|
Rhodamine 123
Rhodamine 123 is a chemical compound and a dye. It is often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers. Rhodamine dyes are used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA. Rhodamine fluorescence can also be used as a measure of membrane polarization in live cell assays both within mitochondria and with bacteria. This use relies on the fact that rhodamine 123 accumulates in membranes in a manner which is dependent on membrane polarization. The absorption of rhodamine 123 peaks around 505 nm and luminescence is tunable around 560 nm when used as a laser dye. Its luminescence quantum yield is 0.90.R. F. Kubin and A. N. Fletcher, "Fluorescence quantum yields of some rhodamine dyes.J. Luminescence 27 (1982) 455/ref> R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds, and as a Alcohol fuel, fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Yield
The quantum yield (Φ) of a radiation-induced process is the number of times a specific event occurs per photon absorbed by the system. Applications Fluorescence spectroscopy The fluorescence quantum yield is defined as the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number of photons absorbed.Lakowicz, Joseph R. ''Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy'' (Kluwer Academic / Plenum Publishers 1999) p.10. Fluorescence quantum yield is measured on a scale from 0 to 1.0, but is often represented as a percentage. A quantum yield of 1.0 (100%) describes a process where each photon absorbed results in a photon emitted. Substances with the largest quantum yields, such as rhodamines, display the brightest emissions; however, compounds with quantum yields of 0.10 are still considered quite fluorescent. Quantum yield is defined by the fraction of excited state fluorophores that decay through fluorescence: where \Phi_ is the fluorescence quantum yield, k_ is the rate constant f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staining Dyes
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cells), and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues (highlighting, for example, muscle fibers or connective tissue), cell populations (classifying different blood cells), or organelles within individual cells. In biochemistry, it involves adding a class-specific ( DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify or quantify the presence of a specific compound. Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in flow cytometry, and to flag proteins or nucleic acids in gel electrophoresis. Light microscopes are used for viewing st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodamine Dyes
Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the triarylmethane dyes. They are derivatives of xanthene. Important members of the rhodamine family are Rhodamine 6G, Rhodamine 123, and Rhodamine B. They are mainly used to dye paper and inks, but they lack the lightfastness for fabric dyeing. Use Aside from their major applications, they are often used as a tracer dye, e.g. to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport of water. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers. Rhodamine dyes are used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA. Rhodamine 123 is used in biochemistry to inhibit mitochondrion function. Rhodamine 123 appears to bind to the mitochondrial membranes and inhibit transport processes, especially the electron transport chain, thus slowing down cellular respiration. It is a substrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodamine 6G
Rhodamine 6G is a highly fluorescent rhodamine family dye. It is often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers. Rhodamine dyes are used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA. Forms Rhodamine 6G usually comes in three different forms. Rhodamine 6G chloride is a bronze/red powder with the chemical formula C28H31ClN2O3. Although highly soluble, this formulation is very corrosive to all metals except stainless steel. Other formulations are less soluble, but also less corrosive. Rhodamine 6G perchlorate (C28H31ClN2O7) comes in the form of red crystals, while rhodamine 6G tetrafluoroborate (C28H31BF4N2O3) appears as maroon crystals. Solubility Butanol (40 g/L), ethanol (80 g/L), methanol (400 g/L), propanol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodamine B
Rhodamine B is a chemical compound and a dye. It is often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with fluorometers. Rhodamine B is used in biology as a staining fluorescent dye, sometimes in combination with auramine O, as the auramine-rhodamine stain to demonstrate acid-fast organisms, notably ''Mycobacterium''. Rhodamine dyes are also used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA. It is also used in rose milk, a popular Indian beverage. Other uses Rhodamine B is often mixed with herbicides to show where they have been used. It is also being tested for use as a biomarker in oral rabies vaccines for wildlife, such as raccoons, to identify animals that have eaten a vaccine bait. The rhodamine is incorporated into the animal's whiskers and teeth. Rhodam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodamine
Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the triarylmethane dyes. They are derivatives of xanthene. Important members of the rhodamine family are Rhodamine 6G, Rhodamine 123, and Rhodamine B. They are mainly used to dye paper and inks, but they lack the lightfastness for fabric dyeing. Use Aside from their major applications, they are often used as a tracer dye, e.g. to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport of water. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers. Rhodamine dyes are used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA. Rhodamine 123 is used in biochemistry to inhibit mitochondrion function. Rhodamine 123 appears to bind to the mitochondrial membranes and inhibit transport processes, especially the electron transport chain, thus slowing down cellular respiration. It is a substra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Dye
Laser dyes are dyes used as laser medium in a dye laser. Laser dyes include the coumarins and the rhodamines. Coumarin dyes emit in the green region of the spectrum, whereas rhodamine dyes are used for emission in the yellow-red. The color emitted by the laser dyes depend upon the surrounding medium i.e.the medium in which they are dissolved. However, there are dozens of laser dyes that can be used to span continuously the emission spectrum from the near ultraviolet to the near infrared.F. J. Duarte, ''Tunable Laser Optics'' (Elsevier-Academic, New York, 2003) Appendix of Laser Dyes (includes more than 50 laser dyes) Laser dyes are also used to dope solid-state matrices, such as poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), and ORMOSILs, to provide gain media for solid state dye lasers. Partial list of laser dyes *Coumarins (in various nomenclatures such as Coumarin 480, 490, 504, 521, 504T, 521T) *Fluorescein * polyphenyl ("polyphenyl 1") S. C. Guggenheimer, A. B. Petersen"High P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dye Laser
A dye laser is a laser that uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths, often spanning 50 to 100 nanometers or more. The wide bandwidth makes them particularly suitable for tunable lasers and pulsed lasers. The dye rhodamine 6G, for example, can be tuned from 635 nm (orangish-red) to 560 nm (greenish-yellow), and produce pulses as short as 16 femtoseconds. Moreover, the dye can be replaced by another type in order to generate an even broader range of wavelengths with the same laser, from the near-infrared to the near-ultraviolet, although this usually requires replacing other optical components in the laser as well, such as dielectric mirrors or pump lasers. Dye lasers were independently discovered by P. P. Sorokin and F. P. Schäfer (and colleagues) in 1966. In addition to the usual liquid state, dye lasers are also availa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracer Dye
Dye tracing is a method of tracking and tracing various flows using dye as a flow tracer when added to a liquid. Dye tracing may be used to analyse the flow of the liquid or the transport of objects within the liquid. Dye tracking may be either qualitative, showing the presence of a particular flow, or quantitative, when the amount of the traced dye is measured by special instruments. Fluorescent dyes Fluorescent dyes are often used in situations where there is insufficient lighting (e.g., sewers or cave waters), and where precise quantitative data are required (measured by a fluorometer). In 1871, Fluorescein was among the first fluorescent dyes to be developed. Its disodium salt (under the trademark " Uranine") was developed several years later and still remains among the best tracer dyes.An educational website about karst and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly a protein) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample to be tested are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme and then any unbound antibodies are removed. In the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's substrate is added. If there was binding, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change. Performing an ELISA involves at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
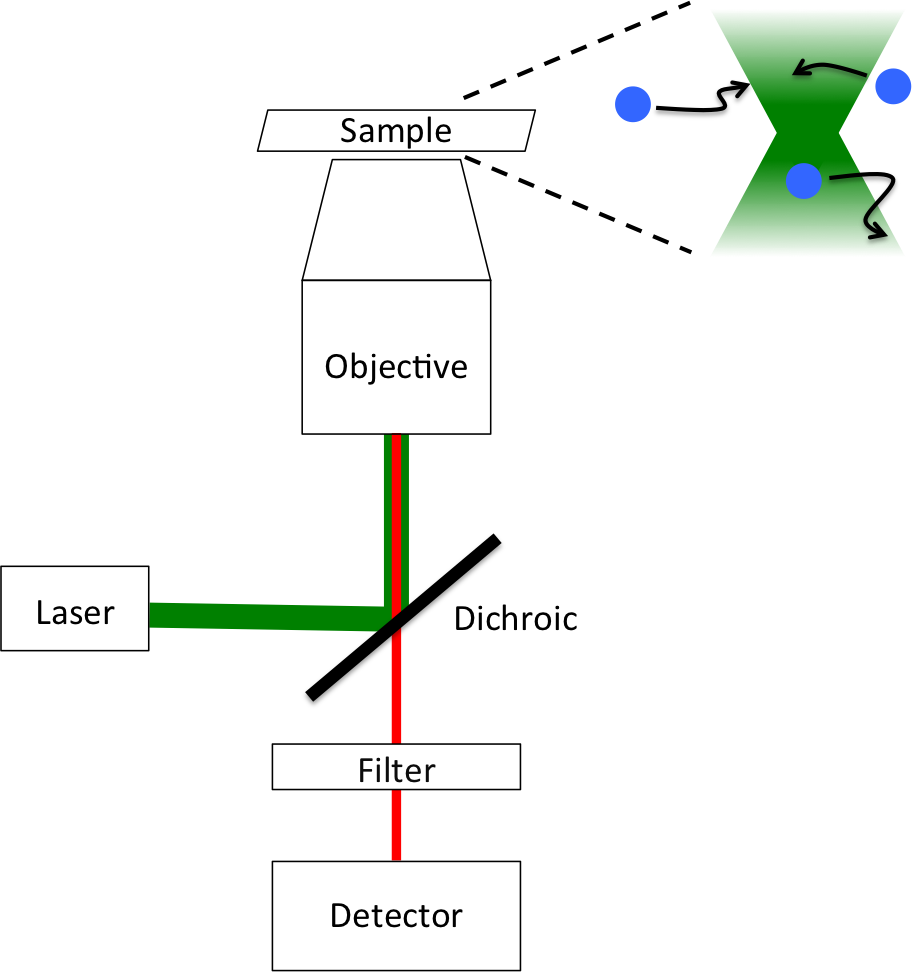
Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) is a statistical analysis, via time correlation, of stationary fluctuations of the fluorescence intensity. Its theoretical underpinning originated from L. Onsager's regression hypothesis. The analysis provides kinetic parameters of the physical processes underlying the fluctuations. One of the interesting applications of this is an analysis of the concentration fluctuations of fluorescent particles (molecules) in solution. In this application, the fluorescence emitted from a very tiny space in solution containing a small number of fluorescent particles (molecules) is observed. The fluorescence intensity is fluctuating due to Brownian motion of the particles. In other words, the number of the particles in the sub-space defined by the optical system is randomly changing around the average number. The analysis gives the average number of fluorescent particles and average diffusion time, when the particle is passing through the space. Eventua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)