Sailing Yachts Of New Zealand on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sailing employs the wind—acting on
 The earliest image suggesting the use of sail on a boat may be on a piece of pottery from
The earliest image suggesting the use of sail on a boat may be on a piece of pottery from

 In the early 1800s, fast blockade-running schooners and brigantines—
In the early 1800s, fast blockade-running schooners and brigantines—
 While the use of sailing vessels for commerce or naval power has been supplanted with engine-driven vessels, there continue to be commercial operations that take passengers on sailing cruises. Modern navies also employ sailing vessels to train cadets in
While the use of sailing vessels for commerce or naval power has been supplanted with engine-driven vessels, there continue to be commercial operations that take passengers on sailing cruises. Modern navies also employ sailing vessels to train cadets in
File:Shrike-port-beam.jpg, ''Close-hauled'': the flag is streaming backwards, the sails are sheeted in tightly.
File:Shrike-reaching.jpg, ''Reaching'': the flag is streaming slightly to the side as the sails are sheeted to align with the apparent wind.
File:Shrike-running.jpg, ''Running'': the wind is coming from behind the vessel; the sails are "wing on wing" to be at right angles to the apparent wind.
File:Forces on sails for three points of sail.jpg, Apparent wind and forces on a ''sailboat''.
As the boat sails further from the wind, the apparent wind becomes smaller and the lateral component becomes less; boat speed is highest on the beam reach. File:Ice boat apparent wind on different points of sail.jpg, Apparent wind on an ''iceboat''.
As the iceboat sails further from the wind, the apparent wind increases slightly and the boat speed is highest on the broad reach. The sail is sheeted in for all three points of sail.
The speed of sailboats through the water is limited by the resistance that results from hull drag in the water. Ice boats typically have the least resistance to forward motion of any sailing craft. Consequently, a sailboat experiences a wider range of apparent wind angles than does an ice boat, whose speed is typically great enough to have the apparent wind coming from a few degrees to one side of its course, necessitating sailing with the sail sheeted in for most points of sail. On conventional sailboats, the sails are set to create lift for those points of sail where it's possible to align the leading edge of the sail with the apparent wind.
For a sailboat, point of sail affects lateral force significantly. The higher the boat points to the wind under sail, the stronger the lateral force, which requires resistance from a keel or other underwater foils, including daggerboard, centerboard, skeg and rudder. Lateral force also induces heeling in a sailboat, which requires resistance by weight of ballast from the crew or the boat itself and by the shape of the boat, especially with a catamaran. As the boat points off the wind, lateral force and the forces required to resist it become less important.
On ice boats, lateral forces are countered by the lateral resistance of the blades on ice and their distance apart, which generally prevents heeling.

 Wind and currents are important factors to plan on for both offshore and inshore sailing. Predicting the availability, strength and direction of the wind is key to using its power along the desired course. Ocean currents, tides and river currents may deflect a sailing vessel from its desired course.
If the desired course is within the no-go zone, then the sailing craft must follow a zig-zag route into the wind to reach its waypoint or destination. Downwind, certain high-performance sailing craft can reach the destination more quickly by following a zig-zag route on a series of broad reaches.
Negotiating obstructions or a channel may also require a change of direction with respect to the wind, necessitating changing of tack with the wind on the opposite side of the craft, from before.
Changing tack is called ''tacking'' when the wind crosses over the bow of the craft as it turns and ''jibing'' (or ''gybing'') if the wind passes over the stern.
Wind and currents are important factors to plan on for both offshore and inshore sailing. Predicting the availability, strength and direction of the wind is key to using its power along the desired course. Ocean currents, tides and river currents may deflect a sailing vessel from its desired course.
If the desired course is within the no-go zone, then the sailing craft must follow a zig-zag route into the wind to reach its waypoint or destination. Downwind, certain high-performance sailing craft can reach the destination more quickly by following a zig-zag route on a series of broad reaches.
Negotiating obstructions or a channel may also require a change of direction with respect to the wind, necessitating changing of tack with the wind on the opposite side of the craft, from before.
Changing tack is called ''tacking'' when the wind crosses over the bow of the craft as it turns and ''jibing'' (or ''gybing'') if the wind passes over the stern.
 ''Tacking'' or ''coming about'' is a maneuver by which a sailing craft turns its bow into and through the wind (referred to as "the eye of the wind") so that the apparent wind changes from one side to the other, allowing progress on the opposite tack. The type of sailing rig dictates the procedures and constraints on achieving a tacking maneuver. Fore-and-aft rigs allow their sails to hang limp as they tack; square rigs must present the full frontal area of the sail to the wind, when changing from side to side; and windsurfers have flexibly pivoting and fully rotating masts that get flipped from side to side.
''Tacking'' or ''coming about'' is a maneuver by which a sailing craft turns its bow into and through the wind (referred to as "the eye of the wind") so that the apparent wind changes from one side to the other, allowing progress on the opposite tack. The type of sailing rig dictates the procedures and constraints on achieving a tacking maneuver. Fore-and-aft rigs allow their sails to hang limp as they tack; square rigs must present the full frontal area of the sail to the wind, when changing from side to side; and windsurfers have flexibly pivoting and fully rotating masts that get flipped from side to side.
File:Wende (Segeln).png, Tacking from the port tack (bottom) to the starboard (top) tack
File:Tacking Intervals.svg, Beating to windward on short (P1), medium (P2), and long (P3) tacks
 A sailing craft can travel directly downwind only at a speed that is less than the wind speed. However, a variety of sailing craft can achieve a higher downwind
A sailing craft can travel directly downwind only at a speed that is less than the wind speed. However, a variety of sailing craft can achieve a higher downwind
 Winds and oceanic currents are both the result of the sun powering their respective fluid media. Wind powers the sailing craft and the ocean bears the craft on its course, as currents may alter the course of a sailing vessel on the ocean or a river.
*''Wind'' – On a global scale, vessels making long voyages must take
Winds and oceanic currents are both the result of the sun powering their respective fluid media. Wind powers the sailing craft and the ocean bears the craft on its course, as currents may alter the course of a sailing vessel on the ocean or a river.
*''Wind'' – On a global scale, vessels making long voyages must take
 Trimming refers to adjusting the lines that control sails, including the sheets that control angle of the sails with respect to the wind, the halyards that raise and tighten the sail, and to adjusting the hull's resistance to heeling, yawing or progress through the water.
Trimming refers to adjusting the lines that control sails, including the sheets that control angle of the sails with respect to the wind, the halyards that raise and tighten the sail, and to adjusting the hull's resistance to heeling, yawing or progress through the water.
 In their most developed version, square sails are controlled by two each of: sheets, braces, clewlines, and reef tackles, plus four buntlines, each of which may be controlled by a crew member as the sail is adjusted. Towards the end of the Age of Sail, steam-powered machinery reduced the number of crew required to trim sail.
Adjustment of the angle of a fore-and-aft sail with respect to the apparent wind is controlled with a line, called a "sheet". On points of sail between close-hauled and a broad reach, the goal is typically to create flow along the sail to maximize power through lift. Streamers placed on the surface of the sail, called tell-tales, indicate whether that flow is smooth or turbulent. Smooth flow on both sides indicates proper trim. A jib and mainsail are typically configured to be adjusted to create a smooth laminar flow, leading from one to the other in what is called the "slot effect".
On downwind points of sail, power is achieved primarily with the wind pushing on the sail, as indicated by drooping tell-tales.
In their most developed version, square sails are controlled by two each of: sheets, braces, clewlines, and reef tackles, plus four buntlines, each of which may be controlled by a crew member as the sail is adjusted. Towards the end of the Age of Sail, steam-powered machinery reduced the number of crew required to trim sail.
Adjustment of the angle of a fore-and-aft sail with respect to the apparent wind is controlled with a line, called a "sheet". On points of sail between close-hauled and a broad reach, the goal is typically to create flow along the sail to maximize power through lift. Streamers placed on the surface of the sail, called tell-tales, indicate whether that flow is smooth or turbulent. Smooth flow on both sides indicates proper trim. A jib and mainsail are typically configured to be adjusted to create a smooth laminar flow, leading from one to the other in what is called the "slot effect".
On downwind points of sail, power is achieved primarily with the wind pushing on the sail, as indicated by drooping tell-tales.
 A sailing vessel heels when the boat leans over to the side in reaction to wind forces on the sails.
A sailing vessel's form stability (the resistance of hull shape to rolling) is the starting point for resisting heeling. Catamarans and iceboats have a wide stance that makes them resistant to heeling. Additional measures for trimming a sailing craft to control heeling include:
* Ballast in the keel, which counteracts heeling as the boat rolls.
* Shifting of weight, which might be crew on a trapeze or moveable ballast across the boat.
* Reducing sail
* Adjusting the depth of underwater foils to control their lateral resistance force and center of resistance
A sailing vessel heels when the boat leans over to the side in reaction to wind forces on the sails.
A sailing vessel's form stability (the resistance of hull shape to rolling) is the starting point for resisting heeling. Catamarans and iceboats have a wide stance that makes them resistant to heeling. Additional measures for trimming a sailing craft to control heeling include:
* Ballast in the keel, which counteracts heeling as the boat rolls.
* Shifting of weight, which might be crew on a trapeze or moveable ballast across the boat.
* Reducing sail
* Adjusting the depth of underwater foils to control their lateral resistance force and center of resistance
 The physics of sailing arises from a balance of forces between the wind powering the sailing craft as it passes over its sails and the resistance by the sailing craft against being blown off course, which is provided in the water by the
The physics of sailing arises from a balance of forces between the wind powering the sailing craft as it passes over its sails and the resistance by the sailing craft against being blown off course, which is provided in the water by the
 ''Lift'' on a sail, acting as an
''Lift'' on a sail, acting as an
File:Sailboat on broad reach with spinnaker.jpg, Spinnaker set for a broad reach, generating both lift, with separated flow, and drag.
File:Spinnaker trimmed for broad reach.jpg, Spinnaker cross-section trimmed for a broad reach showing transition from boundary layer to separated flow where vortex shedding commences.
File:Amante Choate 48 photo D Ramey Logan.jpg, Symmetric spinnaker while running downwind, primarily generating drag.
File:Symmetrical spinnaker with following apparent wind.jpg, Symmetric spinnaker cross-section with following apparent wind, showing vortex shedding.
Virtual Vault
, an online exhibition of Canadian historical art at Library and Archives Canada * Rousmaniere, John, ''The Annapolis Book of Seamanship'', Simon & Schuster, 1999 * ''Chapman Book of Piloting'' (various contributors), Hearst Corporation, 1999 * Herreshoff, Halsey (consulting editor), ''The Sailor's Handbook'', Little Brown and Company, 1983 * Seidman, David, ''The Complete Sailor'', International Marine, 1995 *
sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails ma ...
s, wingsail
A wingsail, twin-skin sail or double skin sail is a variable- camber aerodynamic structure that is fitted to a marine vessel in place of conventional sails. Wingsails are analogous to airplane wings, except that they are designed to provide li ...
s or kite
A kite is a tethered heavier than air flight, heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create Lift (force), lift and Drag (physics), drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. ...
s—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships ...
, sailboat
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.
Types
Although sailboat terminology ...
, raft
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrel ...
, windsurfer, or kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat
An iceboat (occasionally spelled ice boat or traditionally called an ice yacht) is a recreational or competition sailing craft supported on metal runners for traveling over ice. One of the runners is steerable. Originally, such craft were boats ...
) or on ''land'' (land yacht
Land sailing, also known as sand yachting, land yachting or dirtboating, is the act of moving across land in a wheeled vehicle powered by wind through the use of a sail. The term comes from analogy with (water) sailing. Historically, land sai ...
) over a chosen course
Course may refer to:
Directions or navigation
* Course (navigation), the path of travel
* Course (orienteering), a series of control points visited by orienteers during a competition, marked with red/white flags in the terrain, and corresponding ...
, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
.
From prehistory until the second half of the 19th century, sailing craft were the primary means of maritime trade and transportation; exploration across the seas and oceans was reliant on sail for anything other than the shortest distances. Naval power in this period used sail to varying degrees depending on the current technology, culminating in the gun-armed sailing warships of the Age of Sail
The Age of Sail is a periodization, period that lasted at the latest from the mid-16th century, 16th (or mid-15th century, 15th) to the mid-19th century, 19th centuries, in which the dominance of sailing ships in globalization, global trade and ...
. Sail was slowly replaced by steam as the method of propulsion for ships over the latter part of the 19th century – seeing a gradual improvement in the technology of steam through a number of stepwise developments. Steam allowed scheduled services that ran at higher average speeds than sailing vessels. Large improvements in fuel economy allowed steam to progressively outcompete sail in, ultimately, all commercial situations, giving ship-owning investors a better return on capital.
In the 21st century, most sailing represents a form of recreation
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for enjoyment, amusement, or ple ...
or sport
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, ...
. Recreational sailing or yachting
Yachting is the use of recreational boats and ships called '' yachts'' for racing or cruising. Yachts are distinguished from working ships mainly by their leisure purpose. "Yacht" derives from the Dutch word '' jacht'' ("hunt"). With sailboat ...
can be divided into racing
In sport, racing is a competition of speed, in which competitors try to complete a given task in the shortest amount of time. Typically this involves traversing some distance, but it can be any other task involving speed to reach a specific go ...
and cruising. Cruising can include extended offshore and ocean-crossing trips, coastal sailing within sight of land, and daysailing.
Sailing relies on the physics of sails as they derive power from the wind, generating both lift and drag. On a given course, the sails are set to an angle that optimizes the development of wind power, as determined by the apparent wind
Apparent wind is the wind experienced by a moving object.
Definition of apparent wind
The ''apparent wind'' is the wind experienced by an observer in motion and is the relative velocity of the wind in relation to the observer.
The '' velocit ...
, which is the wind as sensed from a moving vessel. The forces transmitted via the sails are resisted by forces from the hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
, keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in B ...
, and rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally air or water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw a ...
of a sailing craft, by forces from skate runners of an iceboat, or by forces from wheels of a land sailing craft which are steering the course. This combination of forces means that it is possible to sail an upwind course as well as downwind. The course with respect to the true wind direction (as would be indicated by a stationary flag) is called a point of sail
A point of sail is a sailing craft's direction of travel under sail in relation to the true wind direction over the surface.
The principal points of sail roughly correspond to 45° segments of a circle, starting with 0° directly into the wind. ...
. Conventional sailing craft cannot derive wind power on a course with a point of sail that is too close into the wind.
History
Throughout history sailing has been a key form of propulsion that allowed greater mobility than travel over land, whether for exploration, trade, transport, or warfare, and that increased the capacity for fishing, compared to that from shore. Until the significant improvements in land transportation that occurred during the 19th century, if water transport was an option, it was faster, cheaper and safer than making the same journey by land. This applied equally to sea crossings, coastal voyages and use of rivers and lakes. Examples of the consequences of this include the largegrain trade
The grain trade refers to the local and international trade in cereals and other food grains such as wheat, barley, maize, and rice. Grain is an important trade item because it is easily stored and transported with limited spoilage, unlike othe ...
in the Mediterranean during the classical period. Cities such as Rome were totally reliant on the delivery by sailing ships of the large amounts of grain needed. It has been estimated that it cost less for a sailing ship of the Roman Empire to carry grain the length of the Mediterranean than to move the same amount 15 miles by road. Rome consumed about 150,000 tons of Egyptian grain each year over the first three centuries AD.
A similar but more recent trade, in coal, was from the mines situated close to the River Tyne to London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
– which was already being carried out in the 14th century and grew as the city increased in size. In 1795, 4,395 cargoes of coal were delivered to London. This would have needed a fleet of about 500 sailing colliers (making 8 or 9 trips a year). This quantity had doubled by 1839. (The first steam-powered collier was not launched until 1852 and sailing colliers continued working into the 20th century.)
Exploration and research
 The earliest image suggesting the use of sail on a boat may be on a piece of pottery from
The earliest image suggesting the use of sail on a boat may be on a piece of pottery from Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, dated to the 6th millennia BCE. The image is thought to show a bipod mast mounted on the hull of a reed boat – no sail is depicted. The earliest representation of a sail, from Egypt, is dated to circa 3100 BCE. The Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
is considered a suitable place for early use of sail for propulsion. This is because the river's current flows from south to north, whilst the prevailing wind direction is north to south. Therefore, a boat of that time could use the current to go north – an unobstructed trip of 750 miles – and sail to make the return trip.
Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Au ...
used sails from some time before 2000 BCE. Their expansion from what is now Southern China and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northe ...
started in 3000 BCE. Their technology came to include outriggers, catamarans, and crab claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC. It is used in many traditional Austronesian cultures in Isl ...
s, which enabled the Austronesian Expansion
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austro ...
at around 3000 to 1500 BCE into the islands of Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
, and thence to Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and ...
, Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
, Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
, and Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
. Since there is no commonality between the boat technology of China and the Austronesians, these distinctive characteristics must have been developed at or some time after the beginning of the expansion. They traveled vast distances of open ocean in outrigger canoe
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull. They can range from small dugout canoes to large plank-built vessels. Outrigger ...
s using navigation methods such as stick charts. The windward sailing capability of Austronesian boats allowed a strategy of sailing to windward on a voyage of exploration, with a return downwind either to report a discovery or if no land was found. This was well suited to the prevailing winds as Pacific islands were steadily colonised.
By the time of the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafari ...
—starting in the 15th century—square-rigged, multi-masted vessels were the norm and were guided by navigation techniques that included the magnetic compass and making sightings of the sun and stars that allowed transoceanic voyages.
During the Age of Discovery, sailing ships figured in European voyages around Africa to China and Japan; and across the Atlantic Ocean to North and South America. Later, sailing ships ventured into the Arctic to explore northern sea routes and assess natural resources. In the 18th and 19th centuries sailing vessels made Hydrographic survey
Hydrographic survey is the science of measurement and description of features which affect maritime navigation, marine construction, dredging, offshore oil exploration/ offshore oil drilling and related activities. Strong emphasis is placed ...
s to develop charts for navigation and, at times, carried scientists aboard as with the voyages of James Cook and the Second voyage of HMS ''Beagle'' with naturalist Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
.
Commerce

 In the early 1800s, fast blockade-running schooners and brigantines—
In the early 1800s, fast blockade-running schooners and brigantines—Baltimore Clipper
A Baltimore Clipper is a fast sailing ship historically built on the mid-Atlantic seaboard of the United States of America, especially at the port of Baltimore, Maryland. An early form of clipper, the name is most commonly applied to two-masted ...
s—evolved into three-masted, typically ship-rigged sailing vessels with fine lines that enhanced speed, but lessened capacity for high-value cargo, like tea from China. Masts were as high as and were able to achieve speeds of , allowing for passages of up to per 24 hours. Clippers yielded to bulkier, slower vessels, which became economically competitive in the mid 19th century. Sail plans with just fore-and-aft sails (schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schoo ...
s), or a mixture of the two (brigantine
A brigantine is a two-masted sailing vessel with a fully square-rigged foremast and at least two sails on the main mast: a square topsail and a gaff sail mainsail (behind the mast). The main mast is the second and taller of the two masts.
Old ...
s, barque
A barque, barc, or bark is a type of sailing vessel with three or more masts having the fore- and mainmasts rigged square and only the mizzen (the aftmost mast) rigged fore and aft. Sometimes, the mizzen is only partly fore-and-aft rigged, b ...
s and barquentine
A barquentine or schooner barque (alternatively "barkentine" or "schooner bark") is a sailing vessel with three or more masts; with a square rigged foremast and fore-and-aft rigged main, mizzen and any other masts.
Modern barquentine sailing ...
s) emerged. Coastal top-sail schooners with a crew as small as two managing the sail handling became an efficient way to carry bulk cargo, since only the fore-sails required tending while tacking and steam-driven machinery was often available for raising the sails and the anchor.
Iron-hulled sailing ships represented the final evolution of sailing ships at the end of the Age of Sail. They were built to carry bulk cargo for long distances in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. They were the largest of merchant sailing ships, with three to five masts and square sails, as well as other sail plan
A sail plan is a description of the specific ways that a sailing craft is rigged. Also, the term "sail plan" is a graphic depiction of the arrangement of the sails for a given sailing craft.>
In the English language, ships were usually describe ...
s. They carried bulk cargoes between continents. Iron-hulled sailing ships were mainly built from the 1870s to 1900, when steamships began to outpace them economically because of their ability to keep a schedule regardless of the wind. Steel hulls also replaced iron hulls at around the same time. Even into the twentieth century, sailing ships could hold their own on transoceanic voyages such as Australia to Europe, since they did not require bunkerage for coal nor fresh water for steam, and they were faster than the early steamers, which usually could barely make . Ultimately, the steamships' independence from the wind and their ability to take shorter routes, passing through the Suez
Suez ( ar, السويس '; ) is a seaport city (population of about 750,000 ) in north-eastern Egypt, located on the north coast of the Gulf of Suez (a branch of the Red Sea), near the southern terminus of the Suez Canal, having the same b ...
and Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a Channel ( ...
s, made sailing ships uneconomical.
Naval power
Until the general adoption of carvel-built ships that relied on an internal skeleton structure to bear the weight of the ship and for gun ports to be cut in the side, sailing ships were just vehicles for delivering fighters to the enemy for engagement. By 1500, Gun ports allowed sailing vessels to sail alongside an enemy vessel and fire a broadside of multiple cannon. This development allowed for naval fleets to array themselves into aline of battle
The line of battle is a tactic in naval warfare in which a fleet of ships forms a line end to end. The first example of its use as a tactic is disputed—it has been variously claimed for dates ranging from 1502 to 1652. Line-of-battle tacti ...
, whereby, warships
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is built and primarily intended for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the armed forces of a state. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are usually faster and ...
would maintain their place in the line to engage the enemy in a parallel or perpendicular line.
Modern applications

 While the use of sailing vessels for commerce or naval power has been supplanted with engine-driven vessels, there continue to be commercial operations that take passengers on sailing cruises. Modern navies also employ sailing vessels to train cadets in
While the use of sailing vessels for commerce or naval power has been supplanted with engine-driven vessels, there continue to be commercial operations that take passengers on sailing cruises. Modern navies also employ sailing vessels to train cadets in seamanship
Seamanship is the art, knowledge and competence of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The'' Oxford Dictionary'' states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea."
It involves topics an ...
. Recreation or sport accounts for the bulk of sailing in modern boats.
Recreation
Recreational sailing can be divided into two categories, day-sailing, where one gets off the boat for the night, and cruising, where one stays aboard. Day-sailing primarily affords experiencing the pleasure of sailing a boat. No destination is required. It is an opportunity to share the experience with others. A variety of boats with no overnight accommodations, ranging in size from to over , may be regarded as day sailors. Cruising on a sailing yacht may be either near-shore or passage-making out of sight of land and entails the use of sailboats that support sustained overnight use. Coastal cruising grounds include areas of the Mediterranean and Black Seas, Northern Europe, Western Europe and islands of the North Atlantic, West Africa and the islands of the South Atlantic, the Caribbean, and regions of North and Central America. Passage-making under sail occurs on routes through oceans all over the world. Circular routes exist between the Americas and Europe, and between South Africa and South America. There are many routes from the Americas, Australia, New Zealand, and Asia to island destinations in the South Pacific. Some cruisers circumnavigate the globe.Sport
Sailing as a sport is organized on a hierarchical basis, starting at theyacht club
A yacht club is a sports club specifically related to yachting.
Description
Yacht clubs are mostly located by the sea, although there some that have been established at a lake or riverside locations. Yacht or sailing clubs have either a mar ...
level and reaching up into national and international federations; it may entail racing yachts, sailing dinghies, or other small, open sailing craft, including iceboats and land yachts. Sailboat racing is governed by World Sailing
World Sailing (WS) is the world governing body for the sport of sailing recognized by the International Olympic Committee and the International Paralympic Committee (IPC).
History
The creation of the International Yacht Racing Union (IYRU) be ...
with most racing formats using the Racing Rules of Sailing. It entails a variety of different disciplines, including:
*Oceanic racing, held over long distances and in open water, often last multiple days and include world circumnavigation
Circumnavigation is the complete navigation around an entire island, continent, or astronomical body (e.g. a planet or moon). This article focuses on the circumnavigation of Earth.
The first recorded circumnavigation of the Earth was the Magel ...
, such as the Vendée Globe
-->
The Vendée Globe is a single-handed (solo) non-stop round the world yacht race. The race was founded by Philippe Jeantot in 1989, and since 1992 has taken place every four years. It is named after the Département of Vendée, in France ...
and The Ocean Race
The Ocean Race is a yacht race around the world, held every three or four years since 1973. Originally named the Whitbread Round the World Race after its initiating sponsor, British brewing company Whitbread, in 2001 it became the Volvo Ocean R ...
.
*Fleet racing, featuring multiple boats in a regatta that comprises multiple races or heats.
*Match racing comprises two boats competing against each other, as is done with the America's Cup
The America's Cup, informally known as the Auld Mug, is a trophy awarded in the sport of sailing. It is the oldest international competition still operating in any sport. America's Cup match races are held between two sailing yachts: one ...
, vying to cross a finish line, first.
*Team racing between two teams of three boats each in a format analogous to match racing.
*Speed sailing to set new records for different categories of craft with oversight by the World Sailing Speed Record Council
The World Sailing Speed Record Council (WSSRC) was founded in 1972, initially to ratify records at the inaugural Weymouth Speed Week held every year since in Portland Harbor.The WSSRC is the body authorized by the World Sailing (formerly Internati ...
.
*Sail boarding has a variety of disciplines particular to that sport.
Navigation

Point of sail
A sailing craft's ability to derive power from the wind depends on thepoint of sail
A point of sail is a sailing craft's direction of travel under sail in relation to the true wind direction over the surface.
The principal points of sail roughly correspond to 45° segments of a circle, starting with 0° directly into the wind. ...
it is on—the direction of travel under sail in relation to the true wind direction over the surface. The principal points of sail roughly correspond to 45° segments of a circle, starting with 0° directly into the wind. For many sailing craft, the arc spanning 45° on either side of the wind is a "no-go" zone,
where a sail is unable to mobilize power from the wind. Sailing on a course as close to the wind as possible—approximately 45°—is termed "close-hauled". At 90° off the wind, a craft is on a "beam reach". At 135° off the wind, a craft is on a "broad reach". At 180° off the wind (sailing in the same direction as the wind), a craft is "running downwind".
In points of sail that range from close-hauled to a broad reach, sails act substantially like a wing, with lift predominantly propelling the craft. In points of sail from a broad reach to down wind, sails act substantially like a parachute, with drag predominantly propelling the craft. For craft with little forward resistance, such as ice boat
An iceboat (occasionally spelled ice boat or traditionally called an ice yacht) is a recreational or competition sailing craft supported on metal runners for traveling over ice. One of the runners is steerable. Originally, such craft were boats ...
s and land yacht
Land sailing, also known as sand yachting, land yachting or dirtboating, is the act of moving across land in a wheeled vehicle powered by wind through the use of a sail. The term comes from analogy with (water) sailing. Historically, land sai ...
s, this transition occurs further off the wind than for sailboat
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.
Types
Although sailboat terminology ...
s and sailing ship
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships ...
s.
Wind direction for points of sail always refers to the ''true wind''—the wind felt by a stationary observer. The ''apparent wind
Apparent wind is the wind experienced by a moving object.
Definition of apparent wind
The ''apparent wind'' is the wind experienced by an observer in motion and is the relative velocity of the wind in relation to the observer.
The '' velocit ...
''—the wind felt by an observer on a moving sailing craft—determines the motive power
''Motive Power'' is a bi-monthly railway related magazine that focuses on diesel locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been d ...
for sailing craft.
Effect on apparent wind
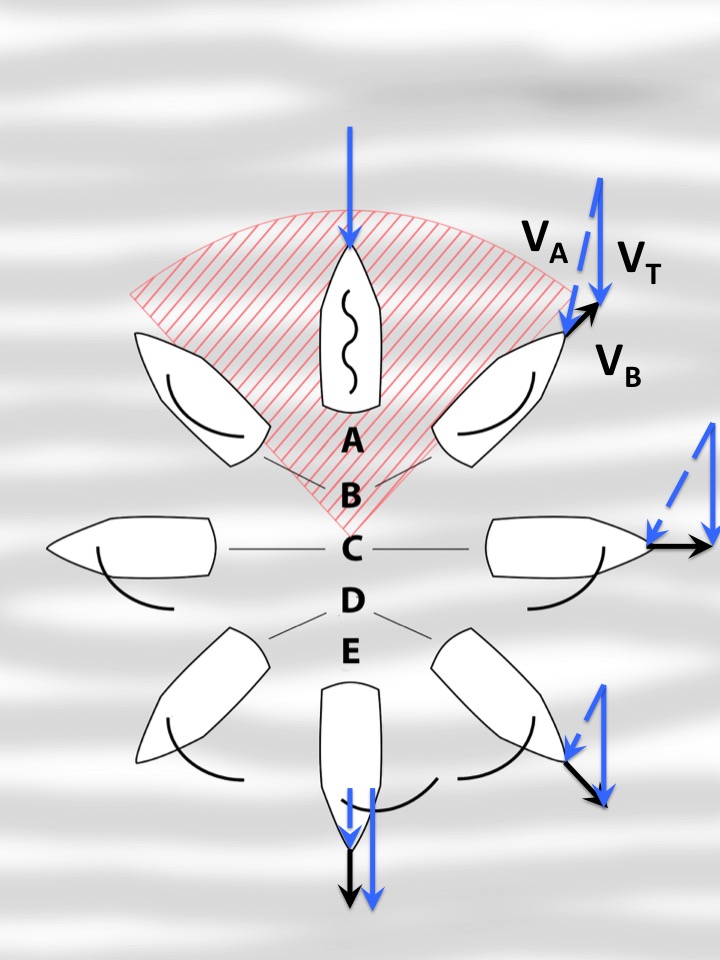
True wind velocity (VT) combines with the sailing craft's velocity (VB) to give the ''apparent wind velocity'' (VA), the air velocity experienced by instrumentation or crew on a moving sailing craft. Apparent wind velocity provides the motive power for the sails on any given point of sail. It varies from being the true wind velocity of a stopped craft in irons in the no-go zone, to being faster than the true wind speed as the sailing craft's velocity adds to the true windspeed on a reach. It diminishes towards zero for a craft sailing dead downwind.As the boat sails further from the wind, the apparent wind becomes smaller and the lateral component becomes less; boat speed is highest on the beam reach. File:Ice boat apparent wind on different points of sail.jpg, Apparent wind on an ''iceboat''.
As the iceboat sails further from the wind, the apparent wind increases slightly and the boat speed is highest on the broad reach. The sail is sheeted in for all three points of sail.
Course under sail
Upwind
A sailing craft can sail on a course anywhere outside of its no-go zone. If the next waypoint or destination is within the arc defined by the no-go zone from the craft's current position, then it must perform a series of tacking maneuvers to get there on a dog-legged route, called ''beating to windward''. The progress along that route is called the ''course made good''; the speed between the starting and ending points of the route is called the ''speed made good'' and is calculated by the distance between the two points, divided by the travel time. The limiting line to the waypoint that allows the sailing vessel to leave it to leeward is called the ''layline''. Whereas some Bermuda-rigged sailing yachts can sail as close as 30° to the wind, most 20th-Century square riggers are limited to 60° off the wind.Fore-and-aft rig
A fore-and-aft rig is a sailing vessel rigged mainly with sails set along the line of the keel, rather than perpendicular to it as on a square rigged vessel.
Description
Fore-and-aft rigged sails include staysails, Bermuda rigged sails, gaff ...
s are designed to operate with the wind on either side, whereas square rig
Square rig is a generic type of sail and rigging arrangement in which the primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spars which are perpendicular, or square, to the keel of the vessel and to the masts. These spars are called '' yards'' ...
s and kite
A kite is a tethered heavier than air flight, heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create Lift (force), lift and Drag (physics), drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. ...
s are designed to have the wind come from one side of the sail only.
Because the lateral wind forces are highest on a sailing vessel, close-hauled and beating to windward, the resisting water forces around the vessel's keel, centerboard, rudder and other foils is also highest to mitigate leeway—the vessel sliding to leeward of its course. Ice boats and land yachts minimize lateral motion with sidewise resistance from their blades or wheels.
=Changing tack by tacking
= ''Tacking'' or ''coming about'' is a maneuver by which a sailing craft turns its bow into and through the wind (referred to as "the eye of the wind") so that the apparent wind changes from one side to the other, allowing progress on the opposite tack. The type of sailing rig dictates the procedures and constraints on achieving a tacking maneuver. Fore-and-aft rigs allow their sails to hang limp as they tack; square rigs must present the full frontal area of the sail to the wind, when changing from side to side; and windsurfers have flexibly pivoting and fully rotating masts that get flipped from side to side.
''Tacking'' or ''coming about'' is a maneuver by which a sailing craft turns its bow into and through the wind (referred to as "the eye of the wind") so that the apparent wind changes from one side to the other, allowing progress on the opposite tack. The type of sailing rig dictates the procedures and constraints on achieving a tacking maneuver. Fore-and-aft rigs allow their sails to hang limp as they tack; square rigs must present the full frontal area of the sail to the wind, when changing from side to side; and windsurfers have flexibly pivoting and fully rotating masts that get flipped from side to side.
Downwind
 A sailing craft can travel directly downwind only at a speed that is less than the wind speed. However, a variety of sailing craft can achieve a higher downwind
A sailing craft can travel directly downwind only at a speed that is less than the wind speed. However, a variety of sailing craft can achieve a higher downwind velocity made good Velocity made good, or VMG, is a term used in sailing, especially in yacht racing, indicating the speed of a sailboat towards (or from) the direction of the wind. The concept is useful because a sailboat cannot sail directly upwind, and thus often c ...
by traveling on a series of broad reaches, punctuated by jibes in between. This is true of ice boats and sand yachts. On the water it was explored by sailing vessels, starting in 1975, and now extends to high-performance skiffs, catamarans and foiling sailboats.
Navigating a channel or a downwind course among obstructions may necessitate changes in direction that require a change of tack, accomplished with a jibe.
=Changing tack by jibing
= ''Jibing'' or ''gybing'' is a sailing maneuver by which a sailing craft turns itsstern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Ori ...
past the eye of the wind so that the apparent wind changes from one side to the other, allowing progress on the opposite tack. This maneuver can be done on smaller boats by pulling the tiller towards yourself (the opposite side of the sail). As with tacking, the type of sailing rig dictates the procedures and constraints for jibing. Fore-and-aft sails with booms, gaffs or sprits are unstable when the free end points into the eye of the wind and must be controlled to avoid a violent change to the other side; square rigs as they present the full area of the sail to the wind from the rear experience little change of operation from one tack to the other; and windsurfers again have flexibly pivoting and fully rotating masts that get flipped from side to side.
Wind and currents
 Winds and oceanic currents are both the result of the sun powering their respective fluid media. Wind powers the sailing craft and the ocean bears the craft on its course, as currents may alter the course of a sailing vessel on the ocean or a river.
*''Wind'' – On a global scale, vessels making long voyages must take
Winds and oceanic currents are both the result of the sun powering their respective fluid media. Wind powers the sailing craft and the ocean bears the craft on its course, as currents may alter the course of a sailing vessel on the ocean or a river.
*''Wind'' – On a global scale, vessels making long voyages must take atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but ...
into account, which causes zones of westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and trend t ...
, easterlies, trade wind
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisp ...
s and high-pressure zones with light winds, sometimes called horse latitude
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a high-pressur ...
s, in between. Sailors predict wind direction and strength with knowledge of high- and low-pressure area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possibl ...
s, and the weather front
A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For ...
s that accompany them. Along coastal areas, sailors contend with diurnal changes in wind direction—flowing off the shore at night and onto the shore during the day.
Local temporary wind shifts are called ''lifts'', when they improve the sailing craft's ability travel along its ''rhumb line
In navigation, a rhumb line, rhumb (), or loxodrome is an arc crossing all meridians of longitude at the same angle, that is, a path with constant bearing as measured relative to true north.
Introduction
The effect of following a rhumb li ...
'' in the direction of the next waypoint. Unfavorable wind shifts are called ''headers''.
*''Currents'' – On a global scale, vessels making long voyages must take major ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contou ...
circulation into account.
Major oceanic currents, like the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Uni ...
in the Atlantic Ocean and the Kuroshio Current
The , also known as the Black or or the is a north-flowing, warm ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean basin. It was named for the deep blue appearance of its waters. Similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, the Ku ...
in the Pacific Ocean require planning for the effect that they will have on a transiting vessel's track. Likewise, tides affect a vessel's track, especially in areas with large tidal ranges, like the Bay of Fundy
The Bay of Fundy (french: Baie de Fundy) is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the U.S. state of Maine. It is an arm of the Gulf of Maine. Its extremely high tidal range is th ...
or along Southeast Alaska
Southeast Alaska, colloquially referred to as the Alaska(n) Panhandle, is the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska, bordered to the east and north by the northern half of the Canadian province of British Columbia (and a small par ...
, or where the tide flows through straits, like Deception Pass
Deception Pass is a strait separating Whidbey Island from Fidalgo Island, in the northwest part of the U.S. state of Washington. It connects Skagit Bay, part of Puget Sound, with the Strait of Juan de Fuca. A pair of bridges known collecti ...
in Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ) is a sound of the Pacific Northwest, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean, and part of the Salish Sea. It is located along the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected m ...
. Mariners use tide and current tables to inform their navigation. Before the advent of motors, it was advantageous for sailing vessels to enter or leave port or to pass through a strait with the tide.
Trimming
 Trimming refers to adjusting the lines that control sails, including the sheets that control angle of the sails with respect to the wind, the halyards that raise and tighten the sail, and to adjusting the hull's resistance to heeling, yawing or progress through the water.
Trimming refers to adjusting the lines that control sails, including the sheets that control angle of the sails with respect to the wind, the halyards that raise and tighten the sail, and to adjusting the hull's resistance to heeling, yawing or progress through the water.
Sails
 In their most developed version, square sails are controlled by two each of: sheets, braces, clewlines, and reef tackles, plus four buntlines, each of which may be controlled by a crew member as the sail is adjusted. Towards the end of the Age of Sail, steam-powered machinery reduced the number of crew required to trim sail.
Adjustment of the angle of a fore-and-aft sail with respect to the apparent wind is controlled with a line, called a "sheet". On points of sail between close-hauled and a broad reach, the goal is typically to create flow along the sail to maximize power through lift. Streamers placed on the surface of the sail, called tell-tales, indicate whether that flow is smooth or turbulent. Smooth flow on both sides indicates proper trim. A jib and mainsail are typically configured to be adjusted to create a smooth laminar flow, leading from one to the other in what is called the "slot effect".
On downwind points of sail, power is achieved primarily with the wind pushing on the sail, as indicated by drooping tell-tales.
In their most developed version, square sails are controlled by two each of: sheets, braces, clewlines, and reef tackles, plus four buntlines, each of which may be controlled by a crew member as the sail is adjusted. Towards the end of the Age of Sail, steam-powered machinery reduced the number of crew required to trim sail.
Adjustment of the angle of a fore-and-aft sail with respect to the apparent wind is controlled with a line, called a "sheet". On points of sail between close-hauled and a broad reach, the goal is typically to create flow along the sail to maximize power through lift. Streamers placed on the surface of the sail, called tell-tales, indicate whether that flow is smooth or turbulent. Smooth flow on both sides indicates proper trim. A jib and mainsail are typically configured to be adjusted to create a smooth laminar flow, leading from one to the other in what is called the "slot effect".
On downwind points of sail, power is achieved primarily with the wind pushing on the sail, as indicated by drooping tell-tales. Spinnaker
A spinnaker is a sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind on courses between a reach (wind at 90° to the course) to downwind (course in the same direction as the wind). Spinnakers are constructed of lightweight fabric, usually n ...
s are light-weight, large-area, highly curved sails that are adapted to sailing off the wind.
In addition to using the sheets to adjust the angle with respect to the apparent wind, other lines control the shape of the sail, notably the outhaul
An outhaul is a control line found on a sailboat. It is an element of the running rigging, used to attach the mainsail clew to the boom and tensions the foot of the sail. It commonly uses a block at the boom end and a cleat on the boom, closer to ...
, halyard
In sailing, a halyard or halliard is a line (rope) that is used to hoist a ladder, sail, flag or yard. The term ''halyard'' comes from the phrase "to haul yards". Halyards, like most other parts of the running rigging, were classically made of ...
, boom vang
A boom vang (US) or kicking strap (UK) (often shortened to "vang" or "kicker") is a line or piston system on a sailboat used to exert downward force on the Boom (sailing), boom and thus control the shape of the sail.
The Collins English Dictionar ...
and backstay. These control the curvature that is appropriate to the windspeed, the higher the wind, the flatter the sail. When the wind strength is greater than these adjustments can accommodate to prevent overpowering the sailing craft, then reducing sail area through reefing, substituting a smaller sail or by other means.
Reducing sail
Reducing sail on square-rigged ships could be accomplished by exposing less of each sail, by tying it off higher up with reefing points. Additionally, as winds get stronger, sails can be furled or removed from the spars, entirely until the vessel is surviving hurricane-force winds under "bare poles". On fore-and-aft rigged vessels, reducing sail may furling the jib and by reefing or partially lowering the mainsail, that is reducing the area of a sail without actually changing it for a smaller sail. This results both in a reduced sail area but also in a lower centre of effort from the sails, reducing the heeling moment and keeping the boat more upright. There are three common methods of reefing the mainsail: *Slab reefing, which involves lowering the sail by about one-quarter to one-third of its full length and tightening the lower part of the sail using anouthaul
An outhaul is a control line found on a sailboat. It is an element of the running rigging, used to attach the mainsail clew to the boom and tensions the foot of the sail. It commonly uses a block at the boom end and a cleat on the boom, closer to ...
or a pre-loaded reef line through a cringle
A cringle is an eye through which to pass a rope. In nautical settings, the word refers to a small hole anywhere along the edge or in the corner of a sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials ...
at the new clew
Sail components include the features that define a sail's shape and function, plus its constituent parts from which it is manufactured. A sail may be classified in a variety of ways, including by its orientation to the vessel (e.g. ''fore-and-a ...
, and hook through a cringle at the new tack.
*In-boom roller-reefing, with a horizontal foil inside the boom. This method allows for standard- or full-length horizontal battens.
*In-mast (or on-mast) roller-reefing. This method rolls the sail up around a vertical foil either inside a slot in the mast, or affixed to the outside of the mast. It requires a mainsail with either no battens
A batten is most commonly a strip of solid material, historically wood but can also be of plastic, metal, or fiberglass. Battens are variously used in construction, sailing, and other fields.
In the lighting industry, battens refer to li ...
, or newly developed vertical battens.
Hull
Hull trim has three aspects, each tied to an axis of rotation, they are controlling: * Heeling (roll about the longitudinal axis) * Helm force (rotation about the vertical axis) * Hull drag (rotation about the horizontal axis amidships) Each is a reaction to forces on sails and is achieved either by weight distribution or by management of the center of force of the underwater foils (keel, daggerboard, etc.), compared with the center of force on the sails.Heeling
 A sailing vessel heels when the boat leans over to the side in reaction to wind forces on the sails.
A sailing vessel's form stability (the resistance of hull shape to rolling) is the starting point for resisting heeling. Catamarans and iceboats have a wide stance that makes them resistant to heeling. Additional measures for trimming a sailing craft to control heeling include:
* Ballast in the keel, which counteracts heeling as the boat rolls.
* Shifting of weight, which might be crew on a trapeze or moveable ballast across the boat.
* Reducing sail
* Adjusting the depth of underwater foils to control their lateral resistance force and center of resistance
A sailing vessel heels when the boat leans over to the side in reaction to wind forces on the sails.
A sailing vessel's form stability (the resistance of hull shape to rolling) is the starting point for resisting heeling. Catamarans and iceboats have a wide stance that makes them resistant to heeling. Additional measures for trimming a sailing craft to control heeling include:
* Ballast in the keel, which counteracts heeling as the boat rolls.
* Shifting of weight, which might be crew on a trapeze or moveable ballast across the boat.
* Reducing sail
* Adjusting the depth of underwater foils to control their lateral resistance force and center of resistance
Helm force
The alignment of center of force of the sails with center of resistance of the hull and its appendices controls whether the craft will track straight with little steering input, or whether correction needs to be made to hold it away from turning into the wind (a weather helm) or turning away from the wind (a lee helm). A center of force behind the center of resistance causes a weather helm. The center of force ahead of the center of resistance causes a lee helm. When the two are closely aligned, the helm is neutral and requires little input to maintain course.Hull drag
Fore-and-aft weight distribution changes the cross-section of a vessel in the water. Small sailing craft are sensitive to crew placement. They are usually designed to have the crew stationed midships to minimize hull drag in the water.Other aspects of seamanship
Seamanship
Seamanship is the art, knowledge and competence of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The'' Oxford Dictionary'' states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea."
It involves topics an ...
encompasses all aspects of taking a sailing vessel in and out of port, navigating it to its destination, and securing it at anchor or alongside a dock. Important aspects of seamanship include employing a common language aboard a sailing craft and the management of lines that control the sails and rigging.
Nautical terms
Nautical terms for elements of a vessel:starboard
Port and starboard are nautical terms for watercraft and aircraft, referring respectively to the left and right sides of the vessel, when aboard and facing the bow (front).
Vessels with bilateral symmetry have left and right halves which a ...
(right-hand side), port or larboard (left-hand side), forward or fore (frontward), aft or abaft (rearward), bow (forward part of the hull), stern (aft part of the hull), beam (the widest part). Spars, supporting sails, include masts, booms, yards, gaffs and poles. Moveable lines that control sails or other equipment are known collectively as a vessel's running rigging
Running rigging is the rigging of a sailing vessel that is used for raising, lowering, shaping and controlling the sails on a sailing vessel—as opposed to the standing rigging, which supports the mast and bowsprit. Running rigging varies betw ...
. Lines that raise sails are called ''halyard
In sailing, a halyard or halliard is a line (rope) that is used to hoist a ladder, sail, flag or yard. The term ''halyard'' comes from the phrase "to haul yards". Halyards, like most other parts of the running rigging, were classically made of ...
s'' while those that strike them are called ''downhauls''. Lines that adjust (trim) the sails are called ''sheets
A bed sheet is a rectangular piece of cloth used either singly or in a pair as bedding, which is larger in length and width than a mattress, and which is placed immediately above a mattress or bed, but below blankets and other bedding (such a ...
''. These are often referred to using the name of the sail they control (such as ''main sheet'' or ''jib sheet''). '' Guys'' are used to control the ends of other spars
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) Women's Reserve, also known as the SPARS (SPARS was the acronym for "Semper Paratus—Always Ready"), was the women's branch of the United States Coast Guard Reserve. It was established by the United States ...
such as spinnaker poles. Lines used to tie a boat up when alongside are called ''docklines'', ''docking cables'' or ''mooring warps''. A ''rode'' is what attaches an anchored boat to its anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal , used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ''ancora'', which itself comes from the Greek ...
.
Management of lines
The following knots are commonly used to handle ropes and lines on sailing craft: *Bowline
The bowline ( or ) is an ancient and simple knot used to form a fixed loop at the end of a rope. It has the virtues of being both easy to tie and untie; most notably, it is easy to untie after being subjected to a load. The bowline is sometimes ...
– forms a loop at the end of a rope or line, useful for lassoing a piling.
* Cleat hitch – affixes a line to a cleat, used with docking lines.
* Clove hitch – two half hitches
Two half-hitches is a type of knot, specifically a binding knot or hitch knot. One variety consists of an overhand knot tied around a post, followed by a half-hitch. This knot is less often referred to as a clove hitch over itself, double half-hi ...
, used for tying onto a post or hanging a fender.
* Figure-eight – a stopper knot, prevents a line from sliding past the opening in a fitting.
* Rolling hitch
The rolling hitch is a knot (see also Magnus hitch) used to attach a rope to a rod, pole, or another rope. A simple friction hitch, it is used for lengthwise pull along an object rather than at right angles. The rolling hitch is designed to re ...
– a friction hitch onto a line or a spar that pulls in one direction and slides in the other.
* Sheet bend – joins two rope ends, when improvising a longer line.
* Reef knot
The reef knot, or square knot, is an ancient and simple binding knot used to secure a rope or line around an object. It is sometimes also referred to as a Hercules knot. The knot is formed by tying a left-handed overhand knot between two end ...
or square knot – used for reefing or storing a sail by tying two ends of a line together.
Lines and halyards are typically coiled neatly for stowage and reuse.
Sail physics
 The physics of sailing arises from a balance of forces between the wind powering the sailing craft as it passes over its sails and the resistance by the sailing craft against being blown off course, which is provided in the water by the
The physics of sailing arises from a balance of forces between the wind powering the sailing craft as it passes over its sails and the resistance by the sailing craft against being blown off course, which is provided in the water by the keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in B ...
, rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally air or water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw a ...
, underwater foils and other elements of the underbody of a sailboat, on ice by the runners of an iceboat
An iceboat (occasionally spelled ice boat or traditionally called an ice yacht) is a recreational or competition sailing craft supported on metal runners for traveling over ice. One of the runners is steerable. Originally, such craft were boats ...
, or on land by the wheels of a sail-powered land vehicle.
Forces on sails depend on wind speed and direction and the speed and direction of the craft. The speed of the craft at a given point of sail contributes to the "apparent wind
Apparent wind is the wind experienced by a moving object.
Definition of apparent wind
The ''apparent wind'' is the wind experienced by an observer in motion and is the relative velocity of the wind in relation to the observer.
The '' velocit ...
"—the wind speed and direction as measured on the moving craft. The apparent wind on the sail creates a total aerodynamic force, which may be resolved into drag
Drag or The Drag may refer to:
Places
* Drag, Norway, a village in Tysfjord municipality, Nordland, Norway
* ''Drág'', the Hungarian name for Dragu Commune in Sălaj County, Romania
* Drag (Austin, Texas), the portion of Guadalupe Street adj ...
—the force component in the direction of the apparent wind—and lift
Lift or LIFT may refer to:
Physical devices
* Elevator, or lift, a device used for raising and lowering people or goods
** Paternoster lift, a type of lift using a continuous chain of cars which do not stop
** Patient lift, or Hoyer lift, mobile ...
—the force component normal (90°) to the apparent wind. Depending on the alignment of the sail with the apparent wind (''angle of attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is ...
''), lift or drag may be the predominant propulsive component. Depending on the angle of attack of a set of sails with respect to the apparent wind, each sail is providing motive force to the sailing craft either from lift-dominant attached flow or drag-dominant separated flow. Additionally, sails may interact with one another to create forces that are different from the sum of the individual contributions of each sail, when used alone.
Apparent wind velocity
The term "velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity i ...
" refers both to speed and direction. As applied to wind, ''apparent wind velocity'' (VA) is the air velocity acting upon the leading edge of the most forward sail or as experienced by instrumentation or crew on a moving sailing craft. In nautical terminology, wind speeds are normally expressed in knots and wind angles in degree
Degree may refer to:
As a unit of measurement
* Degree (angle), a unit of angle measurement
** Degree of geographical latitude
** Degree of geographical longitude
* Degree symbol (°), a notation used in science, engineering, and mathemati ...
s. All sailing craft reach a constant ''forward velocity'' (VB) for a given ''true wind velocity'' (VT) and ''point of sail''. The craft's point of sail affects its velocity for a given true wind velocity. Conventional sailing craft cannot derive power from the wind in a "no-go" zone that is approximately 40° to 50° away from the true wind, depending on the craft. Likewise, the directly downwind speed of all conventional sailing craft is limited to the true wind speed. As a sailboat sails further from the wind, the apparent wind becomes smaller and the lateral component becomes less; boat speed is highest on the beam reach. To act like an airfoil, the sail on a sailboat is sheeted further out as the course is further off the wind. As an iceboat sails further from the wind, the apparent wind increases slightly and the boat speed is highest on the broad reach. In order to act like an airfoil, the sail on an iceboat is sheeted in for all three points of sail.
Lift and drag on sails
 ''Lift'' on a sail, acting as an
''Lift'' on a sail, acting as an airfoil
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is the cross-sectional shape of an object whose motion through a gas is capable of generating significant lift, such as a wing, a sail, or the blades of propeller, rotor, or tur ...
, occurs in a direction ''perpendicular'' to the incident airstream (the apparent wind velocity for the headsail) and is a result of pressure differences between the windward and leeward surfaces and depends on the angle of attack, sail shape, air density, and speed of the apparent wind. The lift force results from the average pressure on the windward surface of the sail being higher than the average pressure on the leeward side. These pressure differences arise in conjunction with the curved airflow. As air follows a curved path along the windward side of a sail, there is a pressure gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p is the "direction and rate of fastest increase". If the gr ...
perpendicular to the flow direction with higher pressure on the outside of the curve and lower pressure on the inside. To generate lift, a sail must present an "angle of attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is ...
" between the chord line of the sail and the apparent wind velocity. The angle of attack is a function of both the craft's point of sail and how the sail is adjusted with respect to the apparent wind.
As the lift generated by a sail increases, so does lift-induced drag
In aerodynamics, lift-induced drag, induced drag, vortex drag, or sometimes drag due to lift, is an aerodynamic drag force that occurs whenever a moving object redirects the airflow coming at it. This drag force occurs in airplanes due to wings or ...
, which together with parasitic drag constitute total ''drag'', which acts in a direction ''parallel'' to the incident airstream. This occurs as the angle of attack increases with sail trim or change of course and causes the lift coefficient
In fluid dynamics, the lift coefficient () is a dimensionless quantity that relates the lift generated by a lifting body to the fluid density around the body, the fluid velocity and an associated reference area. A lifting body is a foil or a ...
to increase up to the point of aerodynamic stall along with the lift-induced drag coefficient
In fluid dynamics, the drag coefficient (commonly denoted as: c_\mathrm, c_x or c_) is a dimensionless quantity that is used to quantify the drag or resistance of an object in a fluid environment, such as air or water. It is used in the drag e ...
. At the onset of stall, lift is abruptly decreased, as is lift-induced drag. Sails with the apparent wind behind them (especially going downwind) operate in a stalled condition.
