|
Turtle (syntax)
In computing, Terse RDF Triple Language (Turtle) is a syntax and file format for expressing data in the Resource Description Framework (RDF) data model. Turtle syntax is similar to that of SPARQL, an RDF query language. It is a common data format for storing RDF data, along with N-Triples, JSON-LD and RDF/XML. RDF represents information using semantic triples, which comprise a subject, predicate, and object. Each item in the triple is expressed as a Web URI. Turtle provides a way to group three URIs to make a triple, and provides ways to abbreviate such information, for example by factoring out common portions of URIs. For example, information about Huckleberry Finn could be expressed as: <http://example.org/books/Huckleberry_Finn> <http://example.org/relation/author> <http://example.org/person/Mark_Twain> . History Turtle was defined by Dave Beckett as a subset of Tim Berners-Lee and Dan Connolly's Notation3 (N3) language, and a superset of the minima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Web
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable. To enable the encoding of semantics with the data, technologies such as Resource Description Framework (RDF) and Web Ontology Language (OWL) are used. These technologies are used to formally represent metadata. For example, Ontology (information science), ontology can describe concepts, relationships between Entity–relationship model, entities, and categories of things. These embedded semantics offer significant advantages such as reasoning engine, reasoning over data and operating with heterogeneous data sources. These standards promote common data formats and exchange protocols on the Web, fundamentally the RDF. According to the W3C, "The Semantic Web provides a common framework that allows data to be shared and reused across application, enterprise, and commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web, the HTML markup language, the URL system, and HTTP. He is a professorial research fellow at the University of Oxford and a professor emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Berners-Lee proposed an information management system on 12 March 1989 and implemented the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and Server (computing), server via the Internet in mid-November. He devised and implemented the first Web browser and Web server and helped foster the Web's subsequent development. He is the founder and emeritus director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which oversees the continued development of the Web. He co-founded (with Rosemary Leith) the World Wide Web Foundation. In April 2009, he was elected as Foreign Associate of the National Academy of Sciences. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
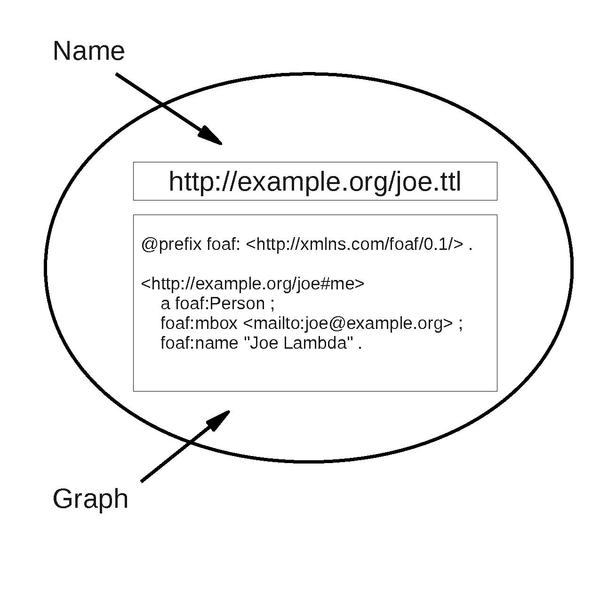
Named Graph
Named graphs are a key concept of Semantic Web architecture in which a set of Resource Description Framework statements (a graph) are identified using a URI, allowing descriptions to be made of that set of statements such as context, provenance information or other such metadata. Named graphs are a simple extension of the RDF data model through which graphs can be created but the model lacks an effective means of distinguishing between them once published on the Web at large. Named graphs and HTTP One conceptualization of the Web is as a graph of document nodes identified with URIs and connected by hyperlink arcs which are expressed within the HTML documents. By doing an HTTP GET on a URI (usually via a Web browser), a somehow-related document may be retrieved. This "follow your nose" approach also applies to RDF documents on the Web in the form of Linked Data, where typically an RDF syntax is used to express data as a series of statements, and URIs within the RDF point to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is a standards organization that oversees global IP address allocation, Autonomous system (Internet), autonomous system number allocation, DNS root zone, root zone management in the Domain Name System (DNS), Internet media type, media types, and other Internet Protocol–related symbols and Internet numbers. Currently it is a function of ICANN, a nonprofit private American corporation established in 1998 primarily for this purpose under a United States Department of Commerce contract. ICANN managed IANA directly from 1998 through 2016, when it was transferred to Public Technical Identifiers (PTI), an affiliate of ICANN that operates IANA today. Before it, IANA was administered principally by Jon Postel at the Information Sciences Institute (ISI) of the University of Southern California (USC) situated at Marina Del Rey (Los Angeles), under a contract USC/ISI had with the United States Department of Defense. In addition, five regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UTF-8
UTF-8 is a character encoding standard used for electronic communication. Defined by the Unicode Standard, the name is derived from ''Unicode Transformation Format 8-bit''. Almost every webpage is transmitted as UTF-8. UTF-8 supports all 1,112,064 valid Unicode code points using a variable-width encoding of one to four one- byte (8-bit) code units. Code points with lower numerical values, which tend to occur more frequently, are encoded using fewer bytes. It was designed for backward compatibility with ASCII: the first 128 characters of Unicode, which correspond one-to-one with ASCII, are encoded using a single byte with the same binary value as ASCII, so that a UTF-8-encoded file using only those characters is identical to an ASCII file. Most software designed for any extended ASCII can read and write UTF-8, and this results in fewer internationalization issues than any alternative text encoding. UTF-8 is dominant for all countries/languages on the internet, with 99% global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIME Type
In information and communications technology, a media type, content type or MIME type is a two-part identifier for file formats and content formats. Their purpose is comparable to filename extensions and uniform type identifiers, in that they identify the intended data format. They are mainly used by technologies underpinning the Internet, and also used on Linux desktop systems. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is the official authority for the standardization and publication of these classifications. Media types were originally defined in Request for Comments (MIME) Part One: Format of Internet Message Bodies (Nov 1996) in November 1996 as a part of the ''MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)'' specification, for denoting type of email message content and attachments; hence the original name, ''MIME type''. Media types are also used by other internet protocols such as HTTP, document file formats such as HTML, and the XDG specifications implemented by Linux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDFLib
RDFLib is a Python library for working with RDF, a simple yet powerful language for representing information. This library contains parsers/serializers for almost all of the known RDF serializations, such as RDF/XML, Turtle, N-Triples, & JSON-LD, many of which are now supported in their updated form (e.g. Turtle 1.1). The library also contains both in-memory and persistent Graph back-ends for storing RDF information and numerous convenience functions for declaring graph namespaces, lodging SPARQL queries and so on. It is in continuous development with the most recent stable releaserdflib 6.1.1having been released on 20 December 2021. It was originally created by Daniel Krech with the first release in November, 2002. A number of other Python projects use rdflib for RDF manipulation, including: OWL-RL- A simple implementation of the OWL2 RL Profile (reasoning engine) pySHACL- a Python SHACL validator pyLDAPI- an add-on module for the Python Flask web framework used to deliver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jena (framework)
Apache Jena is an open source Semantic Web framework for Java. It provides an API to extract data from and write to RDF graphs. The graphs are represented as an abstract "model". A model can be sourced with data from files, databases, URLs or a combination of these. A model can also be queried through SPARQL 1.1. Jena is similar to RDF4J (formerly OpenRDF Sesame); though, unlike RDF4J, Jena provides support for OWL (Web Ontology Language). The framework has various internal reasoners and the Pellet reasoner (an open source Java OWL-DL reasoner) can be set up to work in Jena. Jena supports serialisation of RDF graphs to: *a relational database *RDF/XML *Turtle * TriG *Notation 3 *JSON-LD Versions After Apache integration Jena was integrated as a project under the umbrella of The Apache Software Foundation in April 2012, after having been in the Apache Incubator since November 2010. Before Apache integration Jena was created by HP Labs and was on SourceForge since 2001, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDF4J
Eclipse RDF4J (formerly OpenRDF Sesame) is an open-source framework for storing, querying, and analysing Resource Description Framework (RDF) data. Framework It was created by the Dutch software company Aduna as part of "On-To-Knowledge", a semantic web project that ran from 1999 to 2002. It contains implementations of an in-memory triplestore and an on-disk triplestore, along with two separate Servlet packages that can be used to manage and provide access to these triplestores, on a permanent server. The RDF4J Rio (RDF Input/Output) package contains a simple API for Java-based RDF parsers and writers. Parsers and writers for popular RDF serialisations are distributed along with RDF4J, and users can easily extend the list by putting their parsers and writers on the Java classpath when running their application. RDF4J supports two query languages: SPARQL and SeRQL. RDF4J's RDF database API differs from comparable solutions in that it offers a stackable interface through which f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redland RDF Application Framework
Redland is a set of free software libraries written in C that provide support for the Resource Description Framework (RDF), created by Dave Beckett (a former resident of Redland, Bristol). The packages that form Redland are: * Redland RDF Application Framework providing the C RDF API * Raptor RDF Parser Toolkit for parsing and serializing RDF syntaxes (RDF/XML, N-Triples, Turtle, RSS tag soup, Atom) * Rasqal RDF Query Library for executing RDF queries with RDQL and SPARQL * Redland Language Bindings for APIs to Redland in C#, Java, Objective-C, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby and Tcl Redland is a mature set of libraries, in development since 2000 and closely conformant to the relevant W3C specifications. See also *Semantic Web The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable. To enable the encoding o ... Extern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Web Consortium
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working together in the development of standards for the World Wide Web. W3C has 350 members. The organization has been led by CEO Seth Dobbs since October 2023. W3C also engages in education and outreach, develops software and serves as an open forum for discussion about the Web. History The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) was founded in 1994 by Tim Berners-Lee after he left the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) in October 1994. It was founded at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Laboratory for Computer Science with support from the European Commission, and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, which had pioneered the ARPANET, the most direct predecessor to the modern Internet. It was located in Technology Square (Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dan Connolly (computer Scientist)
Dan Connolly (born 1967) is an American computer scientist who was closely involved with the creation of the World Wide Web as a member of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). Early years and education Connolly was born in 1967 and grew up with four siblings in Prairie Village, in the Kansas City metropolitan area, where he attended Bishop Miege High School. From 1986 to 1990 he attended University of Texas at Austin, earning a B.S. in computer science. Career In October 1991, Connolly was working on the documentation tools team at Convex Computer when he joined the Web project's mailing list to discuss the browser he had written for the X Window System. Soon after he started advocating for HTML to adopt an SGML document type definition. He met Tim Berners-Lee and Robert Cailliau at the HyperText conference in San Antonio, TX, in December 1991. With Berners-Lee he was co-editor of the initial Internet Engineering Task Force's draft specification for HTML. He was also the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |