Ramp Function on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The ramp function is a unary
The ramp function is a unary
real function
In mathematical analysis, and applications in geometry, applied mathematics, engineering, and natural sciences, a function of a real variable is a function whose domain is the real numbers \mathbb, or a subset of \mathbb that contains an interv ...
, whose graph
Graph may refer to:
Mathematics
*Graph (discrete mathematics), a structure made of vertices and edges
**Graph theory, the study of such graphs and their properties
*Graph (topology), a topological space resembling a graph in the sense of discre ...
is shaped like a ramp
An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle from the vertical direction, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six clas ...
. It can be expressed by numerous definitions
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Definitions can be classified into two large categories: intensional definitions (which try to give the sense of a term), and extensional definiti ...
, for example "0 for negative inputs, output equals input for non-negative inputs". The term "ramp" can also be used for other functions obtained by scaling and shifting, and the function in this article is the ''unit'' ramp function (slope 1, starting at 0).
In mathematics, the ramp function is also known as the positive part
In mathematics, the positive part of a real or extended real-valued function is defined by the formula
: f^+(x) = \max(f(x),0) = \begin f(x) & \mbox f(x) > 0 \\ 0 & \mbox \end
Intuitively, the graph of f^+ is obtained by taking the graph of f, ...
.
In machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
, it is commonly known as a ReLU
In the context of artificial neural networks, the rectifier or ReLU (rectified linear unit) activation function is an activation function defined as the positive part of its argument:
: f(x) = x^+ = \max(0, x),
where ''x'' is the input to a neu ...
activation function
In artificial neural networks, the activation function of a node defines the output of that node given an input or set of inputs.
A standard integrated circuit can be seen as a digital network of activation functions that can be "ON" (1) or " ...
or a rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an Power ...
in analogy to half-wave rectification in electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
. In statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of ...
(when used as a likelihood function
The likelihood function (often simply called the likelihood) represents the probability of random variable realizations conditional on particular values of the statistical parameters. Thus, when evaluated on a given sample, the likelihood funct ...
) it is known as a tobit model
In statistics, a tobit model is any of a class of regression models in which the observed range of the dependent variable is censored in some way. The term was coined by Arthur Goldberger in reference to James Tobin, who developed the model in 19 ...
.
This function has numerous applications
Application may refer to:
Mathematics and computing
* Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks
** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a c ...
in mathematics and engineering, and goes by various names, depending on the context. There are differentiable variants of the ramp function.
Definitions
The ramp function () may be defined analytically in several ways. Possible definitions are: * A piecewise function: * The max function: * Themean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude and sign) of a given data set.
For a data set, the ''arithme ...
of an independent variable
Dependent and independent variables are variables in mathematical modeling, statistical modeling and experimental sciences. Dependent variables receive this name because, in an experiment, their values are studied under the supposition or demand ...
and its absolute value
In mathematics, the absolute value or modulus of a real number x, is the non-negative value without regard to its sign. Namely, , x, =x if is a positive number, and , x, =-x if x is negative (in which case negating x makes -x positive), an ...
(a straight line with unity gradient and its modulus): this can be derived by noting the following definition of , for which and
* The Heaviside step function
The Heaviside step function, or the unit step function, usually denoted by or (but sometimes , or ), is a step function, named after Oliver Heaviside (1850–1925), the value of which is zero for negative arguments and one for positive argume ...
multiplied by a straight line with unity gradient:
* The convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is ...
of the Heaviside step function with itself:
* The integral
In mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented i ...
of the Heaviside step function:
* Macaulay brackets
Macaulay brackets are a notation used to describe the ramp function
:\ = \begin 0, & x < 0 \\ x, & x \ge 0. \end
A popular alternative transcription uses angle brackets, ''viz.'' .R(x) := \langle x\rangle
* The
 In
In 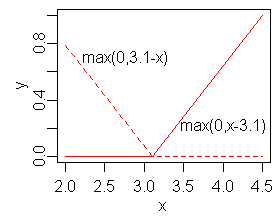 In
In
positive part
In mathematics, the positive part of a real or extended real-valued function is defined by the formula
: f^+(x) = \max(f(x),0) = \begin f(x) & \mbox f(x) > 0 \\ 0 & \mbox \end
Intuitively, the graph of f^+ is obtained by taking the graph of f, ...
of the identity function
Graph of the identity function on the real numbers
In mathematics, an identity function, also called an identity relation, identity map or identity transformation, is a function that always returns the value that was used as its argument, un ...
:
Applications
The ramp function has numerous applications in engineering, such as in the theory ofdigital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are ...
.
finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fina ...
, the payoff of a call option
In finance, a call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a contract between the buyer and the seller of the call option to exchange a security at a set price. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation, to buy an ...
is a ramp (shifted by ''strike price''). Horizontally flipping a ramp yields a put option
In finance, a put or put option is a derivative instrument in financial markets that gives the holder (i.e. the purchaser of the put option) the right to sell an asset (the ''underlying''), at a specified price (the ''strike''), by (or at) a s ...
, while vertically flipping (taking the negative) corresponds to ''selling'' or being "short" an option. In finance, the shape is widely called a "hockey stick
A hockey stick is a piece of sports equipment used by the players in all the forms of hockey to move the ball or puck (as appropriate to the type of hockey) either to push, pull, hit, strike, flick, steer, launch or stop the ball/ puck during pla ...
", due to the shape being similar to an ice hockey stick
An ice hockey stick is a piece of equipment used in ice hockey to shoot, pass, and carry the puck across the ice. Ice hockey sticks are approximately 150–200 cm long, composed of a long, slender shaft with a flat extension at one end c ...
.
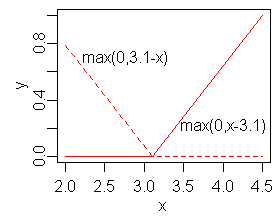 In
In statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of ...
, hinge functions of multivariate adaptive regression splines
In statistics, multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) is a form of regression analysis introduced by Jerome H. Friedman in 1991. It is a non-parametric regression technique and can be seen as an extension of linear models that automaticall ...
(MARS) are ramps, and are used to build regression model
In statistical modeling, regression analysis is a set of statistical processes for estimating the relationships between a dependent variable (often called the 'outcome' or 'response' variable, or a 'label' in machine learning parlance) and one ...
s.
Analytic properties
Non-negativity
In the wholedomain
Domain may refer to:
Mathematics
*Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined
**Domain of definition of a partial function
**Natural domain of a partial function
**Domain of holomorphy of a function
* Do ...
the function is non-negative, so its absolute value
In mathematics, the absolute value or modulus of a real number x, is the non-negative value without regard to its sign. Namely, , x, =x if is a positive number, and , x, =-x if x is negative (in which case negating x makes -x positive), an ...
is itself, i.e.
and
Derivative
Its derivative is theHeaviside step function
The Heaviside step function, or the unit step function, usually denoted by or (but sometimes , or ), is a step function, named after Oliver Heaviside (1850–1925), the value of which is zero for negative arguments and one for positive argume ...
:
Second derivative
The ramp function satisfies the differential equation: where is theDirac delta
In mathematics, the Dirac delta distribution ( distribution), also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function or distribution over the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire ...
. This means that is a Green's function
In mathematics, a Green's function is the impulse response of an inhomogeneous linear differential operator defined on a domain with specified initial conditions or boundary conditions.
This means that if \operatorname is the linear differential ...
for the second derivative operator. Thus, any function, , with an integrable second derivative, , will satisfy the equation:
Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...
where is the Dirac delta
In mathematics, the Dirac delta distribution ( distribution), also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function or distribution over the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire ...
(in this formula, its derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. F ...
appears).
Laplace transform
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace (), is an integral transform
In mathematics, an integral transform maps a function from its original function space into another function space via integra ...
The single-sided Laplace transform
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace (), is an integral transform
In mathematics, an integral transform maps a function from its original function space into another function space via integra ...
of is given as follows,
Algebraic properties
Iteration invariance
Everyiterated function
In mathematics, an iterated function is a function (that is, a function from some set to itself) which is obtained by composing another function with itself a certain number of times. The process of repeatedly applying the same function is ...
of the ramp mapping is itself, as
See also
*Tobit model
In statistics, a tobit model is any of a class of regression models in which the observed range of the dependent variable is censored in some way. The term was coined by Arthur Goldberger in reference to James Tobin, who developed the model in 19 ...
References
{{Reflist Real analysis Special functions