RDRAM on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rambus DRAM (RDRAM), and its successors Concurrent Rambus DRAM (CRDRAM) and Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM), are types of

 Moreover, if a mainboard has a dual- or quad-channel memory subsystem, all of the memory channels must be upgraded simultaneously. 16-bit modules provide one channel of memory, while 32-bit modules provide two channels. Therefore, a dual-channel mainboard accepting 16-bit modules must have RIMMs added or removed in pairs. A dual-channel mainboard accepting 32-bit modules can have single RIMMs added or removed as well. Note that some of the later 32-bit modules had 232 pins as compared to the older 184-pin 16-bit modules.
Moreover, if a mainboard has a dual- or quad-channel memory subsystem, all of the memory channels must be upgraded simultaneously. 16-bit modules provide one channel of memory, while 32-bit modules provide two channels. Therefore, a dual-channel mainboard accepting 16-bit modules must have RIMMs added or removed in pairs. A dual-channel mainboard accepting 32-bit modules can have single RIMMs added or removed as well. Note that some of the later 32-bit modules had 232 pins as compared to the older 184-pin 16-bit modules.
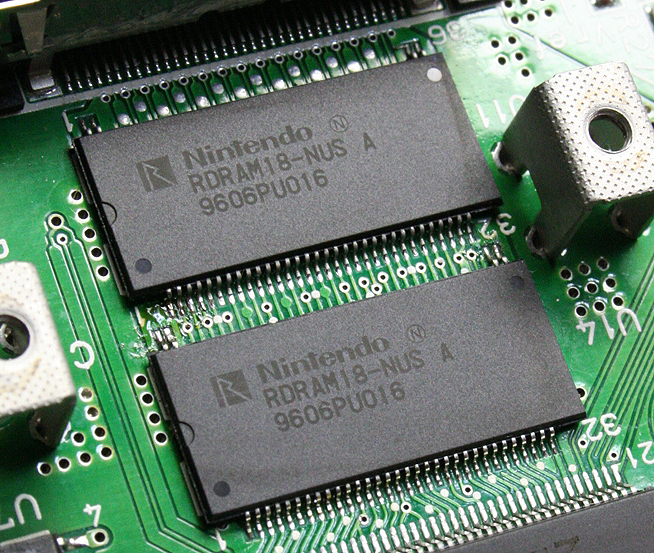 Rambus's RDRAM saw use in two video game consoles, beginning in 1996 with the
Rambus's RDRAM saw use in two video game consoles, beginning in 1996 with the
RDRAM on the Rambus website
* ttp://www.oempcworld.com/support/Install_Rambus.htm How to install RAMBUS memorybr>Illustrated Guide for Installing RDRAM
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rdram SDRAM it:DRAM#Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM)
synchronous dynamic random-access memory
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal.
DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the ...
(SDRAM) developed by Rambus
Rambus Incorporated, founded in 1990, is an American technology company that designs, develops and licenses chip interface technologies and architectures that are used in digital electronics products. The company is well known for inventing ...
from the 1990s through to the early 2000s. The third-generation of Rambus DRAM, DRDRAM was replaced by XDR DRAM
XDR DRAM (extreme data rate dynamic random-access memory) is a high-performance dynamic random-access memory interface. It is based on and succeeds RDRAM. Competing technologies include DDR2 and GDDR4.
Overview
XDR was designed to be effecti ...
. Rambus DRAM was developed for high-bandwidth applications and was positioned by Rambus as replacement for various types of contemporary memories, such as SDRAM.
DRDRAM was initially expected to become the standard in PC memory, especially after Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
agreed to license the Rambus technology for use with its future chipsets. Further, DRDRAM was expected to become a standard for graphics memory. However, RDRAM got embroiled in a standards war with an alternative technology—DDR SDRAM
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 ...
—and quickly lost out on grounds of price and, later, performance. By around 2003, DRDRAM was no longer supported in new personal computers.
PC main memory
The first PC motherboards with support for RDRAM debuted in late 1999, after two major delays. RDRAM was controversial during its widespread use by Intel for having high licensing fees, high cost, being a proprietary standard, and low performance advantages for the increased cost. RDRAM andDDR SDRAM
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 ...
were involved in a standards war. PC-800 RDRAM operated at 400MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one he ...
and delivered 1600 MB/s of bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
over a 16-bit bus. It was packaged as a 184-pin RIMM (Rambus
Rambus Incorporated, founded in 1990, is an American technology company that designs, develops and licenses chip interface technologies and architectures that are used in digital electronics products. The company is well known for inventing ...
in-line memory module) form factor, similar to a DIMM
A DIMM () (Dual In-line Memory Module), commonly called a RAM stick, comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuits. These memory modules are mounted on a printed circuit board and designed for use in personal compute ...
