Phosphorus Acid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Phosphorus oxoacid (or phosphorus acid) is a generic name for any
 *
*
 *
*
 *
*
 The simplest member of this class is:
*
The simplest member of this class is:
*
File:Pyrophosphoric-acid-3D-vdW.png,
File:Tripolyphosphoric-acid-3D-vdW.png, Tripolyphosphoric acid
File:Tetrapolyphosphoric-acid-3D-vdW.png, Tetrapolyphosphoric acid
H6P4O13 File:Trimetaphosphoric-acid-3D-vdW.png, Trimetaphosphoric acid
Another compound that may be included in this class is
*

''Determination of Polyphosphates Using Ion Chromatography with Suppressed Conductivity Detection, Application Note 71'' by Dionex
* * {{Phosphorus compounds * Dietary minerals Inorganic compounds Phosphates Phosphorus(V) compounds Pyrophosphates Reagents for organic chemistry
acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
whose molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioch ...
consists of atoms of phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
, and hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
. There is a potentially infinite number of such compounds. Some of them are unstable and have not been isolated, but the derived anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s and organic groups are present in stable salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantitie ...
s and ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
s. The most important ones—in biology, geology, industry, and chemical research—are the phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, w ...
s, whose esters and salts are the phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
s.
In general, any hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom is acidic, meaning that the –OH group can lose a proton leaving a negatively charged – group and thus turning the acid into a phosphorus oxoanion. Each additional proton lost has an associated acid dissociation constant
In chemistry, an acid dissociation constant (also known as acidity constant, or acid-ionization constant; denoted ) is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction
:HA ...
K''a''1, K''a''2 K''a''3, ..., often expressed by its cologarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation. That means the logarithm of a number to the base is the exponent to which must be raised, to produce . For example, since , the ''logarithm base'' 10 o ...
(pK''a''1, pK''a''2, pK''a''3, ...). Hydrogen atoms bonded directly to phosphorus are generally not acidic.
Classification
The phosphorus oxoacids can be classified by the oxidation state(s) of the phosphorus atom(s), which may vary from +1 to +5. The oxygen atoms are usually in oxidation state -2, but may be in state -1 if the molecule includes peroxide groups.Oxidation state +1
 *
*Hypophosphorous acid
Hypophosphorous acid (HPA), or phosphinic acid, is a phosphorus oxyacid and a powerful reducing agent with molecular formula H3PO2. It is a colorless low-melting compound, which is soluble in water, dioxane
and alcohols. The formula for this ...
(or phosphinic acid), (or ), a monoprotic acid
In computer science, ACID (Atomicity (database systems), atomicity, Consistency (database systems), consistency, Isolation (database systems), isolation, Durability (database systems), durability) is a set of properties of database transactions i ...
(meaning that only one of the hydrogen atoms is acidic). Its salts and esters are called hypophosphite
Phosphinates or hypophosphites are a class of phosphorus compounds conceptually based on the structure of hypophosphorous acid. IUPAC prefers the term phosphinate in all cases, however in practice hypophosphite is usually used to describe inorganic ...
s or phosphinates.
Oxidation state +3
 *
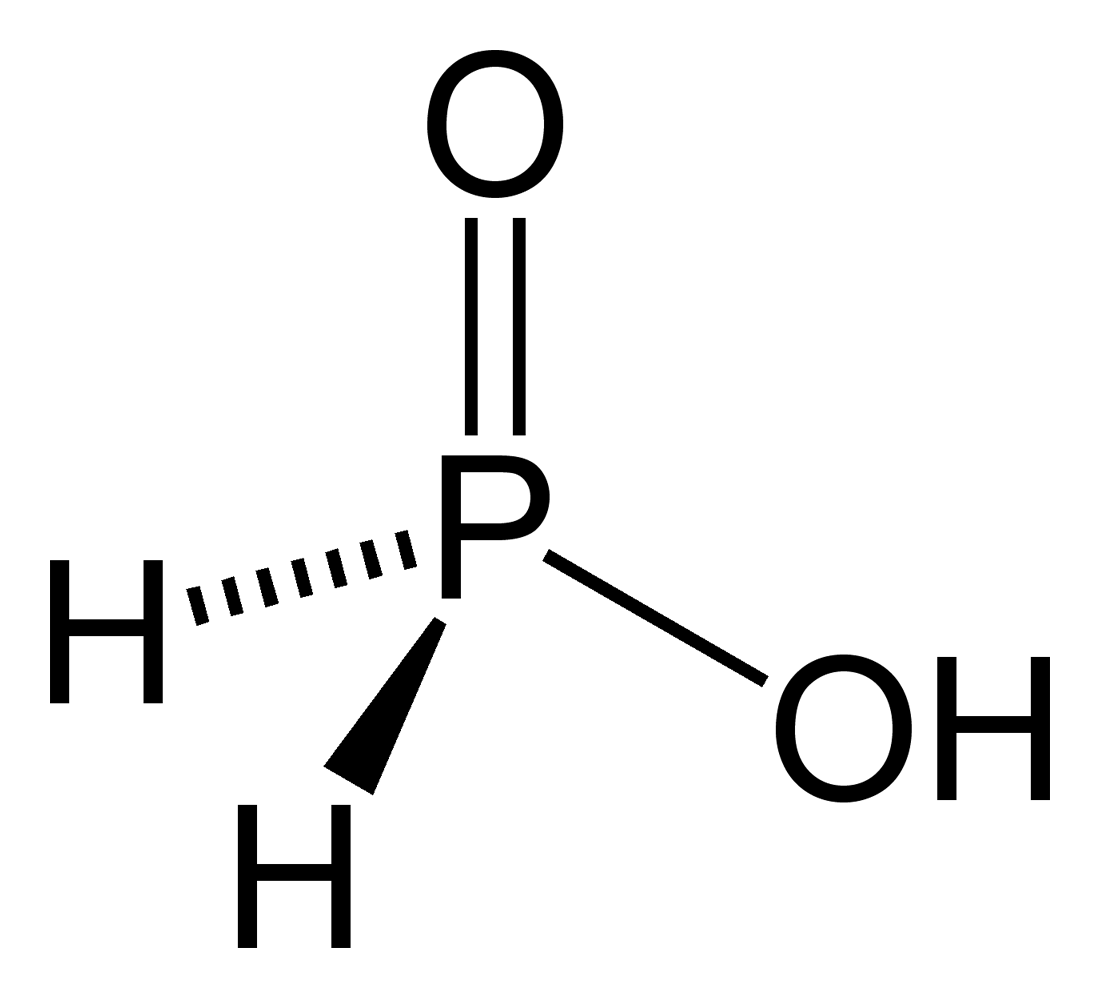
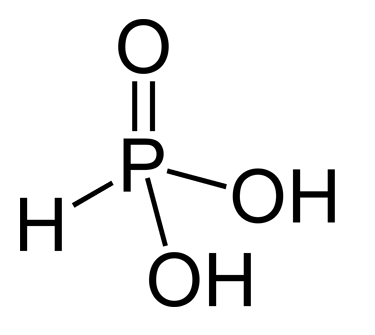
* Phosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid (or phosphonic acid (singular)) is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic (readily ionizes two protons), not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in th ...
(or phosphonic acid), (or ), a diprotic acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
(with only two acidic hydrogens). Its salts and esters are called phosphite
The general structure of a phosphite ester showing the lone pairs on the P
In organic chemistry, a phosphite ester or organophosphite usually refers to an organophosphorous compound with the formula P(OR)3. They can be considered as esters of a ...
s or phosphonates.
Oxidation state +4
Hypophosphoric acid
Hypophosphoric acid is a mineral acid with the formula H4P2O6, with phosphorus in a formal oxidation state of +4. In the solid state it is present as the dihydrate, H4P2O6·2H2O. In hypophosphoric acid the phosphorus atoms are identical and join ...
, (or –). All four hydrogens are acidic. Its salts and esters are hypophosphates.
Oxidation state +5
The most important members of this group are thephosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, w ...
s, where each phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms, one of them through a double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betw ...
, arranged as the corners of a tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
. Two or more of these tetrahedra may be connected by shared single-bonded oxygens, forming linear or branched chains, cycles, or more complex structures. The single-bonded oxygen atoms that are not shared are completed with acidic hydrogen atoms. Their generic formula is H''n''−''x''+2P''n''O3''n''−''x''+1, where ''n'' is the number of phosphorus atoms and ''x'' is the number of fundamental cycles in the molecule's structure.
These acids, and their esters and salts ("phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
s") include some of the best-known and most important compounds of phosphorus.
 The simplest member of this class is:
*
The simplest member of this class is:
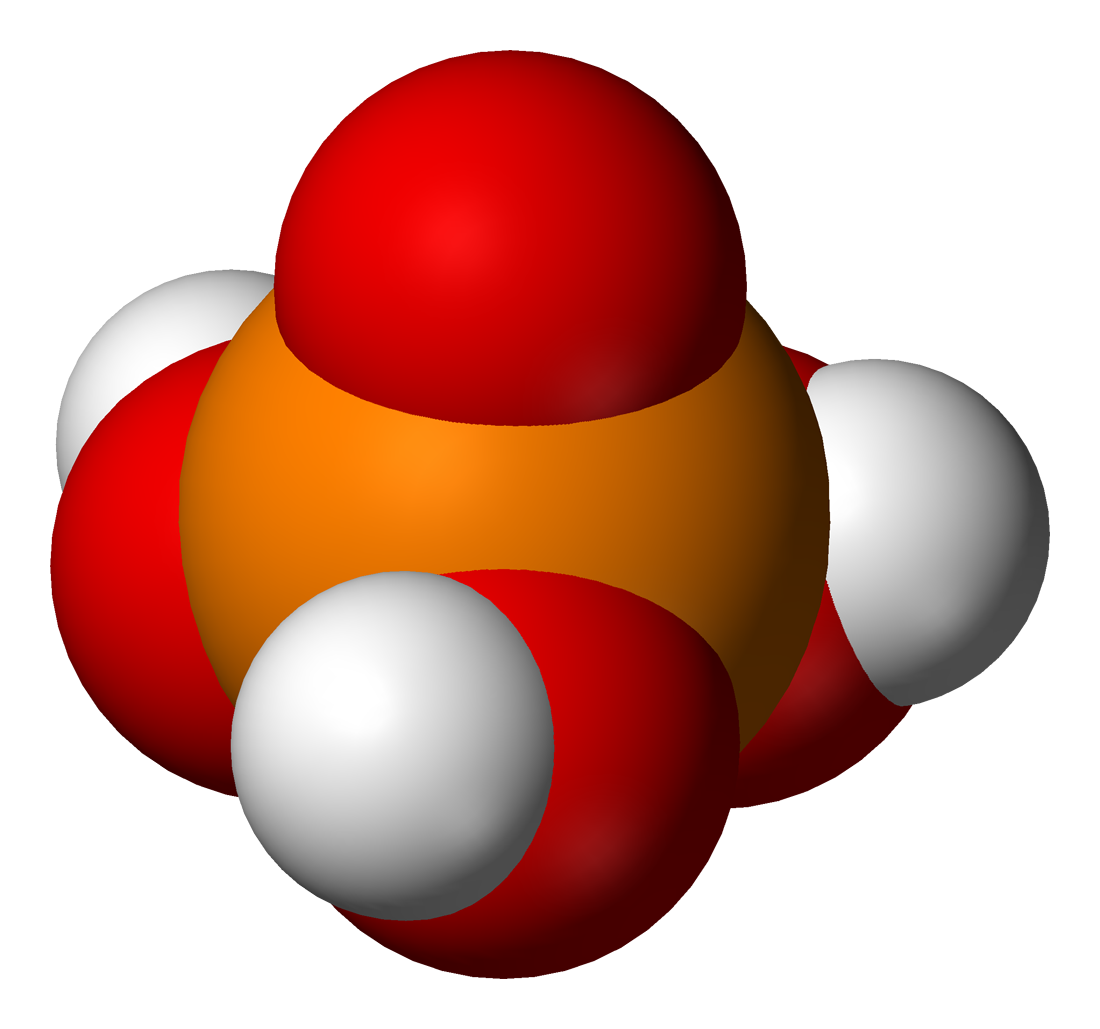
* Phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, w ...
proper (also called orthophosphoric acid or monophosphoric acid), (or ), a triprotic acid. It forms orthophosphate salt and esters, commonly called phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
s.
The smallest compounds of this class with two or more phosphorus atoms are called "oligophosphoric acids", and the larger ones, with linear –P–O– backbones, are "polyphosphoric acids"; with no definite separation between the two. Some of the most important members are:
* Pyrophosphoric acid
Pyrophosphoric acid, also known as diphosphoric acid, is the inorganic compound with the formula H4P2O7 or, more descriptively, HO)2P(O)sub>2O. Colorless and odorless, it is soluble in water, diethyl ether, and ethyl alcohol. The anhydrous acid cr ...
, (or –O–), with four acid hydrogens. Forms pyrophosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among other ...
s.
* Triphosphoric acid
Triphosphoric acid (also tripolyphosphoric acid), with formula H5P3O10, is a condensed form of phosphoric acid. In the family of phosphoric acids, it is the next polyphosphoric acid after pyrophosphoric acid, H4P2O7, also called diphosphoric aci ...
(or tripolyphosphoric acid), (or –O––O–), with five acidic hydrogens. Forms triphosphate
Polyphosphates are salts or esters of polymeric oxyanions formed from tetrahedral PO4 (phosphate) structural units linked together by sharing oxygen atoms. Polyphosphates can adopt linear or a cyclic ring structures. In biology, the polyphosphate e ...
s or tripolyphosphates.
* Tetraphosphoric acid, (or (–O–)2–O–), with six acidic hydrogens. Forms tetraphosphates.
The backbone may be branched, as in:
* Triphosphono phosphoric acid, or P(O)(–)3, a branched isomer of tetrapolyphosphoric acid.
The tetrahedra may be connected to form closed –P–O– chains, as in:
* Trimetaphosphoric acid (or cyclotriphosphoric acid), (or , (–P(O)(OH)–O–)3), a cyclic molecule with three acidic hydrogens. Forms the trimetaphosphate salts and esters.
Metaphosphoric acid
A phosphoric acid, in the general sense, is a phosphorus oxoacid in which each phosphorus (P) atom is in the oxidation state +5, and is bonded to four oxygen (O) atoms, one of them through a double bond, arranged as the corners of a tetrahedron. ...
is a general term for phosphoric acids with a single cycle, (–P(O)(OH)–O–)''n'', whose elemental formula is .
Pyrophosphoric acid
Pyrophosphoric acid, also known as diphosphoric acid, is the inorganic compound with the formula H4P2O7 or, more descriptively, HO)2P(O)sub>2O. Colorless and odorless, it is soluble in water, diethyl ether, and ethyl alcohol. The anhydrous acid cr ...
File:Tripolyphosphoric-acid-3D-vdW.png, Tripolyphosphoric acid
File:Tetrapolyphosphoric-acid-3D-vdW.png, Tetrapolyphosphoric acid
H6P4O13 File:Trimetaphosphoric-acid-3D-vdW.png, Trimetaphosphoric acid
Peroxomonophosphoric acid
Peroxymonophosphoric acid () is an oxyacid of phosphorus. It is a colorless viscous oil. Its salts are called peroxymonophosphates. Another peroxyphosphoric acid is peroxydiphosphoric acid, .
Preparation
Peroxyphosphoric acids were first synt ...
, H3PO5 (or OP(OH)2(OOH)), which can be seen as monophosphoric acid with a peroxide
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of compounds with the structure , where R = any element. The group in a peroxide is called the peroxide group or peroxo group. The nomenclature is somewhat variable.
The most common peroxide is hydrogen p ...
group replacing the oxygen atom in one of the hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
groups
Mixed oxidation states
Some phosphorus oxoacids have two or more P atoms in different oxidation states. One example is * Isohypophosphoric acid, (or H(OH)(O)P−O−P(O)(OH)2), a tetraprotic acid and isomer of hypophosphoric acid, containing P in oxidation state +3 and +5
See also
*Phosphoramidate
Phosphoramidates (sometimes also called amidophosphates) are a class of phosphorus compounds structurally related to phosphates (or organophosphates) via the substitution of an OR for a NR2. They are derivatives of phosphoramidic acids O=P(OH)(NR2 ...
References
Further reading
*External links
''Determination of Polyphosphates Using Ion Chromatography with Suppressed Conductivity Detection, Application Note 71'' by Dionex
* * {{Phosphorus compounds * Dietary minerals Inorganic compounds Phosphates Phosphorus(V) compounds Pyrophosphates Reagents for organic chemistry