Lift and drag are components of the total aerodynamic force on sail, which are resisted by forces in the water (for a boat) or on the traveled surface (for an iceboat or land sailing craft). Sails act in two basic modes; under the ''lift-predominant'' mode, the sail behaves in a manner analogous to a ''wing'' with airflow attached to both surfaces; under the ''drag-predominant'' mode, the sail acts in a manner analogous to a ''parachute'' with airflow in detached flow, eddying around the sail.
Lift predominance (wing mode)
Sails allow progress of a sailing craft to windward, thanks to their ability to generate lift (and the craft's ability to resist the lateral forces that result). Each sail configuration has a characteristic coefficient of lift and attendant coefficient of drag, which can be determined experimentally and calculated theoretically. Sailing craft orient their sails with a favorable angle of attack between the entry point of the sail and the apparent wind even as their course changes. The ability to generate lift is limited by sailing too close to the wind when no effective angle of attack is available to generate lift (causing luffing) and sailing sufficiently off the wind that the sail cannot be oriented at a favorable angle of attack to prevent the sail from stalling withflow separation
In fluid dynamics, flow separation or boundary layer separation is the detachment of a boundary layer from a surface into a wake.
A boundary layer exists whenever there is relative movement between a fluid and a solid surface with viscous ...
.
Drag predominance (parachute mode)
When sailing craft are on a course where the angle between the sail and the apparent wind (the angle of attack) exceeds the point of maximum lift, separation of flow occurs. Drag increases and lift decreases with increasing angle of attack as the separation becomes progressively pronounced until the sail is perpendicular to the apparent wind, when lift becomes negligible and drag predominates. In addition to the sails used upwind,spinnaker
A spinnaker is a sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind on courses between a reach (wind at 90° to the course) to downwind (course in the same direction as the wind). Spinnakers are constructed of lightweight fabric, usually n ...
s provide area and curvature appropriate for sailing with separated flow on downwind points of sail, analogous to parachutes, which provide both lift and drag.
Wind variation with height and time
Wind speed increases with height above the surface; at the same time, wind speed may vary over short periods of time as gusts.Wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizon ...
affects sailing craft in motion by presenting a different wind speed and direction at different heights along the mast
Mast, MAST or MASt may refer to:
Engineering
* Mast (sailing), a vertical spar on a sailing ship
* Flagmast, a pole for flying a flag
* Guyed mast, a structure supported by guy-wires
* Mooring mast, a structure for docking an airship
* Radio mast ...
. Wind shear occurs because of friction above a water surface slowing the flow of air. The ratio of wind at the surface to wind at a height above the surface varies by a power law with an exponent of 0.11-0.13 over the ocean. This means that a wind at 3 m above the water would be approximately at above the water. In hurricane-force winds with at the surface the speed at would be This suggests that sails that reach higher above the surface can be subject to stronger wind forces that move the centre of effort on them higher above the surface and increase the heeling moment. Additionally, apparent wind direction moves aft with height above water, which may necessitate a corresponding twist in the shape of the sail to achieve attached flow with height.
Gusts may be predicted by the same value that serves as an exponent for wind shear, serving as a gust factor. So, one can expect gusts to be about 1.5 times stronger than the prevailing wind speed (a 10-knot wind might gust up to 15 knots). This, combined with changes in wind direction suggest the degree to which a sailing craft must adjust sail angle to wind gusts on a given course.
Hull physics
Waterborne sailing craft rely on the design of the hull and keel to provide minimal forward drag in opposition to the sails' propulsive power and maximum resistance to the sails' lateral forces. In modern sailboats, drag is minimized by control of the hull's shape (blunt or fine), appendages, and slipperiness. The keel or other underwater foils provide the lateral resistance to forces on the sails. Heeling increases both drag and the ability of the boat to track along its desired course. Wave generation for a displacement hull is another important limitation on boat speed.Drag
Drag from its form is described by aprismatic coefficient
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refract light. At least one surface must be angled — elements with two parallel surfaces are ''not'' prisms. The most familiar type of optica ...
, Cp = displaced volume of the vessel divided by waterline length times maximum displaced section area—the maximum value of Cp = 1.0 being for a constant displace cross section area, as would be found on a barge. For modern sailboats, values of 0.53 ≤ Cp ≤ 0.6 are likely because of the tapered shape of the submerged hull towards both ends. Reducing interior volume allows creating a finer hull with less drag. Because a keel or other underwater foil produces lift, it also produces drag, which increases as the boat heels. Wetted area of the hull affects total the amount of friction between the water and the hull's surface, creating another component of drag.
Lateral resistance
Sailboats use some sort of underwater foil to generate lift that maintains the forward direction of the boat under sail. Whereas sails operate at angles of attack between 10° to 90° incident to the wind, underwater foils operate at angles of attack between 0° to 10° incident to the water passing by. Neither their angle of attack nor surface is adjustable (except for moveable foils) and they are never intentionally stalled. Heeling the vessel away from perpendicular into the water significantly degrades the boat's ability to point into the wind.Hull speed and beyond
Hull speed
Hull speed or displacement speed is the speed at which the wavelength of a vessel's bow wave is equal to the waterline length of the vessel. As boat speed increases from rest, the wavelength of the bow wave increases, and usually its crest-to-t ...
is the speed at which the wavelength of a vessel's bow wave is equal to its waterline length
A vessel's length at the waterline (abbreviated to L.W.L)Note: originally Load Waterline Length is the length of a ship or boat at the level where it sits in the water (the ''waterline''). The LWL will be shorter than the length of the boat over ...
and is proportional to the square root of the vessel's length at the waterline. Applying more power does not significantly increase the speed of a displacement vessel beyond hull speed. This is because the vessel is climbing up an increasingly steep bow wave with the addition of power without the wave propagating forward faster.
Planing and foiling vessels are not limited by hull speed, as they rise out of the water without building a bow wave with the application of power. Long narrow hulls, such as those of catamarans, surpass hull speed by piercing
Body piercing, which is a form of body modification, is the practice of puncturing or cutting a part of the human body, creating an opening in which jewelry may be worn, or where an implant could be inserted. The word ''piercing'' can refer to ...
through the bow wave. Hull speed does not apply to sailing craft on ice runners or wheels because they do not displace water.
See also
*Dinghy racing
Dinghy racing is a competitive sport using dinghies, which are small boats which may be rowboats, have an outboard motor, or be sailing dinghies. Dinghy racing has affected aspects of the modern sailing dinghy, including hull design, sail mater ...
*High-performance sailing
High-performance sailing is achieved with low forward surface resistance—encountered by catamarans, sailing hydrofoils, iceboats or land sailing craft—as the sailing craft obtains motive power with its sails or aerofoils at speeds that are ...
*Land sailing
Land sailing, also known as sand yachting, land yachting or dirtboating, is the act of moving across land in a wheeled vehicle powered by wind through the use of a sail. The term comes from analogy with (water) sailing. Historically, land sail ...
* Racing Rules of Sailing
*Sailing at the Summer Olympics
Sailing (also known as yachting until 2000) has been one of the Olympic sports since the Games of the I Olympiad, held in Athens, Greece, in 1896. Despite being scheduled in the first Olympic program, the races were canceled due to severe weathe ...
*Single-handed sailing
The sport and practice of single-handed sailing or solo sailing is sailing with only one crewmember (i.e., only one person on board the vessel). The term usually refers to ocean and long-distance sailing and is used in competitive sailing and ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
*"Transportation and Maps" iVirtual Vault
, an online exhibition of Canadian historical art at Library and Archives Canada * Rousmaniere, John, ''The Annapolis Book of Seamanship'', Simon & Schuster, 1999 * ''Chapman Book of Piloting'' (various contributors), Hearst Corporation, 1999 * Herreshoff, Halsey (consulting editor), ''The Sailor's Handbook'', Little Brown and Company, 1983 * Seidman, David, ''The Complete Sailor'', International Marine, 1995 *
Further reading
* {{authority control