Rhodamine Skeleton on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
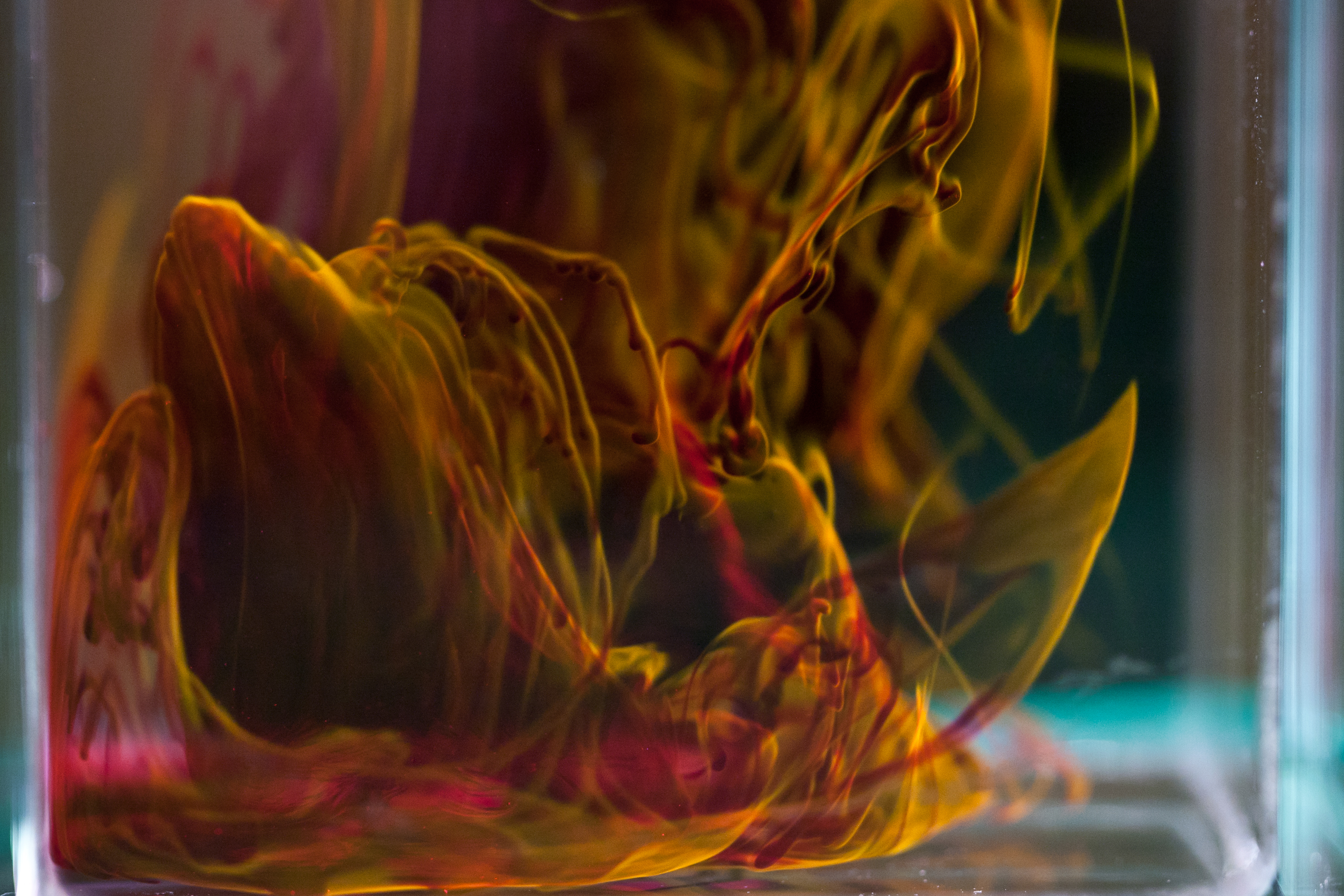 Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the
Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the
Absorption and Emission Spectra of Rhodamine B
*Berlier et al. 2003 J. Histochem Cytochem refers to Alexa 633 as a rhodamine derivative. * Staining dyes Laser gain media Fluorescent dyes
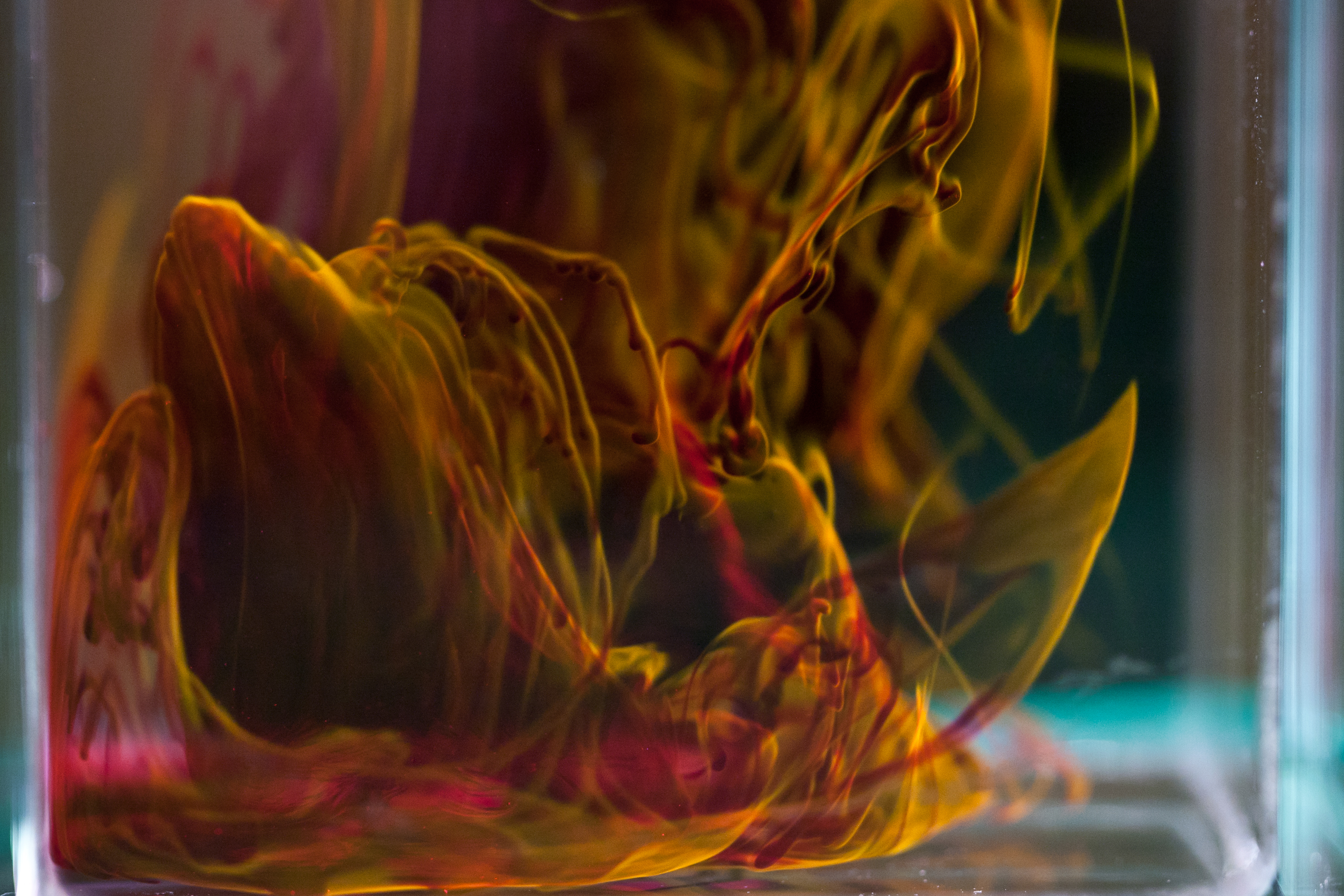 Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the
Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the triarylmethane dye
Triarylmethane dyes are synthetic organic compounds containing triphenylmethane backbones. As dyes, these compounds are intensely colored. They are produced industrially as dyes.
Families
Triarylmethane dyes can be grouped into families accordin ...
s. They are derivatives of xanthene. Important members of the rhodamine family are Rhodamine 6G, Rhodamine 123, and Rhodamine B
Rhodamine B is a chemical compound and a dye. It is often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with fluorometers.
...
. They are mainly used to dye paper and inks, but they lack the lightfastness
Lightfastness is a property of a colourant such as dye or pigment that describes its resistance to fading when exposed to light. Dyes and pigments are used for example for dyeing of fabrics, plastics or other materials and manufacturing paints or ...
for fabric dyeing.
Use
Aside from their major applications, they are often used as atracer dye
Dye tracing is a method of tracking and tracing various flows using dye as a flow tracer when added to a liquid. Dye tracing may be used to analyse the flow of the liquid or the transport of objects within the liquid. Dye tracking may be either qu ...
, e.g. to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport of water. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers. Rhodamine dyes are used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles.
In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the flo ...
, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence ...
. Rhodamine 123 is used in biochemistry to inhibit mitochondrion
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
function. Rhodamine 123 appears to bind to the mitochondrial membranes and inhibit transport processes, especially the electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
, thus slowing down cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
. It is a substrate of P-glycoprotein
P-glycoprotein 1 (permeability glycoprotein, abbreviated as P-gp or Pgp) also known as multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) or ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1 (ABCB1) or cluster of differentiation 243 (CD243) is an important protein ...
(Pgp), which is usually overexpressed in cancer cells. Recent reports indicate that rhodamine 123 may also be a substrate of multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP), or more specifically, MRP1
Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ABCC1'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins t ...
.
In addition to their major applications, rhodamines are used in dye laser as gain media.
Other derivatives
There are many rhodamine derivatives used for imaging purposes, for example Carboxytetramethylrhodamine (TAMRA), tetramethylrhodamine (TMR) and its isothiocyanate derivative (TRITC) and,sulforhodamine 101
Sulforhodamine 101 (SR101) is a red fluorescent dye. In neurophysiological experiments which comprise calcium imaging methods, it can be used for a counterstaining of astrocytes to be able to analyze data from neurons separately. However, in add ...
(and its sulfonyl chloride form Texas Red
Texas Red or sulforhodamine 101 acid chloride is a red fluorescent dye, used in histology for staining cell specimens, for sorting cells with fluorescent-activated cell sorting machines, in fluorescence microscopy applications, and in immunohist ...
) and Rhodamine Red. TRITC is the base rhodamine molecule functionalized with an isothiocyanate
In organic chemistry, isothiocyanate is the functional group , formed by substituting the oxygen in the isocyanate group with a sulfur. Many natural isothiocyanates from plants are produced by enzymatic conversion of metabolites called glucosinol ...
group (−N=C=S), replacing a hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
atom on the bottom ring of the structure. This derivative is reactive towards amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
groups on proteins inside cells. A succinimidyl-ester functional group attached to the rhodamine core, creating NHS-rhodamine, forms another common amine-reactive derivative.
Other derivatives of rhodamine include newer fluorophores such as Alexa 546, Alexa 633, DyLight 550 and DyLight 633, HiLyte fluor 555 HiLyte 594, Janelia Dyes JF549 and JF669
Janelia or Janelia Farm is a mansion and former farm near Ashburn, Virginia, built in 1936 for artist Vinton Liddell Pickens and her husband Robert Pickens, a journalist. The farm property has become the Janelia Research Campus of the Howard ...
have been tailored for various chemical and biological applications where higher photostability, increased brightness, different spectral characteristics, or different attachment groups are needed.
Substituents of the xanthene core are influencing the properties of the xanthene dyes by both electrocnic and steric effects. Specifically designed substituents
A substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule. (In organic chemistry and biochemistry, the terms ''substituent'' and ''functional group'', as well as ''side ...
also allows to allow xanthenes to bear specific funtions activatable upon excitation by visible light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
, e.g. they could act as photoremovable protecting group A photolabile protecting group (PPG; also known as: photoremovable, photosensitive, or photocleavable protecting group) is a chemical modification to a molecule that can be removed with light. PPGs enable high degrees of chemoselectivity as they all ...
for carboxylates
In organic chemistry, a carboxylate is the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid, (or ). It is an ion with negative charge.
Carboxylate salts are salts that have the general formula , where M is a metal and ''n'' is 1, 2,...; ''carboxylate ...
and halides, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
(thus being a photoCORM
A corm, bulbo-tuber, or bulbotuber is a short, vertical, swollen underground plant stem that serves as a storage organ that some plants use to survive winter or other adverse conditions such as summer drought and heat (perennation).
The word ' ...
), or added as a secondary functionality of fluorescent dyes, e.g. fluorescent pH indicators
A pH indicator is a halochromism, halochromic chemical compound added in small amounts to a Solution (chemistry), solution so the pH (acidity or Base (chemistry), basicity) of the solution can be determined visually or spectroscopically by chan ...
.
References
{{reflistExternal links
Absorption and Emission Spectra of Rhodamine B
*Berlier et al. 2003 J. Histochem Cytochem refers to Alexa 633 as a rhodamine derivative. * Staining dyes Laser gain media Fluorescent dyes