|
Trimetaphosphate
A phosphoric acid, in the general sense, is a phosphorus acid, phosphorus oxoacid in which each phosphorus (P) atom is in the oxidation state +5, and is chemical bond, bonded to four oxygen (O) atoms, one of them through a double bond, arranged as the corners of a tetrahedron. Two or more of these tetrahedra may be connected by shared single-bonded oxygens, forming linear or branched chains, cycles, or more complex structures. The single-bonded oxygen atoms that are not shared are completed with acid hydrogen, acidic hydrogen atoms. The general formula of a phosphoric acid is , where ''n'' is the number of phosphorus atoms and ''x'' is the number of cycle basis, fundamental cycles in the molecule's structure, between 0 and (''n''+2)/2. Removal of protons () from ''k'' hydroxyl groups –OH leaves anions generically called phosphates (if ''k'' = ''n''−2''x''+2) or hydrogen phosphates (if ''k'' is between 1 and ''n''−2''x''+1), with general formula [H''n''−2''x''+2−''k''P' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
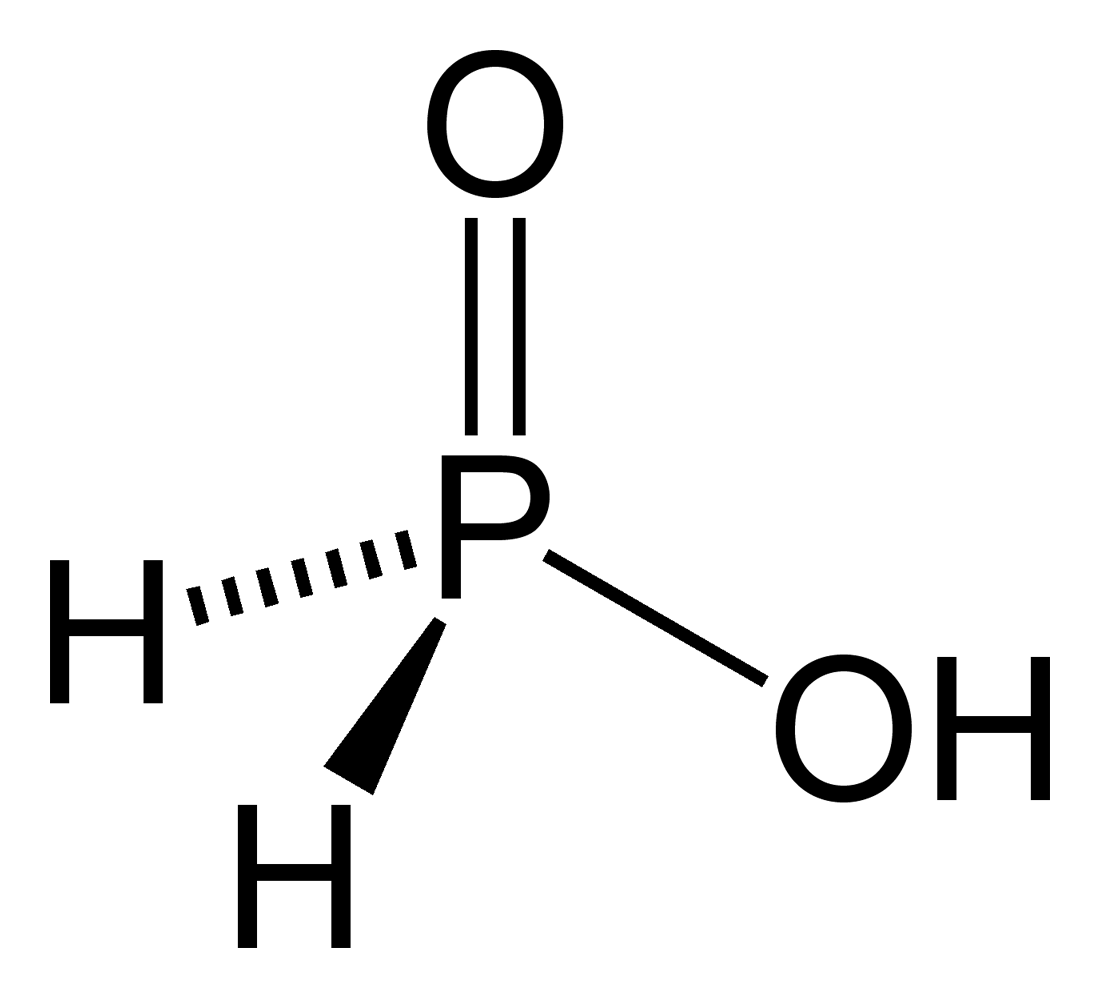
Phosphorus Acid
Phosphorus oxoacid (or phosphorus acid) is a generic name for any acid whose molecule consists of atoms of phosphorus, oxygen, and hydrogen. There is a potentially infinite number of such compounds. Some of them are unstable and have not been isolated, but the derived anions and organic groups are present in stable salts and esters. The most important ones—in biology, geology, industry, and chemical research—are the phosphoric acids, whose esters and salts are the phosphates. In general, any hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom is acidic, meaning that the –OH group can lose a proton leaving a negatively charged – group and thus turning the acid into a phosphorus oxoanion. Each additional proton lost has an associated acid dissociation constant K''a''1, K''a''2 K''a''3, ..., often expressed by its cologarithm (pK''a''1, pK''a''2, pK''a''3, ...). Hydrogen atoms bonded directly to phosphorus are generally not acidic. Classification The phosphorus oxoacids can be classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |