Ritual And Music System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Chinese ritual and music system () is a social system that originated in the
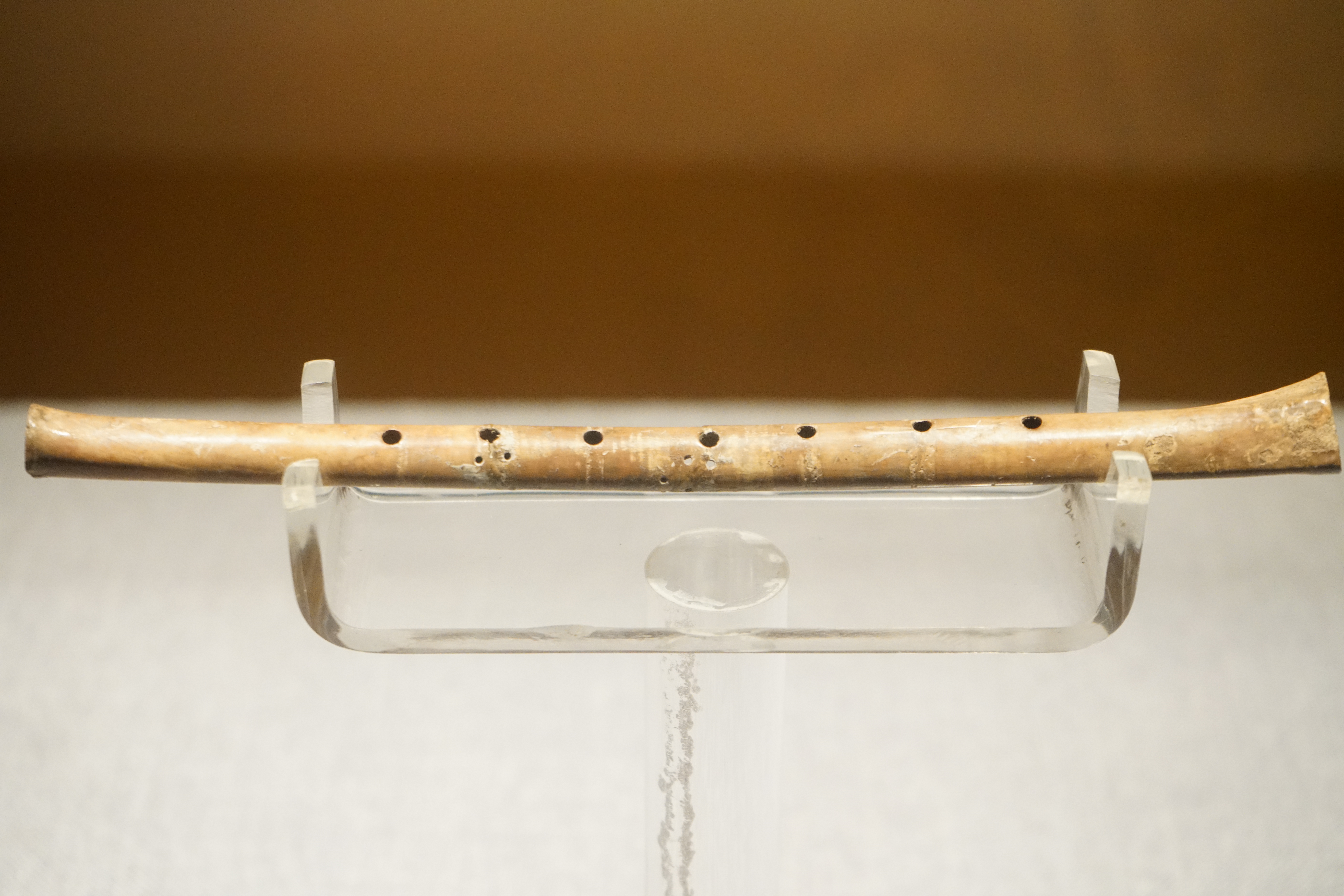 Archaeological evidence indicates that music culture developed in China from a very early period. Excavations in Jiahu Village in
Archaeological evidence indicates that music culture developed in China from a very early period. Excavations in Jiahu Village in  Pictorial representations of dance have been found in Chinese pottery as early as the
Pictorial representations of dance have been found in Chinese pottery as early as the  , appears in the
, appears in the
 Confucius heavily promoted the use of music with rituals or the rites order. The scholar
Confucius heavily promoted the use of music with rituals or the rites order. The scholar
 г
г
ж¬Ҫе®ҡеҸӨд»Ҡең–жӣёйӣҶжҲҗ·經жҝҹеҪҷз·ЁВ·зҰ®е„Җе…ёВ·зҰ®жЁӮзёҪйғЁ
ҖӢпјҢеҮәиҮӘ и’Ӣе»·й”ЎгҖҠ еҸӨд»Ҡең–жӣёйӣҶжҲҗгҖӢ Ancient institutions in East Asia Ancient Chinese institutions Religious Confucianism
Zhou Dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by th ...
