Robotic Resupply Spacecraft on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Unmanned spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are
Unmanned spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are
 *
*
 Unmanned spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are
Unmanned spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, p ...
without people
A person (plural, : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of pr ...
on board, used for robotic spaceflight
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly spacecraft into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such as satellites in or ...
. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input; they may be remote controlled, remote guided or even autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ow ...
, meaning they have a pre-programmed list of operations, which they will execute unless otherwise instructed.
Many habitable spacecraft also have varying levels of robotic features. For example, the space stations Salyut 7
Salyut 7 (russian: Салют-7; en, Salute 7) (a.k.a. DOS-6, short for Durable Orbital Station) was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last vi ...
and Mir
''Mir'' (russian: Мир, ; ) was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to&n ...
, and the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ...
module Zarya Zarya may refer to:
*Zorya, personification of dawn in Slavic mythology
* Zarya (antenna), a type of medium-wave broadcasting antenna used in former Soviet Union
*Zarya (ISS module) is a module of the International Space Station.
* ''Zarya'' (magazi ...
, were capable of remote guided station-keeping and docking maneuvers with both resupply craft and new modules. The most common uncrewed spacecraft categories are robotic spacecraft
A robotic spacecraft is an uncrewed spacecraft, usually under telerobotic control. A robotic spacecraft designed to make scientific research measurements is often called a space probe. Many space missions are more suited to telerobotic rather t ...
, unmanned resupply spacecraft, space probe
A space probe is an artificial satellite that travels through space to collect scientific data. A space probe may orbit Earth; approach the Moon; travel through interplanetary space; flyby, orbit, or land or fly on other planetary bodies; or ent ...
space observatories
A space telescope or space observatory is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched ...
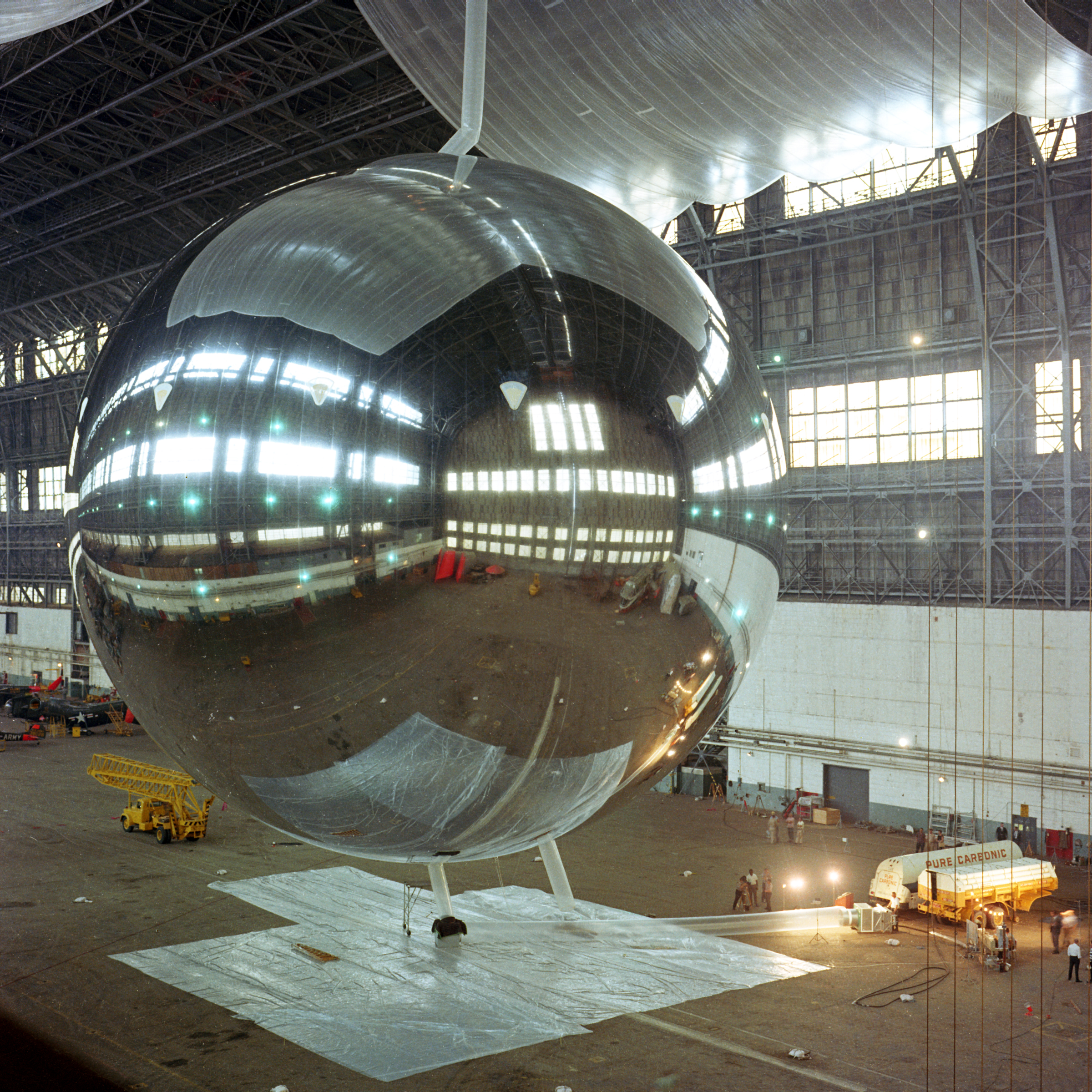
. Not every uncrewed spacecraft is a robotic spacecraft; for example, a reflector ball is a non-robotic uncrewed spacecraft.
Examples
Selected lunar probes
*Luna program
The Luna programme (from the Russian word "Luna" meaning "Moon"), occasionally called ''Lunik'' by western media, was a series of robotic spacecraft missions sent to the Moon by the Soviet Union between 1959 and 1976. Fifteen were successful ...
— USSR Lunar exploration (1959–1976)
* Ranger program
The Ranger program was a series of unmanned space missions by the United States in the 1960s whose objective was to obtain the first close-up images of the surface of the Moon. The Ranger spacecraft were designed to take images of the lunar sur ...
— US Lunar hard-landing probes (1961–1965)
* Zond program
Zond (russian: Зонд, lit=probe) was the name given to two distinct series of Soviet robotic spacecraft launched between 1964 and 1970. The first series, based on the 3MV planetary probe, was intended to gather information about nearby plan ...
— USSR Lunar exploration (1964–1970)
* Surveyor program
The Surveyor program was a NASA program that, from June 1966 through January 1968, sent seven robotic spacecraft to the surface of the Moon. Its primary goal was to demonstrate the feasibility of soft landings on the Moon. The Surveyor craft ...
— US Lunar soft-landing probe (1966–1968)
* Lunar Orbiter program
The Lunar Orbiter program was a series of five uncrewed lunar orbiter missions launched by the United States from 1966 through 1967. Intended to help select Apollo landing sites by mapping the Moon's surface, they provided the first photographs ...
— US Lunar orbital (1966–1967)
* Lunokhod program
Lunokhod ( rus, Луноход, p=lʊnɐˈxot, "Moonwalker") was a series of Soviet robotic lunar rovers designed to land on the Moon between 1969 and 1977. Lunokhod 1 was the first roving remote-controlled robot to land on an extraterrestrial ...
— USSR Lunar Rover
A lunar rover or Moon rover is a space exploration vehicle designed to move across the surface of the Moon. The Apollo Program's Lunar Roving Vehicle was driven on the Moon by members of three American crews, Apollo 15, 16, and 17. Other rov ...
probes (1970–1973)
* MUSES-A
The Hiten spacecraft (ひてん, ), given the English name Celestial Maiden and known before launch as MUSES-A ( Mu Space Engineering Spacecraft A), part of the MUSES Program, was built by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science of Ja ...
(''Hiten Hiten may refer to:
* Hiten (name), Indian given name
* Hiten (spacecraft), Japanese lunar probe
*Tennin
, which may include , , and the specifically female version, the , are a divine kind of spiritual beings found in Japanese Buddhism, the ...
'' and '' Hagoromo'') — Japanese Lunar orbital and hard-landing probes (1990–1993)
* ''Clementine
A clementine (''Citrus × clementina'') is a tangor, a citrus fruit hybrid between a willowleaf mandarin orange ( ''C.'' × ''deliciosa'') and a sweet orange (''C. × sinensis''), named in honor of Clément Rodier, a French missionary who fir ...
'' — US Lunar orbital (1998)
* ''Lunar Prospector
''Lunar Prospector'' was the third mission selected by NASA for full development and construction as part of the Discovery Program. At a cost of $62.8 million, the 19-month mission was designed for a low polar orbit investigation of the Moon, ...
'' — US Lunar orbital (1998–1999)
* ''Smart 1
The Smart #1 (stylised as "smart #1") is a battery electric subcompact crossover SUV developed and produced by Smart Automobile, a joint venture between Mercedes-Benz Group and Geely Holding. It is the first vehicle produced by the joint vent ...
'' — European Lunar orbital (2003)
* ''SELENE
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Selene (; grc-gre, Σελήνη , meaning "Moon"''A Greek–English Lexicon's.v. σελήνη) is the goddess and the personification of the Moon. Also known as Mene, she is traditionally the daughter o ...
'' — Japanese lunar orbiter (2007)
* ''Chang'e 1
Chang'e 1 (; ) was an unmanned Chinese lunar-orbiting spacecraft, part of the first phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. The spacecraft was named after the Chinese Moon goddess, Chang'e.
Chang'e 1 was launched on 24 October 2007 at 10 ...
'' — Chinese lunar orbiter (2007)
* ''Chandrayaan 1
Chandrayaan-1 (, ) was the first Indian lunar probe under the Chandrayaan program. It was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation in October 2008, and operated until August 2009. The mission included a lunar orbiter and an impacto ...
'' — Indian lunar orbiter (2008)
* ''Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit. Data collected by LRO have been described as essential for planning NASA's future human and robotic missions t ...
'' — US Lunar orbiter (2009)
* ''LCROSS
The Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS) was a robotic spacecraft operated by NASA. The mission was conceived as a low-cost means of determining the nature of hydrogen detected at the polar regions of the Moon. Launched immedi ...
'' — US Lunar hard-landing probe (2009)
* ''Chang'e 2
Chang'e 2 (; ) is a Chinese unmanned lunar probe that was launched on 1 October 2010. It was a follow-up to the Chang'e 1 lunar probe, which was launched in 2007. Chang'e 2 was part of the first phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, and ...
'' — Chinese Lunar orbiter (2010)
* ''Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory
The Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) was an American lunar science mission in NASA's Discovery Program which used high-quality gravitational field mapping of the Moon to determine its interior structure. The two small spacecraf ...
'' — US Lunar orbiters (2011)
Mars probes
*Zond program
Zond (russian: Зонд, lit=probe) was the name given to two distinct series of Soviet robotic spacecraft launched between 1964 and 1970. The first series, based on the 3MV planetary probe, was intended to gather information about nearby plan ...
— failed USSR flyby probe
* Mars probe program
The Mars program was a series of uncrewed spacecraft launched by the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1973. The spacecraft were intended to explore Mars, and included flyby probes, landers and orbiters.
Early Mars spacecraft were small, and launch ...
— USSR orbiters and landers
* Viking program
The ''Viking'' program consisted of a pair of identical American space probes, ''Viking 1'' and ''Viking 2'', which landed on Mars in 1976. Each spacecraft was composed of two main parts: an orbiter designed to photograph the surface of Mars f ...
— two NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
orbiters and landers (1974)
* Phobos program
Phobos (Greek for "fear") most commonly refers to:
* Phobos (moon), a moon of Mars
* Phobos (mythology), the Greek god and personification of fear and panic
Phobos may also refer to:
Comics
* Phobos (Marvel Comics)
* Phobos (''W.I.T.C.H.''), a ...
— failed USSR orbiters and Phobos landers
* ''Mars Pathfinder
''Mars Pathfinder'' (''MESUR Pathfinder'') is an American robotic spacecraft that landed a base station with a roving probe on Mars in 1997. It consisted of a lander, renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station, and a lightweight, wheeled robot ...
'' — NASA lander and rover (1997)
* Mars Surveyor '98 program (''Mars Climate Orbiter
The ''Mars Climate Orbiter'' (formerly the Mars Surveyor '98 Orbiter) was a robotic space probe launched by NASA on December 11, 1998, to study the Martian climate, Martian atmosphere, and surface changes and to act as the communications rela ...
'' and ''Mars Polar Lander
The Mars Polar Lander, also known as the Mars Surveyor '98 Lander, was a 290-kilogram robotic spacecraft lander launched by NASA on January 3, 1999, to study the soil and climate of Planum Australe, a region near the south pole on Mars. It for ...
'') — failed NASA probes
* Mars Global Surveyor
''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through the a ...
— NASA orbiter
* Mars Odyssey
''2001 Mars Odyssey'' is a robotic spacecraft orbiting the planet Mars. The project was developed by NASA, and contracted out to Lockheed Martin, with an expected cost for the entire mission of US$297 million. Its mission is to use spectro ...
— NASA orbiter, reached Mars on October 24, 2001
* Mars Observer
The ''Mars Observer'' spacecraft, also known as the ''Mars Geoscience/Climatology Orbiter'', was a robotic space probe launched by NASA on September 25, 1992, to study the Martian surface, atmosphere, climate and magnetic field. During the inte ...
— failed NASA Mars orbiter
* Mars Express
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA). The ''Mars Express'' mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally ref ...
(''Mars Express Orbiter
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA). The ''Mars Express'' mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally ref ...
'' and ''Beagle 2
The ''Beagle 2'' is an inoperative British Mars lander that was transported by the European Space Agency's 2003 ''Mars Express'' mission. It was intended to conduct an astrobiology mission that would have looked for evidence of past life on Mar ...
'') — European orbiter and failed lander 2003
* Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, ''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rover ...
s — NASA rovers (2004)
* ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, an ...
'' — NASA orbiter, entered Martian orbit March 10, 2006
* ''Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
'' — NASA lander, landed May 25, 2008
* '' Mars Science Laboratory'' — NASA rover, launched November 26, 2011
* '' Mars Orbiter Mission '' — Indian orbiter launched by ISRO on 5 November, 2013
* '' Mars 2020'' — NASA rover and helicopter, launched July 30, 2020
Venus probes
*Venera program
The Venera (, , which means "Venus" in Russian) program was the name given to a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus. Ten probes successfully landed on the s ...
— USSR Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
orbiter and lander (1961–1984)
* Pioneer Venus project
The Pioneer Venus project was part of the Pioneer program consisting of two spacecraft, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter and the Pioneer Venus Multiprobe, launched to Venus in 1978. The program was managed by NASA's Ames Research Center.
The Pione ...
— US Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
orbiter and entry probes(1978)
* Vega program
The Vega program (Cyrillic: ВеГа) was a series of Venus missions that also took advantage of the appearance of comet 1P/Halley in 1986. ''Vega 1'' and ''Vega 2'' were uncrewed spacecraft launched in a cooperative effort among the Soviet U ...
— USSR mission to Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
and Comet Halley
Halley's Comet or Comet Halley, officially designated 1P/Halley, is a List of periodic comets, short-period comet visible from Earth every 75–79 years. Halley is the only known short-period comet that is regularly visible to the naked eye fr ...
(1984)
* Magellan probe
The ''Magellan'' spacecraft was a robotic space probe launched by NASA of the United States, on May 4, 1989, to map the surface of Venus by using synthetic-aperture radar and to measure the planetary gravitational field.
The ''Magellan'' pro ...
— US Venus orbiter (1989)
* Venus Express
''Venus Express'' (VEX) was the first Venus exploration mission of the European Space Agency (ESA). Launched in November 2005, it arrived at Venus in April 2006 and began continuously sending back science data from its polar orbit around Venus. ...
— ESA probe sent for the observation of the Venus's weather (2005)
Gas giant probes
*Pioneer program
The Pioneer programs were two series of United States lunar and planetary space probes exploration. The first program, which ran from 1958 to 1960, unsuccessfully attempted to send spacecraft to orbit the Moon, successfully sent one spacecraft to ...
— US Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
flybys
* Voyager program
The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two robotic interstellar probes, ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable alignment of Jupiter and Saturn, to Flyby (spacef ...
— US Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus (mythology), Uranus (Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars (mythology), Mars), grandfather ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
flyby and study of interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
* Galileo probe
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was ...
— US Jupiter orbiter and atmosphere probe (ended 2003)
* '' Cassini-Huygens'' — US-European Saturn orbiter and Titan lander Huygens (1997–2017)
* Juno
Juno commonly refers to:
*Juno (mythology), the Roman goddess of marriage and queen of the gods
*Juno (film), ''Juno'' (film), 2007
Juno may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters
*Juno, in the film ''Jenny, Juno''
*Ju ...
— US Jupiter orbiter (2011–present)
Comet and asteroid probes
 *
* International Cometary Explorer
The International Cometary Explorer (ICE) spacecraft (designed and launched as the International Sun-Earth Explorer-3 (ISEE-3) satellite), was launched 12 August 1978, into a heliocentric orbit. It was one of three spacecraft, along with the mo ...
— passed through gas tail of comet 21P/Giacobini-Zinner (1985)
* Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto ( , ) and Latinised as Giottus, was an Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the Gothic/Proto-Renaissance period. Giot ...
— European — flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* Vega 1 & 2 — USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
— flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* Sakigake
, known before launch as MS-T5, was Japan's first interplanetary spacecraft, and the first deep space probe to be launched by any country other than the USA or the Soviet Union. It aimed to demonstrate the performance of the new launch vehic ...
— Japanese — flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* Suisei Suisei is Japanese for "comet" and the Japanese name for the planet Mercury. It may also stand for:
*Hoshimachi Suisei, Japanese virtual YouTuber
* Suisei (probe)
, originally known as Planet-A, was an unmanned space probe developed by the Ins ...
— Japanese — flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* ''NEAR Shoemaker
''Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous – Shoemaker'' (''NEAR Shoemaker''), renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene Shoemaker, was a robotic space probe designed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laborator ...
'' — US — asteroid 433 Eros
Eros (minor planet designation: (433) Eros), provisional designation is a stony asteroid of the Amor group and the first discovered and second-largest near-Earth object with an elongated shape and a mean diameter of approximately . Visi ...
orbiter, which later landed on the asteroid's surface, launched 1996
* ''Deep Space 1
''Deep Space 1'' (DS1) was a NASA technology demonstration spacecraft which flew by an asteroid and a comet. It was part of the New Millennium Program, dedicated to testing advanced technologies.
Launched on 24 October 1998, the ''Deep Space 1 ...
'' — US — comet 19P/Borrelly
Comet Borrelly or Borrelly's Comet (official designation: 19P/Borrelly) is a periodic comet, which was visited by the spacecraft Deep Space 1 in 2001. The comet last came to perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) on February 1, 2022 and will ...
and asteroid flyby, 1998–2000
* Stardust — US — comet 81P/Wild
Comet 81P/Wild, also known as Wild 2 (pronounced "vilt two") ( ), is a comet named after Swiss astronomer Paul Wild, who discovered it on January 6, 1978, using a 40-cm Schmidt telescope at Zimmerwald, Switzerland.
For most of its 4.5 billion- ...
flyby and sample return, launched 1999, flew-by 2004, returned January 15, 2006
* ''CONTOUR
Contour may refer to:
* Contour (linguistics), a phonetic sound
* Pitch contour
* Contour (camera system), a 3D digital camera system
* Contour, the KDE Plasma 4 interface for tablet devices
* Contour line, a curve along which the function has a ...
'' — US — comet flyby mission (comets 2P, 73P and 6P); lost due to solid rocket motor
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants (fuel/oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder; they were used in warfare by the Arabs, Chinese, Persians ...
failure shortly after launch in 2002
* ''Hayabusa
was a robotic spacecraft developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to return a sample of material from a small near-Earth asteroid named 25143 Itokawa to Earth for further analysis.
''Hayabusa'', formerly known as MUSES-C ...
'' — Japanese — asteroid rendezvous, lander and sample return, launched 2003, returned June 13, 2010
* ''Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The Ro ...
'' — European — comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko orbiter and lander (Philae
; ar, فيلة; cop, ⲡⲓⲗⲁⲕ
, alternate_name =
, image = File:File, Asuán, Egipto, 2022-04-01, DD 93.jpg
, alt =
, caption = The temple of Isis from Philae at its current location on Agilkia Island in Lake Nasse ...
); launched 2004
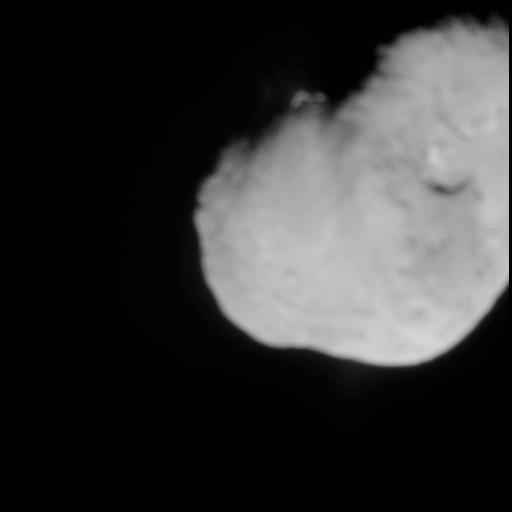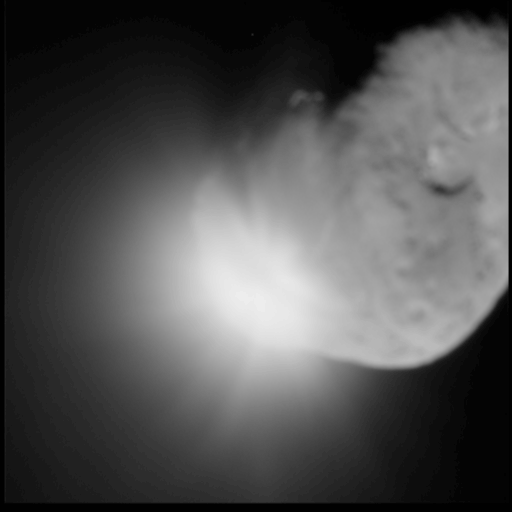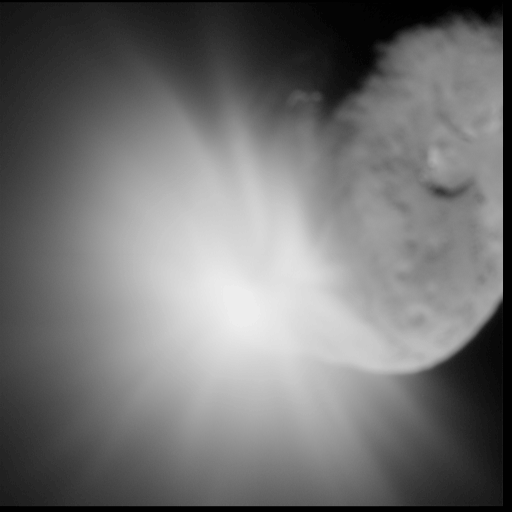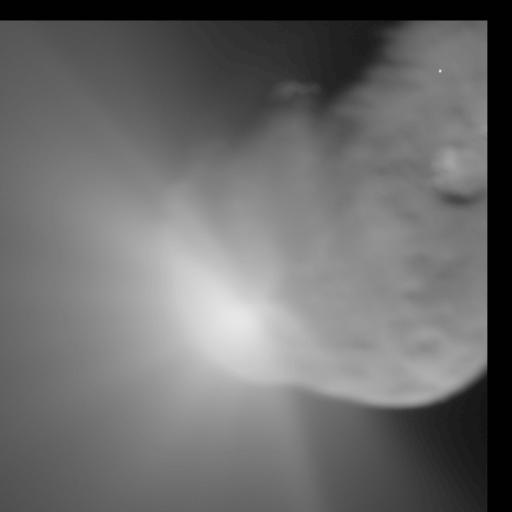
* Deep Impact — successful US comet 9P/Tempel
Tempel 1 (official designation: 9P/Tempel) is a periodic Jupiter-family comet discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1867. It completes an orbit of the Sun every 5.5 years. Tempel 1 was the target of the ''Deep Impact'' space mission, which photogra ...
impactor, launched 2005
* Deep Impact/EPOXI — US — comet 103P/Hartley
Comet Hartley 2, designated as 103P/Hartley by the Minor Planet Center, is a small periodic comet with an orbital period of 6.46 years. It was discovered by Malcolm Hartley in 1986 at the Schmidt Telescope Unit, Siding Spring Observatory, Au ...
flyby (extended Deep Impact mission) — 2010
* Stardust/NExT — US — comet 9P/Tempel
Tempel 1 (official designation: 9P/Tempel) is a periodic Jupiter-family comet discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1867. It completes an orbit of the Sun every 5.5 years. Tempel 1 was the target of the ''Deep Impact'' space mission, which photogra ...
flyby (extended Stardust mission) — 2011
* ''Dawn
Dawn is the time that marks the beginning of twilight before sunrise. It is recognized by the appearance of indirect sunlight being scattered in Earth's atmosphere, when the centre of the Sun's disc has reached 18° below the observer's horizo ...
'' — US launched on September 27, 2007 — orbited Vesta in 2011, and currently orbiting Ceres
Ceres most commonly refers to:
* Ceres (dwarf planet), the largest asteroid
* Ceres (mythology), the Roman goddess of agriculture
Ceres may also refer to:
Places
Brazil
* Ceres, Goiás, Brazil
* Ceres Microregion, in north-central Goiás ...
since 2015
Solar observation probes
*Ulysses
Ulysses is one form of the Roman name for Odysseus, a hero in ancient Greek literature.
Ulysses may also refer to:
People
* Ulysses (given name), including a list of people with this name
Places in the United States
* Ulysses, Kansas
* Ulysse ...
— solar particles and fields (ended 2009)
* Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Bible
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of mankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Book of ...
— first solar wind sample return mission, 2001–2004 (crash)
* ''Interstellar Boundary Explorer
Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX or Explorer 91 or SMEX-10) is a NASA satellite in Earth orbit that uses energetic neutral atoms (ENAs) to image the interaction region between the Solar System and interstellar space. The mission is part of ...
'' (IBEX) — launched October 19, 2008.
* Advanced Composition Explorer
Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE or Explorer 71) is a NASA Explorer program satellite and space exploration mission to study matter comprising energetic particles from the solar wind, the interplanetary medium, and other sources.
Real-tim ...
— solar particles and fields observation at Earth-Sun point
* STEREO
Stereophonic sound, or more commonly stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configuration ...
— pair of probes in solar orbits providing 3D observations of Sun
* SOHO
Soho is an area of the City of Westminster, part of the West End of London. Originally a fashionable district for the aristocracy, it has been one of the main entertainment districts in the capital since the 19th century.
The area was develop ...
— Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, observer for Sun's corona and core located at point
Other Solar System probes
*Zond program
Zond (russian: Зонд, lit=probe) was the name given to two distinct series of Soviet robotic spacecraft launched between 1964 and 1970. The first series, based on the 3MV planetary probe, was intended to gather information about nearby plan ...
— USSR flyby missions to the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
, and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
* Mariner program
The Mariner program was conducted by the American space agency NASA to explore other planets. Between 1962 and late 1973, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) designed and built 10 robotic interplanetary probes named Mariner to explore the in ...
— US Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
, Venus and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
flybys
* MESSENGER
''MESSENGER'' was a NASA robotic space probe that orbited the planet Mercury between 2011 and 2015, studying Mercury's chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field. The name is a backronym for "Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geoche ...
— US Mercury orbiter, launched 2004
* ''New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
'' — US launched on January 19, 2006 — first probe to visit Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the S ...
, successful flyby on 14 July 2015
Interstellar or cosmic observation probes
*Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), originally known as the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP and Explorer 80), was a NASA spacecraft operating from 2001 to 2010 which measured temperature differences across the sky in the cosmic mic ...
— 2001–2010; cosmic microwave background
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all spac ...
Technology demonstrators
*OREX
OREX (Orbital Re-entry Experiment) was a NASDA re-entry demonstrator prototype which was launched in 1994 on the H-II launcher; the satellite was renamed . It was a precursor for the Japanese space shuttle HOPE.
OREX tested various communication ...
(Orbital Re-Entry EXperiment) — Japanese atmospheric reentry and heat shield demonstrator (successfully flown in February 1994)
* Atmospheric Reentry Demonstrator
The Advanced Reentry Demonstrator (ARD) was a European Space Agency (ESA) suborbital reentry vehicle. It was developed and operated for experimental purposes, specifically to validate the multiple reentry technologies integrated upon it and the ve ...
(ARD) — European atmospheric reentry and heat shield demonstrator (successfully flown in October 1998)
* HYFLEX
HYFLEX (Hypersonic Flight Experiment) was a National Space Development Agency of Japan reentry demonstrator prototype which was launched in 1996 on the only flight of the J-I launcher. It was a successor of OREX and was a precursor for the Japan ...
(Hypersonic Flight Experiment) — Japanese uncrewed spaceplane atmospheric reentry demonstrator (successfully flown in February 1996)
* Intermediate eXperimental Vehicle
The Intermediate eXperimental Vehicle (IXV) is a European Space Agency (ESA) experimental suborbital re-entry vehicle. It was developed to serve as a prototype lifting body orbital return vehicle to validate the ESA's work in the field of reus ...
(IXV) — European uncrewed spaceplane atmospheric reentry demonstrator (successfully flown in February 2015)
Uncrewed resupply spacecraft
See also
*List of uncrewed spacecraft by program
Here is an incomplete list of all uncrewed spacecraft categorized by program.
See also
* Timeline of Solar System exploration
This is a timeline of Solar System exploration ordered by date of spacecraft launch. It includes:
*All spacecraft ...
* List of passive satellites
List of passive satellites is a listing of inert or mostly inert satellites, mainly of the Earth. This includes various reflector type satellites typically used for geodesy and atmospheric measurements.
Passive satellites
*Calsphere
**Calspher ...
{{Robotics
Space robots