Similar moonlets may reside in the F Ring. There, "jets" of material may be due to collisions, initiated by perturbations from the nearby small moon Prometheus, of these moonlets with the core of the F Ring. One of the largest F Ring moonlets may be the as-yet unconfirmed object S/2004 S 6. The F Ring also contains transient "fans" which are thought to result from even smaller moonlets, about 1 km in diameter, orbiting near the F Ring core.
One of the recently discovered moons, Aegaeon, resides within the bright arc of G Ring and is trapped in the 7:6 mean-motion resonance with Mimas. This means that it makes exactly seven revolutions around Saturn while Mimas makes exactly six. The moon is the largest among the population of bodies that are sources of dust in this ring.
Ring shepherds


Shepherd satellite
A ring system is a disc or ring, orbiting an astronomical object, that is composed of solid material such as dust and moonlets, and is a common component of satellite systems around giant planets. A ring system around a planet is also known a ...
s are small moons that orbit within, or just beyond, a planet's ring system. They have the effect of sculpting the rings: giving them sharp edges, and creating gaps between them. Saturn's shepherd moons are Pan ( Encke gap), Daphnis ( Keeler gap), Atlas (A Ring), Prometheus (F Ring) and Pandora
In Greek mythology, Pandora (Greek: , derived from , ''pān'', i.e. "all" and , ''dōron'', i.e. "gift", thus "the all-endowed", "all-gifted" or "all-giving") was the first human woman created by Hephaestus on the instructions of Zeus. As Hes ...
(F Ring). These moons together with co-orbitals (see below) probably formed as a result of accretion of the friable ring material on preexisting denser cores. The cores with sizes from one-third to one-half the present-day moons may be themselves collisional shards formed when a parental satellite of the rings disintegrated.
Co-orbitals
Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; la, Ianvs ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janu ...
and Epimetheus are called co-orbital moons. They are of roughly equal size, with Janus being slightly larger than Epimetheus. Janus and Epimetheus have orbits with only a few kilometers difference in semi-major axis, close enough that they would collide if they attempted to pass each other. Instead of colliding, their gravitational interaction causes them to swap orbits every four years.
Inner large
 The innermost large moons of Saturn orbit within its tenuous E Ring, along with three smaller moons of the Alkyonides group.
*
The innermost large moons of Saturn orbit within its tenuous E Ring, along with three smaller moons of the Alkyonides group.
* Mimas
Mimas may refer to:
*Mimas (Giant), son of Gaia in Greek mythology, one of the Gigantes
* Mimas (''Aeneid''), a son of Amycus and Theono, born the same night as Paris, who escorted Aeneas to Italy
*Karaburun, a town and district in Turkey, formerl ...
is the smallest and least massive of the inner round moons, although its mass is sufficient to alter the orbit of Methone. It is noticeably ovoid-shaped, having been made shorter at the poles and longer at the equator (by about 20 km) by the effects of Saturn's gravity. Mimas has a large impact crater one-third its diameter, Herschel, situated on its leading hemisphere. Mimas has no known past or present geologic activity, and its surface is dominated by impact craters. The only tectonic features known are a few arcuate and linear troughs, which probably formed when Mimas was shattered by the Herschel impact.
* Enceladus is one of the smallest of Saturn's moons that is spherical in shape—only Mimas is smaller—yet is the only small Saturnian moon that is currently endogenously active, and the smallest known body in the Solar System that is geologically active today. Its surface is morphologically diverse; it includes ancient heavily cratered terrain as well as younger smooth areas with few impact craters. Many plains on Enceladus are fractured and intersected by systems of lineaments. The area around its south pole was found by ''Cassini'' to be unusually warm and cut by a system of fractures about 130 km long called "tiger stripes", some of which emit jets of water vapor and dust. These jets form a large plume off its south pole, which replenishes Saturn's E ring and serves as the main source of ions in the magnetosphere of Saturn
The magnetosphere of Saturn is the cavity created in the flow of the solar wind by the planet's internally generated magnetic field. Discovered in 1979 by the ''Pioneer 11'' spacecraft, Saturn's magnetosphere is the second largest of any planet ...
. The gas and dust are released with a rate of more than 100 kg/s. Enceladus may have liquid water underneath the south-polar surface. The source of the energy for this cryovolcanism is thought to be a 2:1 mean-motion resonance with Dione. The pure ice on the surface makes Enceladus one of the brightest known objects in the Solar System—its geometrical albedo is more than 140%.
* Tethys is the third largest of Saturn's inner moons. Its most prominent features are a large (400 km diameter) impact crater named Odysseus
Odysseus ( ; grc-gre, Ὀδυσσεύς, Ὀδυσεύς, OdysseúsOdyseús, ), also known by the Latin variant Ulysses ( , ; lat, UlyssesUlixes), is a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the ''Odyssey''. Odysse ...
on its leading hemisphere and a vast canyon system named Ithaca Chasma extending at least 270° around Tethys. The Ithaca Chasma is concentric with Odysseus, and these two features may be related. Tethys appears to have no current geological activity. A heavily cratered hilly terrain occupies the majority of its surface, while a smaller and smoother plains region lies on the hemisphere opposite to that of Odysseus. The plains contain fewer craters and are apparently younger. A sharp boundary separates them from the cratered terrain. There is also a system of extensional troughs radiating away from Odysseus. The density of Tethys (0.985 g/cm3) is less than that of water, indicating that it is made mainly of water ice with only a small fraction of rock.
* Dione Dione may refer to:
Astronomy
*106 Dione, a large main belt asteroid
*Dione (moon), a moon of Saturn
*Helene (moon), a moon of Saturn sometimes referred to as "Dione B"
Mythology
*Dione (Titaness), a Titaness in Greek mythology
*Dione (mythology) ...
is the second-largest inner moon of Saturn. It has a higher density than the geologically dead Rhea, the largest inner moon, but lower than that of active Enceladus. While the majority of Dione's surface is heavily cratered old terrain, this moon is also covered with an extensive network of troughs and lineaments, indicating that in the past it had global tectonic activity. The troughs and lineaments are especially prominent on the trailing hemisphere, where several intersecting sets of fractures form what is called "wispy terrain". The cratered plains have a few large impact craters reaching 250 km in diameter. Smooth plains with low impact-crater counts are also present on a small fraction of its surface. They were probably tectonically resurfaced relatively later in the geological history of Dione. At two locations within smooth plains strange landforms (depressions) resembling oblong impact craters have been identified, both of which lie at the centers of radiating networks of cracks and troughs; these features may be cryovolcanic in origin. Dione may be geologically active even now, although on a scale much smaller than the cryovolcanism of Enceladus. This follows from Cassini magnetic measurements that show Dione is a net source of plasma in the magnetosphere of Saturn, much like Enceladus.
Alkyonides
Three small moons orbit between Mimas and Enceladus: Methone, Anthe, and Pallene. Named after the Alkyonides of Greek mythology, they are some of the smallest moons in the Saturn system. Anthe and Methone have very faint ring arcs along their orbits, whereas Pallene has a faint complete ring. Of these three moons, only Methone has been photographed at close range, showing it to be egg-shaped with very few or no craters.Trojan
Trojan moons are a unique feature only known from the Saturnian system. A trojan body orbits at either the leading L4 or trailing L5Lagrange point
In celestial mechanics, the Lagrange points (; also Lagrangian points or libration points) are points of equilibrium for small-mass objects under the influence of two massive orbiting bodies. Mathematically, this involves the solution of th ...
of a much larger object, such as a large moon or planet. Tethys has two trojan moons, Telesto (leading) and Calypso (trailing), and Dione also has two, Helene (leading) and Polydeuces (trailing). Helene is by far the largest trojan moon, while Polydeuces is the smallest and has the most chaotic
Chaotic was originally a Danish trading card game. It expanded to an online game in America which then became a television program based on the game. The program was able to be seen on 4Kids TV (Fox affiliates, nationwide), Jetix, The CW4Kids ...
orbit. These moons are coated with dusty material that has smoothed out their surfaces.
Outer large
These moons all orbit beyond the E Ring. They are: * Rhea is the second-largest of Saturn's moons. It is even slightly larger than Oberon, the second-largest moon of Uranus. In 2005 ''Cassini'' detected a depletion of electrons in the plasma wake of Rhea, which forms when the co-rotating plasma of Saturn's magnetosphere is absorbed by the moon. The depletion was hypothesized to be caused by the presence of dust-sized particles concentrated in a few faint equatorial rings. Such a ring system would make Rhea the only moon in the Solar System known to have rings. Subsequent targeted observations of the putative ring plane from several angles by ''Cassinis narrow-angle camera turned up no evidence of the expected ring material, leaving the origin of the plasma observations unresolved. Otherwise Rhea has rather a typical heavily cratered surface, with the exceptions of a few large Dione-type fractures (wispy terrain) on the trailing hemisphere and a very faint "line" of material at the equator that may have been deposited by material deorbiting from present or former rings. Rhea also has two very large impact basins on its anti-Saturnian hemisphere, which are about 400 and 500 km across. The first, Tirawa, is roughly comparable to the Odysseus basin on Tethys. There is also a 48 km-diameter impact crater called Inktomi at 112°W that is prominent because of an extended system of bright rays, which may be one of the youngest craters on the inner moons of Saturn. No evidence of any endogenic activity has been discovered on the surface of Rhea. *Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, at 5,149 km diameter, is the second largest moon in the Solar System and Saturn's largest. Out of all the large moons, Titan is the only one with a dense (surface pressure of 1.5 atm), cold atmosphere, primarily made of nitrogen with a small fraction of methane. The dense atmosphere frequently produces bright white convective clouds, especially over the south pole region. On June 6, 2013, scientists at the IAA-CSIC reported the detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the upper atmosphere of Titan. On June 23, 2014, NASA claimed to have strong evidence that nitrogen in the atmosphere of Titan came from materials in the Oort cloud, associated with comets, and not from the materials that formed Saturn in earlier times. The surface of Titan, which is difficult to observe due to persistent atmospheric haze, shows only a few impact craters and is probably very young. It contains a pattern of light and dark regions, flow channels and possibly cryovolcanos. Some dark regions are covered by longitudinal dune fields shaped by tidal winds, where sand is made of frozen water or hydrocarbons. Titan is the only body in the Solar System beside Earth with bodies of liquid on its surface, in the form of methane–ethane lakes in Titan's north and south polar regions. The largest lake, Kraken Mare, is larger than the Caspian Sea. Like Europa and Ganymede, it is believed that Titan has a subsurface ocean made of water mixed with ammonia, which can erupt to the surface of the moon and lead to cryovolcanism. On July 2, 2014, NASA reported the ocean inside Titan may be "as salty as the Earth's Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank ...
".
* Hyperion
Hyperion may refer to:
Greek mythology
* Hyperion (Titan), one of the twelve Titans
* ''Hyperion'', a byname of the Sun, Helios
* Hyperion of Troy or Yperion, son of King Priam
Science
* Hyperion (moon), a moon of the planet Saturn
* ''Hyp ...
is Titan's nearest neighbor in the Saturn system. The two moons are locked in a 4:3 mean-motion resonance with each other, meaning that while Titan makes four revolutions around Saturn, Hyperion makes exactly three. With an average diameter of about 270 km, Hyperion is smaller and lighter than Mimas. It has an extremely irregular shape, and a very odd, tan-colored icy surface resembling a sponge, though its interior may be partially porous as well. The average density of about 0.55 g/cm3 indicates that the porosity exceeds 40% even assuming it has a purely icy composition. The surface of Hyperion is covered with numerous impact craters—those with diameters 2–10 km are especially abundant. It is the only moon besides the small moons of Pluto known to have a chaotic rotation, which means Hyperion has no well-defined poles or equator. While on short timescales the satellite approximately rotates around its long axis at a rate of 72–75° per day, on longer timescales its axis of rotation (spin vector) wanders chaotically across the sky. This makes the rotational behavior of Hyperion essentially unpredictable.
* Iapetus
In Greek mythology, Iapetus (; ; grc, Ἰαπετός, Iapetós), also Japetus, is a Titan, the son of Uranus and Gaia and father of Atlas, Prometheus, Epimetheus, and Menoetius. He was also called the father of Buphagus and Anchiale in other ...
is the third-largest of Saturn's moons. Orbiting the planet at km, it is by far the most distant of Saturn's large moons, and also has the largest orbital inclination, at 15.47°. Iapetus has long been known for its unusual two-toned surface; its leading hemisphere is pitch-black and its trailing hemisphere is almost as bright as fresh snow. ''Cassini'' images showed that the dark material is confined to a large near-equatorial area on the leading hemisphere called Cassini Regio, which extends approximately from 40°N to 40°S. The pole regions of Iapetus are as bright as its trailing hemisphere. ''Cassini'' also discovered a 20 km tall equatorial ridge, which spans nearly the moon's entire equator. Otherwise both dark and bright surfaces of Iapetus are old and heavily cratered. The images revealed at least four large impact basins with diameters from 380 to 550 km and numerous smaller impact craters. No evidence of any endogenic activity has been discovered. A clue to the origin of the dark material covering part of Iapetus's starkly dichromatic surface may have been found in 2009, when NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, f ...
discovered a vast, nearly invisible disk around Saturn, just inside the orbit of the moon Phoebe – the Phoebe ring. Scientists believe that the disk originates from dust and ice particles kicked up by impacts on Phoebe. Because the disk particles, like Phoebe itself, orbit in the opposite direction to Iapetus, Iapetus collides with them as they drift in the direction of Saturn, darkening its leading hemisphere slightly. Once a difference in albedo, and hence in average temperature, was established between different regions of Iapetus, a thermal runaway process of water ice sublimation
Sublimation or sublimate may refer to:
* ''Sublimation'' (album), by Canvas Solaris, 2004
* Sublimation (phase transition), directly from the solid to the gas phase
* Sublimation (psychology), a mature type of defense mechanism
* Sublimate of mer ...
from warmer regions and deposition of water vapor onto colder regions ensued. Iapetus's present two-toned appearance results from the contrast between the bright, primarily ice-coated areas and regions of dark lag, the residue left behind after the loss of surface ice.
Irregular
 Irregular moons are small satellites with large-radii, inclined, and frequently retrograde orbits, believed to have been acquired by the parent planet through a capture process. They often occur as collisional families or groups. The precise size as well as albedo of the irregular moons are not known for sure because the moons are very small to be resolved by a telescope, although the latter is usually assumed to be quite low—around 6% (albedo of Phoebe) or less. The irregulars generally have featureless visible and near infrared spectra dominated by water absorption bands. They are neutral or moderately red in color—similar to C-type, P-type, or D-type asteroids, though they are much less red than
Irregular moons are small satellites with large-radii, inclined, and frequently retrograde orbits, believed to have been acquired by the parent planet through a capture process. They often occur as collisional families or groups. The precise size as well as albedo of the irregular moons are not known for sure because the moons are very small to be resolved by a telescope, although the latter is usually assumed to be quite low—around 6% (albedo of Phoebe) or less. The irregulars generally have featureless visible and near infrared spectra dominated by water absorption bands. They are neutral or moderately red in color—similar to C-type, P-type, or D-type asteroids, though they are much less red than Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times ...
objects.
Inuit
The Inuit group includes eight prograde outer moons that are similar enough in their distances from the planet (186–297 radii of Saturn), their orbital inclinations (45–50°) and their colors that they can be considered a group. The moons are Ijiraq, Kiviuq, Paaliaq,Siarnaq
Siarnaq, also designated Saturn XXIX, is the second-largest irregular moon of Saturn. It was discovered on 23 September 2000 by a team of astronomers led by Brett J. Gladman. It was named after the Inuit goddess of the sea, Siarnaq, who is more ...
, and Tarqeq
Tarqeq, also known as Saturn LII (provisional designation S/2007 S 1) is a natural satellite of Saturn. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, Jan Kleyna, and Brian G. Marsden on 13 April 2007 from observations taken ...
, along with three unnamed moons Saturn LX
Saturn LX, provisionally known as S/2004 S 29, is a natural satellite of Saturn and a member of the Gallic group. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, and Jan Kleyna on October 7, 2019 from observations taken between ...
, S/2004 S 31
S/2004 S 31 is a natural satellite of Saturn and a member of the Inuit group. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, and Jan Kleyna on October 8, 2019 from observations taken between December 12, 2004 and March 22, 200 ...
, and S/2019 S 1. The largest among them is Siarnaq with an estimated size of about 40 km.
Gallic
The Gallic group are four prograde outer moons that are similar enough in their distance from the planet (207–302 radii of Saturn), their orbital inclination (35–40°) and their color that they can be considered a group. They are Albiorix, Bebhionn, Erriapus, and Tarvos. The largest among these moons is Albiorix with an estimated size of about 32 km. There is an additional satellite S/2004 S 24 that could belong to this group, but more observations are needed to confirm or disprove its categorization. S/2004 S 24 has the most distant prograde orbit of Saturn's known satellites.Norse
The Norse (or Phoebe) group consists of 46 retrograde outer moons. They are Aegir, Angrboda,Alvaldi
Alvaldi (also Ölvaldi; Old Norse 'all-powerful') is a jötunn in Norse mythology, presented as the father of Þjazi.
Saturn's moon Alvaldi is named after him.
Name
The Old Norse name ''Alvadi'' means 'all-powerful'. The name ''Ölvadi'', fo ...
, Beli, Bergelmir
Bergelmir ( ; Old Norse: ) is a jötunn in Norse mythology.
Name
The Old Norse name ''Bergelmir'' has been variously translated as 'bear-yeller', 'mountain-yeller', or 'bare-yeller'. According to linguist Jan de Vries, the name should be read ...
, Bestla, Eggther, Farbauti, Fenrir, Fornjot, Geirrod, Gerd, Greip, Gridr, Gunnlod, Hati, Hyrrokkin, Jarnsaxa, Kari, Loge, Mundilfari, Narvi, Phoebe Phoebe or Phœbe may refer to:
__NOTOC__ People and characters
* Phoebe (given name), a list of people, mythological, biblical and fictional characters
* Phoebe (Greek myth), several characters
* Phoebe, an epithet of Artemis/ Diana and Selene/ L ...
, Skathi, Skoll, Skrymir, Surtur
In Norse mythology, Surtr (Old Norse "black"Orchard (1997:154). "the swarthy one",Simek (2007:303–304) Surtur in modern Icelandic), also sometimes written Surt in English, is a jötunn. Surtr is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in th ...
, Suttungr
In Norse mythology, Suttungr ( ; Old Norse: ) was a ''jötunn'' and the son of Gilling.
Mythology
Suttungr searched for his parents and threatened the dwarven brothers Fjalar and Galar who had killed them, tying them and some other dwarves wh ...
, Thiazzi, Thrymr, Ymir, and fifteen unnamed satellites. After Phoebe, Ymir is the largest of the known retrograde irregular moons, with an estimated diameter of only 18 km. The Norse group may itself consist of several smaller subgroups.
* Phoebe Phoebe or Phœbe may refer to:
__NOTOC__ People and characters
* Phoebe (given name), a list of people, mythological, biblical and fictional characters
* Phoebe (Greek myth), several characters
* Phoebe, an epithet of Artemis/ Diana and Selene/ L ...
, at in diameter, is by far the largest of Saturn's irregular satellites. It has a retrograde orbit and rotates on its axis every 9.3 hours. Phoebe was the first moon of Saturn to be studied in detail by ''Cassini'', in ; during this encounter ''Cassini'' was able to map nearly 90% of the moon's surface. Phoebe has a nearly spherical shape and a relatively high density of about 1.6 g/cm3. ''Cassini'' images revealed a dark surface scarred by numerous impacts—there are about 130 craters with diameters exceeding 10 km. Spectroscopic measurement showed that the surface is made of water ice, carbon dioxide, phyllosilicates, organics and possibly iron bearing minerals. Phoebe is believed to be a captured centaur
A centaur ( ; grc, κένταυρος, kéntauros; ), or occasionally hippocentaur, is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse.
Centaurs are thought of in many Greek myths as being ...
that originated in the Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times ...
. It also serves as a source of material for the largest known ring of Saturn, which darkens the leading hemisphere of Iapetus (see above).
List

Confirmed
The Saturnian moons are listed here by orbital period (or semi-major axis), from shortest to longest. Moons massive enough for their surfaces to have collapsed into a spheroid are highlighted in bold and marked with a blue background, while the irregular moons are listed in red, orange and gray background. The orbits and mean distances of the irregular moons are strongly variable over short timescales due to frequent planetary and solarperturbations
Perturbation or perturb may refer to:
* Perturbation theory, mathematical methods that give approximate solutions to problems that cannot be solved exactly
* Perturbation (geology), changes in the nature of alluvial deposits over time
* Perturbatio ...
, therefore the listed orbital elements of all irregular moons are averaged over a 300-year numerical integration. Their orbital elements are all based on the epoch of 1 January 2000. Note: Orbital elements of regular satellites and Phoebe are with respect to the Laplace plane, while orbital elements of irregular satellites are with respect to the ecliptic.
, , , , , , , , , , outer B Ring , , 2009 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , ( moonlets) , , —, , style="background:white;",  , , , , , , } , , , , , , , , , , Three 1000 km bands within A Ring , , 2006 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Pan , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , } , , , , , , , , , , Three 1000 km bands within A Ring , , 2006 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Pan , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.000 , , 0.0000 , , in Encke Division , , 1990 , , Showalter
, -
, , , , , Daphnis , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.000 , , 0.0000 , , in Encke Division , , 1990 , , Showalter
, -
, , , , , Daphnis , , , , style="background:black;", 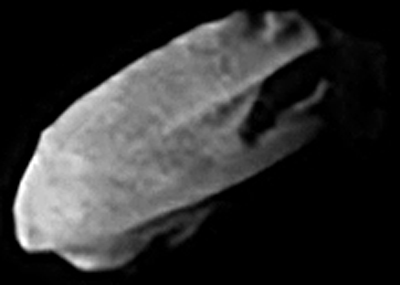 , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.004 , , 0.0000 , , in Keeler Gap , , 2005 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Atlas , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.004 , , 0.0000 , , in Keeler Gap , , 2005 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Atlas , , , , style="background:black;", 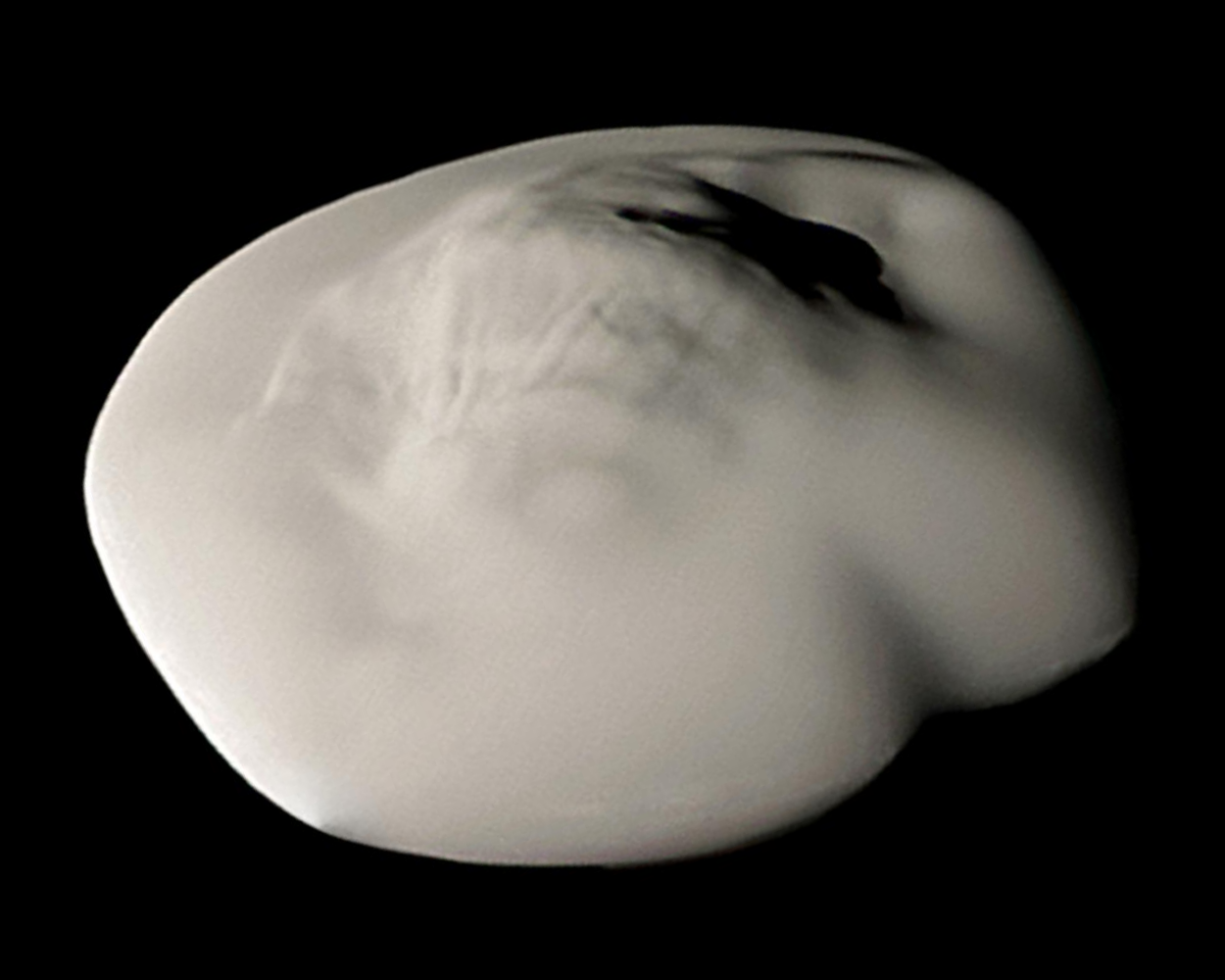 , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.003 , , 0.0012 , , outer A Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , , Prometheus , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.003 , , 0.0012 , , outer A Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , , Prometheus , , , , style="background:black;", 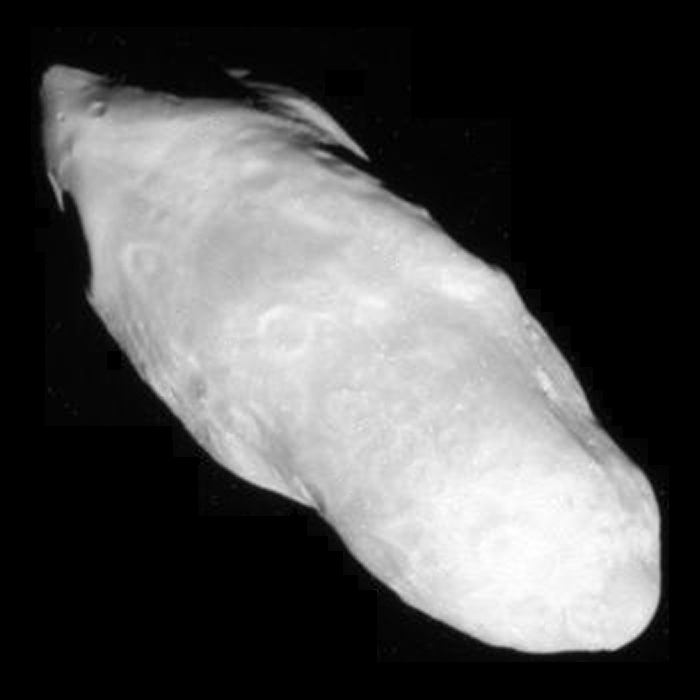 , , , , , , , ,
, , , , 0.008 , , 0.0022 , , inner F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , ,
, , , , , , , ,
, , , , 0.008 , , 0.0022 , , inner F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , ,  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.050 , , 0.0042 , , outer F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , , Epimetheus , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.050 , , 0.0042 , , outer F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , , Epimetheus , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.335 , , 0.0098 , , co-orbital with Janus , , 1977 , , Fountain & Larson
, -
, , , , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.335 , , 0.0098 , , co-orbital with Janus , , 1977 , , Fountain & Larson
, -
, , , , , 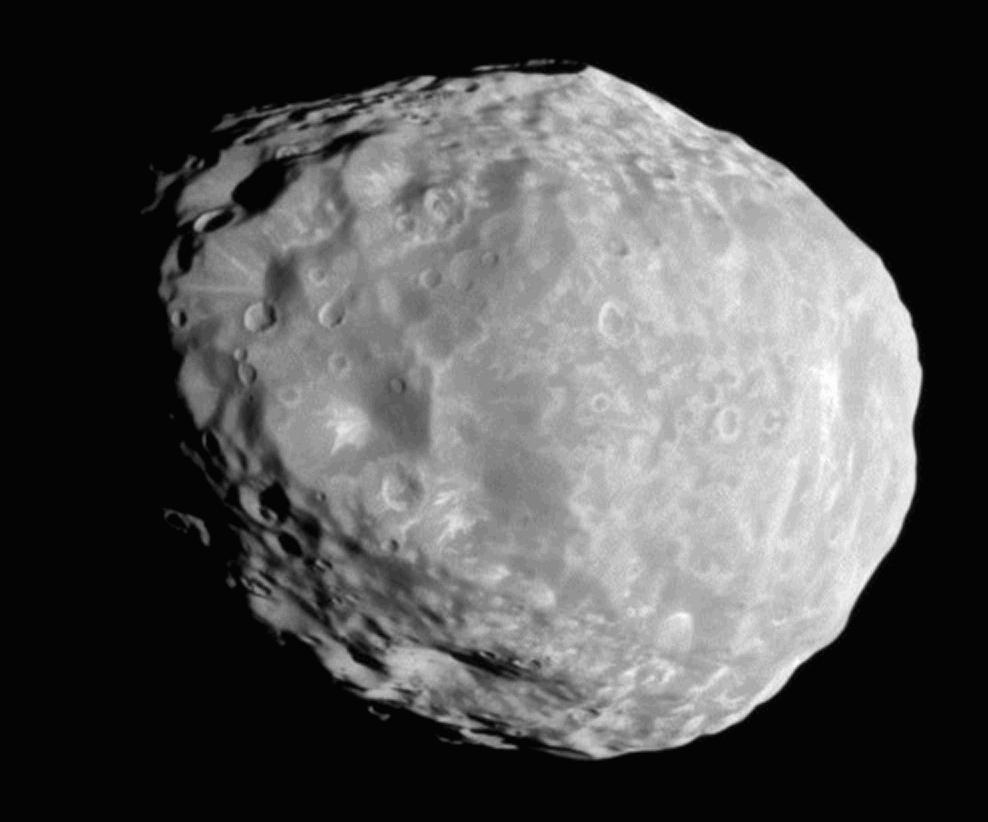 , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.165 , , 0.0068 , , co-orbital with Epimetheus , , 1966 , , Dollfus
, -
, , , , , Aegaeon , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.165 , , 0.0068 , , co-orbital with Epimetheus , , 1966 , , Dollfus
, -
, , , , , Aegaeon , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.001 , , 0.0004 , , G Ring moonlet , , 2008 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 10, , , , †
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.001 , , 0.0004 , , G Ring moonlet , , 2008 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 10, , , , † , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.566 , , , 0.0202 , , , , 1789 , , Herschel
, -
, 11, , , , Methone , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.007 , , 0.0001 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 12, , , , Anthe , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.566 , , , 0.0202 , , , , 1789 , , Herschel
, -
, 11, , , , Methone , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.007 , , 0.0001 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 12, , , , Anthe , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.100 , , 0.0011 , , Alkyonides , , 2007 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 13, , , , Pallene , , , , style="background:white;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.100 , , 0.0011 , , Alkyonides , , 2007 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 13, , , , Pallene , , , , style="background:white;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.181 , , 0.0040 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 14, , , , † Enceladus , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.181 , , 0.0040 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 14, , , , † Enceladus , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.010 , , 0.0047 , , Generates the E ring , , 1789 , , Herschel
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 15, , , , † Tethys , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.010 , , 0.0047 , , Generates the E ring , , 1789 , , Herschel
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 15, , , , † Tethys , , , , style="background:black;",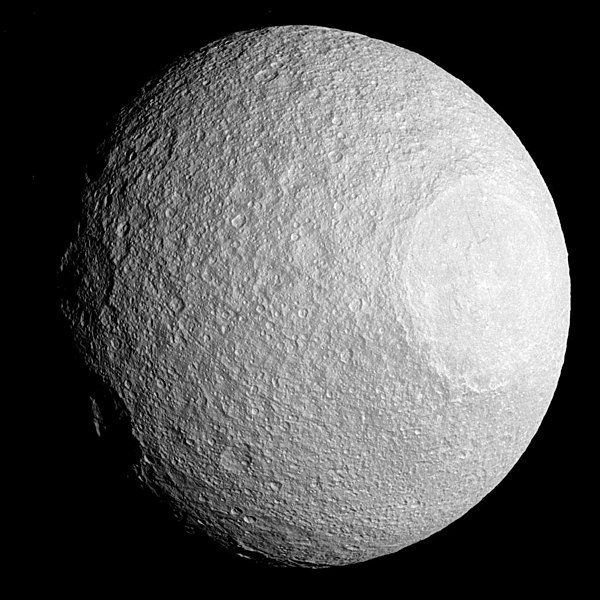  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.168 , , 0.0001 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Telesto , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.168 , , 0.0001 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Telesto , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.158 , , 0.0010 , , leading Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Smith et al.
, -
, , , , , Calypso , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.158 , , 0.0010 , , leading Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Smith et al.
, -
, , , , , Calypso , , , , style="background:black;", 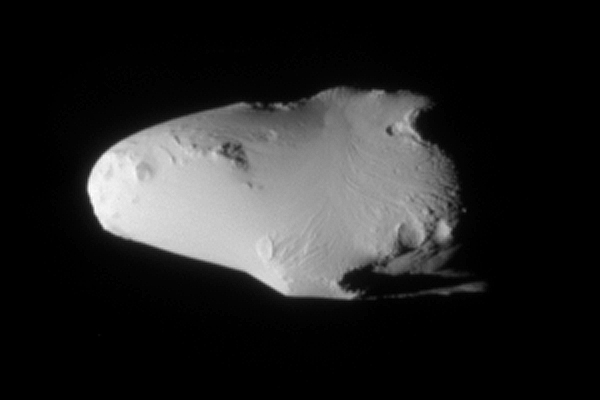 , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.473 , , 0.0010 , , trailing Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Pascu et al.
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 18, , , , †
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.473 , , 0.0010 , , trailing Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Pascu et al.
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 18, , , , † , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.002 , , 0.0022 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Helene , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.002 , , 0.0022 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Helene , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.199 , , 0.0022 , , leading Dione trojan () , , 1980 , , Laques & Lecacheux
, -
, , , , , Polydeuces , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.199 , , 0.0022 , , leading Dione trojan () , , 1980 , , Laques & Lecacheux
, -
, , , , , Polydeuces , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.177 , , 0.0192 , , trailing Dione trojan () , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 21, , , , † Rhea , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.177 , , 0.0192 , , trailing Dione trojan () , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 21, , , , † Rhea , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.327 , , 0.0013 , , , , 1672 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#ccf;"
, 22, , , , ♠
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.327 , , 0.0013 , , , , 1672 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#ccf;"
, 22, , , , ♠ , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.349 , , 0.0288 , , , , 1655 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.349 , , 0.0288 , , , , 1655 , ,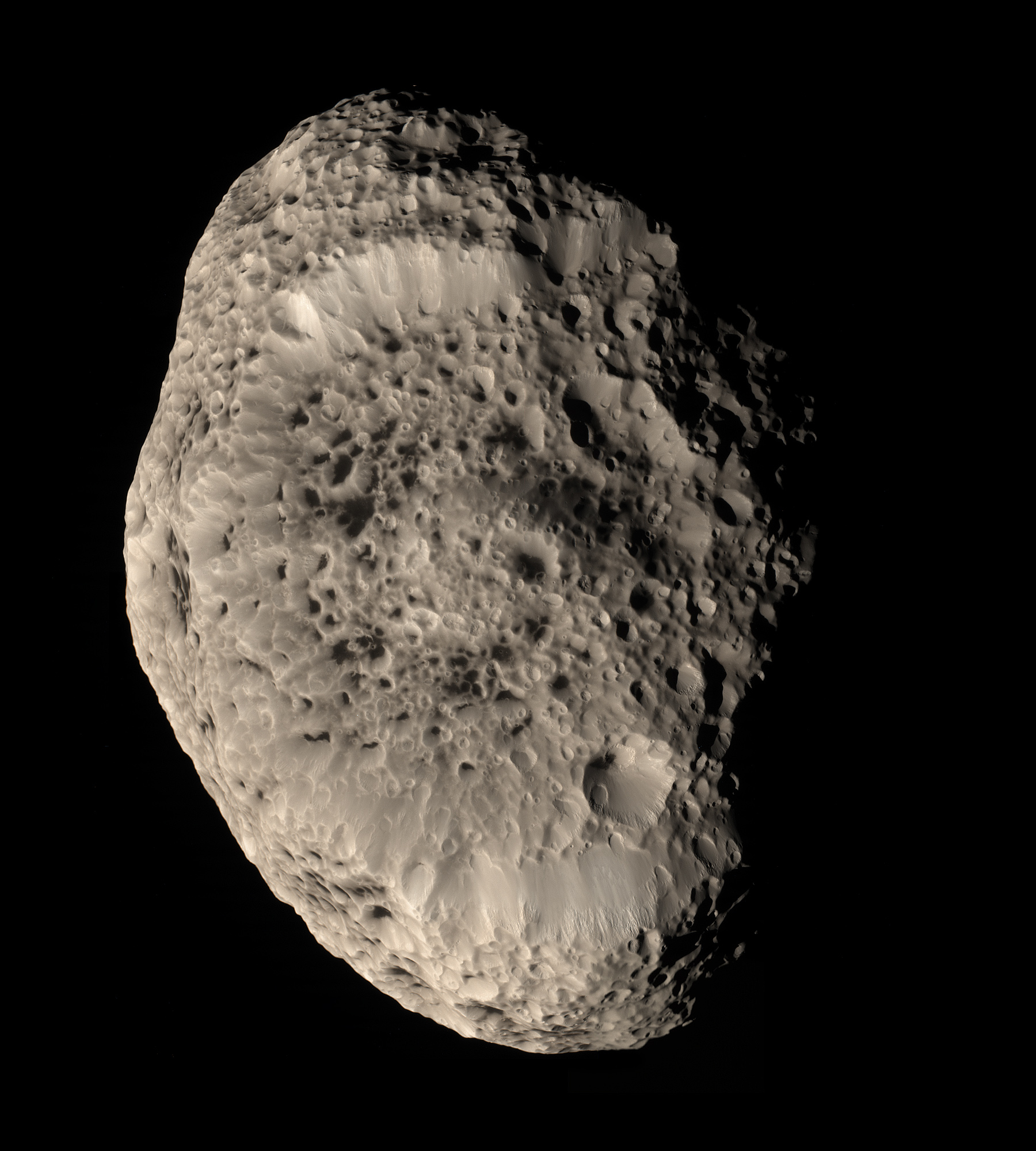  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.568 , , 0.1230 , , in 4:3 resonance with Titan , , 1848 , , Bond & Lassell
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 24, , , , †
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.568 , , 0.1230 , , in 4:3 resonance with Titan , , 1848 , , Bond & Lassell
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 24, , , , † , , , , , , , , , , , , 15.47 , , 0.0286 , , , , 1671 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 25, , , , ‡ S/2019 S 1 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.7 , , 0.5410 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 15.47 , , 0.0286 , , , , 1671 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 25, , , , ‡ S/2019 S 1 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.7 , , 0.5410 , ,  , , , , , , , , , , , , 48.6 , , 0.2120 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 27, , , , ‡ Ijiraq , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 48.6 , , 0.2120 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 27, , , , ‡ Ijiraq , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 47.5 , , 0.2720 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 28, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 47.5 , , 0.2720 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 28, , , , ♣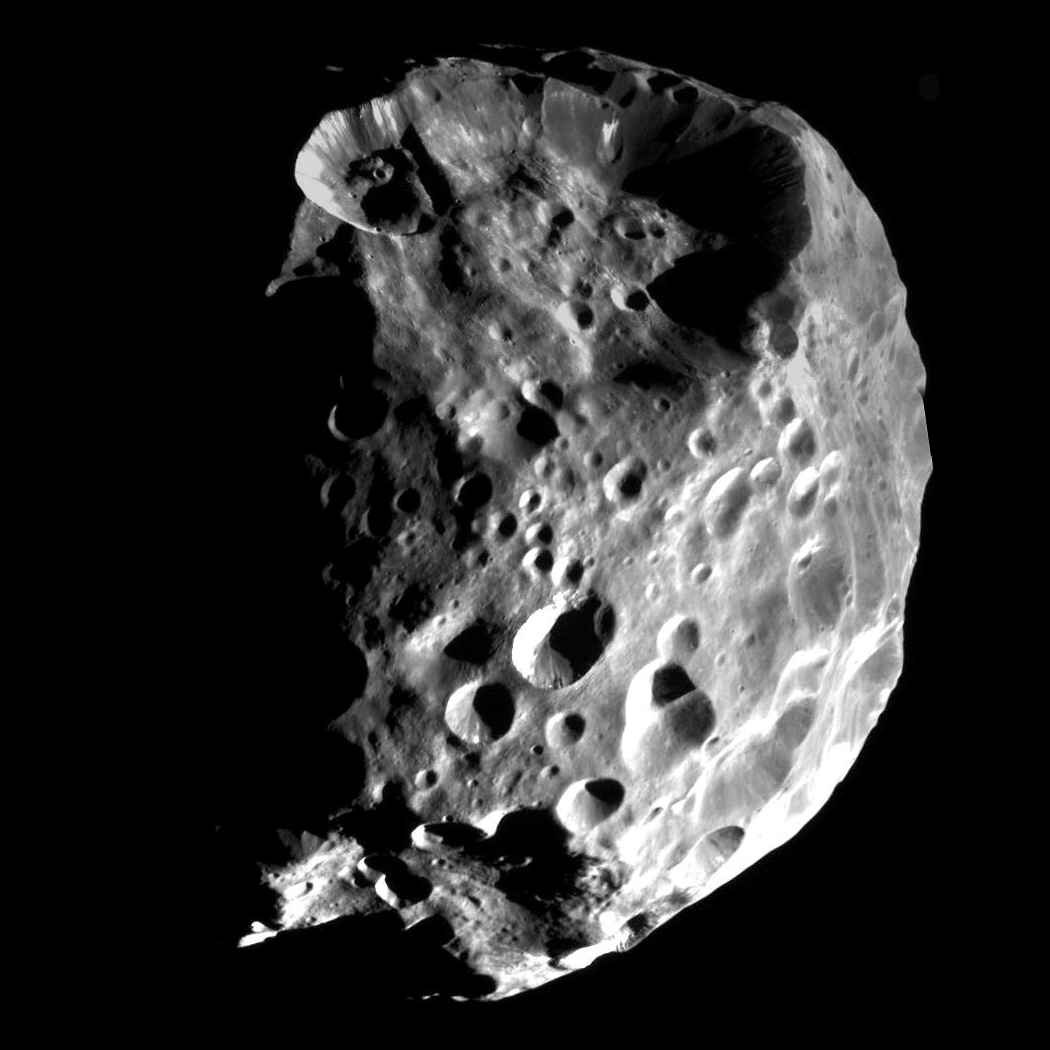 , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.2 , , 0.1640 , , Norse group , , 1899 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 175.2 , , 0.1640 , , Norse group , , 1899 , ,  , , , , , , , , , , , , 44.8 , , 0.3410 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 30, , , , ♣ Skathi , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 44.8 , , 0.3410 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 30, , , , ♣ Skathi , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 152.6 , , 0.2720 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 31, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 37 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.3 , , 0.4460 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 32, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 2 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.2320 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Albiorix , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 152.6 , , 0.2720 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 31, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 37 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.3 , , 0.4460 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 32, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 2 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.2320 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Albiorix , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 34.1 , , 0.4800 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Holman
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Bebhionn , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 34.1 , , 0.4800 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Holman
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Bebhionn , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 37.4 , , 0.4820 , , Gallic group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 35, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 29 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 38.6 , , 0.4850 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 36, , , , ‡
, , , , , , , , , , , , 37.4 , , 0.4820 , , Gallic group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 35, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 29 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 38.6 , , 0.4850 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 36, , , , ‡ , , , , , , , , , , , , 34.5 , , 0.4720 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 38, , , , ♣ Skoll , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 161.0 , , 0.4640 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 39, , , , ‡
, , , , , , , , , , , , 34.5 , , 0.4720 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 38, , , , ♣ Skoll , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 161.0 , , 0.4640 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 39, , , , ‡ , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.3 , , 0.1680 , , Inuit group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 40, , , , ‡
, , , , , , , , , , , , 46.3 , , 0.1680 , , Inuit group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 40, , , , ‡ , , , , , , , , , , , , 45.8 , , 0.2800 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 41, , , , ♦ Tarvos , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 45.8 , , 0.2800 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 41, , , , ♦ Tarvos , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 33.7 , , 0.5380 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 42, , , , ♣ Hyrrokkin , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 33.7 , , 0.5380 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 42, , , , ♣ Hyrrokkin , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 151.5 , , 0.3360 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 43, , , , ♣ Greip , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 151.5 , , 0.3360 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 43, , , , ♣ Greip , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 174.8 , , 0.3150 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 44, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 174.8 , , 0.3150 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 44, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.4 , , 0.2100 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 46, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 167.4 , , 0.2100 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 46, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 158.6 , , 0.1420 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 49, , , , ♣ Narvi , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 158.6 , , 0.1420 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 49, , , , ♣ Narvi , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 145.7 , , 0.4300 , , Norse group , , 2003 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 50, , , , ♣ Jarnsaxa , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.6 , , 0.2180 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 51, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 145.7 , , 0.4300 , , Norse group , , 2003 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 50, , , , ♣ Jarnsaxa , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.6 , , 0.2180 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 51, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.8 , , 0.1140 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 53, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 175.8 , , 0.1140 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 53, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 165.8 , , 0.3710 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 57, , , , ♣ Bestla , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 165.8 , , 0.3710 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 57, , , , ♣ Bestla , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 145.2 , , 0.5200 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 58, , , , ♣ Farbauti , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.5 , , 0.2410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 59, , , , ♣ Thrymr , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 145.2 , , 0.5200 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 58, , , , ♣ Farbauti , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.5 , , 0.2410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 59, , , , ♣ Thrymr , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 177.7 , , 0.4660 , , Norse group, , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 60, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 177.7 , , 0.4660 , , Norse group, , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 60, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.1 , , 0.4760 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 70, , , , ♣ Geirrod , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.3 , , 0.5410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 71, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.3 , , 0.4430 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 72, , , , ♣ Fenrir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 165.0 , , 0.1350 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 73, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 156.1 , , 0.4760 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 70, , , , ♣ Geirrod , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.3 , , 0.5410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 71, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.3 , , 0.4430 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 72, , , , ♣ Fenrir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 165.0 , , 0.1350 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 73, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.7 , , 0.1860 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 75, , , , ♣ Ymir , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 167.7 , , 0.1860 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 75, , , , ♣ Ymir , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 173.5 , , 0.3340 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 76, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 21 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.0 , , 0.4090 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 77, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 39 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.1 , , 0.1020 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#fdd5b1;"
, 78, , , , ♦ S/2004 S 24 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 36.5 , , 0.0720 , , Gallic group? , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 79, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 36 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 152.5 , , 0.6170 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 80, , , , ♣ Thiazzi , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.1 , , 0.5140 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 81, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 34 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 168.3 , , 0.2790 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 82, , , , ♣ Fornjot , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 173.5 , , 0.3340 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 76, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 21 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.0 , , 0.4090 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 77, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 39 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.1 , , 0.1020 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#fdd5b1;"
, 78, , , , ♦ S/2004 S 24 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 36.5 , , 0.0720 , , Gallic group? , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 79, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 36 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 152.5 , , 0.6170 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 80, , , , ♣ Thiazzi , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.1 , , 0.5140 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 81, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 34 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 168.3 , , 0.2790 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 82, , , , ♣ Fornjot , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 170.4 , , 0.2080 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 83, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 26 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 172.9 , , 0.1480 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, , , , , , , , , , , , 170.4 , , 0.2080 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 83, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 26 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 172.9 , , 0.1480 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
 , , , , , , } , , , , , , , , , , Three 1000 km bands within A Ring , , 2006 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Pan , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , } , , , , , , , , , , Three 1000 km bands within A Ring , , 2006 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Pan , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.000 , , 0.0000 , , in Encke Division , , 1990 , , Showalter
, -
, , , , , Daphnis , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.000 , , 0.0000 , , in Encke Division , , 1990 , , Showalter
, -
, , , , , Daphnis , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.004 , , 0.0000 , , in Keeler Gap , , 2005 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Atlas , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.004 , , 0.0000 , , in Keeler Gap , , 2005 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Atlas , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.003 , , 0.0012 , , outer A Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , , Prometheus , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.003 , , 0.0012 , , outer A Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , , Prometheus , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , ,
, , , , 0.008 , , 0.0022 , , inner F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , ,
, , , , , , , ,
, , , , 0.008 , , 0.0022 , , inner F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , , Pandora
In Greek mythology, Pandora (Greek: , derived from , ''pān'', i.e. "all" and , ''dōron'', i.e. "gift", thus "the all-endowed", "all-gifted" or "all-giving") was the first human woman created by Hephaestus on the instructions of Zeus. As Hes ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.050 , , 0.0042 , , outer F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , , Epimetheus , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.050 , , 0.0042 , , outer F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' Voyager 1''
, -
, , , , , Epimetheus , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.335 , , 0.0098 , , co-orbital with Janus , , 1977 , , Fountain & Larson
, -
, , , , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.335 , , 0.0098 , , co-orbital with Janus , , 1977 , , Fountain & Larson
, -
, , , , , Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; la, Ianvs ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janu ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.165 , , 0.0068 , , co-orbital with Epimetheus , , 1966 , , Dollfus
, -
, , , , , Aegaeon , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.165 , , 0.0068 , , co-orbital with Epimetheus , , 1966 , , Dollfus
, -
, , , , , Aegaeon , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.001 , , 0.0004 , , G Ring moonlet , , 2008 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 10, , , , †
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.001 , , 0.0004 , , G Ring moonlet , , 2008 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 10, , , , †Mimas
Mimas may refer to:
*Mimas (Giant), son of Gaia in Greek mythology, one of the Gigantes
* Mimas (''Aeneid''), a son of Amycus and Theono, born the same night as Paris, who escorted Aeneas to Italy
*Karaburun, a town and district in Turkey, formerl ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.566 , , , 0.0202 , , , , 1789 , , Herschel
, -
, 11, , , , Methone , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.007 , , 0.0001 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 12, , , , Anthe , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.566 , , , 0.0202 , , , , 1789 , , Herschel
, -
, 11, , , , Methone , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.007 , , 0.0001 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 12, , , , Anthe , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.100 , , 0.0011 , , Alkyonides , , 2007 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 13, , , , Pallene , , , , style="background:white;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.100 , , 0.0011 , , Alkyonides , , 2007 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 13, , , , Pallene , , , , style="background:white;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.181 , , 0.0040 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 14, , , , † Enceladus , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.181 , , 0.0040 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 14, , , , † Enceladus , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.010 , , 0.0047 , , Generates the E ring , , 1789 , , Herschel
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 15, , , , † Tethys , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.010 , , 0.0047 , , Generates the E ring , , 1789 , , Herschel
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 15, , , , † Tethys , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.168 , , 0.0001 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Telesto , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.168 , , 0.0001 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Telesto , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.158 , , 0.0010 , , leading Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Smith et al.
, -
, , , , , Calypso , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.158 , , 0.0010 , , leading Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Smith et al.
, -
, , , , , Calypso , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.473 , , 0.0010 , , trailing Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Pascu et al.
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 18, , , , †
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.473 , , 0.0010 , , trailing Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Pascu et al.
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 18, , , , †Dione Dione may refer to:
Astronomy
*106 Dione, a large main belt asteroid
*Dione (moon), a moon of Saturn
*Helene (moon), a moon of Saturn sometimes referred to as "Dione B"
Mythology
*Dione (Titaness), a Titaness in Greek mythology
*Dione (mythology) ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.002 , , 0.0022 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Helene , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.002 , , 0.0022 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Helene , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.199 , , 0.0022 , , leading Dione trojan () , , 1980 , , Laques & Lecacheux
, -
, , , , , Polydeuces , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.199 , , 0.0022 , , leading Dione trojan () , , 1980 , , Laques & Lecacheux
, -
, , , , , Polydeuces , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.177 , , 0.0192 , , trailing Dione trojan () , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 21, , , , † Rhea , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.177 , , 0.0192 , , trailing Dione trojan () , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 21, , , , † Rhea , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.327 , , 0.0013 , , , , 1672 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#ccf;"
, 22, , , , ♠
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.327 , , 0.0013 , , , , 1672 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#ccf;"
, 22, , , , ♠Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.349 , , 0.0288 , , , , 1655 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.349 , , 0.0288 , , , , 1655 , , Huygens
Huygens (also Huijgens, Huigens, Huijgen/Huygen, or Huigen) is a Dutch patronymic surname, meaning "son of Hugo". Most references to "Huygens" are to the polymath Christiaan Huygens. Notable people with the surname include:
* Jan Huygen (1563– ...
, -
, 23, , , , Hyperion
Hyperion may refer to:
Greek mythology
* Hyperion (Titan), one of the twelve Titans
* ''Hyperion'', a byname of the Sun, Helios
* Hyperion of Troy or Yperion, son of King Priam
Science
* Hyperion (moon), a moon of the planet Saturn
* ''Hyp ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.568 , , 0.1230 , , in 4:3 resonance with Titan , , 1848 , , Bond & Lassell
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 24, , , , †
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.568 , , 0.1230 , , in 4:3 resonance with Titan , , 1848 , , Bond & Lassell
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 24, , , , †Iapetus
In Greek mythology, Iapetus (; ; grc, Ἰαπετός, Iapetós), also Japetus, is a Titan, the son of Uranus and Gaia and father of Atlas, Prometheus, Epimetheus, and Menoetius. He was also called the father of Buphagus and Anchiale in other ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 15.47 , , 0.0286 , , , , 1671 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 25, , , , ‡ S/2019 S 1 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.7 , , 0.5410 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 15.47 , , 0.0286 , , , , 1671 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 25, , , , ‡ S/2019 S 1 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.7 , , 0.5410 , , Inuit group
The Inuit group is a dynamical grouping of the prograde irregular satellites of Saturn which follow similar orbits. Their semi-major axes range between 11 and 18 Gm, their inclinations between 40° and 50°, and their eccentricities between ...
, , 2019 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 26, , , , ‡ Kiviuq , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 48.6 , , 0.2120 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 27, , , , ‡ Ijiraq , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 48.6 , , 0.2120 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 27, , , , ‡ Ijiraq , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 47.5 , , 0.2720 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 28, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 47.5 , , 0.2720 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 28, , , , ♣Phoebe Phoebe or Phœbe may refer to:
__NOTOC__ People and characters
* Phoebe (given name), a list of people, mythological, biblical and fictional characters
* Phoebe (Greek myth), several characters
* Phoebe, an epithet of Artemis/ Diana and Selene/ L ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.2 , , 0.1640 , , Norse group , , 1899 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 175.2 , , 0.1640 , , Norse group , , 1899 , , Pickering Pickering may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Pickering Nunataks, Alexander Island
Australia
* Pickering, South Australia, the original name (1872–1940) of the town of Wool Bay
* Pickering Brook, Western Australia, Australia
Canada
* Pic ...
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 29, , , , ‡ Paaliaq , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 44.8 , , 0.3410 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 30, , , , ♣ Skathi , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 44.8 , , 0.3410 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 30, , , , ♣ Skathi , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 152.6 , , 0.2720 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 31, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 37 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.3 , , 0.4460 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 32, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 2 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.2320 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Albiorix , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 152.6 , , 0.2720 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 31, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 37 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.3 , , 0.4460 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 32, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 2 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.2320 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Albiorix , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 34.1 , , 0.4800 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Holman
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Bebhionn , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 34.1 , , 0.4800 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Holman
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Bebhionn , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 37.4 , , 0.4820 , , Gallic group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 35, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 29 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 38.6 , , 0.4850 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 36, , , , ‡
, , , , , , , , , , , , 37.4 , , 0.4820 , , Gallic group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 35, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 29 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 38.6 , , 0.4850 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 36, , , , ‡S/2004 S 31
S/2004 S 31 is a natural satellite of Saturn and a member of the Inuit group. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, and Jan Kleyna on October 8, 2019 from observations taken between December 12, 2004 and March 22, 200 ...
, , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 48.3 , , 0.2020 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 37, , , , ♦ Erriapus , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 34.5 , , 0.4720 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 38, , , , ♣ Skoll , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 161.0 , , 0.4640 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 39, , , , ‡
, , , , , , , , , , , , 34.5 , , 0.4720 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 38, , , , ♣ Skoll , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 161.0 , , 0.4640 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 39, , , , ‡Tarqeq
Tarqeq, also known as Saturn LII (provisional designation S/2007 S 1) is a natural satellite of Saturn. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, Jan Kleyna, and Brian G. Marsden on 13 April 2007 from observations taken ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.3 , , 0.1680 , , Inuit group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 40, , , , ‡
, , , , , , , , , , , , 46.3 , , 0.1680 , , Inuit group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 40, , , , ‡Siarnaq
Siarnaq, also designated Saturn XXIX, is the second-largest irregular moon of Saturn. It was discovered on 23 September 2000 by a team of astronomers led by Brett J. Gladman. It was named after the Inuit goddess of the sea, Siarnaq, who is more ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 45.8 , , 0.2800 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 41, , , , ♦ Tarvos , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 45.8 , , 0.2800 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 41, , , , ♦ Tarvos , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 33.7 , , 0.5380 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 42, , , , ♣ Hyrrokkin , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 33.7 , , 0.5380 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 42, , , , ♣ Hyrrokkin , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 151.5 , , 0.3360 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 43, , , , ♣ Greip , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 151.5 , , 0.3360 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 43, , , , ♣ Greip , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 174.8 , , 0.3150 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 44, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 174.8 , , 0.3150 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 44, , , , ♣S/2004 S 13
S/2004 S 13 is a natural satellite of Saturn. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, Jan Kleyna, and Brian G. Marsden on 4 May 2005 from observations taken between 12 December 2004 and 9 March 2005.
S/2004 S 13 is a ...
, , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 168.9 , , 0.2660 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 45, , , , ♣ Mundilfari , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.4 , , 0.2100 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 46, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 167.4 , , 0.2100 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 46, , , , ♣S/2006 S 1
S/2006 S 1 is a natural satellite of Saturn. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, Jan Kleyna, and Brian G. Marsden on June 26, 2006 from observations taken between January 4 and April 30, 2006.
S/2006 S 1 is about 6 ...
, , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.2 , , 0.1050 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 47, , , , ♣ Gridr , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.7 , , 0.1820 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 48, , , , ♣Bergelmir
Bergelmir ( ; Old Norse: ) is a jötunn in Norse mythology.
Name
The Old Norse name ''Bergelmir'' has been variously translated as 'bear-yeller', 'mountain-yeller', or 'bare-yeller'. According to linguist Jan de Vries, the name should be read ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 158.6 , , 0.1420 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 49, , , , ♣ Narvi , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 158.6 , , 0.1420 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 49, , , , ♣ Narvi , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 145.7 , , 0.4300 , , Norse group , , 2003 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 50, , , , ♣ Jarnsaxa , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.6 , , 0.2180 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 51, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 145.7 , , 0.4300 , , Norse group , , 2003 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 50, , , , ♣ Jarnsaxa , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.6 , , 0.2180 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 51, , , , ♣S/2004 S 17
S/2004 S 17 is a natural satellite of Saturn. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, Jan Kleyna, and Brian G. Marsden on 4 May 2005 from observations taken between 13 December 2004 and 5 March 2005.
