Queensland Rugby League Season 1912 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in
 In February 1606, Dutch navigator
In February 1606, Dutch navigator
 A public meeting was held in 1851 to consider the proposed
A public meeting was held in 1851 to consider the proposed  Immigration to Australia and Queensland, in particular, began in the 1850s to support the state economy. During the period from the 1860s until the early 20th century, many labourers, known at the time as
Immigration to Australia and Queensland, in particular, began in the 1850s to support the state economy. During the period from the 1860s until the early 20th century, many labourers, known at the time as
 Following Federation in 1901, the
Following Federation in 1901, the


 With a total area of 1,852,642 square kilometres (715,309 square miles), Queensland is an expansive state with a highly diverse range of climates and geographical features. If Queensland were an independent nation, it would be the world's 16th largest, being approximately the same size as Mexico,
With a total area of 1,852,642 square kilometres (715,309 square miles), Queensland is an expansive state with a highly diverse range of climates and geographical features. If Queensland were an independent nation, it would be the world's 16th largest, being approximately the same size as Mexico,
 Because of its size, there is significant variation in climate across the state. There is ample rainfall along the coastline, with a
Because of its size, there is significant variation in climate across the state. There is ample rainfall along the coastline, with a
In December 2021, Queensland had an estimated population of 5,265,043. Approximately half of the state's population live in Brisbane, and over 70% live in
 Queensland is home to numerous universities. The state's oldest university, the
Queensland is home to numerous universities. The state's oldest university, the


 In 2019, Queensland had a
In 2019, Queensland had a
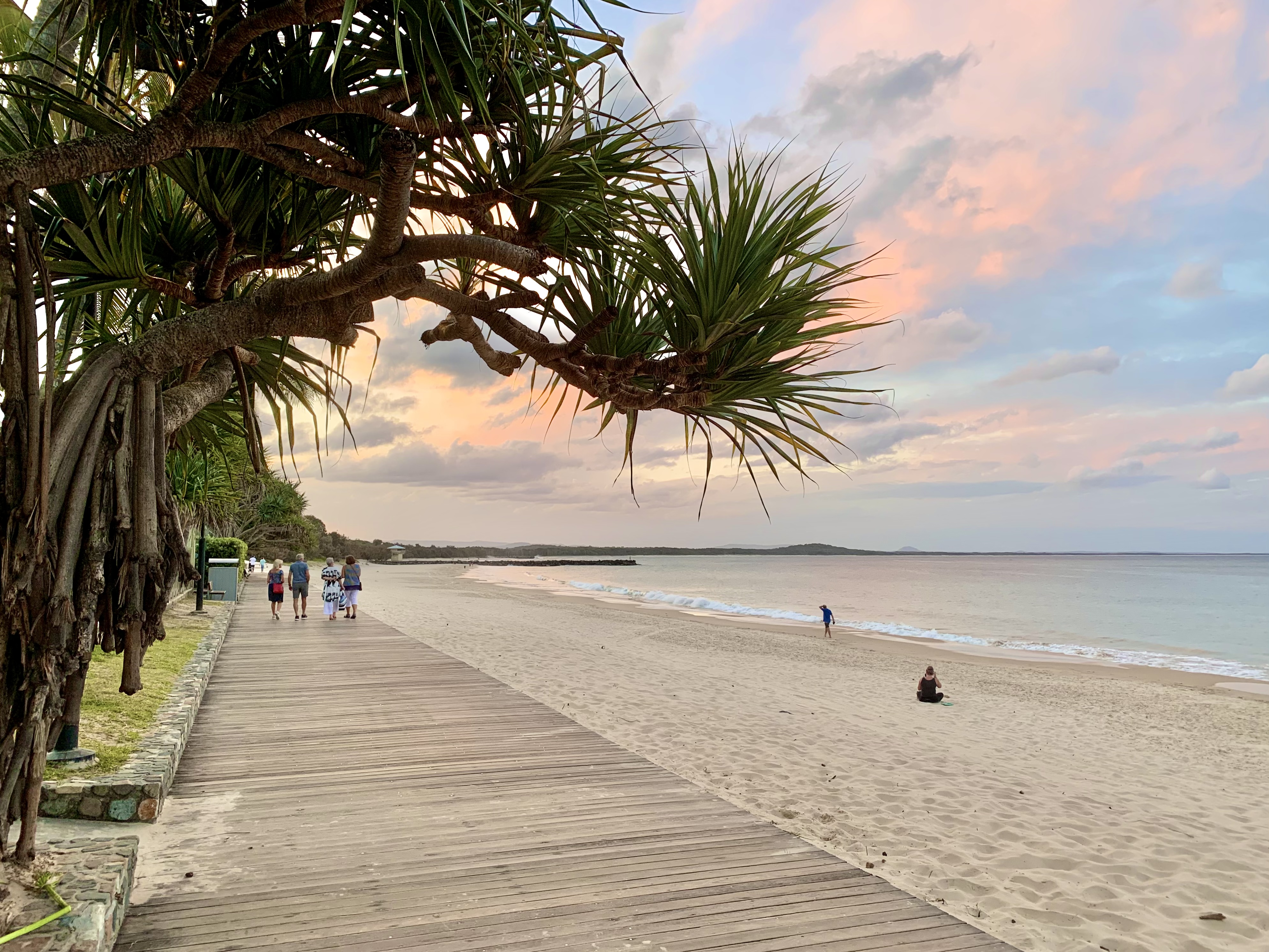
 As a result of its varied landscapes, warm climate and abundant natural environment, tourism is Queensland's leading tertiary industry with millions of interstate and international visitors visiting the state each year. The industry generates $8.8 billion annually, accounting for 4.5% of Queensland's Gross State Product. It has an annual export of $4.0 billion annually. The sector directly employs about 5.7% of Queensland citizens. Accommodation in Queensland caters for nearly 22% of the total expenditure, followed by restaurants/meals (15%), airfares (11%), fuel (11%) and shopping/gifts (11%).
The most visited tourist destinations of Queensland include Brisbane (including
As a result of its varied landscapes, warm climate and abundant natural environment, tourism is Queensland's leading tertiary industry with millions of interstate and international visitors visiting the state each year. The industry generates $8.8 billion annually, accounting for 4.5% of Queensland's Gross State Product. It has an annual export of $4.0 billion annually. The sector directly employs about 5.7% of Queensland citizens. Accommodation in Queensland caters for nearly 22% of the total expenditure, followed by restaurants/meals (15%), airfares (11%), fuel (11%) and shopping/gifts (11%).
The most visited tourist destinations of Queensland include Brisbane (including
 Queensland is home to major art galleries including the Queensland Art Gallery and the Queensland Gallery of Modern Art as well as cultural institutions such as the Queensland Ballet, Opera Queensland, Queensland Theatre Company, and Queensland Symphony Orchestra, all based at the Queensland Cultural Centre in Brisbane. The state is the origin of musicians such as the Bee Gees, The Go-Betweens, The Veronicas, The Saints (Australian band), The Saints, Savage Garden, and Sheppard (band), Sheppard as well as writers such as David Malouf, Nick Earls and Li Cunxin.
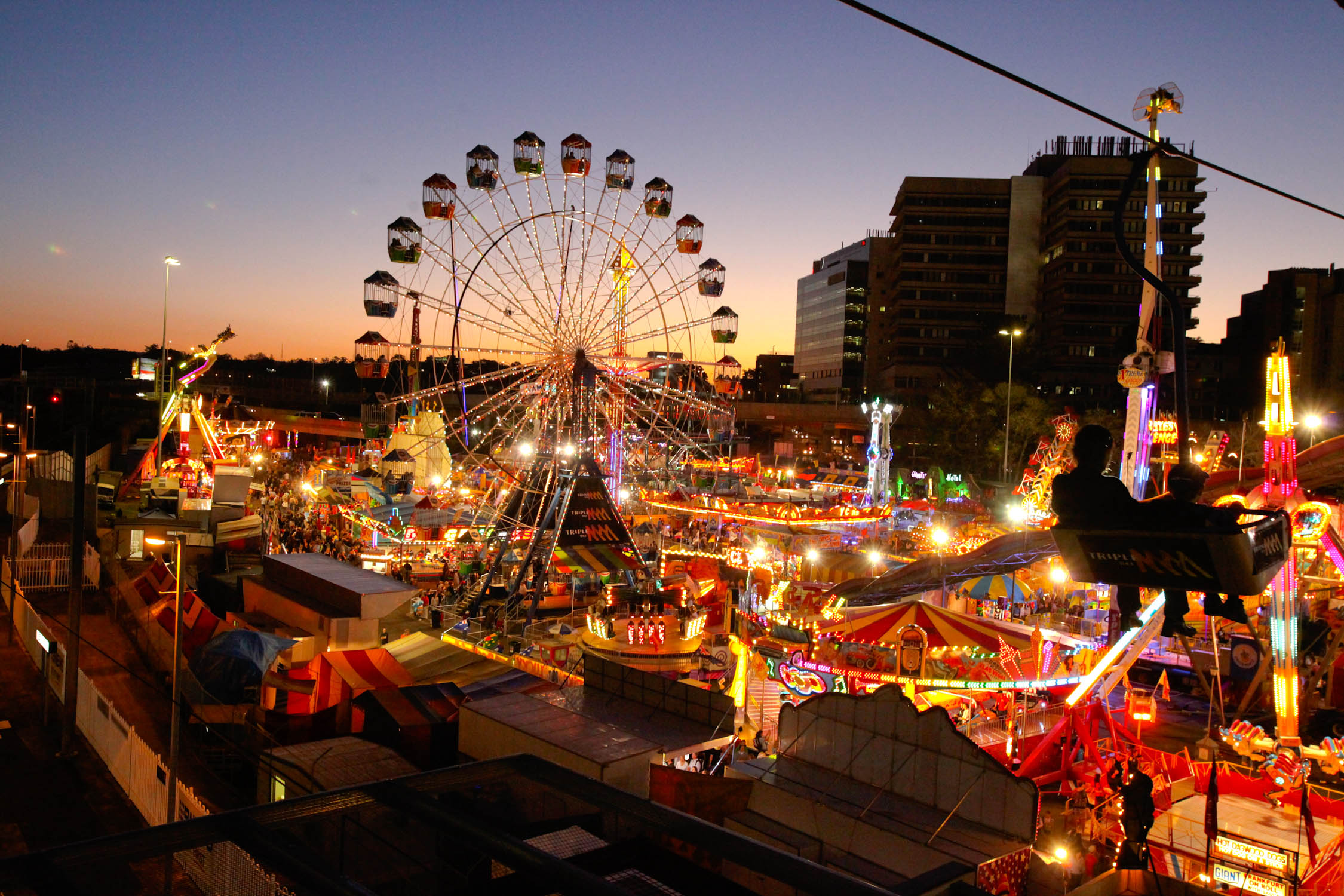
Major annual cultural events include the Ekka, Royal Queensland Exhibition (known locally as the Ekka), an agricultural exhibition held each August at the Brisbane Showgrounds as well as the Brisbane Festival, which includes one of the nation's largest annual fireworks displays called 'Riverfire', and which is held each September.
Queensland is home to major art galleries including the Queensland Art Gallery and the Queensland Gallery of Modern Art as well as cultural institutions such as the Queensland Ballet, Opera Queensland, Queensland Theatre Company, and Queensland Symphony Orchestra, all based at the Queensland Cultural Centre in Brisbane. The state is the origin of musicians such as the Bee Gees, The Go-Betweens, The Veronicas, The Saints (Australian band), The Saints, Savage Garden, and Sheppard (band), Sheppard as well as writers such as David Malouf, Nick Earls and Li Cunxin.
Major annual cultural events include the Ekka, Royal Queensland Exhibition (known locally as the Ekka), an agricultural exhibition held each August at the Brisbane Showgrounds as well as the Brisbane Festival, which includes one of the nation's largest annual fireworks displays called 'Riverfire', and which is held each September.
 The state of Queensland is represented in all of Australia's national sporting competitions and it is also host to a number of domestic and international sporting events. The most popular winter and summer team sports are rugby football, rugby (rugby league and rugby union) and cricket, respectively.
In the National Rugby League, the Brisbane Broncos, North Queensland Cowboys and Gold Coast Titans are based in the state. Rugby league's annual State of Origin series is a major event in the Queensland sporting calendar, with the Queensland rugby league team, Queensland Maroons representing the state.
The state is represented by the Queensland Reds in the Super Rugby (rugby union).
In cricket, the Queensland Bulls represent the state in the Sheffield Shield and the Ryobi One Day Cup, while the Brisbane Heat compete in the Big Bash League.
Queensland is also home to the Brisbane Lions and the Gold Coast Suns in the Australian Football League (Australian rules football), and the Brisbane Roar FC in the A-League (soccer). In netball the Queensland Firebirds went undefeated in the 2011 season as they went on to win the Grand Final. Other sports teams are the Brisbane Bullets and the Cairns Taipans, who compete in the National Basketball League (Australia), National Basketball League.
Swimming is also a popular sport in Queensland, with many of Australian team members and international medalists hailing from the state.
Brisbane will host the 2032 Summer Olympics, marking the third time Australia hosted the Olympic Games following 1956 Summer Olympics, Melbourne 1956 and 2000 Summer Olympics, Sydney 2000. Major recurring sporting events hosted in Queensland include: the Gold Coast 600 (motorsport; since 1994), the Gold Coast Marathon (athletics; since 1979), the NRL All Stars Game (rugby league; since 2010), the Townsville 400 (motorsport; since 2009), the World championship tour (WCT) surfing, Quicksilver Pro and Roxy Pro (surfing) and Australian PGA Championship (golf; since 2000).
The state of Queensland is represented in all of Australia's national sporting competitions and it is also host to a number of domestic and international sporting events. The most popular winter and summer team sports are rugby football, rugby (rugby league and rugby union) and cricket, respectively.
In the National Rugby League, the Brisbane Broncos, North Queensland Cowboys and Gold Coast Titans are based in the state. Rugby league's annual State of Origin series is a major event in the Queensland sporting calendar, with the Queensland rugby league team, Queensland Maroons representing the state.
The state is represented by the Queensland Reds in the Super Rugby (rugby union).
In cricket, the Queensland Bulls represent the state in the Sheffield Shield and the Ryobi One Day Cup, while the Brisbane Heat compete in the Big Bash League.
Queensland is also home to the Brisbane Lions and the Gold Coast Suns in the Australian Football League (Australian rules football), and the Brisbane Roar FC in the A-League (soccer). In netball the Queensland Firebirds went undefeated in the 2011 season as they went on to win the Grand Final. Other sports teams are the Brisbane Bullets and the Cairns Taipans, who compete in the National Basketball League (Australia), National Basketball League.
Swimming is also a popular sport in Queensland, with many of Australian team members and international medalists hailing from the state.
Brisbane will host the 2032 Summer Olympics, marking the third time Australia hosted the Olympic Games following 1956 Summer Olympics, Melbourne 1956 and 2000 Summer Olympics, Sydney 2000. Major recurring sporting events hosted in Queensland include: the Gold Coast 600 (motorsport; since 1994), the Gold Coast Marathon (athletics; since 1979), the NRL All Stars Game (rugby league; since 2010), the Townsville 400 (motorsport; since 2009), the World championship tour (WCT) surfing, Quicksilver Pro and Roxy Pro (surfing) and Australian PGA Championship (golf; since 2000).

 Queensland is served by a number of National Highway (Australia), National Highways and, particularly in South East Queensland, a network of freeways such as the M1 (Queensland), M1. The Department of Transport and Main Roads, Department of Transport & Main Roads oversees the development and operation of main roads and public transport, including taxis and local aviation.
Rail transport in Queensland, Principal rail services are provided by Queensland Rail, predominantly between the major centres east of the Great Dividing Range. Freight rail services in Queensland have been provided mostly by Aurizon and Pacific National, with interstate intermodal services provided by Pacific National and SCT Logistics. Major seaports include the Port of Brisbane, Australia's third busiest by value of goods, as well as those at
Queensland is served by a number of National Highway (Australia), National Highways and, particularly in South East Queensland, a network of freeways such as the M1 (Queensland), M1. The Department of Transport and Main Roads, Department of Transport & Main Roads oversees the development and operation of main roads and public transport, including taxis and local aviation.
Rail transport in Queensland, Principal rail services are provided by Queensland Rail, predominantly between the major centres east of the Great Dividing Range. Freight rail services in Queensland have been provided mostly by Aurizon and Pacific National, with interstate intermodal services provided by Pacific National and SCT Logistics. Major seaports include the Port of Brisbane, Australia's third busiest by value of goods, as well as those at
Government of Queensland
* * * . * . * * {{Authority control Queensland, Former British colonies and protectorates in Oceania States and territories of Australia States and territories established in 1859 kab:Usṭralya
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, established_title = Before federation
, established_date = Colony of Queensland
The Colony of Queensland was a colony of the British Empire from 1859 to 1901, when it became a State in the federal Commonwealth of Australia on 1 January 1901. At its greatest extent, the colony included the present-day State of Queensland, t ...
, established_title2 = Separation from New South Wales
, established_date2 = 6 June 1859
, established_title3 = Federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
, established_date3 = 1 January 1901
, named_for = Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
, demonym =
, capital = Brisbane
Brisbane ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the states and territories of Australia, Australian state of Queensland, and the list of cities in Australia by population, third-most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a populati ...
, largest_city = capital
, coordinates =
, admin_center_type = Administration
, admin_center = 77 local government areas
, leader_title1 = Monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
, leader_name1 = Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to ...
, leader_title2 = Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
, leader_name2 = Jeannette Young
Jeannette Rosita Young (born 1963) is an Australian medical doctor and administrator who is the current governor of the state of Queensland. Before being sworn in as governor, Young was the Chief Health Officer of Queensland from 2005 to 2021.
...
, leader_title3 = Premier
Premier is a title for the head of government in central governments, state governments and local governments of some countries. A second in command to a premier is designated as a deputy premier.
A premier will normally be a head of governm ...
, leader_name3 = Annastacia Palaszczuk
Annastacia Palaszczuk ( , Polish: Annastacia Pałaszczuk, ; born 25 July 1969) is an Australian politician who has been the 39th premier of Queensland since 2015 and the leader of the Queensland branch of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) since ...
( ALP)
, legislature = Parliament of Queensland
The Parliament of Queensland is the legislature of Queensland, Australia. As provided under the Constitution of Queensland, the Parliament consists of the Monarch of Australia and the Legislative Assembly. It has been the only unicameral s ...
, judiciary = Supreme Court of Queensland
The Supreme Court of Queensland is the highest court in the Australian State of Queensland. It was formerly the Brisbane Supreme Court, in the colony of Queensland.
The original jurisdiction of the Supreme Court allows its trial division to he ...
, national_representation = Parliament of Australia
The Parliament of Australia (officially the Federal Parliament, also called the Commonwealth Parliament) is the legislature, legislative branch of the government of Australia. It consists of three elements: the monarch (represented by the ...
, national_representation_type1 = Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, national_representation1 = 12 senators (of 76)
, national_representation_type2 = House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
, national_representation2 = 30 seats (of 151)
, area_km2 = 1851736
, area_land_km2 = 1729742
, area_water_km2 = 121994
, area_rank = 2nd
, area_rank_link = States and territories of Australia#Statistics
, elevation_max_m = 1622
, elevation_max_point = Mount Bartle Frere
Mount Bartle Frere (pronunciation �mæɔnt̥ ˈbɐːɾəɫ ˈfɹɪə Ngajanji: Choorechillum) is the highest mountain in Queensland at an elevation of . The mountain was named after Sir Henry Bartle Frere, 1st Baronet, Sir Henry Bartle Frere ...
, population_estimate = 5,265,043
, population_estimate_rank = 3rd
, population_rank_link = States and territories of Australia#Statistics
, population_estimate_year = December 2021
, population_density_km2 = 2.8
, population_density_sq_mi =
, population_density_rank = 5th
, population_density_rank_link = States and territories of Australia#Statistics
, GDP_nominal = AU$363.524 billion
, GDP_nominal_type = GSP
, GDP_nominal_year = 2020
, GDP_nominal_rank = 3rd
, GDP_nominal_rank_link = List of Australian states and territories by gross state product
, GDP_nominal_per_capita = AU$70,862
, GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 5th
, GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank_link = List of Australian states and territories by gross state product
, HDI = 0.937
, HDI_year = 2019
, HDI_change = increase
, HDI_ref =
, HDI_rank = 5th
, HDI_rank_link = List of Australian states and territories by Human Development Index
, timezone = AEST
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state gov ...
, utc_offset = +10:00
, calling_code =
, postal_code_type = Postal abbreviation
, postal_code = QLD
, website =
, iso_code = AU–QLD
Queensland (, ) is a state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
situated in northeastern Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, and is the second-largest and third-most populous of the Australian states. It is bordered by the Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an states and territories of Australia, Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory ...
, South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
and New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
to the west, southwest and south respectively. To the east, Queensland is bordered by the Coral Sea
The Coral Sea () is a marginal sea of the South Pacific off the northeast coast of Australia, and classified as an interim Australian bioregion. The Coral Sea extends down the Australian northeast coast. Most of it is protected by the Fre ...
and the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
; to its north is the Torres Strait
The Torres Strait (), also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mai ...
, separating the Australian mainland from Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
. With an area of , Queensland is the world's sixth-largest sub-national entity; it is larger than all but 15 countries. Due to its size, Queensland's geographical features and climates are diverse, including tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equatori ...
s, rivers, coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
s, mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
s and sandy beaches in its tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
and sub-tropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north and ...
coastal regions, as well as desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
s and savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
in the semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
and desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
climatic regions of its interior.
Queensland has a population of over 5.2 million, concentrated along the coast and particularly in South East Queensland
South East Queensland (SEQ) is a bio-geographical, metropolitan, political and administrative region of the state of Queensland in Australia, with a population of approximately 3.8 million people out of the state's population of 5.1 million. T ...
. The capital and largest city in the state is Brisbane
Brisbane ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the states and territories of Australia, Australian state of Queensland, and the list of cities in Australia by population, third-most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a populati ...
, Australia's third-largest city. Ten of Australia's thirty largest cities are located in Queensland, with the largest outside Brisbane being the Gold Coast
Gold Coast may refer to:
Places Africa
* Gold Coast (region), in West Africa, which was made up of the following colonies, before being established as the independent nation of Ghana:
** Portuguese Gold Coast (Portuguese, 1482–1642)
** Dutch G ...
, the Sunshine Coast, Townsville
Townsville is a city on the north-eastern coast of Queensland, Australia. With a population of 180,820 as of June 2018, it is the largest settlement in North Queensland; it is unofficially considered its capital. Estimated resident population, 3 ...
, Cairns
Cairns (, ) is a city in Queensland, Australia, on the tropical north east coast of Far North Queensland. The population in June 2019 was 153,952, having grown on average 1.02% annually over the preceding five years. The city is the 5th-most-p ...
, Ipswich, and Toowoomba
Toowoomba ( , nicknamed 'The Garden City' and 'T-Bar') is a city in the Toowoomba Region of the Darling Downs, Queensland, Australia. It is west of Queensland's capital city Brisbane by road. The urban population of Toowoomba as of the 2021 C ...
. The state's population is multicultural, with 28.9% of inhabitants being immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
.
Queensland was first inhabited by Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Islands ...
and Torres Strait Islanders
Torres Strait Islanders () are the Indigenous Melanesian people of the Torres Strait Islands, which are part of the state of Queensland, Australia. Ethnically distinct from the Aboriginal people of the rest of Australia, they are often grouped ...
. Dutch navigator Willem Janszoon
Willem Janszoon (; ), sometimes abbreviated to Willem Jansz., was a Dutch navigator and colonial governor. Janszoon served in the Dutch East Indies in the periods 16031611 and 16121616, including as governor of Fort Henricus on the island of So ...
, the first European to land in Australia, explored the west coast of the Cape York Peninsula
Cape York Peninsula is a large peninsula located in Far North Queensland, Australia. It is the largest unspoiled wilderness in northern Australia.Mittermeier, R.E. et al. (2002). Wilderness: Earth’s last wild places. Mexico City: Agrupación ...
in 1606. In 1770, James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
claimed the east coast of Australia for the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of ...
. In 1788, Arthur Phillip
Admiral Arthur Phillip (11 October 1738 – 31 August 1814) was a British Royal Navy officer who served as the first governor of the Colony of New South Wales.
Phillip was educated at Greenwich Hospital School from June 1751 unti ...
founded the colony of New South Wales, which included all of what is now Queensland. Queensland was explored in subsequent decades, and the Moreton Bay Penal Settlement
The Moreton Bay Penal Settlement operated from 1825 to 1842. It became the city of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia.
History
The Moreton Bay Penal Settlement was established on the Redcliffe Peninsula on Moreton Bay in 1824, under the instruct ...
was established at Brisbane in 1824 by John Oxley
John Joseph William Molesworth Oxley (1784 – 25 May 1828)
was an explorer and surveyor of Australia in the early period of British colonisation. He served as Surveyor General of New South Wales and is perhaps best known for his two exp ...
. Queensland was separated from New South Wales on 6 June 1859 (now commemorated as Queensland Day
Queensland Day is officially celebrated on 6 June as the birthday of the Australian state of Queensland.
History
Moves towards statehood began with a public meeting in 1851 to consider separation of Queensland from the Colony of New South Wa ...
), thereby establishing Queensland as a self-governing
__NOTOC__
Self-governance, self-government, or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any form of ...
Crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Counci ...
with responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive bran ...
, named in honour of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
. Queensland was among the six colonies which became the founding states of Australia with Federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
on 1 January 1901. Since the Bjelke-Petersen
Bjelke-Petersen is the name of an Australian family of Danish descent. The common ancestors of the Australian family are Georg Peter Bjelke-Petersen (born c. 1845), a Danish farmer and master-builder, and his wife Caroline Vilhelmine (maiden name ...
era of the late 20th century, Queensland has received a high level of internal migration from the other states and territories of Australia and remains a popular destination for interstate migration.
Queensland has the third-largest economy among Australian states, with strengths in mining, agriculture, transportation, international education
International education refers to a dynamic concept that involves a journey or movement of people, minds, or ideas across political and cultural frontiers. It is facilitated by the globalization phenomenon, which increasingly erases the constrai ...
, insurance and banking. Nicknamed the ''Sunshine State'' for its tropical and sub-tropical climates, Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, ...
and numerous beaches, tourism is also important to the state's economy.
History
Indigenous history
The Aboriginal occupation of Queensland is thought to predate 50,000 BC, likely via boat or land bridge acrossTorres Strait
The Torres Strait (), also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mai ...
, and became divided into over 90 different language groups.
During the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
, Queensland's landscape became more arid and largely desolate, making food and other supplies scarce, which led to the world's first seed-grinding technology. The end of the glacial period
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
brought about a warming climate, again making the land hospitable, as it brought high rainfall along the eastern coast, stimulating the growth of the state's tropical rainforests.A History of Queensland by Raymond Evans, Cambridge University Press, 2007 .
European colonisation
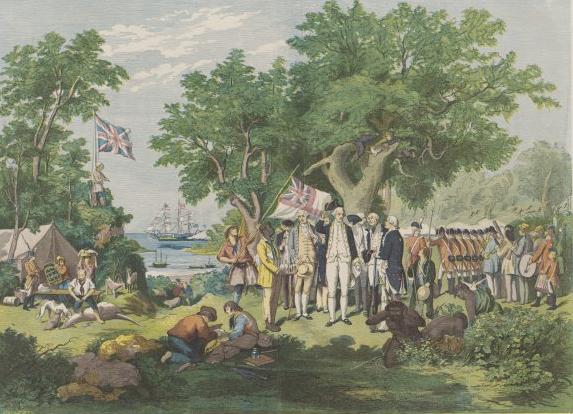
 In February 1606, Dutch navigator
In February 1606, Dutch navigator Willem Janszoon
Willem Janszoon (; ), sometimes abbreviated to Willem Jansz., was a Dutch navigator and colonial governor. Janszoon served in the Dutch East Indies in the periods 16031611 and 16121616, including as governor of Fort Henricus on the island of So ...
landed near the site of what is now Weipa
Weipa () is a coastal mining town in the local government area of Weipa Town in Queensland. It is the largest town on the Cape York Peninsula. It exists because of the enormous bauxite deposits along the coast. The Port of Weipa is mainly involv ...
, on the western shore of Cape York. This was the first recorded landing of a European in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, and it also marked the first reported contact between European and the Aboriginal people of Australia
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Islands ...
. The region was also explored by French and Spanish explorers (commanded by Louis Antoine de Bougainville
Louis-Antoine, Comte de Bougainville (, , ; 12 November 1729 – August 1811) was a French admiral and explorer. A contemporary of the British explorer James Cook, he took part in the Seven Years' War in North America and the American Revolution ...
and Luís Vaez de Torres
Luis is a given name. It is the Spanish form of the originally Germanic name or . Other Iberian Romance languages have comparable forms: (with an accent mark on the i) in Portuguese and Galician, in Aragonese and Catalan, while is archaic ...
, respectively) prior to the arrival of Lieutenant James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
in 1770. Cook claimed the east coast under instruction from King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
of the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of ...
on 22 August 1770 at Possession Island, naming Eastern Australia, including Queensland, 'New South Wales'.
The Aboriginal population declined significantly after a smallpox epidemic
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) cer ...
during the late 18th century. There has been controversy regarding the origins of smallpox in Australia; while many sources have claimed that it originated with European colonisation, this theory has been contradicted by scientific evidence.Campbell, Judy; 2002, ''Invisible Invaders: Smallpox and Other Diseases in Aboriginal Australia 1780–1880'', Carlton, Melbourne University Press, pp60–2, 80–1, 194–6, 201, 216–7 There is circumstantial evidence that Macassan mariners visiting Arnhem Land introduced smallpox to Australia.
In 1823, John Oxley
John Joseph William Molesworth Oxley (1784 – 25 May 1828)
was an explorer and surveyor of Australia in the early period of British colonisation. He served as Surveyor General of New South Wales and is perhaps best known for his two exp ...
, a British explorer, sailed north from what is now Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
to scout possible penal colony sites in Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and Liberal politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, spread over four non-conse ...
(then Port Curtis
Port Curtis is a suburb of Rockhampton in the Rockhampton Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , Port Curtis had a population of 281 people.
Geography
The Fitzroy River bounds the suburb to the north-east. Gavial Creek, a tributary of the ...
) and Moreton Bay
Moreton Bay is a bay located on the eastern coast of Australia from central Brisbane, Queensland. It is one of Queensland's most important coastal resources. The waters of Moreton Bay are a popular destination for recreational anglers and are ...
. At Moreton Bay, he found the Brisbane River
The Brisbane River is the longest river in South East Queensland, Australia, and flows through the city of Brisbane, before emptying into Moreton Bay on the Coral Sea. John Oxley, the first European to explore the river, named it after the Go ...
. He returned in 1824 and established a penal settlement at what is now Redcliffe. The settlement, initially known as Edenglassie
Brisbane ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the states and territories of Australia, Australian state of Queensland, and the list of cities in Australia by population, third-most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a populati ...
, was then transferred to the current location of the Brisbane city centre
Brisbane City is the central suburb and central business district of Brisbane, the state capital of Queensland, Australia. It is colloquially referred to as the "Brisbane CBD" or "the city". It is located on a point on the northern bank of the ...
. Edmund Lockyer
Edmund Lockyer, (21 January 1784 – 10 June 1860) was a British soldier and explorer of Australia.
Born in Plymouth, Devon, Lockyer was the son of Thomas Lockyer, a sailmaker, and his wife Ann. Lockyer began his army career as an ensign in t ...
discovered outcrops of coal along the banks of the upper Brisbane River in 1825. In 1839 transportation of convicts was ceased, culminating in the closure of the Brisbane penal settlement. In 1842 free settlement, which had already commenced, was officially permitted. In 1847, the Port of Maryborough
The Port of Maryborough, Queensland, was opened in 1847 and in 1859 it was declared a port of entry, meaning that overseas and intercolonial vessels could arrive and depart direct, although there appears to have been considerable uncertainty ...
was opened as a wool port. While most early immigrants came from New South Wales, the first free immigrant ship to arrive in Moreton Bay from Europe was the ''Artemisia'', in 1848. In 1857, Queensland's first lighthouse was built at Cape Moreton
Cape Moreton is a rocky headland at the north eastern tip of Moreton Island in South East Queensland, Australia. The surrounding area is part of the Moreton Island National Park. Flinders Reef is north-west of Cape Moreton.
The outcrop is mos ...
.
Earlier than this immigrant ship, was the arrival of the Irish famine orphan girls to Queensland. Devised by the then British Secretary of State for the Colonies, The Earl Grey Scheme established a special emigration scheme which was designed to resettle destitute girls from the workhouses of Ireland during the Great Famine. The very first ship, the “Earl Grey”, departed Ireland for a 124-day sail to Sydney. After controversy developed upon their arrival in Australia, a small group of 37 young orphans, sometimes referred to as The Belfast Girls or the Feisty Colleens, never set foot on Sydney soil, and instead sailed up to Brisbane (then Moreton Bay) on 21 October 1848 on board the ''Ann Mary''. This scheme continued until 1852.
A war, which contemporaries called a "war of extermination
A war of annihilation (german: Vernichtungskrieg) or war of extermination is a type of war in which the goal is the complete annihilation of a State (polity), state, a Ethnic group, people or an ethnic minority through genocide or through the de ...
", erupted between settlers and Aboriginal people in colonial Queensland. The Frontier War was notable for being the most bloody in Australia, perhaps due to Queensland's larger pre-contact indigenous population when compared to the other Australian colonies. The "Native Police Force", employed by the Queensland government, was key in the oppression of the indigenous people.
The largest reported massacre of colonists by Aboriginals was in 1861 on the Nogoa River
The Nogoa River is a river located in Central Queensland, Australia.
Course and features
The river rises on the Carnarvon Range, part of the Great Dividing Range, in the Carnarvon National Park and flows in a generally north easterly direction ...
where 19 people were killed. One author estimates 24,000 Aboriginal men, women and children died at the hands of the Native Police
Australian native police units, consisting of Aboriginal troopers under the command (usually) of at least one white officer, existed in various forms in all Australian mainland colonies during the nineteenth and, in some cases, into the twentie ...
in colonial Queensland between 1859 and 1897 alone.
Independent governance
 A public meeting was held in 1851 to consider the proposed
A public meeting was held in 1851 to consider the proposed separation of Queensland
The Separation of Queensland was an event in 1859 in which the land that forms the present-day State of Queensland in Australia was excised from the Colony of New South Wales and created as a separate Colony of Queensland.
History
European sett ...
from New South Wales. On 6 June 1859, Queen Victoria signed Letters Patent to form the separate colony of Queensland as a self-governing
__NOTOC__
Self-governance, self-government, or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any form of ...
Crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Counci ...
with responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive bran ...
. Brisbane
Brisbane ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the states and territories of Australia, Australian state of Queensland, and the list of cities in Australia by population, third-most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a populati ...
was selected as the capital city. On 10 December 1859, a proclamation was read by George Bowen
Sir George Ferguson Bowen (; 2 November 1821 – 21 February 1899), was an Irish author and colonial administrator whose appointments included postings to the Ionian Islands, Queensland, New Zealand, Victoria, Mauritius and Hong Kong.R. B. Joy ...
, the first Governor of Queensland
The governor of Queensland is the representative in the state of Queensland of the monarch of Australia. In an analogous way to the governor-general of Australia at the national level, the governor Governors of the Australian states, performs c ...
, formally establishing Queensland as a separate colony from New South Wales. On 22 May 1860 the first Queensland election was held and Robert Herbert
Sir Robert George Wyndham Herbert, (12 June 1831 – 6 May 1905), was the first Premier of Queensland, Australia. At 28 years and 181 days of age, he was the youngest person ever to be elected premier of an Australian state.
Early years
Born ...
, Bowen's private secretary, was appointed as the first Premier of Queensland
The premier of Queensland is the head of government in the Australian state of Queensland.
By convention the premier is the leader of the party with a parliamentary majority in the unicameral Legislative Assembly of Queensland. The premier is ap ...
.
In 1865, the first rail line in the state opened between Ipswich
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England, of which it is the county town. The town is located in East Anglia about away from the mouth of the River Orwell and the North Sea. Ipswich is both on the Great Eastern Main Line r ...
and Grandchester. Queensland's economy expanded rapidly in 1867 after James Nash discovered gold on the Mary River near the town of Gympie
Gympie ( ) is a city and a Suburbs and localities (Australia), locality in the Gympie Region, Queensland, Australia. In the Wide Bay-Burnett District, Gympie is about north of the state capital, Brisbane. The city lies on the Mary River (Queen ...
, sparking a gold rush. While still significant, they were on a much smaller scale than the gold rushes of Victoria and New South Wales.
 Immigration to Australia and Queensland, in particular, began in the 1850s to support the state economy. During the period from the 1860s until the early 20th century, many labourers, known at the time as
Immigration to Australia and Queensland, in particular, began in the 1850s to support the state economy. During the period from the 1860s until the early 20th century, many labourers, known at the time as Kanakas
Kanakas were workers (a mix of voluntary and involuntary) from various Pacific Islands employed in British colonies, such as British Columbia (Canada), Fiji, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Papua New Guinea and Queensland (Australia) in the 19t ...
, were brought to Queensland from neighbouring Pacific Island nations to work in the state's sugar cane fields. Some of these people had been kidnapped under a process known as blackbirding
Blackbirding involves the coercion of people through deception or kidnapping to work as slaves or poorly paid labourers in countries distant from their native land. The term has been most commonly applied to the large-scale taking of people in ...
or press ganging, and their employment conditions constituted an allegedly-exploitative form of indentured labour. Italian immigrants
The Italian diaspora is the large-scale emigration of Italians from Italy.
There were two major Italian diasporas in Italian history. The first diaspora began around 1880, two decades after the Risorgimento, Unification of Italy, and ended in the ...
entered the sugar cane industry from the 1890s.
During the 1890s, the six Australian colonies, including Queensland, held a series of referendums which culminated in the Federation of Australia
The Federation of Australia was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia (which also governed what is now the Northern Territory), and Western A ...
on 1 January 1901. During this time, Queensland had a population of half a million people. Since that time Queensland has remained a federated state
A federated state (which may also be referred to as a state, a province, a region, a canton, a land, a governorate, an oblast, an emirate or a country) is a territorial and constitutional community forming part of a federation. Such states d ...
within Australia.
20th century
 Following Federation in 1901, the
Following Federation in 1901, the White Australia policy
The White Australia policy is a term encapsulating a set of historical policies that aimed to forbid people of non-European ethnic origin, especially Asians (primarily Chinese) and Pacific Islanders, from immigrating to Australia, starting i ...
came into effect, which saw all foreign workers in Australia deported under the ''Pacific Island Labourers Act 1901
The Pacific Island Labourers Act 1901 was an Act of the Parliament of Australia which was designed to facilitate the mass deportation of nearly all the Pacific Islanders (called "Kanakas") working in Australia, especially in the Queensland sugar ...
'', which saw the Pacific Islander population of the state decrease rapidly.
In 1905, women voted in state elections for the first time. The state's first university, the University of Queensland
, mottoeng = By means of knowledge and hard work
, established =
, endowment = A$224.3 million
, budget = A$2.1 billion
, type = Public research university
, chancellor = Peter Varghese
, vice_chancellor = Deborah Terry
, city = B ...
, was established in Brisbane in 1909. In 1911, the first alternative treatments for polio were pioneered in Queensland and remain in use across the world today.
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
had a major impact on Queensland. Over 58,000 Queenslanders fought in World War I and over 10,000 of them died.
Australia's first major airline, Qantas
Qantas Airways Limited ( ) is the flag carrier of Australia and the country's largest airline by fleet size, international flights, and international destinations. It is the world's third-oldest airline still in operation, having been founded ...
(originally standing for "Queensland and Northern Territory Aerial Services"), was founded in Winton in 1920 to serve outback Queensland.
In 1922, Queensland abolished the Queensland Legislative Council
The Queensland Legislative Council was the upper house of the parliament in the Australian state of Queensland. It was a fully nominated body which first took office on 1 May 1860. It was abolished by the Constitution Amendment Act 1921, which to ...
, becoming the only Australian state with a unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multic ...
parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
.
In 1935, cane toad
The cane toad (''Rhinella marina''), also known as the giant neotropical toad or marine toad, is a large, terrestrial true toad native to South and mainland Central America, but which has been introduced to various islands throughout Oceania ...
s were deliberately introduced to Queensland from Hawaii in an unsuccessful attempt to reduce the number of French's cane and greyback cane beetle
''Dermolepida albohirtum'', the cane beetle, is a native Australian beetle and a parasite of sugarcane. Adult beetles eat the leaves of sugarcane, but greater damage is done by their larvae hatching underground and eating the roots, which eithe ...
s that were destroying the roots of sugar cane plants, which are integral to Queensland's economy. The toads have remained an environmental pest since that time. In 1962, the first commercial production of oil in Queensland and Australia began at Moonie.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Brisbane became central to the Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
campaign when the AMP Building (now called MacArthur Central
MacArthur Central, also known as MacArthur Central Shopping Centre, in Brisbane, Australia, is a four level shopping centre that incorporates an English Renaissance styled heritage-listed building known as MacArthur Chambers.
MacArthur Central i ...
) was used as the South West Pacific headquarters for General Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was C ...
, chief of the Allied Pacific forces, until his headquarters were moved to Hollandia in August 1944. In 1942, during the war, Brisbane was the site of a violent clash between visiting US military personnel and Australian servicemen and civilians, which resulted in one death and hundreds of injuries. This incident became known colloquially as the Battle of Brisbane
The Battle of Brisbane was a riot between United States military personnel on one side and Australian servicemen and civilians on the other, in Brisbane, Queensland's capital city, on 26 and 27 November 1942, during which time the two nations w ...
.
The end of World War II saw a wave of immigration from across Europe, with many more immigrants coming from southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
Europe than in previous decades.
In the latter decades of the 20th century, the humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
—regulated by the availability of air conditioning—saw Queensland become a popular destination for migrants from interstate. Since that time, Queensland has continuously seen high levels of migration from the other states and territories of Australia.
The final end of the White Australia policy
The White Australia policy is a term encapsulating a set of historical policies that aimed to forbid people of non-European ethnic origin, especially Asians (primarily Chinese) and Pacific Islanders, from immigrating to Australia, starting i ...
in 1973 saw the beginning of a wave of immigration from around the world, and most prominently from Asia, which continues to the present.
In 1981, the Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, ...
off Queensland's northeast coast, one of the world's largest coral reef systems, was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
21st century
In 2003, Queensland adoptedmaroon
Maroon ( US/ UK , Australia ) is a brownish crimson color that takes its name from the French word ''marron'', or chestnut. "Marron" is also one of the French translations for "brown".
According to multiple dictionaries, there are var ...
as the state's official colour. The announcement was made as a result of an informal tradition to use maroon to represent the state in association with sporting events.
After three decades of record population growth, Queensland was impacted by major floods between late 2010 and early 2011, causing extensive damage and disruption across the state.
In 2020, Queensland was impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
. Despite a low number and abrupt decline in cases from April 2020 onward, social distancing
In public health, social distancing, also called physical distancing, (NB. Regula Venske is president of the PEN Centre Germany.) is a set of non-pharmaceutical interventions or measures intended to prevent the spread of a contagious disea ...
requirements were implemented from March 2020 including the closure of the state borders.
Geography

 With a total area of 1,852,642 square kilometres (715,309 square miles), Queensland is an expansive state with a highly diverse range of climates and geographical features. If Queensland were an independent nation, it would be the world's 16th largest, being approximately the same size as Mexico,
With a total area of 1,852,642 square kilometres (715,309 square miles), Queensland is an expansive state with a highly diverse range of climates and geographical features. If Queensland were an independent nation, it would be the world's 16th largest, being approximately the same size as Mexico, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
.
Queensland's eastern coastline borders the Coral Sea
The Coral Sea () is a marginal sea of the South Pacific off the northeast coast of Australia, and classified as an interim Australian bioregion. The Coral Sea extends down the Australian northeast coast. Most of it is protected by the Fre ...
, an arm of the Pacific Ocean. The state is bordered by the Torres Strait
The Torres Strait (), also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mai ...
to the north, with Boigu Island
Boigu Island (also known as Malu Kiyay or Malu Kiwai) is the most northerly inhabited island of Queensland and of Australia. It is part of the Top Western group of the Torres Strait Islands, which lie in the Torres Strait separating Cape York Pe ...
off the coast of New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
representing the northern extreme of its territory. The triangular Cape York Peninsula
Cape York Peninsula is a large peninsula located in Far North Queensland, Australia. It is the largest unspoiled wilderness in northern Australia.Mittermeier, R.E. et al. (2002). Wilderness: Earth’s last wild places. Mexico City: Agrupación ...
, which points toward New Guinea, is the northernmost part of the state's mainland. West of the peninsula's tip, northern Queensland is bordered by the Gulf of Carpentaria
The Gulf of Carpentaria (, ) is a large, shallow sea enclosed on three sides by northern Australia and bounded on the north by the eastern Arafura Sea (the body of water that lies between Australia and New Guinea). The northern boundary is ...
. To the west, Queensland is bordered by the Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an states and territories of Australia, Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory ...
, at the 138th meridian east
The meridian 138° east of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, Australasia, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole.
The 138th meridi ...
, and to the southwest by northeastern South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
. The state's southern border with New South Wales is constituted in the east by the watershed
Watershed is a hydrological term, which has been adopted in other fields in a more or less figurative sense. It may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, called a "watershe ...
from Point Danger to the Dumaresq River
The Dumaresq River ; ( Indigenous Bigambul: ''Karaula'') a perennial stream of the Macintyre catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Northern Tablelands and North West Slopes regions of New South Wales and the Darling D ...
, and the Dumaresq, Macintyre MacIntyre or McIntyre is a Scottish surname, relating to Clan MacIntyre. Its meaning is "Son of the Carpenter or Wright". The corresponding English name is Wright.
People surnamed ''MacIntyre'', ''Macintyre''
* Alasdair MacIntyre, Scottish phil ...
and Barwon rivers. The west of the southern border is defined by the 29th parallel south
The 29th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 29 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Africa, the Indian Ocean, Australasia, the Pacific Ocean and South America.
In Australia, much of the bo ...
(including some minor historical encroachments), until it reaches South Australia.
Like much of eastern Australia, the Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills, that runs rough ...
runs roughly parallel with, and inland from, the coast, and areas west of the range are more arid than the humid coastal regions. The Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, ...
, which is the world's largest coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
system, runs parallel to the state's Coral Sea
The Coral Sea () is a marginal sea of the South Pacific off the northeast coast of Australia, and classified as an interim Australian bioregion. The Coral Sea extends down the Australian northeast coast. Most of it is protected by the Fre ...
coast between the Torres Strait
The Torres Strait (), also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mai ...
and K'gari (Fraser Island)
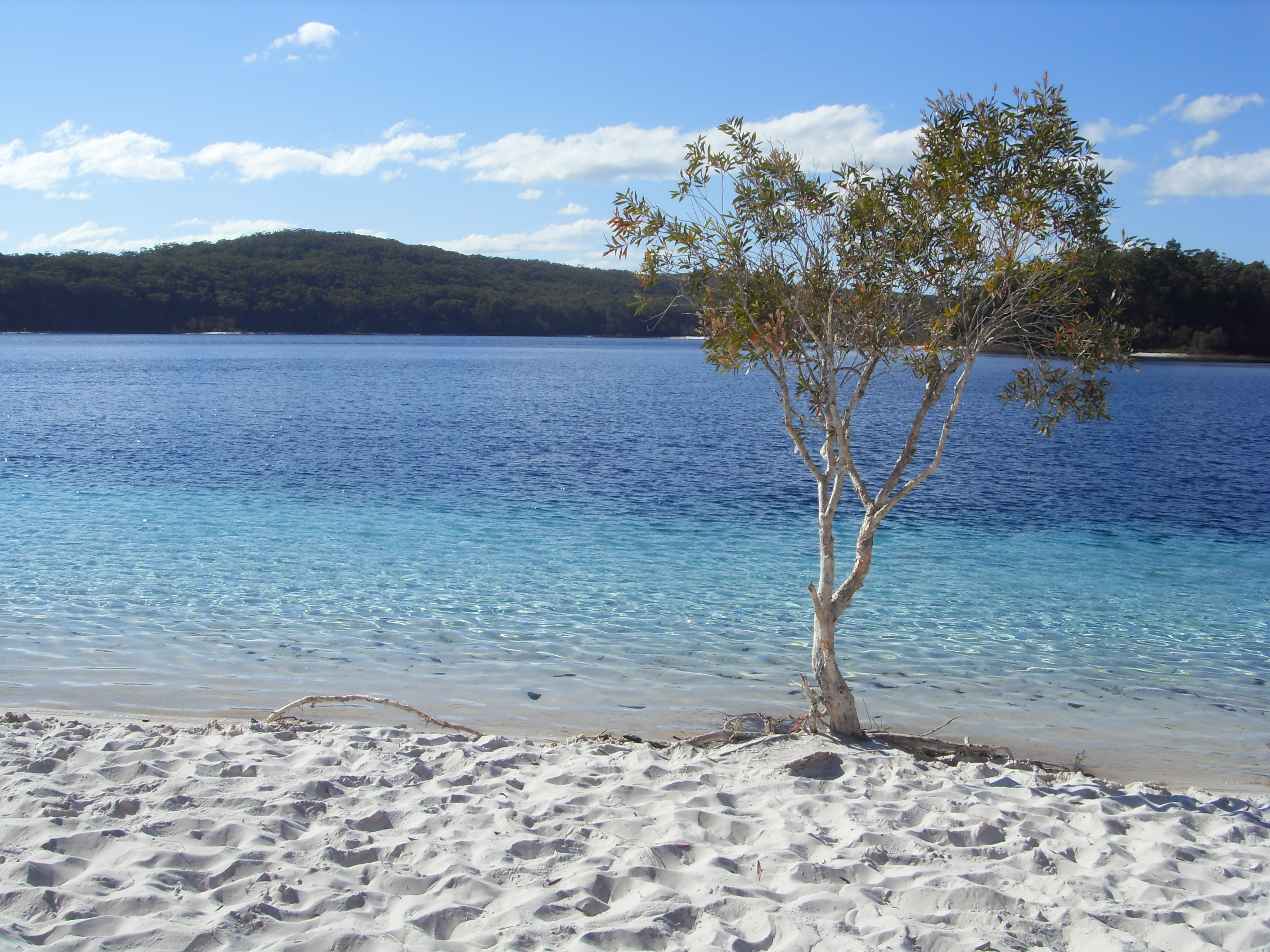
Fraser Island (Butchulla language, Butchulla: ) is a World Heritage List, World Heritage-listed island along the south-eastern coast in the Wide Bay–Burnett region, Queensland, Australia. The island is approximately north of the state capi ...
. Queensland's coastline includes the world's three largest sand islands: K'gari (Fraser Island)
Fraser Island (Butchulla language, Butchulla: ) is a World Heritage List, World Heritage-listed island along the south-eastern coast in the Wide Bay–Burnett region, Queensland, Australia. The island is approximately north of the state capi ...
, Moreton Moreton may refer to:
People Given name
* Moreton John Wheatley (1837–1916), British Army officer and Bailiff of the Royal Parks
Surname
* Alice Bertha Moreton (1901–1977), English sculptor, draughtsman and artist
* Andrew Moreton, a ps ...
and North Stradbroke.
The state contains six World Heritage
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
-listed preservation areas: the Great Barrier Reef along the Coral Sea coast, K'gari (Fraser Island) on the Wide Bay–Burnett
Wide Bay–Burnett is a region of the Australian state of Queensland, located between north of the state capital, Brisbane. The area's population growth has exceeded the state average over the past 20 years, and it is forecast to grow to more ...
region's coastline, the wet tropics in Far North Queensland
Far North Queensland (FNQ) is the northernmost part of the Australian state of Queensland. Its largest city is Cairns and it is dominated geographically by Cape York Peninsula, which stretches north to the Torres Strait, and west to the Gulf C ...
including the Daintree Rainforest
The Daintree Rainforest is a region on the northeast coast of Queensland, Australia, north of Mossman, Queensland, Mossman and Cairns. At around , the Daintree is a part of the largest continuous area of tropical rainforest on the Australia (co ...
, Lamington National Park
The Lamington National Park is a national park, lying on the Lamington Plateau of the McPherson Range on the Queensland/New South Wales border in Australia. From Southport on the Gold Coast the park is to the southwest and Brisbane is north. Th ...
in South East Queensland
South East Queensland (SEQ) is a bio-geographical, metropolitan, political and administrative region of the state of Queensland in Australia, with a population of approximately 3.8 million people out of the state's population of 5.1 million. T ...
, the Riversleigh fossil sites in North West Queensland
The Gulf Country is the region of woodland and savanna grassland surrounding the Gulf of Carpentaria in north western Queensland and eastern Northern Territory on the north coast of Australia. The region is also called the Gulf Savannah. It ...
, and the Gondwana Rainforests
The Gondwana Rainforests of Australia, formerly known as the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves, are the most extensive area of subtropical rainforest in the world. Collectively, the rainforests are a World Heritage Site with fifty separate res ...
in South East Queensland.
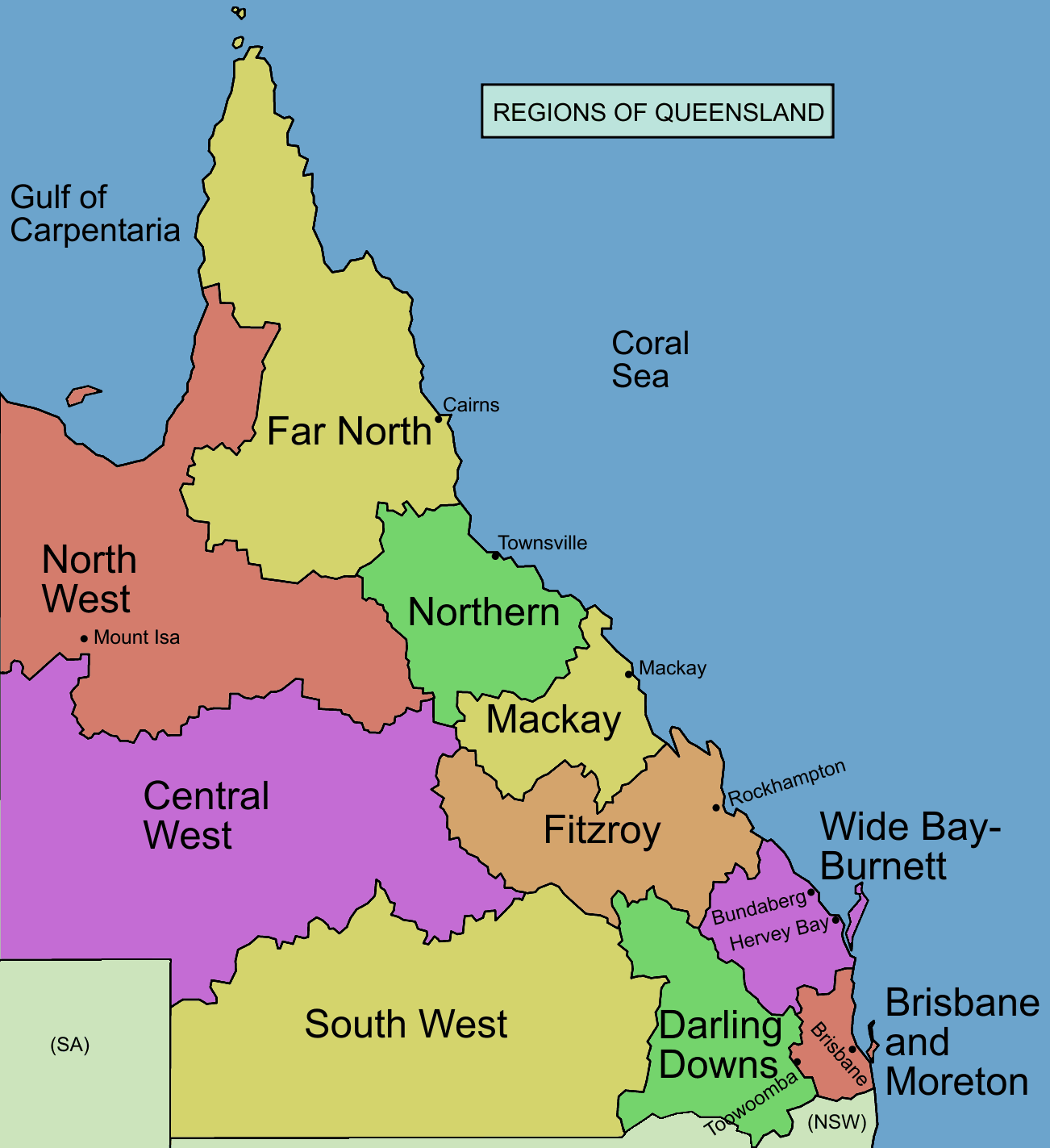
The state is divided into several unofficial regions which are commonly used to refer to large areas of the state's vast geography. These include:
* South East Queensland
South East Queensland (SEQ) is a bio-geographical, metropolitan, political and administrative region of the state of Queensland in Australia, with a population of approximately 3.8 million people out of the state's population of 5.1 million. T ...
in the state's coastal extreme south-eastern corner, an urban region which includes the state's three largest cities: capital city Brisbane and popular coastal tourist destinations the Gold Coast
Gold Coast may refer to:
Places Africa
* Gold Coast (region), in West Africa, which was made up of the following colonies, before being established as the independent nation of Ghana:
** Portuguese Gold Coast (Portuguese, 1482–1642)
** Dutch G ...
and Sunshine Coast. In some definitions, it also includes the city of Toowoomba
Toowoomba ( , nicknamed 'The Garden City' and 'T-Bar') is a city in the Toowoomba Region of the Darling Downs, Queensland, Australia. It is west of Queensland's capital city Brisbane by road. The urban population of Toowoomba as of the 2021 C ...
. South East Queensland accounts for more than 70% of the state's population.
* The Darling Downs
The Darling Downs is a farming region on the western slopes of the Great Dividing Range in southern Queensland, Australia. The Downs are to the west of South East Queensland and are one of the major regions of Queensland. The name was generall ...
in the state's inland south-east, which consists of fertile agricultural (particularly cattle grazing) land and in some definitions includes the city of Toowoomba. The region also includes the mountainous Granite Belt
The Granite Belt is an area of the Great Dividing Range in the Darling Downs region of Queensland and the New England region of New South Wales, Australia. The Granite Belt is centred on the town of Stanthorpe. The cool, high country of the gra ...
, the state's coldest region which occasionally experiences snow.
* Wide Bay–Burnett
Wide Bay–Burnett is a region of the Australian state of Queensland, located between north of the state capital, Brisbane. The area's population growth has exceeded the state average over the past 20 years, and it is forecast to grow to more ...
in the state's coastal south-east, to the north of the South East Queensland region. It is rich in sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalks t ...
farms and includes the cities of Bundaberg
Bundaberg is a city in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia, and is the tenth largest city in the state. Bundaberg's regional area has a population of 70,921, and is a major centre of the Wide Bay–Burnett geographical region. The Bun ...
, Hervey Bay
Hervey Bay () is a city on the coast of the Fraser Coast Region of Queensland, Australia. The city is situated approximately or 3½ hours' highway drive north of the state capital, Brisbane. It is located on the Hervey Bay (Queensland), bay of ...
as well as K'gari (Fraser Island)
Fraser Island (Butchulla language, Butchulla: ) is a World Heritage List, World Heritage-listed island along the south-eastern coast in the Wide Bay–Burnett region, Queensland, Australia. The island is approximately north of the state capi ...
, the world's largest sand island.
* Central Queensland
Central Queensland is an ambiguous geographical division of Queensland ( a state in Australia) that centres on the eastern coast, around the Tropic of Capricorn. Its major regional centre is Rockhampton. The region extends from the Capricorn Coas ...
on the state's central coastline, which is dominated by cattle farmland and coal mining. It contains the Capricorn Coast
The Capricorn Coast is a stretch of coastline in Central Queensland, Australia and is part of the Shire of Livingstone (formerly part of Rockhampton Region).
Geography
The Capricorn Coasts takes its name from Cape Capricorn () on Curtis Is ...
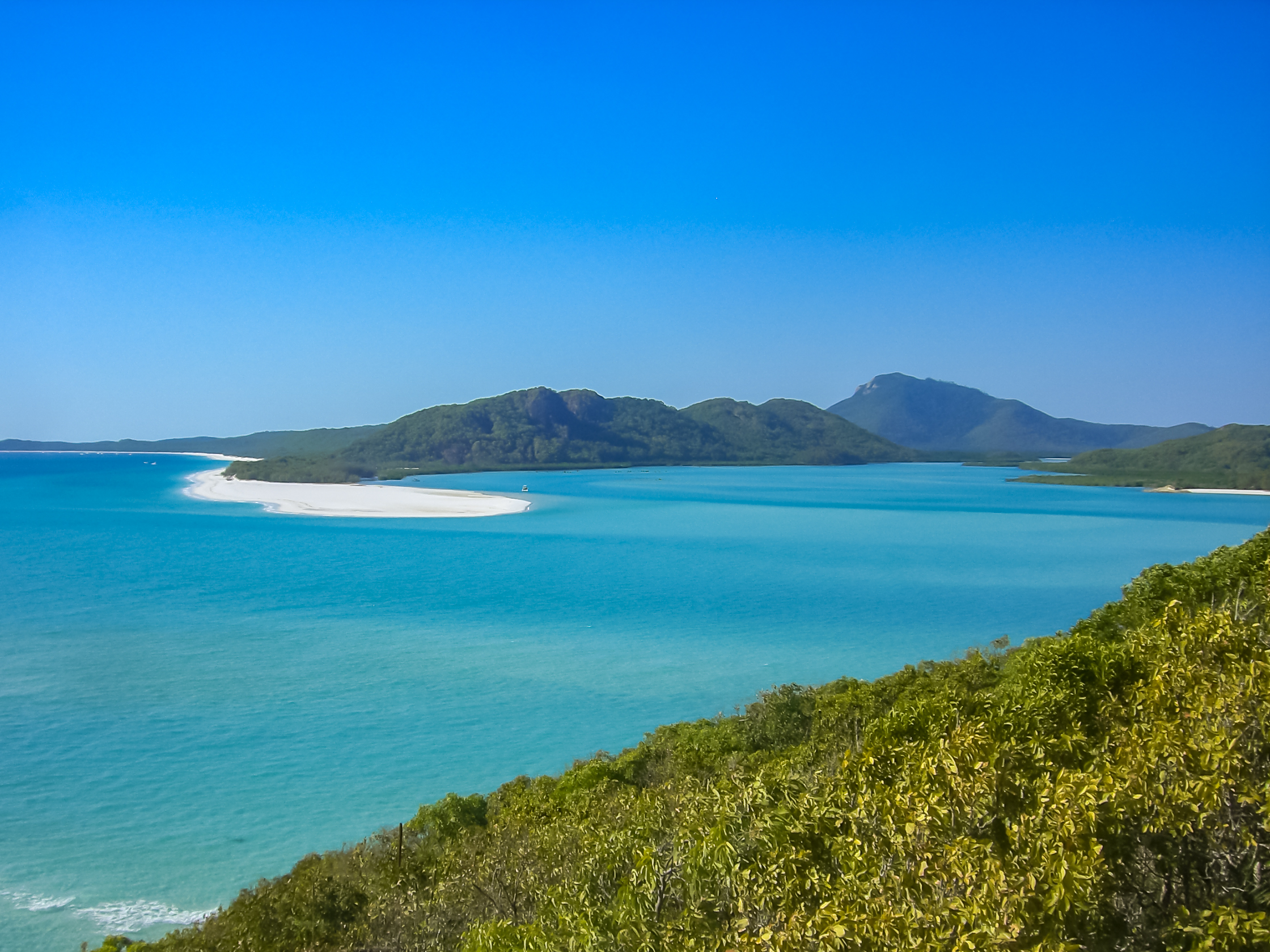
and Whitsunday Islands
The Whitsunday Islands are 74 continental islands of various sizes off the central coast of Queensland, Australia, north of Brisbane. The northernmost of the islands are off the coast by the town of Bowen, while the southernmost islands are ...
tourist regions, as well as the cities of Rockhampton
Rockhampton is a city in the Rockhampton Region of Central Queensland, Australia. The population of Rockhampton in June 2021 was 79,967, Estimated resident population, 30 June 2018. making it the fourth-largest city in the state outside of the ...
and Mackay Mackay may refer to:
*Clan Mackay, the Scottish clan from which the surname "MacKay" derives
Mackay may also refer to:
Places Australia
* Mackay Region, a local government area
** Mackay, Queensland, a city in the above region
*** Mackay Airpor ...
.
* North Queensland
North Queensland or the Northern Region is the northern part of the Australian state of Queensland that lies just south of Far North Queensland. Queensland is a massive state, larger than many countries, and its tropical northern part has been ...
on the state's northern coastline, which is dominated by cattle farmland and mining and which includes the city of Townsville
Townsville is a city on the north-eastern coast of Queensland, Australia. With a population of 180,820 as of June 2018, it is the largest settlement in North Queensland; it is unofficially considered its capital. Estimated resident population, 3 ...
.
* Far North Queensland
Far North Queensland (FNQ) is the northernmost part of the Australian state of Queensland. Its largest city is Cairns and it is dominated geographically by Cape York Peninsula, which stretches north to the Torres Strait, and west to the Gulf C ...
on the state's extreme northern coastline along the Cape York Peninsula
Cape York Peninsula is a large peninsula located in Far North Queensland, Australia. It is the largest unspoiled wilderness in northern Australia.Mittermeier, R.E. et al. (2002). Wilderness: Earth’s last wild places. Mexico City: Agrupación ...
, which includes tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equatori ...
, the state's highest mountain, Mount Bartle Frere
Mount Bartle Frere (pronunciation �mæɔnt̥ ˈbɐːɾəɫ ˈfɹɪə Ngajanji: Choorechillum) is the highest mountain in Queensland at an elevation of . The mountain was named after Sir Henry Bartle Frere, 1st Baronet, Sir Henry Bartle Frere ...
, the Atherton Tablelands
The Atherton Tableland is a fertile plateau which is part of the Great Dividing Range in Queensland, Australia.
The principal river flowing across the plateau is the Barron River. It was dammed to form an irrigation reservoir named Lake Tinar ...
pastoral region (dominated by sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalks t ...
and tropical fruit
A tropical fruit one that typically grows in warm climates, or equatorial areas.
Tropical fruits
Varieties of tropical fruit include:
* Acerola ( West Indian Cherry or Barbados Cherry)
*Ackee
*Banana
*Barbadine (granadilla; maracujá-açu in ...
s), the most visited section of the Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, ...
, as well as the city of Cairns
Cairns (, ) is a city in Queensland, Australia, on the tropical north east coast of Far North Queensland. The population in June 2019 was 153,952, having grown on average 1.02% annually over the preceding five years. The city is the 5th-most-p ...
.
* South West Queensland
South West Queensland is a remote region in the Australian state of Queensland which covers . The region lies to the south of Central West Queensland and west of the Darling Downs and includes the Maranoa district and parts of the Channel Countr ...
in the state's inland south-west, which is a primarily agricultural region dominated by cattle farmland, and which includes the Channel Country
The Channel Country is a region of outback Australia mostly in the state of Queensland but also in parts of South Australia, Northern Territory and New South Wales. The name comes from the numerous intertwined rivulets that cross the region ...
region of intertwining rivulets.
* Central West Queensland
Central West Queensland is a remote region in the Australian state of Queensland which covers 396,650.2 km2. The region lies to the north of South West Queensland and south of the Gulf Country. It has a population of approximately 12,387 peo ...
in the state's inland central-west, dominated by cattle farmland and which includes the city of Longreach
Longreach is a town and a locality in the Longreach Region, Queensland, Australia. It is the administrative centre of the Longreach Regional Council, which was established in 2008 as a merger of the former Longreach, Ilfracombe, and Isisford s ...
.
* The Gulf Country
The Gulf Country is the region of woodland and savanna grassland surrounding the Gulf of Carpentaria in north western Queensland and eastern Northern Territory on the north coast of Australia. The region is also called the Gulf Savannah. It ...
(also known as North West Queensland), in the state's inland north-west along the Gulf of Carpentaria
The Gulf of Carpentaria (, ) is a large, shallow sea enclosed on three sides by northern Australia and bounded on the north by the eastern Arafura Sea (the body of water that lies between Australia and New Guinea). The northern boundary is ...
, which is dominated by savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
and mining and includes the city of Mount Isa
The City of Mount Isa is a local government area in north west Queensland. The City covers the urban locality of Mount Isa, the administrative centre, and surrounding area, sharing a boundary with the Northern Territory to the west.
Mount Isa ...
.
Climate
monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
al wet season in the tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
north, and humid sub-tropical conditions along the southern coastline. Low rainfall and hot humid summers are typical for the inland and west. Elevated areas in the south-eastern inland can experience temperatures well below freezing in mid-winter providing frost
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor in an above-freezing atmosphere coming in contact with a solid surface whose temperature is below freezing, and resulting in a phase change from water vapor (a gas) ...
and, rarely, snowfall
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout ...
