|
Vega Program
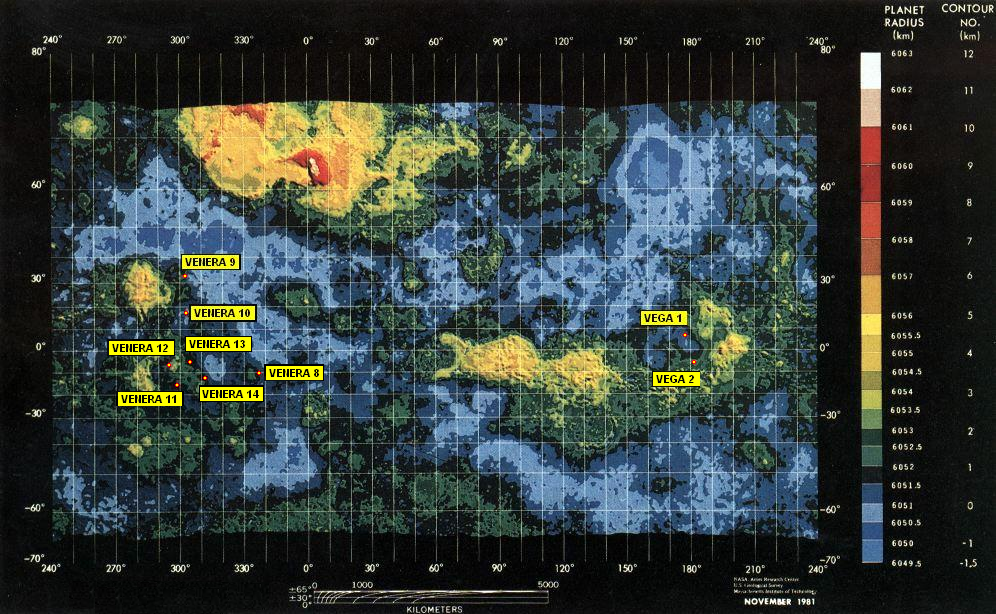
The Vega program (Cyrillic: ВеГа) was a series of Venus missions that also took advantage of the appearance of comet 1P/Halley in 1986. '' Vega 1'' and '' Vega 2'' were uncrewed spacecraft launched in a cooperative effort among the Soviet Union (who also provided the spacecraft and launch vehicle) and Austria, Bulgaria, France, Hungary, the German Democratic Republic, Poland, Czechoslovakia, and the Federal Republic of Germany in December 1984. They had a two-part mission to investigate Venus and also flyby Halley's Comet. The flyby of Halley's Comet had been a late mission change in the Venera program following on from the cancellation of the American Halley mission in 1981. A later Venera mission was canceled and the Venus part of the ''Vega 1'' mission was reduced. Because of this, the craft was designated VeGa, a contraction of ''Venera'' and ''Gallei'' (Венера and Галлей respectively, the Russian words for "Venus" and "Halley"). The spacecraft design was b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera
The Venera (, , which means "Venus" in Russian) program was the name given to a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus. Ten probes successfully landed on the surface of the planet, including the two Vega program and Venera-Halley probes, while thirteen probes successfully entered the Venusian atmosphere. Due to the extreme surface conditions on Venus, the probes could only survive for a short period on the surface, with times ranging from 23 minutes to two hours. The ''Venera'' program established a number of precedents in space exploration, among them being the first human-made devices to enter the atmosphere of another planet ( Venera 3 on 1 March 1966), the first to make a soft landing on another planet ( Venera 7 on 15 December 1970), the first to return images from another planet's surface ( Venera 9 on 8 June 1975), the first to record sounds on another planet ( Venera 13 on 30 October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakh SSR
; kk, Қазақ Советтік Социалистік Республикасы) *1991: Republic of Kazakhstan (russian: Республика Казахстан; kk, Қазақстан Республикасы) , linking_name = the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic , year_start = 1936 , event_start = Elevation to a Union Republic , date_start = 5 December , event1 = Jeltoqsan riots , date_event1 = 16 December 1986 , event2 = Sovereignty declared , date_event2 = 25 October 1990 , event3 = Renamed Republic of Kazakhstan , date_event3 = 10 December 1991 , event4 = Independence declared , date_event4 = 16 December 1991 , date_end = 26 December , event_end = Independence recognised , year_end = 1991 , p1 = Kazakh ASSR , s1 = Kazakhstan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyuratam
Töretam ( kk, link=no, Төретам, Töretam; russian: link=no, Тюратам, Tyuratam) is a station on the main Moscow to Tashkent railway, located in Kazakhstan. The name means "Töre's grave" in the Kazakh language. Töre, or more formally, Töre-Baba, was a noble and descendant of Genghis Khan. Töretam is near the Baikonur Cosmodrome, a Russianformerly Sovietspaceport, and near the city of Baikonur (formerly Leninsk), which was constructed to service the cosmodrome. History In the mid-1950s, the Soviet Union announced that space activities were being conducted from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, which was assumed to be near the city of Baiqongyr, in the Kazakh SSR. In reality, the launch facilities were located to the southwest at Töretam near the city of Leninsk (renamed to Baiqongyr, after the cosmodrome, after the fall of the Soviet Union). At a press conference for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, Jules Bergman of ABC News said, Baikonur, if you'll look on the coordina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur Cosmodrome
''Baiqoñyr ğaryş ailağy'' rus, Космодром Байконур''Kosmodrom Baykonur'' , image = Baikonur Cosmodrome Soyuz launch pad.jpg , caption = The Baikonur Cosmodrome's " Gagarin's Start" Soyuz launch pad prior to the rollout of Soyuz TMA-13, 10 October 2008. , LID = GC0015 , type = Spaceport , owner-oper = Roscosmos Russian Aerospace Forces , location = Kazakhstan (leased to Russia) , opened = , built = , timezone = UTC+06:00 , utc = +06:00 , elevation-m = 90 , metric-elev = y , coordinates = , website = , image_map = , image_mapsize = , image_map_alt = , image_map_caption = , pushpin_map = Kazakhstan#Russia#Soviet Union , push ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
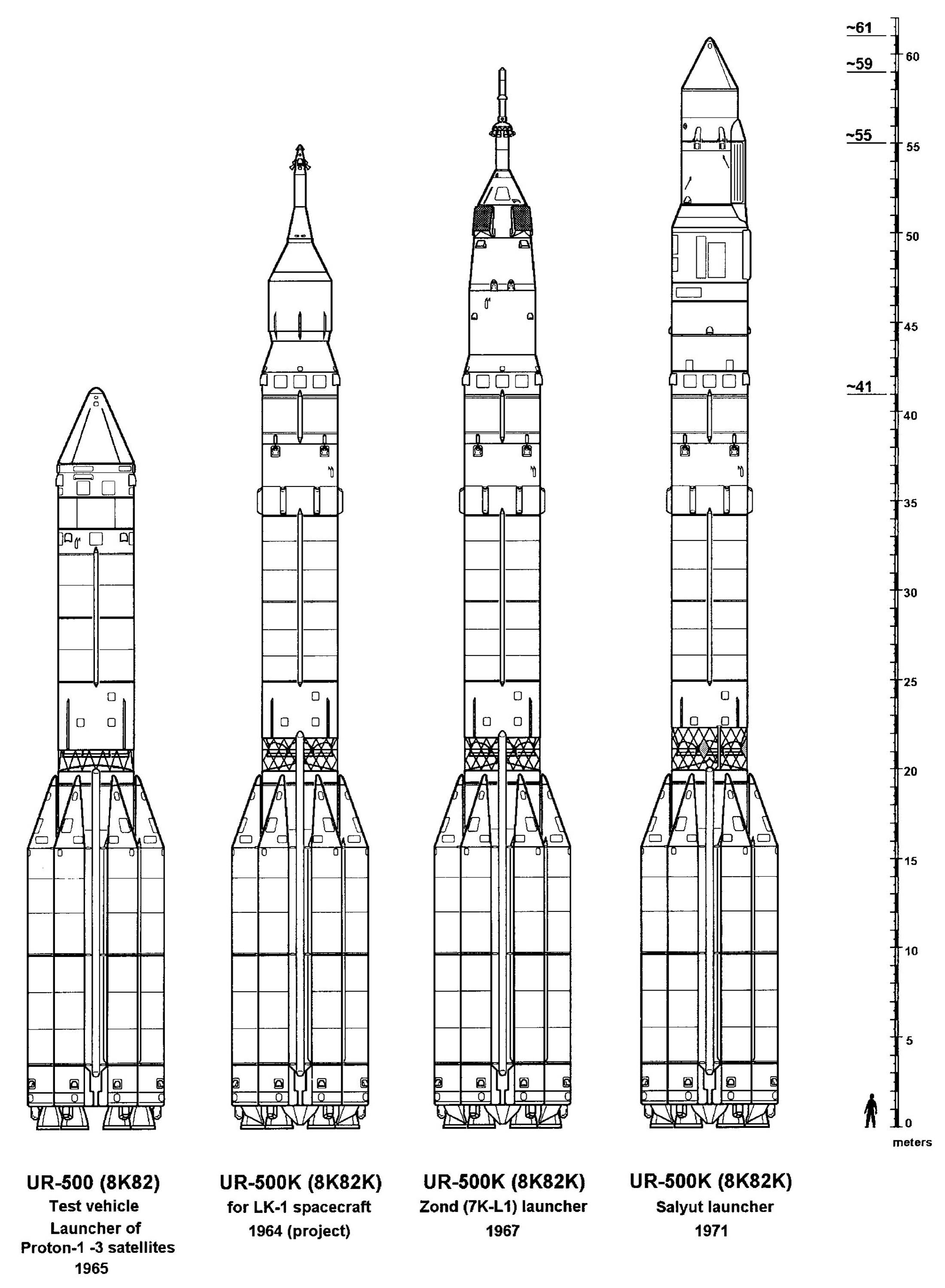
Proton-K
The Proton-K, also designated Proton 8K82K after its GRAU index or SL-12 after its model number, 8K82K, was a Russian, previously Soviet, carrier rocket derived from the earlier Proton. It was built by Khrunichev, and launched from sites 81 and 200 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The maiden flight on 10 March 1967 carried a Soyuz 7K-L1 as part of the Zond program. During the so-called Moon Race these Proton/Soyuz/Zond flights consisted of several uncrewed test flights of Soyuz spacecraft to highly elliptical or circumlunar orbits with the unrealized aim of landing Soviet cosmonauts on the Moon. It was retired from service in favour of the modernised Proton-M, making its 310th and final launch on 30 March 2012. Vehicle description The baseline Proton-K was a three-stage rocket. Thirty were launched in this configuration, with payloads including all of the Soviet Union's ''Salyut'' space stations, all Mir modules with the exception of the Docking Module, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil. The first magnetometer capable of measuring the absolute magnetic intensity at a point in space was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall effect, which is still widely used. Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field, in geophysical surveys, to detect magnetic anomalies of various types, and to determine the dipole moment of magnetic materials. In an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed. In visible light a spectrometer can separate white light and measure individual narrow bands of color, called a spectrum. A mass spectrometer measures the spectrum of the masses of the atoms or molecules present in a gas. The first spectrometers were used to split light into an array of separate colors. Spectrometers were developed in early studies of physics, astronomy, and chemistry. The capability of spectroscopy to determine chemical composition drove its advancement and continues to be one of its primary uses. Spectrometers are used in astronomy to analyze the chemical composition of stars and planets, and spectrometers gather data on the origin of the universe. Examples of spectrometer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khimki
Khimki ( rus, Химки, p=ˈxʲimkʲɪ) is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, 18.25 kilometres northwest of central Moscow, and immediately beyond the Moscow city boundary. History Origins and formation Khimki was initially a railway station that existed since 1850 on the Moscow – Saint Petersburg Railway. The Moskva-Volga Canal was constructed between 1932 and 1937 on which Khimki lies on the west bank. Khimki was then officially founded in 1939. Khimki in the Battle of Moscow The German attack starting the Battle of Moscow (code-named ‘Operation Typhoon’) began on 2 October 1941. The attack on a broad front brought German forces to occupy the village of Krasnaya Polyana (now in the town of Lobnya) to Moscow's North West. Krasnaya Polyana was taken on 30 November. Many sources state that at least one German army patrol visited Khimki. Similarly many sources state this as the closest point the Germans reached to Moscow (Khimki at the time was from the edge of Moscow). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavochkin
NPO Lavochkin (russian: НПО Лавочкина, OKB-301, also called Lavochkin Research and Production Association or shortly Lavochkin Association, LA) is a Russian aerospace company. It is a major player in the Russian space program, being the developer and manufacturer of the Fregat upper stage, as well as interplanetary probes such as Fobos-Grunt. As of 2015, it was headed by Sergei Lemeshevskii. On August 10, 2017 the Lavochkin Association's Board of Directors appointed Vladimir Kolmykov Director General of the enterprise. Overview The company develops and manufactures spacecraft such as the Fregat rocket upper stages, satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a contractor for a number of military programs, such as the Oko early warning satellite, Prognoz and Araks programmes as well as the civilian program Kupon. One of the company's most notable projects was the participation in the failed Fobos-Grunt sample return mission. NPO Lavochkin has also developed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vega Model - Udvar-Hazy Center
Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only from the Sun, and one of the most luminous stars in the Sun's neighborhood. It is the fifth-brightest star in the night sky, and the second-brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus. Vega has been extensively studied by astronomers, leading it to be termed "arguably the next most important star in the sky after the Sun". Vega was the northern pole star around 12,000 BCE and will be so again around the year 13,727, when its declination will be . Vega was the first star other than the Sun to have its image and spectrum photographed. It was one of the first stars whose distance was estimated through parallax measurements. Vega has functioned as the baseline for calibrating the photometric brightness scale and was one of the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perihelion
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion. General description There are two apsides in any elliptic orbit. The name for each apsis is created from the prefixes ''ap-'', ''apo-'' (), or ''peri-'' (), each referring to the farthest and closest point to the primary body the affixing necessary suffix that describes the primary body in the orbit. In this case, the suffix for Earth is ''-gee'', so the apsides' names are ''apogee'' and ''perigee''. For the Sun, its suffix is ''-helion'', so the names are ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion''. According to Newton's laws of motion, all periodic orbits are ellipses. The barycenter of the two bodies may lie well within the bigger body—e.g., the Earth–Moon barycenter is about 75% of the way from Earth's center to its surface. If, compared to the larger mass, the smaller mass is negligible (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)