S/2004 S 17 is ab ...
, , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.9 , , 0.1790 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 52, , , , ♣Suttungr
In Norse mythology, Suttungr ( ; Old Norse: ) was a ''jötunn'' and the son of Gilling.
Mythology
Suttungr searched for his parents and threatened the dwarven brothers Fjalar and Galar who had killed them, tying them and some other dwarves wh ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.8 , , 0.1140 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 53, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 175.8 , , 0.1140 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 53, , , , ♣S/2007 S 3
S/2007 S 3 is a natural satellite of Saturn. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, Jan Kleyna, and Brian G. Marsden on 1 May 2007 from observations taken between 18 January and 19 April 2007.
S/2007 S 3 is about 5 k ...
, , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.1620 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 54, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 12 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.0 , , 0.3250 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 55, , , , ♣ Eggther , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 166.3 , , 0.1570 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 56, , , , ♣ Hati , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 165.8 , , 0.3710 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 57, , , , ♣ Bestla , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 165.8 , , 0.3710 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 57, , , , ♣ Bestla , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 145.2 , , 0.5200 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 58, , , , ♣ Farbauti , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.5 , , 0.2410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 59, , , , ♣ Thrymr , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 145.2 , , 0.5200 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 58, , , , ♣ Farbauti , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.5 , , 0.2410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 59, , , , ♣ Thrymr , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 177.7 , , 0.4660 , , Norse group, , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 60, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 177.7 , , 0.4660 , , Norse group, , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 60, , , , ♣S/2004 S 7
S/2004 S 7 is a natural satellite of Saturn. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, Jan Kleyna, and Brian G. Marsden on 4 May 2005 from observations taken between 12 December 2004 and 8 March 2005.
S/2004 S 7 is abou ...
, , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.3 , , 0.4620 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 61, , , , ♣ Angrboda , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 177.4 , , 0.2160 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 62, , , , ♣ Beli , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.7 , , 0.0870 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 63, , , , ♣ Aegir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 166.7 , , 0.2520 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 64, , , , ♣ Gerd , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 174.3 , , 0.5190 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 65, , , , ♣ Gunnlod , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 158.9 , , 0.2540 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 66, , , , ♣ Skrymir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 176.6 , , 0.4370 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 67, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 28 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 169.4 , , 0.1600 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 68, , , , ♣Alvaldi
Alvaldi (also Ölvaldi; Old Norse 'all-powerful') is a jötunn in Norse mythology, presented as the father of Þjazi.
Saturn's moon Alvaldi is named after him.
Name
The Old Norse name ''Alvadi'' means 'all-powerful'. The name ''Ölvadi'', fo ...
, , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 176.8 , , 0.2370 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 69, , , , ♣ Kari , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.1 , , 0.4760 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 70, , , , ♣ Geirrod , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.3 , , 0.5410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 71, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.3 , , 0.4430 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 72, , , , ♣ Fenrir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 165.0 , , 0.1350 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 73, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 156.1 , , 0.4760 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 70, , , , ♣ Geirrod , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.3 , , 0.5410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 71, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.3 , , 0.4430 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 72, , , , ♣ Fenrir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 165.0 , , 0.1350 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 73, , , , ♣Surtur
In Norse mythology, Surtr (Old Norse "black"Orchard (1997:154). "the swarthy one",Simek (2007:303–304) Surtur in modern Icelandic), also sometimes written Surt in English, is a jötunn. Surtr is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in th ...
, , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 169.7 , , 0.4460 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 74, , , , ♣ Loge , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.7 , , 0.1860 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 75, , , , ♣ Ymir , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 167.7 , , 0.1860 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 75, , , , ♣ Ymir , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 173.5 , , 0.3340 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 76, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 21 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.0 , , 0.4090 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 77, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 39 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.1 , , 0.1020 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#fdd5b1;"
, 78, , , , ♦ S/2004 S 24 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 36.5 , , 0.0720 , , Gallic group? , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 79, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 36 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 152.5 , , 0.6170 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 80, , , , ♣ Thiazzi , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.1 , , 0.5140 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 81, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 34 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 168.3 , , 0.2790 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 82, , , , ♣ Fornjot , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 173.5 , , 0.3340 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 76, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 21 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.0 , , 0.4090 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 77, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 39 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.1 , , 0.1020 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#fdd5b1;"
, 78, , , , ♦ S/2004 S 24 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 36.5 , , 0.0720 , , Gallic group? , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 79, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 36 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 152.5 , , 0.6170 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 80, , , , ♣ Thiazzi , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.1 , , 0.5140 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 81, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 34 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 168.3 , , 0.2790 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 82, , , , ♣ Fornjot , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 170.4 , , 0.2080 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 83, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 26 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 172.9 , , 0.1480 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, , , , , , , , , , , , 170.4 , , 0.2080 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 83, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 26 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 172.9 , , 0.1480 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
Unconfirmed
The following objects (observed by '' Cassini'') have not been confirmed as solid bodies. It is not yet clear if these are real satellites or merely persistent clumps within the F Ring.Spurious
Two moons were claimed to be discovered by different astronomers but never seen again. Both moons were said to orbit betweenTitan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
and Hyperion
Hyperion may refer to:
Greek mythology
* Hyperion (Titan), one of the twelve Titans
* ''Hyperion'', a byname of the Sun, Helios
* Hyperion of Troy or Yperion, son of King Priam
Science
* Hyperion (moon), a moon of the planet Saturn
* ''Hyp ...
.
* Chiron which was supposedly sighted by Hermann Goldschmidt in 1861, but never observed by anyone else.
* Themis was allegedly discovered in 1905 by astronomer William Pickering, but never seen again. Nevertheless, it was included in numerous almanacs and astronomy books until the 1960s.
Hypothetical
In 2022, scientists of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology proposed the hypothetical former moonChrysalis
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in their ...
, using data from the Cassini–Huygens
''Cassini–Huygens'' ( ), commonly called ''Cassini'', was a space research, space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, i ...
mission. Chrysalis would have orbited between Titan and Iapetus, but its orbit would have gradually become more eccentric until it was torn apart by Saturn. 99% of its mass would have been absorbed by Saturn, while the remaining 1% would have formed Saturn's rings.
Temporary
Much like Jupiter, asteroids and comets will infrequently make close approaches to Saturn, even more infrequently becoming captured into orbit of the planet. The comet P/2020 F1 (Leonard) is calculated to have made a close approach of km ( mi to Saturn on 8 May 1936, closer than the orbit of Titan to the planet, with anorbital eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values betwee ...
of only . The comet may have been orbiting Saturn prior to this as a temporary satellite, but difficulty modelling the non-gravitational forces makes whether or not it was indeed a temporary satellite uncertain.
Other comets and asteroids may have temporarily orbited Saturn at some point, but none are presently known to have.
Formation
It is thought that the Saturnian system of Titan, mid-sized moons, and rings developed from a set-up closer to theGalilean moons
The Galilean moons (), or Galilean satellites, are the four largest moons of Jupiter: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. They were first seen by Galileo Galilei in December 1609 or January 1610, and recognized by him as satellites of Jupiter ...
of Jupiter, though the details are unclear. It has been proposed either that a second Titan-sized moon broke up, producing the rings and inner mid-sized moons, or that two large moons fused to form Titan, with the collision scattering icy debris that formed the mid-sized moons. On June 23, 2014, NASA claimed to have strong evidence that nitrogen in the atmosphere of Titan came from materials in the Oort cloud, associated with comets, and not from the materials that formed Saturn in earlier times. Studies based on Enceladus's tidal-based geologic activity and the lack of evidence of extensive past resonances in Tethys, Dione, and Rhea's orbits suggest that the moons up to and including Rhea may be only 100 million years old.
See also
* List of natural satellitesNotes
References
External links
* Scott S. SheppardSaturn Moons
* * * *
at '' The New York Times'' * Planetary Societybr>blog post
(2017-05-17) by
Emily Lakdawalla
Emily Stewart Lakdawalla (born February 8, 1975) is an American planetary geologist and former Senior Editor of The Planetary Society, contributing as both a science writer and a blogger. She has also worked as a teacher and as an environmental ...
with images giving comparative sizes of the moons
* Tilmann DenkOuter Moons of Saturn
{{DEFAULTSORT:Moons Of Saturn Lists of moons