Rolls Royce Eagle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first
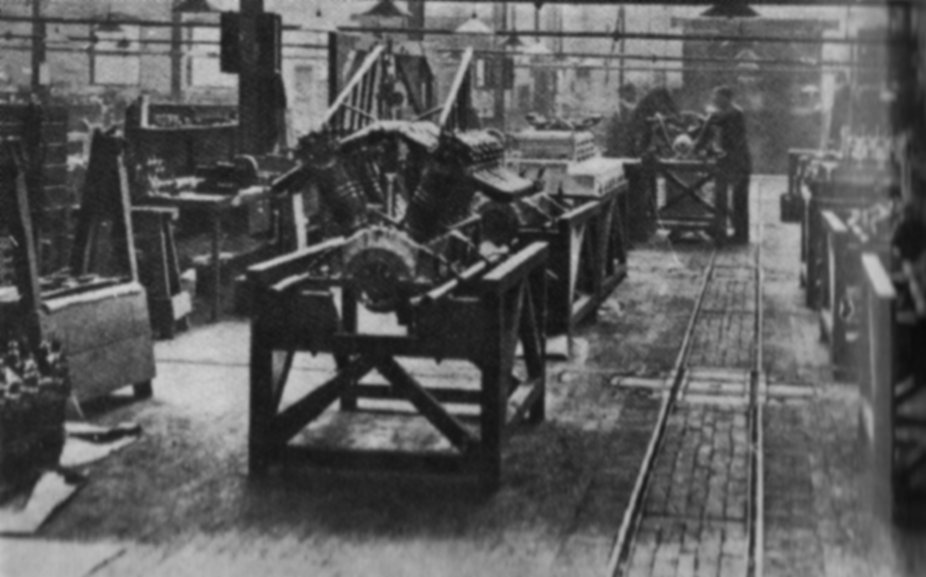 Development of the new 20 litre engine was led by
Development of the new 20 litre engine was led by
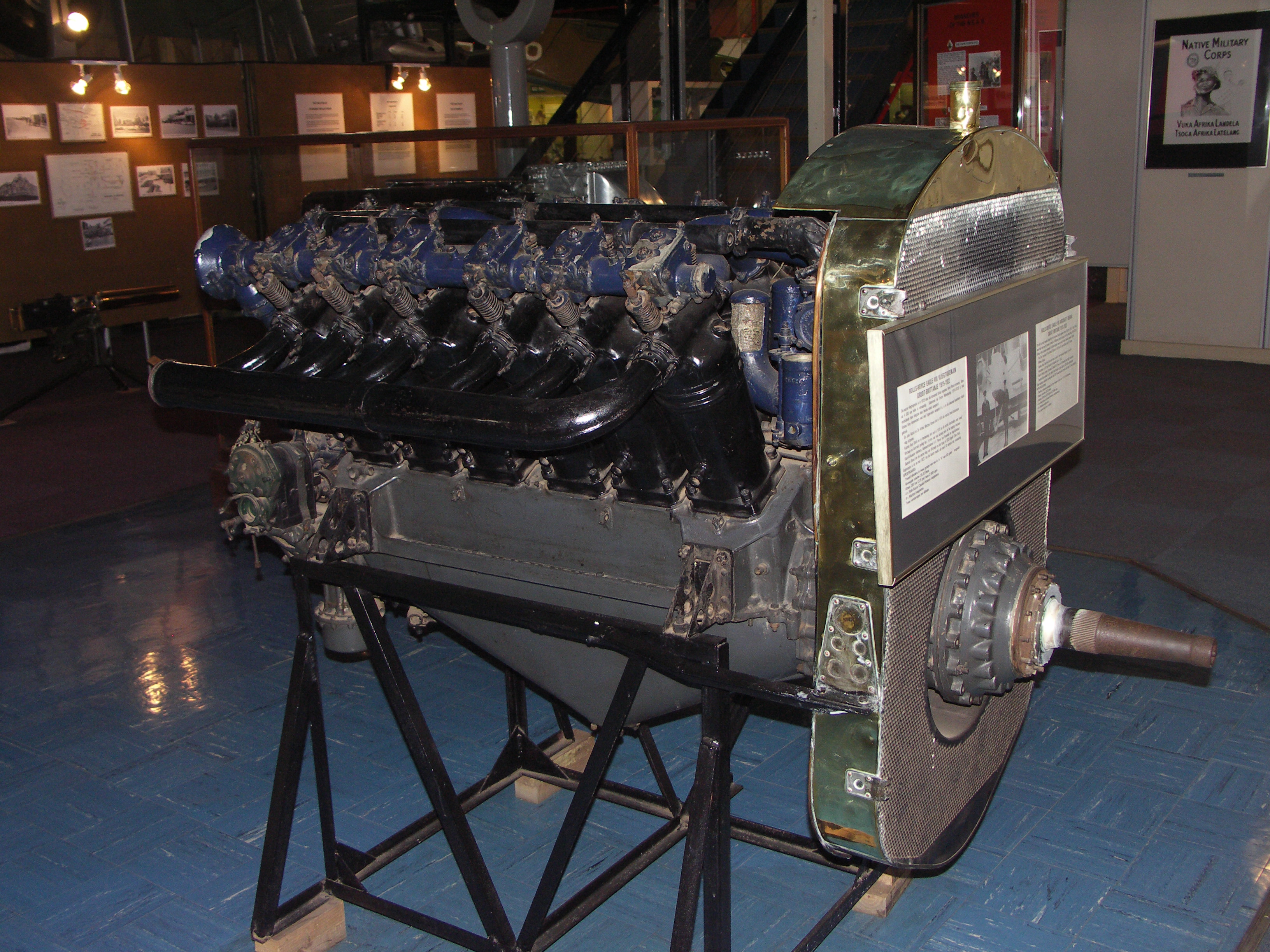 ;Eagle V (''Rolls-Royce 275 hp Mk I'')
:(1916-17), 275 hp, high-lift
;Eagle V (''Rolls-Royce 275 hp Mk I'')
:(1916-17), 275 hp, high-lift
 Examples of the Rolls-Royce Eagle are on display at the:
*
Examples of the Rolls-Royce Eagle are on display at the:
* Derby Industrial Museum - Eagle engine
Retrieved: 3 August 2009
{{Rolls-Royce aeroengines
aircraft engine
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many ...
to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited
Rolls-Royce was a British luxury car and later an aero-engine manufacturing business established in 1904 in Manchester by the partnership of Charles Rolls and Henry Royce. Building on Royce's good reputation established with his cranes, they ...
. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O
The Handley Page Type O was a biplane bomber used by Britain during the First World War. When built, the Type O was the largest aircraft that had been built in the UK and one of the largest in the world. There were two main variants, the Handl ...
bombers and a number of other military aircraft.
The Eagle was the first engine to make a non-stop trans-Atlantic crossing by aeroplane when two Eagles powered the converted Vickers Vimy
The Vickers Vimy was a British heavy bomber aircraft developed and manufactured by Vickers Limited. Developed during the latter stages of the First World War to equip the Royal Flying Corps (RFC), the Vimy was designed by Reginald Kirshaw "Rex" ...
bomber on the transatlantic flight of Alcock and Brown
British aviators John Alcock and Arthur Brown made the first non-stop transatlantic flight in June 1919. They flew a modified First World War Vickers Vimy bomber from St. John's, Newfoundland, to Clifden, County Galway, Ireland. The Secretar ...
in June 1919.
Background
At the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, theRoyal Aircraft Factory
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a cit ...
asked Rolls-Royce to develop a new air-cooled engine. Despite initial reluctance they agreed on condition that it be cooled by water rather than air, as this was the company's area of expertise.
Design and development
 Development of the new 20 litre engine was led by
Development of the new 20 litre engine was led by Henry Royce
Sir Frederick Henry Royce, 1st Baronet, (27 March 1863 – 22 April 1933) was an English engineer famous for his designs of car and aeroplane engines with a reputation for reliability and longevity. With Charles Rolls (1877–1910) and Claude ...
from his home in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
. Based initially on the 7.4 litre 40/50 Rolls-Royce Silver Ghost
The Rolls-Royce Silver Ghost name refers both to a car model and one specific car from that series.
Originally named the " 40/50 h.p." the chassis was first made at Royce's Manchester works, with production moving to Derby in July 1908, ...
engine, and drawing also on the design of a 7.2 litre Daimler DF80 aero engine used in a 1913 Grand Prix Mercedes that had been acquired, the power was increased by doubling the number of cylinders to twelve and increasing their stroke to , although their bore remained at of the 40/50. The engine was also run faster, and an epicyclic reduction gear was designed to keep the propeller speed below 1,100 rpm. To reduce inertia and improve performance the valvetrain design was changed from sidevalves to a SOHC
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine where the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion cha ...
design, closely following the original "side-slot" rocker arm design philosophy used on the contemporary German Mercedes D.I
The Mercedes D.I (also known as the Type E6F) was a six-cylinder, water-cooled, SOHC valvetrain inline engine developed in Germany for use in aircraft in 1913. Developing 75 kW (100 hp), it powered many German military aircraft during t ...
, Mercedes D.II
The Mercedes D.II was a six-cylinder, SOHC valvetrain liquid-cooled inline aircraft engine built by Daimler during the early stages of World War I. Producing about 110 to 120 hp, it was at the low-end of the power range of contemporary eng ...
and Mercedes D.III
The Mercedes D.III, or F1466 as it was known internally, was a six-cylinder SOHC valvetrain liquid-cooled inline aircraft engine built by Daimler and used on a wide variety of German aircraft during World War I. The initial versions were introd ...
straight-six aviation powerplants.
On 3 January 1915 the Admiralty
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
*Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
*Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
* Admiralty, Traf ...
ordered twenty-five of the new engines. The Eagle first ran on a test bed at Rolls-Royce's Derby
Derby ( ) is a city and unitary authority area in Derbyshire, England. It lies on the banks of the River Derwent in the south of Derbyshire, which is in the East Midlands Region. It was traditionally the county town of Derbyshire. Derby gai ...
works in February 1915, producing at 1,600 rpm. This was quickly increased to 1,800, then in August 1915 to 2,000 rpm where it produced . After further testing, it was decided to approve the engine for production at 1,800 rpm and ; 1,900 rpm was allowed for short periods. The engine first flew on a Handley Page O/100
The Handley Page Type O was a biplane bomber used by Britain during the First World War. When built, the Type O was the largest aircraft that had been built in the UK and one of the largest in the world. There were two main variants, the Handle ...
bomber in December 1915, the first flight of a Rolls-Royce aero engine.
The Eagle was developed further during 1916 and 1917, with power being progressively increased from to , followed by , and then , and finally by February 1918 by which time eight Eagle variants had been produced. Throughout World War I Rolls-Royce struggled to build Eagles in the quantities required by the War Office
The War Office was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, when its functions were transferred to the new Ministry of Defence (MoD). This article contains text from ...
, but the company resisted pressure to license other manufacturers to produce it, fearing that the engine's much admired quality would risk being compromised.
After the War, a Mark IX version of the Eagle was developed for civilian use. Production continued until 1928, and in total 4,681 Eagle engines were built.
Time between overhaul
Time between overhauls (abbreviated as TBO or TBOH) is the manufacturer's recommended number of running hours or calendar time before an aircraft engine or other component requires overhaul.
On rotorcraft, many components have recommended or man ...
(TBO) for later Eagles was around 100–180 hours.
Variants
''Note:'' ;Eagle I (''Rolls-Royce 250 hp Mk I'') :(1915), 225 hp, 104 engines produced in both left and right hand tractor versions. ;Eagle II (''Rolls-Royce 250 hp Mk II'') :(1916), 250 hp, 36 built at Derby. ;Eagle III (''Rolls-Royce 250 hp Mk III'') :(1917-1927), 250 hp, increasedcompression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values.
A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the stati ...
(4.9:1), strengthened piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
s. 110 built at Derby.
;Eagle IV (''Rolls-Royce 250 hp Mk IV'')
:(1916-17), 270/286 hp, 36 built at Derby.
 ;Eagle V (''Rolls-Royce 275 hp Mk I'')
:(1916-17), 275 hp, high-lift
;Eagle V (''Rolls-Royce 275 hp Mk I'')
:(1916-17), 275 hp, high-lift camshaft
A camshaft is a shaft that contains a row of pointed cams, in order to convert rotational motion to reciprocating motion. Camshafts are used in piston engines (to operate the intake and exhaust valves), mechanically controlled ignition systems ...
, 100 built at Derby.
;Eagle VI (''Rolls-Royce 275 hp Mk II'')
:(1917), 275 hp, first use of twin spark plugs
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air ...
, 300 built at Derby.
;Eagle VII (''Rolls-Royce 275 hp Mk III'')
:(1917-18), 275 hp, 200 built at Derby.
;Eagle VIII
:(1917-1922), 300 hp, extensive modifications, 3,302 built at Derby.
;Eagle IX
:(1922-1928), 360 hp, developed as a civil use engine, 373 built at Derby.
Applications
*Admiralty N.S.3 North Sea Airship
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
* Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
* Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
*Admiralty, Tr ...
* Admiralty 23 Class Airship
*Airco DH.4
The Aircraft Manufacturing Company Limited (Airco) was an early British aircraft manufacturer. Established during 1912, it grew rapidly during the First World War, referring to itself as the largest aircraft company in the world by 1918.
Air ...
* Airco DH.9
* Airco DH.10 Amiens
* Airco DH.16
*ANEC III
The ANEC III was a 1920s British six-seat passenger and mail carrier aircraft built by Air Navigation and Engineering Company Limited at Addlestone, Surrey.
History
Following a requirement for a passenger and mail carrier for the Australian co ...
*BAT F.K.26
The BAT F.K.26 was a British single-engined four-passenger biplane transport aircraft produced by British Aerial Transport Company Limited of London at the end of World War I.
Design and development
As the First World War drew to a close the a ...
* Blackburn Blackburd
* Curtiss H.12 Large America
* Curtiss-Wanamaker Triplane
*Dornier Do E
The Dornier Do E was a small German flying boat of 1924, designed for reconnaissance missions.
Development
Conceptually, the Do E was very similar to the successful Dornier Wal, but smaller and single-engined. It was of all-metal construction, ...
*Dornier Wal
The Dornier Do J ''Wal'' ("whale") is a twin-engine German flying boat of the 1920s designed by ''Dornier Flugzeugwerke''. The Do J was designated the Do 16 by the Reich Air Ministry (''RLM'') under its aircraft designation system of 1933.
De ...
*Fairey III
The Fairey Aviation Company Fairey III was a family of British reconnaissance biplanes that enjoyed a very long production and service history in both landplane and seaplane variants. First flying on 14 September 1917, examples were still in us ...
*Fairey Campania
The Fairey Campania was a British ship-borne, patrol and reconnaissance aircraft of the First World War and Russian Civil War. It was a single-engine, two-seat biplane with twin main floats and backward-folding wings. The Campania was the first ...
*Felixstowe F.2
The Felixstowe F.2 was a 1917 British flying boat class designed and developed by Lieutenant Commander John Cyril Porte RN at the naval air station, Felixstowe during the First World War adapting a larger version of his superior Felixstowe F. ...
*Felixstowe F.3
The Felixstowe F.3 was a British First World War flying boat, successor to the Felixstowe F.2 designed by Lieutenant Commander John Cyril Porte RN at the naval air station, Felixstowe.
Design and development
In February 1917, the first pro ...
* Felixstowe F.4
*Felixstowe F.5
The Felixstowe F.5 was a British First World War flying boat designed by Lieutenant Commander John Cyril Porte RN of the Seaplane Experimental Station, Felixstowe.
Design and development
Porte designed a better hull for the larger Curtiss H-12 ...
*Fokker F.VII
The Fokker F.VII, also known as the Fokker Trimotor, was an airliner produced in the 1920s by the Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker, Fokker's American subsidiary Atlantic Aircraft Corporation, and other companies under licence.
Design and dev ...
*Grahame-White G.W.E.7
The Grahame-White G.W.E.7 was a British twin-engined transport biplane, designed by M Boudot and built by Grahame-White Aviation Company at Hendon.
Development
The G.W.E.7 was a luxury transport biplane with folding wings, it seated four pas ...
* Handasyde H.2
*Handley Page Type O
The Handley Page Type O was a biplane bomber used by Britain during the First World War. When built, the Type O was the largest aircraft that had been built in the UK and one of the largest in the world. There were two main variants, the Handl ...
*Handley Page V/1500
The Handley Page V/1500 was a British night-flying heavy bomber built by Handley Page towards the end of the First World War. It was a large four-engined biplane, which resembled a larger version of Handley Page's earlier O/100 and O/400 bombers ...
*Handley Page Type W
The Handley Page W.8, W.9 and W.10 were British two- and three-engine medium-range biplane airliners designed and built by Handley Page.
The W.8 (also known as the H.P.18) was the company's first purpose-built civil airliner although it was ...
*Hawker Horsley
The Hawker Horsley was a British single-engined biplane bomber of the 1920s. It was the last all-wooden aircraft built by Hawker Aircraft, and served as a medium day bomber and torpedo bomber with Britain's Royal Air Force between 1926 and 1935 ...
* Porte Baby
* Porte Super Baby
*Martinsyde F.1
__NOTOC__
The Martinsyde F.1 was a British two-seat biplane fighter designed and built by Martinsyde Limited, only two prototypes were built.
Design and development
The F.1 was designed as a fighter for the Royal Flying Corps and it was a la ...
* Rohrbach Ro II
* Rohrbach Ro III
* Royal Aircraft Factory F.E.2
*Royal Aircraft Factory F.E.4
The Royal Aircraft Factory F.E.4 was a twin-engine biplane aircraft built by the Royal Aircraft Factory in 1916. Intended as a cannon armed ground-attack aircraft, it was unsuccessful, only two being built.
Design and development
Shortly after ...
*Royal Aircraft Factory R.E.7
__NOTOC__
The Royal Aircraft Factory R.E.7 was a British two-seat light bomber and reconnaissance biplane designed by the Royal Aircraft Factory and built under contracts by the Coventry Ordnance Works, Austin, Napier and Siddeley-Deasy for the ...
*Short Bomber
The Short Bomber was a British two-seat long-range reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo-carrying aircraft designed by Short Brothers as a land-based development of the very successful Short Type 184 (of which more than 900 were built and many exp ...
* Short N.1B Shirl
*Short Type 184
The Short Admiralty Type 184, often called the Short 225 after the power rating of the engine first fitted, was a British two-seat reconnaissance, bombing and torpedo carrying folding-wing seaplane designed by Horace Short of Short Brothers. It ...
*Sopwith Atlantic
The Sopwith Atlantic was an experimental British long-range aircraft of 1919. It was a single-engined biplane that was designed and built to be the first aeroplane to cross the Atlantic Ocean non-stop. It took off on an attempt to cross the A ...
*Sopwith Wallaby
The Sopwith Wallaby was a British single-engined long-range biplane built during 1919 by Sopwith Aviation Company at Kingston upon Thames.
Development
The Wallaby was designed to compete in an Australian government £10,000 prize for an Englan ...
*Sopwith Tractor Triplane Sopwith may refer to:
* Douglas George Sopwith (1906–1970), Scottish engineer
* Karl Sopwith (1873–1945), English clergyman
* Sopwith Aviation Company, British aircraft manufacturer
* ''Sopwith'' (video game)
* Thomas Sopwith (disambiguation)
...
* Supermarine Commercial Amphibian
* Supermarine Scarab
* Supermarine Sea Eagle
*Supermarine Swan
The Supermarine Swan was a 1920s British experimental amphibian aircraft built by Supermarine at Woolston, Southampton. The single aircraft that was built was used for a passenger service between England and France.
Design and development
The ...
* Van Berkel W-B
*Vickers F.B.11
The Vickers F.B.11 was a prototype British three-seat escort fighter of the First World War. A large single-engined biplane, it carried one gunner in a nacelle mounted on the upper wing to give an allround field of fire. Only a single exampl ...
*Vickers Valparaiso
The Vickers Valparaiso was a British light bomber biplane of the 1920s. It was designed by Vickers as a development of its Vickers Vixen, Vixen for export, being sold to Portugal and Chile.
Development and design
The Vickers Valparaiso was a d ...
*Vickers Vernon
The Vickers Vernon was a British biplane troop carrier used by the Royal Air Force. It entered service in 1921, and was the first dedicated troop transport of the RAF.
