RO-RO on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Roll-on/roll-off (RORO or ro-ro)
File:Roro faehre.jpg, Loading a ro-ro passenger car ferry
File:PROCYON LEADER.jpg, ''Procyon Leader'' - stern quarter ramp
File:101031 Italie sud 128.jpg,
''Toyota Maru No. 10''
Japan's first pure car carrier, and in 1973 built the ''European Highway'', the largest pure car carrier (PCC) at that time, which carried 4,200 automobiles. Today's pure car carriers and their close cousins, the pure car/truck carrier (PCTC), are distinctive ships with a box-like superstructure running the entire length and breadth of the hull, fully enclosing the cargo. They typically have a stern ramp and a side ramp for dual loading of thousands of vehicles (such as cars, trucks, heavy machineries, tracked units,
File:Roll-On Roll-Off (RO-RO) ship, starboard ramp.jpg, A pure car carrier ship's starboard side showing side


 The first modern train ferry was ''
The first modern train ferry was ''
 During
During
 At the end of the first world war vehicles were brought back from France to Richborough Port drive-on-drive-off using the train ferry. During the war British servicemen recognised the great potential of landing ships and craft. The idea was simple; if you could drive tanks, guns and lorries directly onto a ship and then drive them off at the other end directly onto a beach, then theoretically you could use the same landing craft to carry out the same operation in the civilian commercial market, providing there were reasonable port facilities. From this idea grew the worldwide roll-on/roll-off
At the end of the first world war vehicles were brought back from France to Richborough Port drive-on-drive-off using the train ferry. During the war British servicemen recognised the great potential of landing ships and craft. The idea was simple; if you could drive tanks, guns and lorries directly onto a ship and then drive them off at the other end directly onto a beach, then theoretically you could use the same landing craft to carry out the same operation in the civilian commercial market, providing there were reasonable port facilities. From this idea grew the worldwide roll-on/roll-off  The first RORO service crossing the
The first RORO service crossing the 
 The first roll-on/roll-off vessel that was purpose-built to transport loaded semi trucks was ''Searoad of Hyannis'', which began operation in 1956. While modest in capacity, it could transport three semi trailers between Hyannis in Massachusetts and Nantucket Island, even in ice conditions.
In 1957, the US military issued a contract to the Sun Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company in
The first roll-on/roll-off vessel that was purpose-built to transport loaded semi trucks was ''Searoad of Hyannis'', which began operation in 1956. While modest in capacity, it could transport three semi trailers between Hyannis in Massachusetts and Nantucket Island, even in ice conditions.
In 1957, the US military issued a contract to the Sun Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company in
ship
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished ...
s are cargo ship
A cargo ship or freighter is a merchant ship that carries cargo, goods, and materials from one port to another. Thousands of cargo carriers ply the world's seas and oceans each year, handling the bulk of international trade. Cargo ships are usu ...
s designed to carry wheeled cargo
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including trans ...
, such as cars, motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruising ...
s, truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame constructi ...
s, semi-trailer truck
A semi-trailer truck, also known as a semitruck, (or semi, eighteen-wheeler, big rig, tractor-trailer or, by synecdoche, a semitrailer) is the combination of a tractor unit and one or more semi-trailers to carry freight. A semi-traile ...
s, bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
es, trailers
Trailer may refer to: a
Transportation
* Trailer (vehicle), an unpowered vehicle pulled by a powered vehicle
** Bicycle trailer, a wheeled frame for hitching to a bicycle to tow cargo or passengers
** Full-trailer
** Semi-trailer
**Horse trail ...
, and railroad cars, that are driven on and off the ship on their own wheels or using a platform vehicle, such as a self-propelled modular transporter
Self-propelled may refer to
* Human-powered transport, humans moving themselves (and their cargo) via their own muscle energy
* Machines that power their own movement:
** Automobile (from ''auto-'' + ''mobile'', "self-moving")
** Locomotive (fr ...
. This is in contrast to lift-on/lift-off
Lift-on/lift-off or LoLo ships are cargo ships with on-board cranes
to load and unload cargo. While the common abbreviation of ''lift-on/lift-off'' is ''LoLo'', it is sometimes abbreviated as ''LOLO'', ''LO/LO'' or ''Lo/Lo''. Ships with cranes ...
(LoLo) vessels, which use a crane to load and unload cargo.
RORO vessels have either built-in or shore-based ramps
An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle from the vertical direction, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six clas ...
or ferry slip
A ferry slip is a specialized docking facility that receives a ferryboat or train ferry. A similar structure called a barge slip receives a barge or car float that is used to carry wheeled vehicles across a body of water.
Often a ferry intend ...
s that allow the cargo to be efficiently rolled on and off the vessel when in port. While smaller ferries that operate across river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
s and other short distances often have built-in ramps, the term RORO is generally reserved for large oceangoing vessels. The ramps and doors may be located in the stern, bow, or sides, or any combination thereof.
Description
Types of RORO vessels includeferries
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water tax ...
, cruiseferries
A cruiseferry is a ship that combines the features of a cruise ship and a Ro-Pax ferry. Many passengers travel with the ships for the cruise experience, staying only a few hours at the destination port or not leaving the ship at all, while ot ...
, cargo ship
A cargo ship or freighter is a merchant ship that carries cargo, goods, and materials from one port to another. Thousands of cargo carriers ply the world's seas and oceans each year, handling the bulk of international trade. Cargo ships are usu ...
s, barge
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels ...
s, and RoRo service for air deliveries. New automobiles that are transported by ship are often moved on a large type of RORO called a pure car carrier (PCC) or pure car/truck carrier (PCTC).
Elsewhere in the shipping industry, cargo is normally measured by the tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
, but RORO cargo is typically measured in '' lanes in metres'' (LIMs). This is calculated by multiplying the cargo length in metres by the number of decks and by its width in lanes (lane width differs from vessel to vessel, and there are several industry standards). On PCCs, cargo capacity is often measured in RT or RT43 units (based on a 1966 Toyota Corona, the first mass-produced car to be shipped in specialised car-carriers and used as the basis of RORO vessel size. 1 RT is approximately 4m of lane space required to store a 1.5m wide Toyota Corona) or in car-equivalent units ( CEU).
The largest RORO passenger ferry is , a 75,100 GT cruise ferry that entered service in September 2007 for Color Line. Built in Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
by Aker Finnyards, it is long and wide, and can carry 550 cars, or 1270 lane meters of cargo.
The RORO passenger ferry with the greatest car-carrying capacity is ''Ulysses'' (named after a novel by James Joyce
James Augustine Aloysius Joyce (2 February 1882 – 13 January 1941) was an Irish novelist, poet, and literary critic. He contributed to the modernist avant-garde movement and is regarded as one of the most influential and important writers of ...
), owned by Irish Ferries
Irish Ferries is an Irish ferry and transport company that operates passenger and freight services on routes between Ireland, Britain and Continental Europe, including Dublin Port–Holyhead; Rosslare Europort to Pembroke as well as Dublin ...
. ''Ulysses'' entered service on 25 March 2001 and operates between Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of th ...
and Holyhead. The 50,938 GT ship is long and wide, and can carry 1342 cars/4101 lane meters of cargo.
Train ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry railway vehicles. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the front and/or rear to give access to the wharves. In the United States, train ...
and roll-on/roll-off between Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
File:Ulysses Arriving In Dublin.jpg, ROPAX ferry, MS ''Ulysses'', approaching Dublin Port, Ireland
File:SuperSpeed 2.jpg, Fast ROPAX cruiseferry, MS ''SuperSpeed 2'', between Larvik
Larvik () is a List of cities in Norway, town and Municipalities of Norway, municipality in Vestfold in Vestfold og Telemark Counties of Norway, county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Larvik. The municipality ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
and Hirtshals
Hirtshals is a town and seaport on the coast of Skagerrak on the island of Vendsyssel-Thy at the top of the Jutland peninsula in northern Denmark, Europe. It is located in Hjørring municipality in Region Nordjylland. The town of Hirtshals has a p ...
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
File:Queenscliff ferry terminal.jpg, Ferry terminal for the Peninsula Searoad Transport
Searoad Ferries (formerly known as Peninsula Searoad Transport) is an Australian company that operates a roll-on/roll-off vehicle and passenger ferry service between the heads of Port Phillip, near Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
The route ...
service, with cars leaving a ferry
Car carriers
The first cargo ships specially fitted for the transport of large quantities of cars came into service in the early 1960s. These ships still had their own loading gear and so-called hanging decks inside. They were, for example, chartered by the GermanVolkswagen AG
Volkswagen AG (), known internationally as the Volkswagen Group, is a German multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial ...
to transport vehicles to the U.S. and Canada. During the 1970s, the market for exporting and importing cars has increased dramatically and the number and type of ROROs has increased also.
In 1970 Japan's K Line
is a Japanese transportation company. It owns a fleet that includes dry cargo ships (bulk carriers), container ships, liquefied natural gas carriers, Ro-Ro ships, tankers, and container terminals. It used to be the fourteenth largest contai ...
built th''Toyota Maru No. 10''
Japan's first pure car carrier, and in 1973 built the ''European Highway'', the largest pure car carrier (PCC) at that time, which carried 4,200 automobiles. Today's pure car carriers and their close cousins, the pure car/truck carrier (PCTC), are distinctive ships with a box-like superstructure running the entire length and breadth of the hull, fully enclosing the cargo. They typically have a stern ramp and a side ramp for dual loading of thousands of vehicles (such as cars, trucks, heavy machineries, tracked units,
Mafi roll trailer
A roll trailer is a trailer platform that requires towing by a powered vehicle. It is commonly used for the transport of heavy static goods and materials in the maritime shipping industry. Roll trailers are similar to shipping flat racks contai ...
s, and loose statics), and extensive automatic fire control systems.
The PCTC has liftable decks to increase vertical clearance, as well as heavier decks for "high-and-heavy" cargo. A 6,500-unit car ship, with 12 decks, can have three decks which can take cargo up to with liftable panels to increase clearance from on some decks. Lifting decks to accommodate higher cargo reduces the total capacity.
These vessels can achieve a cruising speed of at eco-speed, while at full speed can achieve more than .
With the building of Wallenius Wilhelmsen Logistics's 8,000 car-equivalent unit (CEU) car carrier ''Faust
Faust is the protagonist of a classic German legend based on the historical Johann Georg Faust ( 1480–1540).
The erudite Faust is highly successful yet dissatisfied with his life, which leads him to make a pact with the Devil at a crossroa ...
'' out of Stockholm in June 2007, car carriers entered a new era of the large car and truck carrier (LCTC). Currently, the largest are Höegh Autoliners, six Horizon class vessels with capacity of 8,500 CEU each.
The car carrier ''Auriga Leader
''Auriga Leader'' is a car carrier, owned by Nippon Yusen Kaisha, and used for mobile machineries and cars worldwide; for example, Mitsubishi vehicles from Japan to the rest of the world. A small amount of the ship's power is produced by photovolt ...
'', belonging to Nippon Yusen
Nippon Yūsen Kabushiki Kaisha (Japan Mail Shipping Line), also known as NYK Line, is a Japanese shipping company and is a member of the Mitsubishi ''keiretsu''. The company headquarters are located in Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. It operates a flee ...
Kaisha, built in 2008 with a capacity of 6,200 cars, is the world's first partially solar powered ship.
ramp
An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle from the vertical direction, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six clas ...
File:MV Tønsberg R01.jpg, , the largest car/truck carrier
File:Cross Sound Ferry MV "John H" interior.jpg, Vehicle bay of the ''John H'', of Cross Sound Ferry
Seaworthiness
The seagoing RORO car ferry, with large external doors close to the waterline and open vehicle decks with few internal bulkheads, has a reputation for being a high-risk design, to the point where the acronym is sometimes derisively expanded to "roll on/roll over". An improperly secured loading door can cause a ship to take on water and sink, as happened in 1987 with . Water sloshing on the vehicle deck can set up afree surface effect
The free surface effect is a mechanism which can cause a watercraft to become unstable and capsize.
It refers to the tendency of liquids — and of unbound aggregates of small solid objects, like seeds, gravel, or crushed ore, whose behavior app ...
, making the ship unstable and causing it to capsize
Capsizing or keeling over occurs when a boat or ship is rolled on its side or further by wave action, instability or wind force beyond the angle of positive static stability or it is upside down in the water. The act of recovering a vessel fro ...
. Free surface water on the vehicle deck was determined by the court of inquiry to be the immediate cause of the 1968 capsize of the in New Zealand. It also contributed to the wreck of .
Despite these inherent risks, the very high freeboard
In sailing and boating, a vessel's freeboard
is the distance from the waterline to the upper deck level, measured at the lowest point of sheer where water can enter the boat or ship. In commercial vessels, the latter criterion measured relativ ...
raises the seaworthiness of these vessels. For example, the car carrier listed 60 degrees to its port side in 2006, but did not sink, since its high enclosed sides prevented water from entering.
In late January 2016 was listing off France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
after cargo shifted on the ship. Salvage crews secured the vessel and it was hauled into the port of Bilbao, Spain.
Some RORO ship casualties are mentioned here
Here is an adverb that means "in, on, or at this place". It may also refer to:
Software
* Here Technologies, a mapping company
* Here WeGo (formerly Here Maps), a mobile app and map website by Here Technologies, Here
Television
* Here TV (form ...
.
RORO variations

History
At first, wheeled vehicles carried as cargo on oceangoing ships were treated like any other cargo. Automobiles had their fuel tanks emptied and their batteries disconnected before being hoisted into the ship's hold, where they were chocked and secured. This process was tedious and difficult, and vehicles were subject to damage and could not be used for routine travel. An early roll-on/roll-off service was atrain ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry railway vehicles. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the front and/or rear to give access to the wharves. In the United States, train ...
, started in 1833 by the Monkland and Kirkintilloch Railway
The Monkland and Kirkintilloch Railway was an early mineral railway running from a colliery at Monklands to the Forth and Clyde Canal at Kirkintilloch, Scotland. It was the first railway to use a rail ferry, the first public railway in Scotla ...
, which operated a wagon ferry on the Forth and Clyde Canal
The Forth and Clyde Canal is a canal opened in 1790, crossing central Scotland; it provided a route for the seagoing vessels of the day between the Firth of Forth and the Firth of Clyde at the narrowest part of the Scottish Lowlands. This allowe ...
in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
.
Invention
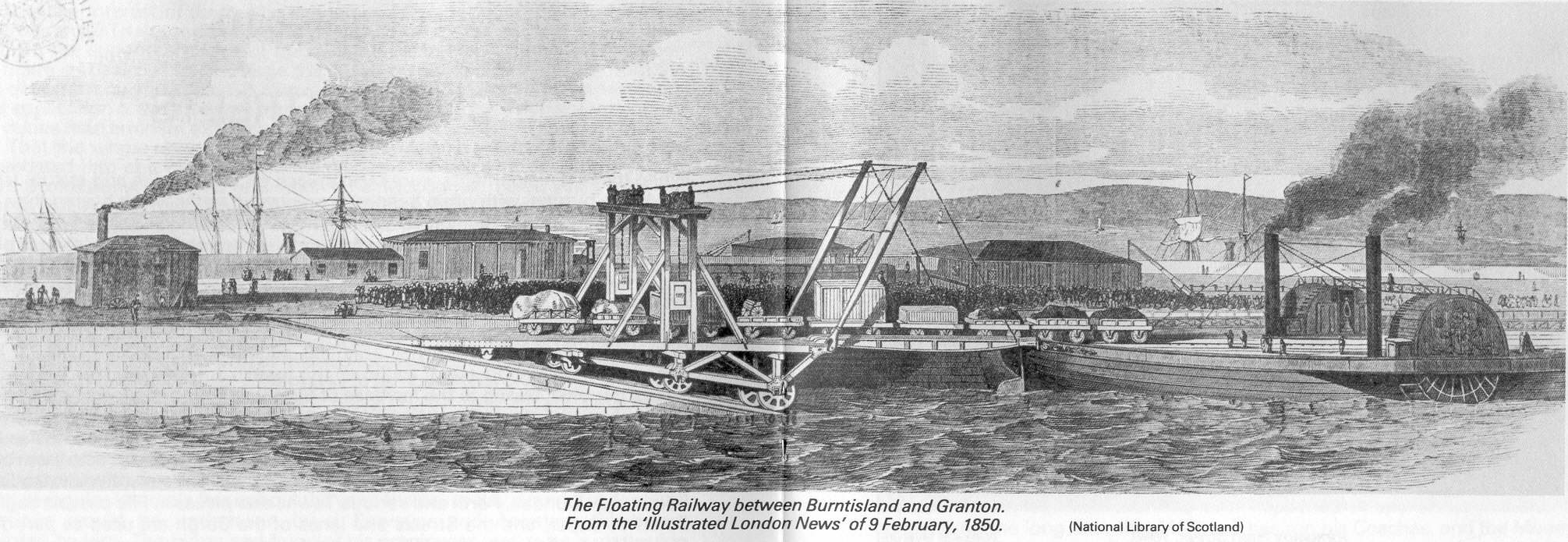
 The first modern train ferry was ''
The first modern train ferry was ''Leviathan
Leviathan (; he, לִוְיָתָן, ) is a sea serpent noted in theology and mythology. It is referenced in several books of the Hebrew Bible, including Psalms, the Book of Job, the Book of Isaiah, the Book of Amos, and, according to some ...
'', built in 1849. The Edinburgh, Leith and Newhaven Railway
The Edinburgh, Leith and Newhaven Railway was a railway company formed in 1836 to connect the city of Edinburgh with the harbours on the Firth of Forth. When the line connected to Granton, the company name was changed to the Edinburgh, Leith and ...
was formed in 1842 and the company wished to extend the East Coast Main Line further north to Dundee
Dundee (; sco, Dundee; gd, Dùn Dè or ) is Scotland's fourth-largest city and the 51st-most-populous built-up area in the United Kingdom. The mid-year population estimate for 2016 was , giving Dundee a population density of 2,478/km2 or ...
and Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), and ...
. As bridge technology was not yet capable enough to provide adequate support for the crossing over the Firth of Forth, which was roughly five miles across, a different solution had to be found, primarily for the transport of goods, where efficiency was key.
The company hired the up-and-coming civil engineer Thomas Bouch
Sir Thomas Bouch (; 25 February 1822 – 30 October 1880) was a British railway engineer. He was born in Thursby, near Carlisle, Cumberland, and lived in Edinburgh. As manager of the Edinburgh and Northern Railway he introduced the first roll ...
who argued for a train ferry with a roll-on/roll-off mechanism to maximise the efficiency of the system. Ferries were to be custom-built, with railway lines and matching harbour facilities at both ends to allow the rolling stock to easily drive on and off. To compensate for the changing tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravity, gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide t ...
s, adjustable ramps were positioned at the harbours and the gantry structure height was varied by moving it along the slipway. The wagons were loaded on and off with the use of stationary steam engines.
Although others had had similar ideas, Bouch was the first to put them into effect, and did so with an attention to detail (such as design of the ferry slip
A ferry slip is a specialized docking facility that receives a ferryboat or train ferry. A similar structure called a barge slip receives a barge or car float that is used to carry wheeled vehicles across a body of water.
Often a ferry intend ...
) which led a subsequent President of the Institution of Civil Engineers
The Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) is an independent professional association for civil engineers and a charitable body in the United Kingdom. Based in London, ICE has over 92,000 members, of whom three-quarters are located in the UK, whi ...
to settle any dispute over priority of invention with the observation that "there was little merit in a simple conception of this kind, compared with a work practically carried out in all its details, and brought to perfection."
The company was persuaded to install this train ferry service for the transportation of goods wagons across the Firth of Forth from Burntisland in Fife
Fife (, ; gd, Fìobha, ; sco, Fife) is a council area, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. It is situated between the Firth of Tay and the Firth of Forth, with inland boundaries with Perth and Kinross (i ...
to Granton. The ferry itself was built by Thomas Grainger
Thomas Grainger FRSE (12 November 1794 – 25 July 1852) was a Scottish civil engineer and surveyor. He was joint partner with John Miller in the prominent engineering firm of Grainger & Miller.
Life
Grainger was born at Gogar Green near R ...
, a partner of the firm Grainger and Miller.
The service commenced on 3 February 1850. It was called "The Floating Railway" and intended as a temporary measure until the railway could build a bridge, but this was not opened until 1890, its construction delayed in part by repercussions from the catastrophic failure of Thomas Bouch
Sir Thomas Bouch (; 25 February 1822 – 30 October 1880) was a British railway engineer. He was born in Thursby, near Carlisle, Cumberland, and lived in Edinburgh. As manager of the Edinburgh and Northern Railway he introduced the first roll ...
's Tay Rail Bridge
The Tay Bridge ( gd, Drochaid-rèile na Tatha) carries the railway across the Firth of Tay in Scotland between Dundee and the suburb of Wormit in Fife. Its span is . It is the second bridge to occupy the site.
Plans for a bridge over the Tay t ...
.
Expansion
Train-ferry services were used extensively duringWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. From 10 February 1918, high volumes of railway rolling stock, artillery and supplies for the Front were shipped to France from the "secret port" of Richborough
Richborough () is a settlement north of Sandwich on the east coast of the county of Kent, England. Richborough lies close to the Isle of Thanet. The population of the settlement is included in the civil parish of Ash.
Although now some dist ...
, near Sandwich on the South Coast of England.
This involved three train-ferries to be built, each with four sets of railway line on the main deck to allow for up to 54 railway wagons to be shunted directly on and off the ferry. These train-ferries could also be used to transport motor vehicles along with railway rolling stock. Later that month a second train-ferry was established from the Port of Southampton
The Port of Southampton is a passenger and cargo port in the central part of the south coast of England. The modern era in the history of the Port of Southampton began when the first dock was inaugurated in 1843. The port has been owned and op ...
on the South East Coast. In the first month of operations at Richborough, 5,000 tons were transported across the Channel, by the end of 1918 it was nearly 261,000 tons.
There were many advantages of the use of train-ferries over conventional shipping in World War I. It was much easier to move the large, heavy artillery and tanks that this kind of modern warfare required using train-ferries as opposed to repeated loading and unloading of cargo. By manufacturers loading tanks, guns and other heavy items for shipping to the front directly on to railway wagons, which could be shunted on to a train-ferry in England and then shunted directly on to the French Railway Network, with direct connections to the Front Lines, many man hours of unnecessary labour were avoided.
An analysis done at the time found that to transport 1,000 tons of war material from the point of manufacture to the front by conventional means involved the use of 1,500 labourers, whereas when using train-ferries that number decreased to around 100 labourers. This was of utmost importance, as by 1918, the British Railway companies were experiencing a severe shortage of labour with hundreds of thousands of skilled and unskilled labourers away fighting at the front. The increase of heavy traffic because of the war effort meant that economies and efficiency in transport had to be made wherever possible.
After the signing of the Armistice on 11 November 1918, train ferries were used extensively for the return of material from the Front. Indeed, according to war office statistics, a greater tonnage of material was transported by train ferry from Richborough in 1919 than in 1918. As the train ferries had space for motor transport as well as railway rolling stock, thousands of lorries, motor cars and "B Type" buses used these ferries to return to England.
The landing ship, tank
 During
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, landing ships were the first purpose-built seagoing ships enabling road vehicles to roll directly on and off. The British evacuation from Dunkirk in 1940 demonstrated to the Admiralty
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
*Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
*Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
* Admiralty, Traf ...
that the Allies needed relatively large, ocean-going ships capable of shore-to-shore delivery of tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engi ...
s and other vehicles in amphibious assault
Amphibious warfare is a type of offensive military operation that today uses naval ships to project ground and air power onto a hostile or potentially hostile shore at a designated landing beach. Through history the operations were conducted ...
s upon the continent of Europe. As an interim measure, three 4000 to 4800 GRT tankers, built to pass over the restrictive bars of Lake Maracaibo
Lake Maracaibo (Spanish: Lago de Maracaibo; Anu: Coquivacoa) is a lagoon in northwestern Venezuela, the largest lake in South America and one of the oldest on Earth, formed 36 million years ago in the Andes Mountains. The fault in the northern se ...
, Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, were selected for conversion because of their shallow draft. Bow doors and ramps were added to these ships, which became the first tank landing ships.
The first purpose-built LST design was . It was a scaled down design from ideas penned by Churchill. To carry 13 Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1 ...
infantry tanks, 27 vehicles and nearly 200 men (in addition to the crew) at a speed of 18 knots, it could not have the shallow draught that would have made for easy unloading. As a result, each of the three (''Boxer'', ''Bruiser'', and ''Thruster'') ordered in March 1941 had a very long ramp stowed behind the bow doors.
In November 1941, a small delegation from the British Admiralty arrived in the United States to pool ideas with the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
's Bureau of Ships with regard to development of ships and also including the possibility of building further ''Boxer''s in the US. During this meeting, it was decided that the Bureau of Ships would design these vessels. As with the standing agreement these would be built by the US so British shipyards could concentrate on building vessels for the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
. The specification called for vessels capable of crossing the Atlantic and the original title given to them was "Atlantic Tank Landing Craft" (Atlantic (T.L.C.)). Calling a vessel long a "craft" was considered a misnomer and the type was re-christened "Landing Ship, Tank (2)", or "LST (2)".
The LST(2) design incorporated elements of the first British LCTs from their designer, Sir Rowland Baker, who was part of the British delegation. This included sufficient buoyancy in the ships' sidewalls that they would float even with the tank deck flooded. The LST(2) gave up the speed of HMS ''Boxer'' at only but had a similar load while drawing only forward when beaching. In three separate acts dated 6 February 1942, 26 May 1943, and 17 December 1943, Congress provided the authority for the construction of LSTs along with a host of other auxiliaries, destroyer escort
Destroyer escort (DE) was the United States Navy mid-20th-century classification for a warship designed with the endurance necessary to escort mid-ocean convoys of merchant marine ships.
Development of the destroyer escort was promoted by th ...
s, and assorted landing craft. The enormous building program quickly gathered momentum. Such a high priority was assigned to the construction of LSTs that the previously laid keel of an aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a ...
was hastily removed to make room for several LSTs to be built in her place. The keel of the first LST was laid down on 10 June 1942 at Newport News, Virginia
Newport News () is an independent city in the U.S. state of Virginia. At the 2020 census, the population was 186,247. Located in the Hampton Roads region, it is the 5th most populous city in Virginia and 140th most populous city in the Uni ...
, and the first standardized LSTs were floated out of their building dock in October. Twenty-three were in commission by the end of 1942.
ROROs for road vehicles
 At the end of the first world war vehicles were brought back from France to Richborough Port drive-on-drive-off using the train ferry. During the war British servicemen recognised the great potential of landing ships and craft. The idea was simple; if you could drive tanks, guns and lorries directly onto a ship and then drive them off at the other end directly onto a beach, then theoretically you could use the same landing craft to carry out the same operation in the civilian commercial market, providing there were reasonable port facilities. From this idea grew the worldwide roll-on/roll-off
At the end of the first world war vehicles were brought back from France to Richborough Port drive-on-drive-off using the train ferry. During the war British servicemen recognised the great potential of landing ships and craft. The idea was simple; if you could drive tanks, guns and lorries directly onto a ship and then drive them off at the other end directly onto a beach, then theoretically you could use the same landing craft to carry out the same operation in the civilian commercial market, providing there were reasonable port facilities. From this idea grew the worldwide roll-on/roll-off ferry
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water taxi ...
industry of today. In the period between the wars Lt. Colonel Frank Bustard
Colonel Frank Bustard OBE (1886 – 22 January 1974) was a British shipping pioneer who established the commercial use of Roll-on/roll-off, ro-ro ships using converted tank landing craft.
Bustard was born in Liverpool, Lancashire in 1886 th ...
formed the Atlantic Steam Navigation Company
The Atlantic Steam Navigation Company was founded in 1934 with the original object of providing a no-frills transatlantic passenger service. A combination of difficult economic conditions and then World War II frustrated these early ambitions. ...
, with a view to cheap transatlantic travel; this never materialised, but during the war he observed trials on Brighton Sands of an LST in 1943 when its peacetime capabilities were obvious.
In the spring of 1946 the company approached the Admiralty with a request to purchase three of these vessels. The Admiralty were unwilling to sell, but after negotiations agreed to let the ASN have the use of three vessels on bareboat charter at a rate of £13 6s 8d per day. These vessels were LSTs ''3519'', ''3534'', and ''3512''. They were renamed '' Empire Baltic'', , and , perpetuating the name of White Star Line
The White Star Line was a British shipping company. Founded out of the remains of a defunct packet company, it gradually rose up to become one of the most prominent shipping lines in the world, providing passenger and cargo services between t ...
ships in combination with the "Empire" ship naming of vessels in government service during the war.
On the morning of 11 September 1946 the first voyage of the Atlantic Steam Navigation Company took place when ''Empire Baltic'' sailed from Tilbury
Tilbury is a port town in the borough of Thurrock, Essex, England. The present town was established as separate settlement in the late 19th century, on land that was mainly part of Chadwell St Mary. It contains a 16th century fort and an ancie ...
to Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"N ...
with a full load of 64 vehicles for the Dutch Government. The original three LSTs were joined in 1948 by another vessel, ''LST 3041
''LST 3041'' was a Landing Ship, Tank that served in the Royal Navy at the end of World War II, before being converted to a commercial ferry. She was later requisitioned by the Navy during the Suez Crisis, and was scrapped in 1960.
Description
T ...
'', renamed ''Empire Doric'', after the ASN were able to convince commercial operators to support the new route between Preston and the Northern Ireland port of Larne
Larne (, , the name of a Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic territory) is a town on the east coast of County Antrim, Northern Ireland, with a population of 18,755 at the United Kingdom census, 2011, 2011 Census. It is a major passenger and freight Roll-on/ro ...
. The first sailing of this new route was on 21 May 1948 by ''Empire Cedric''. After the inaugural sailing ''Empire Cedric'' continued on the Northern Ireland service, offering initially a twice-weekly service. ''Empire Cedric '' was the first vessel of the ASN fleet to hold a passenger certificate, and was allowed to carry fifty passengers. Thus ''Empire Cedric'' became the first vessel in the world to operate as a commercial/passenger roll-on/roll-off ferry, and the ASN became the first commercial company to offer this type of service.
 The first RORO service crossing the
The first RORO service crossing the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
began from Dover in 1953. In 1954, the British Transport Commission
The British Transport Commission (BTC) was created by Clement Attlee's post-war Labour government as a part of its nationalisation programme, to oversee railways, canals and road freight transport in Great Britain (Northern Ireland had the se ...
(BTC) took over the ASN under the Labour Governments nationalization
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to pri ...
policy. In 1955 another two LSTs where chartered into the existing fleet, ''Empire Cymric
''Empire Cymric'' was a Ferry that was built in 1944 by Harland & Wolff Ltd, Belfast as LST (3) HMS ''LST 3010'' for the Royal Navy. She was transferred to the Koninklijke Marine in 1945, serving as HNLMS ''LST 3010''. In 1947, she was tr ...
'' and '' Empire Nordic'', bringing the fleet strength to seven. The Hamburg service was terminated in 1955, and a new service was opened between Antwerp and Tilbury. The fleet of seven ships was to be split up with the usual three ships based at Tilbury and the others maintaining the Preston to Northern Ireland service.
During late 1956, the entire fleet of ASN were taken over for use in the Mediterranean during the Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 Wa ...
, and the drive-on/drive-off services were not re-established until January 1957. At this point ASN were made responsible for the management of twelve Admiralty LST(3)s brought out of reserve as a result of the Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 Wa ...
too late to see service.

Further developments
 The first roll-on/roll-off vessel that was purpose-built to transport loaded semi trucks was ''Searoad of Hyannis'', which began operation in 1956. While modest in capacity, it could transport three semi trailers between Hyannis in Massachusetts and Nantucket Island, even in ice conditions.
In 1957, the US military issued a contract to the Sun Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company in
The first roll-on/roll-off vessel that was purpose-built to transport loaded semi trucks was ''Searoad of Hyannis'', which began operation in 1956. While modest in capacity, it could transport three semi trailers between Hyannis in Massachusetts and Nantucket Island, even in ice conditions.
In 1957, the US military issued a contract to the Sun Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company in Chester, Pennsylvania
Chester is a city in Delaware County, Pennsylvania, United States. Located within the Philadelphia Metropolitan Area, it is the only city in Delaware County and had a population of 32,605 as of the 2020 census.
Incorporated in 1682, Chester i ...
, for the construction of a new type of motorized vehicle carrier. The ship, USNS ''Comet'', had a stern ramp as well as interior ramps, which allowed cars to drive directly from the dock, onto the ship, and into place. Loading and unloading was sped up dramatically. ''Comet'' also had an adjustable chocking system for locking cars onto the decks and a ventilation system to remove exhaust gases that accumulate during vehicle loading.
During the 1982 Falklands War
The Falklands War ( es, link=no, Guerra de las Malvinas) was a ten-week undeclared war between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982 over two British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands and its territorial de ...
, was requisitioned as an emergency aircraft and helicopter transport for British Hawker Siddeley Harrier
The Hawker Siddeley Harrier is a British military aircraft. It was the first of the Harrier series of aircraft and was developed in the 1960s as the first operational ground attack and reconnaissance aircraft with vertical/short takeoff an ...
STOVL
A short take-off and vertical landing aircraft (STOVL aircraft) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is able to take off from a short runway (or take off vertically if it does not have a heavy payload) and land vertically (i.e. with no runway). The ...
fighter planes; one Harrier was kept fueled, armed, and ready to VTOL launch for emergency air protection against long range Argentine aircraft. ''Atlantic Conveyor'' was sunk by Argentine Exocet
The Exocet () is a French-built anti-ship missile whose various versions can be launched from surface vessels, submarines, helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft.
Etymology
The missile's name was given by M. Guillot, then the technical director ...
missiles after offloading the Harriers to proper aircraft carriers, but the vehicles and helicopters still aboard were lost.
After the war, a concept called the shipborne containerized air-defense system (SCADS) proposed a modular system to quickly convert a large RORO into an emergency aircraft carrier with ski jump, fueling systems, radar, defensive missiles, munitions, crew quarters, and work spaces. The entire system could be installed in about 48 hours on a container ship or RORO, when needed for operations up to a month unsupplied. The system could quickly be removed and stored again when the conflict was over. The Soviets flying Yakovlev Yak-38
The Yakovlev Yak-38 (russian: Яковлев Як-38; NATO reporting name: "Forger") was the Soviet Naval Aviation's only operational VTOL strike fighter aircraft in addition to being its first operational carrier-based fixed-wing aircraft. It ...
fighters also tested operations using the civilian RORO ships ''Agostinio Neto'' and ''Nikolai Cherkasov''.
See also
*BC Ferries
British Columbia Ferry Services Inc., operating as BC Ferries (BCF), is a former provincial Crown corporation, now operating as an independently managed, publicly owned Canadian company. BC Ferries provides all major passenger and vehicle ferr ...
* Car float
A railroad car float or rail barge is a specialised form of lighter with railway tracks mounted on its deck used to move rolling stock across water obstacles, or to locations they could not otherwise go. An unpowered barge, it is towed by a t ...
* Cruise ferry
A cruiseferry is a ship that combines the features of a cruise ship and a Ro-Pax ferry. Many passengers travel with the ships for the cruise experience, staying only a few hours at the destination port or not leaving the ship at all, while oth ...
* Frank Bustard
Colonel Frank Bustard OBE (1886 – 22 January 1974) was a British shipping pioneer who established the commercial use of Roll-on/roll-off, ro-ro ships using converted tank landing craft.
Bustard was born in Liverpool, Lancashire in 1886 th ...
* Intermodal container
An intermodal container, often called a shipping container, is a large standardized shipping container, designed and built for intermodal freight transport, meaning these containers can be used across different Mode of transport, modes of trans ...
* Konkan Railway Corporation
* List of cargo types Primary maritime cargo types
References
{{Container shipping companies
Intermodal containers
Economic globalization
Freight transport
...
* List of roll-on/roll-off vessel accidents
This is a list of roll-on/roll-off vessels involved in maritime incidents and accidents.
References
{{Reflist
RORO
Roll-on/roll-off (RORO or ro-ro) ships are cargo ships designed to carry wheeled cargo, such as cars, motorcycles, trucks, se ...
* Roll-on/roll-off discharge facility
A roll-on/roll-off discharge facility (RRDF) is a floating platform that provides a roadway between a ship's ramp and lighterage. It is constructed by connecting multiple causeway sections.
Ports equipped with roll-on/roll-off wharfs include:
...
* Rolling highway
In rail transportation, a rolling highway or rolling road is a form of combined transport involving the conveying of road trucks by rail, referred to as Ro-La trains. The concept is a form of piggyback transportation.
The technical challen ...
* RORO ferry service, Gujarat
DG Sea Connect is a Roll-on/roll-off, RORO/ROPAX ferry service connecting Ghogha and Hazira in Gulf of Khambhat in Gujarat state of India. The original route to Dahej was opened in 2017 and suspended in early 2020 due to lack of financial feasib ...
* Société des traversiers du Québec
* Train ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry railway vehicles. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the front and/or rear to give access to the wharves. In the United States, train ...
* USNS Sea Lift (T-LSV-9)
The USNS ''Sea Lift'' (T-LSV-9) was a roll on/roll off (Ro/Ro) cargo ship built for the United States Navy's Military Sea Transportation Service (MSTS), currently the Military Sealift Command (MSC). She became the first ship of Ro/Ro-type to del ...
USN Ro Ro ship
* Washington State Ferries
Washington State Ferries (WSF) is a government agency that operates automobile and passenger ferry service in the U.S. state of Washington as part of the Washington State Department of Transportation. It runs ten routes serving 20 terminals loc ...
* Yacht transport
Yacht transport is the shipping of a yacht to a destination instead of sailing or motoring it. Yacht transport is an alternative to the traditional passaging (sailing or motoring) to reach desired
destinations around the globe. Transport when c ...
References
Further reading
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Roll On Roll Off Cargo ships Ship types Freight transport Scottish inventions no:RoRo-skip#Bilskip