. The climate of the coastal regions is influenced by warm ocean waters, keeping the region free from extremes of temperature and providing moisture for rainfall.
There are six predominant climatic zones in Queensland, based on temperature and humidity:
* Hot humid summer, warm humid winter (far north and coastal): Cairns
Cairns (, ) is a city in Queensland, Australia, on the tropical north east coast of Far North Queensland. The population in June 2019 was 153,952, having grown on average 1.02% annually over the preceding five years. The city is the 5th-most-p ...
, Innisfail
* Hot humid summer, warm dry winter (north and coastal): Townsville
Townsville is a city on the north-eastern coast of Queensland, Australia. With a population of 180,820 as of June 2018, it is the largest settlement in North Queensland; it is unofficially considered its capital. Estimated resident population, 3 ...
, Mackay Mackay may refer to:
*Clan Mackay, the Scottish clan from which the surname "MacKay" derives
Mackay may also refer to:
Places Australia
* Mackay Region, a local government area
** Mackay, Queensland, a city in the above region
*** Mackay Airpor ...
* Hot humid summer, mild dry winter (coastal elevated areas and coastal south-east): Brisbane
Brisbane ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the states and territories of Australia, Australian state of Queensland, and the list of cities in Australia by population, third-most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a populati ...
, Bundaberg
Bundaberg is a city in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia, and is the tenth largest city in the state. Bundaberg's regional area has a population of 70,921, and is a major centre of the Wide Bay–Burnett geographical region. The Bun ...
, Rockhampton
Rockhampton is a city in the Rockhampton Region of Central Queensland, Australia. The population of Rockhampton in June 2021 was 79,967, Estimated resident population, 30 June 2018. making it the fourth-largest city in the state outside of the ...
* Hot dry summer, mild dry winter (central inland and north-west): Mt Isa
Mount Isa ( ) is a city in the Gulf Country region of Queensland, Australia. It came into existence because of the vast mineral deposits found in the area. Mount Isa Mines (MIM) is one of the most productive single mines in world history, ba ...
, Emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr. and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991) ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p ...
, Longreach
Longreach is a town and a locality in the Longreach Region, Queensland, Australia. It is the administrative centre of the Longreach Regional Council, which was established in 2008 as a merger of the former Longreach, Ilfracombe, and Isisford s ...
* Hot dry summer, cool dry winter (southern inland): Roma
Roma or ROMA may refer to:
Places Australia
* Roma, Queensland, a town
** Roma Airport
** Roma Courthouse
** Electoral district of Roma, defunct
** Town of Roma, defunct town, now part of the Maranoa Regional Council
*Roma Street, Brisbane, a ...
, Charleville Charleville can refer to:
Australia
* Charleville, Queensland, a town in Australia
**Charleville railway station, Queensland
France
* Charleville, Marne, a commune in Marne, France
*Charleville-Mézières, a commune in Ardennes, France
** C ...
, Goondiwindi
Goondiwindi () is a rural town and locality in the Goondiwindi Region, Queensland, Australia. It is on the border of Queensland and New South Wales. In the , Goondiwindi had a population of 6,355 people.
Geography
Goondiwindi is on the MacInt ...
* Warm humid summer, cold dry winter (elevated south-eastern areas): Toowoomba
Toowoomba ( , nicknamed 'The Garden City' and 'T-Bar') is a city in the Toowoomba Region of the Darling Downs, Queensland, Australia. It is west of Queensland's capital city Brisbane by road. The urban population of Toowoomba as of the 2021 C ...
, Warwick
Warwick ( ) is a market town, civil parish and the county town of Warwickshire in the Warwick District in England, adjacent to the River Avon. It is south of Coventry, and south-east of Birmingham. It is adjoined with Leamington Spa and Whi ...
, Stanthorpe
Stanthorpe is a rural town and locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , Stanthorpe had a population of 5,406 people.
The area surrounding the town is known as the Granite Belt.
Geography
Stanthorpe lies on the New ...
The annual mean climatic statistics for selected Queensland cities are shown below:
The coastal far north of the state is the wettest region in Australia, with Mount Bellenden Ker
Mount Bellenden Ker is the second-highest mountain in Queensland, Australia, with a height of . It is named after the botanist John Bellenden Ker Gawler. Located south of Cairns, Queensland, Cairns near Babinda, Queensland, Babinda, it is adj ...
, south of Cairns, holding many Australian rainfall records with its annual average rainfall of over . Snow is rare in Queensland, although it does fall with some regularity along the far southern border with New South Wales, predominantly in the Stanthorpe district although on rare occasions further north and west. The most northerly snow ever recorded in Australia occurred near Mackay Mackay may refer to:
*Clan Mackay, the Scottish clan from which the surname "MacKay" derives
Mackay may also refer to:
Places Australia
* Mackay Region, a local government area
** Mackay, Queensland, a city in the above region
*** Mackay Airpor ...
; however, this was exceptional.
Natural disasters are often a threat in Queensland: severe tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
s can impact the central and northern coastlines and cause severe damage, with recent examples including Larry
Larry is a masculine given name in English, derived from Lawrence (given name), Lawrence or Laurence. It can be a shortened form of those names.
Larry may refer to the following:
People Arts and entertainment
*Larry D. Alexander, American arti ...
, Yasi, Ita and Debbie
Debbie (or Debby or Deb) is a feminine given name, commonly but not always short for Deborah (or Debra and related variants).
Notable people
* Debbie Allen, American actress, choreographer and film director
* Debbie Armstrong, American athlete
* ...
. Flooding from rain-bearing systems can also be severe and can occur anywhere in Queensland. One of the deadliest and most damaging floods in the history of the state occurred in early 2011. Severe springtime thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are someti ...
s generally affect the south-east and inland of the state and can bring damaging winds, torrential rain, large hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
and even tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, altho ...
es. The strongest tornado ever recorded in Australia occurred in Queensland near Bundaberg
Bundaberg is a city in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia, and is the tenth largest city in the state. Bundaberg's regional area has a population of 70,921, and is a major centre of the Wide Bay–Burnett geographical region. The Bun ...
in November 1992. Droughts and bushfires
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identif ...
can also occur; however, the latter are generally less severe than those that occur in southern states.
The highest official maximum temperature recorded in the state was at Birdsville Police Station on 24 December 1972, although the Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is a satellite-based sensor used for earth and climate measurements. There are two MODIS sensors in Earth orbit: one on board the Terra (EOS AM) satellite, launched by NASA in 1999 ...
(MODIS) on NASA's Aqua satellite measured a ground surface temperature of . Queensland has the highest average maximums of any Australian state, and Stanthorpe
Stanthorpe is a rural town and locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , Stanthorpe had a population of 5,406 people.
The area surrounding the town is known as the Granite Belt.
Geography
Stanthorpe lies on the New ...
, Hervey Bay
Hervey Bay () is a city on the coast of the Fraser Coast Region of Queensland, Australia. The city is situated approximately or 3½ hours' highway drive north of the state capital, Brisbane. It is located on the Hervey Bay (Queensland), bay of ...
, Mackay Mackay may refer to:
*Clan Mackay, the Scottish clan from which the surname "MacKay" derives
Mackay may also refer to:
Places Australia
* Mackay Region, a local government area
** Mackay, Queensland, a city in the above region
*** Mackay Airpor ...
, Atherton, Weipa
Weipa () is a coastal mining town in the local government area of Weipa Town in Queensland. It is the largest town on the Cape York Peninsula. It exists because of the enormous bauxite deposits along the coast. The Port of Weipa is mainly involv ...
and Thursday Island
Thursday Island, colloquially known as TI, or in the Kawrareg dialect, Waiben or Waibene, is an island of the Torres Strait Islands, an archipelago of at least 274 small islands in the Torres Strait. TI is located approximately north of Cape ...
are the only large population centres not to have recorded a temperature above . The lowest recorded minimum temperature is at Stanthorpe on 23 June 1961 and at The Hermitage (near Warwick
Warwick ( ) is a market town, civil parish and the county town of Warwickshire in the Warwick District in England, adjacent to the River Avon. It is south of Coventry, and south-east of Birmingham. It is adjoined with Leamington Spa and Whi ...
) on 12 July 1965. Temperatures below are, however, generally uncommon over the majority of populated Queensland.
Demographics
South East Queensland
South East Queensland (SEQ) is a bio-geographical, metropolitan, political and administrative region of the state of Queensland in Australia, with a population of approximately 3.8 million people out of the state's population of 5.1 million. T ...
. Nonetheless, Queensland is the second most decentralised state in Australia after Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
. Since the 1980s, Queensland has consistently been the fastest-growing state in Australia, as it receives high levels of both international immigration and migration from interstate. There have however been short periods where Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
and Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
have grown faster.
Cities
Ten of Australia's thirty largest cities are located in Queensland. In 2019, the largest cities in the state by population of their Greater Capital City Statistical Area or Significant Urban Area (metropolitan areas) as defined by theAustralian Bureau of Statistics
The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) is the independent statutory agency of the Australian Government responsible for statistical collection and analysis and for giving evidence-based advice to federal, state and territory governments ...
were:
Ancestry and immigration
Early settlers during the 19th century were largelyEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, Scottish and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, while there was a wave of immigration from southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and eastern Europe (most notably Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
) in the decades following the second world war
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. In the 21st century, Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
(most notably China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
) has been the primary source of immigration.
At the 2016 census, the most commonly nominated ancestries were:
The 2016 census showed that 28.9% of Queensland's inhabitants were born overseas. Only 54.8% of inhabitants had both parents born in Australia, with the next most common birthplaces being New Zealand, England, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, Mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
and South Africa. Brisbane has the 26th largest immigrant population among world metropolitan areas.
4% of the population, or 186,482 people, identified as Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
(Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Islands ...
and Torres Strait Islanders
Torres Strait Islanders () are the Indigenous Melanesian people of the Torres Strait Islands, which are part of the state of Queensland, Australia. Ethnically distinct from the Aboriginal people of the rest of Australia, they are often grouped ...
) in 2016.
Language
At the , 81.2% of inhabitants spoke only English at home, with the next most common languages beingMandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
(1.5%), Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam.
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overse ...
(0.6%), Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding are ...
(0.5%), Spanish (0.4%) and Italian (0.4%).
At the , 80.5% of inhabitants spoke only English at home, with the next most common languages being Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
(1.6%), Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam.
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overse ...
(0.6%), Punjabi (0.6%) and Spanish (0.6%).
Religion
At the , the most commonly cited religious affiliations were 'No religion' (29.2%),Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
(21.7%) and Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
(15.3%).
According to the , 45.7% of the population follows Christianity and 41.2% identified as having No religion About 5% of people are affiliated with a non-Christian religion, mainly Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
(1.4%), Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
(1.3%) and Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
(1.2%).
Education
 Queensland is home to numerous universities. The state's oldest university, the
Queensland is home to numerous universities. The state's oldest university, the University of Queensland
, mottoeng = By means of knowledge and hard work
, established =
, endowment = A$224.3 million
, budget = A$2.1 billion
, type = Public research university
, chancellor = Peter Varghese
, vice_chancellor = Deborah Terry
, city = B ...
, was established in 1909 and frequently ranks among the world's top 50. Other major universities include Queensland University of Technology
Queensland University of Technology (QUT) is a public research university located in the urban coastal city of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. QUT is located on two campuses in the Brisbane area viz. Gardens Point and Kelvin Grove. The univ ...
, Griffith University
Griffith University is a public research university in South East Queensland on the east coast of Australia. Formally founded in 1971, Griffith opened its doors in 1975, introducing Australia's first degrees in environmental science and Asian s ...
, the University of Southern Queensland
The University of Southern Queensland (branded as UniSQ and formerly branded as USQ) is a medium-sized, regional university based in Toowoomba, Queensland, Australia, with three university campuses at Toowoomba, Springfield and Ipswich. It offe ...
, the University of the Sunshine Coast
The University of the Sunshine Coast (UniSC) is a public university based on the Sunshine Coast, Queensland, Australia. After opening with 524 students in 1996 as the Sunshine Coast University College, it was later renamed the University of the ...
, James Cook University
James Cook University (JCU) is a public university in North Queensland, Australia. The second oldest university in Queensland, JCU is a teaching and research institution. The university's main campuses are located in the tropical cities of Cairn ...
(which was the state's first university outside of South East Queensland
South East Queensland (SEQ) is a bio-geographical, metropolitan, political and administrative region of the state of Queensland in Australia, with a population of approximately 3.8 million people out of the state's population of 5.1 million. T ...
), Central Queensland University
Central Queensland University (alternatively known as CQUniversity) is an Australian public university based in central Queensland. CQUniversity is the only Australian university with a campus presence in every mainland state. Its main campus ...
and Bond University
Bond University is Australia's first private not-for-profit university and is located in Robina, a suburb in the City of Gold Coast, Queensland. Since its founding on 15 May 1989, Bond University has primarily been a teaching-focused higher ed ...
(which was Australia's first private university).
International education
International education refers to a dynamic concept that involves a journey or movement of people, minds, or ideas across political and cultural frontiers. It is facilitated by the globalization phenomenon, which increasingly erases the constrai ...
is an important industry, with 134,312 international students enrolled in the state in 2018, largely focused on Brisbane. Most of the state's international students are from Asia.
At the primary and secondary levels, Queensland is home to numerous state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
and private schools.
Economy



 In 2019, Queensland had a
In 2019, Queensland had a gross state product
Gross regional domestic product (GRDP), gross domestic product of region (GDPR), or gross state product (GSP) is a statistic that measures the size of a region's economy. It is the aggregate of gross value added (GVA) of all resident producer unit ...
of A$357,044 million, the third-highest in the nation after New South Wales and Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
. The construction of sea port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
s and railways along Queensland's coast in the 19th century set up the foundations for the state's export-oriented mining and agricultural sectors. Since the 1980s, a sizeable influx of interstate and overseas migrants, large amounts of federal government investment, increased mining of vast mineral deposits and an expanding aerospace sector have contributed to the state's economic growth.
Primary industries include bananas, pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae. The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been cultivated for many centuri ...
s, peanuts, a wide variety of other tropical and temperate fruit and vegetables, grain crops, wineries
A winery is a building or property that produces wine, or a business involved in the production of wine, such as a wine company. Some wine companies own many wineries. Besides wine making equipment, larger wineries may also feature warehouses, b ...
, cattle raising, cotton, sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
, and wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
. The mining industry includes bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(O ...
, coal, silver, lead, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, gold and copper.
Secondary industries are mostly further processing of the above-mentioned primary produce. For example, bauxite is shipped by sea from Weipa
Weipa () is a coastal mining town in the local government area of Weipa Town in Queensland. It is the largest town on the Cape York Peninsula. It exists because of the enormous bauxite deposits along the coast. The Port of Weipa is mainly involv ...
and converted to alumina at Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and Liberal politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, spread over four non-conse ...
. There is also copper refining and the refining of sugar cane to sugar at a number of mills along the eastern coastline.
Major tertiary industries are retail, tourism and international education
International education refers to a dynamic concept that involves a journey or movement of people, minds, or ideas across political and cultural frontiers. It is facilitated by the globalization phenomenon, which increasingly erases the constrai ...
. In 2018, there were 134,312 international students enrolled in the state, largely focused on Brisbane. Most of the state's international students are from Asia.
Brisbane is categorised as a global city, and is among Asia-Pacific cities with largest GDPs. It has strengths in mining, banking, insurance, transportation, information technology, real estate and food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inge ...
. Some of the largest companies headquartered in Brisbane, all among Australia's largest, include Suncorp Group, Virgin Australia, Aurizon, Bank of Queensland, Flight Centre, CUA (company), CUA, Sunsuper, QSuper, Domino's Pizza Enterprises, Star Entertainment Group, ALS Limited, ALS, TechnologyOne, NEXTDC, Super Retail Group, New Hope Coal, Jumbo Interactive, National Storage, Collins Foods and Boeing Australia.
Tourism
 As a result of its varied landscapes, warm climate and abundant natural environment, tourism is Queensland's leading tertiary industry with millions of interstate and international visitors visiting the state each year. The industry generates $8.8 billion annually, accounting for 4.5% of Queensland's Gross State Product. It has an annual export of $4.0 billion annually. The sector directly employs about 5.7% of Queensland citizens. Accommodation in Queensland caters for nearly 22% of the total expenditure, followed by restaurants/meals (15%), airfares (11%), fuel (11%) and shopping/gifts (11%).
The most visited tourist destinations of Queensland include Brisbane (including
As a result of its varied landscapes, warm climate and abundant natural environment, tourism is Queensland's leading tertiary industry with millions of interstate and international visitors visiting the state each year. The industry generates $8.8 billion annually, accounting for 4.5% of Queensland's Gross State Product. It has an annual export of $4.0 billion annually. The sector directly employs about 5.7% of Queensland citizens. Accommodation in Queensland caters for nearly 22% of the total expenditure, followed by restaurants/meals (15%), airfares (11%), fuel (11%) and shopping/gifts (11%).
The most visited tourist destinations of Queensland include Brisbane (including Moreton Moreton may refer to:
People Given name
* Moreton John Wheatley (1837–1916), British Army officer and Bailiff of the Royal Parks
Surname
* Alice Bertha Moreton (1901–1977), English sculptor, draughtsman and artist
* Andrew Moreton, a ps ...
and South Stradbroke Island, South Stradbroke islands and the Gold Coast
Gold Coast may refer to:
Places Africa
* Gold Coast (region), in West Africa, which was made up of the following colonies, before being established as the independent nation of Ghana:
** Portuguese Gold Coast (Portuguese, 1482–1642)
** Dutch G ...
) as well as the Sunshine Coast, the Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, ...
, Cairns
Cairns (, ) is a city in Queensland, Australia, on the tropical north east coast of Far North Queensland. The population in June 2019 was 153,952, having grown on average 1.02% annually over the preceding five years. The city is the 5th-most-p ...
, Port Douglas, Queensland, Port Douglas, the Daintree Rainforest
The Daintree Rainforest is a region on the northeast coast of Queensland, Australia, north of Mossman, Queensland, Mossman and Cairns. At around , the Daintree is a part of the largest continuous area of tropical rainforest on the Australia (co ...
, K'gari (Fraser Island), K'gari and the Whitsunday Islands
The Whitsunday Islands are 74 continental islands of various sizes off the central coast of Queensland, Australia, north of Brisbane. The northernmost of the islands are off the coast by the town of Bowen, while the southernmost islands are ...
.
Brisbane is the third most popular destination in Australia following Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
and Melbourne. Major attractions in its metropolitan area include South Bank Parklands, the Queensland Cultural Centre (including the Queensland Museum, Queensland Art Gallery, Gallery of Modern Art, Brisbane, Gallery of Modern Art, Queensland Performing Arts Centre and State Library of Queensland), Brisbane City Hall, City Hall, the Story Bridge, the Howard Smith Wharves, ANZAC Square, Brisbane, ANZAC Square, St John's Cathedral (Brisbane), St John's Cathedral, Fortitude Valley, Queensland, Fortitude Valley (including Fortitude Valley, Queensland#Commercial area, James Street and Chinatown, Brisbane, Chinatown), West End, Queensland, West End, the Teneriffe, Queensland, Teneriffe woolstores precinct, the Brisbane River
The Brisbane River is the longest river in South East Queensland, Australia, and flows through the city of Brisbane, before emptying into Moreton Bay on the Coral Sea. John Oxley, the first European to explore the river, named it after the Go ...
and its Brisbane River#Brisbane Riverwalk, Riverwalk network, the City Botanic Gardens, Roma Street Parkland, New Farm Park (including the Brisbane Powerhouse), the Kangaroo Point Cliffs and park, the Lone Pine Koala Sanctuary, the Mount Coot-tha Forest, Mount Coot-tha Reserve (including Mount Coot-tha Lookout and Brisbane Botanic Gardens, Mount Coot-tha, Mount Coot-tha Botanic Gardens), the D'Aguilar Range and D'Aguilar National Park, National Park, as well as Moreton Bay
Moreton Bay is a bay located on the eastern coast of Australia from central Brisbane, Queensland. It is one of Queensland's most important coastal resources. The waters of Moreton Bay are a popular destination for recreational anglers and are ...
(including Moreton Moreton may refer to:
People Given name
* Moreton John Wheatley (1837–1916), British Army officer and Bailiff of the Royal Parks
Surname
* Alice Bertha Moreton (1901–1977), English sculptor, draughtsman and artist
* Andrew Moreton, a ps ...
, North Stradbroke and Bribie Island, Bribie islands, and coastal suburbs such as Shorncliffe, Queensland, Shorncliffe, Wynnum, Queensland, Wynnum and those on the Redcliffe Peninsula).
The Gold Coast
Gold Coast may refer to:
Places Africa
* Gold Coast (region), in West Africa, which was made up of the following colonies, before being established as the independent nation of Ghana:
** Portuguese Gold Coast (Portuguese, 1482–1642)
** Dutch G ...
is home to numerous popular surf beaches such as those at Surfers Paradise, Queensland, Surfers Paradise and Burleigh Heads, Queensland, Burleigh Heads. It also includes the largest concentration of amusement parks in Australia, including Dreamworld (Australian theme park), Dreamworld, Warner Bros. Movie World, Movie World, Sea World (Australia), Sea World, Wet'n'Wild Water World, Wet 'n' Wild and WhiteWater World, as well as the Currumbin Wildlife Sanctuary. The Gold Coast's hinterland includes Lamington National Park
The Lamington National Park is a national park, lying on the Lamington Plateau of the McPherson Range on the Queensland/New South Wales border in Australia. From Southport on the Gold Coast the park is to the southwest and Brisbane is north. Th ...
in the McPherson Range.
The Sunshine Coast includes popular surfing and beach destinations including Noosa Heads, Queensland, Noosa Heads and Mooloolaba. It is also home to UnderWater World, Queensland, UnderWater World and Steve Irwin's Australia Zoo. Its hinterland includes the Glass House Mountains National Park.
Cairns
Cairns (, ) is a city in Queensland, Australia, on the tropical north east coast of Far North Queensland. The population in June 2019 was 153,952, having grown on average 1.02% annually over the preceding five years. The city is the 5th-most-p ...
is renowned as the gateway to the Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, ...
, Far North Queensland
Far North Queensland (FNQ) is the northernmost part of the Australian state of Queensland. Its largest city is Cairns and it is dominated geographically by Cape York Peninsula, which stretches north to the Torres Strait, and west to the Gulf C ...
(including Port Douglas, Queensland, Port Douglas) and the Daintree Rainforest
The Daintree Rainforest is a region on the northeast coast of Queensland, Australia, north of Mossman, Queensland, Mossman and Cairns. At around , the Daintree is a part of the largest continuous area of tropical rainforest on the Australia (co ...
. The Whitsunday Islands
The Whitsunday Islands are 74 continental islands of various sizes off the central coast of Queensland, Australia, north of Brisbane. The northernmost of the islands are off the coast by the town of Bowen, while the southernmost islands are ...
off the coast of North Queensland
North Queensland or the Northern Region is the northern part of the Australian state of Queensland that lies just south of Far North Queensland. Queensland is a massive state, larger than many countries, and its tropical northern part has been ...
are a popular tourist destinations for their resort facilities and access to the Great Barrier Reef.
Politics and government
One of the six founding States and territories of Australia, states of Australia, Queensland has been afederated state
A federated state (which may also be referred to as a state, a province, a region, a canton, a land, a governorate, an oblast, an emirate or a country) is a territorial and constitutional community forming part of a federation. Such states d ...
subject to the Constitution of Australia, Australian Constitution since 1 January 1901. It is Sovereign state, sovereign, other than in the Section 51 of the Constitution of Australia, matters ceded in the Australian Constitution to the federal government. It is a parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy. The Constitution of Queensland sets out the operation of the state's government. The state's constitution contains several entrenched clause, entrenched provisions which cannot be changed in the absence of a referendum. There is also a Statutory law, statutory bill of rights, the Queensland Human Rights Act (2019). Queensland's system of government is influenced by the Westminster system and Politics of Australia, Australia's federal system of government.
The government is Separation of powers in Australia, separated into three branches:
* Legislature: the unicameralism, unicameral Parliament of Queensland
The Parliament of Queensland is the legislature of Queensland, Australia. As provided under the Constitution of Queensland, the Parliament consists of the Monarch of Australia and the Legislative Assembly. It has been the only unicameral s ...
, comprising the Legislative Assembly of Queensland, Legislative Assembly and the Monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
(represented by the Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
);
* Executive: the Executive Council of Queensland, which formalises decisions of the Cabinet of Queensland, which is composed of the Premier
Premier is a title for the head of government in central governments, state governments and local governments of some countries. A second in command to a premier is designated as a deputy premier.
A premier will normally be a head of governm ...
and other ministers of state appointed by the Governor on the advice of Parliament;
* Judiciary: the Supreme Court of Queensland, Supreme Court and other state courts, whose judges are appointed by the Governor on advice of Parliament.
Executive (government), Executive authority is nominally vested in the Governor of Queensland
The governor of Queensland is the representative in the state of Queensland of the monarch of Australia. In an analogous way to the governor-general of Australia at the national level, the governor Governors of the Australian states, performs c ...
(currently Jeannette Young
Jeannette Rosita Young (born 1963) is an Australian medical doctor and administrator who is the current governor of the state of Queensland. Before being sworn in as governor, Young was the Chief Health Officer of Queensland from 2005 to 2021.
...
) who represents and is appointed by the Monarchy of Australia, Monarch of Australia (currently Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to ...
) on the advice of the Premier of Queensland
The premier of Queensland is the head of government in the Australian state of Queensland.
By convention the premier is the leader of the party with a parliamentary majority in the unicameral Legislative Assembly of Queensland. The premier is ap ...
. The Premier, who is the state's Head of government, along with the Cabinet of Queensland (whose decisions are formalised by the Executive Council of Queensland, Executive Council), exercise executive authority in practice. The Premier is appointed by the Governor and Responsible government, must have support of the Legislative Assembly of Queensland. The Premier is in practice a leading member of the Legislative Assembly and parliamentary leader of his or her political party, or coalition of parties, and members of Cabinet will be drawn from the same party or coalition. The current Premier and Deputy Premier of Queensland, Deputy Premier are Annastacia Palaszczuk
Annastacia Palaszczuk ( , Polish: Annastacia Pałaszczuk, ; born 25 July 1969) is an Australian politician who has been the 39th premier of Queensland since 2015 and the leader of the Queensland branch of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) since ...
and Steven Miles (politician), Steven Miles of the Australian Labor Party, Labor Party respectively. Government House, Brisbane, Government House at Paddington, Queensland, Paddington in Brisbane is the seat of the Governor, having replaced Old Government House, Queensland, Old Government House at Gardens Point, Brisbane, Gardens Point in Brisbane's Brisbane central business district, CBD in the early 20th century. The executive branch simply referred to as the Queensland Government.
Legislature, Legislative authority is exercised by the Parliament of Queensland, Queensland Parliament which uniquely for Australian states is unicameralism, unicameral, containing only one house, the Legislative Assembly. The Parliament was bicameral legislature, bicameral until 1922, when the Queensland Legislative Council, Legislative Council was abolished by the Labor "suicide squad", so called because they were appointed for the purpose of voting to abolish their own offices. Bill (law), Bills receive royal assent from the Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
before being passed into law. The Parliament's seat is at Parliament House, Brisbane, Parliament House at Gardens Point, Brisbane, Gardens Point in Brisbane's CBD. Members of the Legislative Assemby represent Electoral districts of Queensland, 93 electoral districts. Elections in Queensland are held at the end of each fixed four-year parliamentary term, and are determined by instant-runoff voting.
The state's judiciary consists of the Supreme Court of Queensland
The Supreme Court of Queensland is the highest court in the Australian State of Queensland. It was formerly the Brisbane Supreme Court, in the colony of Queensland.
The original jurisdiction of the Supreme Court allows its trial division to he ...
and the District Court of Queensland, established by the Queensland Constitution, as well as the Magistrates Court of Queensland and other courts and tribunals established by legislation. Cases may be appealed to the High Court of Australia. As with all Australian states and territories, Queensland has a Common law legal system. The Supreme and District courts are headquartered at the Queen Elizabeth II Courts of Law, Brisbane, Queen Elizabeth II Courts of Law in Brisbane's CBD.
The state's politics are traditionally regarded as being Conservatism in Australia, conservative relative to other states. Historically, the lack of an upper house, a former gerrymander favouring rural electoral districts as well as the former system of optional preferential voting has meant that Queensland had a long tradition of domination by strong-willed, populism, populist premiers, often accused of authoritarian tendencies, holding office for long periods. This tendency was exemplified by the government of the state's longest-serving Premier Joh Bjelke-Petersen.
Local government
Local government is the mechanism by which Local government areas of Queensland, local government areas can manage their own affairs to the extent permitted by the Local Government Act 2009. Queensland is divided into 77 local government areas, which are created by the state government under legislation. Each local government area has a council responsible for providing a range of local services and utilities. Local councils derive their income from both rates and charges on resident ratepayers, and grants and subsidies from the state and federal governments.Federal representation
In the federalParliament of Australia
The Parliament of Australia (officially the Federal Parliament, also called the Commonwealth Parliament) is the legislature, legislative branch of the government of Australia. It consists of three elements: the monarch (represented by the ...
, Queensland accounts for 30 of the 151 Divisions of the Australian House of Representatives, electoral divisions in the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
(on the basis of population size) and 12 of the 76 seats in the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
(on the basis of equality between the states).
The current partisan makeup of Queensland's House of Representatives delegation is 21 Liberal National Party of Queensland, Liberal National, 5 Australian Labor Party, Labor, 3 Australian Greens, and 1 Katter's Australian Party.
The current partisan makeup of Queensland's Senate delegation is 5 Liberal National Party of Queensland, Liberal National, 3 Australian Labor Party, Labor, 2 Pauline Hanson's One Nation, One Nation and 2 Australian Greens, Green.
Culture
 Queensland is home to major art galleries including the Queensland Art Gallery and the Queensland Gallery of Modern Art as well as cultural institutions such as the Queensland Ballet, Opera Queensland, Queensland Theatre Company, and Queensland Symphony Orchestra, all based at the Queensland Cultural Centre in Brisbane. The state is the origin of musicians such as the Bee Gees, The Go-Betweens, The Veronicas, The Saints (Australian band), The Saints, Savage Garden, and Sheppard (band), Sheppard as well as writers such as David Malouf, Nick Earls and Li Cunxin.
Major annual cultural events include the Ekka, Royal Queensland Exhibition (known locally as the Ekka), an agricultural exhibition held each August at the Brisbane Showgrounds as well as the Brisbane Festival, which includes one of the nation's largest annual fireworks displays called 'Riverfire', and which is held each September.
Queensland is home to major art galleries including the Queensland Art Gallery and the Queensland Gallery of Modern Art as well as cultural institutions such as the Queensland Ballet, Opera Queensland, Queensland Theatre Company, and Queensland Symphony Orchestra, all based at the Queensland Cultural Centre in Brisbane. The state is the origin of musicians such as the Bee Gees, The Go-Betweens, The Veronicas, The Saints (Australian band), The Saints, Savage Garden, and Sheppard (band), Sheppard as well as writers such as David Malouf, Nick Earls and Li Cunxin.
Major annual cultural events include the Ekka, Royal Queensland Exhibition (known locally as the Ekka), an agricultural exhibition held each August at the Brisbane Showgrounds as well as the Brisbane Festival, which includes one of the nation's largest annual fireworks displays called 'Riverfire', and which is held each September.
Sport
 The state of Queensland is represented in all of Australia's national sporting competitions and it is also host to a number of domestic and international sporting events. The most popular winter and summer team sports are rugby football, rugby (rugby league and rugby union) and cricket, respectively.
In the National Rugby League, the Brisbane Broncos, North Queensland Cowboys and Gold Coast Titans are based in the state. Rugby league's annual State of Origin series is a major event in the Queensland sporting calendar, with the Queensland rugby league team, Queensland Maroons representing the state.
The state is represented by the Queensland Reds in the Super Rugby (rugby union).
In cricket, the Queensland Bulls represent the state in the Sheffield Shield and the Ryobi One Day Cup, while the Brisbane Heat compete in the Big Bash League.
Queensland is also home to the Brisbane Lions and the Gold Coast Suns in the Australian Football League (Australian rules football), and the Brisbane Roar FC in the A-League (soccer). In netball the Queensland Firebirds went undefeated in the 2011 season as they went on to win the Grand Final. Other sports teams are the Brisbane Bullets and the Cairns Taipans, who compete in the National Basketball League (Australia), National Basketball League.
Swimming is also a popular sport in Queensland, with many of Australian team members and international medalists hailing from the state.
Brisbane will host the 2032 Summer Olympics, marking the third time Australia hosted the Olympic Games following 1956 Summer Olympics, Melbourne 1956 and 2000 Summer Olympics, Sydney 2000. Major recurring sporting events hosted in Queensland include: the Gold Coast 600 (motorsport; since 1994), the Gold Coast Marathon (athletics; since 1979), the NRL All Stars Game (rugby league; since 2010), the Townsville 400 (motorsport; since 2009), the World championship tour (WCT) surfing, Quicksilver Pro and Roxy Pro (surfing) and Australian PGA Championship (golf; since 2000).
The state of Queensland is represented in all of Australia's national sporting competitions and it is also host to a number of domestic and international sporting events. The most popular winter and summer team sports are rugby football, rugby (rugby league and rugby union) and cricket, respectively.
In the National Rugby League, the Brisbane Broncos, North Queensland Cowboys and Gold Coast Titans are based in the state. Rugby league's annual State of Origin series is a major event in the Queensland sporting calendar, with the Queensland rugby league team, Queensland Maroons representing the state.
The state is represented by the Queensland Reds in the Super Rugby (rugby union).
In cricket, the Queensland Bulls represent the state in the Sheffield Shield and the Ryobi One Day Cup, while the Brisbane Heat compete in the Big Bash League.
Queensland is also home to the Brisbane Lions and the Gold Coast Suns in the Australian Football League (Australian rules football), and the Brisbane Roar FC in the A-League (soccer). In netball the Queensland Firebirds went undefeated in the 2011 season as they went on to win the Grand Final. Other sports teams are the Brisbane Bullets and the Cairns Taipans, who compete in the National Basketball League (Australia), National Basketball League.
Swimming is also a popular sport in Queensland, with many of Australian team members and international medalists hailing from the state.
Brisbane will host the 2032 Summer Olympics, marking the third time Australia hosted the Olympic Games following 1956 Summer Olympics, Melbourne 1956 and 2000 Summer Olympics, Sydney 2000. Major recurring sporting events hosted in Queensland include: the Gold Coast 600 (motorsport; since 1994), the Gold Coast Marathon (athletics; since 1979), the NRL All Stars Game (rugby league; since 2010), the Townsville 400 (motorsport; since 2009), the World championship tour (WCT) surfing, Quicksilver Pro and Roxy Pro (surfing) and Australian PGA Championship (golf; since 2000).
Symbols and emblems
The official state emblems of Queensland are prescribed in the Emblems of Queensland Act 2005.Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
granted the Queensland Coat of Arms to the Colony of Queensland in 1893, making it the oldest State Arms in Australia. It depicts Queensland's primary industries in the 19th century with a sheaf of wheat, the heads of a bull and a ram, and a column of gold rising from a heap of quartz. Two stalks of sugar cane which surround the state badge at the top, and below is Queensland's state motto, ''Audax at Fidelis'', which means "Bold but Faithful". In 1977, Elizabeth II, Queen Elizabeth II granted the supporting animals, the brolga and the red deer.
In November 2003 maroon
Maroon ( US/ UK , Australia ) is a brownish crimson color that takes its name from the French word ''marron'', or chestnut. "Marron" is also one of the French translations for "brown".
According to multiple dictionaries, there are var ...
was officially named as Queensland's state colour, after many years of association with Queensland sporting teams.
The koala was officially named the animal or faunal, emblem of Queensland in 1971, after a newspaper poll showed strong public support. The Queensland Government introduced the poll due to a proposal by state tourism ministers for all states to adopt a faunal emblem. In January 1986 that the brolga was announced as the official bird emblem of Queensland, after many years on the Coat of Arms.
The Dendrobium bigibbum, Cooktown orchid became known as Queensland's floral emblem in 1959, during celebrations to mark the state's centenary, and the Amphiprion akindynos, Barrier Reef Anemone Fish was officially named as Queensland's aquatic emblem in March 2005.
The sapphire was named the official state gem for Queensland in August 1985.
Infrastructure
Transport

 Queensland is served by a number of National Highway (Australia), National Highways and, particularly in South East Queensland, a network of freeways such as the M1 (Queensland), M1. The Department of Transport and Main Roads, Department of Transport & Main Roads oversees the development and operation of main roads and public transport, including taxis and local aviation.
Rail transport in Queensland, Principal rail services are provided by Queensland Rail, predominantly between the major centres east of the Great Dividing Range. Freight rail services in Queensland have been provided mostly by Aurizon and Pacific National, with interstate intermodal services provided by Pacific National and SCT Logistics. Major seaports include the Port of Brisbane, Australia's third busiest by value of goods, as well as those at
Queensland is served by a number of National Highway (Australia), National Highways and, particularly in South East Queensland, a network of freeways such as the M1 (Queensland), M1. The Department of Transport and Main Roads, Department of Transport & Main Roads oversees the development and operation of main roads and public transport, including taxis and local aviation.
Rail transport in Queensland, Principal rail services are provided by Queensland Rail, predominantly between the major centres east of the Great Dividing Range. Freight rail services in Queensland have been provided mostly by Aurizon and Pacific National, with interstate intermodal services provided by Pacific National and SCT Logistics. Major seaports include the Port of Brisbane, Australia's third busiest by value of goods, as well as those at Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and Liberal politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, spread over four non-conse ...
, Townsville
Townsville is a city on the north-eastern coast of Queensland, Australia. With a population of 180,820 as of June 2018, it is the largest settlement in North Queensland; it is unofficially considered its capital. Estimated resident population, 3 ...
and Bundaberg
Bundaberg is a city in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia, and is the tenth largest city in the state. Bundaberg's regional area has a population of 70,921, and is a major centre of the Wide Bay–Burnett geographical region. The Bun ...
. There are large coal export facilities at Hay Point, Queensland, Hay Point, Gladstone and Abbot Point. Major sugar export facilities are located at Lucinda, Queensland, Lucinda and Mackay Mackay may refer to:
*Clan Mackay, the Scottish clan from which the surname "MacKay" derives
Mackay may also refer to:
Places Australia
* Mackay Region, a local government area
** Mackay, Queensland, a city in the above region
*** Mackay Airpor ...
.
Brisbane Airport is the main international and domestic gateway serving the state, and is the List of the busiest airports in Australia, third busiest in Australia. Other international airports include the Gold Coast Airport, Cairns International Airport and Townsville Airport. Regional airports with scheduled domestic flights include Toowoomba Wellcamp Airport, Great Barrier Reef Airport, Hervey Bay Airport, Bundaberg Airport, Mackay Airport, Mount Isa Airport, Whitsunday Coast Airport, Proserpine / Whitsunday Coast Airport, Rockhampton Airport, and Sunshine Coast Airport.
South East Queensland
South East Queensland (SEQ) is a bio-geographical, metropolitan, political and administrative region of the state of Queensland in Australia, with a population of approximately 3.8 million people out of the state's population of 5.1 million. T ...
has an integrated public transport system operated by TransLink (South East Queensland), TransLink, which provides services bus transport in Queensland, bus, Queensland Rail City network, rail, G:link, light rail and RiverCity Ferries, Brisbane's ferry services through Queensland Rail and contracted operators. The region is divided into seven Fare zones radiating outwards from the Brisbane central business district, which is the central hub for the system. The Queensland Rail City network consists of 152 train stations along 13 suburban rail lines and across the region, and predominantly within Brisbane's metropolitan area. There is also a large bus network including Brisbane's large dedicated bus rapid transit network, the Busways in Brisbane, Brisbane busway network. Brisbane's popular RiverCity Ferries, ferry services include the CityCat, Cross River and CityHopper services which have dedicated wharves along the Brisbane River
The Brisbane River is the longest river in South East Queensland, Australia, and flows through the city of Brisbane, before emptying into Moreton Bay on the Coral Sea. John Oxley, the first European to explore the river, named it after the Go ...
. The G:link, Queensland's only light rail network, operates on the Gold Coast.
Other utilities
Queensland Health operates and administers the state's public health system. There are sixteen regional Health and Hospital Services corresponding to geographical regions which are responsible for delivering public health services within their regions. Major public hospitals include the Royal Brisbane and Women's Hospital, Princess Alexandra Hospital, Brisbane, Princess Alexandra Hospital, the Mater Group, Mater Hospital, the Queen Elizabeth II Jubilee Hospital, and the Queensland Children's Hospital in Brisbane, as well as the Townsville University Hospital, Cairns Hospital, Gold Coast Hospital and Gold Coast University Hospital in the regional cities. There are smaller public hospitals, as well as private hospitals, around the state.See also
* Outline of Australia * Index of Australia-related articles *Queensland Day
Queensland Day is officially celebrated on 6 June as the birthday of the Australian state of Queensland.
History
Moves towards statehood began with a public meeting in 1851 to consider separation of Queensland from the Colony of New South Wa ...
* Blackbirding
Notes
References
External links
*Government of Queensland
* * * . * . * * {{Authority control Queensland, Former British colonies and protectorates in Oceania States and territories of Australia States and territories established in 1859 kab:Usṭralya