to maintain the social order. Together with the patriarchal system, it constituted the social system of the entire ancient China and had a great influence on the politics, culture, art and thought of later generations. The feudal system
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
and the Well-field system
The well-field system () was a Chinese land redistribution method existing between the ninth century BCE (late Western Zhou dynasty) to around the end of the Warring States period. Its name comes from Chinese character wikt:дә•, дә• (''jЗҗng'') ...
were two other institutions that developed at that time. According to legend it was founded by the Duke of Zhou
Dan, Duke Wen of Zhou (), commonly known as the Duke of Zhou (), was a member of the royal family of the early Zhou dynasty who played a major role in consolidating the kingdom established by his elder brother King Wu. He was renowned for acting ...
and King Wu of Zhou
King Wu of Zhou () was the first king of the Zhou dynasty of ancient China. The chronology of his reign is disputed but is generally thought to have begun around 1046 BC and ended three years later in 1043 BC.
King Wu's ancestral name was ...
.
The Ritual Music System is divided into two parts: ritual and music. The part of ritual mainly divides people's identity and social norms, and finally forms a hierarchy. The music part is mainly based on the hierarchical system of etiquette, using music to alleviate social conflicts.
The system developed from older shamanic traditions and was seen as having cosmological significance, it was seen as representing the balance between Yin and Yang
Yin and yang ( and ) is a Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosophical concept that describes opposite but interconnected forces. In Chinese cosmology, the universe creates itself out of a primary chaos of material energy, organized into the c ...
and the Five Elements.
The regulations on ritual and music strengthened people's concept of hierarchy, played a symbolic role in establishing authority, alongside standardizing rule across the civilization.
Predecessors
 Archaeological evidence indicates that music culture developed in China from a very early period. Excavations in Jiahu Village in
Archaeological evidence indicates that music culture developed in China from a very early period. Excavations in Jiahu Village in Wuyang County
Wuyang County () is a county in the central part of Henan province, China. It is both the westernmost and southernmost county-level division of the prefecture-level city of Luohe
Luohe (; postal: Loho) is a prefecture-level city in central Hena ...
, Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
found bone flutes
During regular archaeological excavations, several flutes that date to the European Upper Paleolithic were discovered in caves in the Swabian Alb region of Germany. Dated and tested independently by two laboratories, in England and Germany, the ...
dated to 9,000 years ago, and clay music instruments called Xun thought to be 7,000 years old have been found in the Hemudu sites in Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , also romanized as Chekiang) is an eastern, coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable cities include Ningbo and Wenzhou. Zhejiang is bordered by Jiang ...
and Banpo
Banpo is an archaeological site discovered in 1953 by Shi Xingbang, and located in the Yellow River Valley just east of Xi'an, China. It contains the remains of several well organized Neolithic settlements, like Jiangzhai, carbon dated t ...
in Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by #Name, other names, is the list of capitals in China, capital of Shaanxi, Shaanxi Province. A Sub-provincial division#Sub-provincial municipalities, sub-provincial city o ...
.
 Pictorial representations of dance have been found in Chinese pottery as early as the
Pictorial representations of dance have been found in Chinese pottery as early as the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
period (before 2000 BCE), showing people dancing in a line holding hands. The earliest Chinese character for "dance", oracle bones
Oracle bones () are pieces of ox scapula and turtle plastron, which were used for pyromancy вҖ“ a form of divination вҖ“ in ancient China, mainly during the late Shang dynasty. ''Scapulimancy'' is the correct term if ox scapulae were used for the ...
and represents a dancer holding oxtails in each hand. According to the ''LГјshi Chunqiu
The ''LГјshi Chunqiu'', also known in English as ''Master LГј's Spring and Autumn Annals'', is an encyclopedic Chinese classic text compiled around 239 BC under the patronage of the Qin Dynasty Chancellor LГј Buwei. In the evaluation of Michae ...
'' (compiled around 239 BCE): "In former times, the people of the Getian clan (и‘ӣеӨ©ж°Ҹ) would dance in pairs r threes
R, or r, is the eighteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ar'' (pronounced ), plural ''ars'', or in Irelan ...
with oxtails in hand, stamping their feet and singing eight stanzas."
Primitive dance in ancient China was also associated with sorcery and shamanic ritual. An early shape of the Chinese character for sorcerer, '' wu'' (е·«), represented dancing shamans or their sleeves; ''wu'' therefore described someone who danced as a mean of communication between gods and men. There are many ancient records of shamans and sorcerers who danced, for example performing the rain dance at time of drought. The rain dance (иҲһйӣ©, wЗ”yГә) platform is mentioned in many ancient texts including the ''Analects
The ''Analects'' (; ; Old Chinese: '' ЕӢ(r)aК”''; meaning "Selected Sayings"), also known as the ''Analects of Confucius'', the ''Sayings of Confucius'', or the ''Lun Yu'', is an ancient Chinese book composed of a large collection of sayings a ...
'' of Confucius
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=KЗ’ng FЕ«zЗҗ, "Master KЗ’ng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=KЗ’ngzЗҗ, labels=no; вҖ“ ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. C ...
.Zhou Institution
According to tradition, ''yayue
''Yayue'' () was a form of classical music and dance performed at the royal court and temples in ancient China. The basic conventions of ''yayue'' were established in the Western Zhou. Together with law and rites, it formed the formal represent ...
'' was created by the Duke of Zhou
Dan, Duke Wen of Zhou (), commonly known as the Duke of Zhou (), was a member of the royal family of the early Zhou dynasty who played a major role in consolidating the kingdom established by his elder brother King Wu. He was renowned for acting ...
under commission from King Wu of Zhou
King Wu of Zhou () was the first king of the Zhou dynasty of ancient China. The chronology of his reign is disputed but is generally thought to have begun around 1046 BC and ended three years later in 1043 BC.
King Wu's ancestral name was ...
, shortly after the latter's conquest of Shang
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and f ...
. Incorporated within ''yayue'' were elements of shamanistic
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritu ...
or religious traditions, as well as early Chinese folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has b ...
, which formed the backbone of the Ritual Music System. Dance
Dance is a performing art form consisting of sequences of movement, either improvised or purposefully selected. This movement has aesthetic and often symbolic value. Dance can be categorized and described by its choreography, by its repertoir ...
was also closely associated with ''yayue'' music, each ''yayue'' pieces may have a ceremonial or ritual dance associated with it. The most important ''yayue'' piece of the Zhou dynasty were the Six Great Dances, each associated with a legendary or historical figure. Note some of alternate names given for these dances, such as Xianchi (е’ёжұ ), Dashao (еӨ§йҹ¶), and Dazhang (еӨ§з« ) Note some of alternate names given for these dances, such as Xianchi (е’ёжұ ), Dashao (еӨ§йҹ¶), and Dazhang (еӨ§з« )
*''Yunmen Dajuan'' (йӣІй–ҖеӨ§еҚ·), from the Yellow Emperor
The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch or by his Chinese name Huangdi (), is a deity ('' shen'') in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes included among the mytho-historical Three Soverei ...
era, performed for the veneration of the sky.
*''Daxian'' ( еӨ§е’ё, or ''Dazhang'' еӨ§з« ), from the Emperor Yao
Emperor Yao (; traditionally c. 2356 вҖ“ 2255 BCE) was a legendary Chinese ruler, according to various sources, one of the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors.
Ancestry and early life
Yao's ancestral name is Yi Qi () or Qi (), clan name i ...
era, for the veneration of the earth.
*''Daqing'' (еӨ§зЈ¬, or ''Dashao'' еӨ§йҹ¶), from the Emperor Shun
Emperor Shun () was a legendary leader of ancient China, regarded by some sources as one of the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors being the last of the Five Emperors. Tradition holds that he lived sometime between 2294 and 2184 BC. Tradition a ...
era, for the veneration of Gods of the Four Directions, or the sun, moon, stars and seas, the dancers may have dressed up as birds and beasts. One of the earliest documents, ''Shujing
The ''Book of Documents'' (''ShЕ«jД«ng'', earlier ''Shu King'') or ''Classic of History'', also known as the ''Shangshu'' (вҖңVenerated DocumentsвҖқ), is one of the Five Classics of ancient Chinese literature. It is a collection of rhetorica ...
'', mentioned the ritual of "beating on the stones as all the wild animals dance". The performance of the dance was highly regarded by Confucius.
*''Daxia'' ( еӨ§еӨҸ), was a dance performed in praise of Yu the Great
Yu the Great (еӨ§зҰ№) was a legendary king in ancient China who was famed for his introduction of flood control, his establishment of the Xia dynasty which inaugurated dynastic rule in China, and his upright moral character. He figures prominen ...
of the Xia dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In tradi ...
, famous for his work on flood control. In this dance, 64 performers danced bare-chested wearing fur caps and white skirts. The movements of the dance may imitate the manual labour performed during flood control.
*''Dahu'' (еӨ§жҝ©), from Tang of Shang
Cheng Tang (), personal name Zi LГј (), recorded on oracle bones as Da Yi (еӨ§д№ҷ), was the first king of the Shang dynasty in Chinese history. Traditionally considered a virtuous ruler, he overthrew Jie, the last ruler of the Xia dynasty.
Rise ...
dating to the end of the Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In tradi ...
, for the veneration of female ancestors.
*''Dawu'' ( еӨ§жӯҰ), in praise of King Wu of Zhou
King Wu of Zhou () was the first king of the Zhou dynasty of ancient China. The chronology of his reign is disputed but is generally thought to have begun around 1046 BC and ended three years later in 1043 BC.
King Wu's ancestral name was ...
, used for ancestral worship. It was military focused in addition
Music in the Zhou Dynasty was conceived as a cosmological manifestation of the sound of nature integrated into the binary universal order of yin and yang
Yin and yang ( and ) is a Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosophical concept that describes opposite but interconnected forces. In Chinese cosmology, the universe creates itself out of a primary chaos of material energy, organized into the c ...
, and this concept has enduring influence later Chinese thinking on music. "Correct" music according to Zhou concept would involve instruments correlating to the five elements of nature and would bring harmony to nature. Around or before the 7th century BC, a system of pitch generation and pentatonic scale
A pentatonic scale is a musical scale with five notes per octave, in contrast to the heptatonic scale, which has seven notes per octave (such as the major scale and minor scale).
Pentatonic scales were developed independently by many ancien ...
was derived from a cycle-of-fifths theory.
The ''Book of Rites
The ''Book of Rites'', also known as the ''Liji'', is a collection of texts describing the social forms, administration, and ceremonial rites of the Zhou dynasty as they were understood in the Warring States and the early Han periods. The ''Book o ...
'' records a number of situations where ''yayue'' might be performed. These included ceremonies
A ceremony (, ) is a unified ritualistic event with a purpose, usually consisting of a number of artistic components, performed on a special occasion.
The word may be of Etruscan origin, via the Latin '' caerimonia''.
Church and civil (secular) ...
in honour of Heaven and Earth, the gods or the ancestors. There were also detailed rules on the way they were to be performed at diplomatic
Diplomatics (in American English, and in most anglophone countries), or diplomatic (in British English), is a scholarly discipline centred on the critical analysis of documents: especially, historical documents. It focuses on the conventions, p ...
meetings. ''Yayue'' was also used in outdoor activities, such as aristocratic archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In m ...
contests, during hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
expeditions, and after the conclusion of a successful military campaign. ''Yayue'' was characterised by its rigidity of form. When performed, it was stately and formal, serving to distinguish the aristocratic classes. It was sometimes also accompanied by lyrics
Lyrics are words that make up a song, usually consisting of verses and choruses. The writer of lyrics is a lyricist. The words to an extended musical composition such as an opera are, however, usually known as a "libretto" and their writer, a ...
. Some of these are preserved in the '' Book of Songs''.
Spring and Autumn Period reactions
With the decline of the importance ceremony in the interstate relations of theSpring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives fr ...
, so did ''yayue''. Confucius
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=KЗ’ng FЕ«zЗҗ, "Master KЗ’ng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=KЗ’ngzЗҗ, labels=no; вҖ“ ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. C ...
famously lamented the decline of classical music and the rites. Marquess Wen of Wei
Marquess Wen of Wei (WГЁi WГ©n HГіu; died 396 BCE) was the first Marquess to rule the State of Wei during the Warring States period of Chinese history (475 вҖ“ 220 BCE). Born Wei Si (йӯҸж–Ҝ), he belonged to the House of Wei, one of the noble ...
was said to prefer the popular music of Wey and Zheng Zheng may refer to:
*Zheng (surname), Chinese surname (й„ӯ, йғ‘, ''ZhГЁng'')
*Zheng County, former name of Zhengzhou, capital of Henan, China
*Guzheng (), a Chinese zither with bridges
*Qin Shi Huang (259 BC вҖ“ 210 BC), emperor of the Qin Dynasty, ...
to the ancient court music, listening to which he may fall asleep. Confucius
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=KЗ’ng FЕ«zЗҗ, "Master KЗ’ng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=KЗ’ngzЗҗ, labels=no; вҖ“ ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. C ...
, faced with the social chaos of the Spring and Autumn period, strongly advocated the restoration of the Ritual Music System of the Western Zhou, and advocated "restoring rituals to oneself". social problems
A social issue is a problem that affects many people within a society. It is a group of common problems in present-day society and ones that many people strive to solve. It is often the consequence of factors extending beyond an individual's cont ...
and realize a harmonious society in which the world is "righteous".
Chinese philosophers took varying approaches to music. To Confucius
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=KЗ’ng FЕ«zЗҗ, "Master KЗ’ng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=KЗ’ngzЗҗ, labels=no; вҖ“ ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. C ...
, a correct form of music is important for the cultivation and refinement of the individual, and the Confucian system considers the formal music ''yayue
''Yayue'' () was a form of classical music and dance performed at the royal court and temples in ancient China. The basic conventions of ''yayue'' were established in the Western Zhou. Together with law and rites, it formed the formal represent ...
'' to be morally uplifting and the symbol of a good ruler and stable government. Some popular forms of music, however, were considered corrupting in the Confucian view. Mozi
Mozi (; ; Latinized as Micius ; вҖ“ ), original name Mo Di (), was a Chinese philosopher who founded the school of Mohism during the Hundred Schools of Thought period (the early portion of the Warring States period, вҖ“221 BCE). The ancie ...
on the other hand condemned making music, and argued in ''Against Music'' (йқһжЁӮ) that music is an extravagance and indulgence that serves no useful purpose and may be harmful. According to Mencius
Mencius ( ); born MГЁng KД“ (); or MГЁngzЗҗ (; 372вҖ“289 BC) was a Chinese Confucianism, Confucian Chinese philosophy, philosopher who has often been described as the "second Sage", that is, second to Confucius himself. He is part of Confuc ...
, a powerful ruler once asked him whether it was moral if he preferred popular music to the classics. The answer was that it only mattered that the ruler loved his subjects.
Confucius not only advocated and advocated the restoration of the Ritual Music System, but also practiced it physically. Legend has it that he asked Laozi
Laozi (), also known by numerous other names, was a semilegendary ancient Chinese Taoist philosopher. Laozi ( zh, ) is a Chinese honorific, generally translated as "the Old Master". Traditional accounts say he was born as in the state
...
about rituals and became so obsessed with music that he "did not know the taste of meat for three months".
 Confucius heavily promoted the use of music with rituals or the rites order. The scholar
Confucius heavily promoted the use of music with rituals or the rites order. The scholar Li Zehou
Li Zehou (; 13 June 1930 вҖ“ 2 November 2021) was a Chinese scholar of philosophy and intellectual history. He resided in the United States.. coloradocollege.edu He is considered an important modern scholar of Chinese history and culture whose ...
argued that Confucianism is based on the idea of rites. Rites serve as the starting point for each individual and that these sacred social functions allow each person's human nature to be harmonious with reality. Given this, Confucius believed that "music is the harmonization of heaven and earth; the rites is the order of heaven and earth". Thus the application of music in rites creates the order that makes it possible for society to prosper.
The Confucian approach to music was heavily inspired by the Shijing
The ''Classic of Poetry'', also ''Shijing'' or ''Shih-ching'', translated variously as the ''Book of Songs'', ''Book of Odes'', or simply known as the ''Odes'' or ''Poetry'' (; ''ShД«''), is the oldest existing collection of Chinese poetry, co ...
and the Classic of Music
The ''Classic of Music'' () was a Confucian classic text lost by the time of the Han dynasty. It is sometimes referred to as the "Sixth Classic" (for example, by Sima Qian) and is thought to have been important in the traditional interpretations ...
, which was said to be the sixth Confucian classic until it was lost during the Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC вҖ“ 9 AD, 25вҖ“220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221вҖ“207 BC) and a warr ...
. The Shijing serves as one of the current Confucian classics and is a book on poetry that contains a diversified variety of poems as well as folk songs. Confucius is traditionally ascribed with compiling these classics within his school. In the Analects, Confucius described the importance of the art in the development of society:
In ancient China the social status of musicians was much lower than that of painters, though music was seen as central to the harmony and longevity of the state. Almost every emperor took folk songs seriously, sending officers to collect songs to record the popular culture. One of the Confucianist Classics, The Classic of Poetry
The ''Classic of Poetry'', also ''Shijing'' or ''Shih-ching'', translated variously as the ''Book of Songs'', ''Book of Odes'', or simply known as the ''Odes'' or ''Poetry'' (; ''ShД«''), is the oldest existing collection of Chinese poetry, co ...
, contained many folk songs dating from 800 BC to about 400 BC.Later history
The Imperial Music Bureau, first established in theQin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=з§Ұжңқ, p=QГӯn chГЎo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in WadeвҖ“Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first Dynasties in Chinese history, dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin (state), ...
(221вҖ“207 BC), was greatly expanded under the emperor Han Wudi
Emperor Wu of Han (156 вҖ“ 29 March 87BC), formally enshrined as Emperor Wu the Filial (), born Liu Che (еҠүеҫ№) and courtesy name Tong (йҖҡ), was the seventh emperor of the Han dynasty of ancient China, ruling from 141 to 87 BC. His reign las ...
(140вҖ“87 BC) and charged with supervising court music and military music and determining what folk music would be officially recognized. In subsequent dynasties, the development of Chinese music was influenced by the musical traditions of Central Asia which also introduced elements of Indian music.A History of Sino-Indian Relations: 1st Century A.D. to 7th Century A.D. by Yukteshwar Kumar. p.76
Zhou yayue
''Yayue'' () was a form of classical music and dance performed at the royal court and temples in ancient China. The basic conventions of ''yayue'' were established in the Western Zhou. Together with law and rites, it formed the formal represent ...
was lost in the Han dynasty
During the Han dynasty the bureau served a purpose of incorporating elements from folk music into ritual music. The music became increasingly secularized as it became more removed from its shamanic roots.
In the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690вҖ“705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
incorporation of elements from popular music occurred once again
During the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960вҖ“1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
, with Neo-Confucianism
Neo-Confucianism (, often shortened to ''lЗҗxuГ©'' зҗҶеӯё, literally "School of Principle") is a moral, ethical, and metaphysical Chinese philosophy
Chinese philosophy originates in the Spring and Autumn period () and Wa ...
becoming the new orthodoxy, ''yayue'' was again in ascendancy with major development, and a ''yayue'' orchestra in this era consisted of over 200 instrumentalists. A notable ritual was called "The Great Feast" where the emperor would drink wine. Two important texts from the Song dynasty describing ''yayue'' performances are Zhu Xi
Zhu Xi (; ; October 18, 1130 вҖ“ April 23, 1200), formerly romanized Chu Hsi, was a Chinese calligrapher, historian, philosopher, poet, and politician during the Song dynasty. Zhu was influential in the development of Neo-Confucianism. He con ...
's ''Complete Explanation of the Classic of Etiquette and Its Commentary'' (е„ҖзҰ®з¶“еӮійҖҡи§Ј) and ''Collection of Music'' (жЁӮжӣё) by Chen Yang (йҷіжҡҳ). In 1116, a gift of 428 ''yayue'' instruments as well as 572 costumes and dance objects was given to Korea by Emperor Huizong upon request by the Emperor Yejong of Goryeo
Yejong of Goryeo (11 February 1079 вҖ“ 15 May 1122) (r. 1105вҖ“1122) was the 16th monarch of the Korean Goryeo dynasty. He was the eldest son of Sukjong of Goryeo, King Sukjong and Queen Myeongui, and succeeded to the throne upon his father's dea ...
. As a result, elements of Song dynasty ''yayue'' music such as melodies are still preserved in Korea.
Lowering faith in government meant a decline in the system in the Song and Ming dynasties
Some forms of yayue survived for imperial ceremonies and rituals until the fall of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
when the imperial period of China came to an end. ''Yayue'' however was still performed as part of a Confucian ritual in China until the Communist takeover in 1949 when it completely disappeared. There has been a revival in ''yayue'' in Confucian ritual in Taiwan since the late 1960s, and in mainland China since the 1990s. A major research and modern reconstruction of ''yayue'' of the imperial court was initiated in Taiwan in the 1990s, and in mainland China a performance of ''yayue'' music in 2009 by Nanhua University
Nanhua University (NHU; ) is a university located in Dalin Township, Chiayi County, Taiwan. Founded in 1996 as the Nanhua College of Management, it was elevated to university status in 1999. The university was founded by the Buddhist monk Hs ...
's ''yayue'' music ensemble in Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
also spurred interest in this form of music. There are however questions over the authenticity of these revived and recreated ''yayue'' music and dances, especially the use of modern forms of instruments and various substitutions rather than the more ancient and original forms, nonetheless some argued that such music and dances have always changed over time through succeeding dynasties, and that any changes introduced in the modern era should be seen in this light.
Dance used for politics in the PRC
In the early 20th century, there was a call to "make use of old forms" of literature and art as a means of connecting with the masses. Traditional Chinese dance forms were revised and propagated. In 1943, theChinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and One-party state, sole ruling party of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victoriou ...
launched the new ''yangge
Yangge () is a form of Chinese folk dance developed from a dance known in the Song dynasty as Village Music (). It is very popular in northern China and is one of the most representative form of folk arts. It is popular in both the countryside and ...
'' movement where the ''yangge'' dance was adopted as a means of rallying village support. The new dance is a simplified version of the old dance with socialist elements such as the leader of the holding a sickle instead of umbrella, and it is also known as "struggle yangge" or "reform yangge".
See Also
*Theatre state
In political anthropology, a theatre state is a political state directed towards the performance of drama and ritual rather than more conventional ends such as warfare and welfare. Power in a theatre state is exercised through spectacle. The term ...
* Fengjian
''FД“ngjiГ n'' ( zh, c=е°Ғе»ә, l=enfeoffment and establishment) was a political ideology and governance system in ancient China, whose social structure formed a decentralized system of confederation-like government based on the ruling class consis ...
* Patriarchal system
* Confucian ritual religion
Confucian ritual religion ( s зӨјж•ҷ, t зҰ®ж•ҷ ''LЗҗjiГ o'', "rites' transmission", also called еҗҚж•ҷ ''MГӯngjiГ o'', the "names' transmission"), or the Confucian civil religion, defines the civil religion of China. It consists in the state-en ...
* Music of China
Music of China refers to the music of the Chinese people, which may be the music of the Han Chinese in the course of Chinese history as well as ethnic minorities in today's China. It also includes music produced by people of Chinese origin in som ...
* History of Chinese dance
Dance in China has a long recorded history. Depictions of dancing in China appeared over 4,000 years ago. The early dances may be folk dances or ritual dances, some of which developed into court dances. The most important of the early dances serve ...
* Yayue
''Yayue'' () was a form of classical music and dance performed at the royal court and temples in ancient China. The basic conventions of ''yayue'' were established in the Western Zhou. Together with law and rites, it formed the formal represent ...
References
{{reflistExternal Links
:ж¬Ҫе®ҡеҸӨд»Ҡең–жӣёйӣҶжҲҗ·經жҝҹеҪҷз·ЁВ·зҰ®е„Җе…ёВ·зҰ®жЁӮзёҪйғЁ
ҖӢпјҢеҮәиҮӘ и’Ӣе»·й”ЎгҖҠ еҸӨд»Ҡең–жӣёйӣҶжҲҗгҖӢ Ancient institutions in East Asia Ancient Chinese institutions Religious Confucianism