(dual in-line memory module). Data is transferred on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal, a technique known as DDR
DDR or ddr may refer to:
*ddr, ISO 639-3 code for the Dhudhuroa language
*DDr., title for a double doctorate in Germany
*DDR, station code for Dadar railway station, Mumbai, India
*' (German Democratic Republic), official name of the former East ...
. To emphasize the advantages of the DDR technique, this type of RAM was marketed at speeds twice the actual clock rate, i.e. the 400 MHz Rambus standard was named PC-800. This was significantly faster than the previous standard, PC-133 SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal.
DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the ...
, which operated at 133 MHz and delivered 1066 MB/s of bandwidth over a 64-bit bus using a 168-pin DIMM
A DIMM () (Dual In-line Memory Module), commonly called a RAM stick, comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuits. These memory modules are mounted on a printed circuit board and designed for use in personal compute ...
form factor.

 Moreover, if a mainboard has a dual- or quad-channel memory subsystem, all of the memory channels must be upgraded simultaneously. 16-bit modules provide one channel of memory, while 32-bit modules provide two channels. Therefore, a dual-channel mainboard accepting 16-bit modules must have RIMMs added or removed in pairs. A dual-channel mainboard accepting 32-bit modules can have single RIMMs added or removed as well. Note that some of the later 32-bit modules had 232 pins as compared to the older 184-pin 16-bit modules.
Moreover, if a mainboard has a dual- or quad-channel memory subsystem, all of the memory channels must be upgraded simultaneously. 16-bit modules provide one channel of memory, while 32-bit modules provide two channels. Therefore, a dual-channel mainboard accepting 16-bit modules must have RIMMs added or removed in pairs. A dual-channel mainboard accepting 32-bit modules can have single RIMMs added or removed as well. Note that some of the later 32-bit modules had 232 pins as compared to the older 184-pin 16-bit modules.
Module specifications
Continuity modules
The design of many common Rambus memory controllers dictated that memory modules be installed in sets of two. Any remaining open memory slots must be filled with continuity RIMMs (CRIMMs). These modules provide no extra memory and only served to propagate the signal to termination resistors on the motherboard instead of providing a dead end, where signals would reflect. CRIMMs appear physically similar to regular RIMMs, except that they lack integrated circuits (and their heat-spreaders).Performance
Compared to other contemporary standards, Rambus showed increase in latency, heat output, manufacturing complexity, and cost. Because of more complex interface circuitry and increased number of memory banks, RDRAM die size was larger than that of contemporary SDRAM chips, resulting in a 10–20% price premium at 16 Mbit densities (adding about a 5% penalty at 64 Mbit). Note that the most common RDRAM densities are 128 Mbit and 256 Mbit. PC-800 RDRAM operated with a latency of 45 ns, more than that of other SDRAM varieties of the time. RDRAM memory chips also put out significantly more heat than SDRAM chips, necessitating heatspreaders on all RIMM devices. RDRAM includes additional circuitry (such as packet demultiplexers) on each chip, increasing manufacturing complexity compared to SDRAM. RDRAM was also up to four times more expensive than PC-133 SDRAM due to a combination of higher manufacturing costs and high license fees. PC-2100DDR SDRAM
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 ...
, introduced in 2000, operated with a clock rate of 133 MHz and delivered 2100 MB/s over a 64-bit bus using a 184-pin DIMM form factor.
With the introduction of the Intel 840 (Pentium III), Intel 850
The Intel 850 chipset was the first chipset available for the Pentium 4 processor, and was simultaneously released in November 2000. It consists of an 82850 memory controller hub and an 82801BA I/O controller hub.
This chipset outperforms the A ...
(Pentium 4), Intel 860 (Pentium 4 Xeon) chipsets, Intel added support for dual-channel PC-800 RDRAM, doubling bandwidth to 3200 MB/s by increasing the bus width to 32 bits. This was followed in 2002 by the Intel 850E chipset, which introduced PC-1066 RDRAM, increasing total dual-channel bandwidth to 4200 MB/s. In 2002, Intel released the E7205 Granite Bay chipset, which introduced dual-channel DDR support (for a total bandwidth of 4200 MB/s) at a slightly lower latency than competing RDRAM. The bandwidth of Granite Bay matched that of the i850E chipset using PC-1066 DRDRAM with considerably lower latency.
To achieve RDRAM's 800 MHz clock rate, the memory module runs on a 16-bit bus instead of a 64-bit bus in contemporary SDRAM DIMM. At the time of the Intel 820 launch some RDRAM modules operated at rates less than 800 MHz.
Benchmarks
Benchmark tests conducted in 1998 and 1999 showed most everyday applications to run minimally slower with RDRAM. In 1999, benchmarks comparing the Intel 840 and Intel 820 RDRAM chipsets with theIntel 440BX
The Intel 440BX (codenamed Seattle) is a chipset from Intel, supporting Pentium II, Pentium III, and Celeron processors. It is also known as the i440BX and was released in April 1998. The official part number is 82443BX.
Features
The 440BX orig ...
SDRAM chipset led to the conclusion that the performance gain of RDRAM did not justify its cost over SDRAM, except for use in workstations. In 2001, benchmarks pointed out that single-channel DDR266 SDRAM modules could closely match dual-channel 800 MHz RDRAM in everyday applications.
Marketing history
In November 1996, Rambus entered into a development and license contract with Intel. Intel announced that it would only support the Rambus memory interface for itsmicroprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circ ...
s and had been granted rights to purchase one million shares of Rambus' stock at $10 per share.
As a transition strategy, Intel planned to support PC-100 SDRAM DIMMs on future Intel 82x chipsets using Memory Translation Hub (MTH). In 2000, Intel recalled the Intel 820 motherboard, which featured the MTH, due to occasional occurrences of hanging
Hanging is the suspension of a person by a noose or ligature around the neck.Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd ed. Hanging as method of execution is unknown, as method of suicide from 1325. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' states that hanging i ...
and spontaneous reboots caused by simultaneous switching noise. Since then, no production Intel 820 motherboards contain MTH.
In 2000, Intel began to subsidize RDRAM by bundling retail boxes of Pentium 4
Pentium 4 is a series of single-core CPUs for desktops, laptops and entry-level servers manufactured by Intel. The processors were shipped from November 20, 2000 until August 8, 2008. The production of Netburst processors was active from 2000 u ...
s with two RIMMs. Intel began to phase out these subsidies in 2001.
In 2003, Intel introduced the 865 and 875 chipsets with dual-channel DDR SDRAM support, which were marketed as high-end replacements of the 850 chipset. Furthermore, the future memory roadmap did not include RDRAM.
Other uses
Video game consoles
 Rambus's RDRAM saw use in two video game consoles, beginning in 1996 with the
Rambus's RDRAM saw use in two video game consoles, beginning in 1996 with the Nintendo 64
The (N64) is a home video game console developed by Nintendo. The successor to the Super Nintendo Entertainment System, it was released on June 23, 1996, in Japan, on September 29, 1996, in North America, and on March 1, 1997, in Europe and ...
. The Nintendo console used 4 MB RDRAM running with a 500 MHz clock on a 9-bit bus, providing 500 MB/s bandwidth. RDRAM allowed N64 to be equipped with a large amount of memory bandwidth while maintaining a lower cost due to design simplicity. RDRAM's narrow bus allowed circuit board designers to use simpler design techniques to minimize cost. The memory, however, was disliked for its high random-access latencies. In the N64, the RDRAM modules are cooled by a passive heatspreader assembly. Nintendo also included a provision for upgrading the system memory with the Expansion Pak accessory, allowing certain games to be enhanced with either enhanced graphics, higher resolution or increased framerate. A Jumper Pak dummy unit is included with the console due to the aforementioned design quirks of RDRAM.
The Sony PlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October 2000, in Europe on 24 November 2000, and in Australia on 3 ...
was equipped with 32 MB of RDRAM and implemented a dual-channel configuration resulting in 3200 MB/s available bandwidth.
Texas Instruments DLP
RDRAM was used inTexas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globa ...
' Digital Light Processing
Digital Light Processing (DLP) is a set of chipsets based on optical micro-electro-mechanical technology that uses a digital micromirror device. It was originally developed in 1987 by Larry Hornbeck of Texas Instruments. While the DLP imagin ...
(DLP) systems.
Video cards
Cirrus Logic implemented RDRAM support in their ''Laguna'' graphics chip, with two members of the family: the 2D-only 5462 and the 5464, a 2D chip with 3D acceleration. Both have 2 MB of memory and PCI port. Cirrus Logic GD5465 has extended 4 MB Rambus memory, dual-channel memory support and uses faster AGP port. RDRAM offered a potentially faster user experience than competing DRAM technologies with its high bandwidth. The chips were used on the Creative Graphics Blaster MA3xx series, among others.See also
* List of device bandwidths * SLDRAM, an alternative open standardReferences
External links
RDRAM on the Rambus website
* ttp://www.oempcworld.com/support/Install_Rambus.htm How to install RAMBUS memorybr>Illustrated Guide for Installing RDRAM
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rdram SDRAM it:DRAM#Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM)