Pergamum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful
 Pergamon lies on the north edge of the Caicus plain in the historic region of
Pergamon lies on the north edge of the Caicus plain in the historic region of
MYSIA, Pergamon. Mid 5th century BCE.jpg, Possible coinage of the Greek ruler
EmenesICoin.JPG, Image of Philetaerus on a coin of Eumenes I
Pergamon188BCE.jpg, The ''
 Nevertheless, under the brothers Eumenes II and Attalus II, Pergamon reached its apex and was rebuilt on a monumental scale. It had retained the same dimensions for a long interval after its founding by Philetaerus, covering c. . After 188 BC a massive new city wall was constructed, long and enclosing an area of approximately . The Attalids' goal was to create a second
Nevertheless, under the brothers Eumenes II and Attalus II, Pergamon reached its apex and was rebuilt on a monumental scale. It had retained the same dimensions for a long interval after its founding by Philetaerus, covering c. . After 188 BC a massive new city wall was constructed, long and enclosing an area of approximately . The Attalids' goal was to create a second
 In 88 BC,
In 88 BC, 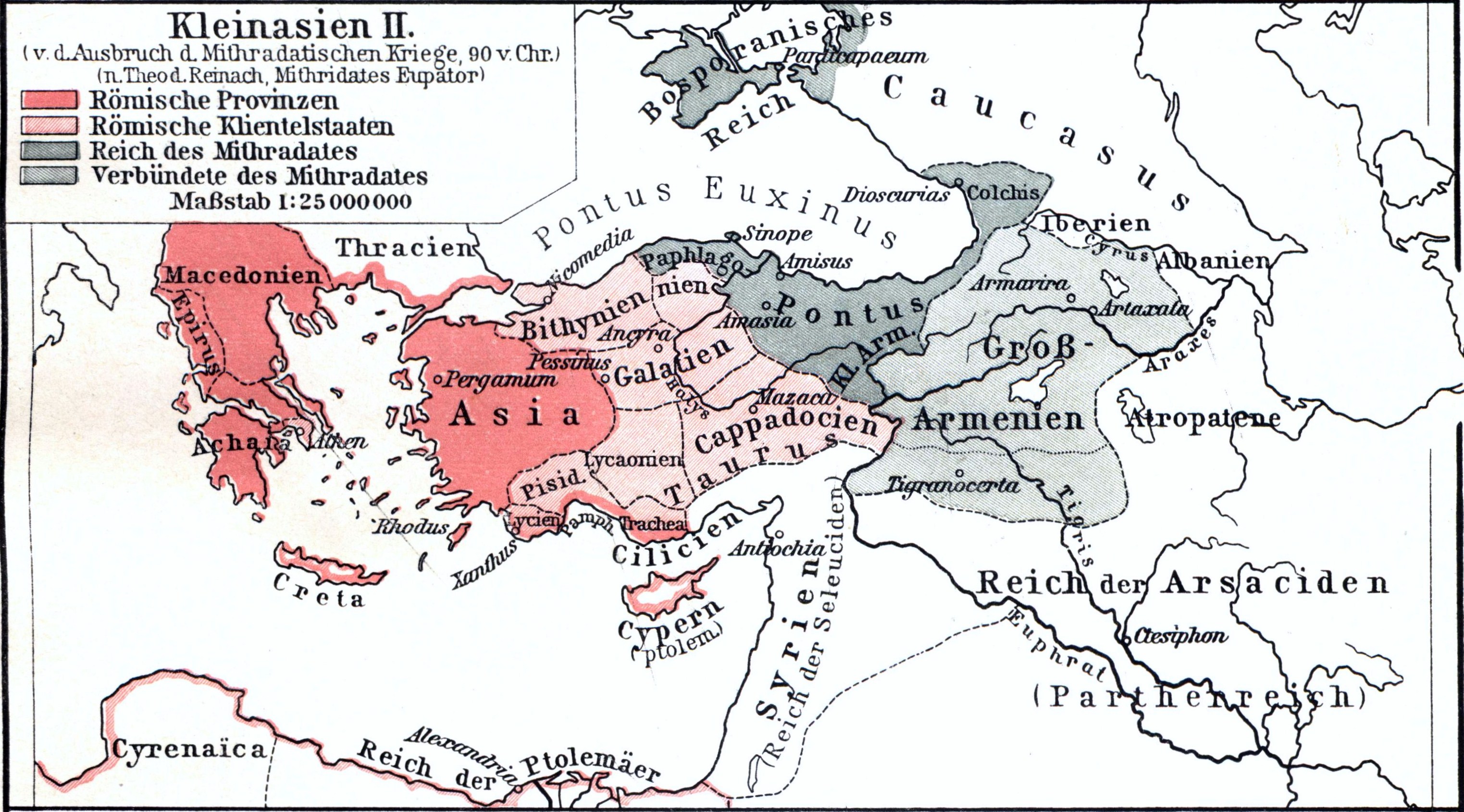 Yet it was only under
Yet it was only under  In the middle of the 2nd century Pergamon was one of the largest cities in the province, and had around 200,000 inhabitants.
In the middle of the 2nd century Pergamon was one of the largest cities in the province, and had around 200,000 inhabitants.
 Pergamon, which traced its founding back to
Pergamon, which traced its founding back to
 The first mention of Pergamon in written records after ancient times comes from the 13th century. Beginning with
The first mention of Pergamon in written records after ancient times comes from the 13th century. Beginning with  As a result of these efforts, Carl Humann, who had been carrying out low-level excavations at Pergamon for the previous few years and had discovered for example the architrave inscription of the Temple of Demeter in 1875, was entrusted with carry out work in the area of the altar of Zeus in 1878, where he continued to work until 1886. With the approval of the
As a result of these efforts, Carl Humann, who had been carrying out low-level excavations at Pergamon for the previous few years and had discovered for example the architrave inscription of the Temple of Demeter in 1875, was entrusted with carry out work in the area of the altar of Zeus in 1878, where he continued to work until 1886. With the approval of the
 The well-preserved dates from the Hellenistic period and had space for around 10,000 people, in 78 rows of seats. At a height of 36 metres, it is the steepest of all ancient theatres. The seating area (''koilon'') is divided horizontally by two walkways, called ''diazomata'', and vertically by stairways into seven sections in the lowest part of the theatre and six in the middle and upper sections. Below the theatre is a and up to terrace, which rested on a high retaining wall and was framed on the long side by a
The well-preserved dates from the Hellenistic period and had space for around 10,000 people, in 78 rows of seats. At a height of 36 metres, it is the steepest of all ancient theatres. The seating area (''koilon'') is divided horizontally by two walkways, called ''diazomata'', and vertically by stairways into seven sections in the lowest part of the theatre and six in the middle and upper sections. Below the theatre is a and up to terrace, which rested on a high retaining wall and was framed on the long side by a
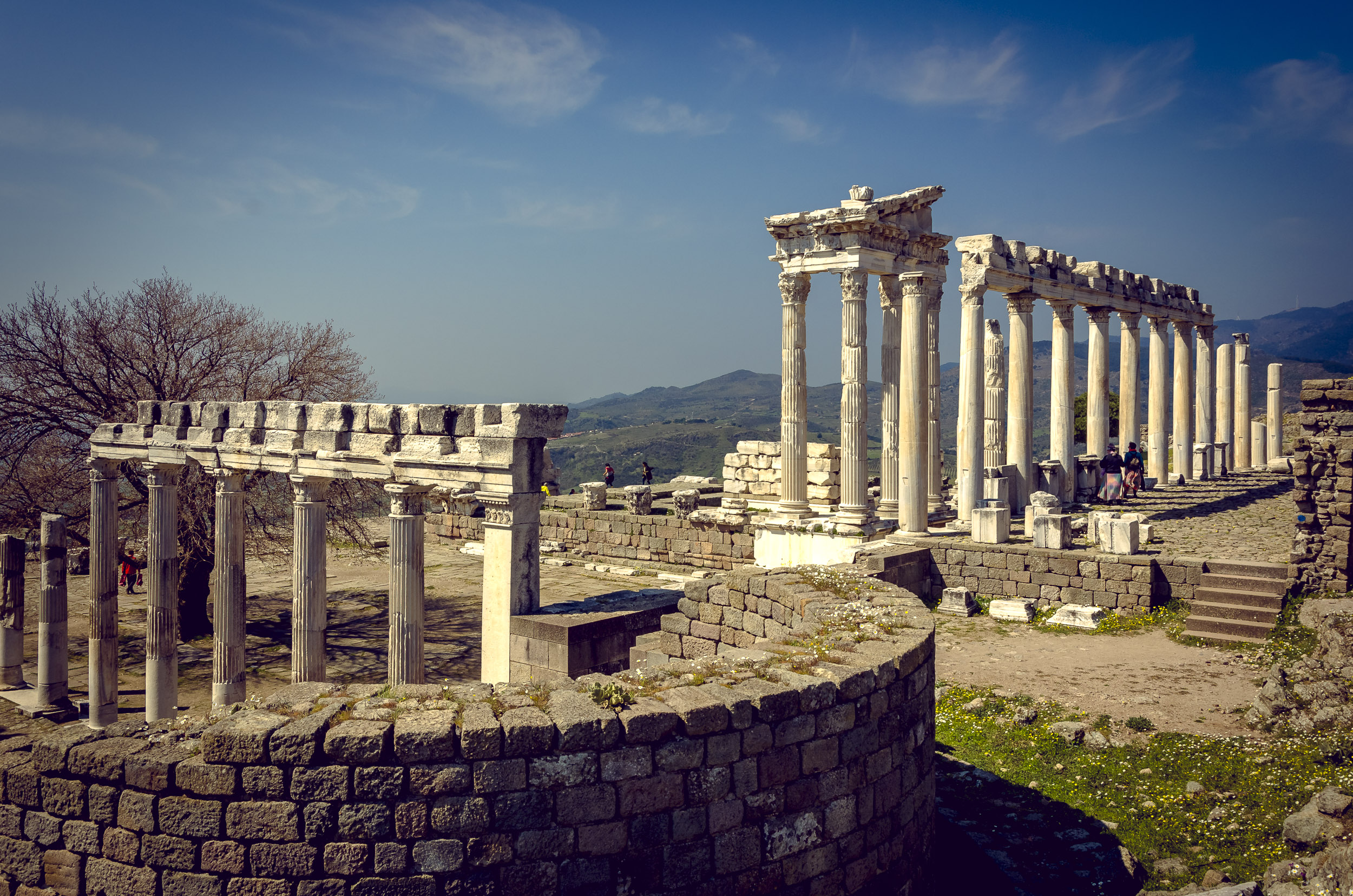 On the highest point of the citadel is the Temple for
On the highest point of the citadel is the Temple for
 Pergamon's oldest temple is a sanctuary of Athena from the 4th century BC. It was a north-facing
Pergamon's oldest temple is a sanctuary of Athena from the 4th century BC. It was a north-facing
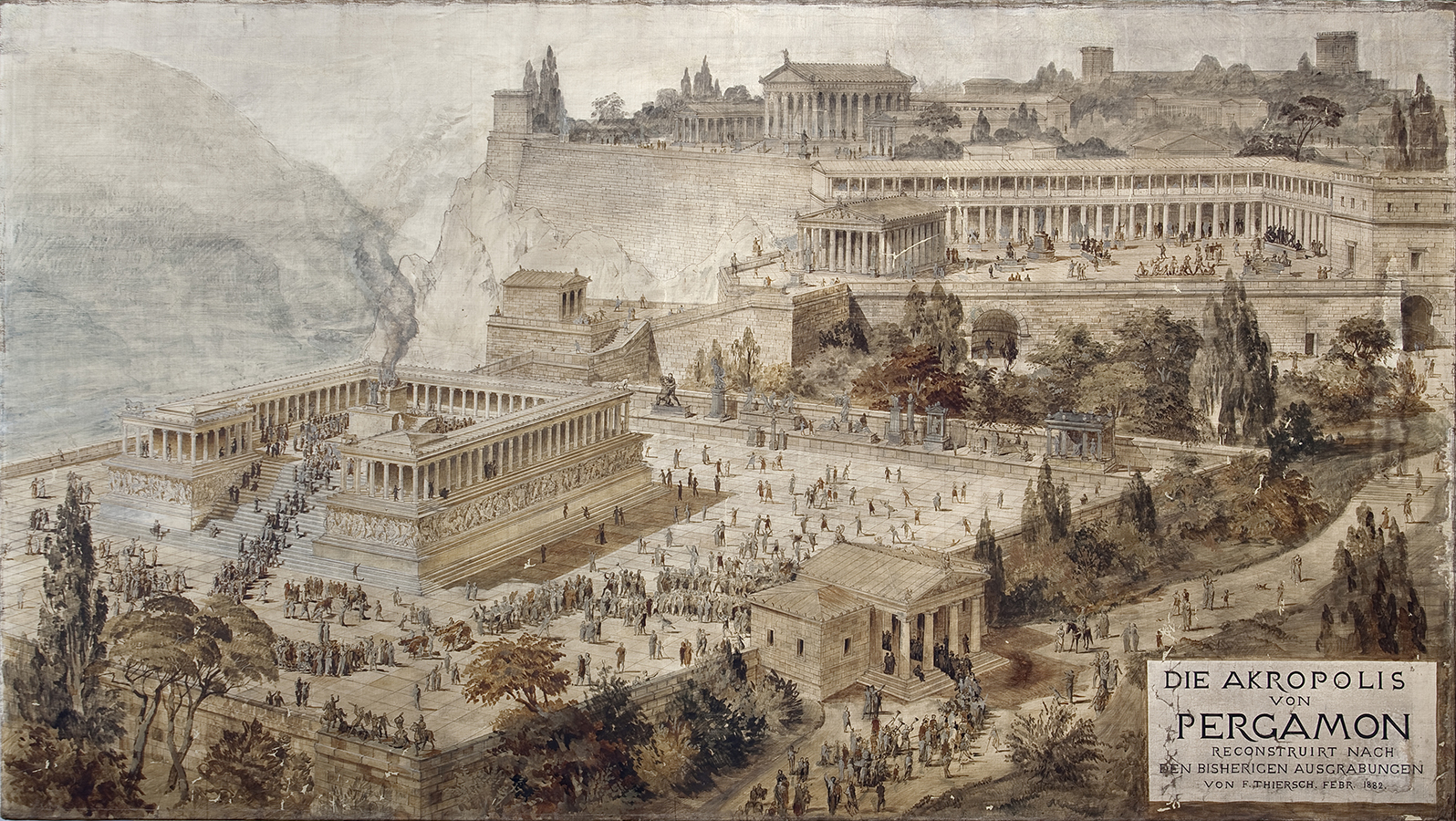 Other notable structures still in existence on the upper part of the Acropolis include:
*The Royal palaces
*The Heroön – a shrine where the kings of Pergamon, particularly Attalus I and Eumenes II, were worshipped.
*The Upper Agora
*The Roman baths complex
*Diodorus Pasporos heroon
*Arsenals
The site is today easily accessible by the Bergama Acropolis Gondola from the base station in northeastern Bergama.
Other notable structures still in existence on the upper part of the Acropolis include:
*The Royal palaces
*The Heroön – a shrine where the kings of Pergamon, particularly Attalus I and Eumenes II, were worshipped.
*The Upper Agora
*The Roman baths complex
*Diodorus Pasporos heroon
*Arsenals
The site is today easily accessible by the Bergama Acropolis Gondola from the base station in northeastern Bergama.
 A large gymnasium area was built in the 2nd century BC on the south side of the Acropolis. It consisted of three terraces, with the main entrance at the southeast corner of the lowest terrace. The lowest and southernmost terrace is small and almost free of buildings. It is known as the Lower Gymnasium and has been identified as the boys' gymnasium. The middle terrace was around 250 metres long and 70 metres wide at the centre. On its north side there was a two-story hall. In the east part of the terrace there was a small
A large gymnasium area was built in the 2nd century BC on the south side of the Acropolis. It consisted of three terraces, with the main entrance at the southeast corner of the lowest terrace. The lowest and southernmost terrace is small and almost free of buildings. It is known as the Lower Gymnasium and has been identified as the boys' gymnasium. The middle terrace was around 250 metres long and 70 metres wide at the centre. On its north side there was a two-story hall. In the east part of the terrace there was a small
 The sanctuary of Hera Basileia ('the Queen') lay north of the upper terrace of the gymnasium. Its structure sits on two parallel terraces, the south one about 107.4 metres above sea level and the north one about 109.8 metres above sea level. The Temple of Hera sat in the middle of the upper terrace, facing to the south, with a
The sanctuary of Hera Basileia ('the Queen') lay north of the upper terrace of the gymnasium. Its structure sits on two parallel terraces, the south one about 107.4 metres above sea level and the north one about 109.8 metres above sea level. The Temple of Hera sat in the middle of the upper terrace, facing to the south, with a
 The Sanctuary of Demeter occupied an area of 50 x 110 metres on the middle level of the south slope of the citadel. The sanctuary was old; its activity can be traced back to the fourth century BC.
The sanctuary was entered through a Propylon from the east, which led to a courtyard surrounded by stoas on three sides. In the centre of the western half of this courtyard, stood the Ionic temple of
The Sanctuary of Demeter occupied an area of 50 x 110 metres on the middle level of the south slope of the citadel. The sanctuary was old; its activity can be traced back to the fourth century BC.
The sanctuary was entered through a Propylon from the east, which led to a courtyard surrounded by stoas on three sides. In the centre of the western half of this courtyard, stood the Ionic temple of
 south of the Acropolis at (39° 7′ 9″ N, 27° 9′ 56″ E), down in the valley, there was the Sanctuary of
south of the Acropolis at (39° 7′ 9″ N, 27° 9′ 56″ E), down in the valley, there was the Sanctuary of
 Pergamon's other notable structure is the great temple of the Egyptian gods
Pergamon's other notable structure is the great temple of the Egyptian gods
message
sent to the Pergamon Church in the
Digitisation
* Band I 2: Alexander Conze: ''Stadt und Landschaft'' ity and Landscape(1913
Digitisation
* Band I 3: Alexander Conze (ed.): ''Stadt und Landschaft'' ity and Landscape3: Friedrich Graeber: ''Die Wasserleitungen'' he Aqueducts(1913
DigitisationDigitisation of the tables for I, 1–3
* Volume I 4: Günther Garbrecht: ''Die Wasserversorgung von Pergamon''
Digitisation Digitisation of the tables
* Volume III 1: Jakob Schrammen: ''Der grosse Altar – der obere Markt''
DigitisationDigitisation of the tables
* Volume III 2:
DigitisationDigitisation of the tables
* Volume IV: Richard Bohn: ''Die Theater-Terrasse'' he Theatre Terrace(1896
DigitisationDigitisation of the tables
* Volume V 1: Georg Kawerau –
DigitisationDigitisation of the tables
* Volume V 2: Hermann Stiller: ''Das Traianeum'' he Trajaneum Berlin 189
Digitisation
http://digi.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/diglit/pergamon1895b Digitisation of the tables] * Volume VI: Paul Schazmann: ''Das Gymnasion. Der Tempelbezirk der Hera Basileia''
DigitisationDigitisation of the tables
* Volume VII 1:
Digitisation
* Volume VII 2: Franz Winter: ''Die Skulpturen mit Ausnahme der Altarreliefs'' he Sculpture, aside from the Altar Reliefs(1908
DigitisationDigitisation of the tables
* Volume VIII 1: Max Fränkel (ed.): ''Die Inschriften von Pergamon''
Digitisation
* Volume VIII 2: Max Fränkel (ed.): ''Die Inschriften von Pergamon ''
Digitisation
* Volume VIII 3: Christian Habicht,
Rosa Valderrama, "Pergamum"
brief history
Photographic tour of old and new Pergamon, including the museum
* ttp://www.pergamon.secondpage.de/index_en.html 3D-visualization and photos of Pergamon* {{Authority control Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Archaeological sites in the Aegean Region Buildings and structures in İzmir Province Former populated places in Turkey History of İzmir Province History of Turkey New Testament cities Tourist attractions in İzmir Province Asia (Roman province) Populated places in ancient Aeolis Populated places in ancient Mysia Bergama District Former kingdoms
ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
city in Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It ...
on a promontory
A promontory is a raised mass of land that projects into a lowland or a body of water (in which case it is a peninsula). Most promontories either are formed from a hard ridge of rock that has resisted the erosive forces that have removed the so ...
on the north side of the river Caicus (modern-day Bakırçay
Bakırçay ( la, Caicus, ) is a river in Turkey. It rises in the Gölcük Dağları mountains and debouches into the Gulf of Çandarlı.
In antiquity, the Bakırçay was or formed part of the ''Kaikos'' or ''Caicus'' River which flowed near the ...
) and northwest of the modern city of Bergama
Bergama is a populous district, as well as the center city of the same district, in İzmir Province in western Turkey. By excluding İzmir's metropolitan area, it is one of the prominent districts of the province in terms of population and is l ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
.
During the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
, it became the capital of the Kingdom of Pergamon
The Kingdom of Pergamon or Attalid kingdom was a Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (; grc-x-koine, Δυναστ ...
in 281–133 BC under the Attalid dynasty
The Kingdom of Pergamon or Attalid kingdom was a Ancient Greece, Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Anatolia, Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (; g ...
, who transformed it into one of the major cultural centres of the Greek world. Many remains of its monuments can still be seen and especially the masterpiece of the Pergamon Altar
The Pergamon Altar () was a monumental construction built during the reign of the Ancient Greek King Eumenes II in the first half of the 2nd century BC on one of the terraces of the acropolis of Pergamon in Anatolia, Asia Minor.
The structure wa ...
. Pergamon was the northernmost of the seven churches of Asia
The Seven Churches of Revelation, also known as the Seven Churches of the Apocalypse and the Seven Churches of Asia, are seven major Churches of Early Christianity, as mentioned in the New Testament Book of Revelation. All of them are located in ...
cited in the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book of R ...
.
The city is centered on a mesa
A mesa is an isolated, flat-topped elevation, ridge or hill, which is bounded from all sides by steep escarpments and stands distinctly above a surrounding plain. Mesas characteristically consist of flat-lying soft sedimentary rocks capped by ...
of andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predomi ...
, which formed its acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, ...
. This mesa falls away sharply on the north, west, and east sides, but three natural terraces on the south side provide a route up to the top. To the west of the acropolis, the Selinus River (modern Bergamaçay) flows through the city, while the Ketios river (modern Kestelçay) passes by to the east.
Pergamon was added to the UNESCO World Heritage
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
List in 2014.
Location
 Pergamon lies on the north edge of the Caicus plain in the historic region of
Pergamon lies on the north edge of the Caicus plain in the historic region of Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
in the northwest of Turkey. The Caicus river breaks through the surrounding mountains and hills at this point and flows in a wide arc to the southwest. At the foot of the mountain range to the north, between the rivers Selinus and Cetius, there is the massif of Pergamon which rises 335 metres above sea level. The site is only 26 km from the sea, but the Caicus plain is not open to the sea, since the way is blocked by the Karadağ massif. As a result, the area has a strongly inland character. In Hellenistic times, the town of Elaia at the mouth of the Caicus served as the port of Pergamon. The climate is Mediterranean with a dry period from May to August, as is common along the west coast of Asia Minor.
The Caicus valley is mostly composed of volcanic rock, particularly andesite and the Pergamon massif is also an intrusive stock
In finance, stock (also capital stock) consists of all the shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided.Longman Business English Dictionary: "stock - ''especially AmE'' one of the shares into which ownership of a company ...
of andesite. The massif is about one kilometre wide and around 5.5 km long from north to south. It consists of a broad, elongated base and a relatively small peak - the upper city. The side facing the Cetius river is a sharp cliff, while the side facing the Selinus is a little rough. On the north side, the rock forms a 70 m wide spur of rock. To the southeast of this spur, which is known as the 'Garden of the Queen', the massif reaches its greatest height and breaks off suddenly immediately to the east. The upper city extends for another 250 m to the south, but it remains very narrow, with a width of only 150 m. At its south end the massif falls gradually to the east and south, widening to around 350 m and then descends to the plain towards the southwest.
History
Pre-Hellenistic period
Settlement of Pergamon can be detected as far back as the Archaic period, thanks to modest archaeological finds, especially fragments of pottery imported from the west, particularly eastern Greece andCorinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
, which date to the late 8th century BC. Earlier habitation in the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
cannot be demonstrated, although Bronze Age stone tools are found in the surrounding area.
The earliest mention of Pergamon in literary sources comes from Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, wikt:Ξενοφῶν, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Anci ...
's ''Anabasis
Anabasis (from Greek ''ana'' = "upward", ''bainein'' = "to step or march") is an expedition from a coastline into the interior of a country. Anabase and Anabasis may also refer to:
History
* ''Anabasis Alexandri'' (''Anabasis of Alexander''), a ...
'', since the march of the Ten Thousand
The Ten Thousand ( grc, οἱ Μύριοι, ''oi Myrioi'') were a force of mercenary units, mainly Greeks, employed by Cyrus the Younger to attempt to wrest the throne of the Persian Empire from his brother, Artaxerxes II. Their march to the Bat ...
under Xenophon's command ended at Pergamon in 400/399 BC. Xenophon, who calls the city Pergamos, handed over the rest of his Greek troops (some 5,000 men according to Diodorus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
) to Thibron
''Thibron'' is a genus of insect in the family Tetrigidae (the groundhoppers), tribe Tetrigini, from the central part of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At abou ...
, who was planning an expedition against the Persian satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with consid ...
s Tissaphernes
Tissaphernes ( peo, *Ciçafarnāʰ; grc-gre, Τισσαφέρνης; xlc, 𐊋𐊆𐊈𐊈𐊀𐊓𐊕𐊑𐊏𐊀 , ; 445395 BC) was a Persian soldier and statesman, Satrap of Lydia and Ionia. His life is mostly known from the works of Thuc ...
and Pharnabazus, at this location in March 399 BC. At this time Pergamon was in the possession of the family of Gongylos
Gongylos ( grc, Γογγύλος), from Eretria in Euboea, was a 5th-century Greek statesman who served as an intermediary between the Spartans and Xerxes I of the Achaemenid Empire, and was a supporter of the latter.
After the defeat of the ...
from Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th centur ...
, a Greek favourable to the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
who had taken refuge in Asia Minor and obtained the territory of Pergamon from Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of ...
, and Xenophon was hosted by his widow Hellas.
In 362 BC, Orontes, satrap of Mysia, used Pergamon as his base for an unsuccessful revolt against the Persian Empire. Only with Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
were Pergamon and the surrounding area removed from Persian control. There are few traces of the pre-Hellenistic city, since in the following period the terrain was profoundly changed and the construction of broad terraces involved the removal of almost all earlier structures. Parts of the temple of Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarded as the patron and protectress of ...
, as well as the walls and foundations of the altar in the sanctuary of Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter (; Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although s ...
, go back to the fourth century.
Gongylos
Gongylos ( grc, Γογγύλος), from Eretria in Euboea, was a 5th-century Greek statesman who served as an intermediary between the Spartans and Xerxes I of the Achaemenid Empire, and was a supporter of the latter.
After the defeat of the ...
, wearing the Persian cap on the reverse, as ruler of Pergamon for the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
. Pergamon, Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
, circa 450 BC. The name of the city ΠΕΡΓ ("PERG"), appears for the first on this coinage, and is the first evidence for the name of the city.
MYSIA, Adramyteion. Orontes, Satrap of Mysia. Circa 357-352 BC.jpg, Coin of Orontes, Achaemenid Satrap of Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
(including Pergamon), Adramyteion. Circa 357-352 BC
Hellenistic period
Lysimachus
Lysimachus (; Greek: Λυσίμαχος, ''Lysimachos''; c. 360 BC – 281 BC) was a Thessalian officer and successor of Alexander the Great, who in 306 BC, became King of Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedon.
Early life and career
Lysimachus was b ...
, King of Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
, took possession in 301 BC, and the town was enlarged by his lieutenant Philetaerus
Philetaerus (; grc, Φιλέταιρος, ''Philétairos'', c. 343 –263 BC) was the founder of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon in Anatolia.
Early life and career under Lysimachus
Philetaerus was born in Tieium (Greek: ''Tieion''), a small ...
. In 281 BC the kingdom of Thrace collapsed and Philetaerus became an independent ruler, founding the Attalid dynasty
The Kingdom of Pergamon or Attalid kingdom was a Ancient Greece, Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Anatolia, Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (; g ...
. His family ruled Pergamon from 281 until 133 BC: Philetaerus 281–263; Eumenes I
Eumenes I ( grc-gre, Εὐμένης) was dynast (ruler) of the city of Pergamon in Asia Minor from 263 BC until his death in 241 BC. He was the son of Eumenes, the brother of Philetaerus, the founder of the Attalid dynasty, and Satyra, daug ...
263–241; Attalus I
Attalus I ( grc, Ἄτταλος Α΄), surnamed ''Soter'' ( el, , "Savior"; 269–197 BC) ruled Pergamon, an Ionian Greek polis (what is now Bergama, Turkey), first as dynast, later as king, from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the fi ...
241–197; Eumenes II
Eumenes II Soter (; grc-gre, Εὐμένης Σωτήρ; ruled 197–159 BC) was a ruler of Pergamon, and a son of Attalus I Soter and queen Apollonis and a member of the Attalid dynasty of Pergamon.
Biography
The eldest son of king Attalus ...
197–159; Attalus II
Attalus II Philadelphus ( Greek: Ἄτταλος Β΄ ὁ Φιλάδελφος, ''Attalos II Philadelphos'', which means "Attalus the brother-loving"; 220–138 BC) was a Greek King of Pergamon and the founder of the city of Attalia (Antal ...
159–138; and Attalus III
Attalus III ( el, Ἄτταλος Γ΄) Philometor Euergetes ( – 133 BC) was the last Attalid king of Pergamon, ruling from 138 BC to 133 BC.
Biography
Attalus III was the son of king Eumenes II and his queen Stratonice of Pergamon, and h ...
138–133. Philetaerus controlled only Pergamon and its immediate environs, but the city acquired much new territory under Eumenes I. In particular, after the Battle of Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
in 261 BC against Antiochus I
Antiochus I Soter ( grc-gre, Ἀντίοχος Σωτήρ, ''Antíochos Sōtér''; "Antiochus the Saviour"; c. 324/32 June 261 BC) was a Greek king of the Seleucid Empire. Antiochus succeeded his father Seleucus I Nicator in 281 BC and reigned du ...
, Eumenes was able to appropriate the area down to the coast and some way inland. Despite this increase of his domain, Eumenes did not take a royal title. In 238 his successor Attalus I defeated the Galatians Galatians may refer to:
* Galatians (people)
* Epistle to the Galatians, a book of the New Testament
* English translation of the Greek ''Galatai'' or Latin ''Galatae'', ''Galli,'' or ''Gallograeci'' to refer to either the Galatians or the Gauls in ...
, to whom Pergamon had paid tribute under Eumenes I. Attalus thereafter declared himself leader of an entirely independent Pergamene kingdom.
The Attalids became some of the most loyal supporters of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
in the Hellenistic world. Attalus I allied with Rome against Philip V of Macedon
Philip V ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 238–179 BC) was king ( Basileus) of Macedonia from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by an unsuccessful struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon ag ...
, during the first
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
Macedonian Wars
The Macedonian Wars (214–148 BC) were a series of conflicts fought by the Roman Republic and its Greek allies in the eastern Mediterranean against several different major Greek kingdoms. They resulted in Roman control or influence over Greece ...
. In the Roman–Seleucid War
The Seleucid War (192–188 BC), also known as the War of Antiochos or the Syrian War, was a military conflict between two coalitions led by the Roman Republic and the Seleucid Empire. The fighting took place in modern day southern Greece, the A ...
, Pergamon joined the Romans' coalition against Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the res ...
, and was rewarded with almost all the former Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
domains in Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
at the Peace of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopylae ...
in 188 BC. The kingdom's territories thus reached their greatest extent. Eumenes II supported Rome again in the Third Macedonian War
The Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC, King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman ...
, but the Romans heard rumours of his conducting secret negotiations with their opponent Perseus of Macedon
Perseus ( grc-gre, Περσεύς; 212 – 166 BC) was the last king ('' Basileus'') of the Antigonid dynasty, who ruled the successor state in Macedon created upon the death of Alexander the Great. He was the last Antigonid to rule Macedon, af ...
. On this basis, Rome denied any reward to Pergamon and attempted to replace Eumenes with the future Attalus II, who refused to cooperate. These incidents cost Pergamon its privileged status with the Romans, who granted it no further territory.
Kingdom of Pergamon
The Kingdom of Pergamon or Attalid kingdom was a Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (; grc-x-koine, Δυναστ ...
'', shown at its greatest extent in 188 BC
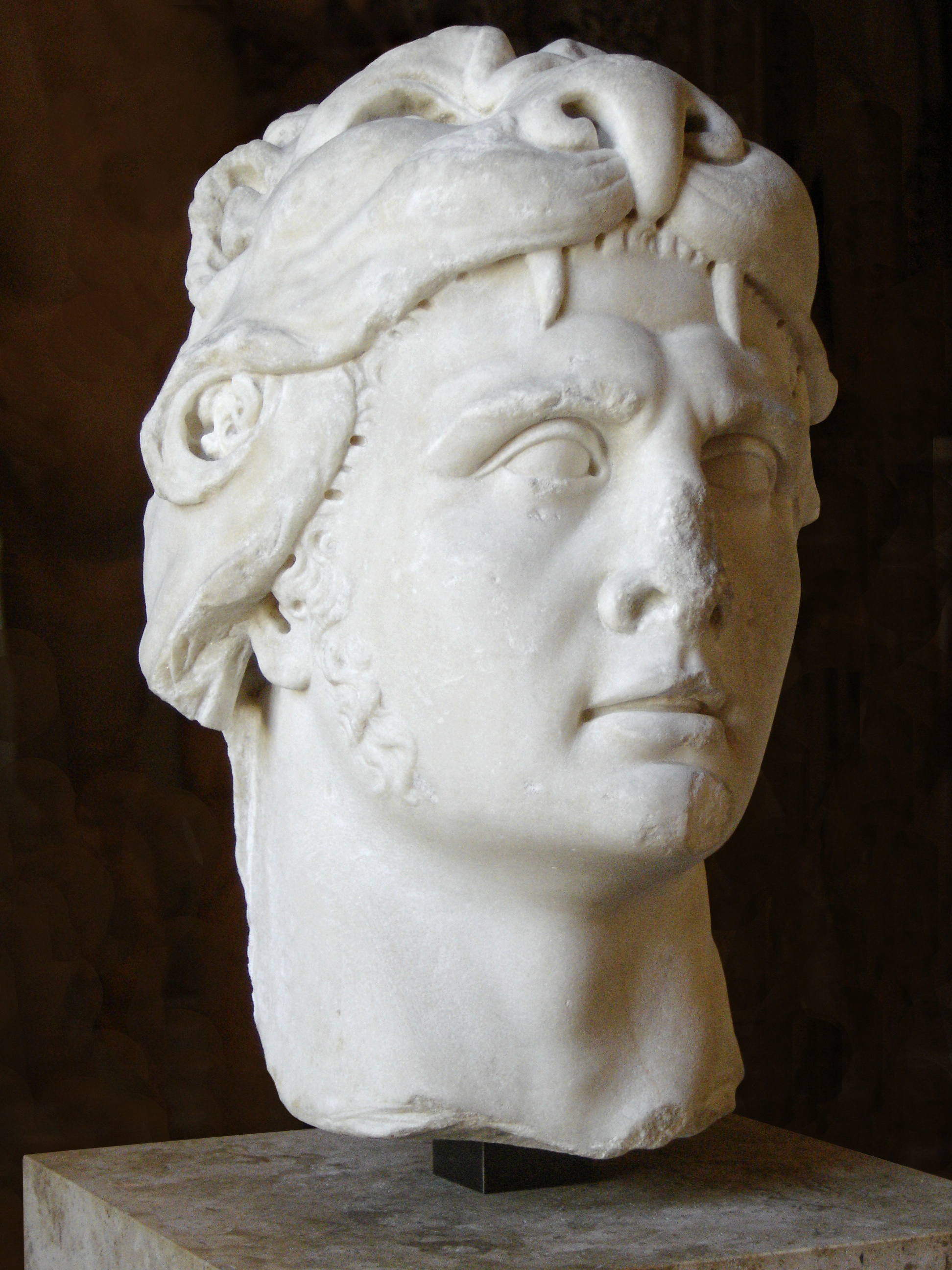
File:AtaloPergamo.jpg, Over-life-size portrait head, probably of Attalus I, from early in the reign of Eumenes II
 Nevertheless, under the brothers Eumenes II and Attalus II, Pergamon reached its apex and was rebuilt on a monumental scale. It had retained the same dimensions for a long interval after its founding by Philetaerus, covering c. . After 188 BC a massive new city wall was constructed, long and enclosing an area of approximately . The Attalids' goal was to create a second
Nevertheless, under the brothers Eumenes II and Attalus II, Pergamon reached its apex and was rebuilt on a monumental scale. It had retained the same dimensions for a long interval after its founding by Philetaerus, covering c. . After 188 BC a massive new city wall was constructed, long and enclosing an area of approximately . The Attalids' goal was to create a second Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, a cultural and artistic hub of the Greek world. They remodeled their Acropolis after the Acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, ...
in Athens, and the Library of Pergamon
The Library of Pergamum in Pergamum, Asia Minor or Anatolia (present day Turkey). It was one of the most important libraries in the ancient world.
The city of Pergamum
Founded sometime during 3rd century BC, during the Hellenistic Age, Perga ...
was renowned as second only to the Library of Alexandria
The Great Library of Alexandria in Alexandria, Egypt, was one of the largest and most significant libraries of the ancient world. The Library was part of a larger research institution called the Mouseion, which was dedicated to the Muses, th ...
. Pergamon was also a flourishing center for the production of parchment
Parchment is a writing material made from specially prepared untanned skins of animals—primarily sheep, calves, and goats. It has been used as a writing medium for over two millennia. Vellum is a finer quality parchment made from the skins of ...
, whose name is a corruption of ''pergamenos'', meaning "from Pergamon". Despite this etymology, parchment had been used in Asia Minor long before the rise of the city; the story that it was invented by the Pergamenes, to circumvent the Ptolemies' monopoly on papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a ...
production, is not true. Surviving epigraphic documents show how the Attalids supported the growth of towns by sending in skilled artisans and by remitting taxes. They allowed the Greek cities in their domains to maintain nominal independence, and sent gifts to Greek cultural sites like Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), in ancient times was a sacred precinct that served as the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient classical world. The oracle ...
, Delos, and Athens. The two brothers Eumenes II and Attalus II displayed the most distinctive trait of the Attalids: a pronounced sense of family without rivalry or intrigue - rare amongst the Hellenistic dynasties. Attalus II bore the epithet 'Philadelphos', 'he who loves his brother', and his relations with Eumenes II were compared to the harmony between the mythical brothers Cleobis and Biton.
When Attalus III died without an heir in 133 BC, he bequeathed the whole of Pergamon to Rome. This was challenged by Aristonicus, who claimed to be Attalus III's brother and led an armed uprising against the Romans with the help of Blossius
Gaius Blossius (; 2nd century BC) was, according to Plutarch, a philosopher and student of the Stoic philosopher Antipater of Tarsus, from the city of Cumae in Campania, Italy, who (along with the Greek rhetorician, Diophanes) instigated Roman ...
, a famous Stoic philosopher
Stoicism is a school of Hellenistic philosophy founded by Zeno of Citium in Athens in the early 3rd century Common Era, BCE. It is a philosophy of personal virtue ethics informed by its system of logic and its views on the natural world, asser ...
. For a period he enjoyed success, defeating and killing the Roman consul P. Licinius Crassus and his army, but he was defeated in 129 BC by the consul M. Perperna. The kingdom of Pergamon was divided between Rome, Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
, and Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
, with the bulk of its territory becoming the new Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
. The city itself was declared free and served briefly as capital of the province, before this distinction was transferred to Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in t ...
.
Roman period
 In 88 BC,
In 88 BC, Mithridates VI Eupator
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
made Pergamon his headquarters in his first war against Rome, in which he was defeated. The victorious Romans deprived Pergamon of all its benefits and of its status as a free city. Henceforth the city was required to pay tribute and accommodate and supply Roman troops, and the property of many of the inhabitants was confiscated. Imported Pergamene goods were among the luxuries enjoyed by Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingd ...
. The members of the Pergamene aristocracy, especially Diodorus Pasparus in the 70s BC, used their own possessions to maintain good relationships with Rome, by acting as donors for the development of the city. Numerous honorific inscriptions indicate Pasparus' work and his exceptional position in Pergamon at this time.
Pergamon still remained a famous city, and was the seat of a ''conventus
In Ancient Rome territorial organization, a ''conventus iuridicus'' was the capital city of a subdivision of some provinces (Dalmatia, Hispania, Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either consi ...
'' (regional assembly). Its neocorate A neocorate was a rank or dignity granted by the Roman Senate and the Emperor under the Empire to certain cities which had built temples to the Emperor or had established cults of members of the Imperial family. The city itself was referred to as ' ...
, granted by Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
, was the first manifestation of the imperial cult
An imperial cult is a form of state religion in which an emperor or a dynasty of emperors (or rulers of another title) are worshipped as demigods or deities. "Cult" here is used to mean "worship", not in the modern pejorative sense. The cult may ...
in the province of Asia. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
refers to the city as the most important in the province and the local aristocracy continued to reach the highest circles of power in the 1st century AD, like Aulus Julius Quadratus who was consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throug ...
in 94 and 105.
 Yet it was only under
Yet it was only under Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
and his successors that a comprehensive redesign and remodelling took place, with the construction of a Roman 'new city' at the base of the Acropolis. The city was the first in the province to receive a second neocorate, from Trajan in AD 113/4. Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
raised the city to the rank of metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural center for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications.
A big c ...
in 123 and thereby elevated it above its local rivals, Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in t ...
and Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to promi ...
. An ambitious building programme was carried out: massive temples, a stadium, a theatre
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The perform ...
, a huge forum and an amphitheatre
An amphitheatre (British English) or amphitheater (American English; both ) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ...
were constructed. In addition, at the city limits the shrine to Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of ...
(the god of healing) was expanded into a lavish spa. This sanctuary grew in fame and was considered one of the most famous healing centers of the Roman world.
 In the middle of the 2nd century Pergamon was one of the largest cities in the province, and had around 200,000 inhabitants.
In the middle of the 2nd century Pergamon was one of the largest cities in the province, and had around 200,000 inhabitants. Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of ...
, the most famous physician of antiquity aside from Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
, was born at Pergamon and received his early training at the Asclepeion. At the beginning of the 3rd century Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor S ...
granted the city a third neocorate, but a decline had already set in. The economic strength of Pergamon collapsed during the crisis of the Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis (AD 235–284), was a period in which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed. The crisis ended due to the military victories of Aurelian and with the ascensi ...
, as the city was badly damaged in an earthquake in 262 and was sacked by the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
shortly thereafter. In late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, it experienced a limited economic recovery.
Byzantine period
In AD 663/4, Pergamon was captured by raidingArabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
for the first time. As a result of the ongoing Arab threat, the area of settlement retracted to the acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, ...
, which the Emperor Constans II () fortified with a wall built of spolia
''Spolia'' (Latin: 'spoils') is repurposed building stone for new construction or decorative sculpture reused in new monuments. It is the result of an ancient and widespread practice whereby stone that has been quarried, cut and used in a built ...
.
During the middle Byzantine period, the city was part of the Thracesian Theme, and from the time of Leo VI the Wise
Leo VI, called the Wise ( gr, Λέων ὁ Σοφός, Léōn ho Sophós, 19 September 866 – 11 May 912), was Byzantine Emperor from 886 to 912. The second ruler of the Macedonian dynasty (although his parentage is unclear), he was very well r ...
() of the Theme of Samos. 7th-century sources attest an Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
community in Pergamon, probably formed of refugees from the Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
; this community produced the emperor Philippicus
Philippicus ( la, Filepicus; el, Φιλιππικός, Philippikós) was Byzantine emperor from 711 to 713. He took power in a coup against the unpopular emperor Justinian II, and was deposed in a similarly violent manner nineteen months later. ...
(). In 716, Pergamon was sacked again by the armies of Maslama ibn Abd al-Malik
Maslama ibn ʿAbd al-Malik ( ar, مسلمة بن عبد الملك, in Greek sources , ''Masalmas''; – 24 December 738) was an Umayyad prince and one of the most prominent Arab generals of the early decades of the 8th century, leading severa ...
. It was again rebuilt and refortified after the Arabs abandoned their Siege of Constantinople
The following is a list of sieges of Constantinople, a historic city located in an area which is today part of Istanbul, Turkey. The city was built on the land that links Europe to Asia through Bosporus and connects the Sea of Marmara and the ...
in 717–718.
Pergamon suffered from the Seljuk Seljuk or Saljuq (سلجوق) may refer to:
* Seljuk Empire (1051–1153), a medieval empire in the Middle East and central Asia
* Seljuk dynasty (c. 950–1307), the ruling dynasty of the Seljuk Empire and subsequent polities
* Seljuk (warlord) (di ...
invasion of western Anatolia after the Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and th ...
in 1071. Attacks in 1109 and 1113 largely destroyed the city, which was only rebuilt, by Emperor Manuel I Komnenos
Manuel I Komnenos ( el, Μανουήλ Κομνηνός, translit=Manouíl Komnenos, translit-std=ISO; 28 November 1118 – 24 September 1180), Romanization of Greek, Latinized Comnenus, also called Porphyrogennetos (; "born in the purple"), w ...
(), around 1170. It likely became the capital of the new theme of Neokastra Neokastra ( el, Νεόκαστρα, "new fortresses", formally θέμα Νεοκάστρων; in Latin sources ''Neocastri'' or ''Neochastron'') was a Byzantine province ( theme) of the 12th–13th centuries in north-western Asia Minor (modern Turke ...
, established by Manuel. Under Isaac II Angelos
Isaac II Angelos or Angelus ( grc-gre, Ἰσαάκιος Κομνηνός Ἄγγελος, ; September 1156 – January 1204) was Byzantine Emperor from 1185 to 1195, and again from 1203 to 1204.
His father Andronikos Doukas Angelos was a ...
(), the local see was promoted to a metropolitan bishopric
A metropolis religious jurisdiction, or a metropolitan archdiocese, is an episcopal see whose bishop is the metropolitan bishop or archbishop of an ecclesiastical province. Metropolises, historically, have been important cities in their provinces.
...
, having previously been a suffragan diocese
A suffragan diocese is one of the dioceses other than the metropolitan archdiocese that constitute an ecclesiastical province. It exists in some Christian denominations, in particular the Catholic Church, the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria ...
of the Metropolis of Ephesus
The Metropolis of Ephesus ( el, Μητρόπολις Εφέσου) was an ecclesiastical territory ( metropolis) of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople in western Asia Minor, modern Turkey. Christianity was introduced already in the cit ...
.
After the Sack of Constantinople
The sack of Constantinople occurred in April 1204 and marked the culmination of the Fourth Crusade. Crusader armies captured, looted, and destroyed parts of Constantinople, then the capital of the Byzantine Empire. After the capture of the ...
in 1204 during the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
, Pergamon became part of the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhouse ...
. When Emperor Theodore II Laskaris
Theodore II Doukas Laskaris or Ducas Lascaris ( gr, Θεόδωρος Δούκας Λάσκαρις, Theodōros Doukas Laskaris; 1221/1222 – 16 August 1258) was Emperor of Nicaea from 1254 to 1258. He was the only child of Emperor John II ...
() visited Pergamon in 1250, he was shown the house of Galen, but he saw that the theatre had been destroyed and, except for the walls which he paid some attention to, only the vaults over the Selinus seemed noteworthy to him. The monuments of the Attalids and the Romans were only plundered ruins by this time.
With the expansion of the Anatolian beyliks, Pergamon was absorbed into the beylik of Karasids
The Karasids or Karasid dynasty ( Ottoman قرا صي; Modern Turkish ''Karesioğulları'', ''Karesioğulları Beyliği''), also known as the Principality of Karasi and Beylik of Karasi (''Karasi Beyliği'' or ''Karesi Beyliği'' ), was an Anatoli ...
shortly after 1300, and then conquered by the Ottoman beylik
The rise of the Ottoman Empire is a period of history that started with the emergence of the Ottoman principality (Osmanlı Beyliği) in , and ended circa 1453. This period witnessed the foundation of a political entity ruled by the Ottoman D ...
. The Ottoman Sultan Murad III had two large alabaster
Alabaster is a mineral or rock that is soft, often used for carving, and is processed for plaster powder. Archaeologists and the stone processing industry use the word differently from geologists. The former use it in a wider sense that includes ...
urns transported from the ruins of Pergamon and placed on two sides of the nave in the Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
in Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
.
Pergamon in myth
 Pergamon, which traced its founding back to
Pergamon, which traced its founding back to Telephus
In Greek mythology, Telephus (; grc-gre, Τήλεφος, ''Tēlephos'', "far-shining") was the son of Heracles and Auge, who was the daughter of king Aleus of Tegea. He was adopted by Teuthras, the king of Mysia, in Asia Minor, whom he succeeded ...
, the son of Heracles
Heracles ( ; grc-gre, Ἡρακλῆς, , glory/fame of Hera), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive ...
, is not mentioned in Greek myth or epic of the archaic or classical periods. However, in the Epic Cycle the Telephus myth is already connected with the area of Mysia. Searching for his mother, Telephus visits Mysia on the advice of an oracle. There he becomes Teuthras
In Greek mythology, Teuthras ( Ancient Greek: Τεύθρας, gen. Τεύθραντος) was a king of Mysia, and mythological eponym of the town of Teuthrania.
Mythology
Teuthras received Auge, the ill-fated mother of Telephus, and either ...
' son-in-law or foster-son and inherits his kingdom of Teuthrania
Teuthrania ( grc, Τευθρανία) was a town in the western part of ancient Mysia, and the name of its district about the river Caicus, which was believed to be derived from a legendary Mysian king Teuthras. This king is said to have adopt ...
, encompassing the area between Pergamon and the mouth of the Caicus. Telephus refuses to participate in the Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and has ...
, but his son Eurypylus In Greek mythology, Eurypylus (; grc, Εὐρύπυλος ''Eurypylos'') was the name of several different people:
* Eurypylus, was a Thessalian king, son of Euaemon and Ops. He was a former suitor of Helen thus he led the Thessalians during Tr ...
fights on the side of the Trojans
Trojan or Trojans may refer to:
* Of or from the ancient city of Troy
* Trojan language, the language of the historical Trojans
Arts and entertainment Music
* '' Les Troyens'' ('The Trojans'), an opera by Berlioz, premiered part 1863, part 189 ...
. This material was dealt with in a number of tragedies, such as Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; grc-gre, Αἰσχύλος ; c. 525/524 – c. 456/455 BC) was an ancient Greek tragedian, and is often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek ...
' ''Mysi'', Sophocles
Sophocles (; grc, Σοφοκλῆς, , Sophoklễs; 497/6 – winter 406/5 BC)Sommerstein (2002), p. 41. is one of three ancient Greek tragedians, at least one of whose plays has survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or co ...
' ''Aleadae'', and Euripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful e ...
' ''Telephus'' and ''Auge'', but Pergamon does not seem to have played any role in any of them. The adaptation of the myth is not entirely smooth.
Thus, on the one hand, Eurypylus who must have been part of the dynastic line as a result of the appropriation of the myth, was not mentioned in the hymn sung in honour of Telephus in the Asclepieion. Otherwise he does not seem to have been paid any heed. But the Pergamenes made offerings to Telephus and the grave of his mother Auge
In Greek mythology, Auge (; Ancient Greek: Αὐγή 'sunbeam, daylight, dawn') was the daughter of Aleus the king of Tegea in Arcadia, and the virgin priestess of Athena Alea. She was also the mother of the hero Telephus by Heracles.
Auge had ...
was located in Pergamon near the Caicus. Pergamon thus entered the Trojan epic cycle, with its ruler said to have been an Arcadia
Arcadia may refer to:
Places Australia
* Arcadia, New South Wales, a suburb of Sydney
* Arcadia, Queensland
* Arcadia, Victoria
Greece
* Arcadia (region), a region in the central Peloponnese
* Arcadia (regional unit), a modern administrative un ...
n who had fought with Telephus against Agamemnon
In Greek mythology, Agamemnon (; grc-gre, Ἀγαμέμνων ''Agamémnōn'') was a king of Mycenae who commanded the Greeks during the Trojan War. He was the son, or grandson, of King Atreus and Queen Aerope, the brother of Menelaus, the husb ...
when he landed at the Caicus, mistook it for Troy and began to ravage the land.
On the other hand, the story was linked to the foundation of the city with another myth – that of Pergamus
In Greek mythology, Pergamus (; Ancient Greek: Πέργαμος) was the son of the warrior Neoptolemus and Andromache. It is said that Andromache returned to Asia Minor with her youngest son, Pergamus who there founded the town named after himsel ...
, the eponymous
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
hero of the city. He also belonged to the broader cycle of myths related to the Trojan War as the grandson of Achilles
In Greek mythology, Achilles ( ) or Achilleus ( grc-gre, Ἀχιλλεύς) was a hero of the Trojan War, the greatest of all the Greek warriors, and the central character of Homer's ''Iliad''. He was the son of the Nereid Thetis and Peleus, k ...
through his father Neoptolemus
In Greek mythology, Neoptolemus (; ), also called Pyrrhus (; ), was the son of the warrior Achilles and the princess Deidamia, and the brother of Oneiros. He became the mythical progenitor of the ruling dynasty of the Molossians of ancient Ep ...
and of Eetion
In Greek mythology, Eëtion or Eetion (; grc, Ἠετίων ''Ēetíōn'' ) was the king of the Cilician Thebe.
Family
Eetion was the father of Andromache, wife of Hector, and of seven sons, including Podes.
Mythology
In Book 6 of the '' ...
of Thebe
Thebe may refer to:
* Any of several female characters in Greek mythology - see List of mythological figures named Thebe
* Thebe (moon), a moon of Jupiter
* Thebe (currency), 1/100 of a Botswana pula
* Thebe, an Amazons, Amazon
* Thebe, alternate ...
through his mother Andromache
In Greek mythology, Andromache (; grc, Ἀνδρομάχη, ) was the wife of Hector, daughter of Eetion, and sister to Podes. She was born and raised in the city of Cilician Thebe, over which her father ruled. The name means 'man battler ...
(concubine to Neoptolemus after the death of Hector
In Greek mythology, Hector (; grc, Ἕκτωρ, Hektōr, label=none, ) is a character in Homer's Iliad. He was a Trojan prince and the greatest warrior for Troy during the Trojan War. Hector led the Trojans and their allies in the defense o ...
of Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in prese ...
). With his mother, he was said to have fled to Mysia where he killed the ruler of Teuthrania and gave the city his own name. There he built a heroon for his mother after her death. In a less heroic version, Grynos the son of Eurypylus named a city after him in gratitude for a favour. These mythic connections seem to be late and are not attested before the 3rd century BC. Pergamus' role remained subordinate, although he did receive some cult worship. Beginning in the Roman period, his image appears on civic coinage and he is said to have had a heroon in the city. Even so, he provided a further, deliberately crafted link to the world of Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
ic epic. Mithridates VI was celebrated in the city as a new Pergamus.
However, for the Attalids, it was apparently the genealogical connection to Heracles that was crucial, since all the other Hellenistic dynasties had long established such links: the Ptolemies derived themselves directly from Heracles, the Antigonids
The Antigonid dynasty (; grc-gre, Ἀντιγονίδαι) was a Hellenistic dynasty of Dorian Greek provenance, descended from Alexander the Great's general Antigonus I Monophthalmus ("the One-Eyed") that ruled mainly in Macedonia.
History
...
inserted Heracles into their family tree in the reign of Philip V Philip V may refer to:
* Philip V of Macedon (221–179 BC)
* Philip V of France (1293–1322)
* Philip II of Spain, also Philip V, Duke of Burgundy (1526–1598)
* Philip V of Spain
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was ...
at the end of the 3rd century BC at the latest, and the Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
claimed descent from Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
. All of these claims derive their significance from Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
, who claimed descent from Heracles, through his father Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
.
In their constructive adaptation of the myth, the Attalids stood within the tradition of the other, older Hellenistic dynasties, who legitimized themselves through divine descent, and sought to increase their own prestige. The inhabitants of Pergamon enthusiastically followed their lead and took to calling themselves ''Telephidai'' () and referring to Pergamon itself in poetic registers as the 'Telephian city' ().
History of research and excavation
 The first mention of Pergamon in written records after ancient times comes from the 13th century. Beginning with
The first mention of Pergamon in written records after ancient times comes from the 13th century. Beginning with Ciriaco de' Pizzicolli
Cyriacus of Ancona or Ciriaco de' Pizzicolli (31 July 1391 – 1453/55) was a restlessly itinerant Italian humanist and antiquarian who came from a prominent family of merchants in Ancona, a maritime republic on the Adriatic. He has been calle ...
in the 15th century, ever more travellers visited the place and published their accounts of it. The key description is that of Thomas Smith, who visited the Levant in 1668 and transmitted a detailed description of Pergamon, to which the great 17th century travellers Jacob Spon
Jacob Spon (or Jacques; in English dictionaries given as James) (1647 in Lyon – 25 December 1685, in Vevey, Switzerland) was a French doctor and archaeologist, was a pioneer in the exploration of the monuments of Greece, and a scholar of inte ...
and George Wheler George Wheler may refer to:
* Sir George Wheler (travel writer) (1651–1724), English clergyman and travel writer
* George Wheler (politician) (1836–1908), Canadian mill owner and political figure
See also
* Wheler baronets
* George Wheeler (d ...
were able to add nothing significant in their own accounts.
In the late 18th century, these visits were reinforced by a scholarly (especially ancient historical) desire for research, epitomised by Marie-Gabriel-Florent-Auguste de Choiseul-Gouffier
Marie-Gabriel-Florent-Auguste de Choiseul (27 September 1752, Paris – 20 June 1817, Aix-la-Chapelle), called Auguste de Choiseul-Gouffier (), was a French diplomat and aristocrat from the Gouffier branch of the Choiseul family. A member of the ...
, a traveller in Asia Minor and French ambassador to the Sublime Porte
The Sublime Porte, also known as the Ottoman Porte or High Porte ( ota, باب عالی, Bāb-ı Ālī or ''Babıali'', from ar, باب, bāb, gate and , , ), was a synecdoche for the central government of the Ottoman Empire.
History
The nam ...
in Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
from 1784 to 1791. At the beginning of the 19th century, Charles Robert Cockerell produced a detailed account and Otto Magnus von Stackelberg Otto Magnus von Stackelberg may refer to:
* Otto Magnus von Stackelberg (ambassador) (1736–1800), Russian diplomat
* Otto Magnus von Stackelberg (archaeologist) (1786–1837), Estonian archeologist
{{hndis, Stackelberg, Otto Magnus von ...
made important sketches. A proper, multi-page description with plans, elevations, and views of the city and its ruins was first produced by Charles Texier
Félix Marie Charles Texier (22 August 1802, Versailles – 1 July 1871, Paris) was a French historian, architect and archaeologist. Texier published a number of significant works involving personal travels throughout Asia Minor and the Middle Eas ...
when he published the second volume of his ''Description de l’Asie mineure''.
In 1864–5, the German engineer Carl Humann visited Pergamon for the first time. For the construction of the road from Pergamon to Dikili
Dikili is a coastal town and a district of İzmir Province in the Aegean Region of Turkey. The district is quite picturesque both along its shoreline and in its inland parts, and is a popular summer resort. The central town of Dikili is situated ...
for which he had undertaken planning work and topographical studies, he returned in 1869 and began to focus intensively on the legacy of the city. In 1871, he organised a small expedition there under the leadership of Ernst Curtius
Ernst Curtius (; 2 September 181411 July 1896) was a German archaeologist, historian and museum director.
Biography
He was born in Lübeck. On completing his university studies he was chosen by C. A. Brandis to accompany him on a journey to ...
. As a result of this short but intensive investigation, two fragments of a great frieze were discovered and transported to Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
for detailed analysis, where they received some interest, but not a lot. It is not clear who connected these fragments with the Great Altar in Pergamon mentioned by Lucius Ampelius
The ''Liber Memorialis'' is an ancient book in Latin featuring an extremely concise summary—a kind of index—of universal history from earliest times to the reign of Trajan. It was written by Lucius Ampelius, who was possibly a tutor or ...
. However, when the archaeologist Alexander Conze
Alexander Christian Leopold Conze (10 December 1831 – 19 July 1914) was a German archaeologist, who specialized in ancient Greek art.
He was a native of Hanover, and studied at the universities of Göttingen and Berlin. In 1855 he obtained his ...
took over direction of the department of ancient sculpture at the Royal Museums of Berlin, he quickly initiated a programme for the excavation and protection of the monuments connected to the sculpture, which were widely suspected to include the Great Altar.
 As a result of these efforts, Carl Humann, who had been carrying out low-level excavations at Pergamon for the previous few years and had discovered for example the architrave inscription of the Temple of Demeter in 1875, was entrusted with carry out work in the area of the altar of Zeus in 1878, where he continued to work until 1886. With the approval of the
As a result of these efforts, Carl Humann, who had been carrying out low-level excavations at Pergamon for the previous few years and had discovered for example the architrave inscription of the Temple of Demeter in 1875, was entrusted with carry out work in the area of the altar of Zeus in 1878, where he continued to work until 1886. With the approval of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, the reliefs discovered there were transported to Berlin, where the Pergamon Museum
The Pergamon Museum (; ) is a listed building on the Museum Island in the historic centre of Berlin. It was built from 1910 to 1930 by order of German Emperor Wilhelm II according to plans by Alfred Messel and Ludwig Hoffmann in Stripped Clas ...
was opened for them in 1907. The work was continued by Conze, who aimed for the most complete possible exposure and investigation of the historic city and citadel that was possible. He was followed by the architectural historian Wilhelm Dörpfeld
Wilhelm Dörpfeld (26 December 1853 – 25 April 1940) was a German architect and archaeologist, a pioneer of stratigraphic excavation and precise graphical documentation of archaeological projects. He is famous for his work on Bronze Age site ...
from 1900 to 1911, who was responsible for the most important discoveries. Under his leadership the Lower Agora, the House of Attalos, the Gymnasion, and the Sanctuary of Demeter were brought to light.
The excavations were interrupted by the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and were only resumed in 1927 under the leadership of Theodor Wiegand
Theodor Wiegand (October 30, 1864 – December 19, 1936) was one of the more famous German archaeologists.
Wiegand was born in Bendorf, Rhenish Prussia. He studied at the universities of Munich, Berlin, and Freiburg
Freiburg im Breisgau ...
, who remained in this post until 1939. He concentrated on further excavation of the upper city, the Asklepieion, and the Red Hall. The Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
also caused a break in work at Pergamon, which lasted until 1957. From 1957 to 1968, Erich Boehringer worked on the Asklepieion in particular, but also carried out important work on the lower city as a whole and performed survey work, which increased knowledge of the countryside surrounding the city. In 1971, after a short pause, Wolfgang Radt succeeded him as leader of excavations and directed the focus of research on the residential buildings of Pergamon, but also on technical issues, like the water management system of the city which supported a population of 200,000 at its height. He also carried out conservation projects which were of vital importance for maintaining the material remains of Pergamon. Since 2006, the excavations have been led by Felix Pirson.
Most of the finds from the Pergamon excavations before the First World War were taken to the Pergamon Museum in Berlin, with a smaller portion going to the İstanbul Archaeological Museum after it was opened in 1891. After the First World War the Bergama Museum was opened, which has received all finds discovered since then.
In May 2022, archaeologists announced the discovery of a 1,800-year-old well-preserved geometric patterned floor mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
around the Red Basilica
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
.
Infrastructure and housing
Pergamon is a good example of a city that expanded in a planned and controlled manner. Philetairos transformed Pergamon from an archaic settlement into a fortified city. He or his successor Attalos I built a wall around the whole upper city, including the plateau to the south, the upper agora and some of the housing – further housing must have been found outside these walls. Because of the growth of the city, the streets were expanded and the city was monumentalised. Under Attalos I some minor changes were made to the city of Philetairos. During the reign of Eumenes II and Attalos II, there was a substantial expansion of the city. A new street network was created and a new city wall, with a monumental gatehouse called the Gate of Eumenes, was built south of the Acropolis. The wall, with numerous gates, now surrounded the entire hill, not just the upper city and the flat area to the southwest, all the way to the Selinus river. Numerous public buildings were constructed, as well as a new marketplace south of the acropolis and a new gymnasion in the east. The southeast slope and the whole western slope of the hill were now settled and opened up by streets. The plan of Pergamon was affected by the extreme steepness of the site. As a result of this, the streets had to turn hairpin corners, so that the hill could be climbed as comfortably and quickly as possible. For the construction of buildings and laying out of the agoras, extensive work on the cliff-face and terracing had to be carried out. A consequence of the city's growth was the construction of new buildings over old ones, since there was not sufficient space. Separate from this, a new area was laid out in Roman times, consisting of a whole new city west of the Selinus river, with all necessary infrastructure, including baths, theatres, stadiums, and sanctuaries. This Roman new city was able to expand without any city walls constraining it because of the absence of external threats.Housing
Generally, most of the Hellenistic houses at Pergamon were laid out with a small, centrally-located and roughly square courtyard, with rooms on one or two sides of it. The main rooms are often stacked in two levels on the north side of the courtyard. A wide passage or colonnade on the north side of the courtyard often opened onto foyers, which enabled access to other rooms. An exact north-south arrangement of the city blocks was not possible because of the topographical situation and earlier construction. Thus the size and arrangement of the rooms differed from house to house. From the time of Philetairos, at the latest, this kind of courtyard house was common and it was ever more widespread as time went on, but not universal. Some complexes were designed as Prostas houses, similar to designs seen atPriene
Priene ( grc, Πριήνη, Priēnē; tr, Prien) was an ancient Greek city of Ionia (and member of the Ionian League) located at the base of an escarpment of Mycale, about north of what was then the course of the Maeander River (now called th ...
. Others had wide columned halls in front of main rooms to the north. Especially in this latter type there is often a second story accessed by stairways. In the courtyards there were often cisterns, which captured rain water from the sloping roofs above. For the construction under Eumenes II, a city block of 35 x 45 m can be reconstructed, subject to significant variation as a result of the terrain.
Open spaces
From the beginning of the reign of Philetairos, civic events in Pergamon were concentrated on the Acropolis. Over time the so-called 'Upper agora' was developed at the south end of this. In the reign of Attalos I, a Temple of Zeus was built there. To the north of this structure there was a multi-story building, which propbably had a function connected to the marketplace. With progressive development of the open space, these buildings were demolished, while the Upper Agora itself took on a more strongly commercial function, while still a special space as a result of the temple of Zeus. In the course of the expansion of the city under Eumenes, the commercial character of the Upper Agora was further developed. The key signs of this development are primarily the halls built under Eumenes II, whose back chambers were probably used for trade. In the west, the 'West Chamber' was built which might have served as a market administration building. After these renovations, the Upper Agora thus served as a centre for trade and spectacle in the city. Because of significant new construction in the immediate vicinity – the renovation of the Sanctuary of Athena and the Pergamon altar and the redesign of the neighbouring area - the design and organisational principle of the Upper Agora underwent a further change. Its character became much more spectacular and focussed on the two new structures looming over it, especially the altar which was visible on its terrace from below since the usualstoa
A stoa (; plural, stoas,"stoa", ''Oxford English Dictionary'', 2nd Ed., 1989 stoai, or stoae ), in ancient Greek architecture, is a covered walkway or portico, commonly for public use. Early stoas were open at the entrance with columns, usually ...
surrounding it was omitted from the design.
The 80 m long and 55 m wide 'Lower Agora' was built under Eumenes II and was not significantly altered until Late Antiquity. As with the Upper Agora, the rectangular form of the agora was adapted to the steep terrain. The construction consisted in total of three levels. Of these the Upper Level and the 'Main Level' opened onto a central courtyard. On the lower level there were rooms only on the south and east sides because of the slope of the land, which led through a colonnade to the exterior of the space. The whole market area extended over two levels with a large columned hall in the centre, which contained small shop spaces and miscellaneous rooms.
Streets and bridges
The course of the main street, which winds up the hill to the Acropolis with a series of hairpin turns, is typical of the street system of Pergamon. On this street were shops and warehouses. The surface of the street consisted of andesite blocks up to 5 metres wide, 1 metre long and 30 cm deep. The street included a drainage system, which carried the water down the slope. Since it was the most important street of the city, the quality of the material used in its construction was very high. Philetairos' design of the city was shaped above all by circumstantial considerations. Only under Eumenes II was this approach discarded and the city plan begins to show signs of an overall plan. Contrary to earlier attempts at an orthogonal street system, a fan-shaped design seems to have been adopted for the area around the gymnasium, with streets up to four metres wide, apparently intended to enable effective traffic flow. In contrast to it, Philetairos' system of alleys was created unsystematically, although the topic is still under investigation. Where the lay of the land prevented the laying of a street, small alleys were installed as connections instead. In general, therefore, there are large, broad streets (''plateiai'') and small, narrow connecting streets (''stenopoi''). The nearly 200 metre widePergamon Bridge
The Pergamon Bridge is a Roman substruction bridge over the Selinus river (modern ''Bergama Çayı'') in the ancient city of Pergamon (today Bergama), modern-day Turkey. The wide structure, the largest of its kind in antiquity, was designed dur ...
under the forecourt of the Red Basilica
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
in the centre of Bergama is the largest bridge substruction from antiquity.
Water supply
The inhabitants of Pergamon were supplied with water by an effective system. In addition to cisterns, there was a system of nine pipes (seven Hellenistic ceramic pipes and two open Roman channels. The system provided around 30,000–35,000 cubic metres of water per day. The Madradağ aqueduct was a ceramic pipe with a diameter of 18 cm which already brought water to the citadel from a source over 40 kilometres away in the Madradağ mountains at 1174 m above sea level in the Hellenistic period. Their significance for architectural history lies in the form of the last kilometres from the mountains through a valley to the Akropolis. The pipe consisted of three channels, which ended 3 km north of the citadel, before reaching the valley, and emptied into a pool, which included a doublesedimentation tank
Sedimentation is a physical water treatment process using gravity to remove suspended solids from water. Solid particles entrained by the turbulence of moving water may be removed naturally by sedimentation in the still water of lakes and oceans. ...
. This pool was 35 metres higher than the summit of the citadel. The pipe from the pool to the Acropolis consisted of only a single channel – a lead pipe pressurised to 200 mH2O. The water was able to cross the valley between the pool and the citadel with the help of this pressurised conduit. It functioned as a communicating vessel, such that the water rose to the height of the citadel on its own as a result of the pressurised pipe.
Main sights
Upper Acropolis
Pergamon Altar
The most famous structure from the city is the monumental altar, which was probably dedicated to Zeus and Athena. The foundations are still located in the Upper city, but the remains of the Pergamon frieze, which originally decorated it, are displayed in the Pergamon museum in Berlin, where the parts of the frieze taken to Germany have been installed in a partial reconstruction. For the altar's construction, the required flat area was skillfully created through terracing, in order to allow it to be oriented in relation to the neighbouring Temple of Athena. The base of the altar measured around 36 x 33 metres and was decorated on the outside with a detailed depiction inhigh relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the ...
of the Gigantomachy
In Greek and Roman mythology, the Giants, also called Gigantes (Greek: Γίγαντες, ''Gígantes'', Γίγας, ''Gígas''), were a race of great strength and aggression, though not necessarily of great size. They were known for the Giganto ...
, the battle between the Olympian gods and the Giants. The frieze is 2.30 metres high and has a total length of 113 metres, making it the second longest frieze surviving from antiquity, after the Parthenon Frieze
The Parthenon frieze is the high-relief Pentelic marble sculpture created to adorn the upper part of the Parthenon’s naos. It was sculpted between c. 443 and 437 BC, most likely under the direction of Pheidias. Of the 160 meters (524 ft) ...
in Athens. A staircase cut into the base on the western side leads up to the upper structure, which is surrounded by a colonnade, and consists of a colonnaded courtyard, separated from the staircase by a colonnade. The interior walls of this colonnade had a further frieze, depicting the life of Telephus
In Greek mythology, Telephus (; grc-gre, Τήλεφος, ''Tēlephos'', "far-shining") was the son of Heracles and Auge, who was the daughter of king Aleus of Tegea. He was adopted by Teuthras, the king of Mysia, in Asia Minor, whom he succeeded ...
, the son of Heracles and mythical founder of Pergamon. This frieze is around 1.60 metres high and thus is clearly smaller than the outer frieze.
In the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book of R ...
, the faith of the Pergamon believers, who "dwell where Satan’s throne is" is commended by the author. Many scholars believe that the "seat
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but also headquarters in a wider sense.
Types of seat
The following are examples of different kinds of seat:
* Armchair (furniture), ...
of Satan
Satan,, ; grc, ὁ σατανᾶς or , ; ar, شيطانالخَنَّاس , also known as Devil in Christianity, the Devil, and sometimes also called Lucifer in Christianity, is an non-physical entity, entity in the Abrahamic religions ...
" refers to the Pergamon Altar, due to its resemblance to a gigantic throne
A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign on state occasions; or the seat occupied by a pope or bishop on ceremonial occasions. "Throne" in an abstract sense can also refer to the monar ...
.
Theatre
 The well-preserved dates from the Hellenistic period and had space for around 10,000 people, in 78 rows of seats. At a height of 36 metres, it is the steepest of all ancient theatres. The seating area (''koilon'') is divided horizontally by two walkways, called ''diazomata'', and vertically by stairways into seven sections in the lowest part of the theatre and six in the middle and upper sections. Below the theatre is a and up to terrace, which rested on a high retaining wall and was framed on the long side by a
The well-preserved dates from the Hellenistic period and had space for around 10,000 people, in 78 rows of seats. At a height of 36 metres, it is the steepest of all ancient theatres. The seating area (''koilon'') is divided horizontally by two walkways, called ''diazomata'', and vertically by stairways into seven sections in the lowest part of the theatre and six in the middle and upper sections. Below the theatre is a and up to terrace, which rested on a high retaining wall and was framed on the long side by a stoa
A stoa (; plural, stoas,"stoa", ''Oxford English Dictionary'', 2nd Ed., 1989 stoai, or stoae ), in ancient Greek architecture, is a covered walkway or portico, commonly for public use. Early stoas were open at the entrance with columns, usually ...
. Coming from the Upper market, one could enter this from a tower-building at the south end. This terrace had no space for the circular orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families.
There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, c ...
, which was normal in a Greek theatre, so only a wooden stage building was built which could be taken down when there was no performance taking place. Thus, the view along the terrace to the Temple of Dionysos at the northern end was unimpeded. A marble stage building was only built in the 1st century BC. Additional theatres were built in the Roman period, one in the Roman new city and the other in the sanctuary of Asclepius.
Trajaneum
 On the highest point of the citadel is the Temple for
On the highest point of the citadel is the Temple for Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
and Zeus Philios. The temple sits on a podium on top of a vaulted terrace. The temple itself was a Corinthian Corinthian or Corinthians may refer to:
*Several Pauline epistles, books of the New Testament of the Bible:
**First Epistle to the Corinthians
**Second Epistle to the Corinthians
**Third Epistle to the Corinthians (Orthodox)
*A demonym relating to ...
peripteros
A peripteros (a peripteral building, grc-gre, περίπτερος) is a type of ancient Greek or Roman temple surrounded by a portico with columns. It is surrounded by a colonnade ('' pteron'') on all four sides of the ''cella'' (''naos''), crea ...
temple, about 18 metres wide with six columns on the short sides and nine columns on the long sides, and two rows of columns in antis
An anta (pl. antæ, antae, or antas; Latin, possibly from ''ante'', "before" or "in front of"), or sometimes parastas (pl. parastades), is an architectural term describing the posts or pillars on either side of a doorway or entrance of a Greek ...
. To the north, the area was closed off by a high stoa, while on the west and east sides it was surrounded by simple ashlar walls, until further stoas were inserted in Hadrian's reign.
During the excavations fragments of statues of Trajan and Hadrian were found in the rubble of the cella
A cella (from Latin for small chamber) or naos (from the Greek ναός, "temple") is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple in classical antiquity. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a hermit's or ...
, including their portrait heads, as well as fragments of the cult statue of Zeus Philios.
Temple of Dionysus
At Pergamon, Dionysus had the epithet ''Kathegemon'', 'the guide', and was already worshiped in the last third of the 3rd century BC, when the Attalids made him the chief god of their dynasty. In the 2nd century BC, Eumenes II (probably) built a temple for Dionysus at the northern end of the theatre terrace. The marble temple sits on a podium, 4.5 metres above the level of the theatre terrace and was an Ionicprostyle
Prostyle is an architectural term designating temples (especially Greek and Roman) featuring a row of columns on the front. The term is often used as an adjective when referring to the portico of a classical building, which projects from the m ...
temple. The pronaos
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cult ...
was four columns wide and two columns deep and was accessed by a staircase of twenty-five steps. Only a few traces of the Hellenistic structure survive. The majority of the surviving structure derives from a reconstruction of the temple which probably took place under Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor S ...
, or perhaps under Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
.
Temple of Athena
 Pergamon's oldest temple is a sanctuary of Athena from the 4th century BC. It was a north-facing
Pergamon's oldest temple is a sanctuary of Athena from the 4th century BC. It was a north-facing Doric Doric may refer to:
* Doric, of or relating to the Dorians of ancient Greece
** Doric Greek, the dialects of the Dorians
* Doric order, a style of ancient Greek architecture
* Doric mode, a synonym of Dorian mode
* Doric dialect (Scotland)
* Doric ...
peripteros
A peripteros (a peripteral building, grc-gre, περίπτερος) is a type of ancient Greek or Roman temple surrounded by a portico with columns. It is surrounded by a colonnade ('' pteron'') on all four sides of the ''cella'' (''naos''), crea ...
temple with six columns on the short side and ten on the long side and a cella
A cella (from Latin for small chamber) or naos (from the Greek ναός, "temple") is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple in classical antiquity. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a hermit's or ...
divided into two rooms. The foundations, measuring around 12.70 x 21.80 metres, are still visible today. The columns were around 5.25 metres high, 0.75 metres in diameter, and the distance between the columns was 1.62 metres, so the colonnade was very light for a temple of this period. This is matched by the shape of the triglyph
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are ...
s, which usually consist of a sequence of two triglyphs and two metope
In classical architecture, a metope (μετόπη) is a rectangular architectural element that fills the space between two triglyphs in a Doric frieze, which is a decorative band of alternating triglyphs and metopes above the architrave of a bu ...
s, but are instead composed of three of triglyphs and three metopes. The columns of the temple are unfluted and retained bossage
Bossage is uncut stone that is laid in place in a building, projecting outward from the building, to later be carved into decorative moldings, capitals, arms, etc.
Bossages are also rustic work, consisting of stones which seem to advance beyond ...
, but it is not clear whether this was a result of carelessness or incompleteness.
A two-story stoa surrounding the temple on three sides was added under Eumenes II, along with the propylon
In ancient Greek architecture, a propylaea, propylea or propylaia (; Greek: προπύλαια) is a monumental gateway. They are seen as a partition, specifically for separating the secular and religious pieces of a city. The prototypical Gre ...
in the southeast corner, which is now found, largely reconstructed, in the Pergamon Museum
The Pergamon Museum (; ) is a listed building on the Museum Island in the historic centre of Berlin. It was built from 1910 to 1930 by order of German Emperor Wilhelm II according to plans by Alfred Messel and Ludwig Hoffmann in Stripped Clas ...
in Berlin. The balustrade of the upper level of the north and east stoas was decorated with reliefs depicting weapons which commemorated Eumenes II's military victory. The construction mixed Ionic columns and Doric triglyphs (of which five triglyphs and metopes survive). In the area of the sanctuary, Attalos I and Eumenes II constructed victory monuments, most notably the Gallic dedications. The northern stoa seems to have been the site of the Library of Pergamon.
Library
The Library of Pergamon was the second largest in the ancient Greek world after theLibrary of Alexandria
The Great Library of Alexandria in Alexandria, Egypt, was one of the largest and most significant libraries of the ancient world. The Library was part of a larger research institution called the Mouseion, which was dedicated to the Muses, th ...
, containing at least 200,000 scrolls. The location of the library building is not certain. Since the 19th century excavations, it has generally been identified with an annex of the northern stoa of the sanctuary of Athena in the Upper Citadel, which was built by Eumenes II. Inscriptions in the gymnasium which mention a library might indicate, however, that the building was located in that area.
Other structures
 Other notable structures still in existence on the upper part of the Acropolis include:
*The Royal palaces
*The Heroön – a shrine where the kings of Pergamon, particularly Attalus I and Eumenes II, were worshipped.
*The Upper Agora
*The Roman baths complex
*Diodorus Pasporos heroon
*Arsenals
The site is today easily accessible by the Bergama Acropolis Gondola from the base station in northeastern Bergama.
Other notable structures still in existence on the upper part of the Acropolis include:
*The Royal palaces
*The Heroön – a shrine where the kings of Pergamon, particularly Attalus I and Eumenes II, were worshipped.
*The Upper Agora
*The Roman baths complex
*Diodorus Pasporos heroon
*Arsenals
The site is today easily accessible by the Bergama Acropolis Gondola from the base station in northeastern Bergama.
Lower Acropolis
Gymnasium
 A large gymnasium area was built in the 2nd century BC on the south side of the Acropolis. It consisted of three terraces, with the main entrance at the southeast corner of the lowest terrace. The lowest and southernmost terrace is small and almost free of buildings. It is known as the Lower Gymnasium and has been identified as the boys' gymnasium. The middle terrace was around 250 metres long and 70 metres wide at the centre. On its north side there was a two-story hall. In the east part of the terrace there was a small
A large gymnasium area was built in the 2nd century BC on the south side of the Acropolis. It consisted of three terraces, with the main entrance at the southeast corner of the lowest terrace. The lowest and southernmost terrace is small and almost free of buildings. It is known as the Lower Gymnasium and has been identified as the boys' gymnasium. The middle terrace was around 250 metres long and 70 metres wide at the centre. On its north side there was a two-story hall. In the east part of the terrace there was a small prostyle
Prostyle is an architectural term designating temples (especially Greek and Roman) featuring a row of columns on the front. The term is often used as an adjective when referring to the portico of a classical building, which projects from the m ...
temple in the Corinthian order
The Corinthian order (Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order ...
. A roofed stadium
A stadium ( : stadiums or stadia) is a place or venue for (mostly) outdoor sports, concerts, or other events and consists of a field or stage either partly or completely surrounded by a tiered structure designed to allow spectators to stand o ...
, known as the Basement Stadium is located between the middle terrace and the upper terrace.
The upper terrace measured 150 x 70 metres square, making it the largest of the three terraces. It consisted of a courtyard surrounded by stoas and other structures, measuring roughly 36 x 74 metres. This complex is identified as a palaestra
A palaestra ( or ;
also (chiefly British) palestra; grc-gre, παλαίστρα) was any site of an ancient Greek wrestling school. Events requiring little space, such as boxing and wrestling, took place there. Palaestrae functioned both indep ...
and had a theatre-shaped lecture hall beyond the northern stoa, which is probably of Roman date and a large banquet hall in the centre. Further rooms of uncertain function were accessible from the stoas. In the west was a south-facing Ionic antae temple
An antae temple, also a ''distyle in antis'' temple, is a special name given to a type of ancient Greek or Roman temple that has side walls that extend to form a porch at the front or rear (or both) and terminated in structural pillars that were ca ...
, the central sanctuary of the gymnasium. The eastern area was replaced with a bath complex in Roman times. Further Roman baths were constructed to the west of the Ionic temple.
Sanctuary of Hera
exedra
An exedra (plural: exedras or exedrae) is a semicircular architectural recess or platform, sometimes crowned by a semi-dome, and either set into a building's façade or free-standing. The original Greek sense (''ἐξέδρα'', a seat out of d ...
to the west and a building whose function is very unclear to the east. The two terraces were linked by a staircase of eleven steps around 7.5 metres wide, descending from the front of the temple.
The temple was about 7 metres wide by 12 metres long, and sat on a three-stepped foundation. It was a Doric Doric may refer to:
* Doric, of or relating to the Dorians of ancient Greece
** Doric Greek, the dialects of the Dorians
* Doric order, a style of ancient Greek architecture
* Doric mode, a synonym of Dorian mode
* Doric dialect (Scotland)
* Doric ...
tetrastyle prostyle
Prostyle is an architectural term designating temples (especially Greek and Roman) featuring a row of columns on the front. The term is often used as an adjective when referring to the portico of a classical building, which projects from the m ...
temple, with three triglyph
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are ...
s and metope
In classical architecture, a metope (μετόπη) is a rectangular architectural element that fills the space between two triglyphs in a Doric frieze, which is a decorative band of alternating triglyphs and metopes above the architrave of a bu ...
s for each span in the entablature. All the other buildings in the sanctuary were made out of trachyte
Trachyte () is an extrusive igneous rock composed mostly of alkali feldspar. It is usually light-colored and aphanitic (fine-grained), with minor amounts of mafic minerals, and is formed by the rapid cooling of lava enriched with silica and al ...
, but the visible part of the temple was made of marble, or at least had a marble cladding. The base of the cult image inside the cella supported three cult statues.
The surviving remains of the inscription on the architrave indicate that the building was the temple of Hera Basileia and that it was erected by Attalus II.
Sanctuary of Demeter
 The Sanctuary of Demeter occupied an area of 50 x 110 metres on the middle level of the south slope of the citadel. The sanctuary was old; its activity can be traced back to the fourth century BC.
The sanctuary was entered through a Propylon from the east, which led to a courtyard surrounded by stoas on three sides. In the centre of the western half of this courtyard, stood the Ionic temple of
The Sanctuary of Demeter occupied an area of 50 x 110 metres on the middle level of the south slope of the citadel. The sanctuary was old; its activity can be traced back to the fourth century BC.
The sanctuary was entered through a Propylon from the east, which led to a courtyard surrounded by stoas on three sides. In the centre of the western half of this courtyard, stood the Ionic temple of Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter (; Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although s ...
, a straightforward Antae temple
An antae temple, also a ''distyle in antis'' temple, is a special name given to a type of ancient Greek or Roman temple that has side walls that extend to form a porch at the front or rear (or both) and terminated in structural pillars that were ca ...
, measuring 6.45 x 12.7 metres, with a porch in the Corinthian order
The Corinthian order (Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order ...
which was added in the time of Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius (Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatoria ...
. The rest of the structure was of Hellenistic date, built in local marble and had a marble frieze decorated with bucrania
Bucranium (plural ''bucrania''; Latin, from Greek ''βουκράνιον'', referring to the skull of an ox) was a form of carved decoration commonly used in Classical architecture. The name is generally considered to originate with the practic ...
. About 9.5 metres in front of the east-facing building, there was an altar, which was 7 metres long and 2.3 metres wide. The temple and the altar were built for Demeter by Philetaerus, his brother Eumenes, and their mother Boa.
In the east part of the courtyard, there were more than ten rows of seating laid out in front of the northern stoa for participants in the mysteries of Demeter. Roughly 800 initiates could fit in these seats.
Other structures
The lower part of the Acropolis also contains the following structures: *the House of Attalus *the Lower Agora and *the Gate of EumenesAt the foot of the Acropolis
Sanctuary of Asclepius
 south of the Acropolis at (39° 7′ 9″ N, 27° 9′ 56″ E), down in the valley, there was the Sanctuary of
south of the Acropolis at (39° 7′ 9″ N, 27° 9′ 56″ E), down in the valley, there was the Sanctuary of Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of ...
(also known as the Asclepium), the god of healing. The Asclepium was approached along an 820-meter colonnaded sacred way. In this place people with health problems could bathe in the water of the sacred spring, and in the patients' dreams Asclepius would appear in a vision to tell them how to cure their illness. Archeology has found many gifts and dedications that people would make afterwards, such as small terracotta body parts, no doubt representing what had been healed. Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of ...
, the most famous doctor in the ancient Roman Empire and personal physician of Emperor Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
, worked in the Asclepium for many years. Notable extant structures in the Asclepium include:
*the Roman theater
*the North Stoa
*the South Stoa
*the Temple of Asclepius
*a circular treatment center (sometimes known as the Temple of Telesphorus)
*a healing spring
*an underground passageway
*a library
*the Via Tecta (or the Sacred Way, which is a colonnaded street leading to the sanctuary) and
*a propylon
In ancient Greek architecture, a propylaea, propylea or propylaia (; Greek: προπύλαια) is a monumental gateway. They are seen as a partition, specifically for separating the secular and religious pieces of a city. The prototypical Gre ...
Serapis Temple
 Pergamon's other notable structure is the great temple of the Egyptian gods
Pergamon's other notable structure is the great temple of the Egyptian gods Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingd ...
and/or Serapis
Serapis or Sarapis is a Graeco-Egyptian deity. The cult of Serapis was promoted during the third century BC on the orders of Greek Pharaoh Ptolemy I Soter of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt as a means to unify the Greeks and Egyptians in his r ...
, known today as the "Red Basilica
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
" (or ''Kızıl Avlu'' in Turkish), about south of the Acropolis at (39 7' 19" N, 27 11' 1" E). It consists of a main building and two round towers within an enormous ''temenos'' or sacred area. The temple towers flanking the main building had courtyards with pools used for ablutions at each end, flanked by stoas on three sides. The forecourt of the Temple of Isis/Sarapis is still supported by the Pergamon Bridge
The Pergamon Bridge is a Roman substruction bridge over the Selinus river (modern ''Bergama Çayı'') in the ancient city of Pergamon (today Bergama), modern-day Turkey. The wide structure, the largest of its kind in antiquity, was designed dur ...
, the largest bridge substruction of antiquity.
According to Christian tradition
Christian tradition is a collection of traditions consisting of practices or beliefs associated with Christianity. These ecclesiastical traditions have more or less authority based on the nature of the practices or beliefs and on the group in que ...
, in the year 92 Saint Antipas, the first bishop of Pergamum The Metropolis of Pergamon ( el, Μητρόπολις Περγάμου) was an ecclesiastical territory (diocese) of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople in western Asia Minor, modern Turkey. Christianity in the city of Pergamon (modern Be ...
ordained by John the Apostle
John the Apostle ( grc, Ἰωάννης; la, Ioannes ; Ge'ez: ዮሐንስ;) or Saint John the Beloved was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Generally listed as the youngest apostle, he was the son of Zebedee a ...
, was a victim of an early clash between Serapis worshippers and Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
. An angry mob is said to have burned Saint Antipas alive in front of the Temple inside a brazen bull
The brazen bull, also known as the bronze bull, Sicilian bull, or bull of Phalaris, was a torture and execution device designed in ancient Greece. According to Diodorus Siculus, recounting the story in '' Bibliotheca historica'', Perilaus (or P ...
-like incense
Incense is aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also b ...
burner
Burner may refer to:
* Gas burner, coal burner or oil burner, a mechanical device that burns a gas or liquid fuel in a controlled manner
** Laboratory gas burners:
*** Bunsen burner
*** Meker–Fisher burner
*** Teclu burner
** Hot-air balloon de ...
, which represented the bull
A bull is an intact (i.e., not castrated) adult male of the species ''Bos taurus'' (cattle). More muscular and aggressive than the females of the same species (i.e., cows), bulls have long been an important symbol in many religions,
includin ...
god
In monotheism, monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator deity, creator, and principal object of Faith#Religious views, faith.Richard Swinburne, Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Ted Honderich, Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Ox ...
Apis. His martyrdom
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an external ...
is one of the first recorded in Christian history
The history of Christianity concerns the Christian religion, Christian countries, and the Christians with their various denominations, from the 1st century to the present. Christianity originated with the ministry of Jesus, a Jewish teach ...
, highlighted by the Christian Scripture
A biblical canon is a set of texts (also called "books") which a particular Jewish or Christian religious community regards as part of the Bible.
The English word ''canon'' comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek , meaning "ruler, rule" or "measu ...
itself through thmessage
sent to the Pergamon Church in the
Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book of R ...
.
Inscriptions
Greek inscriptions discovered at Pergamon include the rules of the town clerks, the so-called Astynomoi inscription, which has added to understanding of Greek municipal laws and regulations, including how roads were kept in repair, regulations regarding the public and private water supply and lavatories.Notable people
*Epigonus
Epigonus ( el, Ἐπίγονος) of Pergamum was the chief among the court sculptors to the Attalid dynasty at Pergamum in the late third century BCE. Biography
Pliny the Elder, who offers the only surviving list of the sculptors of this inf ...
(3rd century BC), Greek sculptor.
*Andronicus of Pergamum
Andronicus of Pergamum was an ambassador of Attalus II Philadelphus. He was sent to Rome in 156 BCE, to inform the Roman Senate that Prusias II of Bithynia had attacked the territories of Attalus.
Prusias later sent his son Nicomedes II of Bithyni ...
(2nd century BC), Attalid ambassador to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
.
*Biton of Pergamon
Biton of Pergamon ( gr, Βίτων) was an ancient Greek writer and engineer, who lived in the second or third century BC. Only two of his works are known: a lost book on optics, entitled ''Optics'', and an extant short treatise on siege machines, ...
(2nd or 3rd century BC), Greek writer and engineer.
*Hegesinus of Pergamon
Hegesinus of Pergamon ( grc-gre, Ἡγησίνους, Hēgēsínous), was an Academic Skeptic philosopher from Pergamon. He was the successor of Evander and the immediate predecessor of Carneades as the leader (scholarch) of the Platonic Academy, ...
(c. 160 BC), Academic philosopher.
*Sosus of Pergamon
Sosus of Pergamon was a Greek mosaic artist of the second century BC. He is the only mosaic artist whose name was recorded in literature. After the conquests of Alexander the Great, the Greeks of major centers such as Pergamon and Alexandria disp ...
(2nd century BC), Greek mosaic artist.
*Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
(1st century BC), rhetor and teacher to Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
.
* Cratippus of Pergamon (1st century BC), Peripatetic philosopher.
*Antipas of Pergamum
According to Eastern Orthodox traditions, according to the Commentary on the Apocalypse of Andreas of Caesarea, it is believed that Saint Antipas was the Antipas referred to in the Book of , as the verse says: "I know thy works, and where thou d ...
(1st century AD), Christian martyr and saint.
*Aristocles (1st century AD), a Greek sophist
* Aelius Nicon (2nd century AD), Greek architect and builder.
*Aeschrion of Pergamon
Aeschrion ( Gr. ) of Pergamon was a physician in the 2nd century AD. He was one of Galen's tutors, who says that he belonged to the sect of the Empirici, and that he had a great knowledge of pharmacy and materia medica. Aeschrion was the inven ...
(2nd century AD), physician and tutor to Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of ...
.
*Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of ...
(c. 129–200/216 AD), Greek physician.
*Oribasius
Oribasius or Oreibasius ( el, Ὀρειβάσιος; c. 320 – 403) was a Greek medical writer and the personal physician of the Roman emperor Julian. He studied at Alexandria under physician Zeno of Cyprus before joining Julian's retinue. He ...
(c. 320-403 AD), Greek physician
*Aedesius
Aedesius ( grc-gre, Αἰδέσιος, died 355 AD) was a Neoplatonist philosopher and mystic born of a noble Cappadocian family.
Career
Aedesius was born into a wealthy Cappadocian family, but he moved to Syria, where he was apprenticed to Iamb ...
(4th century), Neoplatonic philosopher
*Sosipatra
Sosipatra ( grc-gre, Σωσιπάτρα) was a Neoplatonist philosopher and mystic who lived in Ephesus and Pergamon in the first half of the 4th century CE. The story of her life is told in Eunapius' ''Lives of the Sophists''.
Biography
Early ...
(4th century), Neoplatonic philosopher
*Telephus, a Greek grammarian
See also
* Allianoi *List of ancient Greek cities
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* *Hansen, Esther V. (1971). ''The Attalids of Pergamon''. Ithaca, New York:Cornell University Press
The Cornell University Press is the university press of Cornell University; currently housed in Sage House, the former residence of Henry William Sage. It was first established in 1869, making it the first university publishing enterprise in th ...
; London: Cornell University Press Ltd. .
*Kekeç, Tevhit. (1989). ''Pergamon''. Istanbul, Turkey: Hitit Color. .
*Kosmetatou, Elizabeth (2003) "The Attalids of Pergamon," in Andrew Erskine, ed., ''A Companion to the Hellenistic World''. Oxford: Blackwell: pp. 159–174. .
*McEvedy, Colin (2012). ''Cities of the Classical World''. Penguin Global
*Nagy, Gregory (1998). "The Library of Pergamon as a Classical Model," in Helmut Koester, ed., ''Pergamon: Citadel of the Gods''. Harrisburg PA: Trinity Press International: 185-232.
*Nagy, Gregory (2007). "The Idea of the Library as a Classical Model for European Culture," http://chs.harvard.edu/publications.sec/online_print_books.ssp/. Center for Hellenic Studies
The Center for Hellenic Studies (CHS) is a research institute for classics located in Washington, D.C. at 3100 NW Whitehaven Street. It is affiliated with Harvard University.
Nestled in Rock Creek Park behind Embassy Row, the Center for Hell ...
*
*Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, wikt:Ξενοφῶν, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Anci ...
. ''Xenophon in Seven Volumes'', Carleton L. Brownson. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA; William Heinemann, Ltd., London. vol. 1 (1918), vol. 2 (1921), vol. 3 (1922).
Further reading
*Hansen, Esther Violet. 1971. ''The Attalids of Pergamon''. 2nd ed., rev., and expanded. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. *Radt, Wolfgang. 1984. ''Pergamon, Archeological Guide''. 3rd ed. Istanbul: Türkiye Turing Ve Otomobil Kurumu. *Shipley, Graham. 2000. ''The Greek world after Alexander 323–30 BC''. London: Routledge. *Walbank, Frank W. 1993. ''The Hellenistic world''. Revised ed. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Univ. Press.''Altertümer von Pergamon''
The archaeological reports from Pergamon are published in German as ''Altertümer von Pergamon'' (de Gruyter, Berlin). * Band I 1:Alexander Conze
Alexander Christian Leopold Conze (10 December 1831 – 19 July 1914) was a German archaeologist, who specialized in ancient Greek art.
He was a native of Hanover, and studied at the universities of Göttingen and Berlin. In 1855 he obtained his ...
: ''Stadt und Landschaft'' ity and Landscape(1912Digitisation
* Band I 2: Alexander Conze: ''Stadt und Landschaft'' ity and Landscape(1913
Digitisation
* Band I 3: Alexander Conze (ed.): ''Stadt und Landschaft'' ity and Landscape3: Friedrich Graeber: ''Die Wasserleitungen'' he Aqueducts(1913
Digitisation
* Volume I 4: Günther Garbrecht: ''Die Wasserversorgung von Pergamon''
he Water Supply System of Pergamon
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
(2001)
* Volume II: Richard Bohn
Karl Theodor Richard Bohn (29 December 1849 – 22 August 1898 in Görlitz) was a German archaeological architect born in Berlin.
Beginning in 1868, he studied architecture in Berlin, and in 1877 participated in the archaeological dig at Olym ...
: ''Das Heiligtum der Athena Polias Nikephoros'' he Sanctuary of Athena Polias Nikephoros(1885Digitisation
* Volume III 1: Jakob Schrammen: ''Der grosse Altar – der obere Markt''
he Great Altar - The Upper Agora
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
(1906Digitisation
* Volume III 2:
Hermann Winnefeld
Hermann Winnefeld (4 September 1862, Überlingen – 30 April 1918, Berlin) was a German classical archaeologist.
He studied classics in Heidelberg and Bonn from 1881 to 1884, and subsequently became a research assistant at the ''Großherzo ...
: ''Die Friese des groszen Altars'' he Frieze of the Great Altar(1910Digitisation
* Volume IV: Richard Bohn: ''Die Theater-Terrasse'' he Theatre Terrace(1896
Digitisation
* Volume V 1: Georg Kawerau –
Theodor Wiegand
Theodor Wiegand (October 30, 1864 – December 19, 1936) was one of the more famous German archaeologists.
Wiegand was born in Bendorf, Rhenish Prussia. He studied at the universities of Munich, Berlin, and Freiburg
Freiburg im Breisgau ...
: ''Die Paläste der Hochburg'' he Palace of the Citadel(1930Digitisation
* Volume V 2: Hermann Stiller: ''Das Traianeum'' he Trajaneum Berlin 189
Digitisation
http://digi.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/diglit/pergamon1895b Digitisation of the tables] * Volume VI: Paul Schazmann: ''Das Gymnasion. Der Tempelbezirk der Hera Basileia''
he Gymnasium. The Temple Area of Hera Basileia
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
(1923Digitisation
* Volume VII 1:
Franz Winter
Franz Winter (4 February 1861 in Braunschweig – 11 February 1930 in Bonn) was a German archaeologist. He specialized in ancient Greek and Roman art, being particularly known for his analyses of individual statues, such as the Apollo Belvedere.
...
: ''Die Skulpturen mit Ausnahme der Altarreliefs'' he Sculpture, aside from the Altar Reliefs(1908Digitisation
* Volume VII 2: Franz Winter: ''Die Skulpturen mit Ausnahme der Altarreliefs'' he Sculpture, aside from the Altar Reliefs(1908
Digitisation
* Volume VIII 1: Max Fränkel (ed.): ''Die Inschriften von Pergamon''
he Inscriptions of Pergamon
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
(1890Digitisation
* Volume VIII 2: Max Fränkel (ed.): ''Die Inschriften von Pergamon ''
he Inscriptions of Pergamon
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
(1895Digitisation
* Volume VIII 3: Christian Habicht,
Michael Wörrle
Michael may refer to:
People
* Michael (given name), a given name
* Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael
Given name "Michael"
* Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and ...
: ''Die Inschriften des Asklepieions'' he Inscriptions of the Asclepium(1969)
* Volume IX: Erich Boehringer – Friedrich Krauss
Friedrich Salomon Krauss (7 October 1859, Požega, Kingdom of Hungary – 29 May 1938, Vienna, Austria) was a Croatian Austrian Jewish sexologist, ethnographer, folklorist, and Slavist.
Education
In 1877–78, Krauss attended the University ...
: ''Das Temenos für den Herrscherkult'' he Temenos for the Ruler Cult(1937)
* Volume X: Ákos von Szalay – Erich Boehringer et al.: ''Die hellenistischen Arsenale. Garten der Königin'' he Hellenistic Arsenal. Garden of the Queen(1937)
* Volume XI 1: Oskar Ziegenaus Oskar may refer to:
* oskar (gene), the Drosophila gene
* Oskar (given name) Oscar or Oskar is a masculine given name of Irish origin.
Etymology
The name is derived from two elements in Irish: the first, ''os'', means "deer"; the second element, ' ...
, Gioia de Luca: ''Das Asklepieion. Der südliche Temenosbezirk in hellenistischer und frührömischer Zeit'' he Asclepium. The North Temple Area and Surrounding Complex in the Hellenistic and Early Roman Periods(1968)
* Volume XI 2: Oskar Ziegenaus, Gioia de Luca: ''Das Asklepieion. Der nördliche Temenosbezirk und angrenzende Anlagen in hellenistischer und frührömischer Zeit'' he Asclepium. The North Temple Area and Surrounding Complex in the Hellenistic and Early Roman Periods1975)
* Volume XI 3: Oskar Ziegenaus: ''Das Asklepieion. Die Kultbauten aus römischer Zeit an der Ostseite des Heiligen Bezirks'' he Asclepium. The Cult Buildings of the Roman Period on the East Side of the Sacred Area(1981)
* Volume XI 4: Gioia de Luca: ''Das Asklepieion. Via Tecta und Hallenstraße. Die Funde'' he Asclepium. Via Tecta and Stoas1984)
* Volume XI 5: Adolf Hoffmann, Gioia de Luca: ''Das Asklepieion. Die Platzhallen und die zugehörigen Annexbauten in römischer Zeit'' he Asclepium. The Halls and Associated Annexes in the Roman Period(2011)
* Volume XII: Klaus Nohlen, Wolfgang Radt: ''Kapıkaya. Ein Felsheiligtum bei Pergamon'' apıkaya. A Cliff-Sanctuary near Pergamon(1978)
* Volume XIII: Carl Helmut Bohtz: ''Das Demeter-Heiligtum'' he Sanctuary of Demeter
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
(1981)
* Volume XIV: Doris Pinkwart, Wolf Stammnitz, ''Peristylhäuser westlich der Unteren Agora'' eristyle Houses west of the Lower Agora(1984)
* Volume XV 1: Meinrad N. Filges, Wolfgang Radt: ''Die Stadtgrabung. Das Heroon'' he City Excavation. The Heroon(1986)
* Volume XV 2: Klaus Rheidt: ''Die Stadtgrabung. Die byzantinische Wohnstadt'' he City Excavation. The Byzantine Residential City(1991)
* Volume XV 3: Ulrike Wulf: ''Die Stadtgrabung. Die hellenistischen und römischen Wohnhäuser von Pergamon. Unter Berücksichtigung der Anlagen zwischen der Mittel- und der Ostgasse'' he City Excavation. The Hellenistic and Roman Residential Housing of Pergamon. In Light of Investigation of the Areas between Central and East Streets(1999)
* Volume XV 4: Holger Schwarzer: ''Das Gebäude mit dem Podiensaal in der Stadtgrabung von Pergamon. Studien zu sakralen Banketträumen mit Liegepodien in der Antike'' he building with the Podium-hall in the City Excavation of Pergamon. Studies of Sacral Banqueting Halls with Raised Platforms in Antiquity(2008)
* Volume XVI 1: Manfred Klinkott: ''Die byzantinischen Befestigungsanlagen von Pergamon mit ihrer Wehr- und Baugeschichte'' he Byzantine Fortifications of Pergamon with their Military and Architectural History(2001)
External links
Rosa Valderrama, "Pergamum"
brief history
Photographic tour of old and new Pergamon, including the museum
* ttp://www.pergamon.secondpage.de/index_en.html 3D-visualization and photos of Pergamon* {{Authority control Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Archaeological sites in the Aegean Region Buildings and structures in İzmir Province Former populated places in Turkey History of İzmir Province History of Turkey New Testament cities Tourist attractions in İzmir Province Asia (Roman province) Populated places in ancient Aeolis Populated places in ancient Mysia Bergama District Former kingdoms