sabinene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sabinene is a natural bicyclic monoterpene with the molecular formula C10H16. It is isolated from the
essential oil
An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile (easily evaporated at normal temperatures) chemical compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils, aetheroleum, or simply as the o ...
s of a variety of plants including Marjoram, holm oak Holm oak may refer to:
* '' Quercus ilex'', tree native to South and Southeast Europe and parts of France
* '' Quercus rotundifolia'', tree native to the Iberian Peninsula and Northwest Africa
* ''Quercus agrifolia
''Quercus agrifolia'', the Cal ...
(''Quercus ilex'') and Norway spruce
''Picea abies'', the Norway spruce or European spruce, is a species of spruce native to Northern, Central and Eastern Europe.
It has branchlets that typically hang downwards, and the largest cones of any spruce, 9–17 cm long. It is very close ...
(''Picea abies''). It has a strained ring system with a cyclopentane ring fused to a cyclopropane
Cyclopropane is the cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)3, consisting of three methylene groups (CH2) linked to each other to form a ring. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure. Cyclopropane itself ...
ring.
Sabinene is one of the chemical compounds that contributes to the spiciness of black pepper and is a major constituent of carrot seed oil. It also occurs in tea tree oil at a low concentration. It is also present in the essential oil obtained from nutmeg, '' Laurus nobilis'', and '' Clausena anisata''.
Biosynthesis
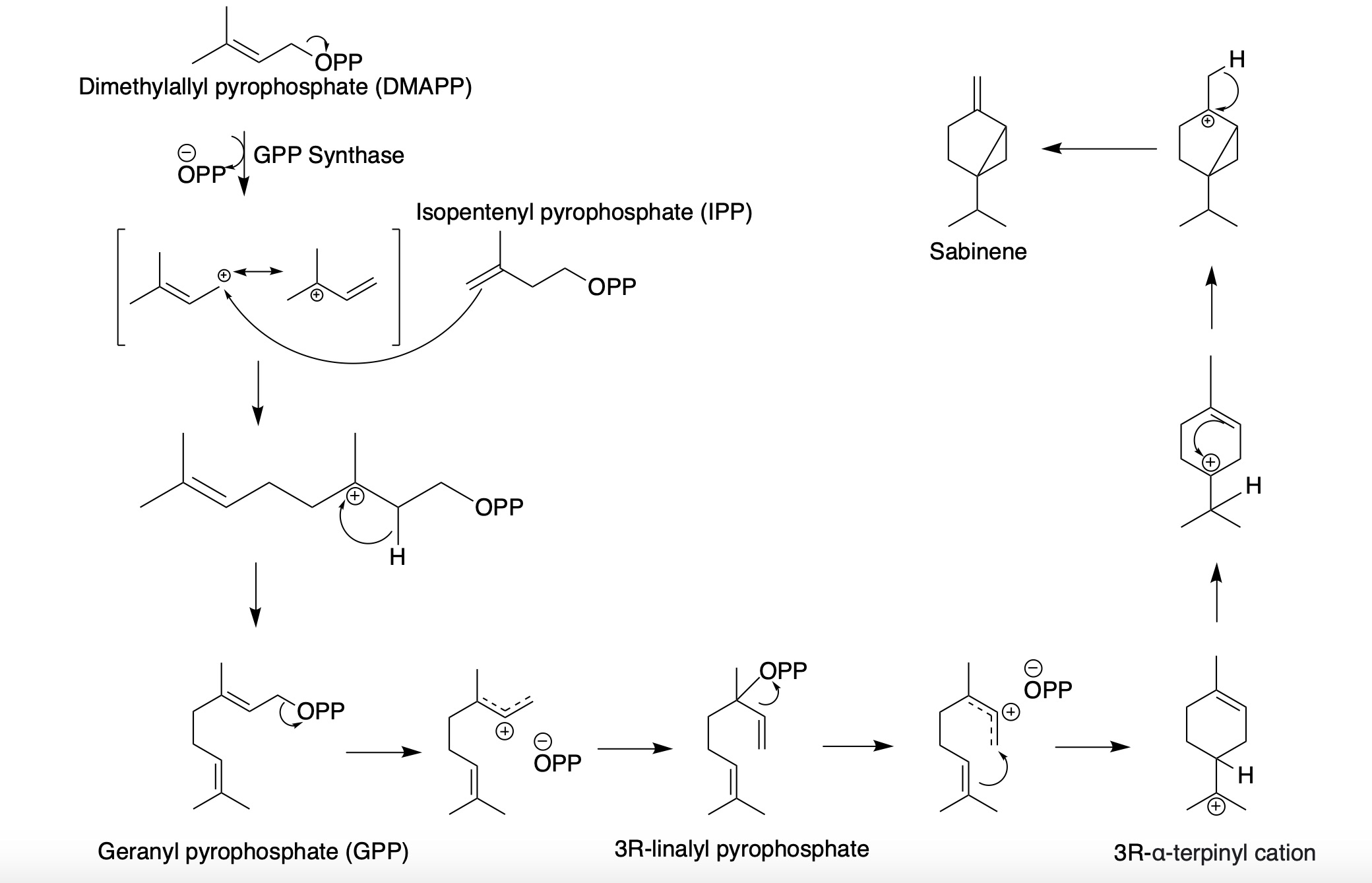
Sabinene, a bicyclic monoterpene, is present in the (+) and (-)enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer ( /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''; from Ancient Greek ἐνάντιος ''(enántios)'' 'opposite', and μέρος ''(méros)'' 'part') – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical ant ...
s. It is biosynthesized from the common terpenoid precursor, geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) that undergoes polycyclization catalyzed by sabinene synthase (SabS). GPP is formed from the terpenoid synthesis pathway with the starter units, isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP). The starter units, IPP and DMAPP, can be synthesized from either the mevalonate (MVA) or the methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway. With the head-to-tail condensation of IPP and DMAPP catalyzed by GPP synthase, GPP is formed. Sabinene synthase (SabS) then catalyzes the ionization and isomerization of GPP to form 3R-linalyl pyrophosphate. Further ionization and cyclization results in the formation of sabinene.

See also
* Thujene, a double bond isomer of sabineneReferences
Hydrocarbons Alkene derivatives Monoterpenes Cyclopropanes Cyclopentanes Isopropyl compounds {{hydrocarbon-stub