Quad Store on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
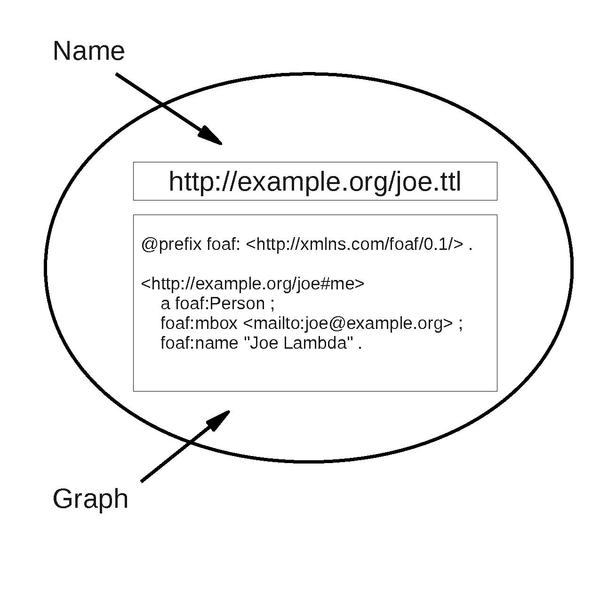 Named graphs are a key concept of Semantic Web architecture in which a set of
Named graphs are a key concept of Semantic Web architecture in which a set of
 Named graphs are a formalization of the intuitive idea that the contents of an RDF document (a graph) on the Web can be considered to be named by the URI of the document. This considerably simplifies techniques for managing chains of provenance for pieces of data and enabling fine-grained access control to the source data. Additionally, trust can be managed through the publisher applying a digital signature to the data in the named graph. (Support for these facilities was originally intended to come from RDF reification, however, that approach proved problematic.)
Named graphs are a formalization of the intuitive idea that the contents of an RDF document (a graph) on the Web can be considered to be named by the URI of the document. This considerably simplifies techniques for managing chains of provenance for pieces of data and enabling fine-grained access control to the source data. Additionally, trust can be managed through the publisher applying a digital signature to the data in the named graph. (Support for these facilities was originally intended to come from RDF reification, however, that approach proved problematic.)
@prefix foaf: a foaf:Person .
foaf:homepage .
foaf:mbox .
foaf:name "Joe Lambda" .
''This data has been written in a more verbose form than necessary to show the triple structures''
The homepage of the person with the email address can be obtained using the
PREFIX foaf:
WHERE
The FROM NAMED here identifies the target graph for the query.
/ref> (which includes syntaxes for representing named graphs), but they do form part of the
 Named graphs are a key concept of Semantic Web architecture in which a set of
Named graphs are a key concept of Semantic Web architecture in which a set of Resource Description Framework The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standard originally designed as a data model for metadata. It has come to be used as a general method for description and exchange of graph data. RDF provides a variety of ...
statements (a graph
Graph may refer to:
Mathematics
*Graph (discrete mathematics), a structure made of vertices and edges
**Graph theory, the study of such graphs and their properties
*Graph (topology), a topological space resembling a graph in the sense of discre ...
) are identified using a URI Uri may refer to:
Places
* Canton of Uri, a canton in Switzerland
* Úri, a village and commune in Hungary
* Uri, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province
* Uri, Jammu and Kashmir, a town in India
* Uri (island), an island off Malakula Isla ...
, allowing descriptions to be made of that set of statements such as context, provenance information or other such metadata.
Named graphs are a simple extension of the RDF data model through which graphs can be created but the model lacks an effective means of distinguishing between them once published on the Web
Web most often refers to:
* Spider web, a silken structure created by the animal
* World Wide Web or the Web, an Internet-based hypertext system
Web, WEB, or the Web may also refer to:
Computing
* WEB, a literate programming system created b ...
at large.
Named graphs and HTTP
One conceptualization of the Web is as a graph of document nodes identified with URIs and connected byhyperlink
In computing, a hyperlink, or simply a link, is a digital reference to data that the user can follow or be guided by clicking or tapping. A hyperlink points to a whole document or to a specific element within a document. Hypertext is text ...
arcs which are expressed within the HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScri ...
documents. By doing an HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...
GET on a URI (usually via a Web browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...
), a somehow-related document may be retrieved. This "follow your nose" approach also applies to RDF documents on the Web in the form of Linked Data
In computing, linked data (often capitalized as Linked Data) is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but ...
, where typically an RDF syntax is used to express data as a series of statements, and URI Uri may refer to:
Places
* Canton of Uri, a canton in Switzerland
* Úri, a village and commune in Hungary
* Uri, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province
* Uri, Jammu and Kashmir, a town in India
* Uri (island), an island off Malakula Isla ...
s within the RDF point to other resources. This Web of data has been described by Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web. He is a Professorial Fellow of Computer Science at the University of Oxford and a profe ...
as the "Giant Global Graph".
 Named graphs are a formalization of the intuitive idea that the contents of an RDF document (a graph) on the Web can be considered to be named by the URI of the document. This considerably simplifies techniques for managing chains of provenance for pieces of data and enabling fine-grained access control to the source data. Additionally, trust can be managed through the publisher applying a digital signature to the data in the named graph. (Support for these facilities was originally intended to come from RDF reification, however, that approach proved problematic.)
Named graphs are a formalization of the intuitive idea that the contents of an RDF document (a graph) on the Web can be considered to be named by the URI of the document. This considerably simplifies techniques for managing chains of provenance for pieces of data and enabling fine-grained access control to the source data. Additionally, trust can be managed through the publisher applying a digital signature to the data in the named graph. (Support for these facilities was originally intended to come from RDF reification, however, that approach proved problematic.)
Named graphs and RDF stores
While named graphs may appear on the Web as simple linked documents (i.e.Linked Data
In computing, linked data (often capitalized as Linked Data) is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but ...
), they are also very useful for managing sets of RDF data within an RDF store. In particular, the scope of a SPARQL
SPARQL (pronounced " sparkle" , a recursive acronym for SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language) is an RDF query language—that is, a semantic query language for databases—able to retrieve and manipulate data stored in Resource Description ...
query may be limited to a specific set of named graphs.
Example
Assume the following (Turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked ...
) RDF document has been placed in a SPARQL
SPARQL (pronounced " sparkle" , a recursive acronym for SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language) is an RDF query language—that is, a semantic query language for databases—able to retrieve and manipulate data stored in Resource Description ...
-capable store with the name .
SPARQL
SPARQL (pronounced " sparkle" , a recursive acronym for SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language) is an RDF query language—that is, a semantic query language for databases—able to retrieve and manipulate data stored in Resource Description ...
query:
Named graphs and quads
Prior to the publication of the papers describing named graphs, there was considerable discussion about fulfilling their role within a store by using anarity
Arity () is the number of arguments or operands taken by a function, operation or relation in logic, mathematics, and computer science. In mathematics, arity may also be named ''rank'', but this word can have many other meanings in mathematics. In ...
above that of RDF triple statements: where ''triples'' have the form ''subject predicate object'', ''quads'' would have a form along the lines of ''subject predicate object context''. Named graphs can be represented this way, as ''subject predicate object graphname'', with the advantage that the ''graphname'' part will be a URI, giving the quad Web-global scope compared to arbitrary local statement names. This way of representing quads resp. quad-statements was incorporated in the specification of N-Quads
N-Triples is a format for storing and transmitting data. It is a line-based, plain text serialisation format for RDF (Resource Description Framework) graphs, and a subset of the Turtle (Terse RDF Triple Language) format. N-Triples should not be c ...
.
Formal definition
A paper from the WWW 2005 conference by Carroll et al. includes a formal definition of named graphs.Specifications
There is currently no specification for named graphs in themselves beyond that described in Carroll et al. (2005) and Carroll and Stickler (2004)TriX : RDF Triples in XML/ref> (which includes syntaxes for representing named graphs), but they do form part of the
SPARQL
SPARQL (pronounced " sparkle" , a recursive acronym for SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language) is an RDF query language—that is, a semantic query language for databases—able to retrieve and manipulate data stored in Resource Description ...
Protocol and RDF Query Language specification.
Proposed specifications
* TriX - Named Graphs inXML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. ...
* TriG
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. T ...
- Named Graphs in Turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked ...
* N-Quads
N-Triples is a format for storing and transmitting data. It is a line-based, plain text serialisation format for RDF (Resource Description Framework) graphs, and a subset of the Turtle (Terse RDF Triple Language) format. N-Triples should not be c ...
- Named Graphs in N-Triples
N-Triples is a format for storing and transmitting data. It is a line-based, plain text serialisation format for RDF (Resource Description Framework) graphs, and a subset of the Turtle (Terse RDF Triple Language) format. N-Triples should not be ...
See also
*References