The Vernon was a development of the Vickers Vimy Commercial, a passenger v ...
*Vickers Viking
The Vickers Viking was a British single-engine amphibious aircraft designed for military use shortly after World War I. Later versions of the aircraft were known as the Vickers Vulture and Vickers Vanellus.
Design and development
Researc ...
*Vickers Vulcan
The Vickers Vulcan was a British single-engine biplane airliner of the 1920s built by Vickers Limited at Brooklands Aerodrome, Surrey. It carried eight passengers and a pilot.
Development
The Vickers Vulcan was designed by Rex Pierson of ...
*Vickers Vulture
The Vickers Viking was a British single-engine amphibious aircraft designed for military use shortly after World War I. Later versions of the aircraft were known as the Vickers Vulture and Vickers Vanellus.
Design and development
Researc ...
*Vickers Vimy
The Vickers Vimy was a British heavy bomber aircraft developed and manufactured by Vickers Limited. Developed during the latter stages of the First World War to equip the Royal Flying Corps (RFC), the Vimy was designed by Reginald Kirshaw "Rex" ...
*Wight Converted Seaplane
The Wight Converted Seaplane was a British twin-float patrol seaplane produced by John Samuel White & Company Limited (Wight Aircraft).
Design and development
Developed from the unsuccessful Wight Bomber for use as an anti-submarine patrol ai ...
Engines on display
 Examples of the Rolls-Royce Eagle are on display at the:
*
Examples of the Rolls-Royce Eagle are on display at the:
* Polish Aviation Museum
The Polish Aviation Museum ( pl, Muzeum Lotnictwa Polskiego w Krakowie) is a large museum of historic aircraft and aircraft engines in Kraków, Poland. It is located at the site of the no-longer functional Kraków-Rakowice-Czyżyny Air ...
, Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
* Science Museum
A science museum is a museum devoted primarily to science. Older science museums tended to concentrate on static displays of objects related to natural history, paleontology, geology, industry and industrial machinery, etc. Modern trends in mu ...
, London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
* Canada Aviation Museum
The Canada Aviation and Space Museum (french: link=no, Musée de l'Aviation et de l'Espace du Canada) (formerly the Canada Aviation Museum and National Aeronautical Collection) is Canada's national aviation history museum. The museum is located ...
* South African National Museum of Military History
The South African National War Museum in Johannesburg was officially opened by Prime Minister Jan Smuts on 29 August 1947 to preserve the history of South Africa's involvement in the Second World War. In 1975, the museum was renamed the South Af ...
, Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a megacity, and is one of the 100 largest urban areas in the world. According to Demo ...
* South African Air Force Museum
The South African Air Force Museum houses exhibits and restores material related to the history of the South African Air Force. The museum is divided into three locations, AFB Swartkop outside Pretoria, AFB Ysterplaat in Cape Town and at the Por ...
, Port Elizabeth
Gqeberha (), formerly Port Elizabeth and colloquially often referred to as P.E., is a major seaport and the most populous city in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It is the seat of the Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipality, Sou ...
One of the two Eagles that powered Alcock and Brown's historic transatlantic flight is on display at the Derby Industrial Museum
Derby Silk Mill, formerly known as Derby Industrial Museum, is a museum of industry and history in Derby, England. The museum is located on the former site of Lombe's Mill, a historic silk mill which marks the southern end of the Derwent Valley ...
.Retrieved: 3 August 2009
Specifications (Eagle IX)
See also
References
Notes
Bibliography
* Lumsden, Alec. ''British Piston Engines and their Aircraft''. Marlborough, Wiltshire: Airlife Publishing, 2003. . * Pugh, Peter. ''The Magic of a Name - The Rolls-Royce Story: The First 40 Years''. Duxford, Cambridge: Icon Books, 2001. . * Rubbra, A.A.''Rolls-Royce Piston Aero Engines - A Designer Remembers''. Rolls-Royce Heritage Trust. Historical Series no 16. * Taulbut, Derek S. ''Eagle - Henry Royce’s First Aero Engine'', Rolls-Royce Heritage Trust, 2011. .External links
{{Rolls-Royce aeroengines
Eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just ...
1910s aircraft piston engines
Airship engines