|
TriG (syntax)
TriG is a serialization format for RDF (Resource Description Framework) graphs. It is a plain text format for serializing named graph Named graphs are a key concept of Semantic Web architecture in which a set of Resource Description Framework statements (a graph) are identified using a URI, allowing descriptions to be made of that set of statements such as context, provenance ...s and RDF Datasets which offers a compact and readable alternative to the XML-based TriX syntax. Example This example encodes three interlinked named graphs: * http://www.example.org/exampleDocument#G1 * http://www.example.org/exampleDocument#G2 * http://www.example.org/exampleDocument#G3 @prefix rdf: . @prefix xsd: . @prefix swp: . @prefix dc: . @prefix ex: . @prefix : . :G1 :G2 :G3 External links TriG Specification (2007)RDF 1.1 TriG W3C Recommendation (2014)Yacker TriG validator which does not handle sub-graphs, and does not validate the above example. Resource Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freie Universität Berlin
The Free University of Berlin (, often abbreviated as FU Berlin or simply FU) is a public university, public research university in Berlin, Germany. It was founded in West Berlin in 1948 with American support during the early Cold War period as a West Berlin, Western continuation of the Humboldt University of Berlin, Friedrich Wilhelm University, or the University of Berlin, whose traditions and faculty members it retained. The Friedrich Wilhelm University (which was renamed the Humboldt University of Berlin, Humboldt University), being in East Berlin, was subject to East Germany's comparatively restrictive information laws. The ''Free University'' 's name referred to West Berlin's status as part of the intellectual continua of the Western "Free World, ''Free'' World", contrasting with communist-controlled East Berlin. In 2008, as part of a joint effort, the Free University of Berlin, along with the Hertie School of Governance, and WZB Berlin Social Science Center, WZB Social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Web
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable. To enable the encoding of semantics with the data, technologies such as Resource Description Framework (RDF) and Web Ontology Language (OWL) are used. These technologies are used to formally represent metadata. For example, Ontology (information science), ontology can describe concepts, relationships between Entity–relationship model, entities, and categories of things. These embedded semantics offer significant advantages such as reasoning engine, reasoning over data and operating with heterogeneous data sources. These standards promote common data formats and exchange protocols on the Web, fundamentally the RDF. According to the W3C, "The Semantic Web provides a common framework that allows data to be shared and reused across application, enterprise, and commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Description Framework
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a method to describe and exchange graph data. It was originally designed as a data model for metadata by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It provides a variety of syntax notations and formats, of which the most widely used is Turtle ( Terse RDF Triple Language). RDF is a directed graph composed of triple statements. An RDF graph statement is represented by: (1) a node for the subject, (2) an arc from subject to object, representing a predicate, and (3) a node for the object. Each of these parts can be identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). An object can also be a literal value. This simple, flexible data model has a lot of expressive power to represent complex situations, relationships, and other things of interest, while also being appropriately abstract. RDF was adopted as a W3C recommendation in 1999. The RDF 1.0 specification was published in 2004, and the RDF 1.1 specification in 2014. SPARQL is a standard query ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtle (syntax)
In computing, Terse RDF Triple Language (Turtle) is a syntax and file format for expressing data in the Resource Description Framework (RDF) data model. Turtle syntax is similar to that of SPARQL, an RDF query language. It is a common data format for storing RDF data, along with N-Triples, JSON-LD and RDF/XML. RDF represents information using semantic triples, which comprise a subject, predicate, and object. Each item in the triple is expressed as a Web URI. Turtle provides a way to group three URIs to make a triple, and provides ways to abbreviate such information, for example by factoring out common portions of URIs. For example, information about Huckleberry Finn could be expressed as: <http://example.org/books/Huckleberry_Finn> <http://example.org/relation/author> <http://example.org/person/Mark_Twain> . History Turtle was defined by Dave Beckett as a subset of Tim Berners-Lee and Dan Connolly's Notation3 (N3) language, and a superset of the minima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
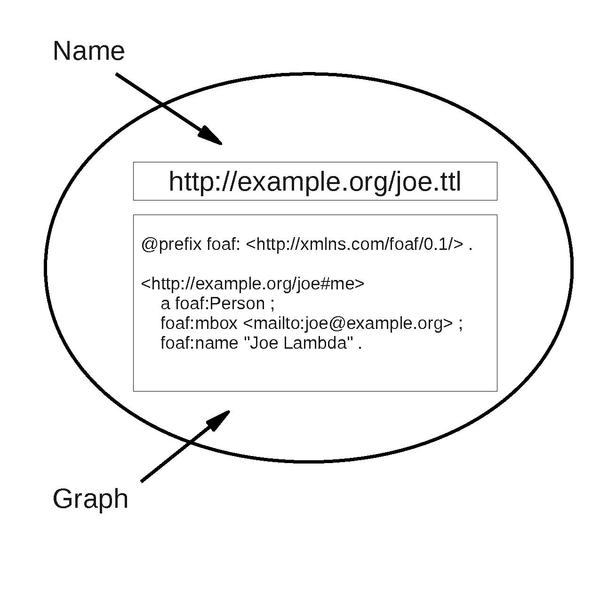
Named Graph
Named graphs are a key concept of Semantic Web architecture in which a set of Resource Description Framework statements (a graph) are identified using a URI, allowing descriptions to be made of that set of statements such as context, provenance information or other such metadata. Named graphs are a simple extension of the RDF data model through which graphs can be created but the model lacks an effective means of distinguishing between them once published on the Web at large. Named graphs and HTTP One conceptualization of the Web is as a graph of document nodes identified with URIs and connected by hyperlink arcs which are expressed within the HTML documents. By doing an HTTP GET on a URI (usually via a Web browser), a somehow-related document may be retrieved. This "follow your nose" approach also applies to RDF documents on the Web in the form of Linked Data, where typically an RDF syntax is used to express data as a series of statements, and URIs within the RDF point to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TriX (syntax)
TriX ( Triples in XML) is a serialization format for RDF (Resource Description Framework) graphs. It is an XML format for serializing Named Graphs and RDF Datasets which offers a compact and readable alternative to the XML-based RDF/XML syntax. It was jointly created by HP Labs and Nokia Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporation, originally established as a pulp mill in 1 .... It is suggested that those digital artifacts dependent of the serialization format need means to verify immutability, or digital artifacts including datasets, code, texts, and images are not verifiable nor permanent. Embedding cryptographic hash values to applied URIs has been suggested for structured data files such as nano-publications. Member registration required. Example https://example.org/Bob https://example.org/wife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |