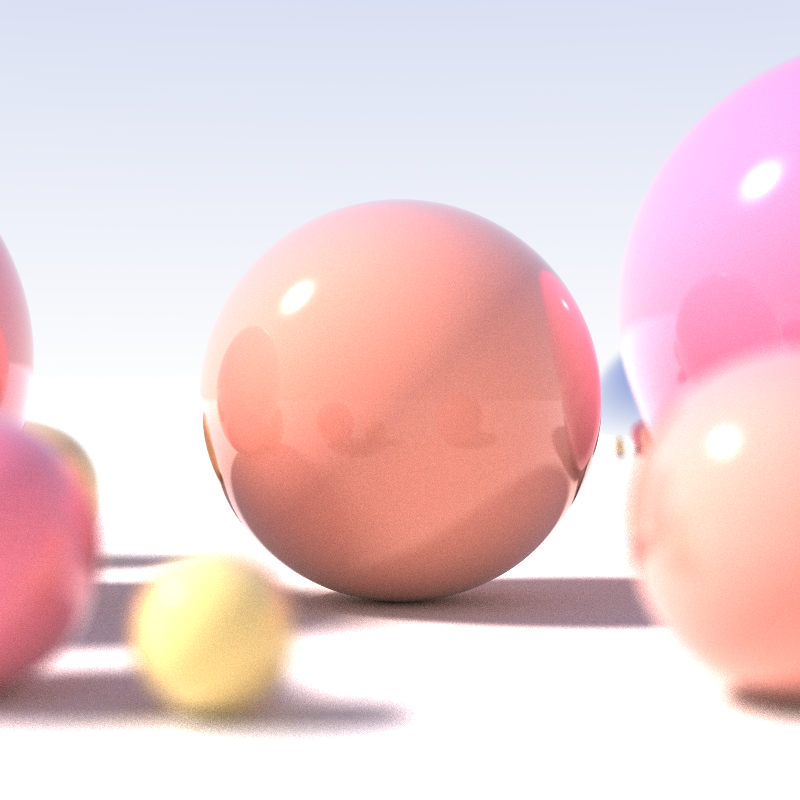
In
3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, or “3D graphics,” sometimes called CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for th ...
, ray tracing is a technique for modeling
light transport for use in a wide variety of
rendering algorithms for generating
digital images
A digital image is an image composed of picture elements, also known as ''pixels'', each with ''finite'', '' discrete quantities'' of numeric representation for its intensity or gray level that is an output from its two-dimensional functions f ...
.
On a spectrum of
computational cost and visual fidelity, ray tracing-based rendering techniques, such as
ray casting,
recursive ray tracing,
distribution ray tracing,
photon mapping and
path tracing, are generally slower and higher fidelity than
scanline rendering methods. Thus, ray tracing was first deployed in applications where taking a relatively long time to render could be tolerated, such as in still computer-generated images, and film and television
visual effects (VFX), but was less suited to
real-time applications such as
video games, where
speed is critical in rendering each
frame.
Since 2018, however,
hardware acceleration
Hardware acceleration is the use of computer hardware designed to perform specific functions more efficiently when compared to software running on a general-purpose central processing unit (CPU). Any transformation of data that can be calcula ...
for real-time ray tracing has become standard on new commercial graphics cards, and graphics APIs have followed suit, allowing developers to use hybrid ray tracing and
rasterization-based rendering in games and other real-time applications with a lesser hit to frame render times.
Ray tracing is capable of simulating a variety of
optical effects, such as
reflection,
refraction,
soft shadows
The umbra, penumbra and antumbra are three distinct parts of a shadow, created by any light source after impinging on an opaque object. Assuming no diffraction, for a collimated beam (such as a point source) of light, only the umbra is cast.
Th ...
,
scattering
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including ...
,
depth of field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the furthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image captured with a camera.
Factors affecting depth of field
For cameras that can only focus on one object dist ...
,
motion blur,
caustics,
ambient occlusion and
dispersion phenomena (such as
chromatic aberration). It can also be used to trace the path of
sound waves
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ...
in a similar fashion to light waves, making it a viable option for more immersive sound design in video games by rendering realistic
reverberation
Reverberation (also known as reverb), in acoustics, is a persistence of sound, after a sound is produced. Reverberation is created when a sound or signal is reflected causing numerous reflections to build up and then decay as the sound is abso ...
and
echoes. In fact, any physical
wave or
particle phenomenon with approximately linear motion can be simulated with
ray tracing.
Ray tracing-based rendering techniques that involve sampling light over a domain generate
image noise artifacts that can be addressed by tracing a very large number of rays or using
denoising
Noise reduction is the process of removing noise from a signal. Noise reduction techniques exist for audio and images. Noise reduction algorithms may distort the signal to some degree. Noise rejection is the ability of a circuit to isolate an un ...
techniques.
History


The idea of ray tracing comes from as early as the 16th century when it was described by
Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer (; ; hu, Ajtósi Adalbert; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer (without an umlaut) or Due ...
, who is credited for its invention.
[.] In
''Four Books on Measurement'', he described an apparatus called a ''Dürer's door'' using a thread attached to the end of a stylus that an assistant moves along the contours of the object to draw. The thread passes through the door's frame and then through a hook on the wall. The thread forms a ray and the hook acts as the center of projection and corresponds to the camera position in ray tracing.
Using a computer for ray tracing to generate shaded pictures was first accomplished by
Arthur Appel
Arthur is a common male given name of Brythonic origin. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. The etymology is disputed. It may derive from the Celtic ''Artos'' meaning “Bear”. Another theory, more wi ...
in 1968. Appel used ray tracing for primary visibility (determining the closest surface to the camera at each image point), and traced secondary rays to the light source from each point being shaded to determine whether the point was in shadow or not.
Later, in 1971, Goldstein and Nagel of
MAGI (Mathematical Applications Group, Inc.) published “3-D Visual Simulation”, wherein ray tracing is used to make shaded pictures of solids by simulating the photographic process in reverse. They cast a ray through each picture element (pixel) in the screen into the scene to identify the visible surface. The first surface intersected by the ray was the visible one. This non-recursive ray tracing-based rendering algorithm is today called "
ray casting". At the ray-surface intersection point found, they computed the surface normal and, knowing the position of the light source, computed the brightness of the pixel on the screen. Their publication describes a short (30 second) film “made using the University of Maryland’s display hardware outfitted with a 16mm camera. The film showed the helicopter and a simple ground level gun emplacement. The helicopter was programmed to undergo a series of maneuvers including turns, take-offs, and landings, etc., until it eventually is shot down and crashed.” A ''
CDC 6600'' computer was used. MAGI produced an animation video called ''MAGI/SynthaVision Sampler'' in 1974.
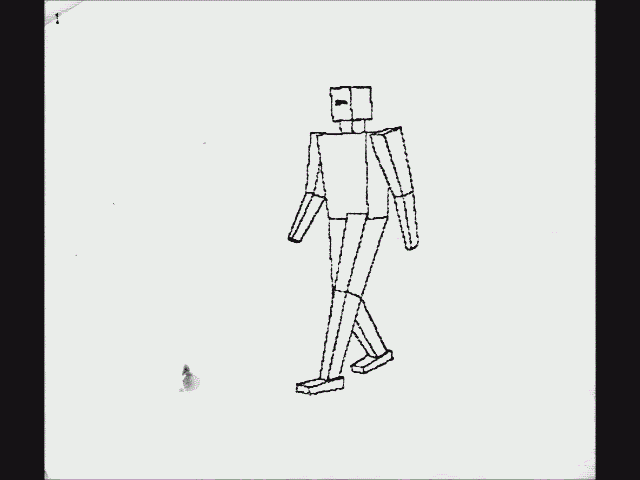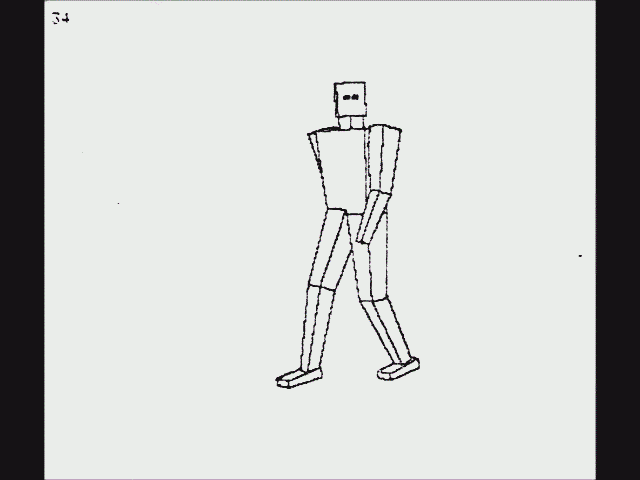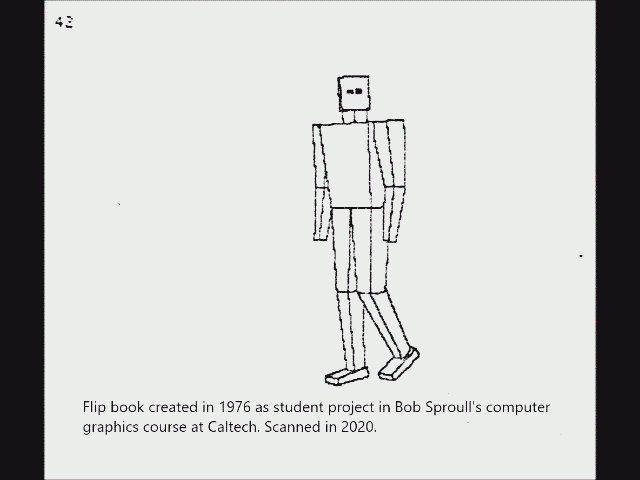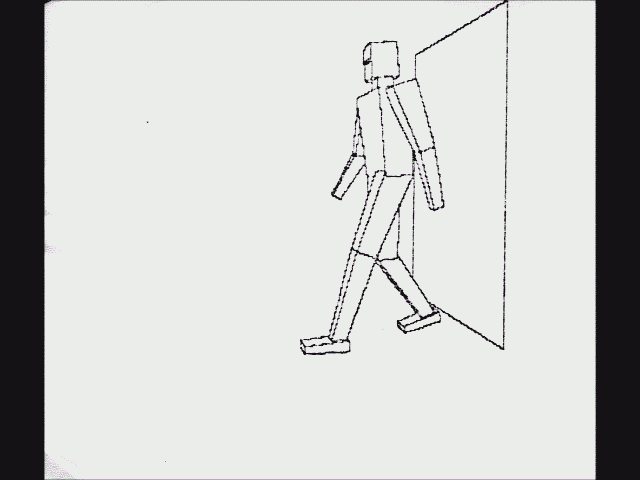
Another early instance of ray casting came in 1976, when Scott Roth created a flip book animation in
Bob Sproull's computer graphics course at
Caltech. The scanned pages are shown as a video on the right. Roth's computer program noted an edge point at a pixel location if the ray intersected a bounded plane different from that of its neighbors. Of course, a ray could intersect multiple planes in space, but only the surface point closest to the camera was noted as visible. The edges are jagged because only a coarse resolution was practical with the computing power of the time-sharing DEC
PDP-10 used. The “terminal” was a
Tektronix storage-tube display for text and graphics. Attached to the display was a printer which would create an image of the display on rolling thermal paper. Roth extended the framework, introduced the term ''
ray casting'' in the context of
computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images with the aid of computers. Today, computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal ...
and
solid modeling
Solid modeling (or solid modelling) is a consistent set of principles for mathematical and computer modeling of three-dimensional shapes '' (solids)''. Solid modeling is distinguished from related areas of geometric modeling and computer graphi ...
, and later published his work while at GM Research Labs.
Turner Whitted John Turner Whitted is an electrical engineer and computer scientist who introduced recursive ray tracing to the computer graphics community with his 1979 paper "An improved illumination model for shaded display". His algorithm proved to be a pract ...
was the first to show recursive ray tracing for mirror reflection and for refraction through translucent objects, with an angle determined by the solid's index of refraction, and to use ray tracing for
anti-aliasing Anti-aliasing may refer to any of a number of techniques to combat the problems of aliasing in a sampled signal such as a digital image or digital audio recording.
Specific topics in anti-aliasing include:
* Anti-aliasing filter, a filter used ...
. Whitted also showed ray traced shadows. He produced a recursive ray-traced film called ''The Compleat Angler'' in 1979 while an engineer at Bell Labs. Whitted's deeply recursive ray tracing algorithm reframed rendering from being primarily a matter of surface visibility determination to being a matter of light transport. His paper inspired a series of subsequent work by others that included
distribution ray tracing and finally
unbiased
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individual, a group, ...
path tracing, which provides the ''
rendering equation
In computer graphics, the rendering equation is an integral equation in which the equilibrium radiance leaving a point is given as the sum of emitted plus reflected radiance under a geometric optics approximation. It was simultaneously introduc ...
'' framework that has allowed computer generated imagery to be faithful to reality.
For decades,
global illumination
Global illumination (GI), or indirect illumination, is a group of algorithms used in 3D computer graphics that are meant to add more realistic lighting to 3D scenes. Such algorithms take into account not only the light that comes directly from ...
in major films using computer generated imagery was faked with additional lights. Ray tracing-based rendering eventually changed that by enabling physically-based light transport. Early feature films rendered entirely using path tracing include ''
Monster House'' (2006), ''
Cloudy with a Chance of Meatballs
''Cloudy with a Chance of Meatballs'' is a children's book written by Judi Barrett and illustrated by Ron Barrett. It was first published in 1978 by Atheneum Books, followed by a 1982 trade paperback edition from sister company Aladdin Paperb ...
'' (2009), and ''
Monsters University
''Monsters University'' is a 2013 American computer-animated monster comedy film produced by Pixar Animation Studios and released by Walt Disney Pictures. It was directed by Dan Scanlon (in his feature directorial debut) and produced by Kori ...
'' (2013).
Algorithm overview

Optical ray tracing describes a method for producing visual images constructed in
3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, or “3D graphics,” sometimes called CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for th ...
environments, with more photorealism than either
ray casting or
scanline rendering techniques. It works by tracing a path from an imaginary eye through each
pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the s ...
in a virtual screen, and calculating the color of the object visible through it.
Scenes in ray tracing are described mathematically by a programmer or by a visual artist (normally using intermediary tools). Scenes may also incorporate data from images and models captured by means such as digital photography.
Typically, each ray must be tested for
intersection
In mathematics, the intersection of two or more objects is another object consisting of everything that is contained in all of the objects simultaneously. For example, in Euclidean geometry, when two lines in a plane are not parallel, thei ...
with some subset of all the objects in the scene. Once the nearest object has been identified, the algorithm will estimate the incoming
light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
at the point of intersection, examine the material properties of the object, and combine this information to calculate the final color of the pixel. Certain illumination algorithms and reflective or translucent materials may require more rays to be re-cast into the scene.
It may at first seem counterintuitive or "backward" to send rays ''away'' from the camera, rather than ''into'' it (as actual light does in reality), but doing so is many orders of magnitude more efficient. Since the overwhelming majority of light rays from a given light source do not make it directly into the viewer's eye, a "forward" simulation could potentially waste a tremendous amount of computation on light paths that are never recorded.
Therefore, the shortcut taken in ray tracing is to presuppose that a given ray intersects the view frame. After either a maximum number of reflections or a ray traveling a certain distance without intersection, the ray ceases to travel and the pixel's value is updated.
Calculate rays for rectangular viewport
On input we have (in calculation we use vector
normalization
Normalization or normalisation refers to a process that makes something more normal or regular. Most commonly it refers to:
* Normalization (sociology) or social normalization, the process through which ideas and behaviors that may fall outside of ...
and
cross product
In mathematics, the cross product or vector product (occasionally directed area product, to emphasize its geometric significance) is a binary operation on two vectors in a three-dimensional oriented Euclidean vector space (named here E), and i ...
):
*
eye position
*
target position
*
field of view
The field of view (FoV) is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation.
Humans a ...
- for humans, we can assume
*
numbers of square pixels on viewport vertical and horizontal direction
*
numbers of actual pixel
*
vertical vector which indicates where is up and down, usually
 In
In 
 The idea of ray tracing comes from as early as the 16th century when it was described by
The idea of ray tracing comes from as early as the 16th century when it was described by  Another early instance of ray casting came in 1976, when Scott Roth created a flip book animation in Bob Sproull's computer graphics course at Caltech. The scanned pages are shown as a video on the right. Roth's computer program noted an edge point at a pixel location if the ray intersected a bounded plane different from that of its neighbors. Of course, a ray could intersect multiple planes in space, but only the surface point closest to the camera was noted as visible. The edges are jagged because only a coarse resolution was practical with the computing power of the time-sharing DEC PDP-10 used. The “terminal” was a Tektronix storage-tube display for text and graphics. Attached to the display was a printer which would create an image of the display on rolling thermal paper. Roth extended the framework, introduced the term '' ray casting'' in the context of
Another early instance of ray casting came in 1976, when Scott Roth created a flip book animation in Bob Sproull's computer graphics course at Caltech. The scanned pages are shown as a video on the right. Roth's computer program noted an edge point at a pixel location if the ray intersected a bounded plane different from that of its neighbors. Of course, a ray could intersect multiple planes in space, but only the surface point closest to the camera was noted as visible. The edges are jagged because only a coarse resolution was practical with the computing power of the time-sharing DEC PDP-10 used. The “terminal” was a Tektronix storage-tube display for text and graphics. Attached to the display was a printer which would create an image of the display on rolling thermal paper. Roth extended the framework, introduced the term '' ray casting'' in the context of  Optical ray tracing describes a method for producing visual images constructed in
Optical ray tracing describes a method for producing visual images constructed in  In
In 
 The idea of ray tracing comes from as early as the 16th century when it was described by
The idea of ray tracing comes from as early as the 16th century when it was described by  Another early instance of ray casting came in 1976, when Scott Roth created a flip book animation in Bob Sproull's computer graphics course at Caltech. The scanned pages are shown as a video on the right. Roth's computer program noted an edge point at a pixel location if the ray intersected a bounded plane different from that of its neighbors. Of course, a ray could intersect multiple planes in space, but only the surface point closest to the camera was noted as visible. The edges are jagged because only a coarse resolution was practical with the computing power of the time-sharing DEC PDP-10 used. The “terminal” was a Tektronix storage-tube display for text and graphics. Attached to the display was a printer which would create an image of the display on rolling thermal paper. Roth extended the framework, introduced the term '' ray casting'' in the context of
Another early instance of ray casting came in 1976, when Scott Roth created a flip book animation in Bob Sproull's computer graphics course at Caltech. The scanned pages are shown as a video on the right. Roth's computer program noted an edge point at a pixel location if the ray intersected a bounded plane different from that of its neighbors. Of course, a ray could intersect multiple planes in space, but only the surface point closest to the camera was noted as visible. The edges are jagged because only a coarse resolution was practical with the computing power of the time-sharing DEC PDP-10 used. The “terminal” was a Tektronix storage-tube display for text and graphics. Attached to the display was a printer which would create an image of the display on rolling thermal paper. Roth extended the framework, introduced the term '' ray casting'' in the context of