|
Apparent Wind
Apparent wind is the wind experienced by a moving object. Definition of apparent wind The ''apparent wind'' is the wind experienced by an observer in motion and is the relative velocity of the wind in relation to the observer. The ''velocity of the apparent wind'' is the vector sum of the ''velocity of the headwind'' (which is the velocity a moving object would experience in still air) plus the ''velocity of the true wind''. The headwind is the additive inverse of the object's velocity; therefore, the ''velocity of the apparent wind'' can also be defined as a vector sum of the ''velocity of the true wind'' minus the ''velocity of the object''. Apparent wind in sailing In sailing, ''apparent wind'' is the speed and direction of wind indicated by a wind instrument (anemometer) on a ''moving'' craft (on water, land or ice) in undisturbed air. It is composed of the ''combined'' speeds and directions of the craft and wind observed by a ''stationary'' wind instrument—the ''true w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Course (navigation)
In navigation, the course of a watercraft or aircraft is the cardinal direction in which the craft is to be steered. The course is to be distinguished from the ''heading'', which is the direction where the watercraft's bow or the aircraft's nose is pointed. Course, track, route and heading The path that a vessel follows over the ground is called a ''ground track'', ''course made good'' or ''course over the ground''. For an aircraft it is simply its ''track''. The intended track is a ''route''. For ships and aircraft, routes are typically straight-line segments between waypoints. A navigator determines the ''bearing'' (the compass direction from the craft's current position) of the next waypoint. Because water currents or wind can cause a craft to drift off course, a navigator sets a ''course to steer'' that compensates for drift. The helmsman or pilot points the craft on a ''heading'' that corresponds to the course to steer. If the predicted drift is correct, then the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
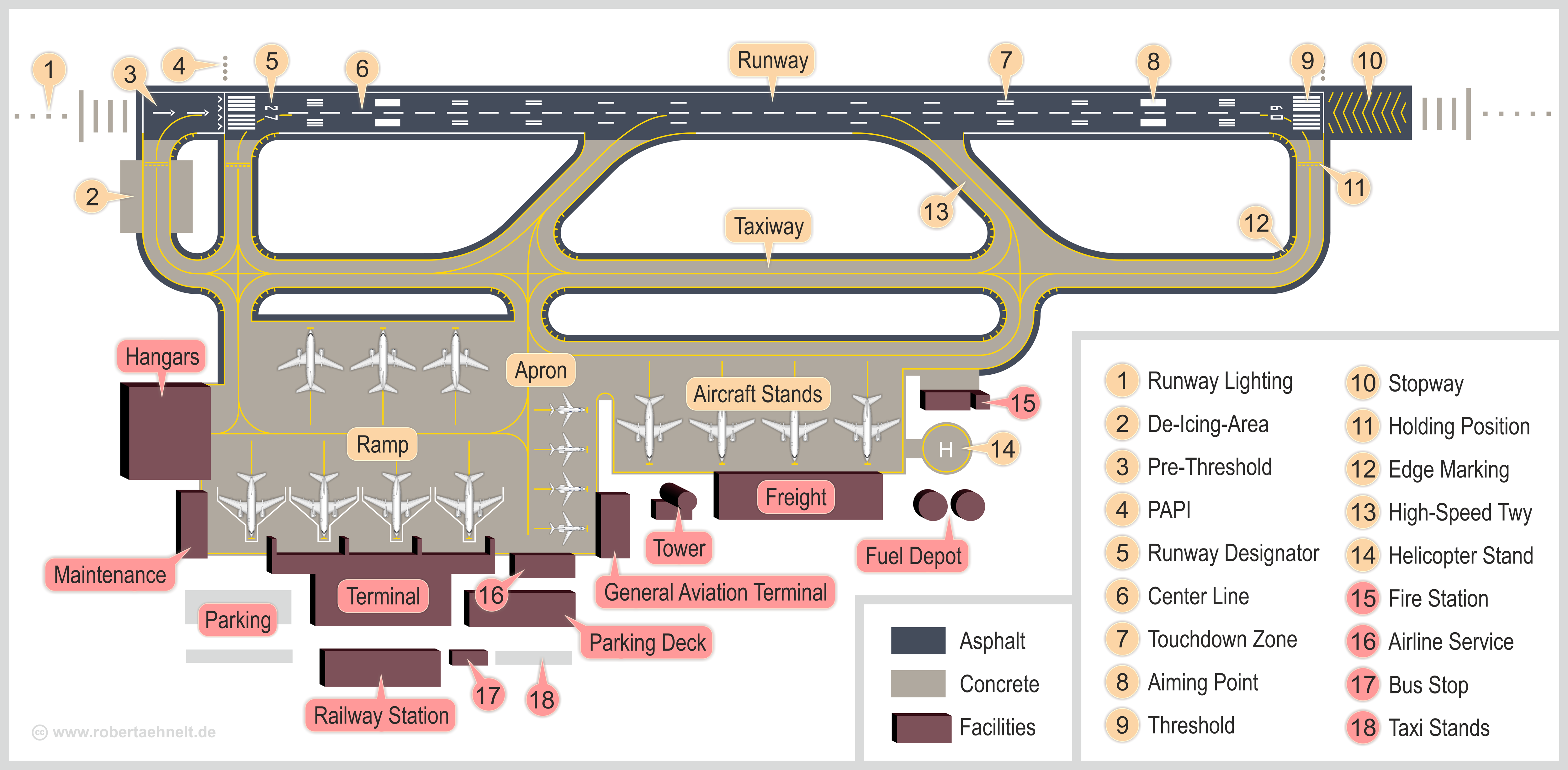
Airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a naval force to project air power worldwide without depending on local bases for staging aircraft operations. Carriers have evolved since their inception in the early twentieth century from wooden vessels used to deploy balloons to nuclear-powered warships that carry numerous fighters, strike aircraft, helicopters, and other types of aircraft. While heavier aircraft such as fixed-wing gunships and bombers have been launched from aircraft carriers, these aircraft have not successfully landed on a carrier. By its diplomatic and tactical power, its mobility, its autonomy and the variety of its means, the aircraft carrier is often the centerpiece of modern combat fleets. Tactically or even strategically, it replaced the battleship in the ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed-wing Aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct from rotary-wing aircraft (in which the wings form a rotor mounted on a spinning shaft or "mast"), and ornithopters (in which the wings flap in a manner similar to that of a bird). The wings of a fixed-wing aircraft are not necessarily rigid; kites, hang gliders, variable-sweep wing aircraft and airplanes that use wing morphing are all examples of fixed-wing aircraft. Gliding fixed-wing aircraft, including free-flying gliders of various kinds and tethered kites, can use moving air to gain altitude. Powered fixed-wing aircraft (airplanes) that gain forward thrust from an engine include powered paragliders, powered hang gliders and some ground effect vehicles. Most fixed-wing aircraft are flown by a pilot on board the craft, but some ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' ("stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers (or surfaces) or between a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, the drag force depends on velocity. Drag force is proportional to the velocity for low-speed flow and the squared velocity for high speed flow, where the distinction between low and high speed is measured by the Reynolds number. Even though the ultimate cause of drag is viscous friction, turbulent drag is independent of viscosity. Drag forces always tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path. Examples Examples of drag include the component of the net aerodynamic or hydrodynamic force acting opposite to the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Sailing
Land sailing, also known as sand yachting, land yachting or dirtboating, is the act of moving across land in a wheeled vehicle powered by wind through the use of a sail. The term comes from analogy with (water) sailing. Historically, land sailing was used as a mode of transportation or recreation. Since the 1950s, it has evolved primarily into a racing sport. Vehicles used in sailing are known as sail wagons, sand yachts, or land yachts. They typically have three (sometimes four) wheels and function much like a sailboat, except that they are operated from a sitting or lying position and steered by pedals or hand levers. Land sailing works best in windy flat areas, and races often happen on beaches, airfields, and dry lake beds in desert regions. Modern land sailors, generally known as "pilots", can go three to four times faster than the wind speed. A gust of wind is considered more beneficial in a land sailing race than a favorable windshift. A similar sport, known as ice yachti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Yachting
An iceboat (occasionally spelled ice boat or traditionally called an ice yacht) is a recreational or competition sailing craft supported on metal runners for traveling over ice. One of the runners is steerable. Originally, such craft were boats with a support structure, riding on the runners and steered with a rear blade, as with a conventional rudder. As iceboats evolved, the structure became a frame with a seat or cockpit for the iceboat sailor, resting on runners. Steering was shifted to the front. Because of their low resistance to forward motion over ice, iceboats are capable of speeds exceeding . Because of their speed, iceboats are used both for recreation and for racing. Racing craft typically carry one person. A related activity, land sailing, employs sailing craft similar to iceboats, but riding on wheels instead of runners. History The history of iceboating began in Europe in areas where smooth ice was found in the bays of the Baltic Sea and the canals of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planing (sailing)
Planing ( ) is the mode of operation for a waterborne craft in which its weight is predominantly supported by hydrodynamic lift, rather than hydrostatic lift (buoyancy). Many forms of marine transport make use of planing, including fast ferries, racing boats, floatplanes, flying boats, seaplanes, and water skis. Most surfboards are planing or semi-planing hulls. Beyond planing, fast vessel designs have seen a transition to hydrofoil designs. History The earliest documented planing sailboat was a proa built in 1898 by Commodore Ralph Munroe. It was capable of speeds of more than twice the hull speed. Planing a sailing dinghy was first popularised by Uffa Fox in Britain. In 1928 Fox introduced planing to the racing world in his International 14 dinghy, ''Avenger''. That year he gained 52 first places, 2 seconds, and 3 third places out of 57 race starts. This performance was noticed by other designers who further developed them. Over the years many dinghies have acquired the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windsurfing
Windsurfing is a wind propelled water sport that is a combination of sailing and surfing. It is also referred to as "sailboarding" and "boardsailing", and emerged in the late 1960s from the aerospace and surf culture of California. Windsurfing gained a popular following across Europe and North America by the late 1970s and had achieved significant global popularity by the 1980s. Windsurfing became an olympic sport in 1984. Newer variants include windfoiling, kiteboarding and wingfoiling. Hydrofoil fins under the board allow the boards to safely lift out of the water and fly silently and smoothly above the surface even in lighter winds. Windsurfing is a recreational, family friendly sport, most popular at flat water locations around the world that offer safety and accessibility for beginner and intermediate participants. Technique and equipment have evolved over the years Major competitive disciplines include slalom, wave and freestyle. Increasingly, "foiling" is replacing trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuselage as the reference line (and also as the longitudinal axis). Some aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |